Potential Genetic Markers Associated with Coloration in Duck: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Candidate Genes Underlying Plumage Coloration in Ducks
2.1. Transcriptomic and Expression Profiling Studies
2.2. Genetic Association and Variant Analysis
2.3. Population Genomics Approaches
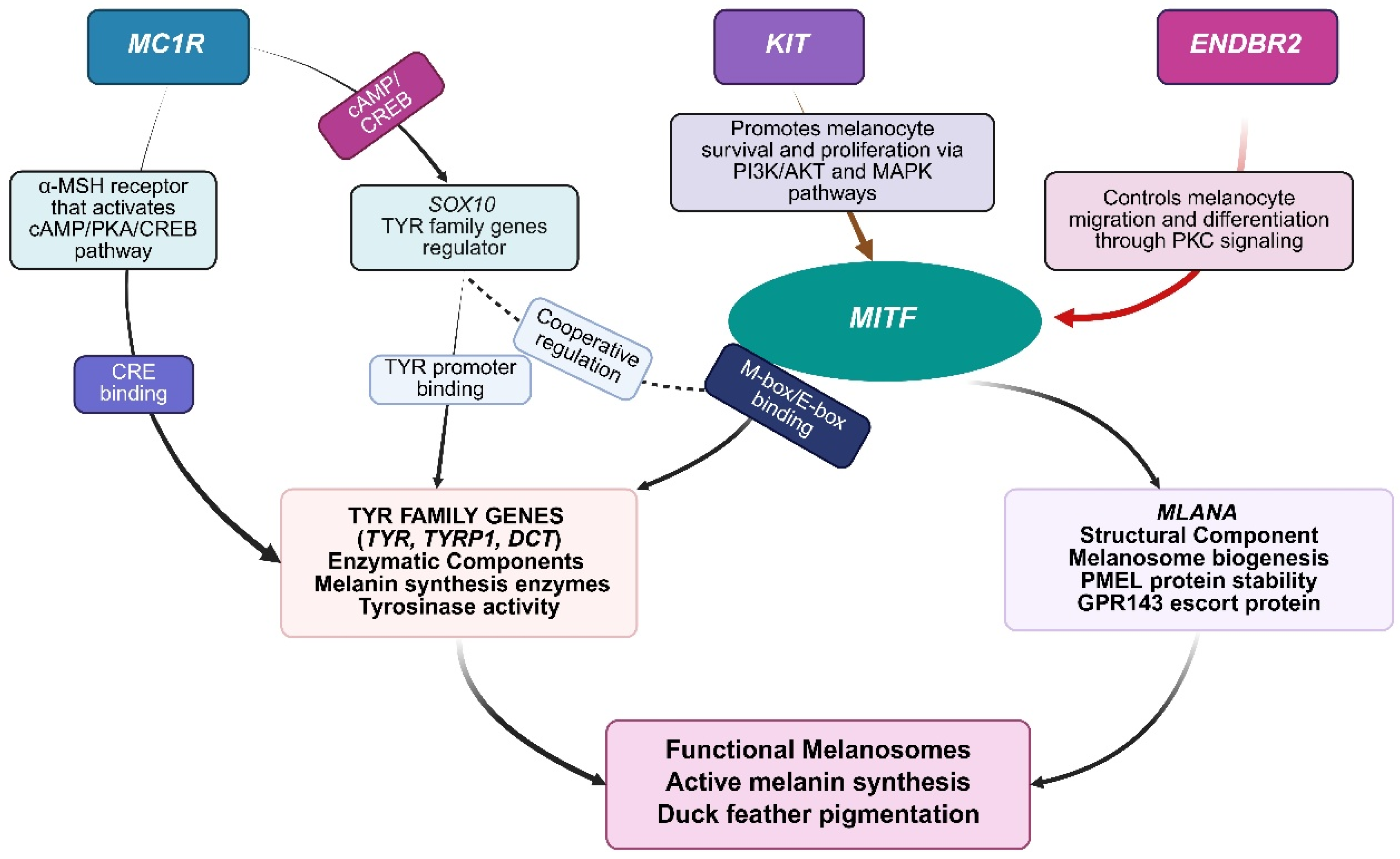
3. Molecular Architecture and Regulatory Mechanisms of Melanogenesis in Duck Plumage Development
3.1. Overview of Core Melanogenesis Genes
3.2. Master Transcriptional Regulation Through MITF
3.3. Melanocortin Receptor Signaling and Pigment Type Determination
3.4. Enzymatic Machinery and Supporting Regulatory Components
3.5. Epistatic Interactions and Hierarchical Gene Networks
3.6. Evolutionary Conservation and Cross-Species Validation
4. Functional Pathway Analysis and Gene Network Integration
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABCB6 | ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 6 |
| ADAMTS12 | ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 12 |
| ADCY9 | Adenylyl cyclase 9 |
| ADGRA1 | Adhesion G protein-coupled receptor A1 |
| ALDH1A3 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family member A3 |
| AP3B1 | Adaptor related protein complex 3 subunit beta 1 |
| ASIP | Agouti signaling protein |
| ATP1B1 | ATPase Na+/K+ transporting subunit beta 1 |
| BANP | BTG3 associated nuclear protein |
| CACNA1I | Calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha1 I |
| CACNA2D4 | Calcium voltage-gated channel auxiliary subunit alpha2delta 4 |
| CAMK2A | Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alpha |
| CCDC112 | Coiled-coil domain containing 112 |
| CCDC80 | Coiled-coil domain containing 80 |
| CCN5 | Cellular communication network factor 5 |
| CEBPA | CCAAT enhancer binding protein alpha |
| CHAC1 | ChaC glutathione-specific gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase 1 |
| CLOCK | Clock circadian regulator |
| cMYB | MYB proto-oncogene |
| CREB | cAMP response-element binding protein |
| CSNK1G3 | Casein kinase 1 gamma 3 |
| DCT | Dopachrome tautomerase (also known as TYRP2) |
| DENND4A | DENN domain containing 4A |
| DGKI | Diacylglycerol kinase iota |
| DOCK1 | Dedicator of cytokinesis 1 |
| DPP8 | Dipeptidyl peptidase 8 |
| EDNRB2 | Endothelin receptor type B2 |
| EIF2S2 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit beta |
| FNDC1 | Fibronectin type III domain containing 1 |
| GDA | Guanine deaminase |
| GMDS | GDP-mannose 4,6-dehydratase |
| GNAO1 | G protein subunit alpha o1 |
| GPR143 | G protein-coupled receptor 143 |
| GPRC5B | G protein-coupled receptor class C group 5 member B |
| GPX3 | Glutathione peroxidase 3 |
| HACD3 | 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydratase 3 |
| HMX1 | H6 family homeobox 1 |
| HOXB9 | Homeobox B9 |
| INTS14 | Integrator complex subunit 14 |
| IPMK | Inositol polyphosphate multikinase |
| KIAA2022 | KIAA2022 |
| KIT | KIT proto-oncogene |
| KITLG | KIT ligand (also known as Stem cell factor) |
| LOC101798015 | Uncharacterized gene |
| LOC101800026 | Uncharacterized gene |
| MB | Myoglobin |
| MC1R | Melanocortin 1 receptor |
| MITF | Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor |
| MLANA | Melan-A (melanoma antigen recognized by T-cells 1) |
| MXI1 | MAX interactor 1 |
| MYOT | Myotilin |
| OCA2 | Oculocutaneous albinism II |
| ODC1 | Ornithine decarboxylase 1 |
| PDIA6 | Protein disulfide isomerase family A member 6 |
| PLIN3 | Perilipin 3 |
| PMEL | Premelanosome protein |
| POU2F3 | POU class 2 homeobox 3 |
| PRKAR2B | Protein kinase cAMP-dependent type II regulatory subunit beta |
| PRKG1 | Protein kinase cGMP-dependent 1 |
| PWWP2A | PWWP domain containing 2A |
| RAB1A | RAB1A, member RAS oncogene family |
| RAB38 | RAB38, member RAS oncogene family |
| RALYL | RALY RNA binding protein like |
| RLIM | Ring finger protein, LIM domain interacting |
| ROR2 | Receptor tyrosine kinase like orphan receptor 2 |
| SETD6 | SET domain containing 6 |
| SLC16A2 | Solute carrier family 16 member 2 |
| SLC24A1 | Solute carrier family 24 member 1 |
| SLC24A5 | Solute carrier family 24 member 5 |
| SLC45A2 | Solute carrier family 45 member 2 |
| SLC7A11 | Solute carrier family 7 member 11 |
| SLC7A5 | Solute carrier family 7 member 5 |
| SMARCA2 | SWI/SNF related matrix associated actin dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily A member 2 |
| SOX10 | SRY-box transcription factor 10 |
| SPATA2 | Spermatogenesis associated 2 |
