PCR-Based Molecular Authentication Method for Sources of Agrimoniae Herba via Comparative Analyses of Complete Chloroplast Genomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Agrimonia Species
2.2. Sequence Variation Among Agrimonia Species
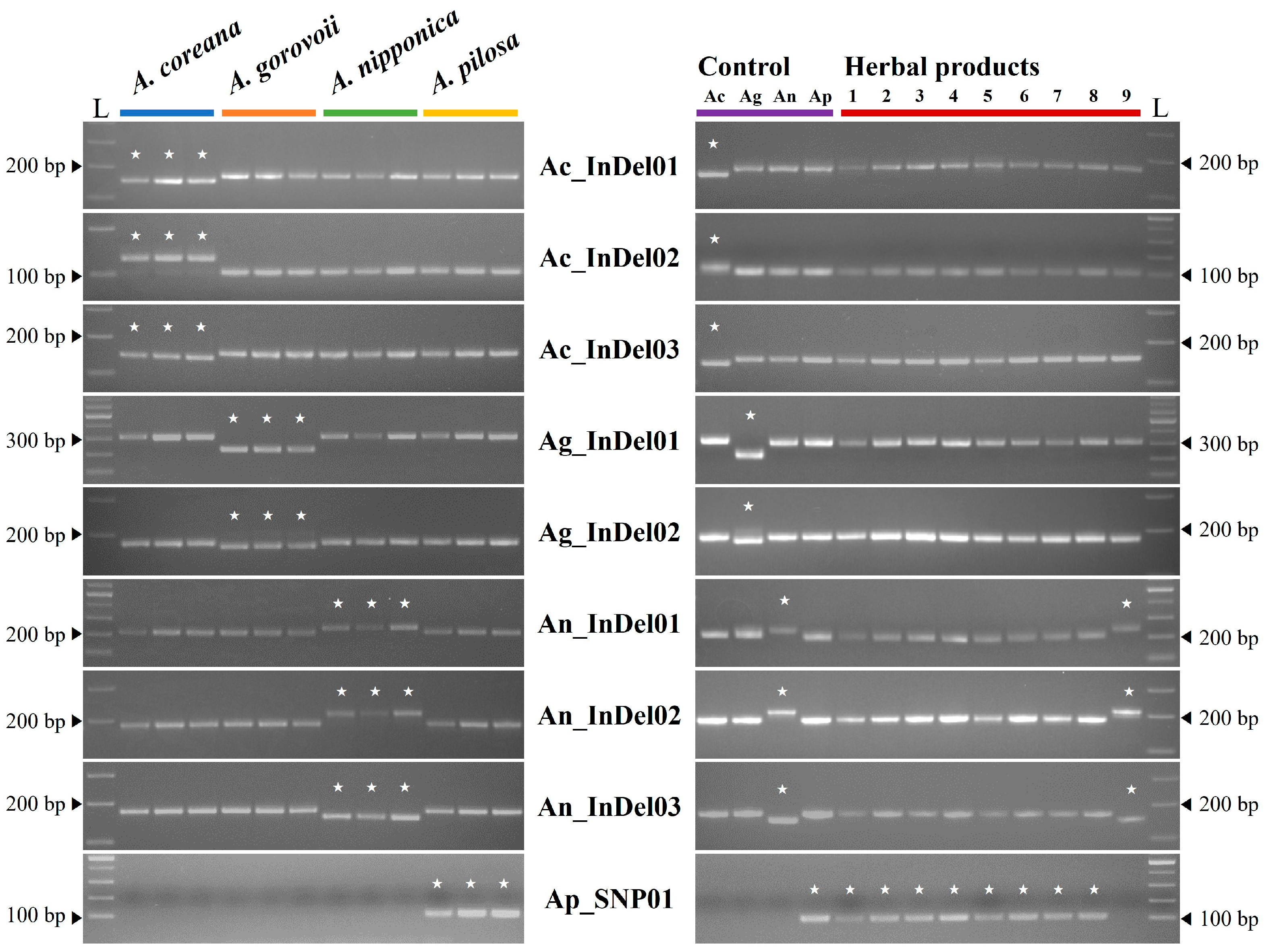
2.3. Development and Application of Species-Specific Markers
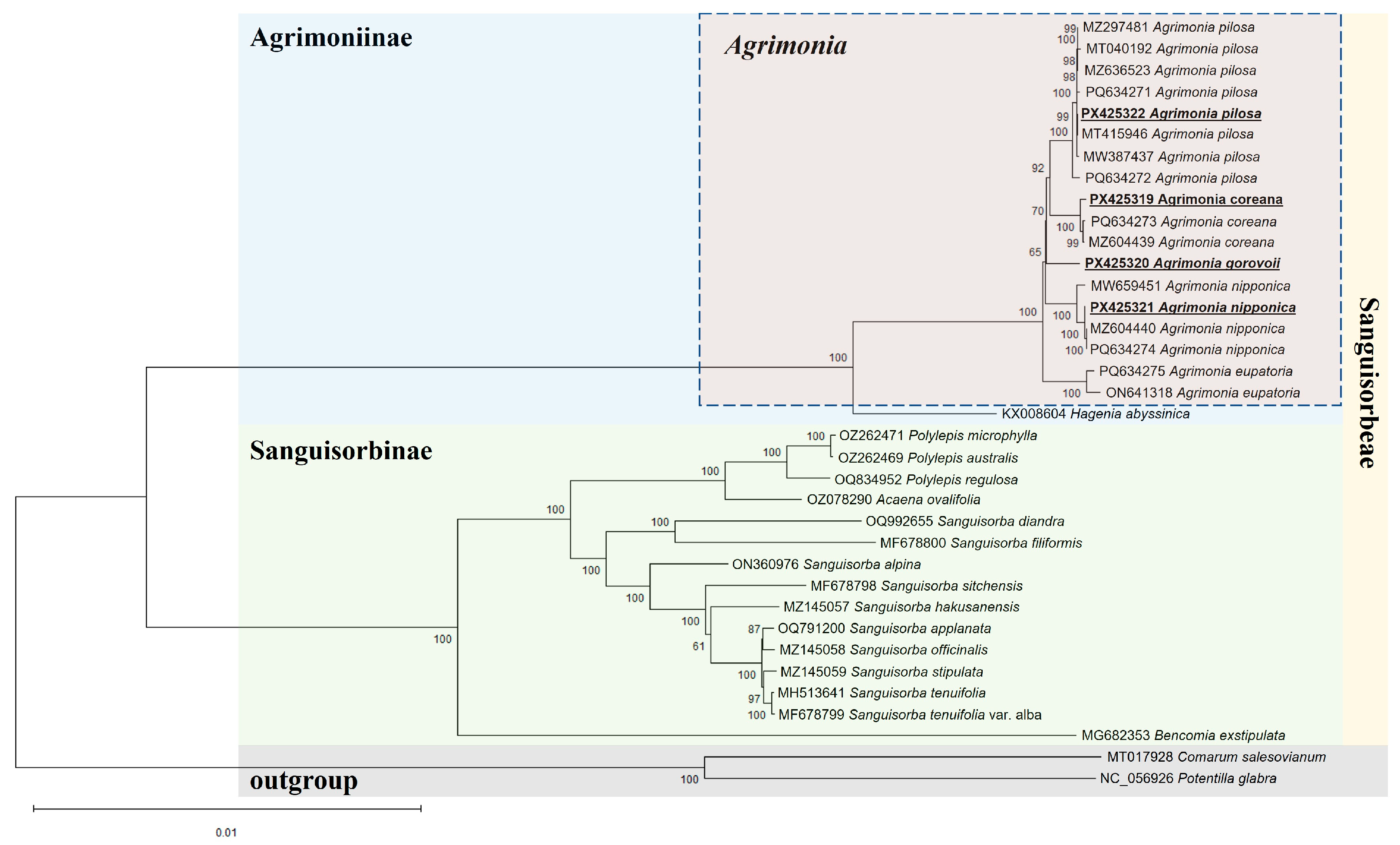
2.4. Phylogenetic Relationships Among Agrimonia and Related Taxa
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and DNA Extraction
4.2. Genome Sequencing and Assembly
4.3. Comparative Analysis
4.4. Marker Development and Application
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chung, K.-S. A Systematic Study of Genus Agrimonia (Rosaceae); The University of Oklahoma: Norman, OK, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Paluch, Z.; Biriczová, L.; Pallag, G.; Marques, E.C.; Vargová, N.; Kmonícková, E. The Therapeutic Effects of Agrimonia L. Physiol. Res. 2020, 69, S555–S571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.H.; Zhang, X.F.; Wu, Y.A.; Yu, S.S.; Zhang, W.; Liu, D.; Yang, K.; Sun, J. Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb.: A review of its traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.Y.; Chi, L.; Ma, C.Y. Agrimonia pilosa: A Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 3742208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Kumar, A.; Nagireddy, A.; Mani, D.N.; Shukla, A.K.; Tiwari, R.; Sundaresan, V. DNA barcoding: An efficient tool to overcome authentication challenges in the herbal market. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfannschmidt, T.; Nilsson, A.; Allen, J.F. Photosynthetic control of chloroplast gene expression. Nature 1999, 397, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.D.; Stein, D.B. Conservation of chloroplast genome structure among vascular plants. Curr. Genet. 