Diffusion-Controlled Release of Bromelain from κ-Carrageenan Nanocomposite Hydrogels Reinforced with Bio-Derived Nanofillers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effects of Nanofillers on Network Architecture (CNC vs. ChNW)
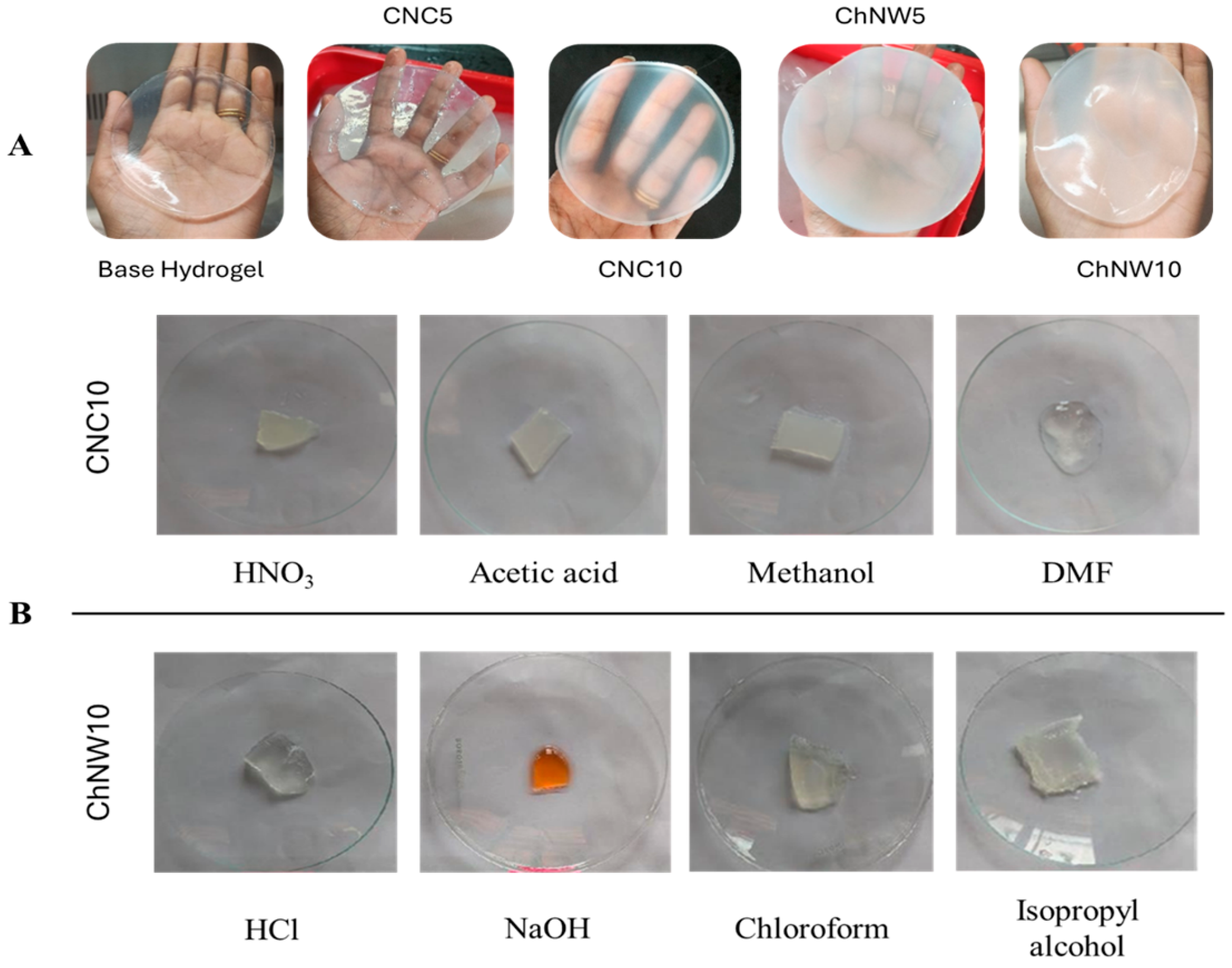
2.1.1. Macroscopic Integrity and Chemical Resilience
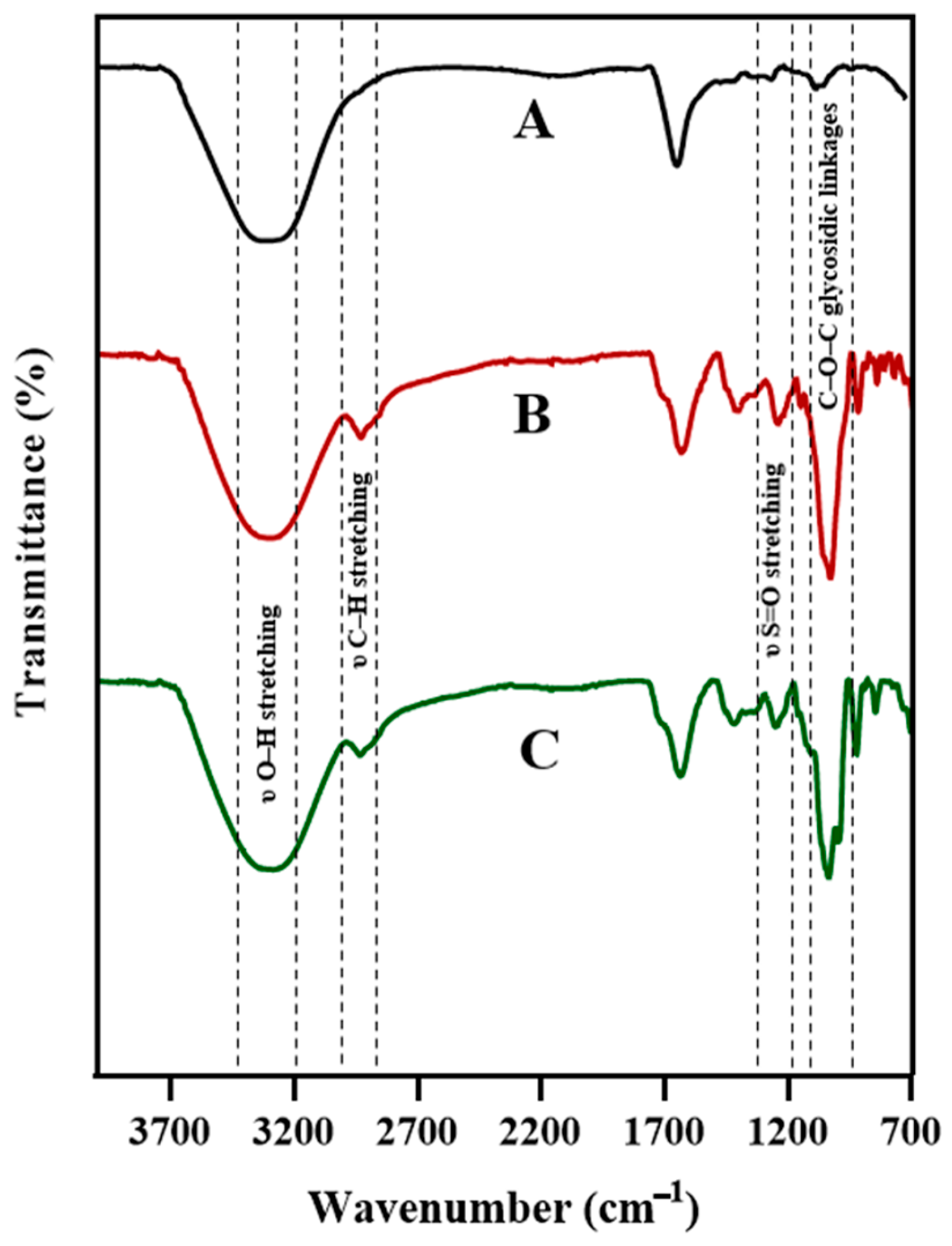
2.1.2. Fourier–Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
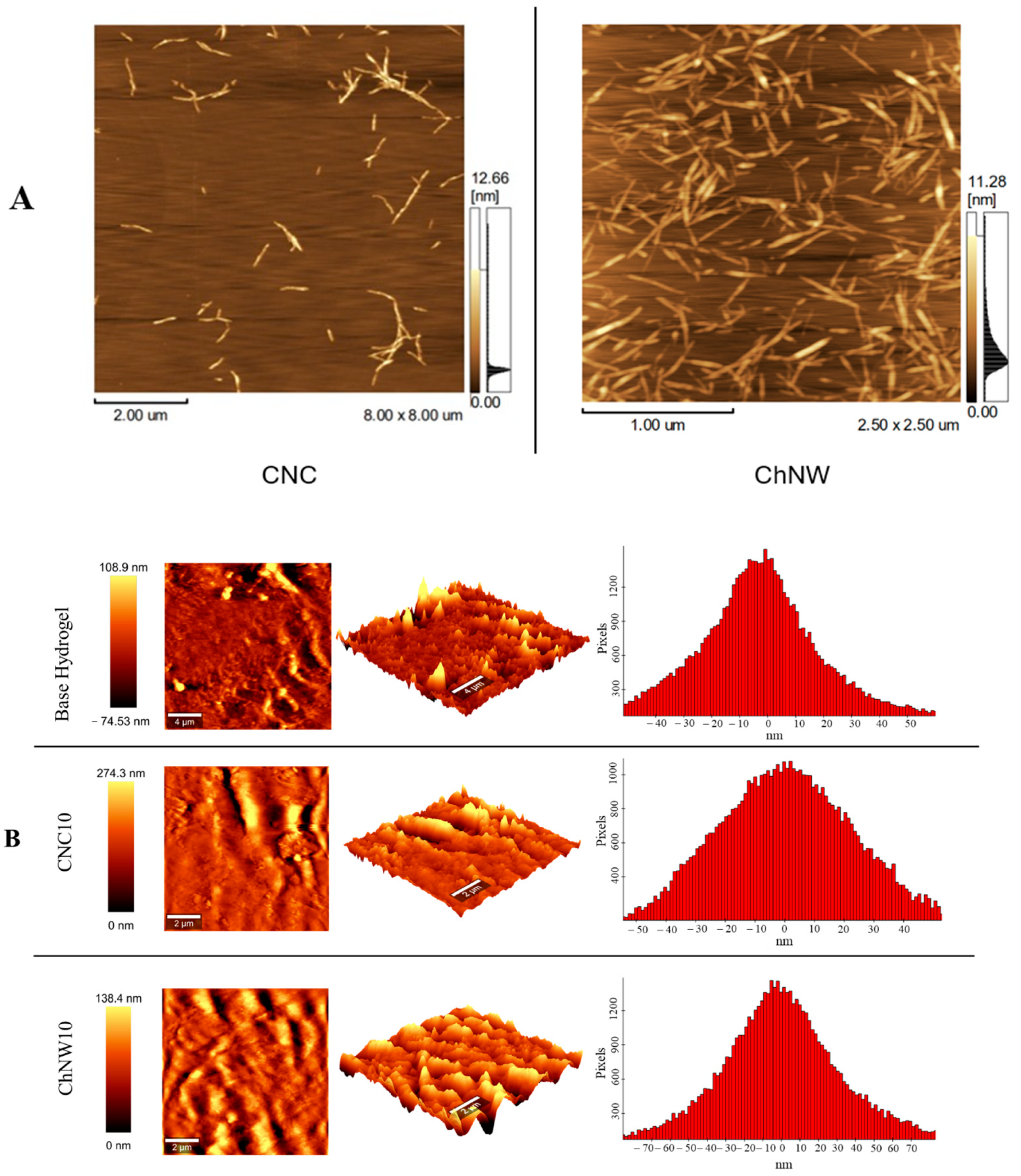
2.1.3. AFM Topography
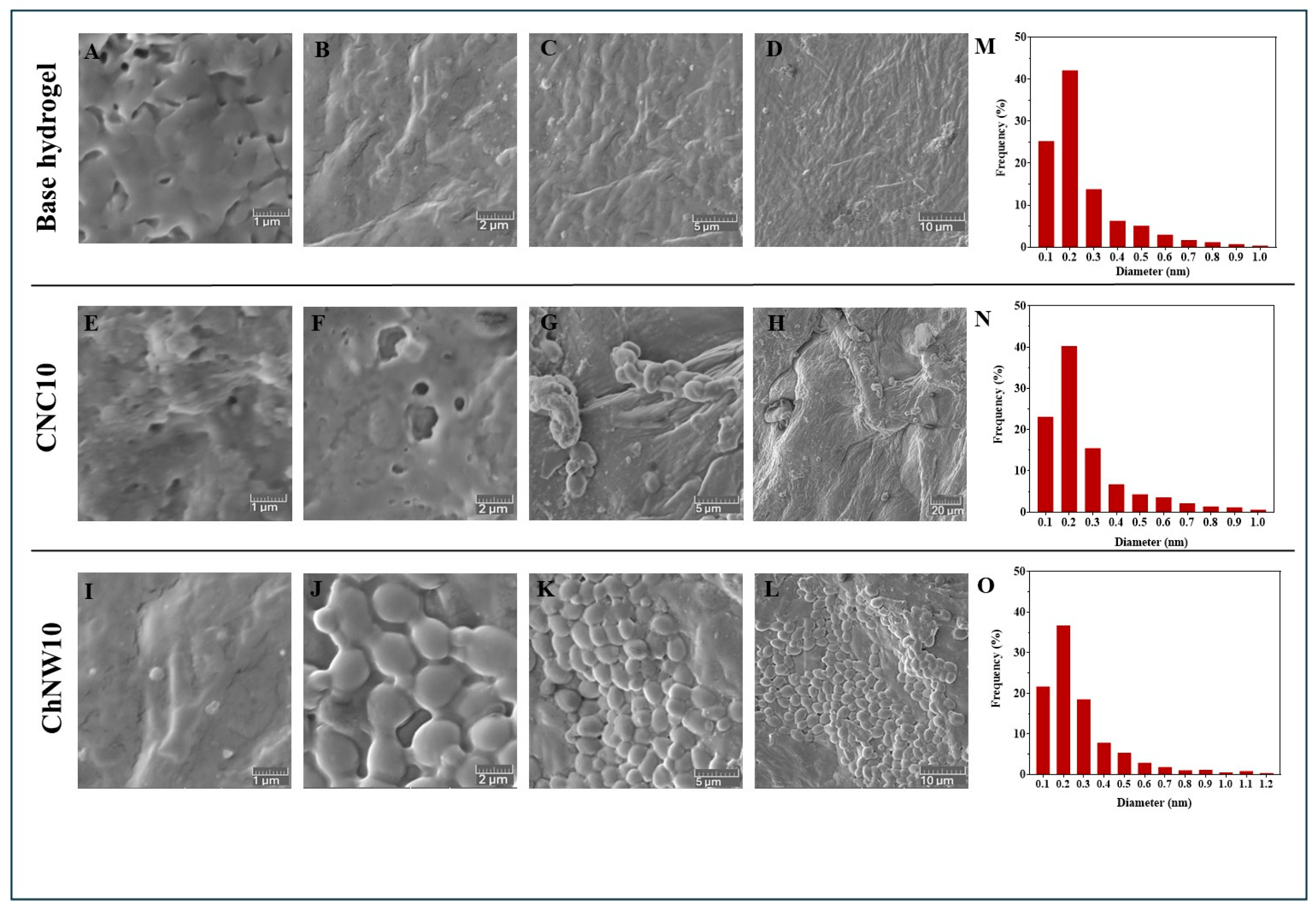
2.1.4. Field-Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE–SEM) Microstructure
2.2. Surface Wettability and Hydration
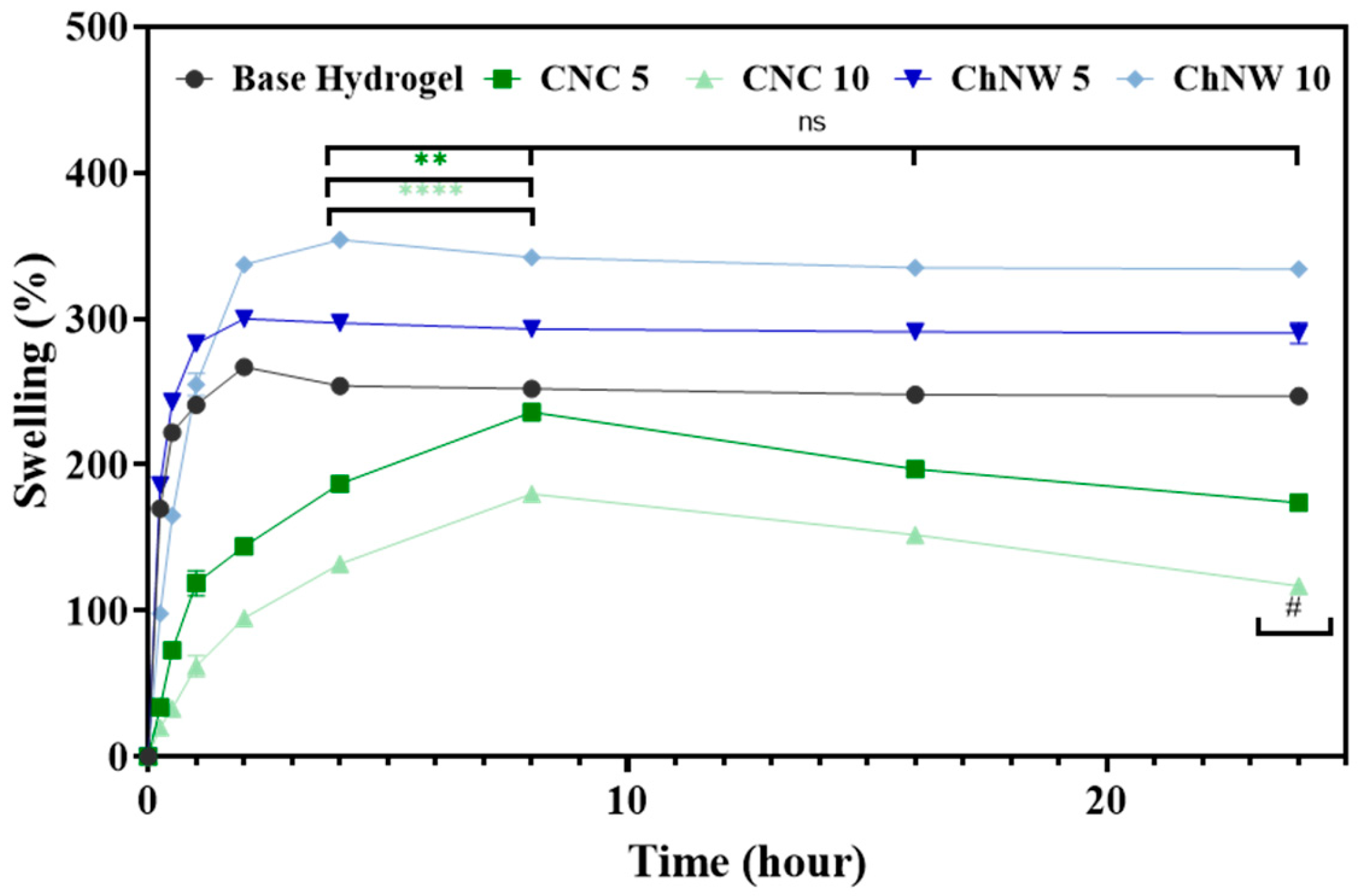
2.3. Bromelain Release Profiles from CNC and ChNW Reinforced Hydrogels
2.4. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity
2.5. Cytocompatibility and Biodegradation
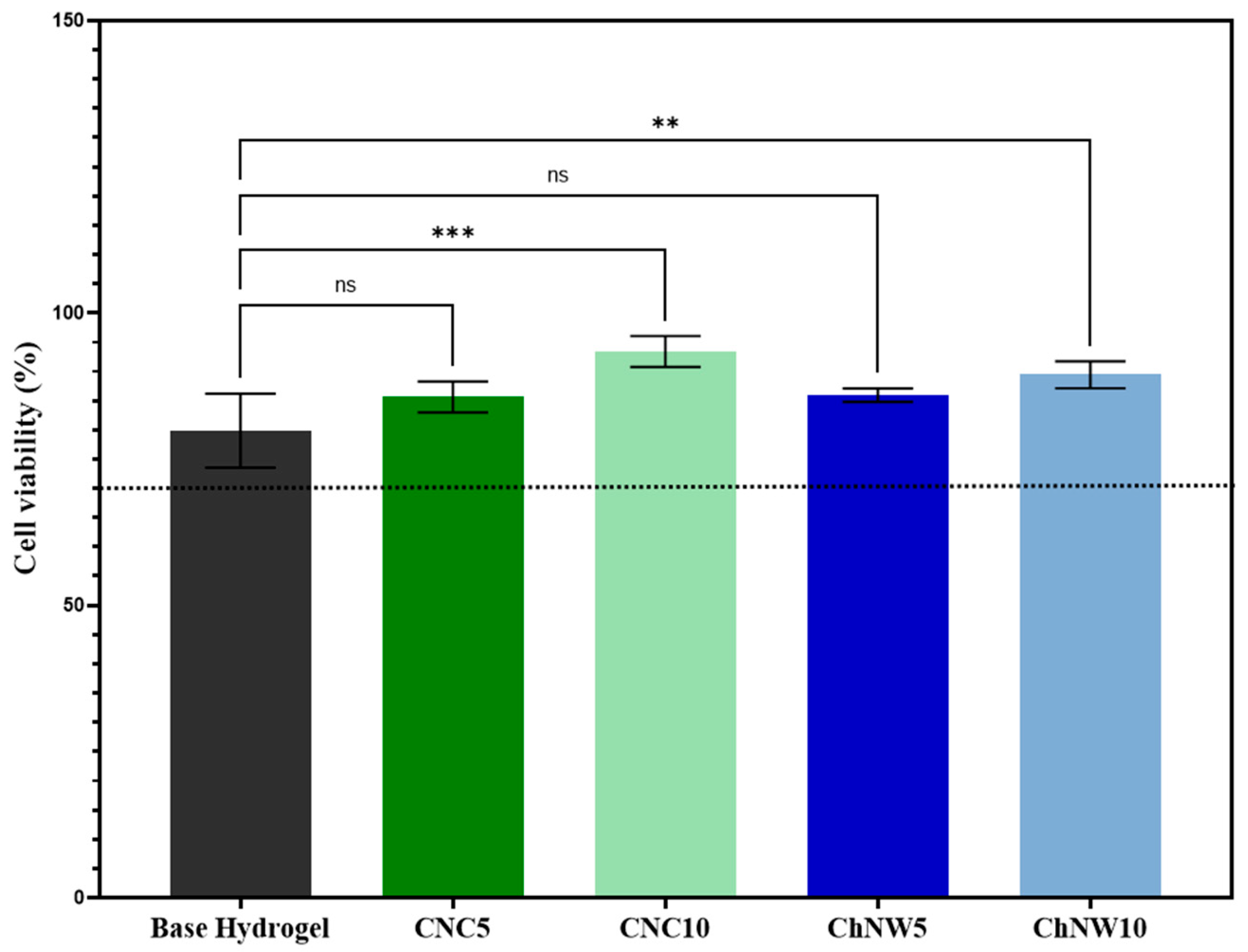
2.5.1. Cytocompatibility (MTT, L929 Fibroblasts)
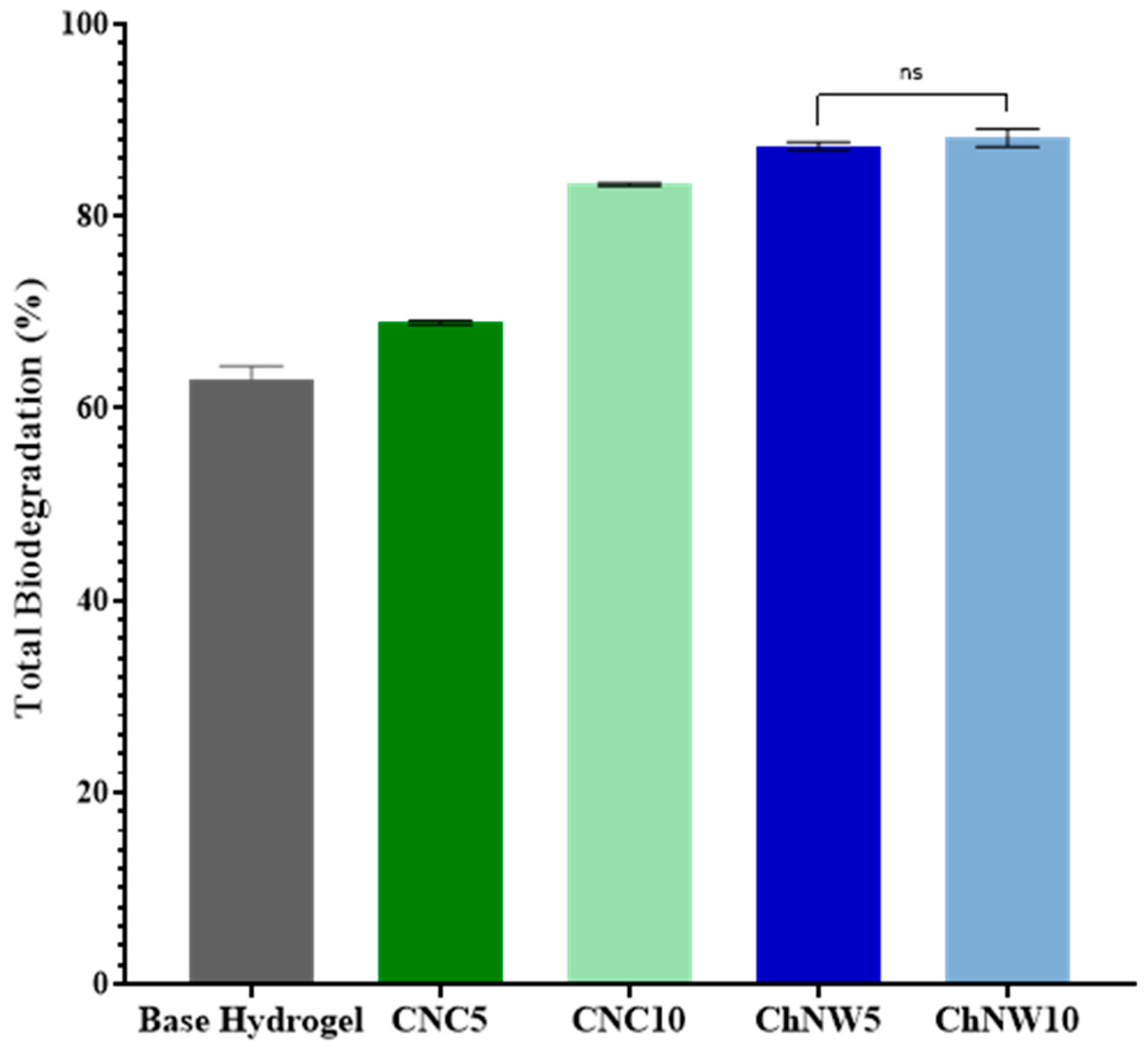
2.5.2. Biodegradation Behaviour
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Hydrogel Fabrication
3.2.1. Base κ-Carrageenan Matrix-Base Hydrogel
3.2.2. Cellulose Nanocrystal (CNC)–Reinforced Hydrogels
3.2.3. Chitin Nanowhisker (ChNW)–Reinforced Hydrogels
3.2.4. Formulations and Coding
3.3. Bromelain Loading
3.3.1. Preparation of Crude Bromelain
3.3.2. Loading into Hydrogels: Timing and Dose
3.4. Physicochemical Characterisation
3.4.1. Hydrogel Integrity and Chemical Resilience
3.4.2. FTIR
3.4.3. FE–SEM
3.4.4. Contact Angle (Wettability)
3.5. Hydration and Degradation
3.5.1. Swelling Behaviour (Time–Dependent)
3.5.2. Biodegradation
3.6. Enzyme Release Kinetics
3.7. Kinetic Analysis of Bromelain Release
3.8. Antibacterial Activity
3.9. Cytocompatibility Assay
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFM | Atomic Force Microscopy |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| CNC | Cellulose nanocrystals |
| CNC5 | κ-carrageenan/CNC hydrogel containing 5 wt% CNC |
| CNC10 | κ-carrageenan/CNC hydrogel containing 10 wt% CNC |
