BTLA-Expressing Memory B Cells Are Associated with Belimumab-Induced Improvement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
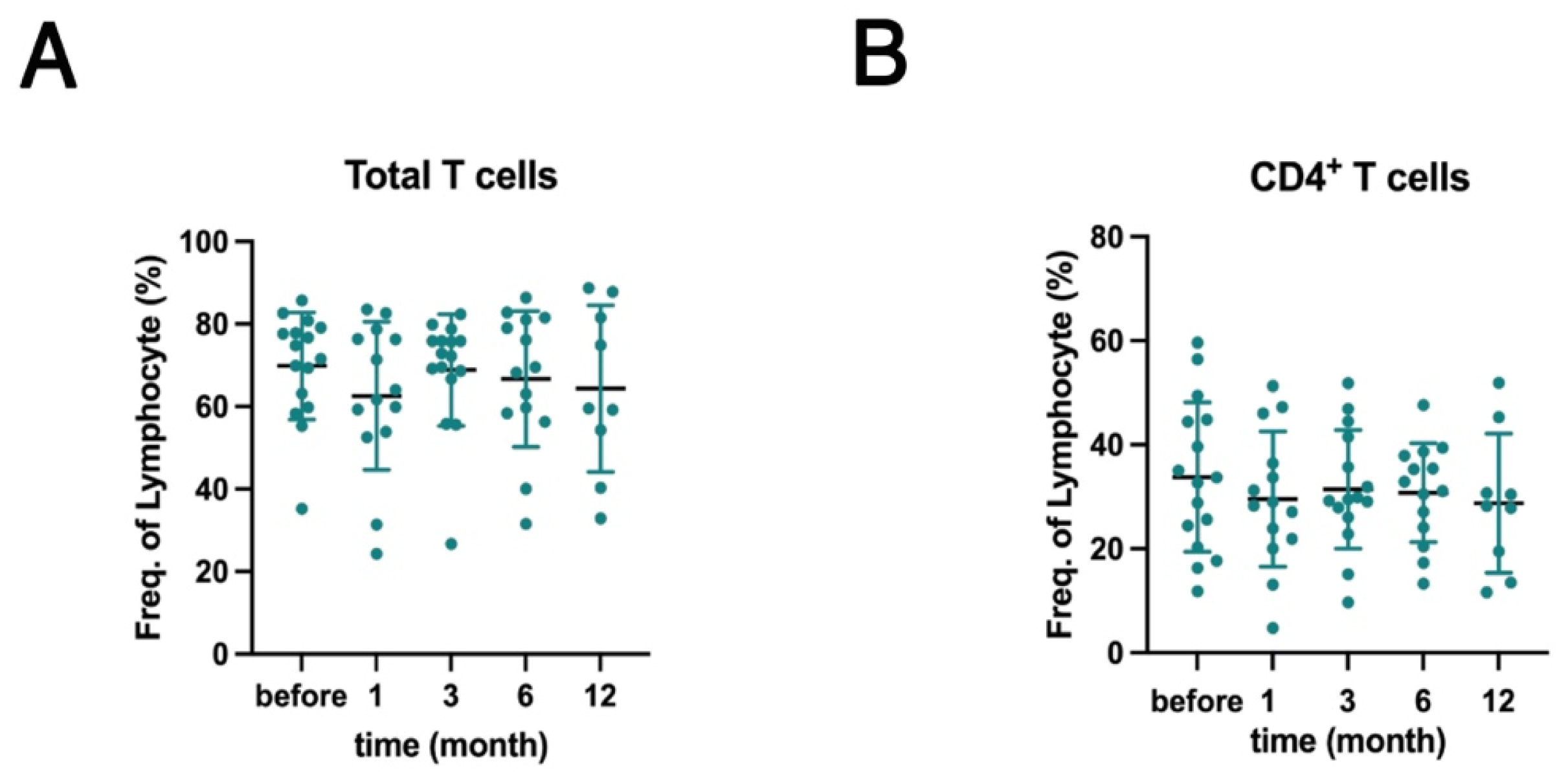
2.1. Effects of Belimumab Treatment on PBMC Subsets
2.2. Correlations Between B Cell Subpopulations and Clinical Data
2.3. Effects of BAFF and B Cell Receptor (BCR) Stimulation on HVEM and BTLA Expression Levels on B Cells
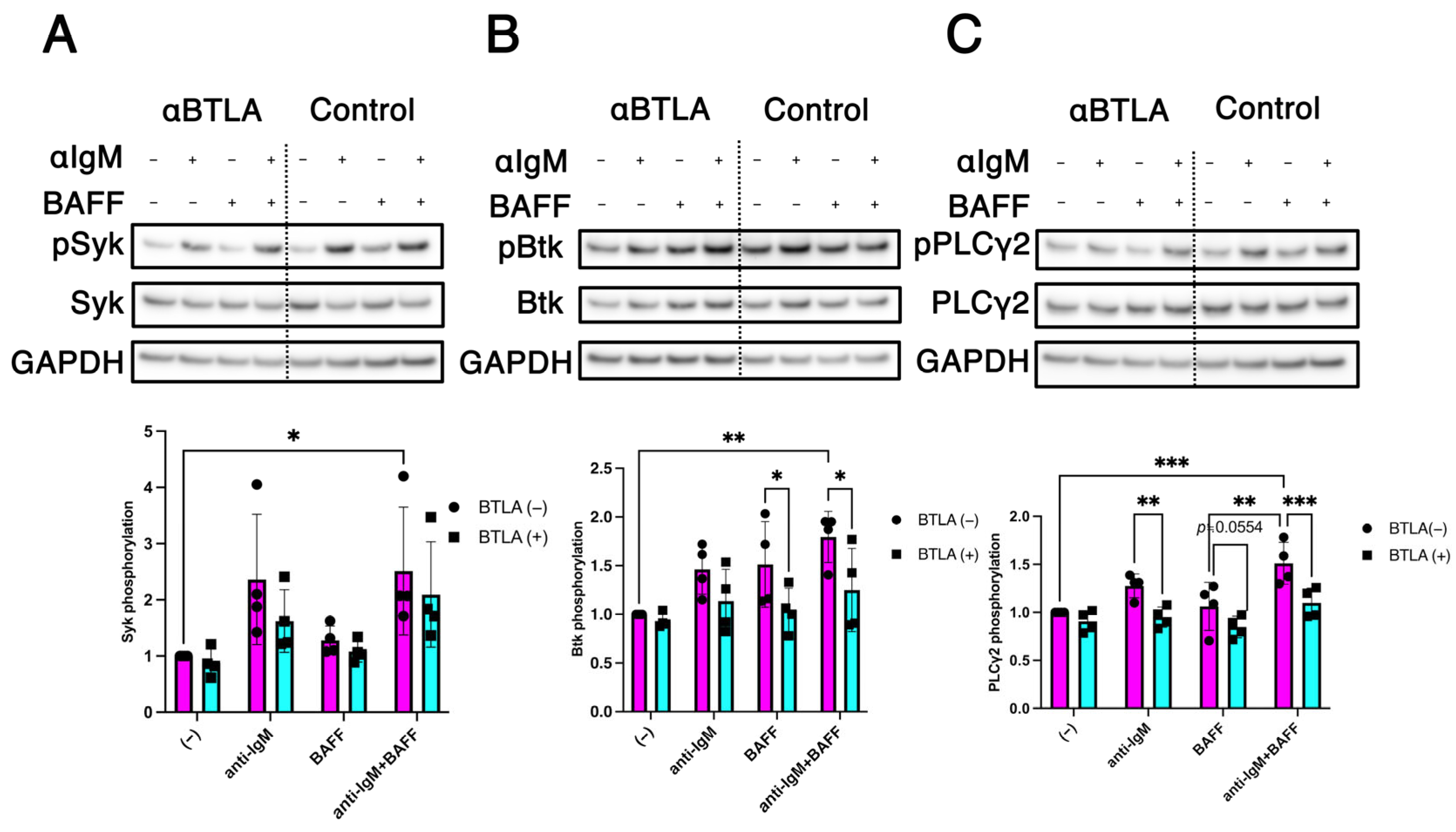
2.4. Modulation of BCR/BAFF-Induced B Cell Intracellular Signaling by BTLA
2.5. BTLA-Mediated Regulation of Non-Canonical NF-κB Signaling in B Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. PBMC Isolation
4.3. Immunofluorescence Staining and Flow Cytometry
4.4. B Cell Isolation and Culture for Flow Cytometry
4.5. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis and Western Blotting
4.6. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BAFF | B cell-activating factor |
| SLE | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| mAb | Monoclonal antibody |
| Ig | Immunoglobulin |
| BTLA | B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator |
| HVEM | Herpes virus entry mediator |
| PBMCs | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
| SLEDAI-2K | SLE disease activity index 2000 |
| BCR | B cell receptor |
| DN | Double-negative |
| Syk | Spleen tyrosine kinase |
| Btk | Bruton tyrosine kinase |
| PLCγ2 | Phospholipase C gamma 2 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-κB |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| mAbs | Monoclonal antibodies |
| APC | Allophycocyanin |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| FACS | Fluorescence-activated cell sorting |
| SD | Standard deviation |
References
- Pers, J.O.; Daridon, C.; Devauchelle, V.; Jousse, S.; Saraux, A.; Jamin, C.; Youinou, P. BAFF overexpression is associated with autoantibody production in autoimmune diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1050, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, M.; Stohl, W.; Chatham, W.; McCune, W.J.; Chevrier, M.; Ryel, J.; Recta, V.; Zhong, J.; Freimuth, W. Association of plasma B lymphocyte stimulator levels and disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 2453–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, W.G.; Lappin, P.; Zanardi, T.; Cai, W.; Corcoran, M.; Zhong, J.; Baker, K.P. Chronic administration of belimumab, a BLyS antagonist, decreases tissue and peripheral blood B-lymphocyte populations in cynomolgus monkeys: Pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, and toxicologic effects. