Optimizing Small RNA Sequencing for Salivary Biomarker Identification: A Comparative Study of Library Preparation Protocols
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
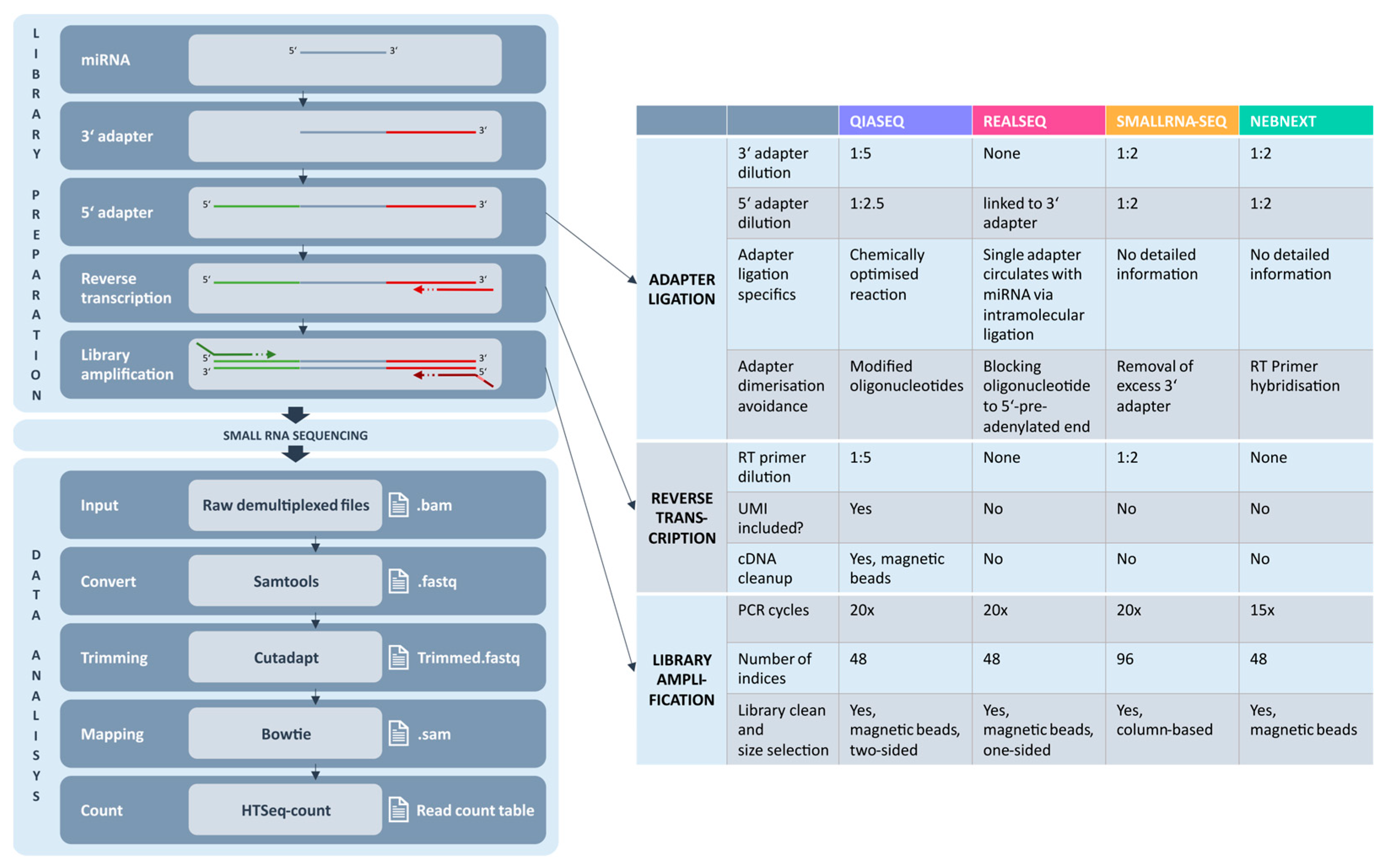
2.1. Experimental Overview of Small RNA Library Preparation Techniques
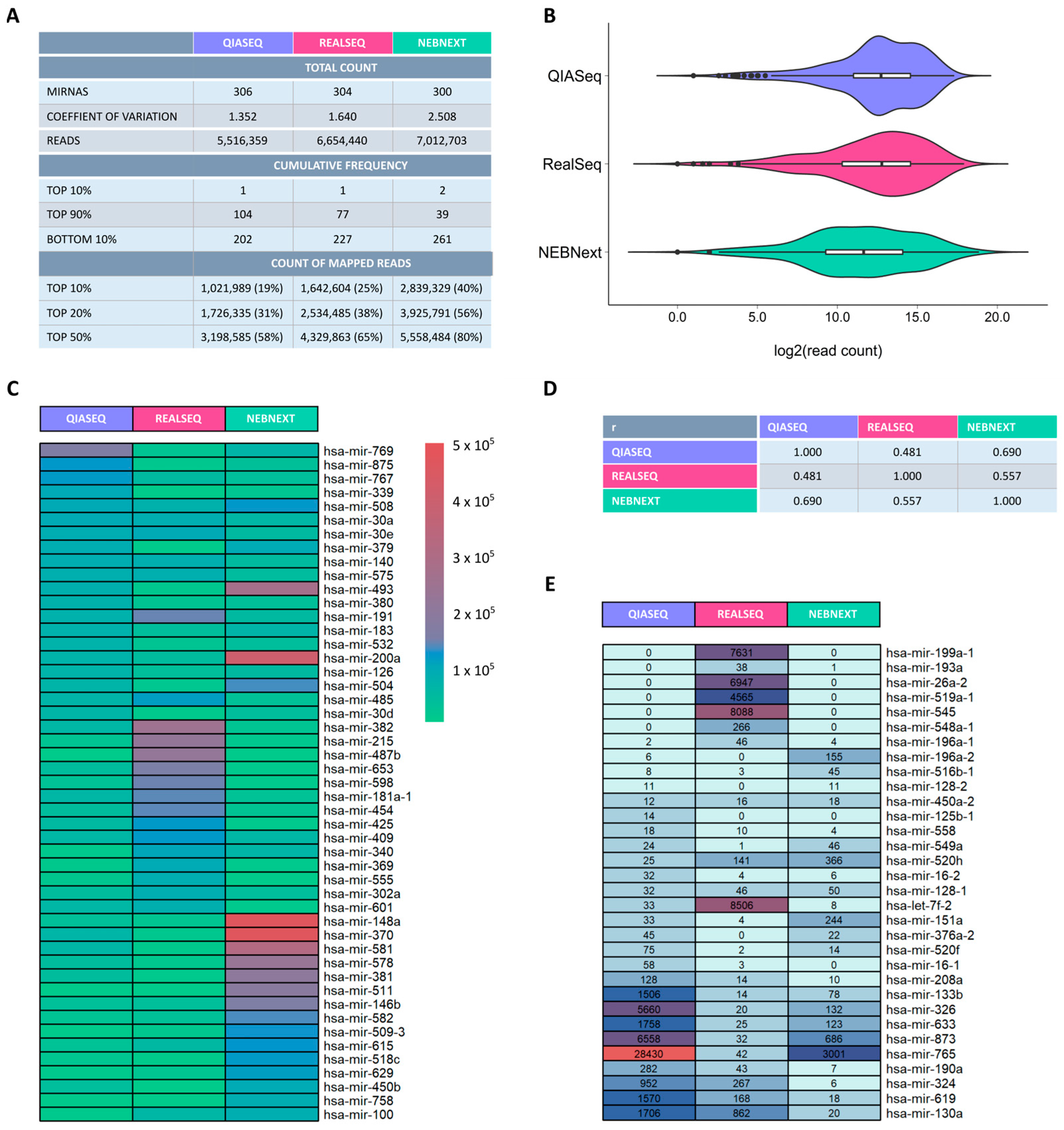
2.2. Quantitative Assessment of miRNA Representation During Small RNA Library Preparation
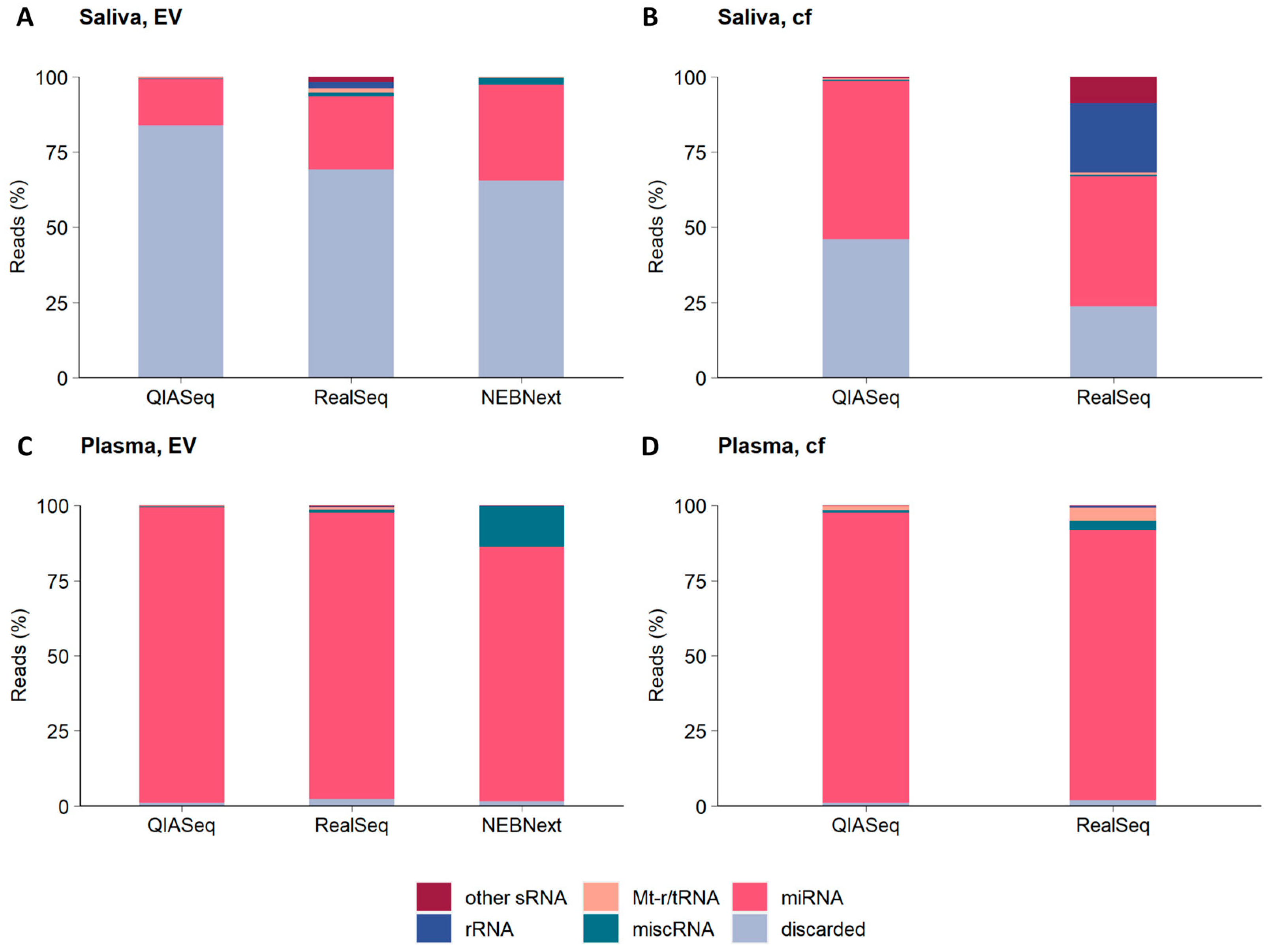
2.3. Distribution of Non-Coding RNA Categories in Cell-Free Saliva and Plasma and the EVs Derived from Them
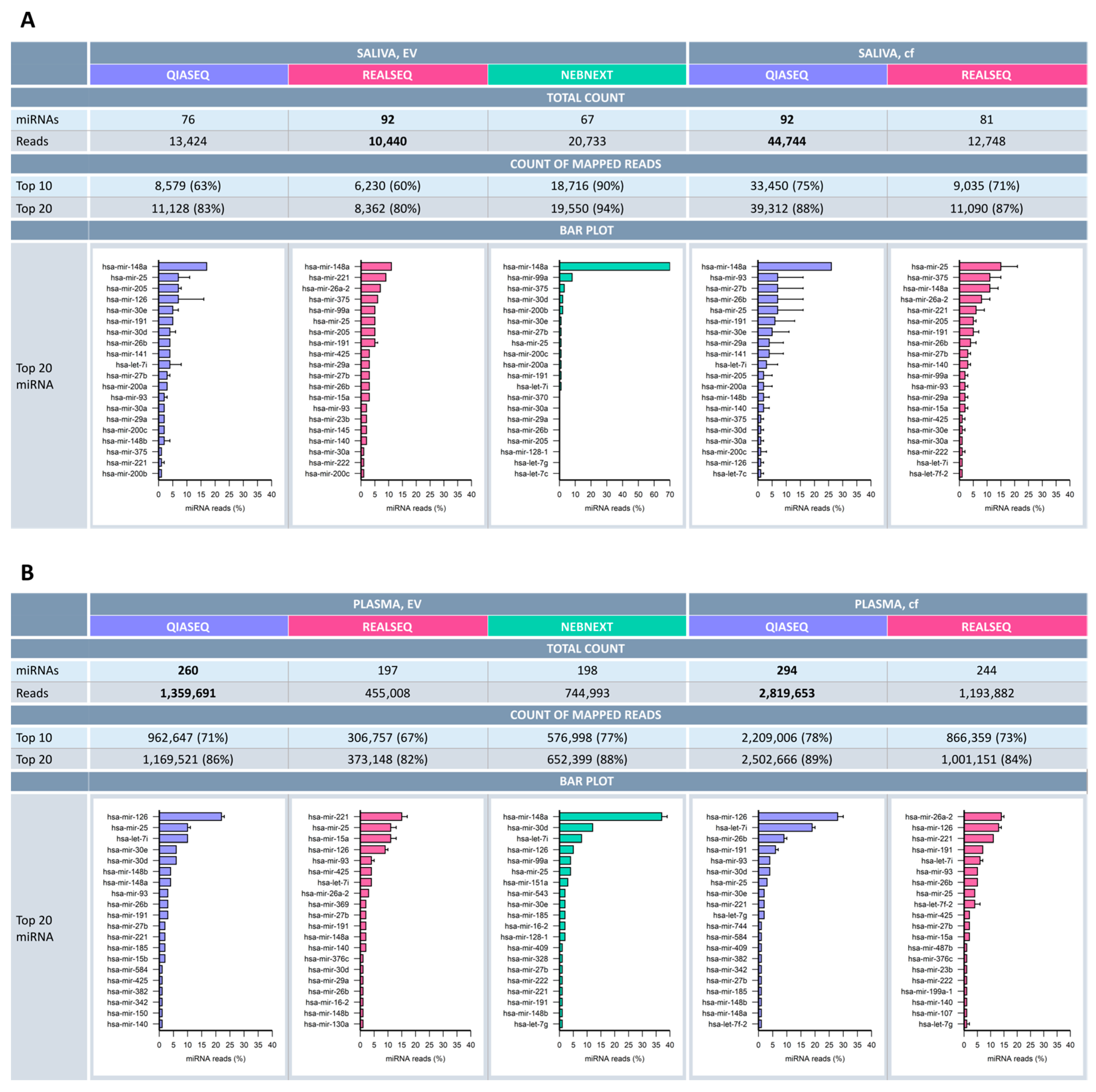
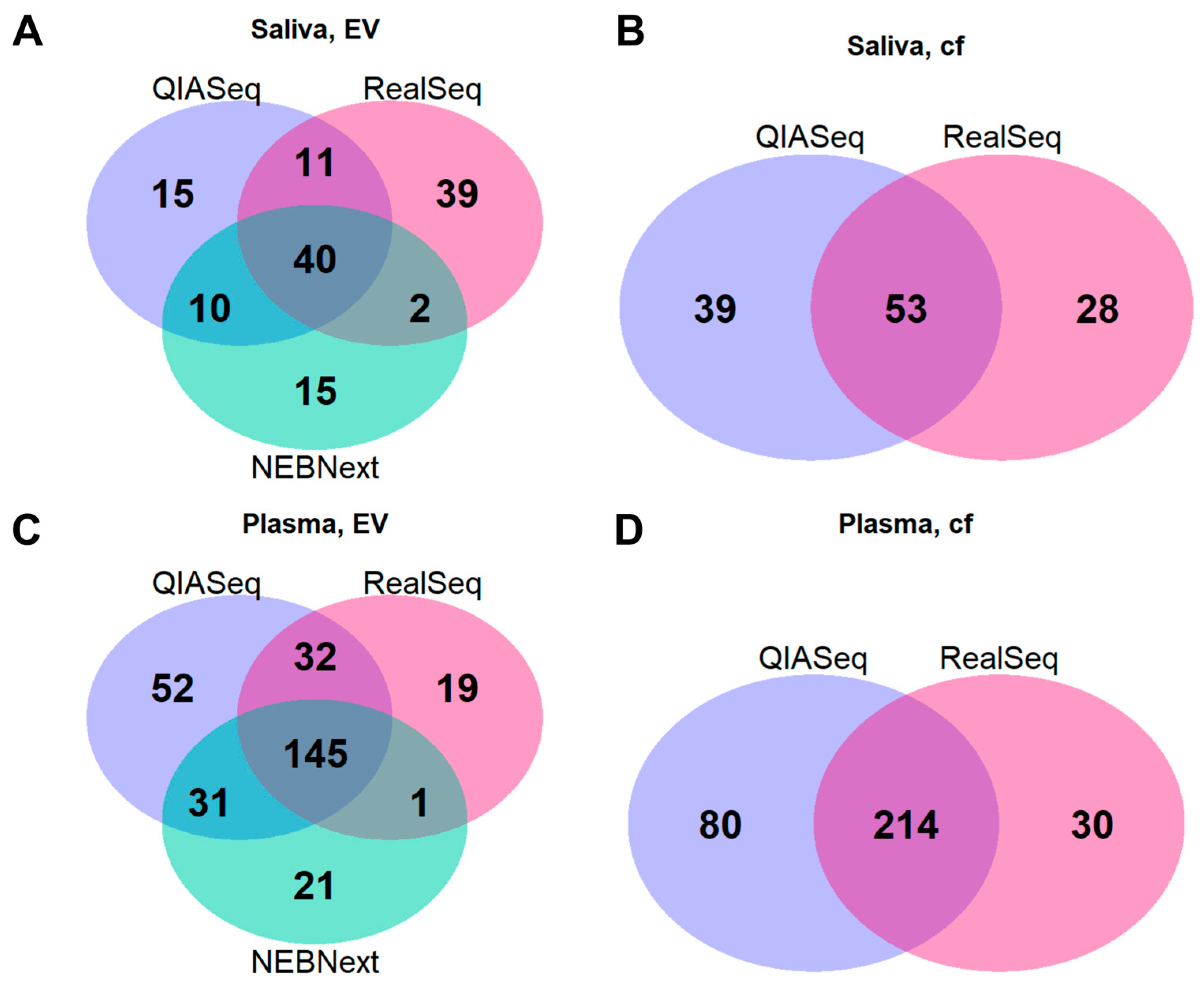
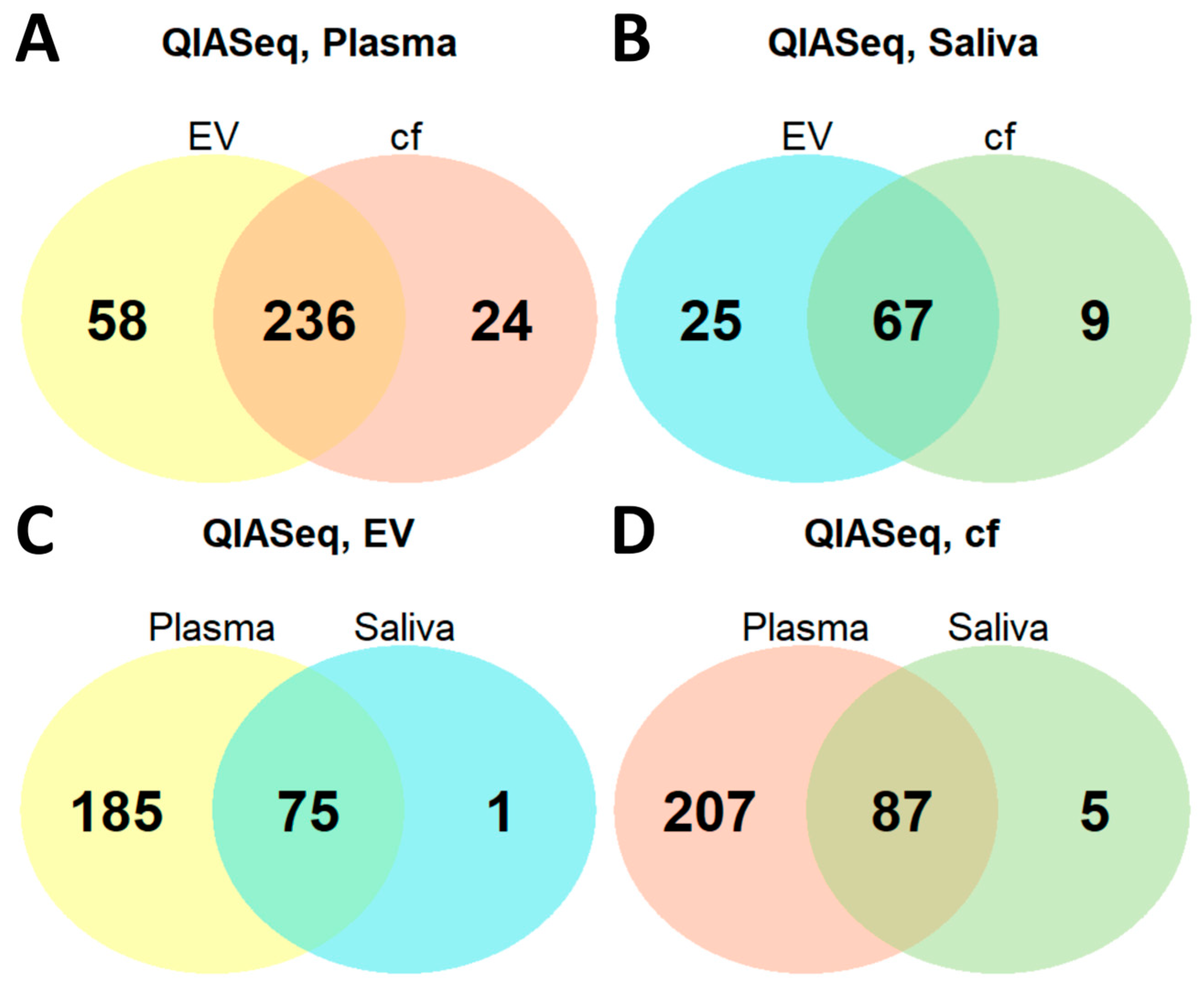
