miRNA-Mediated Regulation of Meloidogyne arenaria Responses in Wild Arachis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
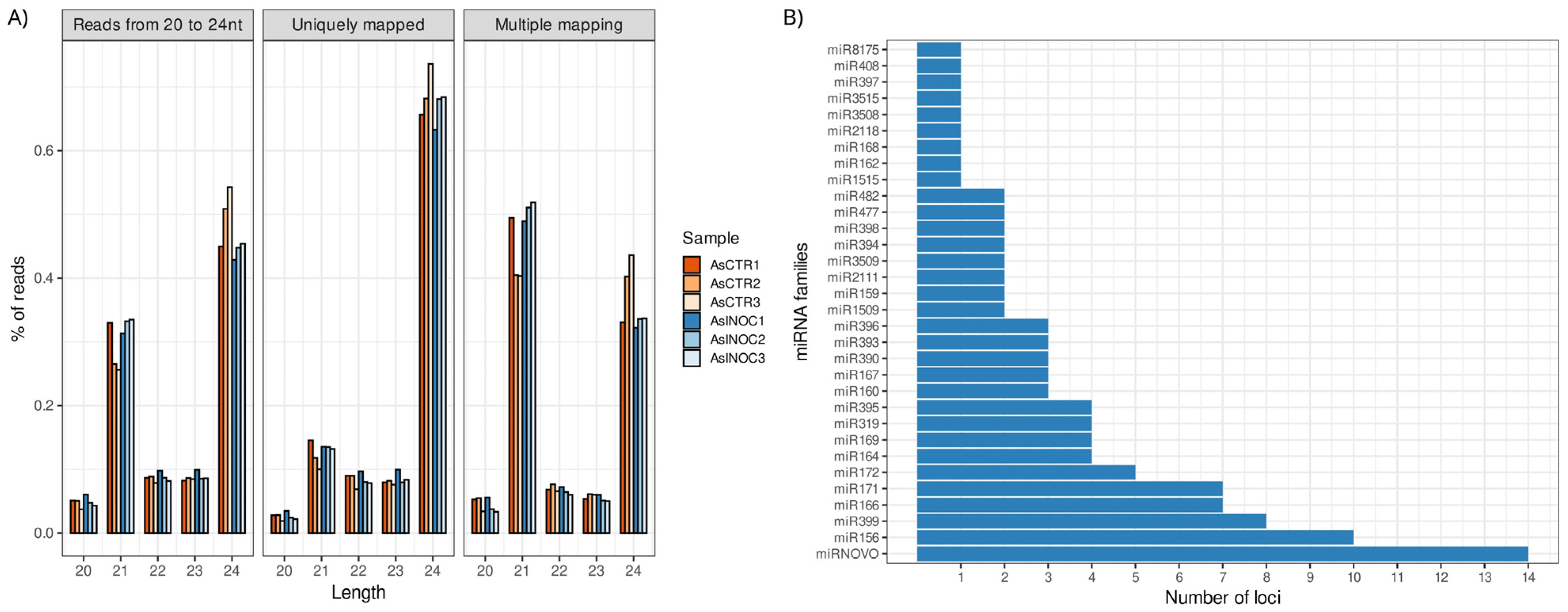
2.1. miRNA Sequencing and Analysis
2.2. A. stenosperma miRNAs Expression During M. arenaria Infection
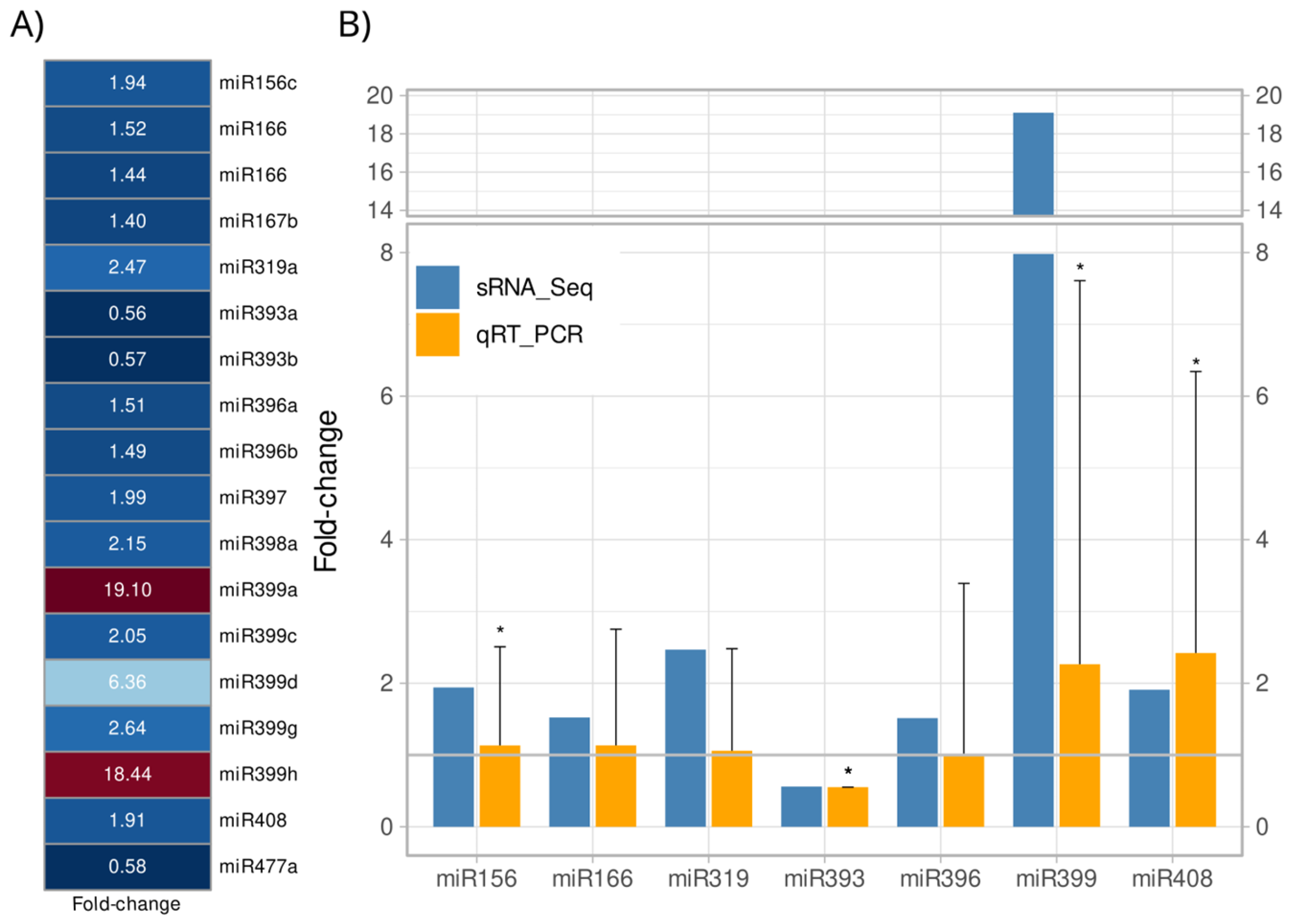
2.3. A. stenosperma Differentially Expressed miRNAs (DEMs) in Response to M. arenaria Infection
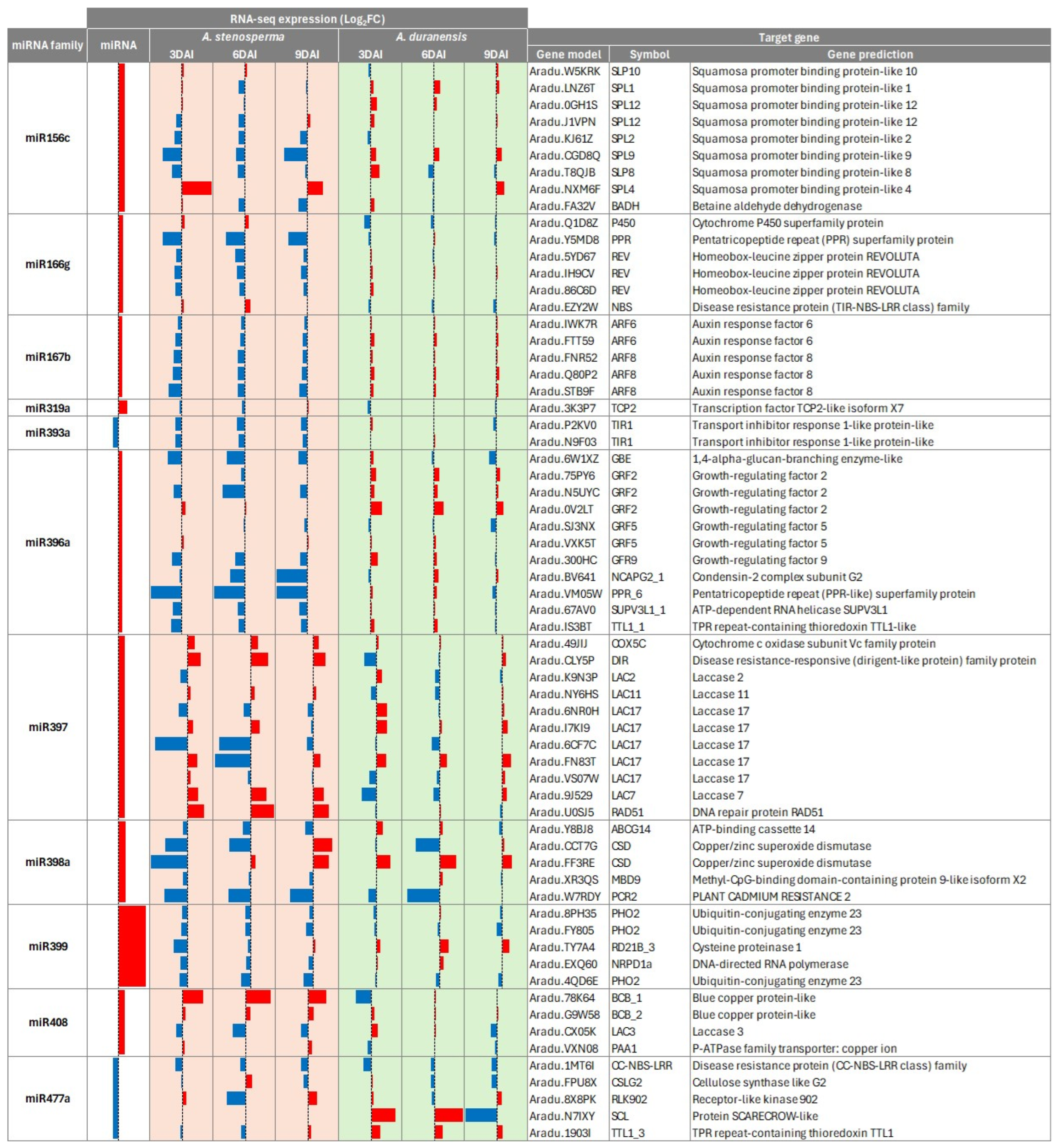
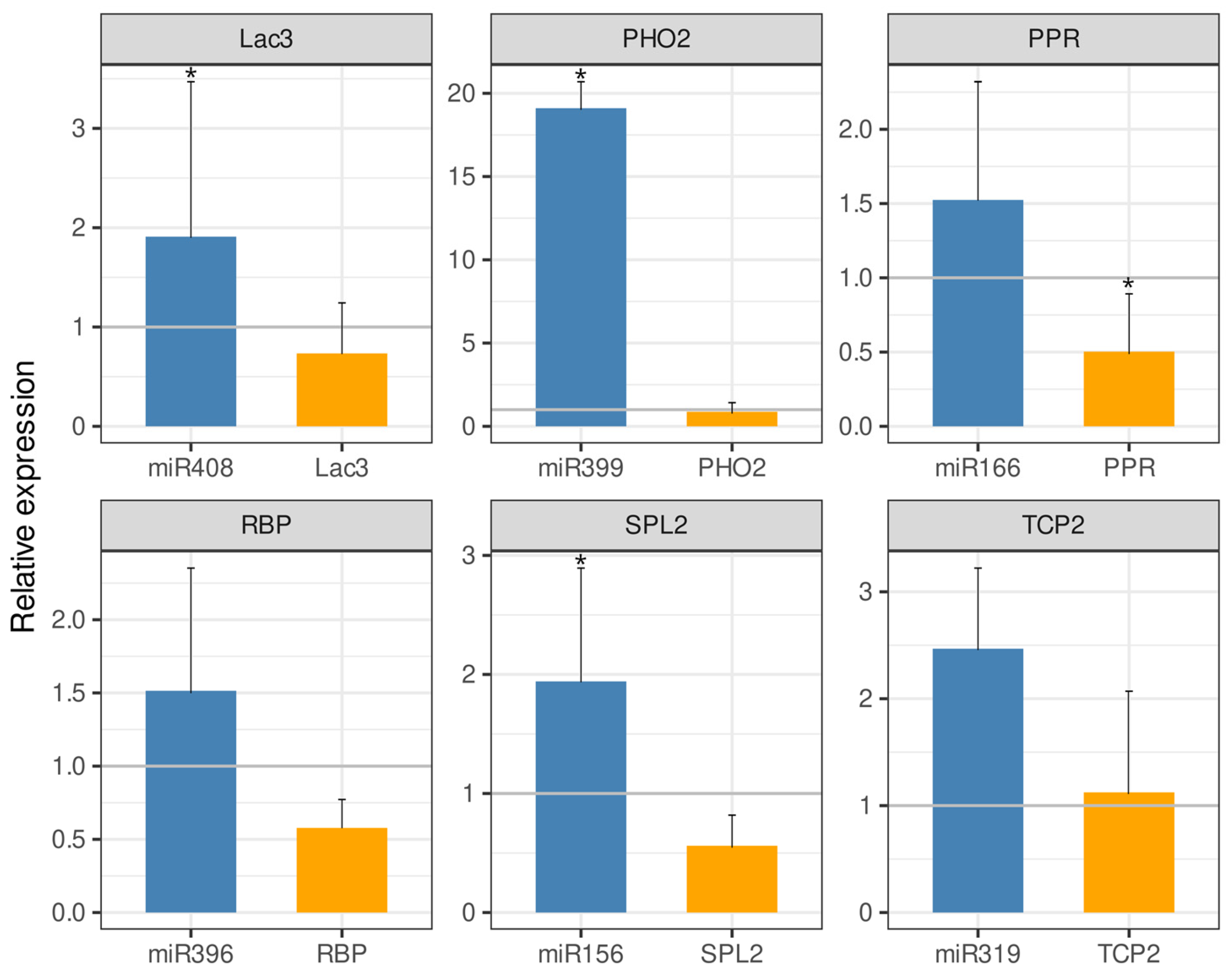
2.4. Correlation of Expression Profiles Between miRNAs and Their Target Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Nematode Bioassays
4.2. miRNA Extraction and Sequencing
4.3. miRNA Identification and Target Prediction
4.4. Differentially Expressed miRNAs (DEMs)
4.5. Expression Analysis by qRT-PCR
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| miRNAs | MicroRNAs |
| DEMs | Differentially Expressed MicroRNAs |
| NLR | Nucleotide-binding site Leucine-Rich |
| RKN | Root-Knot Nematode |
| mRNA | Messenger RNA |
| PR | Pathogenesis-related genes |
| R | Resistance genes |
| AsCTR | Control samples (not inoculated) of Arachis stenosperma |
| AsINOC | Inoculated samples of Arachis stenosperma |
| Mare | Sample of Meloidogyne arenaria |
| Mb | Million base pairs |
| nt | Nucleotides |
| miRNOVO | New miRNA candidates |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| RNA-Seq | RNA sequencing |
| DAI | Days After Inoculation |
| MLP | Major Latex Protein |
| MLO | Mildew Locus O |
| TF | Transcription Factor |
| SPL | Squamosa Promoter-Binding Protein-Like |
| HD-ZIP | Homeodomain-leucine Zipper |
| FC | Fold-change |
| TCP2 | Teosinte branched1/Cycloidea/Proliferating cell factor |
| PHO2 | Phosphatase2 |
| DEG | Differentially Expressed Gene |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| TIR-NBS-LRR | Toll-Interleukin Receptor /Nucleotide-Binding Site/Leucine-Rich Repeat |
| PPR | Pentatricopeptide Repeat |
| CN | Cyst Nematode |
| GRF | Growth Regulating Factor |
| Pi | Phosphate |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| PAMP | Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns |
| CCNL | Cyclin L |
| phasiRNA | Phased secondary small interfering RNAs |
| TNL | TIR-NBS-LRR |
| MYB | Myeloblastosis |
| TNX | Toll-Interleukin Receptor /Nucleotide-Binding Site without LRR domain |
| AP2 | APETALA |
| amiRNA | Artificial miRNA |
| CRISPR | Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats |
| cv | Cultivate |
References
- Islam, W.; Islam, S.U.; Qasim, M.; Wang, L. Host-Pathogen Interactions Modulated by Small RNAs. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 891–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmer, D.; Mauch-Mani, B. Small Yet Mighty—MicroRNAs in Plant-Microbe Interactions. MicroRNA 2013, 2, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, L.; Zhuang, X.; Yu, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, X.; Ji, L.; Pan, Z.; Cao, X.; Mo, B.; et al. MicroRNAs Inhibit the Translation of Target MRNAs on the Endoplasmic Reticulum in Arabidopsis. Cell 2013, 153, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, S.; Fu, Y.; Sunkar, R.; Barbazuk, W.B.; Zhu, J.K.; Yu, O. Novel and Nodulation-Regulated MicroRNAs in Soybean Roots. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chand Jha, U.; Nayyar, H.; Mantri, N.; Siddique, K.H.M. Non-Coding RNAs in Legumes: Their Emerging Roles in Regulating Biotic/Abiotic Stress Responses and Plant Growth and Development. Cells 2021, 10, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Fang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, X. Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Plant Immunity. Plant Commun. 2021, 2, 100180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. MicroRNA: A New Target for Improving Plant Tolerance to Abiotic Stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera-Figueroa, B.E.; Gao, L.; Diop, N.N.; Wu, Z.; Ehlers, J.D.; Roberts, P.A.; Close, T.J.; Zhu, J.K.; Liu, R. Identification and Comparative Analysis of Drought-Associated MicroRNAs in Two Cowpea Genotypes. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, B.; Shi, Y.; Ntambiyukuri, A.; Li, X.; Zhan, J.; Wang, A.; Xiao, D.; He, L. Integration of Small RNA and Degradome Sequencing Reveals the Regulatory Network of Al-Induced Programmed Cell Death in Peanut. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anco, D.J.; Thomas, J.S.; Jordan, D.L.; Shew, B.B.; Monfort, W.S.; Mehl, H.L.; Small, I.M.; Wright, D.L.; Tillman, B.L.; Dufault, N.S.; et al. Peanut Yield Loss in the Presence of Defoliation Caused by Late or Early Leaf Spot. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 1390–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, A.K.; Ozias-Akins, P.; Holbrook, C.C. Recent Technological Advancements for Identifying and Exploiting Novel Sources of Pest and Disease Resistance for Peanut Improvement. Agronomy 2024, 14, 3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimaraes, P.M.; Guimaraes, L.A.; Morgante, C.V.; Silva, O.B.; Araujo, A.C.G.; Martins, A.C.Q.; Saraiva, M.A.P.; Oliveira, T.N.; Togawa, R.C.; Leal-Bertioli, S.C.M.; et al. Root Transcriptome Analysis of Wild Peanut Reveals Candidate Genes for Nematode Resistance. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, A.P.Z.; Vidigal, B.; Danchin, E.G.J.; Togawa, R.C.; Leal-Bertioli, S.C.M.; Bertioli, D.J.; Araujo, A.C.G.; Brasileiro, A.C.M.; Guimaraes, P.M. Comparative Root Transcriptome of Wild Arachis Reveals NBS-LRR Genes Related to Nematode Resistance. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Kirti, P.B. The Genus Arachis: An Excellent Resource for Studies on Differential Gene Expression for Stress Tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1275854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasileiro, A.C.M.; Lacorte, C.; Pereira, B.M.; Oliveira, T.N.; Ferreira, D.S.; Mota, A.P.Z.; Saraiva, M.A.P.; Araujo, A.C.G.; Silva, L.P.; Guimaraes, P.M. Ectopic Expression of an Expansin-like B Gene from Wild Arachis Enhances Tolerance to Both Abiotic and Biotic Stresses. Plant J. 2021, 107, 1681–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Bertioli, S.C.M.; Moretzsohn, M.C.; Roberts, P.A.; Ballén-Taborda, C.; Borba, T.C.O.; Valdisser, P.A.; Vianello, R.P.; Araújo, A.C.G.; Guimarães, P.M.; Bertioli, D.J. Genetic Mapping of Resistance to Meloidogyne arenaria in Arachis stenosperma: A New Source of Nematode Resistance for Peanut. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2016, 6, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, P.M.; Brasileiro, A.C.M.; Mehta, A.; Araujo, A.C.G. Functional Genomics in Peanut Wild Relatives. In The Peanut Genome; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhang, X.J.; Sha, Q.; Chen, Z.D. Gynophore MiRNA Analysis at Different Developmental Stages in Arachis duranensis. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Yang, Q.; Chen, K.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, C.; Pan, R.; Cai, T.; Deng, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; et al. Integrated MicroRNA and Transcriptome Profiling Reveals a MiRNA-Mediated Regulatory Network of Embryo Abortion under Calcium Deficiency in Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Wang, P.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, C.; Xia, H.; Hou, L.; Ju, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, X. Small RNA Profiling and Degradome Analysis Reveal Regulation of MicroRNA in Peanut Embryogenesis and Early Pod Development. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Hu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Mu, G. Multi-Omics and MiRNA Interaction Joint Analysis Highlight New Insights into Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Peanuts (Arachis hypogaea L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 818345, Erratum in Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 929085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, K.; Li, F.; Li, K.; Ning, L.; He, J.; Xin, Z.; Yin, D. Small RNA and Degradome Deep Sequencing Reveals the Roles of MicroRNAs in Seed Expansion in Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 330144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Xia, H.; Cao, T.