Current Knowledge About Aprocitentan in Hypertension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Hypertension
Forms of Hypertension
3. Aprocitentan
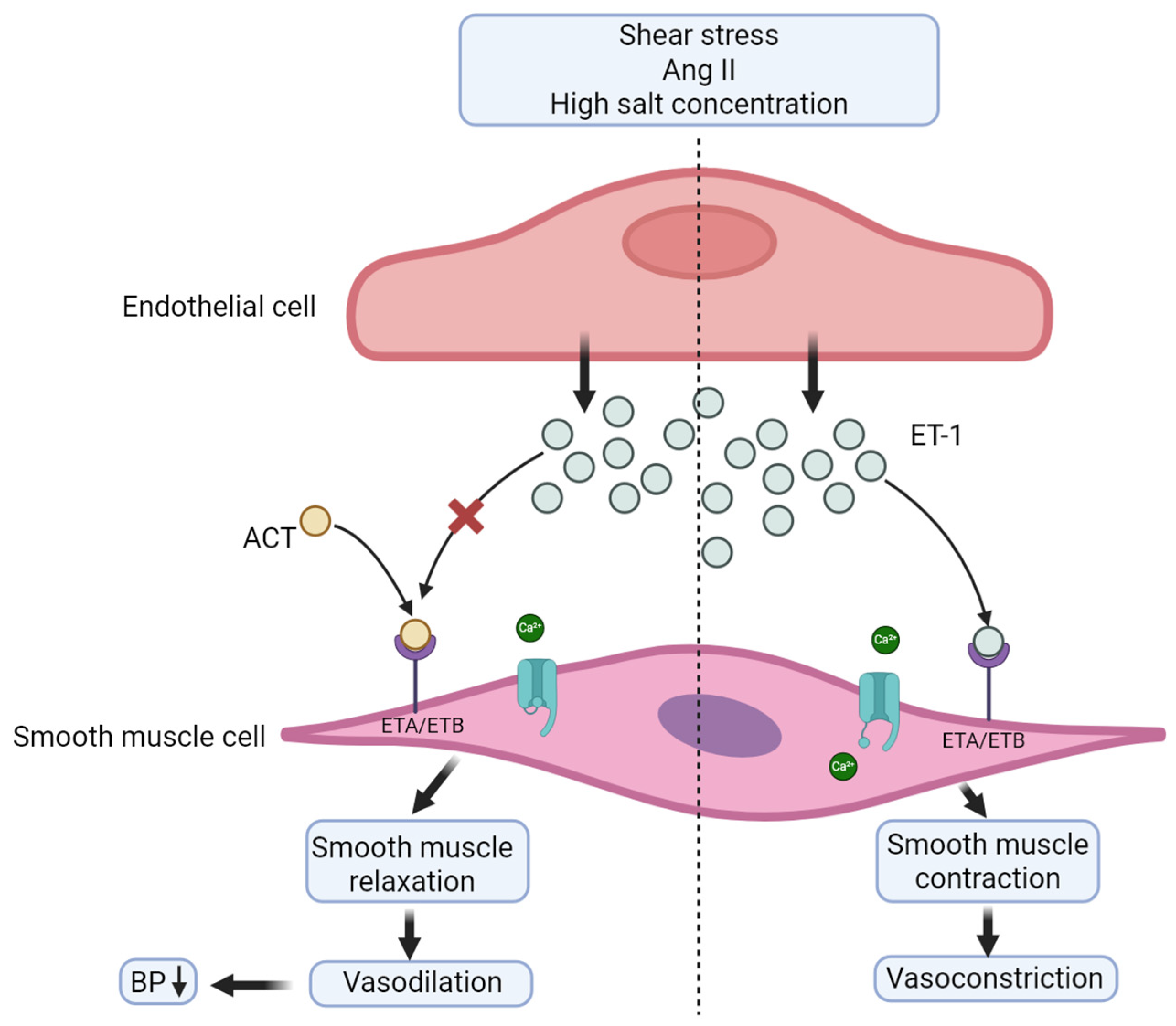
3.1. Mechanism of Action
3.2. Pharmacokinetics
3.3. Interaction
3.4. Indication
4. Clinical Trials
5. Discussion
5.1. Safety and Adverse Effects
5.2. Aprocitentan vs. Standard Treatment
6. Materials and Methods
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | Angiotensin converting enzyme |
| ACEI | ACE inhibitor |
| ACT | Aprocitentan |
| AE | Adverse effect |
| Ang I | Angiotensin I |
| Ang II | Angiotensin II |
| ARBs | Angiotensin receptor blockers |
| BARB | Beta adrenergic receptor-blockers |
| BCRP | Breast cancer resistance protein |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| CCB | Calcium channel blockers |
| CO | Cardiac output |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| DOCA | Deoxycorticosterone acetate |
| ERA | Endothelin receptor antagonist |
| HBPM | Home blood pressure measurements |
| HR | Heart rate |
| HT | Hypertension |
| MAP | Mean arterial pressure |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| RAAS | Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| SHRs | Spontaneously hypertensive rats |
| SV | Stroke volume |
| TPR | Total peripheral resistance |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Brouwers, S.; Sudano, I.; Kokubo, Y.; Sulaica, E.M. Arterial hypertension. Lancet 2021, 398, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveros, E.; Patel, H.; Kyung, S.; Fugar, S.; Goldberg, A.; Madan, N.; Williams, K.A. Hypertension in older adults: Assessment, management, and challenges. Clin. Cardiol. 2020, 43, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Hypertension. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration. Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: A pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet 2021, 398, 957–980, Erratum in Lancet 2022, 399, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearney, P.M.; Whelton, M.; Reynolds, K.; Muntner, P.; Whelton, P.K.; He, J. Global burden of hypertension: Analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 2005, 365, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlGhatrif, M.; Wang, M.; Fedorova, O.V.; Bagrov, A.Y.; Lakatta, E.G. The Pressure of Aging. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 101, 81–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorhouse, R.C.; Webb, D.J.; Kluth, D.C.; Dhaun, N. Endothelin antagonism and its role in the treatment of hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2013, 15, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oparil, S.; Acelajado, M.C.; Bakris, G.L.; Berlowitz, D.R.; Cífková, R.; Dominiczak, A.F.; Grassi, G.; Jordan, J.; Poulter, N.R.; Rodgers, A.; et al. Hypertension. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoo, A.; van Zanten, J.J.; Metsios, G.S.; Carroll, D.; Kitas, G.D. The endothelium and its role in regulating vascular tone. Open Cardiovasc. Med. J. 2010, 4, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo Clinic Staff. High Blood Pressure (Hypertension). Available online: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure/symptoms-causes/syc-20373410 (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Charles, L.; Triscott, J.; Dobbs, B. Secondary Hypertension: Discovering the Underlying Cause. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 96, 453–461. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, J.; Kurschat, C.; Reuter, H. Arterial Hypertension. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2018, 115, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S. Aprocitentan: First Approval. Drugs 2024, 84, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, F.; Verdecchia, P.; Reboldi, G. Aprocitentan, A Dual Endothelin Receptor Antagonist Under Development for the Treatment of Resistant Hypertension. Cardiol. Ther. 2021, 10, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Jiang, X.; Xu, S. Aprocitentan, a dual endothelin-1 (ET-1) antagonist for treating resistant hypertension: Mechanism of action and therapeutic potential. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trensz, F.; Bortolamiol, C.; Kramberg, M.; Wanner, D.; Hadana, H.; Rey, M.; Strasser, D.S.; Delahaye, S.; Hess, P.; Vezzali, E.; et al. Pharmacological Characterization of Aprocitentan, a Dual Endothelin Receptor Antagonist, Alone and in Combination with Blockers of the Renin Angiotensin System, in Two Models of Experimental Hypertension. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 368, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseralallah, L.; Koraysh, S. Aprocitentan: A new emerging prospect in the pharmacotherapy of hypertension. Blood Press. 2024, 33, 2424824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, P.; Danaietash, P.; Flamion, B.; Ménard, J.; Bellet, M. Randomized Dose-Response Study of the New Dual Endothelin Receptor Antagonist Aprocitentan in Hypertension. Hypertension 2020, 75, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidharta, P.N.; Melchior, M.; Kankam, M.K.; Dingemanse, J. Single- and multiple-dose tolerability, safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of the dual endothelin receptor antagonist aprocitentan in healthy adult and elderly subjects. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2019, 13, 949–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontes, M.S.C.; Dingemanse, J.; Sidharta, P.N. Multiple-Dose Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of Aprocitentan, a Dual Endothelin Receptor Antagonist, in Healthy Japanese and Caucasian Subjects. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2021, 10, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104, Erratum in Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidharta, P.N.; Dingemanse, J. Effects of Multiple-Dose Administration of Aprocitentan on the Pharmacokinetics of Rosuvastatin. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2020, 9, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. A Drug-drug Interaction Trial in Healthy Female Participants to Investigate the Effect of Aprocitentan on Combined Hormonal Contraceptives. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06799884?intr=Aprocitentan&rank=12&page=2 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Danaietash, P.; Verweij, P.; Wang, J.G.; Dresser, G.; Kantola, I.; Lawrence, M.K.; Narkiewicz, K.; Schlaich, M.; Bellet, M. Identifying and treating resistant hypertension in PRECISION: A randomized long-term clinical trial with aprocitentan. J. Clin. Hypertens 2022, 24, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaich, M.P.; Bellet, M.; Weber, M.A.; Danaietash, P.; Bakris, G.L.; Flack, J.M.; Dreier, R.F.; Sassi-Sayadi, M.; Haskell, L.P.; Narkiewicz, K.; et al. Dual endothelin antagonist aprocitentan for resistant hypertension (PRECISION): A multicentre, blinded, randomised, parallel-group, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2022, 400, 1927–1937, Erratum in Lancet 2023, 401, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes, M.S.C.; Dingemanse, J.; Halabi, A.; Tomaszewska-Kiecana, M.; Sidharta, P.N. Single-dose pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of the dual endothelin receptor antagonist aprocitentan in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Salam, A.; Pant, R.; Kumar, A.; Dhurjati, R.; Haghdoost, F.; Vidyasagar, K.; Kaistha, P.; Esam, H.; Gnanenthiran, S.R.; et al. Blood pressure-lowering efficacy of antihypertensive drugs and their combinations: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Lancet 2025, 406, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. A Research Study to Show Aprocitentan is Efficacious and Safe to Treat Patients With Uncontrolled Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease. (INSPIRE-CKD). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04162366?intr=Aprocitentan&rank=11&page=2 (accessed on 17 May 2025).
- Mahfooz, K.; Najeed, S.; Tun, H.N.; Khamosh, M.; Grewal, D.; Hussain, A.; Ong, K.; Dharmarajan, L.; Vasavada, A. New Dual Endothelin Receptor Antagonist Aprocitentan in Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2023, 48, 101686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clozel, M. Aprocitentan and the endothelin system in resistant hypertension. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2022, 100, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varzideh, F.; Kansakar, U.; Jankauskas, S.S.; Santulli, G. Aprocitentan: New insights. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 1093406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Fan, B.; Yang, B.; Jia, Z.; Li, B. Aprocitentan: A new development of resistant hypertension. J. Clin. Hypertens 2023, 25, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, R.; Haddaway, M.J.P.; Chris, C.; Pritchard; Luke, A. McGuinness. PRISMA2020: An R package and Shiny App for Producing PRISMA 2020-Compliant Flow Diagrams, with Interactivity for Optimised Digital Transparency and Open Synthesis. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cl2.1230 (accessed on 30 August 2025).