2.4. miRNA Profile Characteristics in Saliva and Plasma
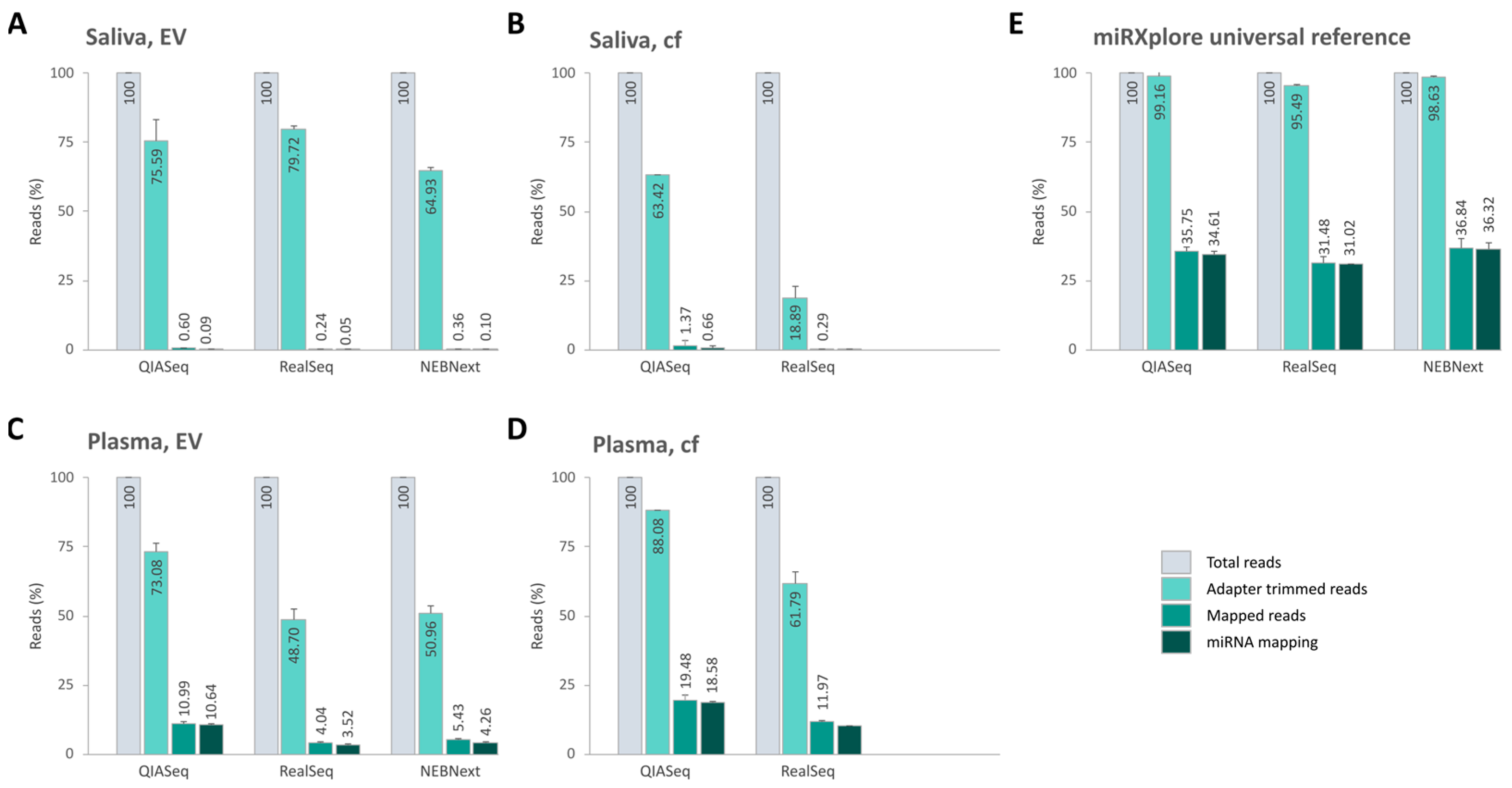
2.5. Sequencing Efficiency
3. Discussion
3.1. Library Preparation and Adapter Strategies
3.2. Sequencing Performance and Kit Exclusion
3.3. Comparative Analysis of Saliva vs. Plasma
3.4. miRNA Detection and Biomarker Relevance
3.5. Library Quality and Mapping Efficiency
3.6. UMIs and Quantification Accuracy
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection and Preprocessing
4.2. Extracellular Vesicle Isolation
4.3. EDTA Removal from Plasma EVs
4.4. DNase and RNase Treatment of EVs
4.5. RNA Isolation from EVs, Plasma and Cell-Free Saliva
4.6. Quantification of Total RNA Amount
4.7. Small RNA Library Preparation for Sequencing