| ST8SIA4 | ST8 alpha-N-acetyl-neuraminide alpha-2,8-sialyltransferase 4 |
| STARD9 | StAR related lipid transfer domain containing 9 |
| STK4 | Serine/threonine kinase 4 |
| STS | Steroid sulfatase |
| SYNPO2 | Synaptopodin 2 |
| TICAM2 | TIR domain containing adaptor molecule 2 |
| TRPM1 | Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 1 |
| TRPM6 | Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 6 |
| TYR | Tyrosinase |
| TYRO3 | TYRO3 protein tyrosine kinase |
| TYRP1 | Tyrosinase-related protein 1 |
| VAMP7 | Vesicle associated membrane protein 7 |
| VWA5A | Von Willebrand factor A domain containing 5A |
| WDR59 | WD repeat domain 59 |
| WNT16 | Wnt family member 16 |
| WNT3A | Wnt family member 3A |
| XBP1 | X-box binding protein 1 |
| YWHAB | Tyrosine 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activation protein beta |
| ZNF106 | Zinc finger protein 106 |
| ZNF704 | Zinc finger protein 704 |
References
- Ye, H.; Ji, C.; Liu, X.; Bello, S.F.; Guo, L.; Fang, X.; Lin, D.; Mo, Y.; Lei, Z.; Cai, B.; et al. Improvement of the accuracy of breeding value prediction for egg production traits in Muscovy duck using low-coverage whole-genome sequence data. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 104812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungkusonmongkol, P.; Wattanachant, S. Carcass characteristics and meat quality of spent laying ducks for potential additional supply to the duck meat market. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2024, 33, 100450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandimali, N.; Bak, S.G.; Park, E.H.; Lim, H.J.; Won, Y.S.; Kim, B.; Lee, S.J. Bioactive peptides derived from duck products and by-products as functional food ingredients. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 113, 105953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qiu, G.; Huang, D.; Ma, Z.; Wei, J.; Zhong, R.; Li, R.; Huang, M.; Gou, J.; Ye, F.; et al. Genetic assessment and Identification of genes related to characterization of Guangdong local goose breeds based on modern and historical genomes. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Zhou, J.; Yihao, Z.; Luo, K.; Zheng, S.; Tang, H.; Wu, Y.; Xuan, R.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Whole genome sequencing revealed genetic structure, domestication, and selection of Chinese indigenous ducks. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 306, 141724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Jing, Y.; Yang, L.; Khan, M.Z.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Ma, W.; Ding, Z.; Li, X.; Qi, C.; et al. Runs of homozygosity and selection signals analysis reveals domestication traits and divergence in local domestic duck breeds. Poult. Sci. 2025, 105, 105404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Zhang, M.; Khan, M.Z.; Yang, L.; Jing, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Genome-wide structural variation analysis and breed comparison of local domestic ducks in Shandong Province, China. Animals 2024, 14, 3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Hou, S.; Zhou, Z. The Duck 1000 Genomes Project: Achievements and perspectives. Anim. Res. One Health 2024, 2, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Yang, L.; Khan, M.Z.; Jing, Y.; Zhang, M.; Qi, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; et al. Joint genomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals candidate genes associated with plumage color traits in Matahu ducks. Animals 2024, 14, 3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Bian, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Q.; Chang, G.; Chen, G. Marginal diversity analysis of conservation of Chinese domestic duck breeds. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crandell, K.E.; Powers, D.R.; Tobalske, B.W. The role of plumage and heat dissipation areas in thermoregulation in doves. J. Exp. Biol. 2025, 228, JEB248200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrill, R.S.; Shultz, A.J. Feather function and the evolution of birds. Biol. Rev. 2023, 98, 540–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Tong, Y.; Dong, R.; Ye, X.; Yu, X. A Breeding Plumage in the Making: The Unique Process of Plumage Coloration in the Crested Ibis in Terms of Chemical Composition and Sex Hormones. Animals 2023, 13, 3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalla, S.; Shawkey, M.D.; D’Alba, L. Thermal effects of plumage coloration. Ibis 2022, 164, 933–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.L.; Chen, H.P.; Rouvier, R.; Poivey, J.P. Selection and crossbreeding in relation to plumage color inheritance in three Chinese egg type duck breeds (Anas Platyrhynchos). Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 27, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, W.; Chen, S.; Xue, L.; Tian, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, J. Whole genome resequencing reveals genetic markers for plumage colour in Jingyuan chicken. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 105666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price-Waldman, R.; Stoddard, M.C. Avian coloration genetics: Recent advances and emerging questions. J. Hered. 2021, 112, 395–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roulin, A.; Ducrest, A.L. Genetics of colouration in birds. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2013, 24, 594–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lin, W.; Li, H.; Yang, F.; Bao, X.; Pan, C.; Lai, L.; Lin, W.; Lin, R. Identification of candidate genes affecting egg weight trait of Putian Black duck based on whole genome resequencing. Anim. Biotechnol. 2025, 36, 2503754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, H.; Seo, D.W.; Park, H.B.; Choi, N.R.; Hoque, M.R.; Bhuiyan, M.S.; Heo, K.N.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.H. Identification of MC1R SNPs and their association with plumage colors in Asian duck. J. Poult. Sci. 2017, 54, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.L.; Chen, H.P.; Rouvier, R.; Marie-Etancelin, C. Genetic parameters of body weight, egg production, and shell quality traits in the Shan Ma laying duck (Anas platyrhynchos). Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 2514–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roulin, A.; Dubey, S.; Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K. Melanin-based plumage coloration and melanin content in organs in the barn owl. J. Ornithol. 2024, 165, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, S.; Feng, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Mabrouk, I.; Cao, H.; Hu, X.; Li, H.; Sun, Y. Sex identification of feather color in geese and the expression of melanin in embryonic dorsal skin feather follicles. Animals 2022, 12, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, D.J.; Paik, S.; Ji, S.; Yeo, J.S. Melanin-based structural coloration of birds and its biomimetic applications. Appl. Microsc. 2021, 51, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diatroptov, M.E.; Opaev, A.S. Melanin- and carotenoid-based coloration of plumage and the level of aggressiveness: The relationship of these parameters in the greenfinch (Chloris chloris, Passeriformes, Fringillidae). Biol. Bull. 2022, 49, 1482–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikova, I.V. Molecular mechanisms and gene regulation of melanic plumage coloration in birds. Russ. J. Genet. 2021, 57, 893–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, L.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Ma, S.; Wang, J.; Bai, L.; Zhang, R.; et al. Transcriptome Reveals Multi Pigmentation Genes Affecting Dorsoventral Pattern in Avian Body. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 560766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Xu, Q.; Huang, Q.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y.; Han, C.; Zhang, R.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Li, L. Genome-wide association analysis reveals that EDNRB2 causes a dose-dependent loss of pigmentation in ducks. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, M.; Cheng, H.; Fan, W.; Yuan, Z.; Gao, Q.; Xu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; et al. Author Correction: An intercross population study reveals genes associated with body size and plumage color in ducks. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3974, Erratum in Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Mou, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, D.; Tang, H.; Hou, S.; Schroyen, M.; Zhou, Z. Unique feather color characteristics and transcriptome analysis of hair follicles in Liancheng White ducks. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bi, Y.; Chen, G.; Bai, H.; Chang, G. Genome-wide analysis identifies candidate genes encoding feather color in ducks. Genes 2022, 13, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Peng, Y.; Yang, L.; Khan, M.Z.; Jing, Y.; Qi, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, N.; Zhang, M.; et al. Whole genome resequencing reveals genetic diversity, population structure, and selection signatures in local duck breeds. BMC Genom. 