Regulatory Machinery of Bacterial Bioflocculant Synthesis and Optimisation and Assessment of Bioflocculation Efficiency in Wastewater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Identification
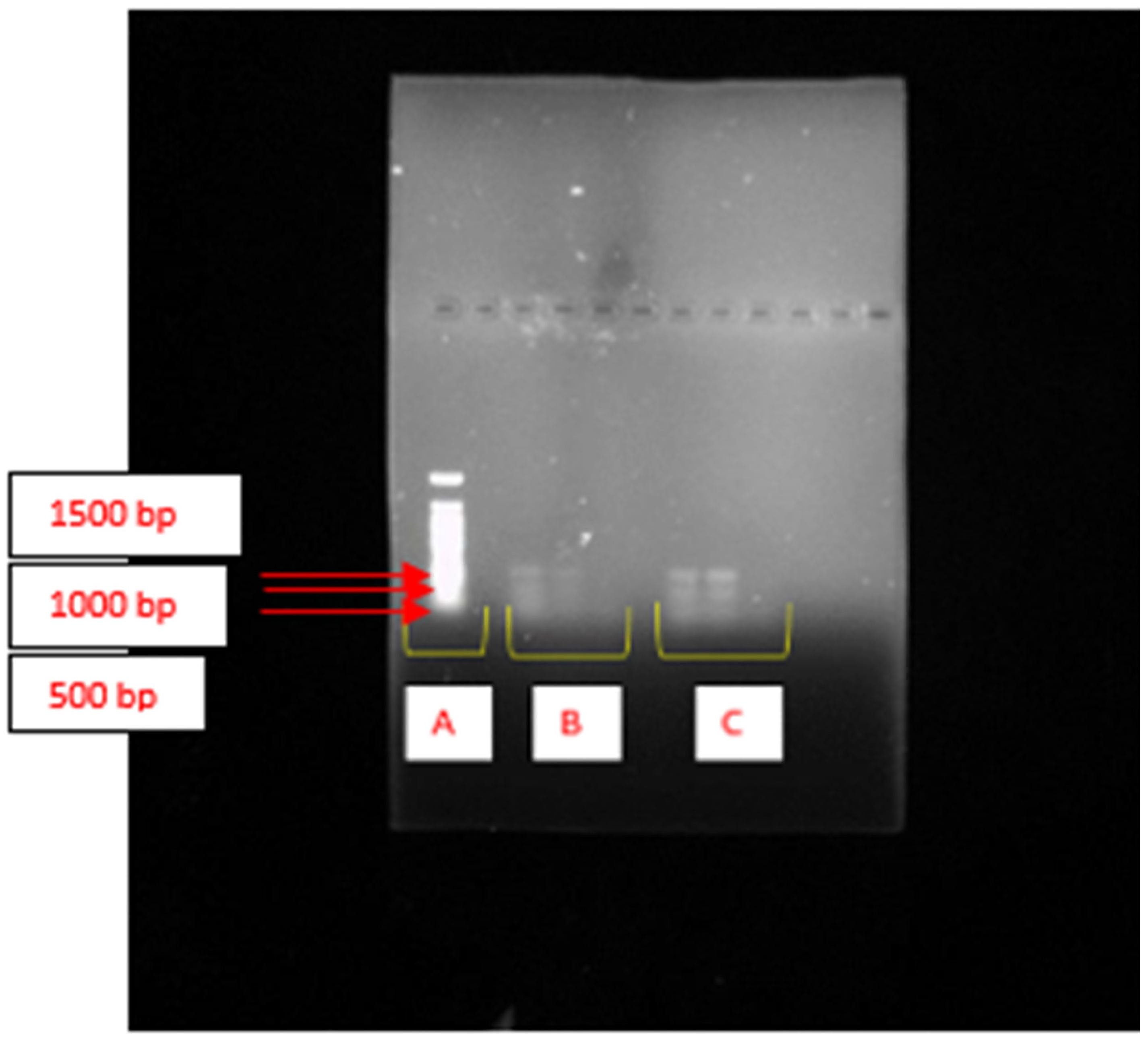
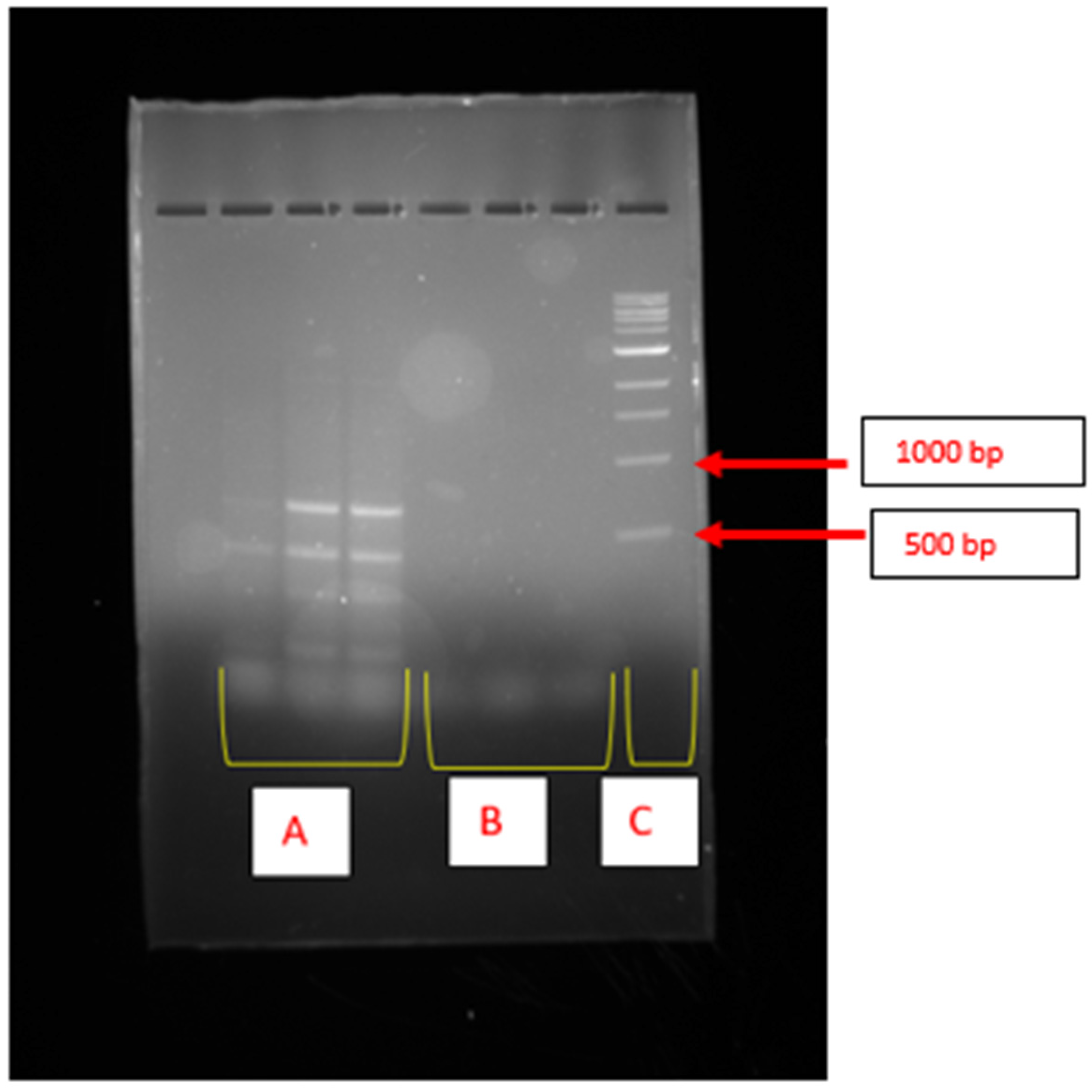
2.2. Cluster Genes Responsible for Bioflocculant Production
2.3. Enzymes Coded by Genes Responsible for Bioflocculant Production
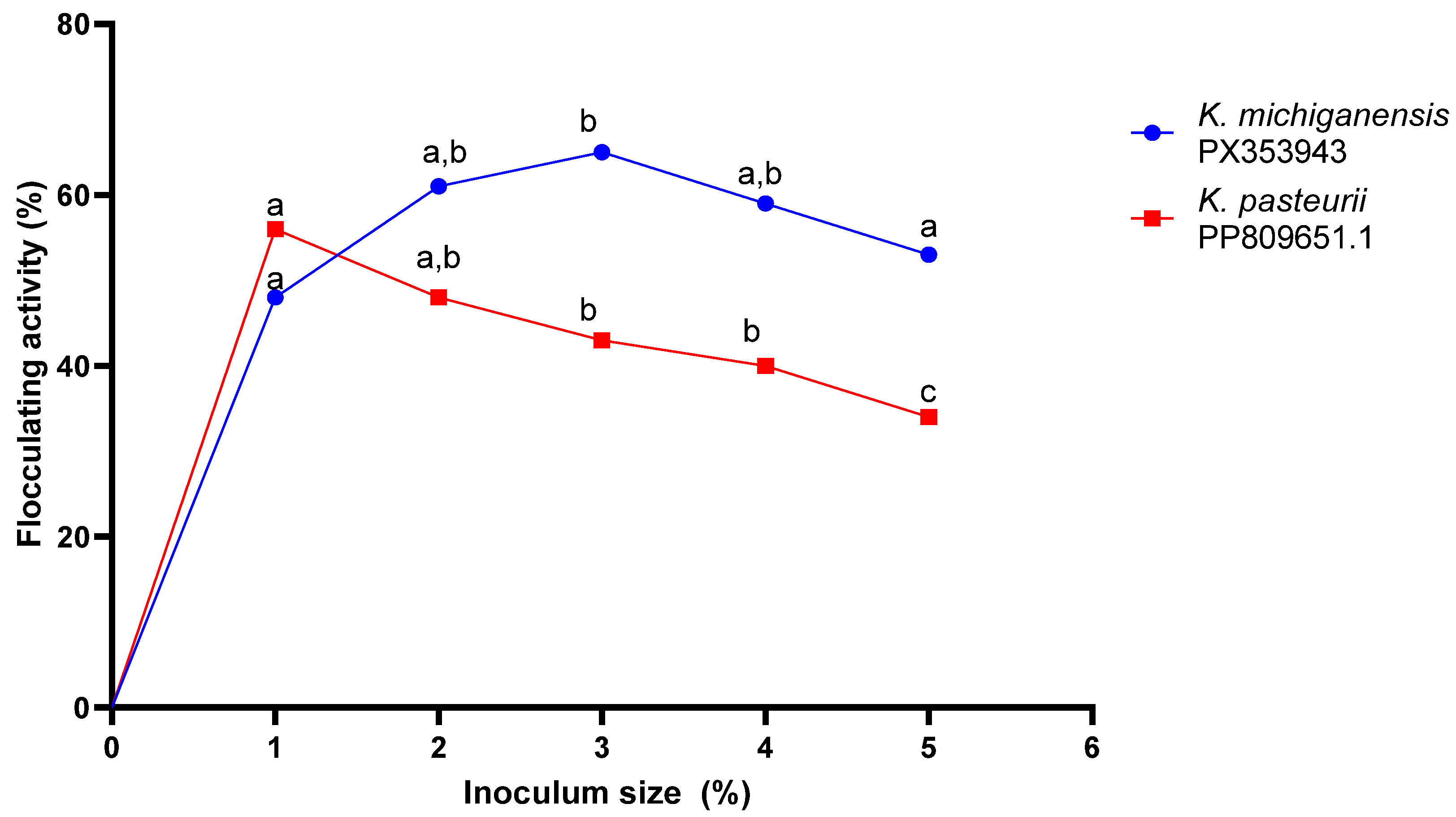
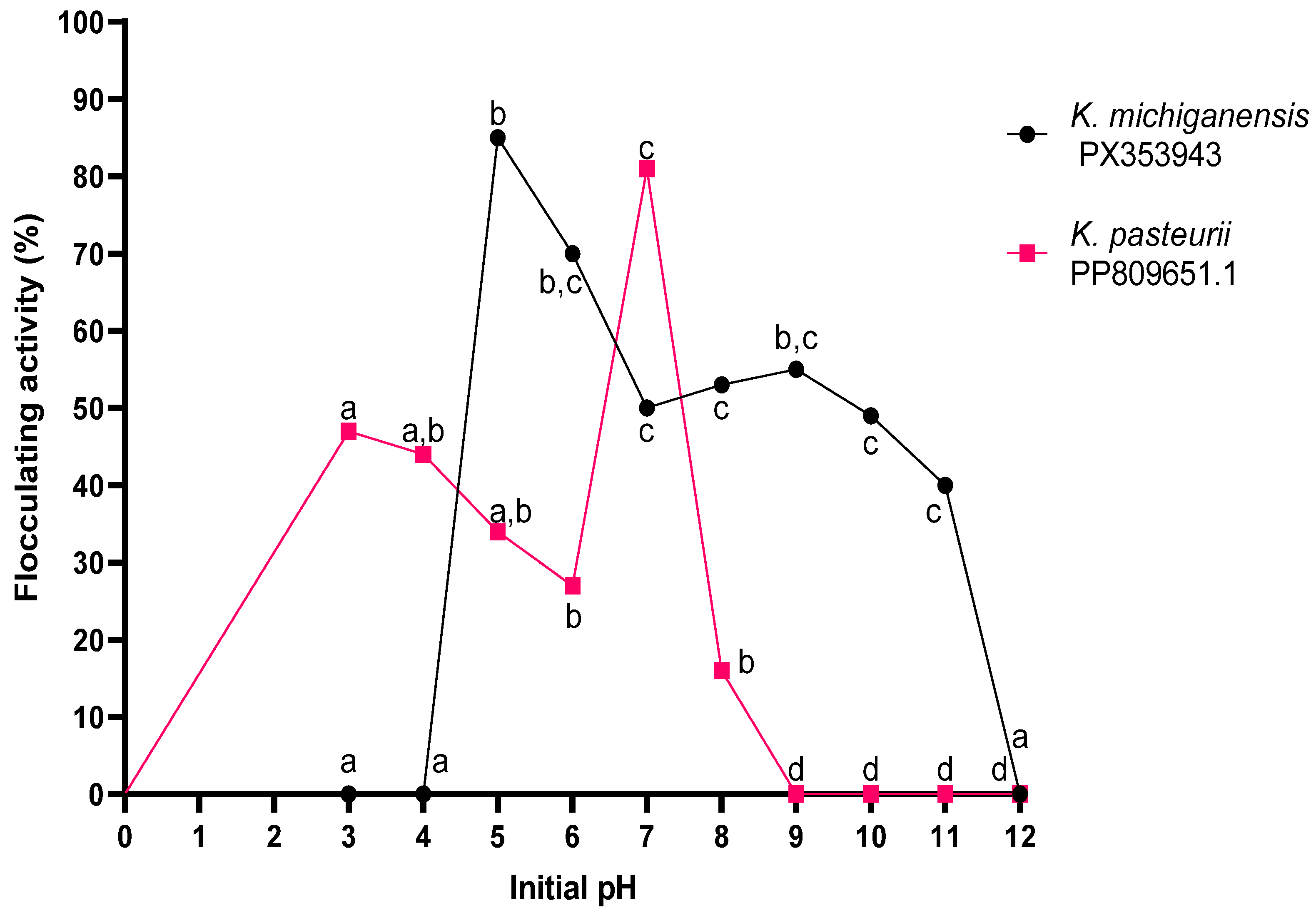
2.4. Optimisation of Conditions
2.4.1. Inoculum Volume
2.4.2. Carbon Sources
2.4.3. Nitrogen Sources
2.4.4. Initial pH
2.4.5. Temperature
2.4.6. Effect of Incubation Time on Bioflocculant Production
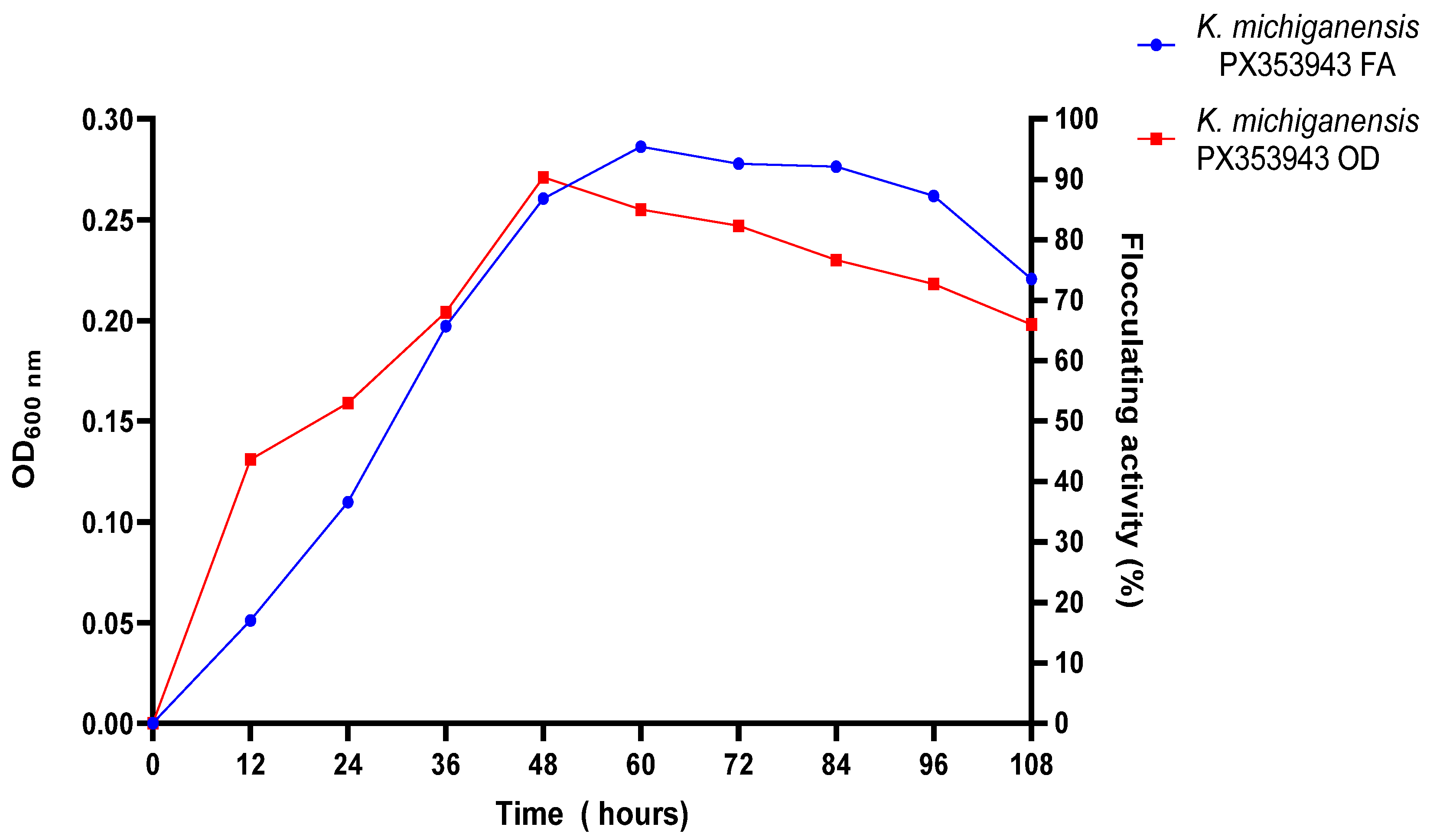
Effect of Time on Bioflocculant Production by K. michiganensis PX353943
Effect of Time on Bioflocculant Production by K. pasteurii PP809651.1
2.5. Bioflocculant Yields
2.6. Application of Purified Bioflocculants in Wastewater Treatment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. Enrichment of Bioflocculant-Producing Bacteria
4.3. Serial Dilution and Isolation of Bioflocculant-Producing Bacteria
4.4. Screening of Bioflocculant-Producing Bacteria
4.4.1. Fermentation
4.4.2. Determination of FA
4.5. Molecular Identification of the Bioflocculant-Producing Bacteria
4.6. Evaluation of BGC and Enzymes Responsible for Bioflocculant Production
4.7. Optimisation of Medium Composition and Culture Conditions
4.7.1. Effect of Inoculum Size on Bioflocculant Production
4.7.2. Effect of Carbon Sources on Bioflocculant Production
4.7.3. Effect of Nitrogen Sources on Bioflocculant Production
4.7.4. Effect Initial of pH on Bioflocculant Production
4.7.5. Effect of Temperature on Bioflocculant Production
4.7.6. Effect of Incubation Time on Bioflocculant Production and Growth Rate
4.8. Extraction and Purification
4.9. Application of the Bioflocculants in Wastewater Treatment
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FA | Flocculating activity |
| BGC | Biosynthetic gene cluster |
| RE | Removal efficiency |
| UDP | Uridine diphosphate |
| OD | Optical density |
| NRPS | Non-ribosomal peptide synthetase |
| PKS | Polyketide synthase |
| COD | Chemical oxygen demand |
| PAC | Polyaluminium chloride |
| EPS | Exopolymeric substances |
References
- Kurniawan, S.B.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Imron, M.F.; Said, N.S.M.; Ismail, N.I.; Hasan, H.A.; Othman, A.R.; Purwanti, I.F. Challenges and opportunities of biocoagulant/bioflocculant application for drinking water and wastewater treatment and its potential for sludge recovery. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okaiyeto, K.; Nwodo, U.U.; Okoli, S.A.; Mabinya, L.V.; Okoh, A.I. Implications for public health demands alternatives to inorganic and synthetic flocculants: Bioflocculants as important candidates. Microbiologyopen 2016, 5, 177–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehizadeh, H.; Yan, N. Recent advances in extracellular biopolymer flocculants. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1506–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nxumalo, C.I.; Ngidi, L.S.; Shandu, J.S.E.; Maliehe, T.S. Isolation of endophytic bacteria from the leaves of Anredera cordifolia CIX1 for metabolites and their biological activities. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; He, N. Characterization of a novel bioflocculant from a marine bacterium and its application in dye wastewater treatment. BMC Biotechnol. 2017, 17, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahadat, M.; Teng, T.T.; Rafatullah, M.; Shaikh, Z.A.; Sreekrishnan, T.R.; Ali, S.W. Bacterial bioflocculants: A review of recent advances and perspectives. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 1139–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, J.N.; Wan Dagang, W.R.Z. Implications for industrial application of bioflocculant demand alternatives to conventional media: Waste as a substitute. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 80, 1807–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, P.; Sun, Y.; Wang, M.; Ma, Y. A bioflocculant from Corynebacterium glutamicum and its application in acid mine wastewater treatment. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1136473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selepe, T.N.; Maliehe, T.S.; Moganedi, K.; Masoko, P.; Mulaudzi, V. Isolation and optimisation of culture conditions for a marine bioflocculant-producing bacterium and application of its bioflocculant in wastewater treatment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, Z.; Yang, L.; Li, Q.; He, N. Increasing the bioflocculant production and identifying the effect of overexpressing epsB on the synthesis of polysaccharide and γ-PGA in Bacillus licheniformis. Microb. Cell Fact. 2017, 16, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamat, S. Molecular basis and genetic regulation of EPS. In Microbial Exopolysaccharides as Novel and Significant Biomaterials; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 45–83. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, N.P. Fungal secondary metabolism: Regulation, function and drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, P.; Li, Z.; Yu, W.; Wang, Z.; Yao, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Deng, X.; He, N. Identification of key genes involved in polysaccharide bioflocculant synthesis in Bacillus licheniformis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 114, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhnert, E.; Navarro-Muñoz, J.C.; Becker, K.; Stadler, M.; Collemare, J.; Cox, R.J. Secondary metabolite biosynthetic diversity in the fungal family Hypoxylaceae and Xylaria hypoxylon. Stud. Mycol. 2021, 99, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Salam, N.; Jiao, J.Y.; Jiang, H.C.; Zhou, E.M.; Yin, Y.R.; Ming, H.; Li, W.J. Diversity of culturable thermophilic actinobacteria in hot springs in Tengchong, China and studies of their biosynthetic gene profiles. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 72, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Jiang, B.; Wei, J.; Liu, J.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L. Transcriptome analysis of polysaccharide-based microbial flocculant MBFA9 biosynthesis regulated by nitrogen source. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Sun, D. Complete genome sequence of a novel bioflocculantproducing strain, Microbacterium paludicola CC3. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, S.; Qiu, J.; Li, A.; Feng, L.; Wu, D.; Zhao, H.P.; Ma, F. Applied microbiology and biotechnology uncovering the biosynthetic pathway of polysaccharide-based microbial flocculant in Agrobacterium tumefaciens F2. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 8479–8488, Correction in Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 8961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvasi, M.; Visscher, P.T.; Martinez, L.C. Exopolymeric substances (EPS) from Bacillus subtilis: Polymers and genes encoding their synthesis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 313, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xia, X.; Chen, X.; Rui, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Dong, M. Complete genome sequence of Lactobacillus helveticus MB2-1, a probiotic bacterium producing exopolysaccharides. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 209, 14–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibberg, D.; Alkhateeb, R.S.; Winkler, A.; Albersmeier, A.; Schatschneider, S.; Albaum, S.; Niehaus, K.; Hublik, G.; Pühler, A.; Vorhölter, F.J. Draft genome of the xanthan producer Xanthomonas campestris NRRL B-1459 (ATCC 13951). J. Biotechnol. 2015, 204, 45–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comstock, L.E.; Coyne, M.J.; Tzianabos, A.O.; Pantosti, A.; Onderdonk, A.B.; Kasper, D.L. Analysis of a capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis locus of Bacteroides fragilis. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 3525–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, S.S.; Amer, S.K.; Selim, M.S.; Rifaat, H.M. Characterization and applications of exopolysaccharide produced by marine Bacillus altitudinis MSH2014 from Ras Mohamed, Sinai, Egypt. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2018, 5, 204–209, Correction in Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2018, 5, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Lu, Y.; Pan, X.; Ling, X. A novel bioflocculant produced by Cobetia marina MCCC1113: Optimization of fermentation conditions by response surface methodology and evaluation of flocculation performance when harvesting microalgae. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2022, 71, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, X.; Du, X.; Wang, C.A.