Intra-Articular Delivery of Nanoemulsified Curcumin Ameliorates Joint Degeneration in a Chemically Induced Model of Osteoarthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
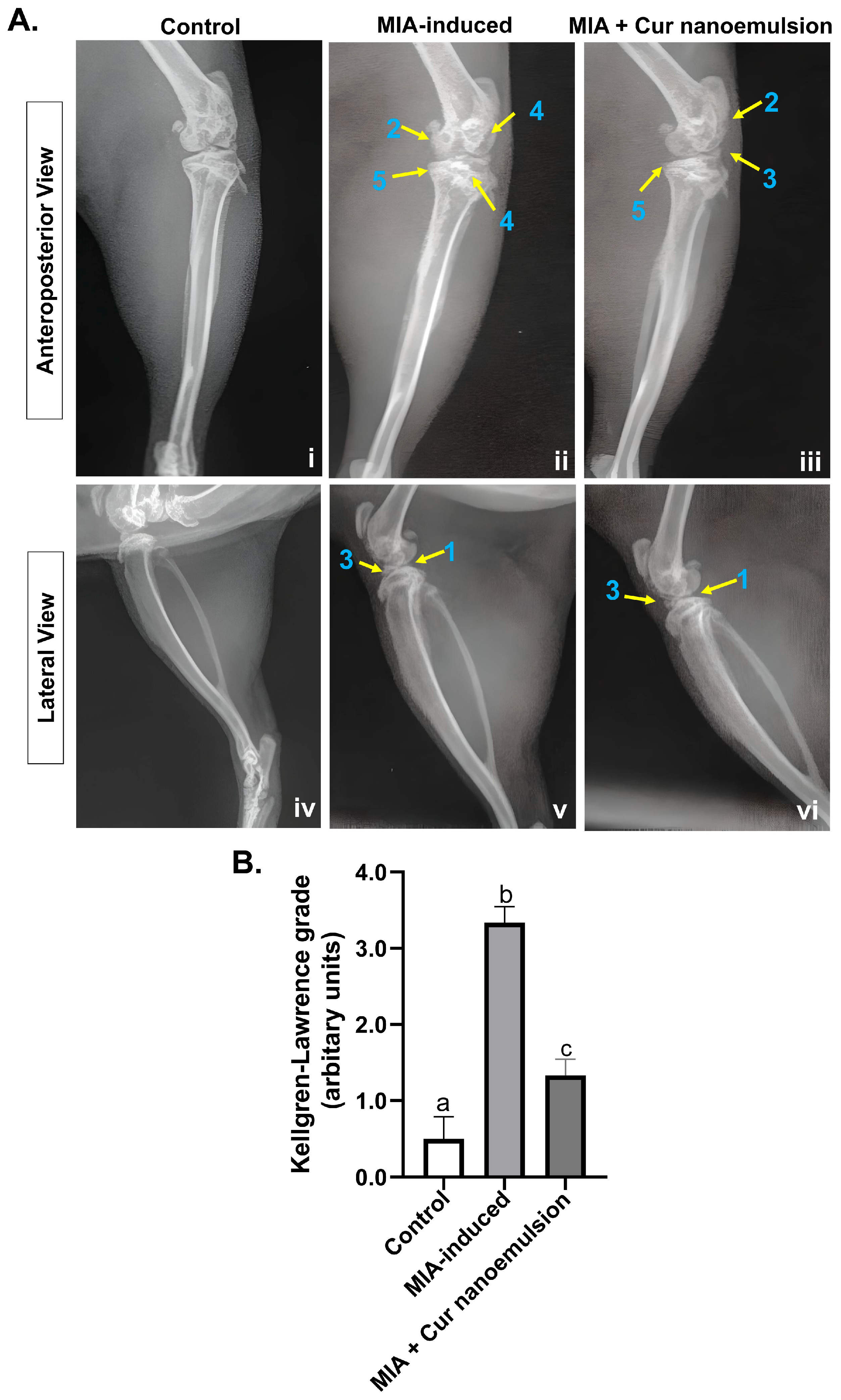
2.1. Curcumin Nanoemulsion Reduced MIA-Induced Knee Joint Edema and Joint Space Narrowing in Osteoarthritic Rats
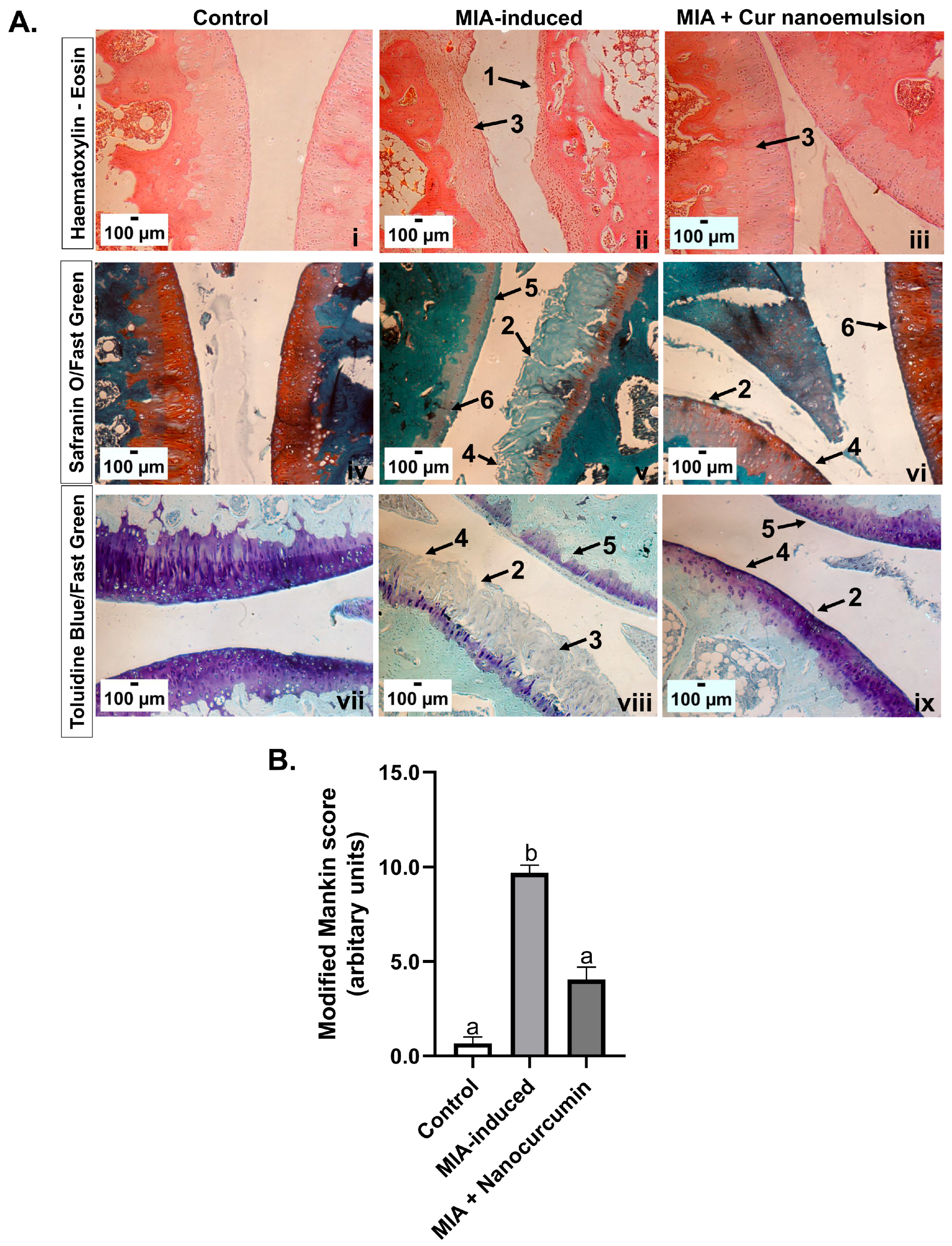
2.2. Curcumin Nanoemulsion Alleviated MIA-Induced Cartilage Fibrillation, Reduced Systemic Oxidative Stress, and Synovial Inflammation in the Knee Joint
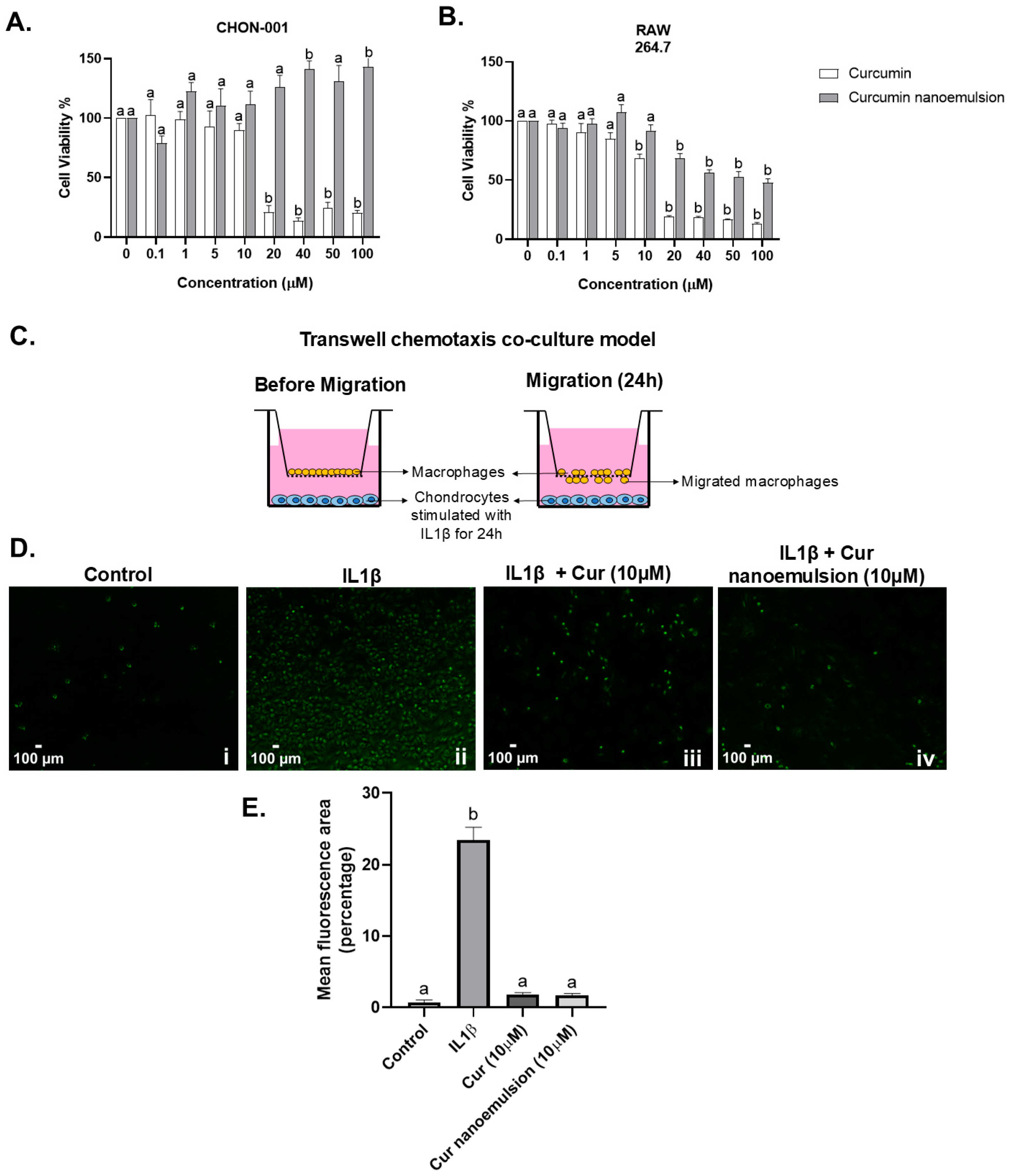
2.3. Curcumin Nanoemulsion Reduced In Vitro Macrophage Migration Towards Chondrocytes in the Presence of IL1β
2.4. Modulation of Pro-Inflammatory Mediators and Matrix Regulators in Chondrocytes Exposed to Curcumin Nanoemulsion
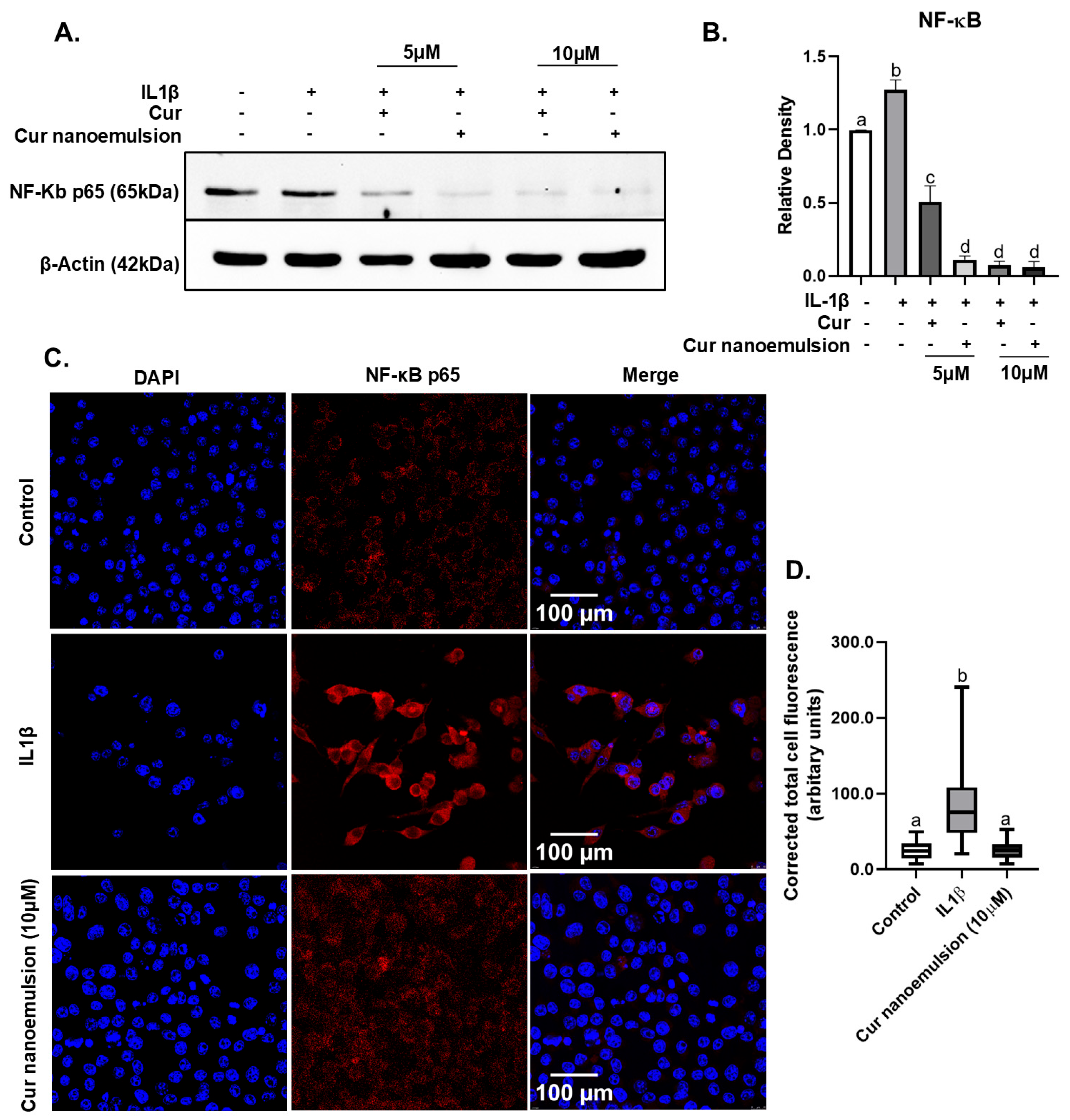
2.5. Curcumin Nanoemulsion Lowered IL1β-Induced Expression of NFκB in Macrophages (RAW264.7)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Nanoemulsion
4.2. Animal Experiment
4.3. X-Ray Imaging and Scoring for Osteoarthritis
4.4. Knee Diameter Measurement
4.5. Collection of Blood and Knee Joints
4.6. Serum Oxidative Stress
4.7. Knee Joint Histology and Staining
4.8. Reagents and Cell Culture
4.9. Cell Viability by MTT Assay
4.10. Immunoblotting
4.11. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.12. Detection of NFκB Localization by Immunocytochemistry
4.13. Transwell Co-Culture Chemotaxis Assay
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karpiński, R.; Prus, A.; Baj, J.; Radej, S.; Prządka, M.; Krakowski, P.; Jonak, K. Articular Cartilage: Structure, Biomechanics, and the Potential of Conventional and Advanced Diagnostics. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregori, D.; Giacovelli, G.; Minto, C.; Barbetta, B.; Gualtieri, F.; Azzolina, D.; Vaghi, P.; Rovati, L.C. Association of Pharmacological Treatments With Long-term Pain Control in Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA 2018, 320, 2564–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Lou, Z.; Zheng, S.; Wu, J.; Yao, Q.; Chen, R.; Kou, L.; Chen, D. Intra-articular drug delivery systems for osteoarthritis therapy: Shifting from sustained release to enhancing penetration into cartilage. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 767–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tao, Y.; Lin, W.; Wang, P. Intra-Articular Drug Delivery for Osteoarthritis Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen, S.V.; Ahmad, R.E.; Hui, W.J.; Suhaeb, A.M.; Murali, M.R.; Shanmugam, R.; Kamarul, T. Histology, glycosaminoglycan level and cartilage stiffness in monoiodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis: Comparative analysis with anterior cruciate ligament transection in rat model and human osteoarthritis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Nam, D.; Kim, J. Pathological Characteristics of Monosodium Iodoacetate-Induced Osteoarthritis in Rats. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2023, 20, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, R.E.; Evans, M.G.; Bove, S.; Morenko, B.; Kilgore, K. Mono-iodoacetate-induced histologic changes in subchondral bone and articular cartilage of rat femorotibial joints: An animal model of osteoarthritis. Toxicol. Pathol. 