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 91, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touma, Z.; Sayani, A.; Pineau, C.A.; Fortin, I.; Matsos, M.; Ecker, G.A.; Chow, A.; Iczkovitz, S. Belimumab use, clinical outcomes and glucocorticoid reduction in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus receiving belimumab in clinical practice settings: Results from the OBSErve Canada Study. Rheumatol. Int. 2017, 37, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, R.; Rovin, B.H.; Houssiau, F.; Malvar, A.; Teng, Y.K.O.; Contreras, G.; Amoura, Z.; Yu, X.; Mok, C.C.; Santiago, M.B.; et al. Two-year, randomized, controlled trial of belimumab in lupus nephritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, N.; Gavrieli, M.; Sedy, J.R.; Yang, J.; Fallarino, F.; Loftin, S.K.; Hurchla, M.A.; Zimmerman, N.; Sim, J.; Zang, X.; et al. BTLA is a lymphocyte inhibitory receptor with similarities to CTLA-4 and PD-1. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oya, Y.; Watanabe, N.; Owada, T.; Oki, M.; Hirose, K.; Suto, A.; Kagami, S.; Nakajima, H.; Kishimoto, T.; Iwamoto, I.; et al. Development of autoimmune hepatitis-like disease and production of autoantibodies to nuclear antigens in mice lacking B and T lymphocyte attenuator. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 2498–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, L.C.; Loyet, K.M.; Calemine-Fenaux, J.; Chauhan, V.; Wranik, B.; Ouyang, W.; Eaton, D.L. A coreceptor interaction between the CD28 and TNF receptor family members B and T lymphocyte attenuator and herpesvirus entry mediator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedy, J.R.; Gavrieli, M.; Potter, K.G.; Hurchla, M.A.; Lindsley, R.C.; Hildner, K.; Scheu, S.; Pfeffer, K.; Ware, C.F.; Murphy, T.L.; et al. B and T lymphocyte attenuator regulates T cell activation through interaction with herpesvirus entry mediator. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibult, M.L.; Rivals, J.P.; Mamessier, E.; Gertner-Dardenne, J.; Pastor, S.; Speiser, D.E.; Derre, L.; Olive, D. CpG-ODN-induced sustained expression of BTLA mediating selective inhibition of human B cells. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 91, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oya, Y.; Watanabe, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; Owada, T.; Oki, M.; Ikeda, K.; Suto, A.; Kagami, S.; Hirose, K.; Kishimoto, T.; et al. Lack of B and T lymphocyte attenuator exacerbates autoimmune disorders and induces Fas-independent liver injury in MRL-lpr/lpr mice. Int. Immunol. 2011, 23, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, M.; Sekigawa, I.; Nozawa, K.; Kaneko, H.; Takasaki, Y.; Takamori, K.; Ogawa, H. Changes in the gene expression of peripheral blood mononuclear cells during the menstrual cycle of females is associated with a gender bias in the incidence of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2009, 27, 260–266. [Google Scholar]