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, Q. Isolation, identification, and optimization of culture conditions of a bioflocculant--producing bacterium Bacillus megaterium sp1 and its application in aquaculture wastewater treatment. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2758168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wareth, G.; Neubauer, H. The Animal-foods-environment interface of Klebsiella pneumoniae in Germany: An observational study on pathogenicity, resistance development and the current situation. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Liang, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, B.; Chen, M.; Liu, Y. Production of a bioflocculant from Klebsiella sp. OS-1 using brewery wastewater as a source. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, C.; Zhang, W.; Liu, M.; Han, Y.; Zhou, J. Production and characteristics of a bioflocculant by Klebsiella pneumoniae YZ-6 isolated from human saliva. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 172, 1282–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, K.; Kurane, R. Production of an extracellular polysaccharide bioflocculant by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1999, 63, 2064–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Xu, A.; Wang, B.; Yang, X.; Hong, W.; Yang, B.; Chen, C.; Liu, H.; Zhou, J. Production of a value-added compound from the H-acid waste water—Bioflocculants by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Colloids Surf. B 2014, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, M.; Yin, X.; Jia, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Shen, Q.; Li, P.; Wang, Z. Production of a novel bioflocculant MNXY1 by Klebsiella pneumoniae strain NY1 and application in precipitation of cyanobacteria and municipal wastewater treatment. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 111, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, H.; Zhou, J. Characterization of a bioflocculant MBF-5 by Klebsiella pneumoniae and its application in Acanthamoeba cysts removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 137, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Yan, X. Diversity of gene clusters for polyketide and nonribosomal peptide biosynthesis revealed by metagenomic analysis of the yellow sea sediment. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.S.; Ryu, E.; Park, S.C. Characterization of the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of a polysaccharide-based bioflocculant from Bacillus subtilis F9. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 136, 103642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthulakshmi, L.; Nellaiah, H.; Kathiresan, T.; Rajini, N.; Christopher, F. Identification and production of bioflocculants by Enterobacter sp. and Bacillus sp. and their characterization studies. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 47, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyvaert, G.; Morel, C.; Joly, J.P.; Decaris, B.; Charron-Bourgoin, F. The eps locus of Streptococcus thermophilus IP6756 is not involved in exopolysaccharide production. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okaiyeto, K.; Nwodo, U.U.; Okoli, A.S.; Mabinya, L.V.; Okoh, A.I. Studies on bioflocculant production by Bacillus sp. AEMREG7. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugbenyen, A.M.; Cosa, S.; Mabinya, L.V.; Okoh, A.I. Bioflocculant production by Bacillus sp. Gilbert isolated from a marine environment in South Africa. App. Biochem. Microbiol. 2014, 50, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.G.; Gong, W.X.; Liu, X.W.; Tian, L.; Yue, Q.Y.; Gao, B.Y. Production of a novel bioflocculant by culture of Klebsiella mobilis using dairy wastewater. Biochem. Eng. J. 2007, 36, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, K.R.; Wong, J.W.C.; Murugesan, K. Production of bioflocculant from Klebsiella pneumoniae: Evaluation of fish waste extract as substrate and flocculation performance. Environ. Technol. 2023, 44, 4046–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makapela, B.; Okaiyeto, K.; Ntozonke, N.; Nwodo, U.U.; Green, E.; Mabinya, L.V.; Okoh, A.I. Assessment of Bacillus pumilus isolated from fresh water milieu for bioflocculant production. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliehe, T.S.; Moganedi, K.; Masoko, P.; Selepe, T.N. Isolation of a marine bacterium and application of its bioflocculant in wastewater treatment. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 13, 584–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebami, G.; Adebayo-Tayo, B.C. Comparative effect of medium composition on bioflocculant production by microorganisms isolated from wastewater samples. Rep. Opin. 2013, 5, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, Y.; Beauregard, P.B.; Vlamakis, H.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. Galactose metabolism plays a crucial role in biofilm formation by Bacillus subtilis. MBio 2012, 3, 1110–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boels, I.C.; Ramos, A.; Kleerebezem, M.; de Vos, W.M. Functional analysis of the Lactococcus lactis galU and galE genes and their impact on sugar nucleotide and exopolysaccharide biosynthesis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3033–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Ma, C.; Chi, Z. Bioflocculant produced by Klebsiella sp. MYC and its application in the treatment of oil-field produced water. J. Ocean Univ. China 2006, 5, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Chen, Y.; Gong, A.D. Development of a defined medium for Corynebacterium glutamicum using urea as nitrogen source. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Yuan, H.; Liu, M.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, D.; Wang, T. Yeast extract: Characteristics, production, applications and future perspectives. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 33, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsilo, P.H.; Basson, A.K.; Ntombela, Z.G.; Maliehe, T.S.; Pullabhotla, R.V. Isolation and optimization of culture conditions of a bioflocculant-producing fungi from Kombucha tea SCOBY. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 12, 950–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, N.; Liu, L. Microbial response to acid stress: Mechanisms and applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendranath, N.V.; Power, R. Relationship between pH and medium dissolved solids in terms of growth and metabolism of lactobacilli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae during ethanol production. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 2239–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondal, A.H.; Hussain, I.; Ijaz, A.B.; Zafar, A.; Ch, B.I.; Zafar, H.; Sohail, M.D.; Niazi, H.; Touseef, M.; Khan, A.A.; et al. Influence of soil pH and microbes on mineral solubility and plant nutrition: A review. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2021, 5, 71–81. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.J.; Tian, Z.M.; Tang, W.; Li, L.; Song, L.Y.; McElmurry, S.P. Production and characterization of high efficiency bioflocculant isolated from Klebsiella sp. ZZ-3. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 171, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yang, H.; Chu, M.; Niu, X.; Huo, X.; Gao, Y.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Outi, K.; et al. Klebsiella. In Beneficial Microbes in Agro-Ecology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 233–257. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Lin, B.; Xia, S.Q.; Wang, X.J.; Yang, A.M. Production and application of a novel bioflocculant by multiple-microorganism consortia using brewery wastewater as carbon source. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehizadeh, H.; Shojaosadati, S.A. Extracellular biopolymeric flocculants: Recent trends and biotechnological importance. Biotechnol. Adv. 2001, 19, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliehe, T.; Basson, A.; Singh, M. Wastewater treatment by a novel bioflocculant from a consortium of Bacillus pumilus JX860616 and Bacillus subtilis CSM5. Biosci. Res. 2020, 17, 1610–1625. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, K.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Optimized production and characterization of cation-independent bioflocculant produced by Klebsiella sp. 59L. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 7981–7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini-Costa, T.D.S.; Vieira, R.F.; Bizzo, H.R.; Silveira, D.; Gimenes, M.A. Secondary metabolites. Chromatogr. Its Appl. 2012, 1, 131–164. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Phan, T.H.M.; Tran, T.N.; Velmurugan, B.K.; Kiefer, R. Production of novel bio-flocculants from Klebsiella variicola BF1 using cassava starch wastewater and its application. Curr. Sci. 2019, 117, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, H.; Li, L.; Liang, J.; Lu, C.; Ding, X.; Guo, W. Optimized Extraction Process and Compositional Analysis of Bioflocculant Produced by Klebsiella M1. BioResources 2019, 14, 3146–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Cruz-Noriega, M.; Rojas-Flores, S.; Benites, S.M.; Quezada Álvarez, M.A.; Otiniano García, N.M.; Rodríguez Yupanqui, M. Use of Leuconostoc mesenteroides to produce a dextran bioflocculant. Environ. Res. Eng. Manag. 2022, 78, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mburu, A.; Njuguna, D.; Nzila, C.; Musieba, F.; Waithaka, A.; Mwangi, G.; Kemunto, A. Comparative treatment of textile dye wastewater with chemical coagulants and bacterial exopolysaccharides. J. Text. Inst. 2024, 116, 2100–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, S.B.; Imron, M.F.; Sługocki, Ł.; Nowakowski, K.; Ahmad, A.; Najiya, D.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Othman, A.R.; Purwanti, I.F.; Hasan, H.A. Assessing the effect of multiple variables on the production of bioflocculant by Serratia marcescens: Flocculating activity, kinetics, toxicity, and flocculation mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maliehe, T.S.; Basson, A.K.; Dlamini, N.G. Removal of pollutants in mine wastewater by a non-cytotoxic polymeric bioflocculant from Alcaligenes faecalis HCB2. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddharth, S.; Aswathanarayan, J.B.; Kuruburu, M.G.; Madhunapantula, S.R.V.; Vittal, R.R. Diketoperazine derivative from marine actinomycetes Nocardiopsis sp. SCA30 with antimicrobial activity against MRSA. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 6173–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastidas-Caldes, C.; Hernández-Alomía, F.; Almeida, M.; Ormaza, M.; Boada, J.; Graham, J.; Calvopiña, M.; Castillejo, P. Molecular identification and antimicrobial resistance patterns of enterobacterales in community urinary tract infections among indigenous women in Ecuador: Addressing microbiological misidentification. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Shen, Q.; Bian, X.; Chen, H.; Fu, J.; Wang, H.; Lei, P.; Guo, Z.; Chen, W.; Li, D.; et al. Simple and rapid direct cloning and heterologous expression of natural product biosynthetic gene cluster in Bacillus subtilis via Red/ET recombineering. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkosi, N.C.; Basson, A.K.; Ntombela, Z.G.; Maliehe, T.S.; Pullabhotla, R.V. Isolation, identification and characterization of bioflocculant-producing bacteria from activated sludge of Vulindlela Wastewater Treatment Plant. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 1, 586–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugbenyen, A.M.; Simonis, J.J.; Basson, A.K. Screening for bioflocculant-producing bacteria from the marine environment of Sodwana Bay, South Africa. Ann. Sci. Technol. 2018, 3, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Tawila, Z.M.; Ismail, S.; Dadrasnia, A.; Usman, M.M. Production and characterization of a bioflocculant produced by Bacillus salmalaya 139SI7 and its applications in wastewater treatment. Molecules 2018, 23, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.W.; Yoo, S.A.; Oh, I.H.; Park, S.H. Characterization of an extracellular flocculating substance produced by a planktonic cyanobacterium, Anabaena sp. Biotechnol. Lett. 1998, 20, 643–646. [Google Scholar]
