The Mutation of piezo1 Weakens the Intermuscular Bones in Zebrafish and Crucian Carp
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
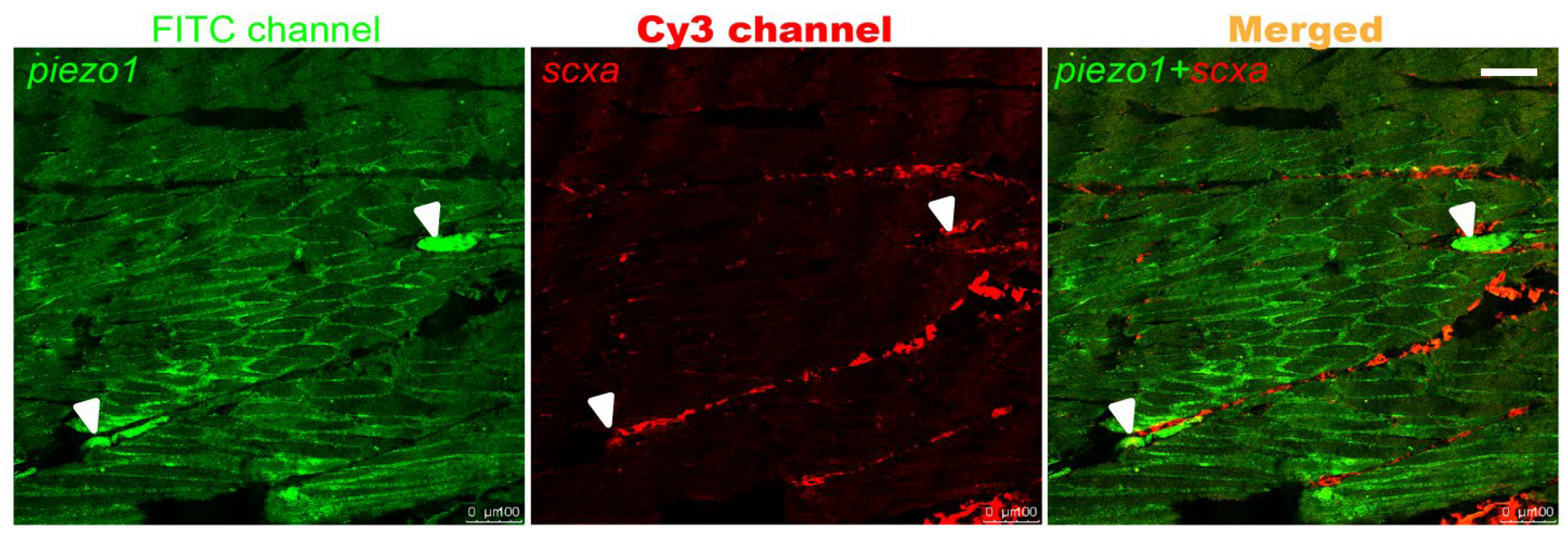
2.1. piezo1 Is Expressed in Zebrafish Tendons
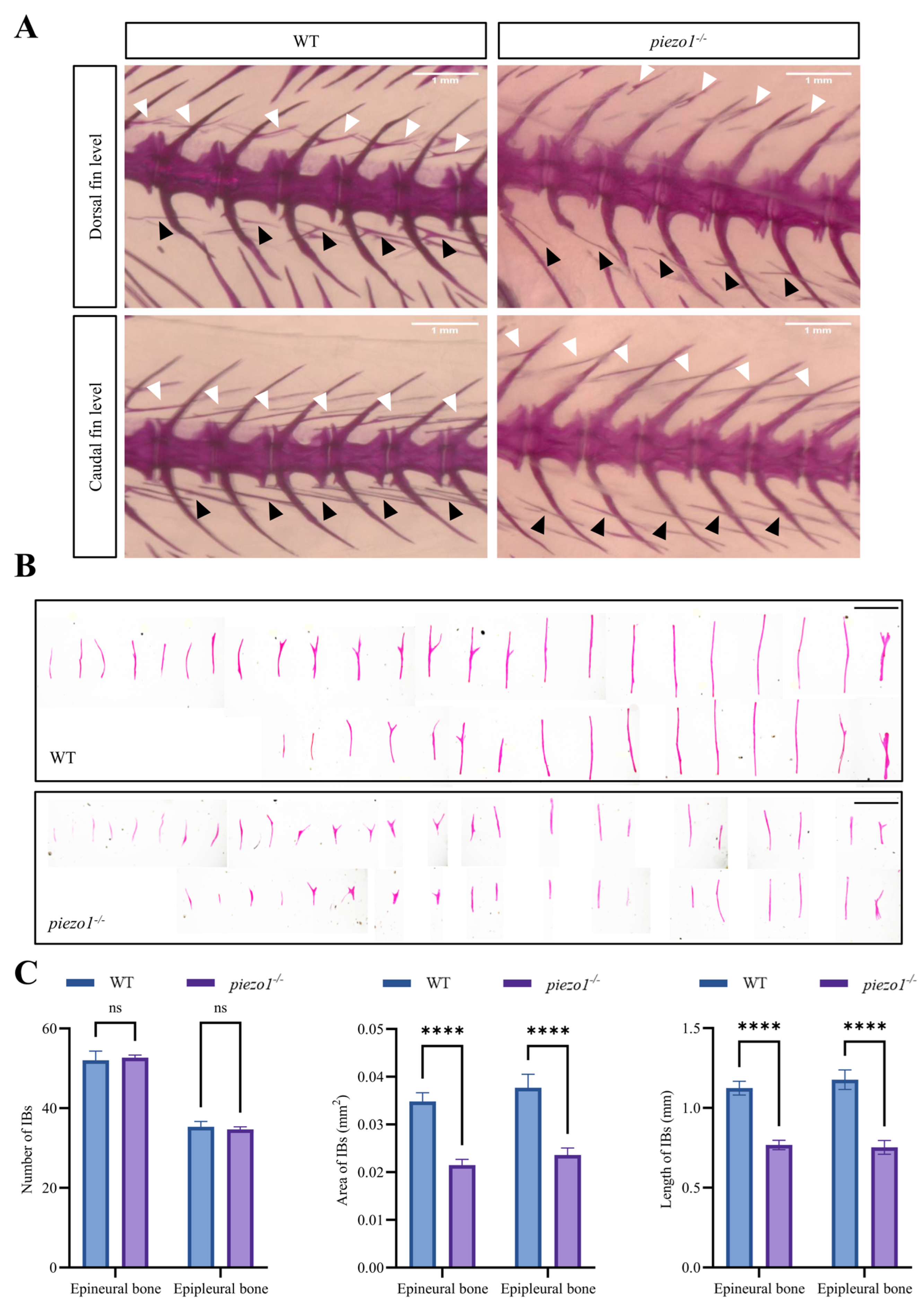
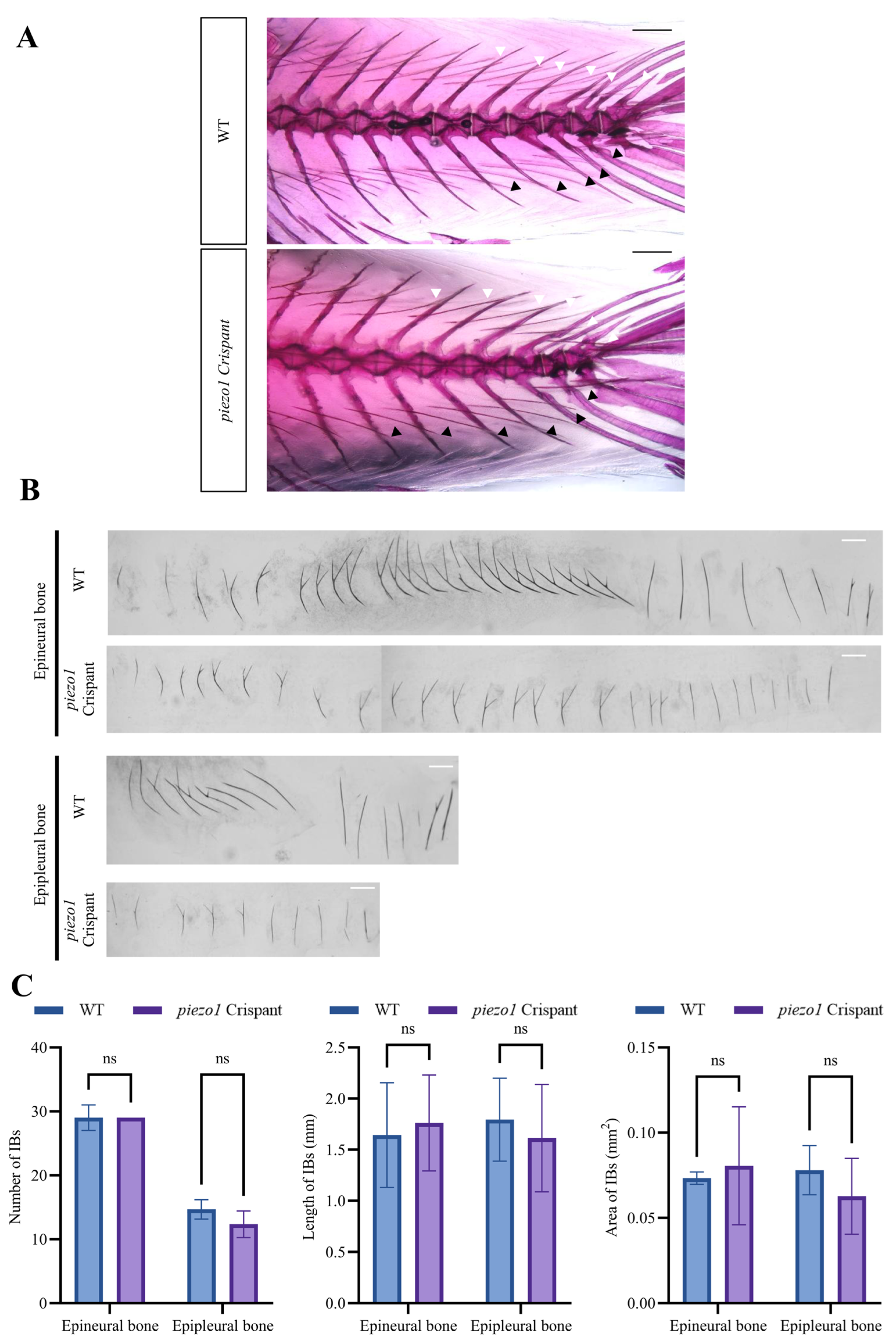
2.2. piezo1 Mutation Significantly Decreases the Area and Length of IBs in Zebrafish
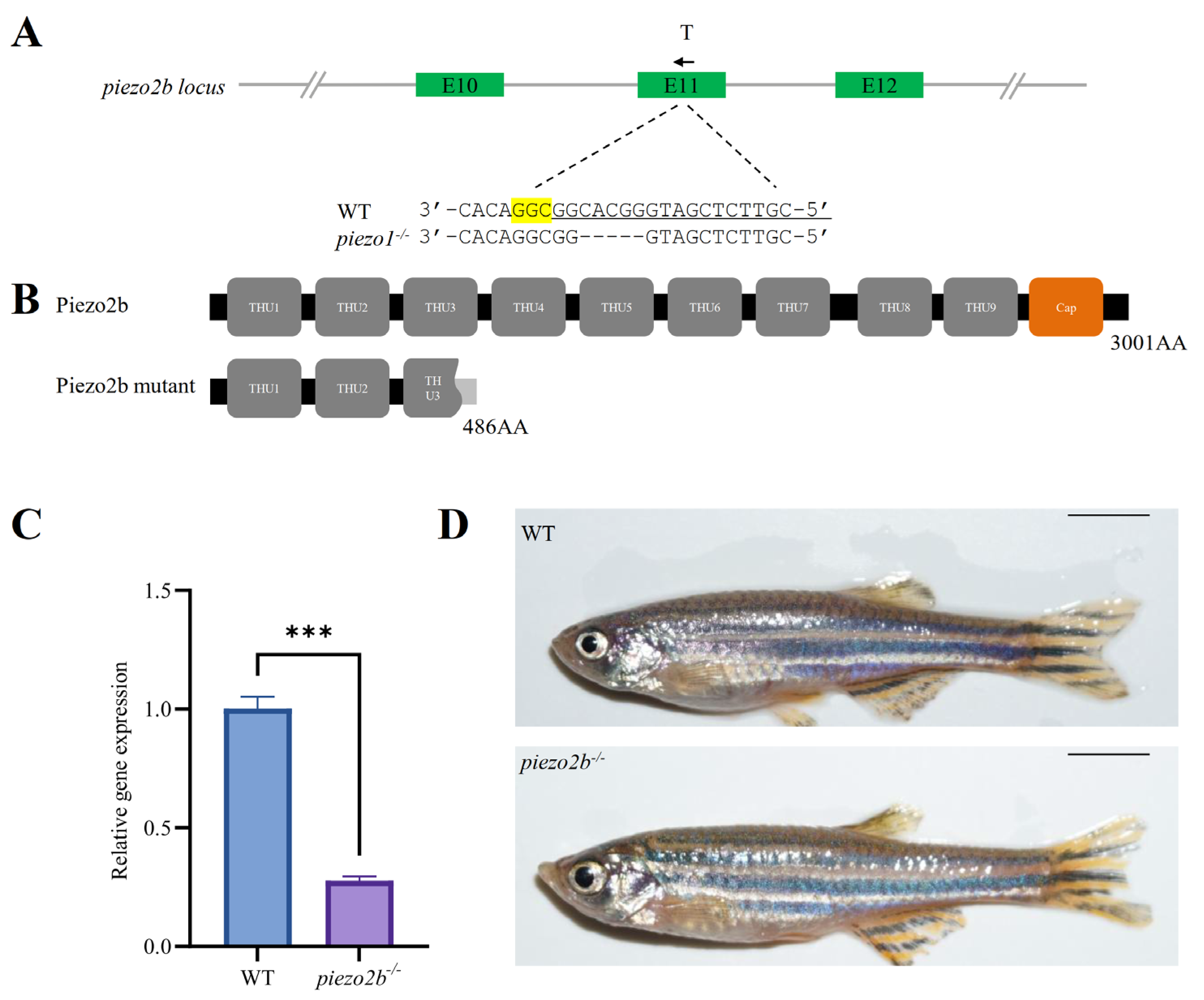
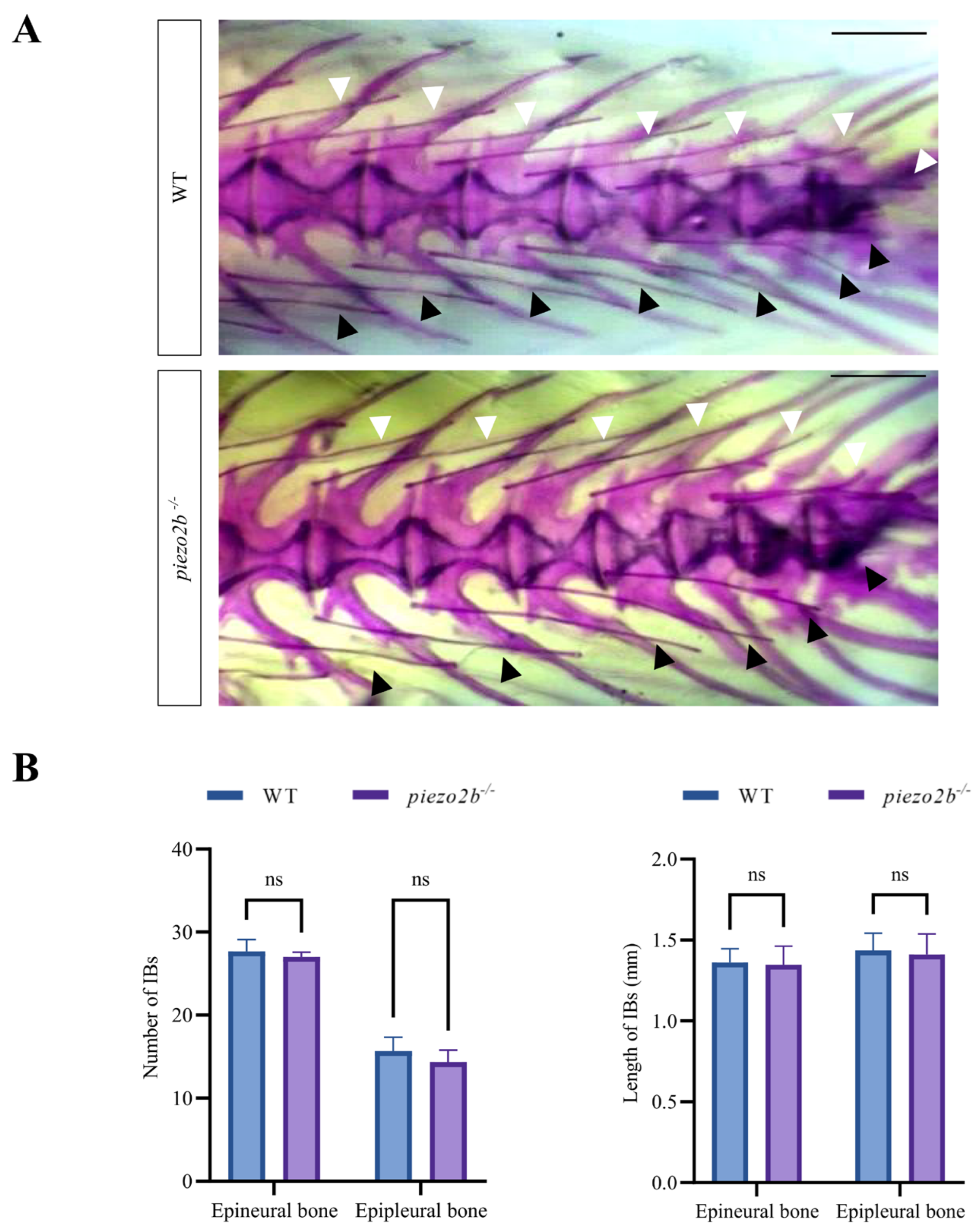
2.3. piezo2b Mutation Does Not Affect IB Development in Zebrafish
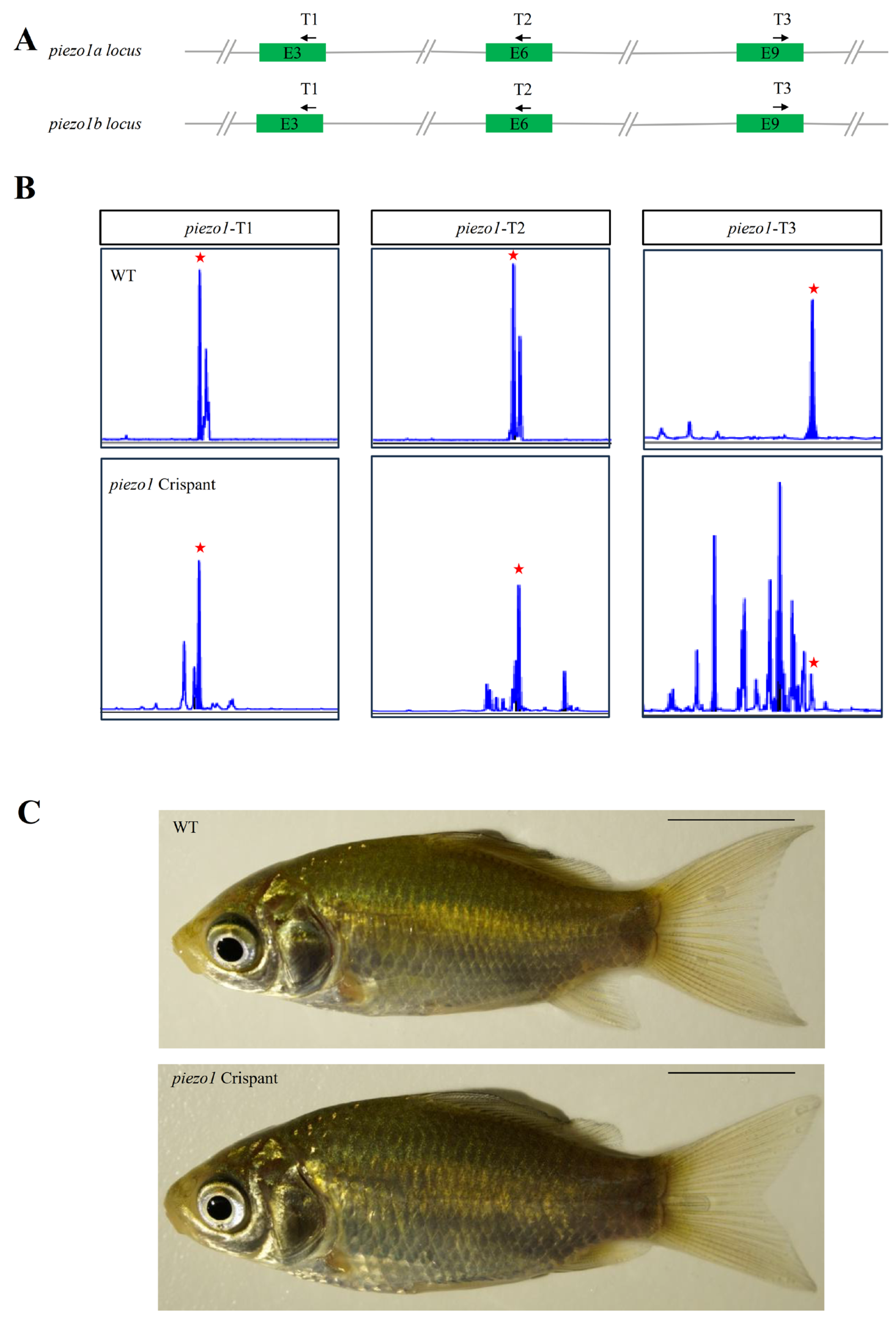
2.4. piezo1 Homologs Knockout Using Crispant in Crucian Carp
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
4.2. FISH
4.3. sgRNA Preparation
4.4. Microinjection and Genotyping
4.5. Establishment of Mutant Fish Lines
4.6. Alizarin Red S Staining
4.7. qRT-PCR
4.8. Data Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arratia, G. Complexities of Early Teleostei and the Evolution of Particular Morphological Structures through Time. Copeia 2015, 103, 999–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B. The Development and Evolution of Intermuscular Bones in Teleosts. JSOU 2025, 34, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, C.; Johnson, G.D. The