Combined Effects of Diosmin, Hesperidin, Ruscus aculeatus, Ananas comosus, and Bromelain on Endothelial Function and Gut Barrier Integrity In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
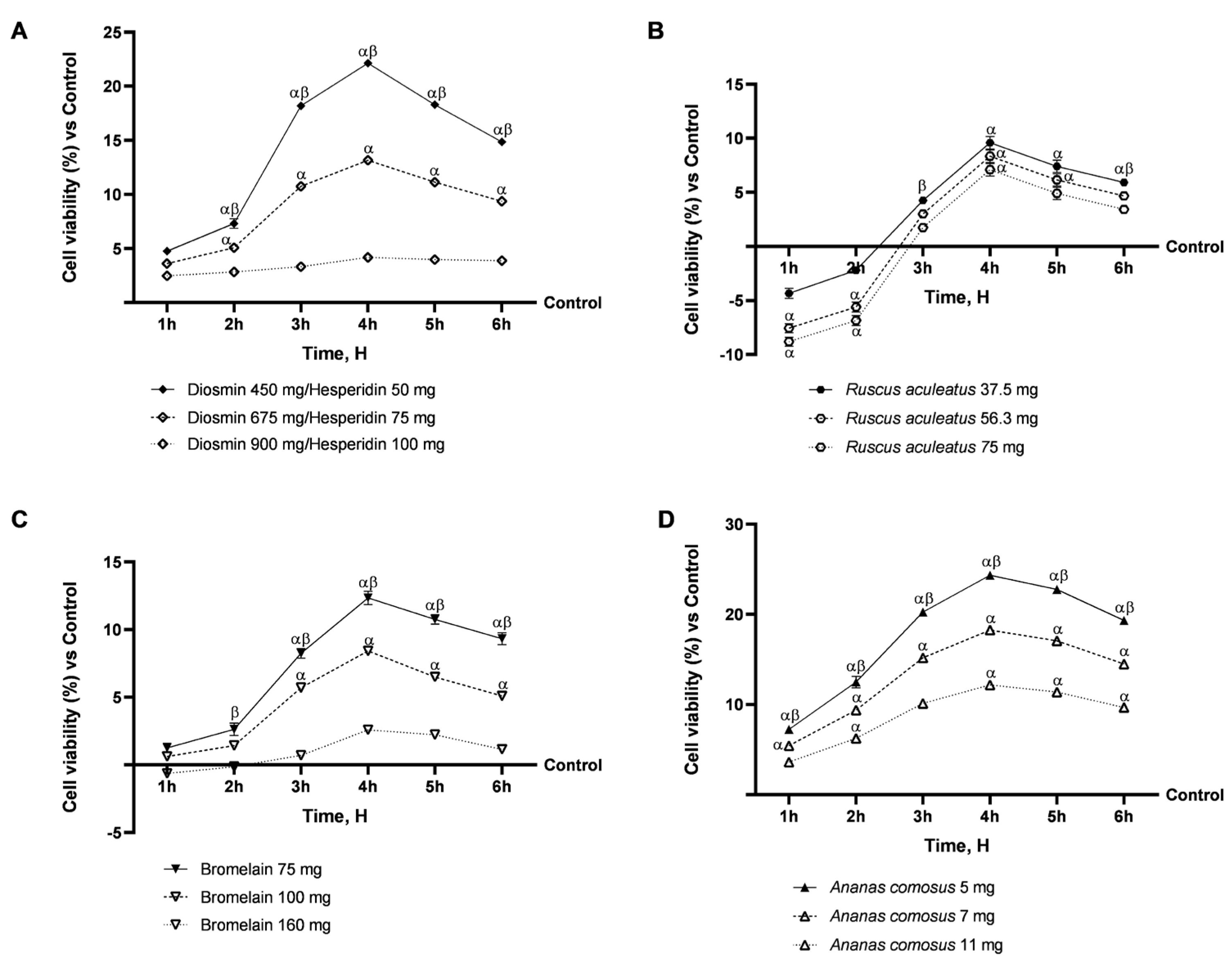
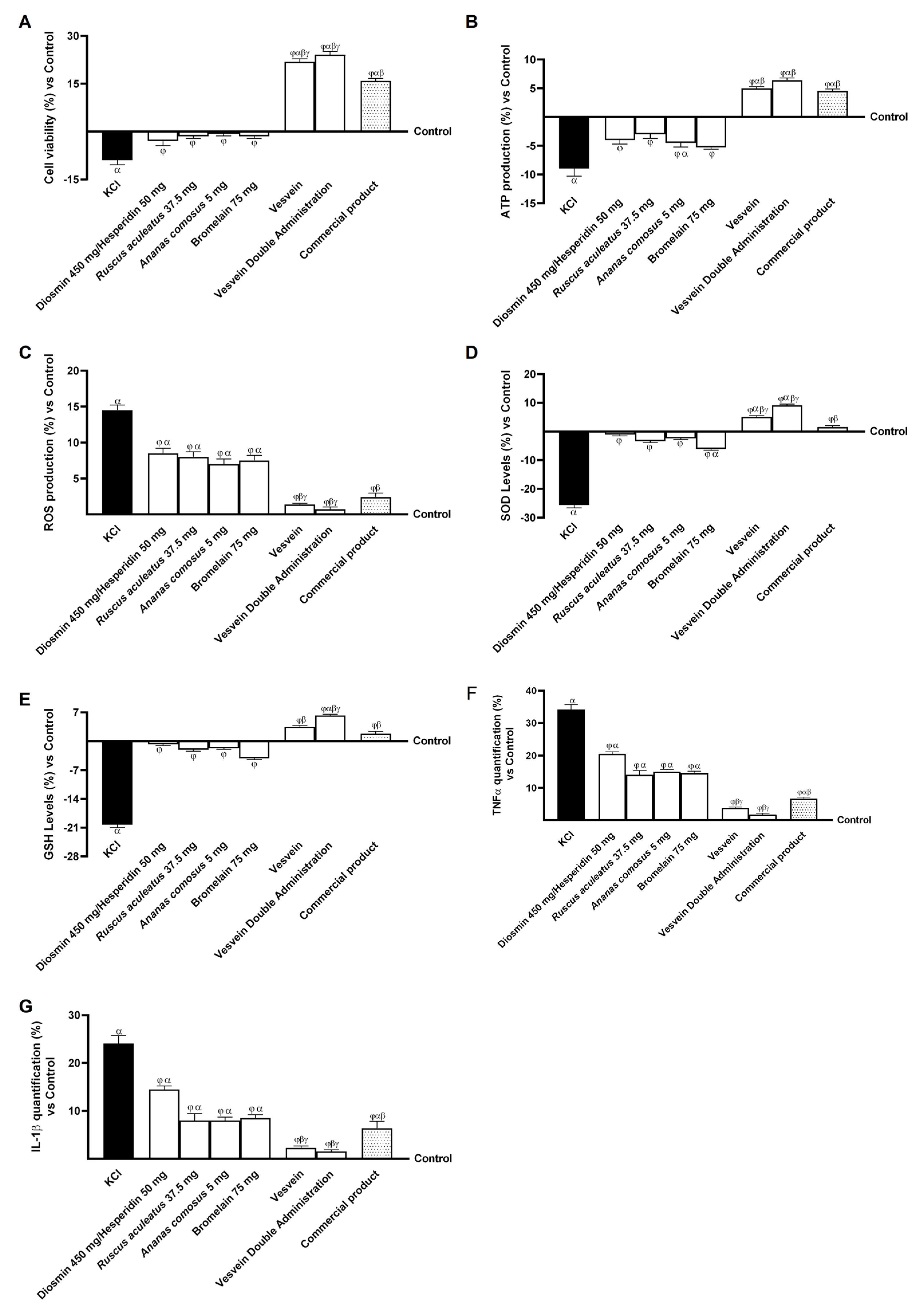
2.1. Safety Evaluation of Vesvein and Individual Agents