- Dlamini, N.G.; Basson, A.K.; Pullabhotla, R.V. Wastewater treatment by a polymeric bioflocculant and iron nanoparticles synthesized from a bioflocculant. Polymers 2020, 12, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Strain PX353943 | Strain PP809651.1 | Strain PX353943 | Strain PP809651.1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Source | FA (%) ± SD | FA (%) ± SD | Nitrogen Source | FA (%) ± SD | FA (%) ± SD |
| Glucose | 65 ± 0.036 a,b | 56 ± 0.037 a | Urea | 13 ± 0.003 a | 64 ± 0.003 a |
| Galactose | 74 ± 0.025 a | 79 ± 0.008 b | Yeast extract | 26 ± 0.130 a,b | 35 ± 0.025 c |
| Sucrose | 56 ± 0.022 b | 50 ± 0.075 a | Tryptophan | 80 ± 0.043 c | 52 ± 0.009 b |
| Xylose | 65 ± 0.146 a,b | 48 ± 0.041 a | (NH4)2SO4 | 74 ± 0.046 c | 58 ± 0.029 a,b |
| Lactose | 65 ± 0.071 a,b | 44 ± 0.007 a | Mixture (urea, yeast extract, and (NH4)2SO4) | 76 ± 0.091 c | 79 ± 0.010 d |
| Starch | – | 67 ± 0.041 a,b | NH4Cl | – | 55 ± 0.058 a,b |
| Malt extract | – | 51 ± 0.018 b | |||
| Casein | – | 59 ± 0.029 a,b | |||
| NH4NO3 | 38 ± 0.018 b | – |
| Flocculant | Turbidity Reduction (%) | COD Removal (%) |
|---|---|---|
| PAC | 94.59 a | 82.00 a |
| Aluminium sulphate | 92.14 a | 76.67 b |
| BF-PX353943 | 71.38 b | 73.33 b |
| BF-PP809651.1 | 90.62 a | 76.00 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mokoboro, S.; Selepe, T.N.; Maliehe, T.S.; Moganedi, K. Regulatory Machinery of Bacterial Bioflocculant Synthesis and Optimisation and Assessment of Bioflocculation Efficiency in Wastewater. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10559. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110559
Mokoboro S, Selepe TN, Maliehe TS, Moganedi K. Regulatory Machinery of Bacterial Bioflocculant Synthesis and Optimisation and Assessment of Bioflocculation Efficiency in Wastewater. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10559. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110559
Chicago/Turabian StyleMokoboro, Stanley, Tlou Nelson Selepe, Tsolanku Sidney Maliehe, and Kgabo Moganedi. 2025. "Regulatory Machinery of Bacterial Bioflocculant Synthesis and Optimisation and Assessment of Bioflocculation Efficiency in Wastewater" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10559. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110559
APA StyleMokoboro, S., Selepe, T. N., Maliehe, T. S., & Moganedi, K. (2025). Regulatory Machinery of Bacterial Bioflocculant Synthesis and Optimisation and Assessment of Bioflocculation Efficiency in Wastewater. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10559. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110559