2025, 26, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, T.; Liu, D.; Yu, S.; Tang, H.; Zhang, H.; Mou, Q.; Zhang, B.; et al. A high-quality assembly revealing the PMEL gene for the unique plumage phenotype in Liancheng ducks. GigaScience 2025, 14, giae114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Xi, Y.; Tang, Q.; Qi, J.; Zhou, Z.; Guo, Z.; Fan, W.; Hu, J.; Xu, Y.; Liang, S.; et al. Genetic fine-mapping reveals single nucleotide polymorphism mutations in the MC1R regulatory region associated with duck melanism. Mol. Ecol. 2023, 32, 3076–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Z.; Song, W.; Lu, L.; Tao, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, W.; Liu, H.; et al. RNA sequencing analysis reveals key genes and pathways associated with feather pigmentation in mule ducks. Anim. Genet. 2025, 56, e70007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Cao, H.; Wu, M.; Zhao, H.; Ji, R.; Zhang, G.; Chen, G.; et al. RNA sequencing and genome-wide association analysis reveal key genes responsible for different feather colors in Youjiang goose. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 105305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Cai, Y.; Cao, C.; He, H.; Guo, S.; Li, N.; Xin, A.; Liu, X. Metabolome and transcriptome analyses reveal the mechanism underlying the differences in skin development between the two duck breeds during embryonic stage. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 105403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Weng, K.; Li, G.; Wang, H.; Tan, Y.; He, D. Genetic and metabolic mechanisms underlying webbed feet pigmentation in geese: Insights from histological, transcriptomic, and metabolomic analyses. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 105233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wei, B.; He, D. Transcriptome analysis of sexual dimorphism in dorsal down coloration in goslings. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Xi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Hu, J.; Han, C.; Bai, L.; et al. Transcriptome analysis reveals genes associated with sexual Dichromatism of head feather color in mallard. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 627974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wang, G.; Liao, J.; Tang, M.; Sun, W. Transcriptome profile analysis of mechanisms of black and white plumage determination in black-bone chicken. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 2373–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.B.; Lu, Y.F.; Duan, X.J. Investigation into the association of FNDC1 and ADAMTS12 gene expression with plumage coloration in Muscovy ducks. Open Life Sci. 2024, 19, 20220877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.B.; Lu, Y.F.; Duan, X.J. Exploration of the genetic influence of MYOT and MB genes on the plumage coloration of Muscovy ducks. Open Life Sci. 2024, 19, 20220836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, T.; Wang, L.; Lv, X.; Yang, W.; Qu, C.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Ning, Z.; Qu, L. Genome-wide association study reveals the genetic basis of duck plumage colors. Genes 2023, 14, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hua, G.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, L.; Hu, X.; Scheben, A.; Wu, Y.; Gong, P.; et al. Duck pan-genome reveals two transposon insertions caused bodyweight enlarging and white plumage phenotype formation during evolution. iMeta 2024, 3, e154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, C.; Yu, W.; Zhao, S.; Gong, Y. Identification of Genes Related to White and Black Plumage Formation by RNA-Seq from White and Black Feather Bulbs in Ducks. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bi, Y.; Chen, G.; Bai, H.; Chang, G. Genome-wide analysis identifies candidate genes encoding beak color of duck. Genes 2022, 13, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bi, Y.; Chen, G.; Bai, H.; Chang, G. Genome-wide association study for screening and identifying potential shin color loci in ducks. Genes 2022, 13, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, L.; Guo, Z.; Fan, W.; Xu, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, M.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis reveals the genetic reasons affecting melanin spot accumulation in beak skin of ducks. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Chen, G.; Chang, G.; Bai, H. Genome-wide association study reveals 2 copy number variations associated with the variation of plumage color in the white duck hybrid population. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Zhao, F.; Xiong, T.; Lai, L.; Li, H.; Lin, W.; Xiao, T.; Lin, W. Genetic mapping identifies SNP mutations in MITF-M promoter associated with melanin formation in Putian black duck. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarjana, T.A.; Zhang, G. Association between synonymous SNPs of SOX10 and plumage color and reproductive traits of ducks. Animals 2022, 12, 3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, F.; Zhu, T.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Wen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Ren, X.; Chen, A.; et al. Whole genome resequencing reveals genomic regions related to red plumage in ducks. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Li, H.; Lin, W.; Yang, F.; Bao, X.; Pan, C.; Lai, L.; Lin, W. Whole-genome selection signature differences between Chaohu and Ji’an red ducks. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, S.; Xi, Y.; Qi, J.; Ma, S.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Bai, L.; He, H.; Xu, H.; et al. Integration of GWAS and eGWAS to screen candidate genes underlying green head traits in male ducks. Anim. Genet. 2023, 54, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twumasi, G.; Wang, H.; Xi, Y.; Qi, J.; Li, L.; Bai, L.; Liu, H. Genome-wide association studies reveal candidate genes associated with pigmentation patterns of single feathers of Tianfu Nonghua ducks. Animals 2023, 14, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Twumasi, G.; Xu, Q.; Xi, Y.; Qi, J.; Yang, Z.; Shen, Z.; Bai, L.; Li, L.; Liu, H. Identification of candidate genes associated with primary feathers of Tianfu Nonghua ducks based on genome-wide association studies. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, Q.; Lin, R.; Chen, H.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, B.; Wang, Y.; Xue, P.; Gan, Q.; Shen, Y.; et al. Genome-wide association study for the primary feather color trait in a native Chinese duck. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1065033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Lyu, G.; Irwin, D.M.; Liu, X.; Feng, C.; Luo, R.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Shang, S.; Zhang, S.; et al. Pooled sequencing analysis of geese (Anser cygnoides) reveals genomic variations associated with feather color. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 650013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.; Tu, X.; Lu, Y.; Gao, Z.; He, X.; Hong, J.; Wu, J.; Wu, D.; Xi, D.; Deng, W. Two High-Quality Cygnus Genome Assemblies Reveal Genomic Variations Associated with Plumage Color. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Cho, E.; Cho, S.; Kim, M.; Chung, W.H.; Choi, J.W.; Choo, H.J.; Lee, J.H. Selection signature analysis using whole genome resequencing data reveals candidate genes for white plumage color in Korean native ducks. Anim. Biosci. 2025, 38, 1594–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Xi, Y.; Ma, S.; Li, Y.; He, H.; Wang, J.; Han, C.; Bai, L.; Mustafa, A.; et al. Understanding the genetic domestication history of the Jianchang duck by genotyping and sequencing of genomic genes under selection. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2020, 10, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Yang, S.; Jia, Z.; Cai, J.; Rong, L.; Wu, X.; Fan, L.; Gong, Y.; Li, S. Identification of genes associated with feather color in Liancheng white duck using FST analysis. Anim. Genet. 2022, 53, 518–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Shao, P.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Lv, X.; Yang, W.; Jia, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhu, B.; Qu, L. Genomic scan revealed KIT gene underlying white/gray plumage color in Chinese domestic geese. Anim. Genet. 2021, 52, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Gu, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Ren, X.; Wang, G.; et al. Genomic analysis reveals candidate genes underlying sex-linked eyelid coloboma, feather color traits, and climatic adaptation in Huoyan geese. Animals 2023, 13, 3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhai, S.; Liu, H.; He, D. A novel codominant plumage color pattern of white breast patches in WugangTong geese was controlled by EDNRB2. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Chen, J.; Luo, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Tian, Y. Identification of differentially expressed genes and microRNAs in the gray and white feather follicles of Shitou geese. Animals 2024, 14, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, D.; Yang, M.; Miao, X.; Huang, Z.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, T.; Li, D.; Feng, C. Dynamic changes in the skin transcriptome for the melanin pigmentation in embryonic chickens. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 104210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.W.; Ran, J.S.; Yu, C.L.; Qiu, M.H.; Zhang, Z.R.; Du, H.R.; Li, Q.Y.; Xiong, X.; Song, X.Y.; Xia, B.; et al. Polymorphism in MC1R, TYR and ASIP genes in different colored feather chickens. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, R.; Hua, T.; Ding, Y.; Bai, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hu, M.; Chen, G.; Wu, X.; Chang, G. Study on changing disciplinarian of beak colors in ducks and the regulation network based on transcriptome sequencing. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, H.; Seo, D.; Choi, N.R.; Bhuiyan, M.S.; Lee, S.H.; Heo, K.N.; Lee, J.H. Identification of polymorphisms in MITF and DCT genes and their associations with plumage colors in Asian duck breeds. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 31, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.; Hua, T.; Guo, Q.; Bai, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bi, Y.; Chen, G.; Wu, X.; Chang, G. Identification of SNPs in MITF associated with beak color of duck. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1161396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Lin, W.; Zhou, S.; Chen, Q.; Pan, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, T. Integrated analysis of mRNA expression, CpG island methylation, and polymorphisms in the MITF gene in ducks (Anas platyrhynchos). BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8512467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, J.; Fan, Y.; Ji, X. The relationship of MITF gene expression and promoter methylation with plumage colour in quail. Br. Poult. Sci. 2025, 65, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraiz, C.; Martínez-Vicente, I.; Maresca, V. The α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone/melanocortin-1 receptor interaction: A driver of pleiotropic effects beyond pigmentation. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2021, 34, 748–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, J.; Zippin, J.H. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) signaling in melanocyte pigmentation and melanomagenesis. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2021, 34, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, J.; Lee, Y.; Hyeong, K.; Ha, J.; Yi, J.; Kim, B.; Oh, D. Detection of exonic variants within the melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) gene in Black Silky, White Leghorn and Golden duckwing Araucana chicken. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 4843–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, T.; Pan, R.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hu, M.; Zhao, W.; Chen, G.; Chang, G.; Bai, H. Identification of InDels in MITF associated with beak color of duck. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 105965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Y.C.; Wei, L.Y.; Chang, Y.Y.; Liu, H.C.; Lee, H.H.; Yu, Y.H.; Chen, M.C. Effects of melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) gene polymorphisms on plumage color in mule ducks. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 2019, 48, e20180180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wang, C.; Xin, Q.; Li, S.; Feng, Y.; Peng, X.; Gong, Y. Non-synonymous SNPs in MC1R gene are associated with the extended black variant in domestic ducks (Anas platyrhynchos). Anim. Genet. 2013, 44, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Han, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y. Effect of polymorphisms in the 5′-flanking sequence of MC1R on feather color in Taihang chickens. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 102192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsudany, S. Sequence variation of MC1R gene in Iraqi native Ducks and its association with feathers colour trait. Euphrates J. Agric. Sci. 2023, 151, 158–165. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhou, B.; He, D.Q.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhu, Q.; Yao, Y.G.; Liu, Y.P. Sequence variation of melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) gene and association with plumage color in domestic geese. J. Poult. Sci. 2014, 51, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, S.; Dong, X.; Yu, Y.; Yao, J.; Luan, P.; Qu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. Genome-wide identification of SNPs and CNVs responsible for plumage color in chicken. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 652. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Pang, Y.Z. Association of Tyrosinase (TYR) and Tyrosinase-related Protein 1 (TYRP1) with Melanic Plumage Color in Korean Quails (Coturnix coturnix). Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 26, 1518–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.X.; Jung, D.; Yao, R. ShinyGO: A graphical gene-set enrichment tool for animals and plants. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2628–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, B.T.; Panzade, G.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W. DAVID ortholog: An integrative tool to enhance functional analysis through orthologs. Bioinformatics 2024, 40, btae615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Matsuura, Y.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG: Biological systems database as a model of the real world. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D672–D677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M. Toward understanding the origin and evolution of cellular organisms. Protein Sci. 2019, 28, 1947–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotera, M.; Yamanishi, Y.; Moriya, Y.; Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. GENIES: Gene network inference engine based on supervised analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W162–W167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Breed | Potential Genes | Screening Method | Color Associated Phenotypic Traits | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Longsheng duck | EDNRB2, MITF, SPATA2, EIF2S2, PLIN3, ATP1B1, CCDC80 | Comparative genomics (FST) | Distinctive coloration phenotype | [5] |
| Matahu duck | MITF, MC1R, TYR, TYRP1, ABCB6, DGKI, GPRC5B, HMX1, STS, ADGRA1, PRKAR2B, HOXB9 | QTL mapping and expression profiling | Melanin biosynthesis, plumage trait determination | [9] |
| Holdobaggy goose | TYRP1, ASIP | Expression profiling | Sex-linked dorsal plumage patterns | [23] |
| Light Brown Mottling duck | ASIP, OCA2, MLANA, MC1R, TYR, TYRP1 | RNA-seq (dorsal vs. ventral embryonic skin) | Dorsoventral color variation | [27] |
| Multiple duck populations | EDNRB2, TYR, KIT, EDNRB, MC1R | RNA-seq (transcriptomic screening) | Melanogenic pathway regulation, feather color correlation | [35] |
| Youjiang goose | TYRP1, EDNRB2, DCT, TYR, MLANA | Integrated RNA-seq and GWAS | Melanogenic pathway, feather coloration | [36] |
| Duck skin tissues | TYR, ASIP, TYRP1, KIT | Transcriptomic analysis | Skin pigmentation control | [37] |
| Magang goose | TYRP1, PMEL, DCT, TYR, OCA2, MC1R, RAB38, WNT16, CAMK2A, MLANA | RNA-seq of webbed feet | Melanin content variation, dose-dependent pigmentation | [38] |
| Hungarian white goose | MC1R, TYR, TYRP1, DCT, MITF | Transcriptomic analysis | Sex-specific pigmentation, sexual dimorphism in goslings | [39] |
| Duck (general) | CHAC1, GPX3 | Transcriptomic profiling | Black feather formation, melanin deposition | [41] |
| Muscovy duck | FNDC1 and ADAMTS12 | quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) | White color | [42] |
| Muscovy duck | MYOT and MB | qPCR | Black plumage color | [43] |
| Multiple duck breeds | MC1R (c.52G>A, c.376G>A) MITF (chr13:15411658A>G, chr13:15412570T>C, chr13:15412592C>G) | GWAS and variant analysis | Black plumage (MC1R); white plumage (MITF) | [44] |
| Multiple duck populations | MITF | Whole-genome sequencing | Plumage color across diverse populations | [29,45,46] |
| Chinese Crested duck and Cherry Valley duck | MITF and EDNRB2 | GWAS | Associated with black and white color plumage | [47] |
| Chinese Crested duck and Cherry Valley duck | MITF and EDNRB2 | GWAS | Regulate melanin synthesis and variation in beak color | [48] |
| Mallards and Pekin ducks | MITF and POU2F3 | GWAS | Melanin deposition in duck beak | [49] |
| Multiple duck breeds | VWA5A, MITF, SOX10 | GWAS with increased marker density | Plumage color coordination | [50] |
