Specific Intratumoral Microbiome Signatures in Human Glioblastoma and Meningioma: Evidence for a Gut–Brain Microbial Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Enrolled Patients
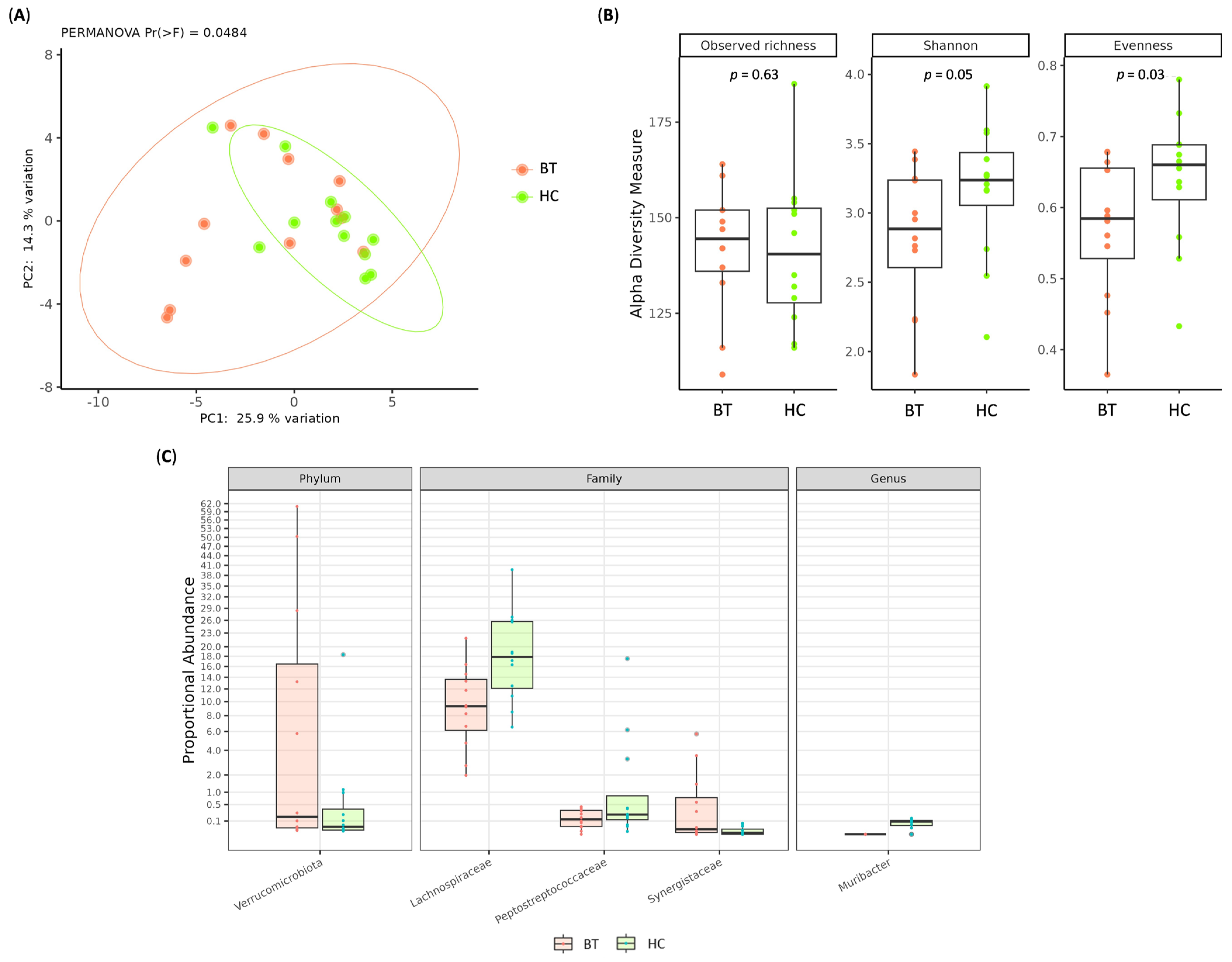
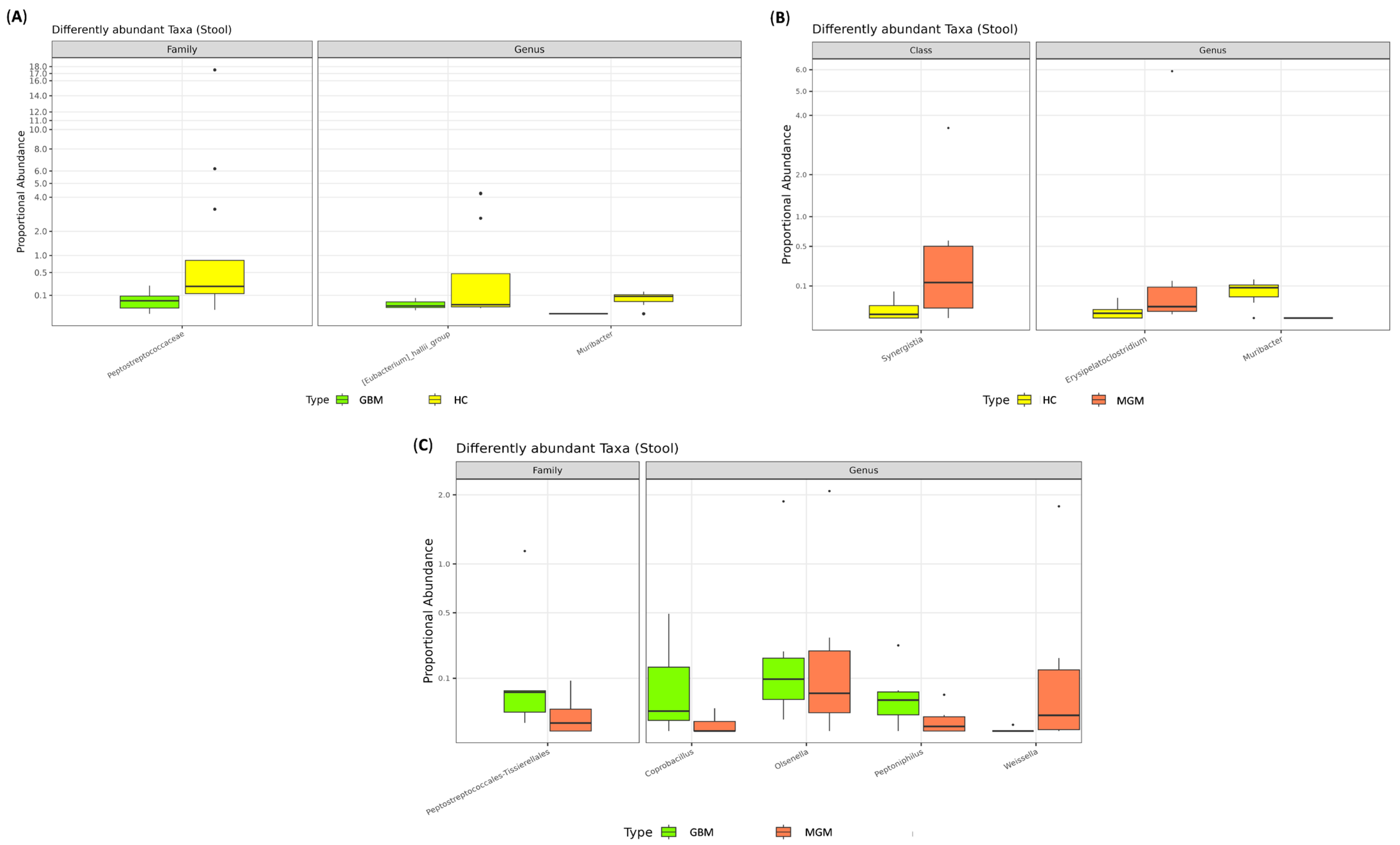
2.2. Gut Microbiota Composition
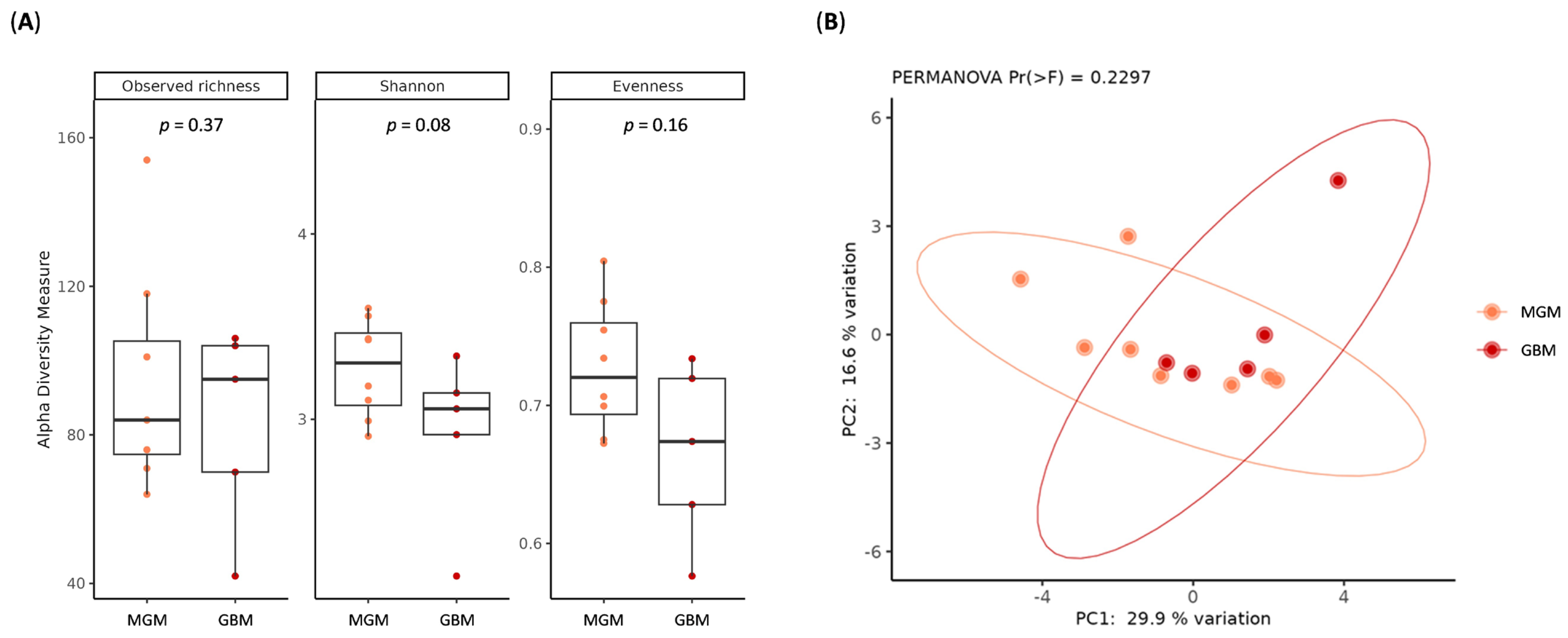
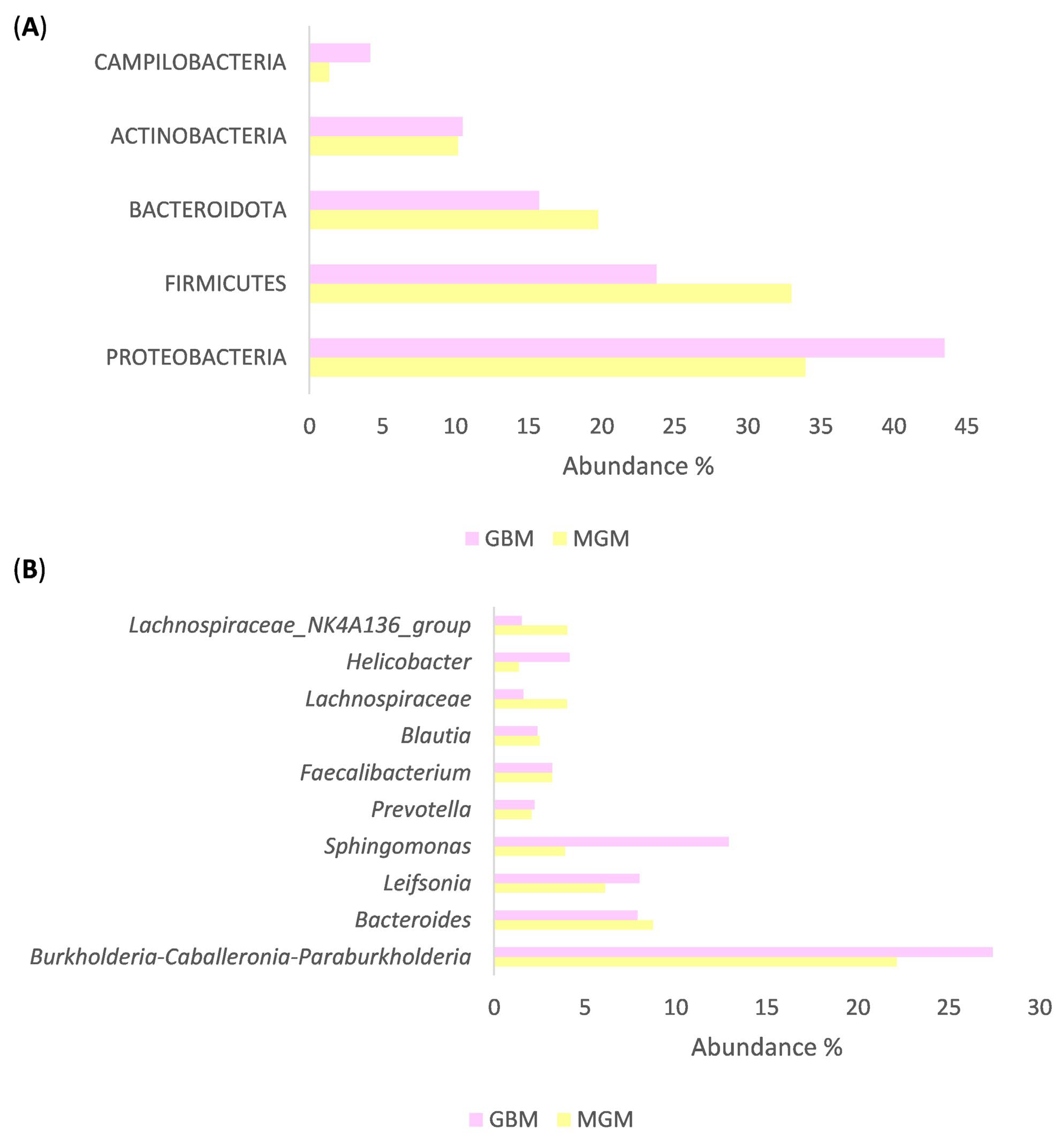
2.3. Characterization of Brain Tumor Tissue Microbiome
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients’ Enrolment
4.2. Fecal and Brain Microbiota Characterization
4.3. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilic, I.; Ilic, M. International patterns and trends in the brain cancer incidence and mortality: An observational study based on the global burden of disease. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Martel, C.; Georges, D.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Clifford, G.M. Global burden of cancer attributable to infections in 2018: A worldwide incidence analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e180–e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejman, D.; Livyatan, I.; Fuks, G.; Gavert, N.; Zwang, Y.; Geller, L.T.; Rotter-Maskowitz, A.; Weiser, R.; Mallel, G.; Gigi, E.; et al. The human tumor microbiome is composed of tumor type–specific intracellular bacteria. Science 2020, 368, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niccolai, E.; Baldi, S.; Nannini, G.; Gensini, F.; Papi, L.; Vezzosi, V.; Bianchi, S.; Orzalesi, L.; Ramazzotti, M.; Amedei, A. Breast cancer: The first comparative evaluation of oncobiome composition between males and females. Biol. Sex Differ. 2023, 14, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantini, G.; Niccolai, E.; Canu, L.; Di Gloria, L.; Baldi, S.; Propato, A.P.; Fei, L.; Nannini, G.; Puglisi, S.; Nesi, G.; et al. Intratumour microbiota modulates adrenocortical cancer responsiveness to mitotane. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2023, 30, e230094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzutsev, A.; Badger, J.H.; Perez-Chanona, E.; Roy, S.; Salcedo, R.; Smith, C.K.; Trinchieri, G. Microbes and Cancer. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 35, 199–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doocey, C.M.; Finn, K.; Murphy, C.; Guinane, C.M. The impact of the human microbiome in tumorigenesis, cancer progression, and biotherapeutic development. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.; Di Gloria, L.; Nannini, G.; Meoni, G.; Niccolai, E.; Ringressi, M.N.; Baldi, S.; Fani, R.; Tenori, L.; Taddei, A.; et al. From adenoma to CRC stages: The oral-gut microbiome axis as a source of potential microbial and metabolic biomarkers of malignancy. Neoplasia 2023, 40, 100901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, G.; Sampson, T.R.; Geschwind, D.H.; Mazmanian, S.K. The Central Nervous System and the Gut Microbiome. Cell 2016, 167, 915–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luczynski, P.; McVey Neufeld, K.-A.; Oriach, C.S.; Clarke, G.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Growing up in a Bubble: Using Germ-Free Animals to Assess the Influence of the Gut Microbiota on Brain and Behavior. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 19, pyw020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, N.M.; Kerby, R.L.; Dill-McFarland, K.A.; Harding, S.J.; Merluzzi, A.P.; Johnson, S.C.; Carlsson, C.M.; Asthana, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; et al. Gut microbiome alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, B.; Guo, J. Parkinson’s disease and gut microbiota: From clinical to mechanistic and therapeutic studies. Transl. Neurodegener. 2023, 12, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangi, S.; Gandhi, R.; Cox, L.M.; Li, N.; von Glehn, F.; Yan, R.; Patel, B.; Mazzola, M.A.; Liu, S.; Glanz, B.L.; et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niccolai, E.; Di Gloria, L.; Trolese, M.C.; Fabbrizio, P.; Baldi, S.; Nannini, G.; Margotta, C.; Nastasi, C.; Ramazzotti, M.; Bartolucci, G.; et al. Host genetics and gut microbiota influence lipid metabolism and inflammation: Potential implications for ALS pathophysiology in SOD1G93A mice. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2024, 12, 174, Erratum in Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2025, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niccolai, E.; Pedone, M.; Martinelli, I.; Nannini, G.; Baldi, S.; Simonini, C.; Di Gloria, L.; Zucchi, E.; Ramazzotti, M.; Spezia, P.G.; et al. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis stratification: Unveiling patterns with virome, inflammation, and metabolism molecules. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 4310–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barandouzi, Z.A.; Starkweather, A.R.; Henderson, W.A.; Gyamfi, A.; Cong, X.S. Altered Composition of Gut Microbiota in Depression: A Systematic Review. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, J.; Wu, F.; Zheng, H.; Peng, Q.; Zhou, H. Altered composition and function of intestinal microbiota in autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-Z.; Huang, Z.-Y.; Zhou, W.-W.; Li, Z.-Y.; Li, X.-P.; Chen, S.-S.; Ma, J.-K. Uncovering the characteristics of the gut microbiota in patients with ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, T.; Zhao, J.; Wang, C.; Sun, H. Current understanding of the human microbiome in glioma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 781741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, K.; Cui, M.; Ye, W.; Zhao, G.; Jin, L.; Chen, X. The progress of gut microbiome research related to brain disorders. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, D.C.; Shoemark, D.K.; Batstone, T.E.; Waterfall, C.M.; Coghill, J.A.; Cerajewska, T.L.; Davies, M.; West, N.X.; Allen-Birt, S.J. 16S rRNA Next Generation Sequencing Analysis Shows Bacteria in Alzheimer’s Post-Mortem Brain. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisa, D.; Alonso, R.; Fernández-Fernández, A.M.; Rábano, A.; Carrasco, L. Polymicrobial Infections In Brain Tissue from Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Xing, C.; Long, W.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, R.-F. Impact of microbiota on central nervous system and neurological diseases: The gut-brain axis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Q.; Lian, W.; Chen, D. Comparison of the Gut Microbiota in Patients with Benign and Malignant Breast Tumors: A Pilot Study. Evol. Bioinform. 2021, 17, 11769343211057573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Q.; Dong, L.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Crosstalk Between the Gut and Brain: Importance of the Fecal Microbiota in Patient with Brain Tumors. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 881071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zeng, W.; Zhang, X.; Pei, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. The role of gut microbiota in patients with benign and malignant brain tumors: A pilot study. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 7847–7859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, L. Metabolic regulation on the immune environment of glioma through gut microbiota. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86 Pt 2, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirsching, H.G.; Galanis, E.; Weller, M. Glioblastoma. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2016, 134, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Galvão, R.P.; Zong, H. Inflammation and Gliomagenesis: Bi-Directional Communication at Early and Late Stages of Tumor Progression. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2013, 1, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dono, A.; Nickles, J.; Rodriguez-Armendariz, A.G.; McFarland, B.C.; Ajami, N.J.; Ballester, L.Y.; Wargo, J.A.; Esquenazi, Y. Glioma and the gut–brain axis: Opportunities and future perspectives. Neurooncol. Adv. 2022, 4, vdac054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ou, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Wen, M.; Zheng, L. Microbiota and glioma: A new perspective from association to clinical translation. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2394166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, G.B.H.; Cox-Holmes, A.N.; Potier, A.C.E.; Marlow, G.H.; McFarland, B.C. Modulation of the Immune Environment in Glioblastoma by the Gut Microbiota. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbreteau, A.; Aubert, P.; Croyal, M.; Naveilhan, P.; Billon-Crossouard, S.; Neunlist, M.; Delneste, Y.; Couez, D.; Aymeric, L. Late-Stage Glioma Is Associated with Deleterious Alteration of Gut Bacterial Metabolites in Mice. Metabolites 2022, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; He, D.; Lai, H.M.; Xu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Li, T.; Liang, J.; Yang, X.; Guo, L.; Ke, Y.; et al. Comprehensive histological imaging of native microbiota in human glioma. J. Biophotonics 2022, 15, e202100351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socała, K.; Doboszewska, U.; Szopa, A.; Serefko, A.; Włodarczyk, M.; Zielińska, A.; Poleszak, E.; Fichna, J.; Wlaź, P. The role of microbiota-gut-brain axis in neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 172, 105840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balan, Y.; Gaur, A.; Sakthivadivel, V.; Kamble, B.; Sundaramurthy, R. Is the Gut Microbiota a Neglected Aspect of Gut and Brain Disorders? Cureus 2021, 13, e19740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnechère, B.; Amin, N.; van Duijn, C. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Neuropsychiatric Diseases—Creation of An Atlas-Based on Quantified Evidence. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 831666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emery, D.C.; Davies, M.; Cerajewska, T.L.; Taylor, J.; Hazell, M.; Paterson, A.; Allen-Birt, S.J.; West, N.X. High resolution 16S rRNA gene Next Generation Sequencing study of brain areas associated with Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 1026260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisa, D.; Alonso, R.; Carrasco, L. Parkinson’s Disease: A Comprehensive Analysis of Fungi and Bacteria in Brain Tissue. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1135–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Khan, F. Gut microbiome in cancer immunotherapy: Current trends, translational challenges and future possibilities. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2023, 1867, 130401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaq, H.M.; Yasin, R.; Mohammad, I.S.; Fan, Y.; Li, H.; Shahzad, M.; Xu, J. The gut-brain-axis: A positive relationship between gut microbial dysbiosis and glioblastoma brain tumour. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Yang, T.; Wang, S.; Jia, Z.; Zhao, L.; Han, X.; Sun, X.; Zong, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, D. Discussion on the relationship between gut microbiota and glioma through Mendelian randomization test based on the brain gut axis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrizz, A.; Dono, A.; Zorofchian, S.; Hines, G.; Takayasu, T.; Husein, N.; Otani, Y.; Arevalo, O.; Choi, H.A.; Savarraj, J.; et al. Glioma and temozolomide induced alterations in gut microbiome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-Z.; Stirling, K.; Yang, J.-J.; Zhang, L. Gut microbiota and diabetes: From correlation to causality and mechanism. World J. Diabetes 2020, 11, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H. Causal relationship between type 2 diabetes and glioblastoma: Bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’RIordan, K.J.; Collins, M.K.; Moloney, G.M.; Knox, E.G.; Aburto, M.R.; Fülling, C.; Morley, S.J.; Clarke, G.; Schellekens, H.; Cryan, J.F. Short chain fatty acids: Microbial metabolites for gut-brain axis signalling. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2022, 546, 111572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engels, C.; Ruscheweyh, H.