Identification of a Novel Salivary Four-miRNA Signature for Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinicopathological Characteristics of the Study Population
2.2. RNA Concentration and Quality Assessment
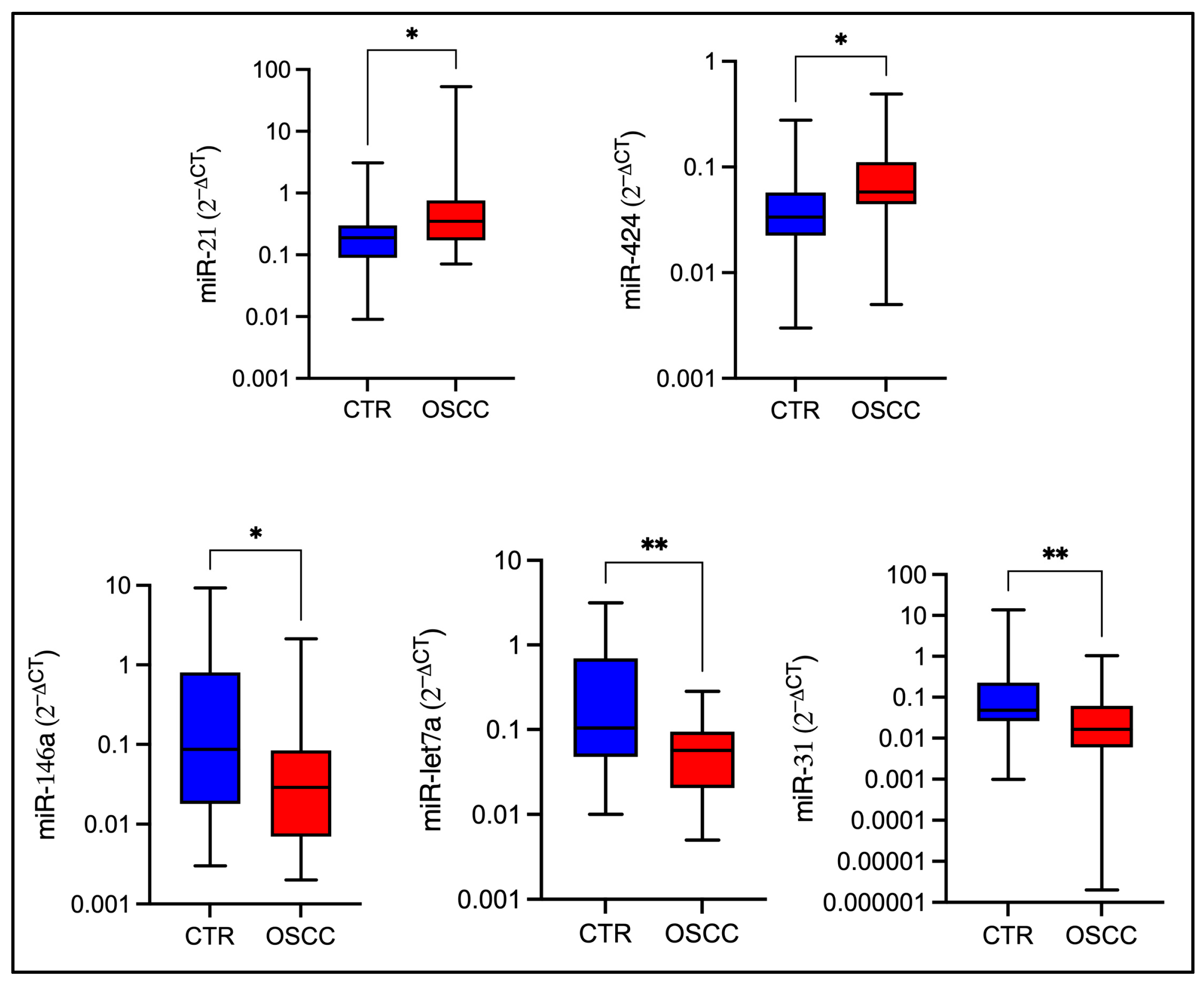
2.3. miRNA Expression Levels in OSCC Patients and Healthy Controls Groups
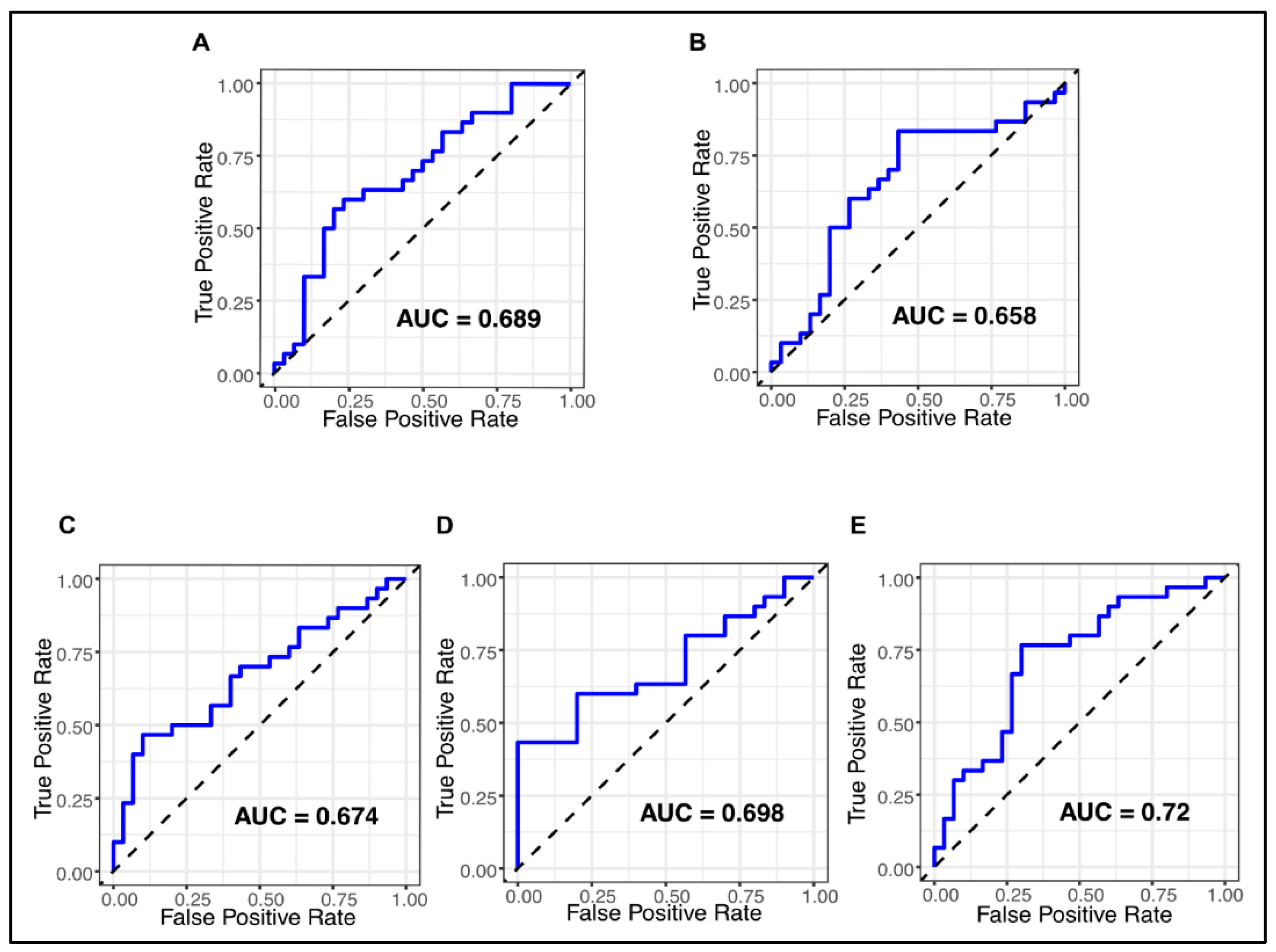
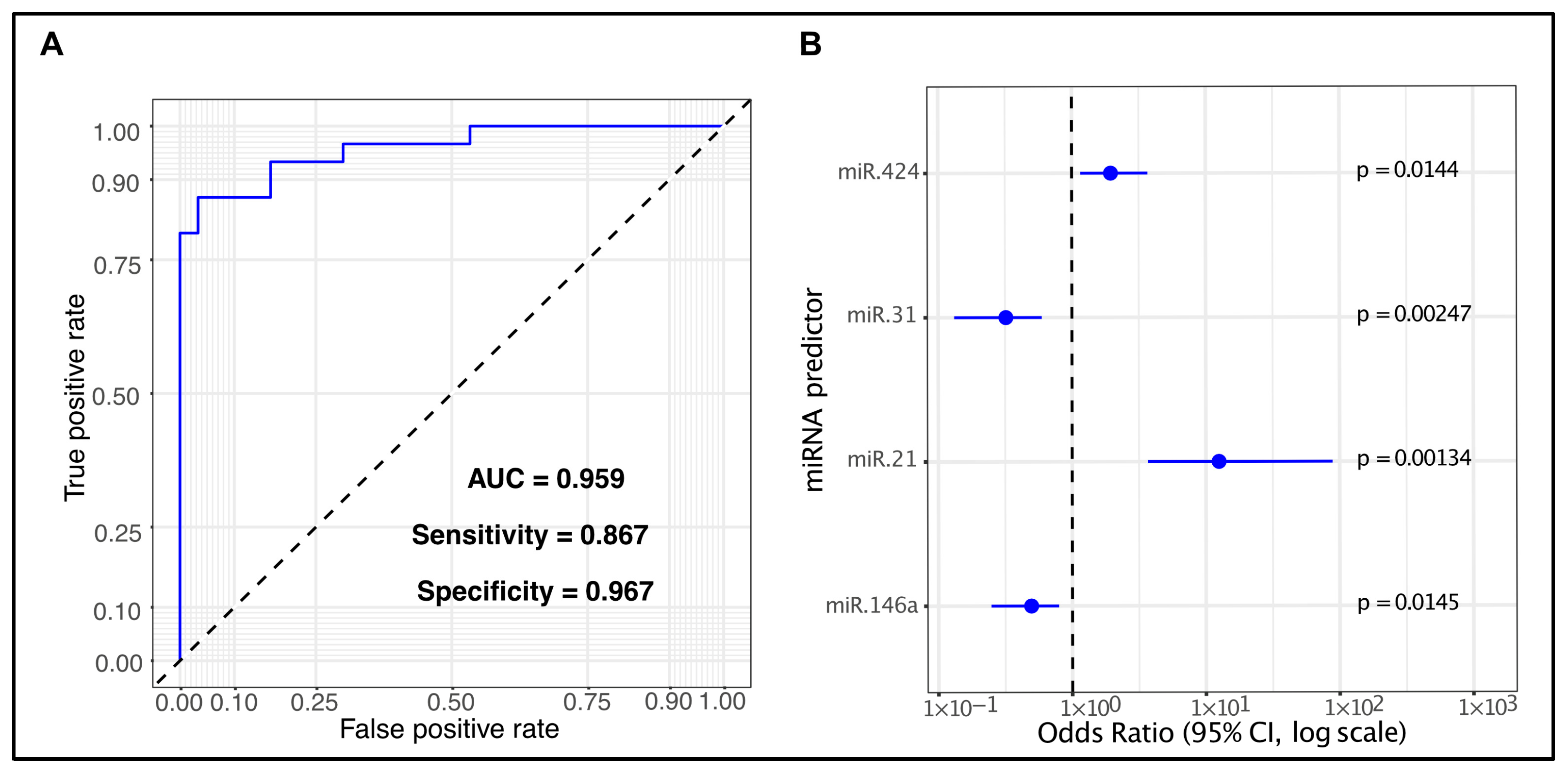
2.4. Assessment of the Diagnostic Potential of Differentially Expressed miRNAs
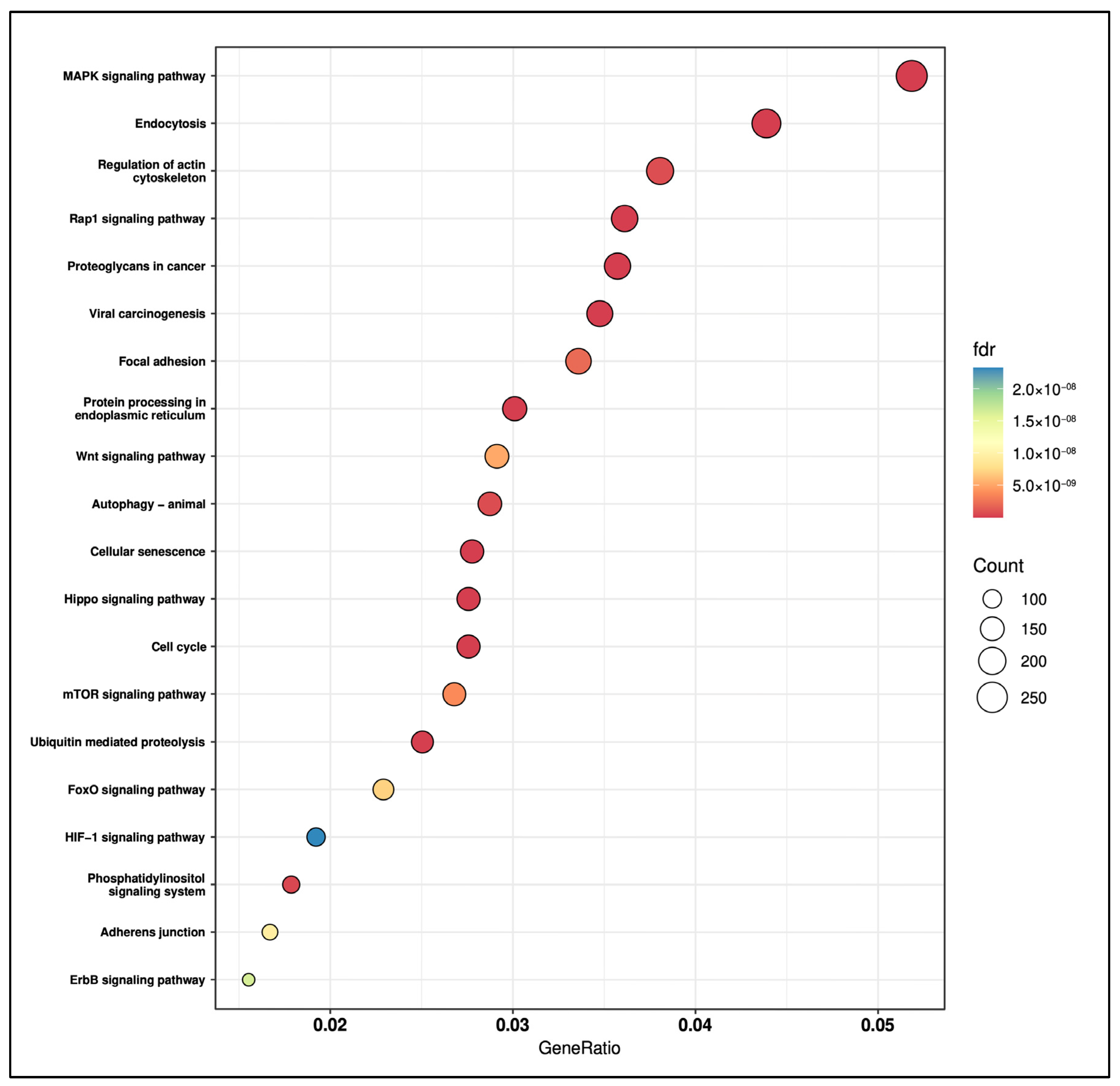
2.5. Pathway Analysis of the Four Salivary miRNA Signature
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients’ Cohort and Sample Collection
4.2. Selection of Candidate miRNAs as Salivary Biomarkers for OSCC
4.3. RNA Extraction
4.4. cDNA Synthesis
4.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.6. qRT-PCR Data Normalization
4.7. Statistical Analysis
4.8. Pathways Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OSCC | Oral squamous cell carcinoma |
| ncRNAs | Non-coding RNAs |
| MiRNAs | MicroRNAs |
| TNM | Tumor, Node, Metastasis |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative real-time PCR |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| ORA | Over-representation analysis |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| FDR | False discover rate |
References
- Mody, M.D.; Rocco, J.W.; Yom, S.S.; Haddad, R.I.; Saba, N.F. Head and neck cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 2289–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Laversanne, M.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2024; Available online: https://gco.iarc.who.int/today (accessed on 17 July 2025).