on Intestinal Epithelium to Exclude Toxicity
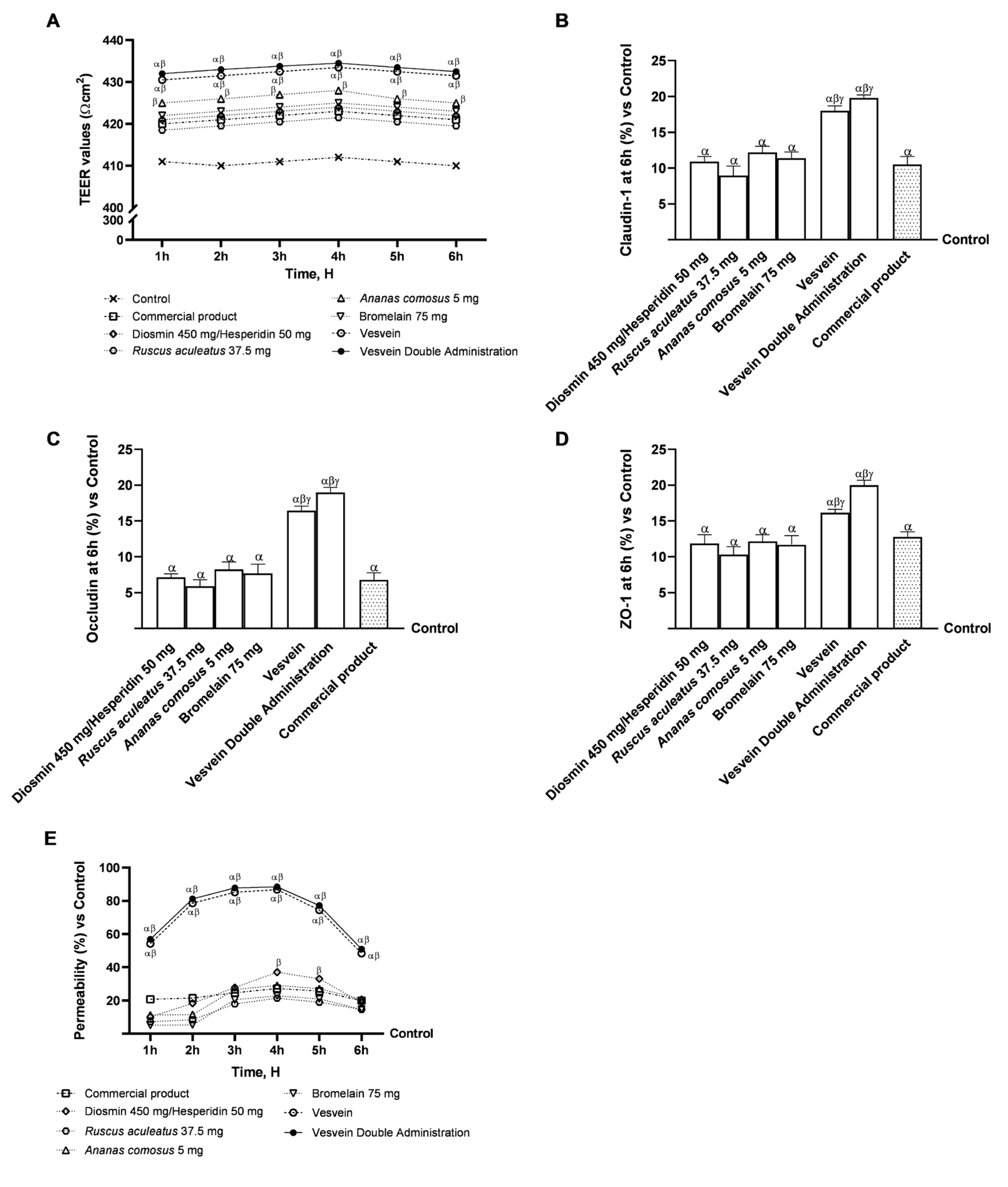
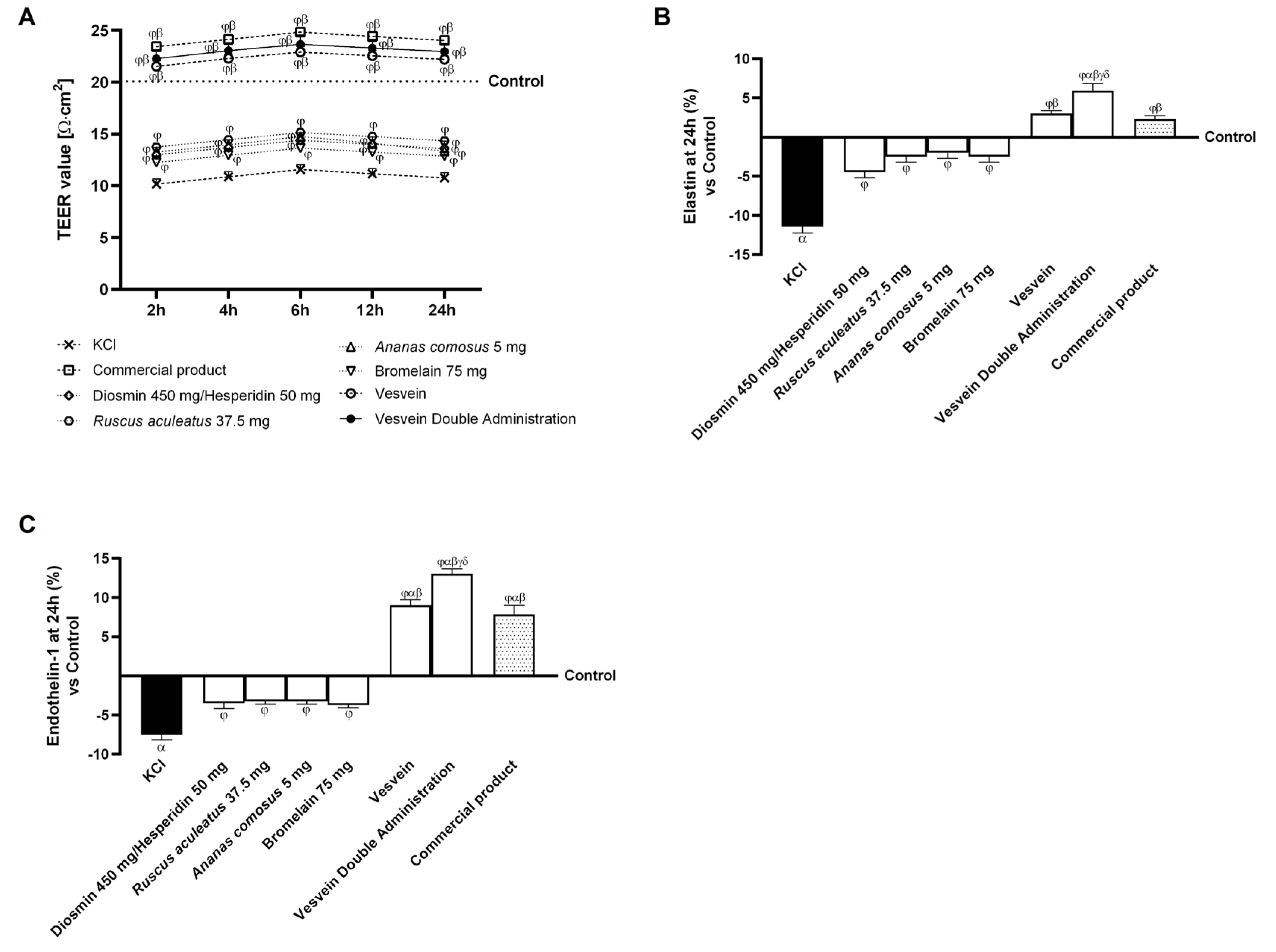
2.2. Integrity and Permeability Analysis