- Sawaf, M.; Fauny, J.D.; Felten, R.; Sagez, F.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Dumortier, H.; Monneaux, F. Defective BTLA functionality is rescued by restoring lipid metabolism in lupus CD4+ T cells. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e99711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, R.; Petri, M.; Zamani, O.; Cervera, R.; Wallace, D.J.; Tegzova, D.; Sanchez-Guerrero, J.; Schwarting, A.; Merrill, J.T.; Chatham, W.W.; et al. A phase III, randomized, placebo-controlled study of belimumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits B lymphocyte stimulator, in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 3918–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi, A.M.; Huang, W.; Wang, T.; Freimuth, W.; Sanz, I.; Furie, R.; Mackay, M.; Aranow, C.; Diamond, B.; Davidson, A. Effect of long-term belimumab treatment on B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: Extension of a phase II, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramskold, D.; Parodis, I.; Lakshmikanth, T.; Sippl, N.; Khademi, M.; Chen, Y.; Zickert, A.; Mikes, J.; Achour, A.; Amara, K.; et al. B cell alterations during BAFF inhibition with belimumab in SLE. eBioMedicine 2019, 40, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedemann, A.; Lettau, M.; Weissenberg, S.Y.; Stefanski, A.L.; Schrezenmeier, E.V.; Rincon-Arevalo, H.; Reiter, K.; Alexander, T.; Hiepe, F.; Lino, A.C.; et al. BTLA expression and function are impaired on SLE B cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 667991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendel, A.C.; Jaroszewski, L.; Linnik, M.D.; Godzik, A. B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator in systemic lupus erythematosus disease pathogenesis. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 116, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.M.; Flaswinkel, H.; Reth, M.; Rajewsky, K. Aberrant B cell development and immune response in mice with a compromised BCR complex. Science 1996, 272, 1804–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, D.J.; Scharenberg, A.M.; Park, H.; Wahl, M.I.; Lin, S.; Kato, R.M.; Fluckiger, A.C.; Witte, O.N.; Kinet, J.P. Activation of BTK by a phosphorylation mechanism initiated by SRC family kinases. Science 1996, 271, 822–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takata, M.; Kurosaki, T. A role for Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in B cell antigen receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase C-gamma 2. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 184, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendel, A.C.; Calemine-Fenaux, J.; Izrael-Tomasevic, A.; Chauhan, V.; Arnott, D.; Eaton, D.L. B and T lymphocyte attenuator regulates B cell receptor signaling by targeting Syk and BLNK. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebenlist, U.; Brown, K.; Claudio, E. Control of lymphocyte development by nuclear factor-kappa B. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claudio, E.; Brown, K.; Park, S.; Wang, H.; Siebenlist, U. BAFF-induced NEMO-independent processing of NF-kappa B2 in maturing B cells. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinners, N.P.; Carlesso, G.; Castro, I.; Hoek, K.L.; Corn, R.A.; Woodland, R.T.; Scott, M.L.; Wang, D.; Khan, W.N. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase mediates NF-kappa B activation and B cell survival by B cell-activating factor receptor of the TNF-R family. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 3872–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.P.; Snedecor, S.J.; Nanji, S.; Lloyd, E.; Bell, C.F. Real-world effectiveness of belimumab in systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic literature review. Rheumatol. Ther. 2022, 9, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanouriakis, A.; Kostopoulou, M.; Andersen, J.; Aringer, M.; Arnaud, L.; Bae, S.C.; Boletis, J.; Bruce, I.N.; Cervera, R.; Doria, A.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus: 2023 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stohl, W.; Schwarting, A.; Okada, M.; Scheinberg, M.; Doria, A.; Hammer, A.E.; Kleoudis, C.; Groark, J.; Bass, D.; Fox, N.L.; et al. Efficacy and safety of subcutaneous belimumab in systemic lupus erythematosus: A fifty-two-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1016–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, D.J.; Stohl, W.; Furie, R.A.; Lisse, J.R.; McKay, J.D.; Merrill, J.T.; Petri, M.A.; Ginzler, E.M.; Chatham, W.W.; McCune, W.J.; et al. A phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study of belimumab in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 61, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowicz, K.; Spodzieja, M.; Lisowska, K.A.; Wardowska, A. The role of the BTLA-HVEM complex in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Cell Immunol. 2022, 376, 104532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintz, M.A.; Felce, J.H.; Chou, M.Y.; Mayya, V.; Xu, Y.; Shui, J.W.; An, J.; Li, Z.; Marson, A.; Okada, T.; et al. The HVEM-BTLA axis restrains T cell help to germinal center B cells and functions as a cell-extrinsic suppressor in lymphomagenesis. Immunity 2019, 51, 310–323.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubergeon, L.; Felten, R.