1986, 10, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kang, J.S.; Park, H.S.; Jeon, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; Yeo, E.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Jeong, D.; Kim, Y.S.; et al. Molecular authentication of Paeonia species for paeonia radix production using plastid and nuclear DNA markers. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2025, 44, 100604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Nguyen, V.B.; Dong, J.Z.; Wang, Y.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, S.C.; Yang, T.J. Evolution of the Araliaceae family inferred from complete chloroplast genomes and 45S nrDNAs of 10 Panax-related species. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.; Jang, Y.; Cho, W.; Lee, S.H.; Shim, H.; Park, J.Y.; Xu, J.; Shen, X.; Liao, B.; Jo, I.-H. High-throughput digital genotyping tools for Panax ginseng based on diversity among 44 complete plastid genomes. Plant Breed. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Giang, V.N.L.; Waminal, N.E.; Park, H.S.; Kim, N.H.; Jang, W.; Lee, J.; Yang, T.J. Comprehensive comparative analysis of chloroplast genomes from seven Panax species and development of an authentication system based on species-unique single nucleotide polymorphism markers. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.X.; Qian, J.; Du, Z.F.; Wang, J.; Duan, B.Z. Complete genome and phylogenetic analysis of Agrimonia pilosa ldb. Mitochondrial DNA B 2020, 5, 1435–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, K.I.; Park, J.; Xi, H.; Min, J. The complete chloroplast genome of Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb. isolated in Korea (Rosaceae): Investigation of intraspecific variations on its chloroplast genomes. Mitochondrial DNA B 2020, 5, 2264–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauz-Santos, L.A. Beyond conservation: The landscape of chloroplast genome rearrangements in angiosperms. New Phytol. 