2003, 31, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gui, T.; Yao, L.; Guo, H.; Lin, Y.L.; Lu, J.; Duffy, M.; Zgonis, M.; Mauck, R.; Dyment, N.; et al. Synovium and infrapatellar fat pad share common mesenchymal progenitors and undergo coordinated changes in osteoarthritis. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2024, 39, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostojic, M.; Zevrnja, A.; Vukojevic, K.; Soljic, V. Immunofluorescence Analysis of NF-kB and iNOS Expression in Different Cell Populations during Early and Advanced Knee Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.C.; Jo, J.; Park, J.; Kang, H.K.; Park, Y. NF-κB Signaling Pathways in Osteoarthritic Cartilage Destruction. Cells 2019, 8, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Morrison, A.; Sun, H.; De Luca, F. Nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) p65 interacts with Stat5b in growth plate chondrocytes and mediates the effects of growth hormone on chondrogenesis and on the expression of insulin-like growth factor-1 and bone morphogenetic protein-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 24726–24734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, M.M.; Emans, P.J.; Surtel, D.A.; Cremers, A.; Voncken, J.W.; Welting, T.J.; van Rhijn, L.W. Activation of NF-κB/p65 facilitates early chondrogenic differentiation during endochondral ossification. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Bhutani, N. Profiling joint tissues at single-cell resolution: Advances and insights. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2024, 20, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hao, R.; Lv, J.; Yuan, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, C.; Ma, D.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, B.; Dai, L.; et al. Targeted knockdown of PGAM5 in synovial macrophages efficiently alleviates osteoarthritis. Bone Res. 2024, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.L.; Harasymowicz, N.S.; Klimak, M.A.; Collins, K.H.; Guilak, F. The role of macrophages in osteoarthritis and cartilage repair. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2020, 28, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ummarino, A.; Gambaro, F.M.; Kon, E.; Torres Andón, F. Therapeutic Manipulation of Macrophages Using Nanotechnological Approaches for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamasaki, M.; Terkawi, M.A.; Onodera, T.; Homan, K.; Iwasaki, N. A Novel Cartilage Fragments Stimulation Model Revealed that Macrophage Inflammatory Response Causes an Upregulation of Catabolic Factors of Chondrocytes In Vitro. Cartilage 2021, 12, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Kubota, K.; Asawa, Y.; Hoshi, K.; Hikita, A. M1-Like Macrophage Contributes to Chondrogenesis In Vitro. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21307, Correction in Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivotto, E.; Minguzzi, M.; D’Adamo, S.; Astolfi, A.; Santi, S.; Uguccioni, M.; Marcu, K.B.; Borzì, R.M. Basal and IL-1β enhanced chondrocyte chemotactic activity on monocytes are co-dependent on both IKKα and IKKβ NF-κB activating kinases. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Chang, B.; Wei, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Piao, L.; Bai, L. Curcumin exerts chondroprotective effects against osteoarthritis by promoting AMPK/PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csaki, C.; Mobasheri, A.; Shakibaei, M. Synergistic chondroprotective effects of curcumin and resveratrol in human articular chondrocytes: Inhibition of IL-1beta-induced NF-kappaB-mediated inflammation and apoptosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.; Hridayanka, K.S.N.; Duttaroy, A.K. Bioactives and their roles in bone metabolism of osteoarthritis: Evidence and mechanisms on gut-bone axis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 14, 1323233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hridayanka, K.S.N.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Basak, S. Bioactive Compounds and Their Chondroprotective Effects for Osteoarthritis Amelioration: A Focus on Nanotherapeutic Strategies, Epigenetic Modifications, and Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratanavaraporn, J.; Soontornvipart, K.; Shuangshoti, S.; Shuangshoti, S.; Damrongsakkul, S. Localized delivery of curcumin from injectable gelatin/Thai silk fibroin microspheres for anti-inflammatory treatment of osteoarthritis in a rat model. Inflammopharmacology 2017, 25, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wang, X.; Liang, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y. A Core-Brush Nanoplatform with Enhanced Lubrication and Anti-Inflammatory Properties for Osteoarthritis Treatment. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2406027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdalla, H.M.; Ahmed, R.R.; Galaly, S.R.; Naguib, I.A.; Alghamdi, B.S.; Ahmed, O.M.; Farghali, A.; Abdul-Hamid, M. Ameliorative Effect of Curcumin Nanoparticles against Monosodium Iodoacetate-Induced Knee Osteoarthritis in Rats. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 8353472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Haddad, M.E.; El-Refaie, W.M.; Hammad, G.O.; El-Massik, M.A. Intra-articular metformin-curcumin cationic PLGA nanoparticles rejuvenate articular structure in MIA induced osteoarthritis model via modulating the crosstalk between miR93, TNFAIP3/TLR/NF-κB and AMPK/SIRT1 trajectories. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 315, 144482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Mi, B.B.; Shahbazi, M.A.; Xia, T.; Xiao, J. Microenvironment-responsive nanomedicines: A promising direction for tissue regeneration. Mil. Med. Res. 2024, 11, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabas, M.; Orhan, C.; Er, B.; Tuzcu, M.; Durmus, A.S.; Ozercan, I.H.; Sahin, N.; Bhanuse, P.; Morde, A.A.; Padigaru, M.; et al. A Next Generation Formulation of Curcumin Ameliorates Experimentally Induced Osteoarthritis in Rats via Regulation of Inflammatory Mediators. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 609629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Lee, C.K.; Song, S.H.; Yun, J.H.; Lee, A.; Park, H.J. Highly bioavailable curcumin powder suppresses articular cartilage damage in rats with mono-iodoacetate (MIA)-induced osteoarthritis. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimpen, J.Y.; Hedley, R.; Ridley, A.; Baldwin, M.J.; Windell, D.; Bhalla, A.; Ramos-Mucci, L.; Buckley, C.D.; Coles, M.C.; Alvand, A.; et al. Cellular characterisation of advanced osteoarthritis knee synovium. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roebuck, M.M.; Jamal, J.; Lane, B.; Wood, A.; Santini, A.; Wong, P.F.; Bou-Gharios, G.; Frostick, S.P. Cartilage debris and osteoarthritis risk factors influence gene expression in the synovium in end stage osteoarthritis. Knee 2022, 37, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.H.; Jain, V.; Gibson, J.; Attarian, D.E.; Haraden, C.A.; Yohn, C.B.; Laberge, R.M.; Gregory, S.; Kraus, V.B. Synovial cell cross-talk with cartilage plays a major role in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.H.; Ghosh, D.; Attari, S.; Ude, C.C.; Laurencin, C.T. Animal Models of Osteoarthritis: Updated Models and Outcome Measures 2016–2023. Regen. Eng. Transl. Med. 2024, 10, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzidaki, M.D.; Mitsou, E. Advancements in Nanoemulsion-Based Drug Delivery Across Different Administration Routes. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, I.; Ikeshima, K.; Matsuzaki, T.; Hoso, M. Histopathological changes in joint capsule and synovial membrane in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016, 24, S398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.D. The normal synovium. Open Rheumatol. J. 2011, 5, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, H.; Nakagawa, Y.; Muneta, T.; Koga, H. A CCL2/MCP-1 antagonist attenuates fibrosis of the infrapatellar fat pad in a rat model of arthritis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2024, 25, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barboza, E.; Hudson, J.; Chang, W.P.; Kovats, S.; Towner, R.A.; Silasi-Mansat, R.; Lupu, F.; Kent, C.; Griffin, T.M. Profibrotic Infrapatellar Fat Pad Remodeling Without M1 Macrophage Polarization Precedes Knee Osteoarthritis in Mice With Diet-Induced Obesity. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, L.A.; Kraiger, M.; Talakic, E.; Fritz, G.A.; Avian, A.; Hofmeister, A.; Leithner, A.; Holzer, G. Microstructural analysis of subchondral bone in knee osteoarthritis. Osteoporos. Int. 2020, 31, 2037–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Sawy, E.R.; Saber, M.M.; Nassar, N.N.; Sayed, N.S.E. Targeting TREM-1 receptors with metformin and pravastatin modulate monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis. Inflammopharmacology 2025, 33, 2737–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Liu, G.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, F.; Wang, L. Curcumin alleviates osteoarthritis in mice by suppressing osteoclastogenesis in subchondral bone via inhibiting NF-κB/JNK signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0309807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwosu, L.N.; Mapp, P.I.; Chapman, V.; Walsh, D.A. Relationship between structural pathology and pain behaviour in a model of osteoarthritis (OA). Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016, 24, 1910–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mende, L.K.; Kuthati, Y.; Wong, C.S. Curcumin and Vitamin D Supplement Attenuates Knee Osteoarthritis Progression in ACLT + MMx Rat Model: Effect on Cartilage Protection and Pain Reduction. Nutrients 2025, 17, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhun, J.; Lee, D.; Na, H.S.; Cho, K.