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Dumortier, H.; Monneaux, F. Subset of DN memory B cells expressing low levels of inhibitory receptor BTLA is enriched in SLE patients. Cells 2024, 13, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J. Syk mediates BCR- and CD40-signaling integration during B cell activation. Immunobiology 2011, 216, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Shakra, M.; Gladman, D.D.; Urowitz, M.B. Malignancy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1996, 39, 1050–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petri, M.; Orbai, A.M.; Alarcon, G.S.; Gordon, C.; Merrill, J.T.; Fortin, P.R.; Bruce, I.N.; Isenberg, D.; Wallace, D.J.; Nived, O.; et al. Derivation and validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2677–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladman, D.D.; Ibanez, D.; Urowitz, M.B. Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 29, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


| Characteristics | Patients |
|---|---|
| Sex; n = 16 | |
| Female; n (%) | 13 (81.2%) |
| Age (years); M (IQR); n = 16 | 41 (32.0–49.8) |
| SLE disease duration (years); M (IQR); n = 16 | 12 (7.5–19.0) |
| SLEDAI-2K; M (IQR); n = 16 | 6 (4.8–8.5) |
| Prednisone equivalent dose (mg/day); M (IQR); n = 16 | 10 (7.3–13.1) |
| Previous exposure to corticosteroids (years); M (IQR); n = 16 | 12 (7.5–19.0) |
| Refractory manifestations; n (%) | |
| Musculoskeletal | 12 (75.0%) |
| Mucocutaneous | 14 (87.5%) |
| Renal | 12 (75.0%) |
| Administration methods; n (%) | |
| Intravenously | 1 (6.2%) |
| Subcutaneously | 15 (93.7%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nishi, T.; Hayakawa, K.; Ikeda, K.; Fujishiro, M.; Kataoka, Y.; Yamaji, K.; Takamori, K.; Tamura, N.; Sekigawa, I.; Morimoto, S. BTLA-Expressing Memory B Cells Are Associated with Belimumab-Induced Improvement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11323. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311323
Nishi T, Hayakawa K, Ikeda K, Fujishiro M, Kataoka Y, Yamaji K, Takamori K, Tamura N, Sekigawa I, Morimoto S. BTLA-Expressing Memory B Cells Are Associated with Belimumab-Induced Improvement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11323. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311323
Chicago/Turabian StyleNishi, Takuya, Kunihiro Hayakawa, Keigo Ikeda, Maki Fujishiro, Yuko Kataoka, Ken Yamaji, Kenji Takamori, Naoto Tamura, Iwao Sekigawa, and Shinji Morimoto. 2025. "BTLA-Expressing Memory B Cells Are Associated with Belimumab-Induced Improvement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11323. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311323
APA StyleNishi, T., Hayakawa, K., Ikeda, K., Fujishiro, M., Kataoka, Y., Yamaji, K., Takamori, K., Tamura, N., Sekigawa, I., & Morimoto, S. (2025). BTLA-Expressing Memory B Cells Are Associated with Belimumab-Induced Improvement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11323. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311323