4.8. Quality Control of Library Amplicons
4.9. Small RNA Sequencing
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| cf | Cell-free |
| EV | Extracellular vesicle |
| mRNA | Messenger RNA |
| miRNA | microRNA |
| ncRNA | Non-coding RNA |
| NGS | Next generation sequencing |
| QC | Quality control |
| qPCR | Quantitative PCR |
| sEV | Small extracellular vesicle |
| TBS | Tris-buffered saline |
| UMIs | Unique molecular indies |
References
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeri, A.; Courtright, A.; Reiman, R.; Carlson, E.; Beecroft, T.; Janss, A.; Siniard, A.; Richholt, R.; Balak, C.; Rozowsky, J.; et al. Total Extracellular Small RNA Profiles from Plasma, Saliva, and Urine of Healthy Subjects. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.A.; Baxter, D.H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, D.Y.; Huang, K.H.; Lee, M.J.; Galas, D.J.; Wang, K. The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roblegg, E.; Coughran, A.; Sirjani, D. Saliva: An all-rounder of our body. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 142, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczor-Urbanowicz, K.E.; Martin Carreras-Presas, C.; Aro, K.; Tu, M.; Garcia-Godoy, F.; Wong, D.T. Saliva diagnostics—Current views and directions. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ou, Y.; Fan, K.; Liu, G. Salivary diagnostics: Opportunities and challenges. Theranostics 2024, 14, 6969–6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrügger, U.