2025, 247, 2571–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, K.H.; Li, W.-H.; Sharp, P.M. Rates of nucleotide substitution vary greatly among plant mitochondrial, chloroplast, and nuclear DNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 9054–9058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.D.; Guo, W.H.; Gupta, S.; Fan, W.S.; Mower, J.P. Evolutionary dynamics of the plastid inverted repeat: The effects of expansion, contraction, and loss on substitution rates. New Phytol. 2016, 209, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, M.; Fujimoto, M.; Arimura, S.; Murata, J.; Tsutsumi, N.; Kadowaki, K. Loss of the rpl32 gene from the chloroplast genome and subsequent acquisition of a preexisting transit peptide within the nuclear gene in Populus. Gene 2007, 402, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millen, R.S.; Olmstead, R.G.; Adams, K.L.; Palmer, J.D.; Lao, N.T.; Heggie, L.; Kavanagh, T.A.; Hibberd, J.M.; Gray, J.C.; Morden, C.W.; et al. Many parallel losses of infA from chloroplast DNA during angiosperm evolution with multiple independent transfers to the nucleus. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruf, S.; Trösch, R.; Schollbach, L.; Kroop, X.; Forner, J.; Gefen-Treves, S.; Henze, A.; Thiele, W.; Schöttler, M.A.; Zoschke, R.; et al. Reverse genetics in the Arabidopsis chloroplast genome identifies rps16 as a transcribed pseudogene. Plant J. 2025, 122, e70198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, E.N.; Ruhlman, T.A.; Sabir, J.S.M.; Hajrah, N.H.; Alharbi, N.S.; Al-Malki, A.L.; Bailey, C.D.; Jansen, R.K. Plastid genome sequences of legumes reveal parallel inversions and multiple losses of rps16 in papilionoids. J. Syst. Evol. 2015, 53, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, T.; Hibbs, M.S.; Yoder, A.D.; Delwiche, C.F.; Donoghue, M.J. The phylogeny of Rosoideae (Rosaceae) based on sequences of the internal transcribed spacers (ITS) of nuclear ribosomal DNA and the region trnL/F of chloroplast DNA. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2003, 164, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.W.; Yang, Y.; Henry, R.J.; Rossetto, M.; Wang, Y.T.; Chen, S.L. Plant DNA barcoding: From gene to genome. Biol. Rev. 2015, 90, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierckxsens, N.; Mardulyn, P.; Smits, G. NOVOPlasty: De novo assembly of organelle genomes from whole genome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.J.; Yu, W.B.; Yang, J.B.; Song, Y.; dePamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.S.; Li, D.Z. GetOrganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; Proc, G.P.D. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillich, M.; Lehwark, P.; Pellizzer, T.; Ulbricht-Jones, E.S.; Fischer, A.; Bock, R.; Greiner, S. GeSeq—Versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W6–W11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, T.; Harris, S.R.; Berriman, M.; Parkhill, J.; McQuillan, J.A. Artemis: An integrated platform for visualization and analysis of high-throughput sequence-based experimental data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiner, S.; Lehwark, P.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3.1: Expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W59–W64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: Multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Suleski, M.; Sanderford, M.; Sharma, S.; Tamura, K. MEGA12: Molecular Evolutionary Genetic Analysis Version 12 for Adaptive and Green Computing. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2024, 41, msae263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
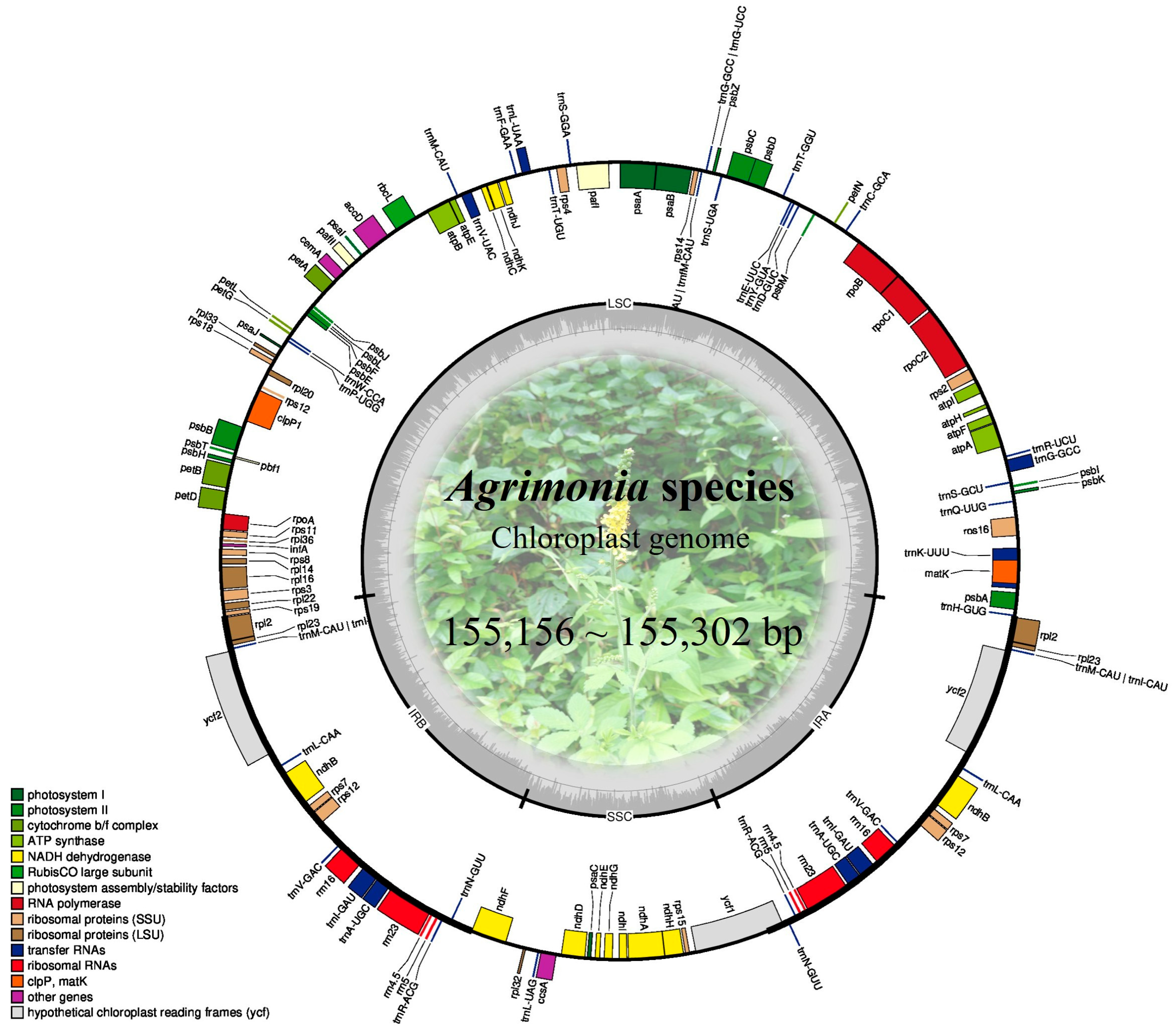

| Species Name | Length (bp) | Number of Unique Genes (PCG/tRNA/rRNA) | GC Content (%) | GenBank Accession No. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSC | SSC | IR | Entire | ||||