on a 3D Model of the Intestinal Barrier In Vitro
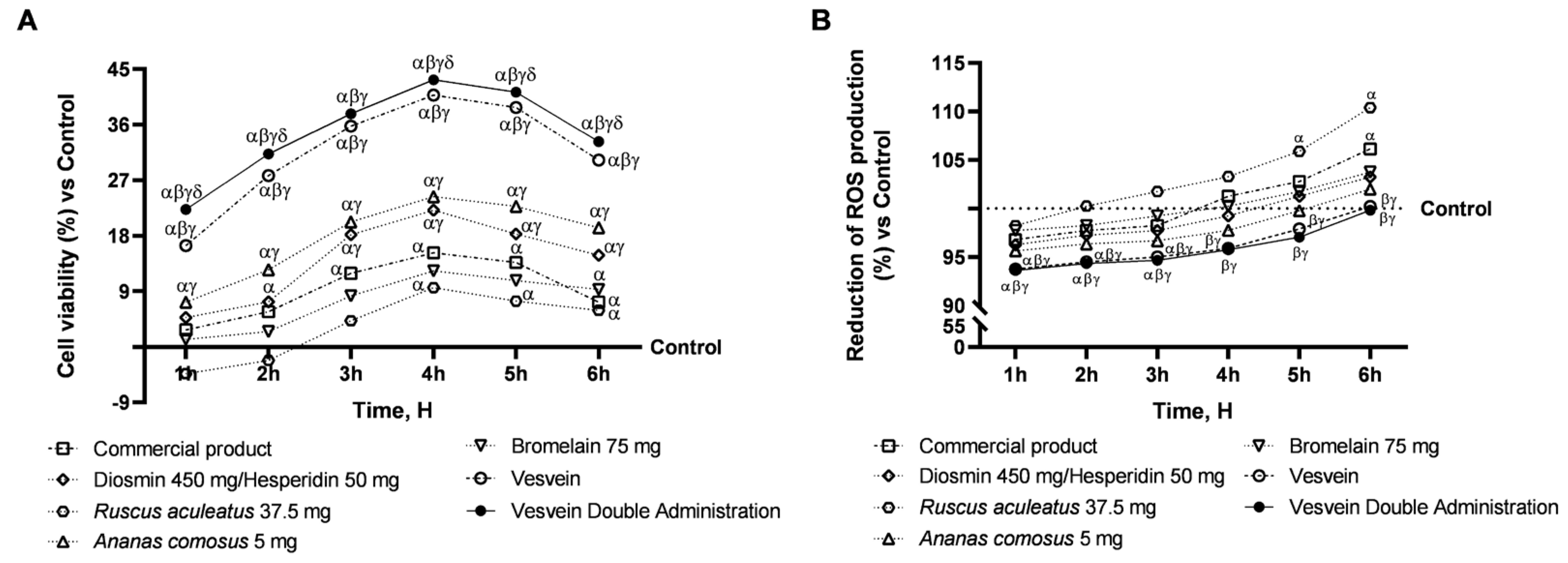
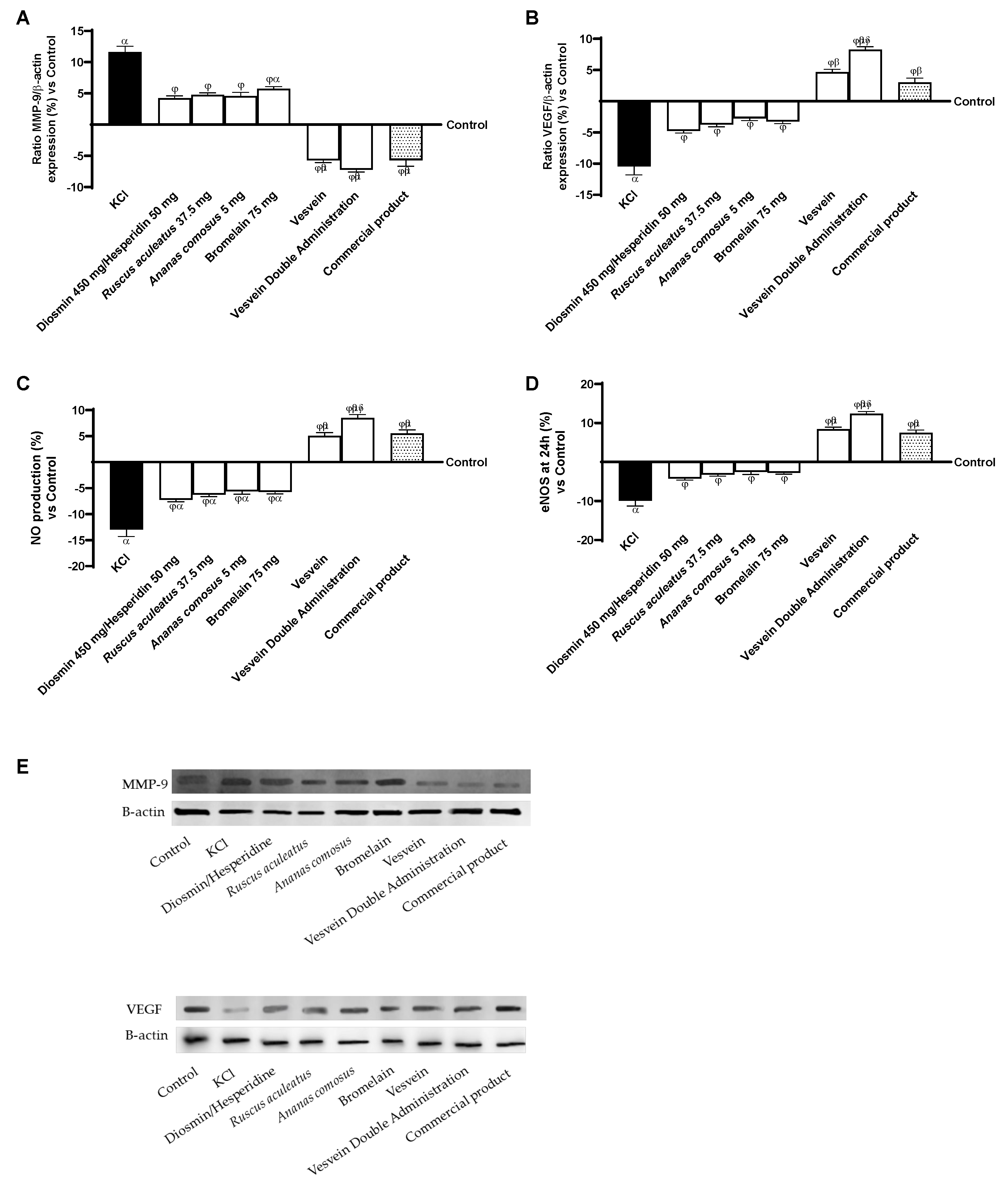
2.3. Effect of Individual Components