| ChNW | Chitin nanowhiskers |
| ChNW5 | κ-carrageenan/ChNW hydrogel containing 5 wt% ChNW |
| ChNW10 | κ-carrageenan/ChNW hydrogel containing 10 wt% ChNW |
| DMF | N,N-Dimethylformamide |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy |
| FE-SEM | Field-emission scanning electron microscopy |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| PEG | Polyethylene Glycol |
| PVA | Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) |
| SD | standard deviation |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| ZOI | Zones of inhibition |
References
- Ho, T.-C.; Chang, C.-C.; Chan, H.-P.; Chung, T.-W.; Shu, C.-W.; Chuang, K.-P.; Duh, T.-H.; Yang, M.-H.; Tyan, Y.-C. Hydrogels: Properties and Applications in Biomedicine. Molecules 2022, 27, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Patel, D.; Hickson, B.; DesRochers, J.; Hu, X. Recent Progress in Biopolymer-Based Hydrogel Materials for Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Xu, F.-J. Rational Design and Latest Advances of Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels for Wound Healing. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 2084–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Zhang, L.; Ou, R.; Xu, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhan, X.-Y.; Li, D. Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels for Wound Dressing: Design Considerations and Clinical Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 845735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jung, Y.; Lee, N.; Lee, I.; Lee, J.H. Nature-Derived Polysaccharide-Based Composite Hydrogels for Promoting Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, D.; Behera, D.; Pattnaik, S.S.; Behera, A.K. Advances in Natural Polymer-Based Hydrogels: Synthesis, Applications, and Future Directions in Biomedical and Environmental Fields. Discov. Polym. 2025, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, M. Enzyme-Responsive Hydrogels as Potential Drug Delivery Systems-State of Knowledge and Future Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minehan, R.L.; Del Borgo, M.P. Controlled Release of Therapeutics from Enzyme-Responsive Biomaterials. Front. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 1, 916985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, J.; Peter, A.; Thajudeen, K.Y.; Pereira, M.D.L.G.; Athira, V.P.; Michel, H. Recent Advances in the Design and Development of Bioink Formulations for Various Biomedical Applications. Results Eng. 2024, 22, 102060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasempour, A.; Naderi Allaf, M.R.; Charoghdoozi, K.; Dehghan, H.; Mahmoodabadi, S.; Bazrgaran, A.; Savoji, H.; Sedighi, M. Stimuli-Responsive Carrageenan-Based Biomaterials for Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 291, 138920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, H.; Tavakoli, S.; Safarpour, F.; Kharaziha, M.; Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Ramakrishna, S.; Berto, F. Recent Advances in Chemically-Modified and Hybrid Carrageenan-Based Platforms for Drug Delivery, Wound Healing, and Tissue Engineering. Polymers 2021, 13, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.A.; Alhalafi, M.H.; Emam, E.-A.M.; Ibrahim, H.; Mosaad, R.M. A Review of Chitosan and Chitosan Nanofiber: Preparation, Characterization, and Its Potential Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Singh, B.; Sharma, S.; Kanwar, S.S. Designing Carrageenan-Based Hydrogels for Drug Delivery Applications: Evaluation of Physiochemical and Biomedical Properties. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2024, 32, 100439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, R.O.; Patil, S.D. Fabrication and Statistical Optimization of Starch-κ-Carrageenan Cross-Linked Hydrogel Composite for Extended Release Pellets of Zaltoprofen. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 2324–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwabebhoh, F.A.; Patwa, R.; Zandraa, O.; Saha, N.; Saha, P. Preparation and Characterization of Injectable Self-Antibacterial Gelatin/Carrageenan/Bacterial Cellulose Hydrogel Scaffolds for Wound Healing Application. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 102415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.; Nikhade, P.; Patel, A.; Mankar, N.; Sedani, S. Bromelain: A Potent Phytomedicine. Cureus 2022, 14, e27876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnavelu, V.; Alitheen, N.B.; Sohila, S.; Kanagesan, S.; Ramesh, R. Potential Role of Bromelain in Clinical and Therapeutic Applications. Biomed. Rep. 2016, 5, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataide, J.; Cefali, L.; Rebelo, M.; Spir, L.; Tambourgi, E.; Jozala, A.; Chaud, M.; Silveira, E.; Gu, X.; Gava Mazzola, P. Bromelain Loading and Release from a Hydrogel Formulated Using Alginate and Arabic Gum. Planta Med. 2017, 83, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.; Paneo, M.A.; Mo’o, F.R.C.; Puluhulawa, L.E.; Latif, M.S. Formulation of Natural Hydrogel from Bromelain Enzyme and Alginate-Chitosan and the in Vivo Effectiveness Test in Healing Burns. J. Med. Pharm. Chem. Res. 2025, 1449, 944–959. [Google Scholar]
- Petrai, N.; Loukelis, K.; Chatzinikolaidou, M. Curcumin-Functionalized Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes with Antimicrobial Activity for Wound Healing. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhi, A.; Hayashi, J.; Eichenbaum, J.; Gutin, M.; Kuntjoro, N.; Khorsandi, D.; Khademhosseini, A. Recent Advances in Nanoengineering Cellulose for Cargo Delivery. J. Control. Release 2019, 294, 53–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvin, C.W.; Satam, C.C.; Liao, J.; Russo, P.S.; Breedveld, V.; Meredith, J.C.; Shofner, M.L. Synergistic Reinforcement of Composite Hydrogels with Nanofiber Mixtures of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Chitin Nanofibers. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicu, R.; Ciolacu, F.; Ciolacu, D.E. Advanced Functional Materials Based on Nanocellulose for Pharmaceutical/Medical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De France, K.J.; Hoare, T.; Cranston, E.D. Review of Hydrogels and Aerogels Containing Nanocellulose. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 4609–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; McClements, D.J.; He, M.; Zheng, L.; Tian, T.; Teng, F.; Li, Y. Preparation and Characterization of Okara Nanocellulose Fabricated Using Sonication or High-Pressure Homogenization Treatments. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 255, 117364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinge, C.; Kandasubramanian, B. Nanocellulose Based Biodegradable Polymers. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 133, 109758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitriani, F.; Aprilia, S.; Arahman, N.; Bilad, M.R.; Amin, A.; Huda, N.; Roslan, J. Isolation and Characterization of Nanocrystalline Cellulose Isolated from Pineapple Crown Leaf Fiber Agricultural Wastes Using Acid Hydrolysis. Polymers 2021, 13, 4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Chacharkar, M.P.; Mathur, A.K. Chitin Membrane for Wound Dressing Application—Preparation, Characterisation and Toxicological Evaluation. Int. Wound J. 2008, 5, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berradi, A.; Lafdali, A.; Ouazzani, N.; Aziz, K.; Mandi, L.; El Achaby, M.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Aziz, F. Development and Characterization of a Carboxymethyl Cellulose-Alginate Hybrid Superabsorbent Hydrogel Designed for Water Management in Agriculture. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 323, 146926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarivate. Web of Science. Available online: https://www.webofscience.com/ (accessed on 29 October 2025).
- VOSviewer. Available online: https://www.vosviewer.com/ (accessed on 29 October 2025).
- Araki, J.; Yamanaka, Y.; Ohkawa, K. Chitin-Chitosan Nanocomposite Gels: Reinforcement of Chitosan Hydrogels with Rod-like Chitin Nanowhiskers. Polym. J. 2012, 44, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.A.; Xie, R.; Liu, J.; Ali, S.; Pawar, K.D.; Sudiana, I.M.; Sun, J. Current Paradigms and Future Challenges in Harnessing Nanocellulose for Advanced Applications in Tissue Engineering: A Critical