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, S.J.; Park, S.H.; Cho, M.L. Curcumin and omega-3 ameliorate experimental osteoarthritis progression in terms of joint pain and mitochondrial dysfunction. J. Inflamm. 2025, 22, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewallen, E.A.; Bonin, C.A.; Li, X.; Smith, J.; Karperien, M.; Larson, A.N.; Lewallen, D.G.; Cool, S.M.; Westendorf, J.J.; Krych, A.J.; et al. The synovial microenvironment of osteoarthritic joints alters RNA-seq expression profiles of human primary articular chondrocytes. Gene 2016, 591, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altindag, O.; Erel, O.; Aksoy, N.; Selek, S.; Celik, H.; Karaoglanoglu, M. Increased oxidative stress and its relation with collagen metabolism in knee osteoarthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2007, 27, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; He, Q.; Chen, C.; Lin, Y.; Xiao, J.; Pan, Z.; Li, M.; Li, S.; Yang, J.; Wang, F.; et al. Combination of curcumin and catalase protects against chondrocyte injury and knee osteoarthritis progression by suppressing oxidative stress. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 168, 115751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, K.; Pu, H.; Peng, R.; Xiao, J.; Liu, C.; Sun, X. Metformin Attenuates the Inflammatory Response via the Regulation of Synovial M1 Macrophage in Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Wei, W.; Li, Z.; Zhou, H.; He, W.; Xia, J.; Li, B.; Yang, Y. SRGN promotes macrophage recruitment through CCL3 in osteoarthritis. Connect. Tissue Res. 2024, 65, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y.; Kijima, K.; Yoshioka, K. Validity evaluation of a rat model of monoiodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis with clinically effective drugs. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2024, 25, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryk, M.; Chwastek, J.; Mlost, J.; Kostrzewa, M.; Starowicz, K. Sodium Monoiodoacetate Dose-Dependent Changes in Matrix Metalloproteinases and Inflammatory Components as Prognostic Factors for the Progression of Osteoarthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 643605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Beuningen, H.M.; van der Kraan, P.M.; Arntz, O.J.; van den Berg, W.B. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 stimulates articular chondrocyte proteoglycan synthesis and induces osteophyte formation in the murine knee joint. Lab. Investig. A J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 1994, 71, 279–290. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Chen, L.; Xu, X.; Li, C.; Huang, C.; Deng, C.X. TGF-beta/Smad3 signals repress chondrocyte hypertrophic differentiation and are required for maintaining articular cartilage. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 153, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ming, J.; Deng, M.