| A. coreana | 84,650 | 18,744 | 25,954 | 155,302 | 112 (79/29/4) | 36.88 | PX425319 |
| A. gorovoii | 84,560 | 18,741 | 25,955 | 155,211 | 36.90 | PX425320 | |
| A. nipponica | 84,514 | 18,723 | 25,962 | 155,161 | 36.90 | PX425321 | |
| A. pilosa | 84,489 | 18,737 | 25,965 | 155,156 | 36.91 | PX425322 | |
| SNPs | Total: 497 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. coreana | A. gorovoii | A. nipponica | A. pilosa | ||||||
| InDels | A. coreana | 118 | 267 | 302 | 241 | ||||
| 61 (354 bp) | |||||||||
| A. gorovoii | 113 (840 bp) | 109 | 283 | 239 | |||||
| 62 (423 bp) | |||||||||
| Total 187 (1333 bp) | A. nipponica | 117 (702 bp) | 119 (726 bp) | 148 | 278 | ||||
| 63 (219 bp) | |||||||||
| A. pilosa | 105 (581 bp) | 108 (691 bp) | 102 (483 bp) | 96 | |||||
| 47 (144 bp) | |||||||||
| Marker Name | Target Species | Target Region | Primer Sequence (5′ -> 3′) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Product Size (bp) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Locus | Position * | ||||||||
| Ac_InDel01 | A. coreana | LSC | atpB–rbcL | 54,969/54,970 | F | GAACCCGATTCCATTGTTTACTT | 56 | T | 155 |
| R | GAAGGTGTTGTCTATAATGATAGGC | O | 172 | ||||||
| Ac_InDel02 | A. coreana | LSC | trnP(UGG) –psaJ | 66,773–66,800 | F | CGCTACATCCCTTTCAATTTG | 58 | T | 130 |
| R | AGATATTTTATTTTGGTATACCAATGGAAG | O | 102 | ||||||
| Ac_InDel03 | A. coreana | IR | trnR(ACG) –trnN(GUU) | 108,808/108,809 | F | CTATGGAATTTTGGCGTGGGT | 56 | T | 144 |
| 131,131/131,312 | R | CGGGGCGTAAAAGTAAAACAT | O | 155 | |||||
| Ag_InDel01 | A. gorovoii | LSC | psbM –trnD(GUC) | 30,206/30,207 | F | ATGATTGAACCGCCCCTACA | 56 | T | 226 |
| R | AGAATACTTCCAGGAATCGCC | O | 306–313 | ||||||
| Ag_InDel02 | A. gorovoii | IR | ycf2 | 87,607/87,608 | F | TGAATTCGGGACAGCTATTCG | 60 | T | 173 |
| 152,163/152,164 | R | AGCCCACTTGTTTCTCGAGA | O | 182 | |||||