State-of-the-Art Review for Biomedicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, R.; Prabaharan, M.; Sudheesh Kumar, P.T.; Nair, S.V.; Tamura, H. Biomaterials Based on Chitin and Chitosan in Wound Dressing Applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedadghavami, A.; Minooei, F.; Mohammadi, M.H.; Khetani, S.; Rezaei Kolahchi, A.; Mashayekhan, S.; Sanati-Nezhad, A. Manufacturing of Hydrogel Biomaterials with Controlled Mechanical Properties for Tissue Engineering Applications. Acta Biomater. 2017, 62, 42–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coco, J.C.; Tundisi, L.L.; dos Santos, É.M.; Fava, A.L.M.; Alves, T.F.; Ataide, J.A.; Chaud, M.V.; Mazzola, P.G. PVA-CO-AAM and Peg-Co-Aam Hydrogels as Bromelain Carriers. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 102483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mala, T.; Anal, A.K. Protection and Controlled Gastrointestinal Release of Bromelain by Encapsulating in Pectin–Resistant Starch Based Hydrogel Beads. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 757176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricardo, P.C.; Serudo, R.L.; Ţălu, Ş.; Lamarão, C.V.; da Fonseca Filho, H.D.; de Araújo Bezerra, J.; Sanches, E.A.; Campelo, P.H. Encapsulation of Bromelain in Combined Sodium Alginate and Amino Acid Carriers: Experimental Design of Simplex-Centroid Mixtures for Digestibility Evaluation. Molecules 2022, 27, 6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10993-5; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Lin, N.; Dufresne, A. Nanocellulose in Biomedicine: Current Status and Future Prospect. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 59, 302–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorfi, M.; Foster, E.J. Recent Advances in Nanocellulose for Biomedical Applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, H.R. Bromelain: Biochemistry, Pharmacology and Medical Use. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, R.; Jain, S.; Shraddha; Kumar, A. Properties and Therapeutic Application of Bromelain: A Review. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 976203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasiku, V.O.; Omolo, C.A.; Devnarain, N.; Ibrahim, U.H.; Rambharose, S.; Faya, M.; Mocktar, C.; Singh, S.D.; Govender, T. Chitosan-Based Hydrogel for the Dual Delivery of Antimicrobial Agents Against Bacterial Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Biofilm-Infected Wounds. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 21994–22010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fissore, A.; Marengo, M.; Santoro, V.; Grillo, G.; Oliaro-Bosso, S.; Cravotto, G.; Piaz, F.; Adinol, S. Extraction and Characterization of Bromelain from Pineapple Core: A Strategy for Pineapple Waste Valorization. Processes 2023, 11, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, B.; Abraham, E.; Pothan, L.; Cordeiro, N.; Faria, M.; Thomas, S. Biodegradable Nanocomposite Films Based on Sodium Alginate and Cellulose Nanofibrils. Materials 2016, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rata, D.M.; Cadinoiu, A.N.; Popa, M.; Atanase, L.I.; Daraba, O.M.; Popescu, I.; Romila, L.E.; Ichim, D.L. Biocomposite Hydrogels for the Treatment of Bacterial Infections: Physicochemical Characterization and In Vitro Assessment. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzola, P.G.; Jozala, A.F.; Novaes, L.C.d.L.; Moriel, P.; Penna, T.C.V. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Determination of Disinfectant and/or Sterilizing Agents. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 45, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balouiri, M.; Sadiki, M.; Ibnsouda, S.K. Methods for in Vitro Evaluating Antimicrobial Activity: A Review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Duration (h) | Base Hydrogel | CNC5 | CNC10 | ChNW5 | ChNW10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 7.1 (3.6) | 7.5 (3.8) | 4.2 (2.1) | 8.0 (4.0) | 6.4 (3.2) |
| 3 | 10.3 (3.2) | 9.9 (2.4) | 5.9 (1.7) | 10.4 (2.4) | 8.2 (1.8) |
| 4 | 14.0 (3.7) | 14.9 (5.0) | 7.1 (1.2) | 12.6 (2.2) | 10.0 (1.8) |