- Beynon, R.A.; Lang, S.; Schimansky, S.; Penfold, C.M.; Waylen, A.; Thomas, S.J.; Pawlita, M.; Waterboer, T.; Martin, R.M.; May, M.; et al. Tobacco smoking and alcohol drinking at diagnosis of head and neck cancer and all-cause mortality: Results from head and neck 5000, a prospective observational cohort of people with head and neck cancer International. J. Cancer J. Int. Du Cancer 2018, 143, 1114–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnakulasuriya, S. Is human papillomavirus a risk factor for oral squamous cell carcinoma: Is oral infection with human papillomavirus (HPV) a risk factor for oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC)? Evid.-Based Dent. 2003, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgaki, M.; Theofilou, V.I.; Pettas, E.; Stoufi, E.; Younis, R.H.; Kolokotronis, A.; Sauk, J.J.; Nikitakis, N.G. Understanding the complex pathogenesis of oral cancer: A comprehensive review. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2021, 132, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colevas, A.D.; Yom, S.S.; Pfister, D.G.; Spencer, S.; Adelstein, D.; Adkins, D.; Brizel, D.M.; Burtness, B.; Busse, P.M.; Caudell, J.J.; et al. NCCN guidelines insights: Head and neck cancers, version 1.2018. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. JNCCN 2018, 16, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almangush, A.; Mäkitie, A.A.; Triantafyllou, A.; de Bree, R.; Strojan, P.; Rinaldo, A.; Hernandez-Prera, J.C.; Suárez, C.; Kowalski, L.P.; Ferlito, A.; et al. Staging and grading of oral squamous cell carcinoma: An update. Oral Oncol. 2020, 107, 104799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Guo, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Bu, J.; Sun, T.; Wei, J. Liquid biopsy in cancer: Current status, challenges and future prospects. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, S.N.; Nisar, S.; Masoodi, T.; Singh, M.; Rizwan, A.; Hashem, S.; El-Rifai, W.; Bedognetti, D.; Batra, S.K.; Haris, M.; et al. Liquid biopsy: A step closer to transform diagnosis, prognosis and future of cancer treatments. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczor-Urbanowicz, K.E.; Martin Carreras-Presas, C.; Aro, K.; Tu, M.; Garcia-Godoy, F.; Wong, D.T. Saliva diagnostics—Current views and directions. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.T.W. Salivaomics. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2012, 143 (Suppl. S10), 19S–24S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Basak, S.; Sarkar, S. Decoding salivary ncRNAomes as novel biomarkers for oral cancer detection and prognosis. Noncoding RNA 2025, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, P.; Sekar, R.; Zahra, H.A.; Jayaraman, S.; Rajagopal, P.; Abdallah, B.M.; Ali, E.M.; Abdelsalam, S.A.; Veeraraghavan, V. Salivaomics to decode non-coding RNAs in oral cancer. A narrative review. Noncoding RNA Res. 2023, 8, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalmatte, A.; Rekha, P.D.; Ratnacaram, C.K. Emerging cell cycle related non-coding RNA biomarkers from saliva and blood for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 9479–9496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Lee, S.; Senavirathne, G.; Lai, E.C. microRNAs in action: Biogenesis, function and regulation. Nat. Rev. Genetics 2023, 24, 816–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoronos, A.A.; Engelman, D.M.; Slack, F.J. OncomiR or tumor suppressor? The duplicity of MicroRNAs in cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3666–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, C.; Roshan, V.G.D.; Khan, I.; Manasa, V.G.; Himal, I.; Kattoor, J.; Thomas, S.; Kondaiah, P.; Kannan, S. MiRNA expression profiling and emergence of new prognostic signature for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volinia, S.; Calin, G.A.; Liu, C.-G.; Ambs, S.; Cimmino, A.; Petrocca, F.; Visone, R.; Iorio, M.; Roldo, C.; Ferracin, M.; et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista-Sánchez, D.; Arriaga-Canon, C.; Pedroza-Torres, A.; De La Rosa-Velázquez, I.A.; González-Barrios, R.; Contreras-Espinosa, L.; Montiel-Manríquez, R.; Castro-Hernández, C.; Fragoso-Ontiveros, V.; Álvarez-Gómez, R.M.; et al. The promising role of miR-21 as a cancer biomarker and its importance in RNA-based therapeutics. Molecular Therapy. Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gombos, K.; Horváth, R.; Szele, E.; Juhász, K.; Gocze, K.; Somlai, K.; Pajkos, G.; Ember, I.; Olasz, L. miRNA Expression Profiles of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 1511–1517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jaksic Karisik, M.; Lazarevic, M.; Mitic, D.; Milosevic Markovic, M.; Riberti, N.; Jelovac, D.; Milasin, J. MicroRNA-21 as a regulator of cancer stem cell properties in oral cancer. Cells 2025, 14, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Askari, A.; Hussen, B.M.; Taheri, M.; Dilmaghani, N.A. Role of miR-424 in the carcinogenesis. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 26, 16–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeljic, K.; Jovanovic, I.; Jovanovic, J.; Magic, Z.; Stankovic, A.; Supic, G. MicroRNA meta-signature of oral cancer: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 2018, 123, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolandparva, F.; Hashemi Nasab, M.S.; Mohamadnia, A.; Garajei, A.; Farhadi Nasab, A.; Bahrami, N. Early diagnosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) by miR-138 and miR-424-5p expression as a cancer marker. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2021, 22, 2185–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, K.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. miR-19a and miR-424 target TGFBR3 to promote epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and migration of tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2018, 12, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J. MiR-31 functions as an oncomir which promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition via regulating BAP1 in cervical cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 6361420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Liang, H.; Fu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liao, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hong, Y.; Zhou, X.; et al. BAP1 suppresses lung cancer progression and is inhibited by miR-31. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 13742–13753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Cao, S.; Li, C.; Xu, M.; Wei, H.; Yang, H.; Sun, Q.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, L. LncRNA PVT1 regulates growth, migration, and invasion of bladder cancer by miR-31/CDK1. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 4799–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creighton, C.J.; Fountain, M.D.; Yu, Z.; Nagaraja, A.K.; Zhu, H.; Khan, M.; Olokpa, E.; Zariff, A.; Gunaratne, P.H.; Matzuk, M.M.; et al. Molecular profiling uncovers a p53-associated role for MicroRNA-31 in inhibiting the proliferation of serous ovarian carcinomas and other cancers. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wu, W.; Ying, Y.; Luo, J.; Xu, X.; Zheng, L.; Wu, W.; Yang, S.; Zhao, S. MicroRNA-31: A pivotal oncogenic factor in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchetti, F.; Tenore, G.; Macali, F.; Vicidomini, T.; Podda, G.M.; Fantozzi, P.J.; Silvestri, V.; Porzio, V.; Valentini, V.; Ottini, L.; et al. Expression analysis of circulating microRNAs in saliva and plasma for the identification of clinically relevant biomarkers for oral squamous cell carcinoma and oral potentially malignant disorders. Cancers 2024, 16, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohtasham, N.; Ghorbani, Z.; Ayatollahi, H.; Arab, F.; Aghaee-Bakhtiari, S.H.; Rasoulian, B.; Mohajertehran, F. Serum mir-31-5p is a reliable biomarker in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma and oral lichen planus. Egypt. J. Med. Hum. Genet. 2024, 25, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-J.; Lin, S.-C.; Yang, C.-C.; Cheng, H.-W.; Chang, K.-W. Exploiting salivary miR-31 as a clinical biomarker of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2012, 34, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.E.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, I.R.; Park, S.M.; Kang, J.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, H.R.; Lee, J.H. MicroRNA-31 regulates expression of wntless in both Drosophila melanogaster and human oral cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.; Rizaev, J.A.; Hjazi, A.; Altalbawy, F.M.A.; Hanumanthaiah, M.; Sharma, K.; Sharma, S.K.; Mustafa, Y.F.; Jawad, M.A.; Zwamel, A.H. Dual role of microRNA-31 in human cancers; focusing on cancer pathogenesis and signaling pathways. Exp. Cell Res. 2024, 442, 114236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taganov, K.D.; Boldin, M.P.; Chang, K.-J.; Baltimore, D. NF-κB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12481–12486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahriar, A.; Ghaleh-aziz Shiva, G.; Ghader, B.; Farhad, J.; Hosein, A.; Parsa, H. The dual role of mir-146a in metastasis and disease progression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 126, 110099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-T.; Yu, C.-C.; Lu, M.-Y.; Chao, S.-C.; Liao, Y.-W.; Yu, C.-H.; Lee, Y.-H. miR-146a participates in the regulation of cancer stemness of oral carcinoma cells. J. Dent. Sci. 2023, 18, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Yan, Y.; Guo, X.; Fang, Y.; Su, Y.; Wang, L.; Pathak, J.L.; Ge, L. MiR-146a Overexpression in oral squamous cell carcinoma potentiates cancer cell migration and invasion possibly via targeting HTT. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, C.; Wemmert, S.; Bochen, F.; Kulas, P.; Linxweiler, M.; Hasenfus, A.; Heinzelmann, J.; Leidinger, P.; Backes, C.; Meese, E.; et al. Characterization of miR- 146a and miR-155 in blood, tissue and cell lines of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients and their impact on cell proliferation and migration. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, A.; Tandon, M.; Alevizos, I.; Illei, G.G. The majority of microRNAs detectable in serum and saliva is concentrated in exosomes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, T.; Tanaka, K.; Kawano, M.; Itonaga, I.; Tsumura, H. Tumor-suppressive microRNA-let-7a inhibits cell proliferation via targeting of E2F2 in osteosarcoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Fang, M.; Qiao, Y. MicroRNA let-7a inhibits proliferation of breast cancer cell by downregulating USP32 expression. Transl. Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadhil, R.S.; Wei, M.Q.; Nikolarakos, D.; Good, D.; Nair, R.G. Salivary microRNA miR-let-7a-5p and miR-3928 could be used as potential diagnostic bio-markers for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0221779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedhoseini, S.; Mohtasham, N.; Saghafi, S.; Alahkhani, N.; Mohajertehran, F.; Afzaljavan, F.; Shakeri, M.T.; Bokharaei, A. Mir-let-7a Differential Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Oral Lichen Planus: Insights for Early Diagnostic Biomarker Development. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2025, 13, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Fan, W. Low expression of miR-let-7a promotes cell growth and invasion through the regulation of c-Myc in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral LGde, S.; Martins, I.M.; Paulo EPde, A.; Pomini, K.T.; Poyet, J.-L.; Maria, D.A. Molecular mechanisms in the carcinogenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma: A literature review. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shebbo, S.; Alateyah, N.; Yassin, E.; Mahmoud, D.E.S.; Tamimi, F.; Anweigi, L.; Elhissi, A.; Abou-Saleh, H.; Elrayess, M.A.; Agouni, A. Unravelling molecular mechanism of oral squamous cell carcinoma and genetic landscape: An insight into disease complexity, available therapies, and future considerations. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1626243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, A.W.; Kappler, M.; Große, I.; Wickenhauser, C.; Seliger, B. Current understanding of the HIF-1-dependent metabolism in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, C.; Salviato, E.; Paderno, A.; Zanotti, L.; Ravaggi, A.; Deganello, A.; Berretti, G.; Gualtieri, T.; Marchini, S.; D’Incalci, M.; et al. Genome-wide study of salivary miRNAs identifies miR-423-5p as promising diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Theranostics 2021, 11, 2987–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Vagenas, D.; Salazar, C.; Kenny, L.; Perry, C.; Calvopiña, D.; Punyadeera, C. Salivary miRNA panel to detect HPV-positive and HPV-negative head and neck cancer patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 99990–100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-A.; Weng, S.-L.; Yang, S.-F.; Chou, C.-H.; Huang, W.-C.; Tu, S.-J.; Chang, T.-H.; Huang, C.-N.; Jong, Y.-J.; Huang, H.-D. A three-MicroRNA signature as a potential biomarker for the early detection of oral cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.J.; Jensen, D.H.; Lelkaitis, G.; Kiss, K.; Charabi, B.W.; Ullum, H.; Specht, L.; Schmidt, A.Y.; Nielsen, F.C.; von Buchwald, C. MicroRNA-based classifiers for diagnosis of oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma in tissue and plasma. Oral Oncol. 2018, 83, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, T.; Koo, K.; Cheng, L.; Vella, L.J.; Hill, A.F.; Reynolds, E.; Nastri, A.; Cirillo, N.; Seers, C.; McCullough, M. Predicting the presence of oral squamous cell carcinoma using commonly dysregulated MicroRNA in oral swirls. Cancer Prev. Res. 2018, 11, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; He, Q.; Liang, J.; Li, W.; Su, Q.; Chen, Z.; Wan, Q.; Zhou, X.; Cao, L.; Sun, J.; et al. MiR-31-5p is a potential circulating biomarker and therapeutic target for oral cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, T.; Seers, C.; Koo, K.; Cheng, L.; Vella, L.J.; Hill, A.F.; Reynolds, E.; Nastri, A.; Cirillo, N.; McCullough, M. Non-invasive screening of a microRNA-based dysregulation signature in oral cancer and oral potentially malignant disorders. Oral Oncol. 2019, 96, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Hiyake, N.; Hamada, T.; Yokoyama, S.; Mori, K.; Yamashiro, K.; Beppu, M.; Sagara, Y.; Sagara, Y.; Sugiura, T. Circulating microRNA panel as a potential novel biomarker for oral squamous cell carcinoma diagnosis. Cancers 2021, 13, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholtz, B.; Horváth, J.; Tar, I.; Kiss, C.; Márton, I.J. Salivary miR-31-5p, miR-345-3p, and miR-424-3p are reliable biomarkers in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Pathogens 2022, 11, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojkovic, G.; Jovanovic, I.; Dimitrijevic, M.; Jovanovic, J.; Tomanovic, N.; Stankovic, A.; Arsovic, N.; Boricic, I.; Zeljic, K. Meta-signature guided investigation of miRNA candidates as potential biomarkers of oral cancer. Oral Dis. 2023, 29, 1550–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, Y.; Jung, S.-N.; Lim, M.A.; Oh, C.; Jin, Y.L.; Kim, H.J.; Nguyen, Q.K.; Chang, J.W.; Won, H.