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Hou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Small RNA and Degradome Deep Sequencing Reveals Peanut MicroRNA Roles in Response to Pathogen Infection. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 33, 1013–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, A.; Zhao, S.; Hou, L.; Xia, H.; Fan, S.; Qiu, J.; et al. Integrated Small RNA and MRNA Expression Profiles Reveal MiRNAs and Their Target Genes in Response to Aspergillus flavus Growth in Peanut Seeds. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.; Sharma, V.; Pandey, A.K.; Nayak, S.N.; Bajaj, P.; Sudini, H.K.; Sharma, S.; Varshney, R.K.; Pandey, M.K. Identification of MiRNAs Associated with Aspergillus flavus Infection and Their Targets in Groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hou, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Yue, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X. Multiple MicroRNAs Are Involved in Regulating Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Resistance to Sclerotium rolfsii at the Early Stage. Trop. Plant Biol. 2022, 15, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, G.; Lu, X.; Dai, S.; Cui, X.; Yuan, M.; Liu, Z. Integrated Analysis of the LncRNA/CircRNA-MiRNA-MRNA Expression Profiles Reveals Novel Insights into Potential Mechanisms in Response to Root-Knot Nematodes in Peanut. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Li, Q.; Davis, K.E.; Patterson, C.; Oo, S.; et al. Response of Root Growth and Development to Nitrogen and Potassium Deficiency as Well as MicroRNA-Mediated Mechanism in Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 695234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, M.; Dhingra, A.; Dawar, P.; Payton, P.; Rock, C.D. The Role of MicroRNAs in Responses to Drought and Heat Stress in Peanut (Arachis hypogaea). Plant Genome 2023, 16, e20350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ren, C.; Xue, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, N.; Sheng, C.; Jiang, H.; Bai, D. Small RNA and Degradome Deep Sequencing Reveals the Roles of MicroRNAs in Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Cold Response. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 920195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, V.; Agarwal, G.; Pazhamala, L.T.; Nayak, S.N.; Kudapa, H.; Khan, A.W.; Doddamani, D.; Sharma, M.; Kavi Kishor, P.B.; Varshney, R.K. Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization, and Expression Analysis of Small RNA Biogenesis Purveyors Reveal Their Role in Regulation of Biotic Stress Responses in Three Legume Crops. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 238864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertioli, D.J.; Cannon, S.B.; Froenicke, L.; Huang, G.; Farmer, A.D.; Cannon, E.K.S.; Liu, X.; Gao, D.; Clevenger, J.; Dash, S.; et al. The Genome Sequences of Arachis duranensis and Arachis ipaensis, the Diploid Ancestors of Cultivated Peanut. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, X.; Yang, Q.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Pan, L.; Chen, M.; Yang, Z.; He, Y.; Liang, X.; Yu, S. Identification and Characterization of MicroRNAs from Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) by High-Throughput Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. MiRBase: From MicroRNA Sequences to Function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axtell, M.J.; Meyers, B.C. Revisiting Criteria for Plant MicroRNA Annotation in the Era of Big Data. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varkonyi-Gasic, E.; Wu, R.; Wood, M.; Walton, E.F.; Hellens, R.P. Protocol: A Highly Sensitive RT-PCR Method for Detection and Quantification of MicroRNAs. Plant Methods 2007, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Yang, N.; Tian, C.; Wen, S.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, A.; Hu, X.; Fang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lai, Z.; et al. The MiR166 Targets CsHDZ3 Genes to Negatively Regulate Drought Tolerance in Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 264, 130735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, R.; Pant, B.D.; Stitt, M.; Scheible, W.R. PHO2, MicroRNA399, and PHR1 Define a Phosphate-Signaling Pathway in Plants. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Huang, D.; Guo, Z.; Kuang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xie, X.; Ma, Z.; Gao, S.; Lerdau, M.T.; Chu, C.; et al. Overexpression of MicroRNA408 Enhances Photosynthesis, Growth, and Seed Yield in Diverse Plants. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2018, 60, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, A.P.Z.; Brasileiro, A.C.M.; Vidigal, B.; Oliveira, T.N.; da Cunha Quintana Martins, A.; Saraiva, M.A.D.P.; de Araújo, A.C.G.; Togawa, R.C.; Grossi-de-Sá, M.F.; Guimaraes, P.M. Defining the Combined Stress Response in Wild Arachis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samynathan, R.; Venkidasamy, B.; Shanmugam, A.; Ramalingam, S.; Thiruvengadam, M. Functional Role of MicroRNA in the Regulation of Biotic and Abiotic Stress in Agronomic Plants. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1272446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Hu, T.; Zhao, J.; Park, M.Y.; Earley, K.W.; Wu, G.; Yang, L.; Poethig, R.S. Developmental Functions of MiR156-Regulated SQUAMOSA PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE (SPL) Genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, S.; Hao, L.; Wang, S.; Li, T. Md-MiR156ab and Md-Mir395 Target WRKY Transcription Factors to Influence Apple Resistance to Leaf Spot Disease. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 256407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Zou, Y.; Hu, J.; Ding, Y. Genome-Wide Analysis of the Rice PPR Gene Family and Their Expression Profiles under Different Stress Treatments. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bresso, E.G.; Chorostecki, U.; Rodriguez, R.E.; Palatnik, J.F.; Schommer, C. Spatial Control of Gene Expression by MiR319-Regulated TCP Transcription Factors in Leaf Development. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 1694–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaraj, A.; Elango, T.; Li, X.; Guo, G. Utilization of MicroRNAs and Their Regulatory Functions for Improving Biotic Stress Tolerance in Tea Plant [Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze]. RNA Biol. 2020, 17, 1365–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaucheret, H.; Mallory, A.C.; Bartel, D.P. AGO1 Homeostasis Entails Coexpression of MIR168 and AGO1 and Preferential Stabilization of MiR168 by AGO1. Mol. Cell 2006, 22, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, K.; Lin, S.I.; Wu, C.C.; Huang, Y.T.; Su, C.L.; Chiou, T.J. Pho2, a Phosphate Overaccumulator, Is Caused by a Nonsense Mutation in a MicroRNA399 Target Gene. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Hao, L.; Wang, S.; Xu, C.; Jiang, F.; Li, T. Characterization of Genome-Wide MicroRNAs and Their Roles in Development and Biotic Stress in Pear. Planta 2019, 249, 693–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Ghany, S.E.; Pilon, M. MicroRNA-Mediated Systemic down-Regulation of Copper Protein Expression in Response to Low Copper Availability in Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 15932–15945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.C.Q.; Mota, A.P.Z.; Carvalho, P.A.S.V.; Passos, M.A.S.; Gimenes, M.A.; Guimaraes, P.M.; Brasileiro, A.C.M. Transcriptome Responses of Wild Arachis to UV-C Exposure Reveal Genes Involved in General Plant Defense and Priming. Plants 2022, 11, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, C.; Da Rocha, M.; Magliano, M.; Ratpopoulo, A.; Revel, B.; Marteu, N.; Magnone, V.; Lebrigand, K.; Cabrera, J.; Barcala, M.; et al. Characterization of MicroRNAs from Arabidopsis Galls Highlights a Role for MiR159 in the Plant Response to the Root-Knot Nematode Meloidogyne incognita. New Phytol. 