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404, Correction in J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.A.; Baba, S.K.; Sadida, H.Q.; Marzooqi, S.A.; Jerobin, J.; Altemani, F.H.; Algehainy, N.; Alanazi, M.A.; Abou-Samra, A.-B.; Kumar, R.; et al. Extracellular vesicles as tools and targets in therapy for diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Théry, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, S.; McPherson, J.D.; McCombie, W.R. Coming of age: Ten years of next-generation sequencing technologies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, E.L.; Jaszczyszyn, Y.; Thermes, C. Library preparation methods for next-generation sequencing: Tone down the bias. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 322, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran-Gale, J.; Kurtz, C.L.; Erdos, M.R.; Sison, C.; Young, A.; Fannin, E.E.; Chines, P.S.; Sethupathy, P. Addressing Bias in Small RNA Library Preparation for Sequencing: A New Protocol Recovers MicroRNAs that Evade Capture by Current Methods. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, R.T.; Sun, Z.; Zhuang, F.; Robb, G.B. Bias in ligation-based small RNA sequencing library construction is determined by adaptor and RNA structure. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaprakash, A.D.; Jabado, O.; Brown, B.D.; Sachidanandam, R. Identification and remediation of biases in the activity of RNA ligases in small-RNA deep sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissels, U.; Wild, S.; Bosio, A. Universal Reference for miRNA Research; Miltenyi Biotec: Bergisch Gladbach, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bissels, U.; Wild, S.; Tomiuk, S.; Holste, A.; Hafner, M.; Tuschl, T.; Bosio, A. Absolute quantification of microRNAs by using a universal reference. RNA 2009, 15, 2375–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensembl. Automatic Annotation of Non-Coding Genes. Available online: https://www.ensembl.org/info/genome/genebuild/ncrna.html (accessed on 13 December 2019).