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, G.; Liu, S. Chemically modified curcumin (CMC2.24) alleviates osteoarthritis progression by restoring cartilage homeostasis and inhibiting chondrocyte apoptosis via the NF-κB/HIF-2α axis. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 98, 1479–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clutterbuck, A.L.; Mobasheri, A.; Shakibaei, M.; Allaway, D.; Harris, P. Interleukin-1beta-induced extracellular matrix degradation and glycosaminoglycan release is inhibited by curcumin in an explant model of cartilage inflammation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1171, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wu, S.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.-P. The roles and regulatory mechanisms of TGF-β and BMP signaling in bone and cartilage development, homeostasis and disease. Cell Res. 2024, 34, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luyten, F.P.; Yu, Y.M.; Yanagishita, M.; Vukicevic, S.; Hammonds, R.G.; Reddi, A.H. Natural bovine osteogenin and recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2B are equipotent in the maintenance of proteoglycans in bovine articular cartilage explant cultures. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 3691–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retting, K.N.; Song, B.; Yoon, B.S.; Lyons, K.M. BMP canonical Smad signaling through Smad1 and Smad5 is required for endochondral bone formation. Development 2009, 136, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thielen, N.G.M.; van der Kraan, P.M.; van Caam, A.P.M. TGFβ/BMP Signaling Pathway in Cartilage Homeostasis. Cells 2019, 8, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, H.; Seo, J.; Choi, K.; Lee, Y.; Park, K.; Kim, S.; Mobasheri, A.; Choi, H. TissueGene-C promotes an anti-inflammatory micro-environment in a rat monoiodoacetate model of osteoarthritis via polarization of M2 macrophages leading to pain relief and structural improvement. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 1237–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Li, H.; Wu, B.; Shang, J.; Jiang, N.; Peng, R.; Xing, B.; Xu, X.; Lu, H. TGF-β1 regulates chondrocyte proliferation and extracellular matrix synthesis via circPhf21a-Vegfa axis in osteoarthritis. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.D.; Gill, G.; Lin, H.; Roth, D.M.; Gu, H.M.; Wang, X.J.; Su, F.Y.; Alabi, A.; Alexiou, M.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Global, but not chondrocyte-specific, MT1-MMP deficiency in adult mice causes inflammatory arthritis. Matrix Biol. 2023, 122, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Xu, X.; Yi, P.; Hao, Y. Curcumin reinforces MSC-derived exosomes in attenuating osteoarthritis via modulating the miR-124/NF-kB and miR-143/ROCK1/TLR9 signalling pathways. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 10855–10865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze-Tanzil, G.; Mobasheri, A.; Sendzik, J.; John, T.; Shakibaei, M. Effects of curcumin (diferuloylmethane) on nuclear factor kappaB signaling in interleukin-1beta-stimulated chondrocytes. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1030, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wu, S.; Mao, X.; Wang, W.; Tai, H. Inhibition effect of curcumin on TNF-α and MMP-13 expression induced by advanced glycation end products in chondrocytes. Pharmacology 2013, 91, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhrmann, C.; Brockmueller, A.; Mueller, A.