| An_InDel01 | A. nipponica | LSC | trnS(GCU) –trnG(GCC) | 8731–8760 | F | CTGGTCAGTACTTAGCCGGG | 56 | T | 246 |
| R | TGTATTGTGCTAAGAAACGCGA | O | 215–219 | ||||||
| An_InDel02 | A. nipponica | LSC | trnV(UAC) –trnM(CAU) | 52,387/52,388 | F | ATTGGCGCGCGTGTAAAC | 56 | T | 152 |
| R | ACTTATAAGCAATACCGATCAAACAGA | O | 170 | ||||||
| An_InDel03 | A. nipponica | LSC | infA | 79,995–80,005 and 80,059–80,075 | F | GTATCCCTCCGAAAGAATGTTGAA | 56 | T | 215 |
| R | GGTTTTGCTTCGGAAAAGGTTC | O | 187 | ||||||
| Ap_SNP01 | A. pilosa | LSC | rps16 | 5051 | F | GTTTGTTGATTAAGGCGAAGTGA | 59 | T | 105 |
| R | TGCTATTCTATACTTCCTTGAAAAGG | O | - | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, W.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, W.J.; Yang, S.; Moon, B.C. PCR-Based Molecular Authentication Method for Sources of Agrimoniae Herba via Comparative Analyses of Complete Chloroplast Genomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211189
Jang W, Lee SH, Kim WJ, Yang S, Moon BC. PCR-Based Molecular Authentication Method for Sources of Agrimoniae Herba via Comparative Analyses of Complete Chloroplast Genomes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):11189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211189
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Woojong, Sae Hyun Lee, Wook Jin Kim, Sungyu Yang, and Byeong Cheol Moon. 2025. "PCR-Based Molecular Authentication Method for Sources of Agrimoniae Herba via Comparative Analyses of Complete Chloroplast Genomes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 11189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211189
APA StyleJang, W., Lee, S. H., Kim, W. J., Yang, S., & Moon, B. C. (2025). PCR-Based Molecular Authentication Method for Sources of Agrimoniae Herba via Comparative Analyses of Complete Chloroplast Genomes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 11189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211189