2017, 216, 882–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewezi, T.; Maier, T.R.; Nettleton, D.; Baum, T.J. The Arabidopsis MicroRNA396-GRF1/GRF3 Regulatory Module Acts as a Developmental Regulator in the Reprogramming of Root Cells during Cyst Nematode Infection. Plant Physiol. 2012, 159, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ferrer, V.; Cabrera, J.; Martinez-Argudo, I.; Artaza, H.; Fenoll, C.; Escobar, C. Silenced Retrotransposons Are Major RasiRNAs Targets in Arabidopsis Galls Induced by Meloidogyne javanica. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 2431–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, J.; Barcala, M.; García, A.; Rio-Machín, A.; Medina, C.; Jaubert-Possamai, S.; Favery, B.; Maizel, A.; Ruiz-Ferrer, V.; Fenoll, C.; et al. Differentially Expressed Small RNAs in Arabidopsis Galls Formed by Meloidogyne javanica: A Functional Role for MiR390 and Its TAS3-Derived TasiRNAs. New Phytol. 2016, 209, 1625–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewezi, T.; Howe, P.; Maier, T.R.; Baum, T.J. Arabidopsis Small RNAs and Their Targets during Cyst Nematode Parasitism. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2008, 21, 1622–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guleria, P.; Mahajan, M.; Bhardwaj, J.; Yadav, S.K. Plant Small RNAs: Biogenesis, Mode of Action and Their Roles in Abiotic Stresses. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2012, 9, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, P.; Shukla, N.; Joshi, G.; VijayaKumar, C.; Jagannath, A.; Agarwal, M.; Goel, S.; Kumar, A. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of MiRNAome from Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) Roots and Root-Knot Nematode (Meloidogyne incognita) during Susceptible Interaction. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.B.; Liu, Y.Q.; Chen, D.Y.; Chen, F.Y.; Fang, X.; Hong, G.J.; Wang, L.J.; Wang, J.W.; Chen, X.Y. Jasmonate Response Decay and Defense Metabolite Accumulation Contributes to Age-Regulated Dynamics of Plant Insect Resistance. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyndt, T.; Goverse, A.; Haegeman, A.; Warmerdam, S.; Wanjau, C.; Jahani, M.; Engler, G.; De Almeida Engler, J.; Gheysen, G. Redirection of Auxin Flow in Arabidopsis thaliana Roots after Infection by Root-Knot Nematodes. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 4559–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Kanno, Y.; Abril-Urias, P.; Seo, M.; Escobar, C.; Tsai, A.Y.L.; Sawa, S. Local Auxin Synthesis Mediated by YUCCA4 Induced during Root-Knot Nematode Infection Positively Regulates Gall Growth and Nematode Development. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1019427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureddine, Y.; Da Rocha, M.; An, J.; Médina, C.; Mejias, J.; Mulet, K.; Quentin, M.; Abad, P.; Zouine, M.; Favery, B.; et al. AUXIN RESPONSIVE FACTOR8 Regulates Development of the Feeding Site Induced by Root-Knot Nematodes in Tomato. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 74, 5752–5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepinski, S.; Leyser, O. The Arabidopsis F-Box Protein TIR1 Is an Auxin Receptor. Nature 2005, 435, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noon, J.B.; Hewezi, T.; Baum, T.J. Homeostasis in the Soybean MiRNA396–GRF Network Is Essential for Productive Soybean Cyst Nematode Infections. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, D.