| 8 | 17.4 (0.9) | 19.1 (1.1) | 10.2 (0.8) | 15.9 (0.8) | 12.2 (0.6) |
| 24 | 24.8 (0.5) | 30.9 (0.7) | 14.4 (0.3) | 21.8 (0.4) | 16.4 (0.3) |
| Bacteria | CNC5 | CNC10 | ChNW5 | ChNW10 | Bromelain Enzyme |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus (+) | 17.1 ± 0.1 ** (94.5%) | 14.3 ± 0.4 **** (79.0%) | 16.2 ± 0.3 **** (89.5%) | 15.3 ± 0.4 **** (84.5%) | 18.1 ± 0.2 (100%) |
| K. pneumoniae (−) | 15.2 ± 0.3 **** (79.2%) | 14.0 ± 0.2 **** (72.9%) | 15.1 ± 0.2 **** (78.6%) | 13.2 ± 0.3 **** (68.0%) | 19.2 ± 0.3 (100%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faria, M.; Bhanumathyamma, D.; Reji, G.M.; Kuttiyatt, A.S.B.; Sivaprasad, G.; Viswanathan, S.P.; Ferreira, A.; Jose, J.; Sadasivan, S.M.; Pothan, L.A.; et al. Diffusion-Controlled Release of Bromelain from κ-Carrageenan Nanocomposite Hydrogels Reinforced with Bio-Derived Nanofillers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311438
Faria M, Bhanumathyamma D, Reji GM, Kuttiyatt ASB, Sivaprasad G, Viswanathan SP, Ferreira A, Jose J, Sadasivan SM, Pothan LA, et al. Diffusion-Controlled Release of Bromelain from κ-Carrageenan Nanocomposite Hydrogels Reinforced with Bio-Derived Nanofillers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311438
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaria, Marisa, Deepa Bhanumathyamma, Gladys Maria Reji, Aswin Sreenivas Baluseri Kuttiyatt, Ghanashyam Sivaprasad, Shanthi Prabha Viswanathan, Artur Ferreira, Jiya Jose, Sreekala Meyyarappallil Sadasivan, Laly Aley Pothan, and et al. 2025. "Diffusion-Controlled Release of Bromelain from κ-Carrageenan Nanocomposite Hydrogels Reinforced with Bio-Derived Nanofillers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311438
APA StyleFaria, M., Bhanumathyamma, D., Reji, G. M., Kuttiyatt, A. S. B., Sivaprasad, G., Viswanathan, S. P., Ferreira, A., Jose, J., Sadasivan, S. M., Pothan, L. A., Cordeiro, N., & Thomas, S. (2025). Diffusion-Controlled Release of Bromelain from κ-Carrageenan Nanocomposite Hydrogels Reinforced with Bio-Derived Nanofillers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311438