and Combinations on the 3D Vein Model
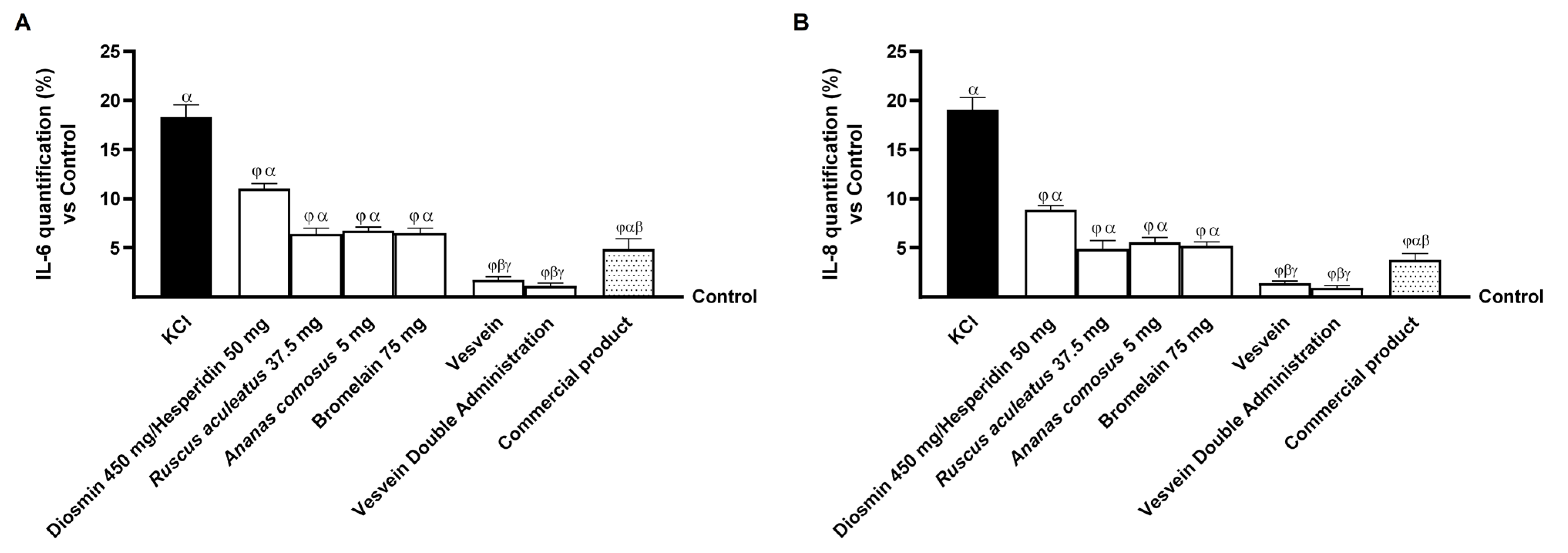
2.4. Effect of Individual Components and Combinations on Maintaining Venous Integrity and Tone
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Chemical Reagents
4.2. Agent Preparation
4.3. Cell Cultures
4.4. Intestinal Barrier In Vitro Model
- C: the initial concentration of fluorescein.
- Jmax: the maximum permeation rate.
- Kt: the Michaelis–Menten constant.
- Results are expressed as the means ± SD (%).