Intermuscular Bones and Ligaments of Teleostean Fishes. In Smithsonian Contributions to Zoology; Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; pp. 1–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemballa, S.; Ebmeyer, L.; Hagen, K.; Hannich, T.; Hoja, K.; Rolf, M.; Treiber, K.; Vogel, F.; Weitbrecht, G. Evolutionary Transformations of Myoseptal Tendons in Gnathostomes. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Liu, X.; Ma, L.; Yang, J.-X. Molecular Mechanisms of Intermuscular Bone Development in Fish: A Review. Zool. Res. 2021, 42, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.-C.; Kuang, Y.-Y.; Zheng, X.-H.; Tong, G.-X.; Li, C.-T.; Sun, X.-W. Comparative Analysis of Intermuscular Bones in Three Strains of Common Carp. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2015, 31, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.-M.; Xiong, X.-M.; Tomljanović, T.; Chen, Y.-L.; Liu, H.; Treer, T.; Gao, Z.-X. Identification and Mapping of SNPs Associated with Number of Intermuscular Bone in Blunt Snout Bream. Aquaculture 2019, 507, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Tong, G.; Yan, T.; Dong, L.; Yang, X.; Dou, D.; Sun, Z.; Liu, T.; Zheng, X.; Yang, J.; et al. Transcriptomic Analysis Provides Insights to Reveal the Bmp6 Function Related to the Development of Intermuscular Bones in Zebrafish. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 821471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, R.-H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.-W.; Li, X.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.-J.; Tong, J.-F.; Wu, Y.; Xia, L.-Y.; Gao, Z.-X.; et al. Creation of Intermuscular Bone-Free Mutants in Amphitriploid Gibel Carp by Editing Two Duplicated Runx2b Homeologs. Aquaculture 2023, 567, 739300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kague, E.; Hughes, S.M.; Lawrence, E.A.; Cross, S.; Martin-Silverstone, E.; Hammond, C.L.; Hinits, Y. Scleraxis Genes Are Required for Normal Musculoskeletal Development and for Rib Growth and Mineralization in Zebrafish. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 9116–9130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Cao, D.; Sun, Z.; Tong, G.; Xu, H.; Yan, T.; Tang, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, T.; et al. Generate a New Crucian Carp (Carassius Auratus) Strain without Intermuscular Bones by Knocking out Bmp6. Aquaculture 2023, 569, 739407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.; Wan, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, D.; Wang, X.; Dong, X.; Gao, Z.-X. Loss of Scleraxis Leads to Distinct Reduction of Mineralized Intermuscular Bone in Zebrafish. Aquac. Fish. 2021, 6, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.-H.; Wan, S.-M.; Chen, Y.-L.; Huysseune, A.; Wu, Y.-M.; Zhou, J.-J.; Hilsdorf, A.W.S.; Wang, W.; Witten, P.E.; Lin, Q.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomes and Runx2b−/− Mutants Reveal the Genetic Signatures of Intermuscular Bone Formation in Zebrafish. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwac152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Li, X.; Feng, C.; Zhang, Z.; Sha, H.; Luo, X.; Zou, G.; Liang, H. Targeting and Editing the Second Exon of Bmp6 Gene Results in a Silver Carp with Reduced Intramuscular Bones. Aquac. Rep. 2025, 40, 102586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; He, C.; Jiang, W.; Liu, S.; Li, F.; Chi, M.; Cheng, S.; Liu, Y. Screening for IBs-Relative Genes by Transcriptome Analysis and Generation IBs-Less Mutants in Culter Alburnus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2023, 47, 101106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danos, N.; Ward, A.B. The Homology and Origins of Intermuscular Bones in Fishes: Phylogenetic or Biomechanical Determinants? Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2012, 106, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A. Phenotypic Plasticity and Heterochrony in Cichlasoma managuense (Pisces, Cichlidae) and Their Implications for Speciation in Cichlid Fishes. Evol. Int. J. Org. Evol. 1987, 41, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.H.; Rabie, A.B.M.; Hägg, U. Indian Hedgehog: A Mechanotransduction Mediator in Condylar Cartilage. J. Dent. Res. 2004, 83, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Lv, Y.; Gong, X.; Wu, J.; Bao, B. Different Ossification Patterns of Intermuscular Bones in Fish with Different Swimming Modes. Biol. Open 2015, 4, 1727–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coste, B.; Mathur, J.; Schmidt, M.; Earley, T.J.; Ranade, S.; Petrus, M.J.; Dubin, A.E.; Patapoutian, A. Piezo1 and Piezo2 Are Essential Components of Distinct Mechanically Activated Cation Channels. Science 2010, 330, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Hou, B.; Tumova, S.; Muraki, K.; Bruns, A.; Ludlow, M.J.; Sedo, A.; Hyman, A.J.; McKeown, L.; Young, R.S.; et al. Piezo1 Integration of Vascular Architecture with Physiological Force. Nature 2014, 515, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, A.; Miyazaki, A.; Kawarabayashi, K.; Shono, M.; Akazawa, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Ueda-Yamaguchi, K.; Kitamura, T.; Yoshizaki, K.; Fukumoto, S.; et al. Piezo Type Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Component 1 Functions as a Regulator of the Cell Fate Determination of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Chi, S.; Li, Y.; Ling, S.; Tan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, F.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Zhong, G.; et al. The Mechanosensitive Piezo1 Channel Is Required for Bone Formation. Elife 2019, 8, e47454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; You, X.; Lotinun, S.; Zhang, L.; Wu, N.; Zou, W. Mechanical Sensing Protein PIEZO1 Regulates Bone Homeostasis via Osteoblast-Osteoclast Crosstalk. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Gao, B.; Fan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Feng, S.; Cong, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yadav, P.S.; Lin, J.; et al. Piezo1/2 Mediate Mechanotransduction Essential for Bone Formation through Concerted Activation of NFAT-YAP1-ß-Catenin. Elife 2020, 9, e52779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli; Aramaki, T.; Watanabe, M.; Kondo, S. Piezo1 Mutant Zebrafish as a Model of Idiopathic Scoliosis. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1321379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Mateos, M.A.; Vejnar, C.E.; Beaudoin, J.-D.; Fernandez, J.P.; Mis, E.K.; Khokha, M.K.; Giraldez, A.J. CRISPRscan: Designing Highly Efficient sgRNAs for CRISPR-Cas9 Targeting in Vivo. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, G.K.; Carrington, B.; Pei, W.; Bishop, K.; Chen, Z.; Fan, C.; Xu, L.; Jones, M.; LaFave, M.C.; Ledin, J.; et al. A High-Throughput Functional Genomics Workflow Based on CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Targeted Mutagenesis in Zebrafish. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 2357–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroll, F.; Powell, G.T.; Ghosh, M.; Gestri, G.; Antinucci, P.; Hearn, T.J.; Tunbak, H.; Lim, S.; Dennis, H.W.; Fernandez, J.M.; et al. A Simple and Effective F0 Knockout Method for Rapid Screening of Behaviour and Other Complex Phenotypes. Elife 2021, 10, e59683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ouyang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zheng, H.; Wang, J.; Fan, C. Essential role of RANK-NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Spinal Deformities: Insights from Largemouth Bass and Zebrafish Models. Aquaculture 2025, 606, 742570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Che, J.; Li, Z.; Bao, B.; Fan, C. The Mutation of piezo1 Weakens the Intermuscular Bones in Zebrafish and Crucian Carp. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210851
Zhang X, Che J, Li Z, Bao B, Fan C. The Mutation of piezo1 Weakens the Intermuscular Bones in Zebrafish and Crucian Carp. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):10851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210851
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xinyu, Jinyuan Che, Zhuang Li, Baolong Bao, and Chunxin Fan. 2025. "The Mutation of piezo1 Weakens the Intermuscular Bones in Zebrafish and Crucian Carp" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 10851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210851
APA StyleZhang, X., Che, J., Li, Z., Bao, B., & Fan, C. (2025). The Mutation of piezo1 Weakens the Intermuscular Bones in Zebrafish and Crucian Carp. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 10851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210851