| Putian black ducks | MITF | GWAS | Associated with regulation of black and white plumage coloration | [51] |
| White Kaiya and white Liancheng ducks | SOX10(g.54065419C>T and g.54070844C>T) | Gene sequencing | Associated with white feathers coloration | [52] |
| Brown Tsaiya and Ji’an Red duck | GMDS, ODC1, PDIA6 | GWAS | Red plumage and feather color variation | [53] |
| Chaohu and Ji’an red ducks | ASIP and LOC101797494 | Whole-genome sequencing | Pigmentation and plumage color | [54] |
| Multiple duck breeds | CACNA1I, WDR59, GNAO1, CACNA2D4, LOC101800026, SYNPO2, MXI1 | GWAS | Green head traits, TYRP1 regulation | [55] |
| Tianfu Nonghua ducks | WNT3A, DOCK1, RAB1A, ALDH1A3, DPP8, HACD3, INTS14, SLC24A1, DENND4A, PRKG1, SETD6, RALYL, ZNF704 | GWAS | Associated with color pigment on the dorsal and ventral feathers of the ducks Regulate pigmentation | [56] |
| Nonghua ducks | STK4, CCN5, and YWHAB | GWAS | Regulate melanin-related pathways or pigment deposition, Associated black spot on feathers and | [57] |
| Longyan Shan-ma ducks | ZNF106, SLC7A5, BANP ZNF106 STARD9, SLC7A5, BANP, LOC101798015, and IPMK | GWAS | Involved in pigmentation and follicle development | [58] |
| Geese | KITLG, MITF, TYRO3, KIT, AP3B1, SMARCA2, ROR2, CSNK1G3, CCDC112, VAMP7, SLC16A2, RLIM, KIAA2022, ST8SIA4, TRPM6, TICAM2 | GWAS | Regulate feather color in geese | [59] |
| Swan populations | TYR, SLC45A2, SLC7A11, PWWP2A | Comparative genomics | Melanin production, plumage coloration | [60] |
| Korean native duck | DCT, KIT, TYR, ADCY9 | Whole-genome resequencing (FST) | Pigmentation pattern differentiation | [61] |
| Jianchang duck | MITF and MC1R | FST analysis | Hemp and white feathers | [62] |
| Liancheng white duck | KIT, CLOCK, MITF, CEBPA | Fixation index (FST) test | White color feather Regulate melanin pathway | [63] |
| Geese | KIT | FST analysis | White/gray plumage color | [64] |
| Huoyan geese | TYRP1 and GDA | Whole-genome resequencing | Feathers color phenotypes and skin pigmentation | [65] |
| Wugangtong goose | EDNRB2 and MLANA | Sanger sequencing | Plumage colors | [66] |
| Shitou geese | TYR, TYRP1, EDNRB2, MLANA, SOX10, SLC45A2, GPR143, TRPM1, OCA2, ASIP, KIT, SLC24A5 | RNA-Seq | White feather follicles | [67] |
| Symbol | Ensembl Gene ID | Species | Chr | Position (Mbp) | nExons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOX10 | ENSAPLG00000015217 | Duck | 1 | 53.368843 | 3 |
| DCT | ENSAPLG00000013837 | Duck | 1 | 163.367528 | 10 |
| TYR | ENSAPLG00000012676 | Duck | 1 | 175.170443 | 4 |
| KIT | ENSAPLG00000004054 | Duck | 4 | 44.96999 | 21 |
| MC1R | ENSAPLG00000000850 | Duck | 12 | 20.222742 | 1 |
| MITF | ENSAPLG00000011965 | Duck | 13 | 15.388146 | 11 |
| MLANA | ENSAPLG00000003877 | Duck | Z | 29.800872 | 4 |
| TYRP1 | ENSAPLG00000013453 | Duck | Z | 34.236291 | 8 |
| Term | Genes | p-Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0043473 | KIT, MITF, DCT, SOX10, TYRP1, TYR | 7.85 × 10−14 | Pigmentation |
| GO:0048066 | KIT, MITF, DCT, SOX10, TYRP1 | 4.26 × 10−13 | Developmental pigmentation |
| GO:0030318 | KIT, MITF, SOX10, TYRP1 | 6.72 × 10−11 | Melanocyte differentiation |
| GO:0042438 | DCT, TYRP1, TYR | 6.14 × 10−9 | Melanin biosynthetic process |
| GO:0002052 | DCT, SOX10 | 1.33 × 10−5 | Positive regulation of neuroblast proliferation |
| Category | Term | p-Value | Genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG_PATHWAY | apla04916: Melanogenesis | 1.10 × 10−9 | MC1R, DCT, TYRP1, KIT, MITF, TYR |
| KEGG_PATHWAY | apla00350: Tyrosine metabolism | 3.36 × 10−4 | DCT, TYRP1, TYR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, M.Z.; Ma, Q.; Wang, C.; Peng, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, C. Potential Genetic Markers Associated with Coloration in Duck: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311460
Khan MZ, Ma Q, Wang C, Peng Y, Zhu M, Wang C. Potential Genetic Markers Associated with Coloration in Duck: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311460
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Muhammad Zahoor, Qingshan Ma, Chunming Wang, Yongdong Peng, Mingxia Zhu, and Changfa Wang. 2025. "Potential Genetic Markers Associated with Coloration in Duck: A Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311460
APA StyleKhan, M. Z., Ma, Q., Wang, C., Peng, Y., Zhu, M., & Wang, C. (2025). Potential Genetic Markers Associated with Coloration in Duck: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311460