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, C.; Roberts, P.A. Expression Analysis of MicroRNAs and Their Target Genes in Cucumis metuliferus Infected by the Root-Knot Nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 111, 101491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Qi, Y.; Cao, S.; Duan, Y.; Huynh, B.L. Identification and Characterization of MicroRNA396 and Its Targets in Cucumis metuliferus Infected with Meloidogyne incognita. South Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 165, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Ahn, H.J.; Chiou, T.J.; Ahn, J.H. The Role of the MiR399-PHO2 Module in the Regulation of Flowering Time in Response to Different Ambient Temperatures in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Cells 2011, 32, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Wang, S.; Todd, T.C.; Johnson, C.D.; Tang, G.; Trick, H.N. Genome-Wide Identification of Soybean MicroRNA Responsive to Soybean Cyst Nematodes Infection by Deep Sequencing. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Val-Torregrosa, B.; Bundó, M.; San Segundo, B. Crosstalk between Nutrient Signalling Pathways and Immune Responses in Rice. Agriculture 2021, 11, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Val-Torregrosa, B.; Bundó, M.; Martín-Cardoso, H.; Bach-Pages, M.; Chiou, T.J.; Flors, V.; Segundo, B.S. Phosphate-Induced Resistance to Pathogen Infection in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2022, 110, 452–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureddine, Y.; Mejias, J.; da Rocha, M.; Thomine, S.; Quentin, M.; Abad, P.; Favery, B.; Jaubert-Possamai, S. Copper MicroRNAs Modulate the Formation of Giant Feeding Cells Induced by the Root Knot Nematode Meloidogyne incognita in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 2022, 236, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, T.; Qiu, L.; Fan, Y.; Wang, L. Novel MiRNA and PhasiRNA Biogenesis Networks in Soybean Roots from Two Sister Lines That Are Resistant and Susceptible to SCN Race 4. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.W.; Lin, J.S.; Li, Y.C.; Jhu, M.Y.; King, Y.C.; Jeng, S.T. MicroR408 Regulates Defense Response upon Wounding in Sweet Potato. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahbaz, M.; Pilon, M. Conserved Cu-MicroRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana Function in Copper Economy under Deficiency. Plants 2019, 8, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klink, V.P.; Overall, C.C.; Alkharouf, N.W.; MacDonald, M.H.; Matthews, B.F. A Time-Course Comparative Microarray Analysis of an Incompatible and Compatible Response by Glycine max (Soybean) to Heterodera glycines (Soybean Cyst Nematode) Infection. Planta 2007, 226, 1423–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, L.I.; Chinnusamy, V.; Sunkar, R. The Role of MicroRNAs and Other Endogenous Small RNAs in Plant Stress Responses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1779, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian, B.A.; Sathishraj, R.; Djanaguiraman, M.; Prasad, P.V.V.; Jugulam, M. Role of Cytochrome P450 Enzymes in Plant Stress Response. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsigmond, L.; Rigó, G.; Szarka, A.; Székely, G.; Ötvös, K.; Darula, Z.; Medzihradszky, K.F.; Koncz, C.; Koncz, Z.; Szabados, L. Arabidopsis PPR40 Connects Abiotic Stress Responses to Mitochondrial Electron Transport. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 1721–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laluk, K.; Abuqamar, S.; Mengiste, T. The Arabidopsis Mitochondria-Localized Pentatricopeptide Repeat Protein PGN Functions in Defense against Necrotrophic Fungi and Abiotic Stress Tolerance. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 2053–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, A.; Aqeel, M.; Lou, Y. PRRs and NB-LRRs: From Signal Perception to Activation of Plant Innate Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaprasad, P.V.; Chen, H.M.; Patel, K.; Bond, D.M.; Santos, B.A.C.M.; Baulcombe, D.C. A MicroRNA Superfamily Regulates Nucleotide Binding Site-Leucine-Rich Repeats and Other MRNAs. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 859–874, Erratum in Plant Cell 2019, 31, 1665–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Zhang, J.; Wu, L.; Qi, Y.; Zhou, J.M. Identification of MicroRNAs Involved in Pathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern-Triggered Plant Innate Immunity. Plant Physiol. 2010, 152, 2222–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Jeong, D.H.; de Paoli, E.; Park, S.; Rosen, B.D.; Li, Y.; González, A.J.; Yan, Z.; Kitto, S.L.; Grusak, M.A.; et al. MicroRNAs as Master Regulators of the Plant NB-LRR Defense Gene Family via the Production of Phased, Trans-Acting SiRNAs. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 2540–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, S.; Kloesges, T.; Rose, L.E. Evolutionarily Dynamic, but Robust, Targeting of Resistance Genes by the MiR482/2118 Gene Family in the Solanaceae. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 3307–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Waseem, M.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhai, J.; Xia, R. MicroRNA482/2118, a MiRNA Superfamily Essential for Both Disease Resistance and Plant Development. New Phytol. 2022, 233, 2047–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Xie, B.; Guan, P.; Jiang, N.; Cui, J. New Insight into the Molecular Mechanism of MiR482/2118 during Plant Resistance to Pathogens. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1026762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Gu, X.; Liu, J.; He, Z. Roles of small RNAs in crop disease resistance. Stress Biol. 2021, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Márquez, D.; Del-Espino, A.; Ruiz-Albert, J.; Bejarano, E.R.; Brodersen, P.; Beuzón, C.R. Regulation of plant immunity via small RNA-mediated control of NLR expression. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 74, 6052–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgante, C.V.; Brasileiro, A.C.M.; Roberts, P.A.; Guimaraes, L.A.; Araujo, A.C.G.; Fonseca, L.N.; Leal-Bertioli, S.C.M.; Bertioli, D.J.; Guimaraes, P.M. A Survey of Genes Involved in Arachis stenosperma Resistance to Meloidogyne arenaria Race 1. Funct. Plant Biol. 2013, 40, 1298–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, B.M.; Arraes, F.; Quintana Martins, A.C.; Freitas Alves, N.S.; Melo, B.P.; Morgante, C.V.; Passos Saraiva, M.A.; Grossi-De-Sá, M.F.; Guimaraes, P.M.; Miranda Brasileiro, A.C. A Novel Soybean Hairy Root System for Gene Functional Validation. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, N.L.; Pimentel, H.; Melsted, P.; Pachter, L. Near-Optimal Probabilistic RNA-Seq Quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 525–527, Erratum in Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences from High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and Memory-Efficient Alignment of Short DNA Sequences to the Human Genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.R.; Yeoh, J.M.; Coruh, C.; Axtell, M.J. Improved Placement of Multi-Mapping Small RNAs. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2016, 6, 2103–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, A.R.; Bernhart, S.H.; Lorenz, R. The ViennaRNA Web Services. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1269, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhao, P.X. psRNATarget: A plant small RNA target analysis server (2017 release). Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W49–W54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. EdgeR: A Bioconductor Package for Differential Expression Analysis of Digital Gene Expression Data. Bioinformatics 2009, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsalu, T.; Vilo, J. ClustVis: A Web Tool for Visualizing Clustering of Multivariate Data Using Principal Component Analysis and Heatmap. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W566–W570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ridzon, D.A.; Broomer, A.J.; Zhou, Z.; Lee, D.H.; Nguyen, J.T.; Barbisin, M.; Xu, N.L.; Mahuvakar, V.R.; Andersen, M.R.; et al. Real-Time Quantification of MicroRNAs by Stem-Loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Fernald, R.D. Comprehensive Algorithm for Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction. J. Comput. Biol. 2005, 12, 1047–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Horgan, G.W.; Dempfle, L. Relative Expression Software Tool (REST) for Group-Wise Comparison and Statistical Analysis of Relative Expression Results in Real-Time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.S.; Maximiano, M.R.; Megias, E.; Pappas, M.; Ribeiro, S.G.; Mehta, A. Quantitative Expression of MicroRNAs in Brassica oleracea Infected with Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 3523–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgante, C.V.; Guimarães, P.M.; Martins, A.C.Q.; Araújo, A.C.G.; Leal-Bertioli, S.C.M.; Bertioli, D.J.; Brasileiro, A.C.M. Reference Genes for Quantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction Expression Studies in Wild and Cultivated Peanut. BMC Res. Notes 2011, 4, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teotia, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, N.; Wang, M.; Liu, H.; Qin, J.; Han, D.; Li, C.; Li, C.E.; Pan, S.; et al. A High-Efficiency Gene Silencing in Plants Using Two-Hit Asymmetrical Artificial MicroRNAs. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 1799–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Cao, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; He, H.; Yao, W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H. MicroRNAs Are Involved in Maize Immunity Against Fusarium Verticillioides Ear Rot. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2020, 18, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossowski, S.; Schwab, R.; Weigel, D. Gene Silencing in Plants Using Artificial MicroRNAs and Other Small RNAs. Plant J. 2008, 53, 674–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Vázquez, L.A.; Castro-Pacheco, A.M.; Pérez-Vargas, R.; Velázquez-Jiménez, J.F.; Paul, S. The Emerging Applications of Artificial MicroRNA-Mediated Gene Silencing in Plant Biotechnology. Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yang, J.; Zhang, N.; Wu, J.; Si, H. Roles of MicroRNAs in Abiotic Stress Response and Characteristics Regulation of Plant. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 919243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guimaraes, P.M.; Martins, A.d.C.Q.; Togawa, R.C.; Saraiva, M.A.d.P.; Lacerda, A.L.M.; Brasileiro, A.C.M.; Grynberg, P. miRNA-Mediated Regulation of Meloidogyne arenaria Responses in Wild Arachis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210824
Guimaraes PM, Martins AdCQ, Togawa RC, Saraiva MAdP, Lacerda ALM, Brasileiro ACM, Grynberg P. miRNA-Mediated Regulation of Meloidogyne arenaria Responses in Wild Arachis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):10824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210824
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuimaraes, Patricia Messenberg, Andressa da Cunha Quintana Martins, Roberto Coiti Togawa, Mario Alfredo de Passos Saraiva, Ana Luiza Machado Lacerda, Ana Cristina Miranda Brasileiro, and Priscila Grynberg. 2025. "miRNA-Mediated Regulation of Meloidogyne arenaria Responses in Wild Arachis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 10824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210824
APA StyleGuimaraes, P. M., Martins, A. d. C. Q., Togawa, R. C., Saraiva, M. A. d. P., Lacerda, A. L. M., Brasileiro, A. C. M., & Grynberg, P. (2025). miRNA-Mediated Regulation of Meloidogyne arenaria Responses in Wild Arachis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 10824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210824