| Parameter | 5 mg ACT | 25 mg ACT | 100 mg ACT | 100 mg ACT (Elderly) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax (μg/mL) | 0.83 | 3.57 | 13.41 | 17.62 |
| tmax (h) | 4.00 | 4.50 | 7.00 | 6.00 |
| t1/2 (h) | 48.83 | 45.69 | 41.69 | 44.71 |
| Title | Design | Results | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Study to evaluate how aprocitentan is safe and how it is absorbed and broken down in the body of Japanese and Caucasian subjects NCT03586570 [20] | Single-center, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, randomized study. Phase 1. 20 participants, 10 Japanese and 10 Caucasian | Cmax = 3.5 h, t½ = 49.1 and 48.8 h for Japanese and Caucasian, respectively. Steady-state conditions were reached within 7–10 days. A greater decrease in mean and median hemoglobin, hematocrit and RBC, was observed, but was not considered clinically relevant | No clinical difference in exposure, safety, and tolerability to aprocitentan on the two ethnic groups were found. The study deemed it unlikely that the PK of aprocitentan would differ significantly between Caucasians and other ethnicities |
| Phase 3 PRECISION study NCT03541174 [25] | Multi-center, blinded, randomized, parallel-group, phase 3 trial The study consisted of 3 sequential parts: part 1 was a 4-week double-blinded, randomized and placebo-controlled part. Part 2 was a 32-week single-blinded part. Part 3 was a 12-week double-blinded randomized, and placebo-controlled withdrawal part. 1965 individuals were screened, and 730 participants were randomly assigned. | Part 1 showed the least square mean change in office SBP was −15.3 mmHg for ACT 12.5 mg, −15.2 mmHg for ACT 25 mg and −11.5 mmHg for placebo. DBP also decreased for both doses, when compared to placebo (−3.9 mmHg and −4.5 mmHg, respectively). It was maintained for patients. Receiving ACT and decreased in patients previously receiving placebo, during part 2. A significant increase in BP was seen with placebo compared to ACT | Aprocitentan was found efficient to lower BP. Additionally, it was found to provide clinically meaningful lowering of SBP and DBP in patients with resistant HT with manageable adverse effects |
| Single-dose pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of the dual endothelin receptor antagonist aprocitentan in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment NCT04252495 [26] | Open-label, phase 1 study 17 participants: subjects were 8 subjects with moderate hepatic impairment matched with 9 healthy subjects 1 subject was excluded due to personal reasons = 16 subjects completed | Cmax was reached at a median of 4 h for both groups. Concentration decreased slowly in both the subjects with moderate hepatic impairment and the healthy subjects, indicated by a t½ of 56.4 h and 48.3 h, respectively | Aprocitentan was found to be absorbed similarly for moderate hepatic impaired compared to healthy subjects. No clinically relevant difference in PK, safety and tolerability was found. Aprocitentan can be administered to subjects with mild and moderate hepatic impairment, without dose adjustment. |
| Dose-finding study with ACT-132577 in participants with essential hypertension NCT02603809 [18] | Multi-center, double-blind, double-dummy, randomized, placebo- and active-reference, parallel group, phase 2, dose-finding study. 490 participants; 430 completed | Clinically relevant decrease in BP occurred, within 2 weeks in the aprocitentan 10, 25 and 50 mg groups. A statistically significant dose–response relationship for the change in mean siDBP was found | Aprocitentan 10, 25, and 50 mg once daily lowered BP in a clinically relevant, dose dependent manner. The maximum effect on BP was observed at 25 mg. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bank-Mikkelsen, E.M.; Grimm, D.; Wehland, M. Current Knowledge About Aprocitentan in Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11431. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311431
Bank-Mikkelsen EM, Grimm D, Wehland M. Current Knowledge About Aprocitentan in Hypertension. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11431. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311431
Chicago/Turabian StyleBank-Mikkelsen, Emilie Mathilde, Daniela Grimm, and Markus Wehland. 2025. "Current Knowledge About Aprocitentan in Hypertension" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11431. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311431
APA StyleBank-Mikkelsen, E. M., Grimm, D., & Wehland, M. (2025). Current Knowledge About Aprocitentan in Hypertension. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11431. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311431