- Ensembl. Biotypes. Available online: https://www.ensembl.org/info/genome/genebuild/biotypes.html (accessed on 13 December 2019).
- Raabe, C.A.; Tang, T.-H.; Brosius, J.; Rozhdestvensky, T.S. Biases in small RNA deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 1414–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinicke, F.; Zhong, X.; Zucknick, M.; Breidenbach, J.; Sundaram, A.Y.M.; Flåm, S.T.; Leithaug, M.; Dalland, M.; Farmer, A.; Henderson, J.M.; et al. Systematic assessment of commercially available low-input miRNA library preparation kits. RNA Biol. 2020, 17, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Duval, M.X.; Kaimal, V.; Cuff, C.; Clarke, S.H. Assessment of methods for serum extracellular vesicle small RNA sequencing to support biomarker development. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1684425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.K.Y.; MacMahon, M.; Woodside, J.V.; Simpson, D.A. A comparison of RNA extraction and sequencing protocols for detection of small RNAs in plasma. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldez, M.D.; Spengler, R.M.; Etheridge, A.; Godoy, P.M.; Barczak, A.J.; Srinivasan, S.; De Hoff, P.L.; Tanriverdi, K.; Courtright, A.; Lu, S.; et al. Comprehensive multi-center assessment of small RNA-seq methods for quantitative miRNA profiling. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 746–757, Erratum in Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberán-Soler, S.; Vo, J.M.; Hogans, R.E.; Dallas, A.; Johnston, B.H.; Kazakov, S.A. Decreasing miRNA sequencing bias using a single adapter and circularization approach. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coenen-Stass, A.M.L.; Magen, I.; Brooks, T.; Ben-Dov, I.Z.; Greensmith, L.; Hornstein, E.; Fratta, P. Evaluation of methodologies for microRNA biomarker detection by next generation sequencing. RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.; Rajpurohit, A.; Burke, E.E.; Williams, C.; Collado-Torres, L.; Kimos, M.; Brandon, N.J.; Cross, A.J.; Jaffe, A.E.; Weinberger, D.R.; et al. Comprehensive assessment of multiple biases in small RNA sequencing reveals significant differences in the performance of widely used methods. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiagen. QIAseq MiRNA Library Kit Handbook: Precision Small RNA Library Prep for Illumina NGS Systems; Qiagen: Venlo, The Netherlands, 2020; p. 331505. [Google Scholar]
- Lexogen. Small RNA-Seq Library Prep Kit: User Guide; 052UG128V0101; 051; Lexogen: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- New England BioLabs. NEBNext Multiplex Small RNA Library Prep Set for Ilumina (Set 1): Instruction Manual; New England BioLabs: Ipswich, MA, USA, 2017; p. E7300. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Wu, P.-H.; Beane, T.; Zamore, P.D.; Weng, Z. Elimination of PCR duplicates in RNA-seq and small RNA-seq using unique molecular identifiers. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 13 December 2019).
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq—A Python Framework to Work with High-Throughput Sequencing Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=pheatmap (accessed on 13 December 2019).
- VennDiagram: Generate High-Resolution Venn and Euler Plots. 2018. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=VennDiagram (accessed on 13 December 2019).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kegler, U.; Ropek, N.; Hofner, M.; Schönthaler, S.; Vierlinger, K.; Nöhammer, C. Optimizing Small RNA Sequencing for Salivary Biomarker Identification: A Comparative Study of Library Preparation Protocols. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11437. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311437
Kegler U, Ropek N, Hofner M, Schönthaler S, Vierlinger K, Nöhammer C. Optimizing Small RNA Sequencing for Salivary Biomarker Identification: A Comparative Study of Library Preparation Protocols. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11437. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311437
Chicago/Turabian StyleKegler, Ulrike, Nathalie Ropek, Manuela Hofner, Silvia Schönthaler, Klemens Vierlinger, and Christa Nöhammer. 2025. "Optimizing Small RNA Sequencing for Salivary Biomarker Identification: A Comparative Study of Library Preparation Protocols" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11437. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311437
APA StyleKegler, U., Ropek, N., Hofner, M., Schönthaler, S., Vierlinger, K., & Nöhammer, C. (2025). Optimizing Small RNA Sequencing for Salivary Biomarker Identification: A Comparative Study of Library Preparation Protocols. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11437. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311437