-L.; Shayan, P.; Shakibaei, M. Curcumin Attenuates Environment-Derived Osteoarthritis by Sox9/NF-kB Signaling Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitcher, T.; Sousa-Valente, J.; Malcangio, M. The Monoiodoacetate Model of Osteoarthritis Pain in the Mouse. JoVE 2016, 111, e53746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahata, A.; Ito, A.; Nakahara, R.; Kishimoto, A.; Imaizumi, A.; Hashimoto, T.; Mukai, S.; Nakagawa, Y.; Kuroki, H. Intra-Articular Injections of Curcumin Monoglucuronide TBP1901 Suppresses Articular Cartilage Damage and Regulates Subchondral Bone Alteration in an Osteoarthritis Rat Model. Cartilage 2021, 13, 153s–167s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, M.D.; Sassoon, A.A.; Fernando, N.D. Classifications in Brief: Kellgren-Lawrence Classification of Osteoarthritis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2016, 474, 1886–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraheem, M.; Mostafa Mahmoud, A.; Abd Elaal Ahmed, N.; Abdel Aziz, H.O.; Elsayed Abo Elnasr, S. Protective effects of colchicine against osteoarthritis in rat induced by monosodium iodoacetate. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2025, 14, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Zalam, H.B.; Abdelsalam, R.M.; Abdel-Rahman, R.F.; Abd-Ellah, M.F.; Khattab, M.M. In Vivo Investigation of the Ameliorating Effect of Tempol against MIA-Induced Knee Osteoarthritis in Rats: Involvement of TGF-β1/SMAD3/NOX4 Cue. Molecules 2021, 26, 6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horváth, Á.I.; Bölcskei, K.; Szentes, N.; Borbély, É.; Tékus, V.; Botz, B.; Rusznák, K.; Futácsi, A.; Czéh, B.; Mátyus, P.; et al. Novel Multitarget Analgesic Candidate SZV-1287 Demonstrates Potential Disease-Modifying Effects in the Monoiodoacetate-Induced Osteoarthritis Mouse Model. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1377081, Correction in Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1646562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerwin, N.; Bendele, A.M.; Glasson, S.; Carlson, C.S. The OARSI histopathology initiative—Recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the rat. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18 (Suppl. 3), S24–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, N.; Laverty, S.; Kraus, V.B.; Aigner, T. Basic methods in histopathology of joint tissues. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18 (Suppl. 3), S113–S116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankin, H.J.; Dorfman, H.; Lippiello, L.; Zarins, A. Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteo-arthritic human hips. II. Correlation of morphology with biochemical and metabolic data. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1971, 53, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, I.; Matsuzaki, T.; Kuroki, H.; Hoso, M. Joint unloading inhibits articular cartilage degeneration in knee joints of a monosodium iodoacetate-induced rat model of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2019, 27, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, S.; Molangiri, A.; Mudavath, S.; Ananthan, R.; Rajanna, A.