-J.; Beerenwinkel, N.; Lacroix, C.; Schwab, C. The Common Gut Microbe Eubacterium hallii also Contributes to Intestinal Propionate Formation. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichardt, N.; Duncan, S.H.; Young, P.; Belenguer, A.; McWilliam Leitch, C.; Scott, K.P.; Flint, H.J.; Louis, P. Phylogenetic distribution of three pathways for propionate production within the human gut microbiota. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile, M.S.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. Inosine in Neurodegenerative Diseases: From the Bench to the Bedside. Molecules 2022, 27, 4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mager, L.F.; Burkhard, R.; Pett, N.; Cooke, N.C.A.; Brown, K.; Ramay, H.; Paik, S.; Stagg, J.; Groves, R.A.; Gallo, M.; et al. Microbiome-derived inosine modulates response to checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy. Science 2020, 369, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, A.; Suthar, P.; Sarmah, D.; Jadhav, P.; Shah, J.; Katamneni, M.; Bhosale, N.; Gupta, V.; Bohra, M.; Baidya, F.; et al. Inosine attenuates post-stroke neuroinflammation by modulating inflammasome mediated microglial activation and polarization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2023, 1869, 166771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, S.; To, K.K.; Zhu, S.; Wang, F.; Fu, L. Tumor-associated macrophages remodel the suppressive tumor immune microenvironment and targeted therapy for immunotherapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2025, 44, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Kang, T.; Chen, S. The role of tumor-associated macrophages in tumor immune evasion. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 150, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, T.Z.; Alabdulqader, A.A.; Sabbah, B.N.; Ouban, A. Brain-inhabiting bacteria and neurodegenerative diseases: The “brain microbiome” theory. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1240945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipos, L.; Banczerowski, P.; Juhász, J.; Fedorcsák, I.; Berényi, G.; Makra, N.; Dunai, Z.A.; Szabó, D.; Erőss, L. Brain Tumors and Beyond: Multi-Compartment Microbiome and Mycobiome Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, R.; Pisa, D.; Fernández-Fernández, A.M.; Carrasco, L. Infection of Fungi and Bacteria in Brain Tissue from Elderly Persons and Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Liu, R.; Su, K.; Gu, Y.; Fang, L.; Fan, Y.; Gao, J.; Ruan, X.; Feng, X. Acupuncture ameliorates breast cancer-related fatigue by regulating the gut microbiota-gut-brain axis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 921119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baj, J.; Forma, A.; Flieger, W.; Morawska, I.; Michalski, A.; Buszewicz, G.; Sitarz, E.; Portincasa, P.; Garruti, G.; Flieger, M.; et al. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Extragastric Diseases—A Focus on the Central Nervous System. Cells 2021, 10, 2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Tang, P.; Hou, C.; Chong, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, P.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, R. Integrated Microbiome and Host Transcriptome Profiles Link Parkinson’s Disease to Blautia Genus: Evidence from Feces, Blood, and Brain. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 875101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Feng, L.; Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Luan, X.; Jiang, Z.; et al. Association Between Oral Microbiota and Human Brain Glioma Grade: A Case-Control Study. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 746568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Weng, X.; Yu, D.; Pan, Z.; Zhao, M.; Cheng, B.; Li, Z. Porphyromonas gingivalis-Derived Lipopolysaccharide Promotes Glioma Cell Proliferation and Migration via Activating Akt Signaling Pathways. Cells 2022, 11, 4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Li, F.; Pan, Y.; Chen, X.; Ma, C.; Zhao, W.; Tang, X. Porphyromonas gingivalis bacteremia increases the permeability of the blood-brain barrier via the Mfsd2a/Caveolin-1 mediated transcytosis pathway. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2023, 15, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Sun, X.; Rajesh, K.; Chalasani, N.; Gelow, K.; Katz, B.; Shah, V.H.; Sanyal, A.J.; Smirnova, E. Effects of Rare Microbiome Taxa Filtering on Statistical Analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 607325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, S.P.; Tangney, M.; Claesson, M.J. Sequence-Based Characterization of Intratumoral Bacteria—A Guide to Best Practice. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karstens, L.; Asquith, M.; Davin, S.; Fair, D.; Gregory, W.T.; Wolfe, A.J.; Braun, J.; McWeeney, S. Controlling for Contaminants in Low-Biomass 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing Experiments. mSystems 2019, 4, e00290-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nearing, J.T.; Douglas, G.M.; Hayes, M.G.; MacDonald, J.; Desai, D.K.; Allward, N.; Jones, C.M.A.; Wright, R.J.; Dhanani, A.S.; Comeau, A.M.; et al. Microbiome differential abundance methods produce different results across 38 datasets. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 342, Correction in Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Glioblastoma | Meningioma | Healthy Controls | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subjects | n = 9 | n = 18 | n = 12 |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 48.0 ± 13.4 | 51.2 ± 13.1 | 44.8 ± 12.7 |
| Gender Male Female | 5 4 | 7 11 | 6 6 |
| Other pathology Diabetes Hypertension | 1 2 | 4 5 | - - |
| Tumor grade Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 | 9 | 15 3 | - - - - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mehelleb, D.; Ghidouche, A.; Baldi, S.; Djoudi, F.; Bertorello, S.; Di Gloria, L.; Ramazzotti, M.; Niccolai, E.; Madaoui, M.; Takbou, I.; et al. Specific Intratumoral Microbiome Signatures in Human Glioblastoma and Meningioma: Evidence for a Gut–Brain Microbial Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311290
Mehelleb D, Ghidouche A, Baldi S, Djoudi F, Bertorello S, Di Gloria L, Ramazzotti M, Niccolai E, Madaoui M, Takbou I, et al. Specific Intratumoral Microbiome Signatures in Human Glioblastoma and Meningioma: Evidence for a Gut–Brain Microbial Axis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311290
Chicago/Turabian StyleMehelleb, Dalila, Abderezak Ghidouche, Simone Baldi, Ferhat Djoudi, Sara Bertorello, Leandro Di Gloria, Matteo Ramazzotti, Elena Niccolai, Menad Madaoui, Idir Takbou, and et al. 2025. "Specific Intratumoral Microbiome Signatures in Human Glioblastoma and Meningioma: Evidence for a Gut–Brain Microbial Axis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311290
APA StyleMehelleb, D., Ghidouche, A., Baldi, S., Djoudi, F., Bertorello, S., Di Gloria, L., Ramazzotti, M., Niccolai, E., Madaoui, M., Takbou, I., Tliba, S., & Amedei, A. (2025). Specific Intratumoral Microbiome Signatures in Human Glioblastoma and Meningioma: Evidence for a Gut–Brain Microbial Axis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311290