-R.; Koo, B.S. A circulating microRNA panel as a novel dynamic monitor for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towle, R.; Dickman, C.T.D.; MacLellan, S.A.; Chen, J.; Prisman, E.; Guillaud, M.; Garnis, C. Identification of a serum-based microRNA signature that detects recurrent oral squamous cell carcinoma before it is clinically evident. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 129, 1810–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakittnen, J.; Ekanayake Weeramange, C.; Wallace, D.F.; Duijf, P.H.G.; Cristino, A.S.; Hartel, G.; Barrero, R.A.; Taheri, T.; Kenny, L.; Vasani, S.; et al. A novel saliva-based miRNA profile to diagnose and predict oral cancer. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2024, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, M.; Spirito, F.; Sovereto, D.; Alovisi, M.; Troiano, G.; Aiuto, R.; Garcovich, D.; Crincoli, V.; Laino, L.; Cazzolla, A.P.; et al. MicroRNA-21 expression as a prognostic biomarker in oral cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapado-González, Ó.; Majem, B.; Muinelo-Romay, L.; Álvarez-Castro, A.; Santamaría, A.; Gil-Moreno, A.; López-López, R.; Suárez-Cunqueiro, M.M. Human salivary microRNAs in cancer. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Rawi, N.; Elmabrouk, N.; Abu Kou, R.; Mkadmi, S.; Rizvi, Z.; Hamdoon, Z. The role of differentially expressed salivary microRNA in oral squamous cell carcinoma. A systematic review. Arch. Oral Biol. 2021, 125, 105108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vageli, D.P.; Doukas, P.G.; Shah, R.; Boyi, T.; Liu, C.; Judson, B.L. A novel saliva and serum miRNA panel as a potential useful index for oral cancer and the association of miR-21 with smoking history: A pilot study. Cancer Prev. Res. 2023, 16, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Gao, L.; Wang, X.; Bi, L.; Wang, Y. MEHP promotes the proliferation of oral cancer cells via down regulation of miR-27b-5p and miR-372-5p. Toxicol. Vitr. 2019, 58, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stasio, D.; Romano, A.; Boschetti, C.E.; Montella, M.; Mosca, L.; Lucchese, A. Salivary miRNAs expression in potentially malignant disorders of the oral mucosa and oral squamous cell carcinoma: A pilot study on miR-21, miR-27b, and miR-181b. Cancers 2022, 15, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtyn, O.; Borikun, T.; Rossylna, O.; Kopchak, A.; Kravets, О. Clinical significance of salivary Mir-21, -155, and -375 in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of oral cavity. Exp. Oncol. 2024, 46, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Chen, Z.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, H.; Mao, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Zheng, J. The simultaneous miR-155-5p overexpression and miR-223-3p inhibition can activate pEMT in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2024, 32, e20240215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, J.R.; Dawes, J.M.; McMahon, S.B.; Bennett, D.L.H.; Orengo, C.; Kohl, M. ReadqPCR and NormqPCR: R packages for the reading, quality checking and normalisation of RT-qPCR quantification cycle (Cq) data. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, C.L.; Jensen, J.L.; Ørntoft, T.F. Normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data: A model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5245–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandesompele, J.; De Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; Van Roy, N.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, RESEARCH0034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Xiao, P.; Chen, D.; Xu, L.; Zhang, B. miRDeepFinder: A miRNA analysis tool for deep sequencing of plant small RNAs. Plant Mol. Biol. 2012, 80, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, Y.; Kechris, K.J.; Tabakoff, B.; Hoffman, P.; Radcliffe, R.A.; Bowler, R.; Mahaffey, S.; Rossi, S.; Calin, G.A.; Bemis, L.; et al. The multiMiR R package and database: Integration of microRNA-target interactions along with their disease and drug associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, e133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Matsuura, Y.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG: Biological systems database as a model of the real world. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D672–D677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenenbaum, D.; Maintainer, B. KEGGREST: Client-Side REST Access to the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG). R Package Version 1.50.0. 2025. Available online: https://bioconductor.org/packages/KEGGREST (accessed on 18 November 2025).
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D457–D462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | OSCC Patients (n = 30) | Healthy Controls (n = 30) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median age | 68 | 60 | |
| Gender | F | 16 (53%) | 18 (60%) |
| M | 14 (47%) | 12 (40%) | |
| Smoke | Yes | 5 (17%) | 6 (20%) |
| No | 11 (37%) | 19 (63%) | |
| Former * | 14 (47%) | 2 (7%) | |
| OSCC stage | I | 4 (13%) | NA |