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Basak, S. Exposure to BPA and BPS during pregnancy disrupts the bone mineralization in the offspring. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 189, 114772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, C.; Niesler, C.U. Rapid quantification of cellular proliferation and migration using ImageJ. BioTechniques 2019, 66, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Type of Gene | Gene Symbol | Control (Unstimulated) | IL1β (10 ng/mL) | IL1β + Cur (10 μM) | IL1β + Cur-Nanoemulsion (10 μM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammatory Modulators | |||||
| NFκB | 1.01 ± 0.04 a | 4.41 ± 0.67 b | 2.37 ± 0.05 c | 2.47 ± 0.07 c | |
| NFκB-IB | 1.01 ± 0.06 a | 2.28 ± 0.32 b | 3.14 ± 0.33 b | 3.58 ± 0.22 bc | |
| TNFα | 1.01 ± 0.04 a | 1.65 ± 0.11 b | 0.90 ± 0.03 a | 0.97 ± 0.09 a | |
| Matrix Regulators | |||||
| TGFβ1 | 1.01 ± 0.02 a | 0.57 ± 0.03 b | 1.35 ± 0.06 a | 1.24 ± 0.17 a | |
| BMP2 | 1.01 ± 0.05 a | 8.61 ± 2.29 b | 12.78 ± 1.07 b | 13.64 ± 1.31 b | |
| SMAD1 | 1.01 ± 0.04 a | 0.95 ± 0.05 a | 2.20 ± 0.07 b | 1.40 ± 0.08 c | |
| SMAD5 | 1.01 ± 0.02 a | 0.70 ± 0.22 a | 0.52 ± 0.02 a | 0.32 ± 0.02 ab | |
| SPARC | 1.01 ± 0.02 a | 0.39 ± 0.13 b | 0.13 ± 0.01 b | 0.18 ± 0.01 b | |
| MMP2 | 1.01 ± 0.01 a | 1.57 ± 0.10 b | 1.56 ± 0.07 b | 1.44 ± 0.18 b | |
| MMP9 | 1.01 ± 0.02 a | 1.94 ± 0.49 b | 0.93 ± 0.16 a | 1.94 ± 0.13 b | |
| MMP14 | 1.01 ± 0.02 a | 0.84 ± 0.23 a | 1.52 ± 0.09 b | 1.47 ± 0.04 ab | |
| TIMP1 | 1.01 ± 0.03 a | 1.98 ± 0.32 b | 2.08 ± 0.18 b | 2.53 ± 0.16 b | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hridayanka, K.S.N.; Roy, S.; Varma, S.; Boga, N.S.; Molangiri, A.; Patil, P.B.; Srinivas, M.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Basak, S. Intra-Articular Delivery of Nanoemulsified Curcumin Ameliorates Joint Degeneration in a Chemically Induced Model of Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211212
Hridayanka KSN, Roy S, Varma S, Boga NS, Molangiri A, Patil PB, Srinivas M, Duttaroy AK, Basak S. Intra-Articular Delivery of Nanoemulsified Curcumin Ameliorates Joint Degeneration in a Chemically Induced Model of Osteoarthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):11212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211212
Chicago/Turabian StyleHridayanka, Kota Sri Naga, Shibsekhar Roy, Saikanth Varma, Navya Sree Boga, Archana Molangiri, Pradeep B. Patil, Myadara Srinivas, Asim K. Duttaroy, and Sanjay Basak. 2025. "Intra-Articular Delivery of Nanoemulsified Curcumin Ameliorates Joint Degeneration in a Chemically Induced Model of Osteoarthritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 11212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211212
APA StyleHridayanka, K. S. N., Roy, S., Varma, S., Boga, N. S., Molangiri, A., Patil, P. B., Srinivas, M., Duttaroy, A. K., & Basak, S. (2025). Intra-Articular Delivery of Nanoemulsified Curcumin Ameliorates Joint Degeneration in a Chemically Induced Model of Osteoarthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 11212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211212


_Kim.png)