| II | 4 (13%) | ||
| III | 5 (17%) | ||
| IV | 14 (47%) | ||
| Tumor location | Tongue and pelvis | 9 (30%) | NA |
| Mandible | 14 (47%) | ||
| Maxilla | 3 (10%) | ||
| Cheek | 4 (13%) | ||
| Groups | RNA Mean Concentration (ng/μL) | A260/280 Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| OSCC | 216.02 | 1.88 |
| Healthy controls | 213.11 | 2.07 |
| Panel | Cohorts | Sample Type | Diagnostic Performance | Method for Panel Generation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-9-5p, miR-127-5p, miR-134-3p, miR-191-5p, miR-222-3p, miR-455-3p | 47 HPV-negative HNSCC patients 113 healthy controls | Unstimulated whole saliva | AUC 0.82 Sensitivity: 60% Specificity: 94% | Logistic regression model | [53] |
| miR-9-5p, miR-134-3p, miR-210-5p, miR-455-3p, miR-196b-3p | 54 HPV-positive HNSCC patients 113 healthy controls | Unstimulated whole saliva | AUC 0.80 Sensitivity: 65% Specificity: 95% | Logistic regression model | [53] |
| miR-150-5p, miR-423-5p | * 82 OSCC patients 50 healthy controls | Plasma | AUC 0.749 (95% CI: 0.678–0.819) Sensitivity: 70.9% Specificity: 72.8% | Logistic regression model | [54] |
| miR-204-5p, miR-193b-5p, miR-370-3p, miR-144-5p | 195 OSCC samples 103 normal oral mucosa samples | FFPE | AUC: 0.92 (95% CI, 0.90–0.97) | Logistic regression model | [55] |
| miR-30a-5p, miR-769-5p | 55 OSCC patients 18 healthy controls | Plasma | AUC: 1 | Logistic regression model | [55] |
| miR-21-5p, let-7c-5p, miR-100-5p | 30 OSCC patients 30 healthy controls | Oral swirl | AUC 0.86 (95% CI: 0.79–1.00) | Dysregulation score/Classification tree | [56] |
| miR-99a-5p, miR-31-5p, miR-138-5p, miR-21-5p, miR-375-3p | 82 oral cancer patients 53 healthy controls | Serum | AUC 0.776 (95% CI: 0.695–0.857) Sensitivity: 76.8% Specificity: 73.6% | Logistic regression model | [57] |
| miR-24-3p, miR-21-5p, let-7c-5p, miR-99a-5p, miR-100-5p | 53 OSCC patients 54 healthy controls | Oral swirl | AUC 0.8676 Sensitivity: 86.8% Specificity: 81.5% | Dysregulation score/Classification tree | [58] |
| miR-106b-5p, miR-423-5p, miR-193b-3p | * 28 OSCC patients 14 healthy controls | Unstimulated whole saliva | AUC: 0.923 [95% CI: 0.908–0.938] Sensitivity: 85.4% Specificity: 85.1% | Logistic regression model | [52] |
| miR-24-3p, miR-20a-5p, miR-122-5p, miR-150-3p, miR-4419a, miR-5100 | * 40 OSCC patients 40 healthy controls | Serum | AUC: 0.844 Sensitivity: 55% Specificity: 92.5% | Fisher’s linear discriminant analysis | [59] |
| miR-345-3p, miR-424-3p, miR-31-5p | 43 OSCC patients 44 healthy controls | Unstimulated whole saliva | AUC 0.8647 (95% CI: 0.7855–0.9439) Sensitivity: 76.7% Specificity: 85.7% | Logistic regression model | [60] |
| miR-31-3p, miR-139-5p, miR-30a-5p | 35 OSCC lesions Matched non-cancerous tissue | Fresh tissue | AUC 0.780 (95% CI: 0.673–0.886) Sensitivity: 94.3% Specificity: 51.4% | Logistic regression model | [61] |
| miR-92a-3p, miR-92b-3p, miR-320c, miR-629-5p | * 23 OSCC patients 15 healthy controls | Serum | AUC 0.899 (95% CI: 0.8431–0.9547) Sensitivity: 73.9% Specificity: 97.8% | Logistic regression model | [62] |
| miR-125b-5p, miR-342-3p | * 65 early-stage OSCC or carcinoma in situ lesions 69 healthy controls | Serum | AUC: 0.801 Sensitivity: 74% Specificity: 74% | LASSO regression | [63] |
| miR-7-5p, miR-10b-5p, miR-182-5p, miR-431-5p, miR-3614-5p, miR-4707-3p, miR-215-5p, miR-486-3p | * 50 oral cancer patients 60 healthy controls | Unstimulated whole saliva | AUC: 0.954 Sensitivity: 86% Specificity: 90% | LASSO regression | [64] |
| miRNA | Target Sequences | References |
|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-21-5p | 5′-UAGCUUAUCAGACUGAUGUUGA-3′ | [65] |
| hsa-miR-31-5p | 5′-AGGCAAGAUGCUGGCAUAGCU-3′ | [32] |
| hsa-miR-16-5p | 5′-UAGCAGCACGUAAAUAUUGGCG -3′ | [66] |
| hsa-miR-191-5p | 5′-CAACGGAAUCCCAAAAGCAGCUG-3′ | [66] |
| hsa-miR-136-5p | 5′-ACUCCAUUUGUUUUGAUGAUGGA-3′ | [67,68] |
| hsa-miR-27b-5p | 5′-AGAGCUUAGCUGAUUGGUGAAC-3′ | [69,70] |
| hsa-miR-146a-5p | 5′-UGAGAACUGAAUUCCAUGGGUU-3′ | [41,42] |
| hsa-let-7a-5p | 5′-UGAGGUAGUAGGUUGUAUAGUU-3′ | [46,47] |
| has-mir-424-3p | 5′-CAAAACGUGAGGCGCUGCUAU-3′ | [25,26] |
| has-mir-155-3p | 5′-CUCCUACAUAUUAGCAUUAACA-3′ | [71,72] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciringione, A.; Lilloni, G.; Moron Dalla Tor, L.; Perlangeli, G.; Rizzi, F.; Poli, T. Identification of a Novel Salivary Four-miRNA Signature for Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311373
Ciringione A, Lilloni G, Moron Dalla Tor L, Perlangeli G, Rizzi F, Poli T. Identification of a Novel Salivary Four-miRNA Signature for Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311373
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiringione, Alessia, Giovanni Lilloni, Lucas Moron Dalla Tor, Giuseppe Perlangeli, Federica Rizzi, and Tito Poli. 2025. "Identification of a Novel Salivary Four-miRNA Signature for Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311373
APA StyleCiringione, A., Lilloni, G., Moron Dalla Tor, L., Perlangeli, G., Rizzi, F., & Poli, T. (2025). Identification of a Novel Salivary Four-miRNA Signature for Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311373