4.5. Vein In Vitro Model
4.6. Experimental Protocol
4.7. Cell Viability
4.8. Reactive Oxygen Species Production
4.9. TJs Analysis
4.10. Determination of ATP Production
4.11. SOD ELISA Kit
4.12. Tumour Necrosis Factor α (TNF-α) Assay Kit
4.13. Interleukin 1β (IL-1β) Assay Kit
4.14. Interleukin 6 Assay Kit
4.15. Interleukin 8 Assay Kit
4.16. Human Elastin ELISA Kit
4.17. Human Endothelin-1 ELISA Kit
4.18. Human eNOS/NOS3 ELISA Kit
4.19. Nitric Oxyde Production
4.20. Western Blot Analysis
4.21. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | One-way analysis of variance |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| CVD | Chronic venous disease |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| DMEM-F12 | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium/Nutrient F-12 Ham’s |
| EC | endothelial cells |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| EGM-2 | Endothelial Growth Medium-2 |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| eNOS | endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| FBS | foetal bovine serum |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| IL-1β | Interleukin 1β |
| MMPs | metalloproteinases |
| MMP-9 | matrix metalloproteinase-9 |
| MPFF | micronised purified flavonoid fraction |
| MTT | A3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| Na3VO4 | sodium orthovanadate |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| PMSF | phenylmethanesulfonylfluoride |
| ROS | radical oxygen species |
| TEER | transepithelial electrical resistance |
| TNF-α | tumour necrosis factor-α |
| TJ | tight junction |
| HUVEC | Human umbilical vein endothelial cells |
| VSMCs | vascular smooth muscle cells |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| Vesvein | mix of 450 mg Diosmin, 50 mg Hesperidin, 37.5 mg Ruscus aculeatus L. extract, 5 mg Ananas comosus L. extract, and 75 mg Bromelain |
| VVs | varicose veins |
| ZO-1 | zona occludens 1 |
Appendix A
References
- Xu, S. Therapeutic potential of blood flow mimetic compounds in preventing endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 155, 104737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, P.; Rengarajan, T.; Thangavel, J.; Nishigaki, Y.; Sakthisekaran, D.; Sethi, G.; Nishigaki, I. The vascular endothelium and human diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhoutte, P.M.; Shimokawa, H.; Feletou, M.; Tang, E.H. Endothelial dysfunction and vascular disease—A 30th anniversary update. Acta Physiol. 2017, 219, 22–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirase, T.; Node, K. Endothelial dysfunction as a cellular mechanism for vascular failure. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 302, H499–H505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Ferreira, R.; Cardoso, R.; Leite-Moreira, A.; Mansilha, A. The Role of Endothelial Dysfunction and Inflammation in Chronic Venous Disease. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 46, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Pérez, F.; Acosta, S.; Rütten, S.; Emonts, C.; Kopp, A.; Henke, H.W.; Bruners, P.; Gries, T.; Rodríguez-Cabello, J.C.; Jockenhoevel, S.; et al. Biohybrid elastin-like venous valve with potential for in situ tissue engineering. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 988533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansilha, A.; Sousa, J. Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Chronic Venous Disease and Implications for Venoactive Drug Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padberg, F.T. Handbook of Venous and Lymphatic Disorders, 5th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergan, J. Molecular mechanisms in chronic venous insufficiency. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2007, 21, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casili, G.; Lanza, M.; Campolo, M.; Messina, S.; Scuderi, S.; Ardizzone, A.; Filippone, A.; Paterniti, I.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Esposito, E. Therapeutic potential of flavonoids in the treatment of chronic venous insufficiency. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2021, 137, 106825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocock, E.S.; Alsaigh, T.; Mazor, R.; Schmid-Schönbein, G.W. Cellular and molecular basis of Venous insufficiency. Vasc. Cell 2014, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffetto, J.D.; Khalil, R.A. Mechanisms of Lower Extremity Vein Dysfunction in Chronic Venous Disease and Implications in Management of Varicose Veins. Vessel.Plus 2021, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannello, F.; Medda, V.; Ligi, D.; Raffetto, J.D. Glycosaminoglycan sulodexide inhibition of MMP-9 gelatinase secretion and activity: Possible pharmacological role against collagen degradation in vascular chronic diseases. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2013, 11, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, B.; Kumar, M.; Khanna, A.K.; Suman, P.K. Clinico-histopathological study of varicose vein and role of matrix metalloproteinases-1, matrix metalloproteinases-9 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in varicose vein formation. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2016, 59, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Horecka, A.; Hordyjewska, A.; Biernacka, J.; Dąbrowski, W.; Zubilewicz, T.; Malec, A.; Musik, I.; Kurzepa, J. Intense remodeling of extracellular matrix within the varicose vein: The role of gelatinases and vascular endothelial growth factor. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 190, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalewski, R.; Małkowski, A.; Sobolewski, K.; Gacko, M. Vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in the varicose vein wall. Acta Angiol. 2011, 17, 141–149. [Google Scholar]
- Serra, R.; Ielapi, N.; Bitonti, A.; Candido, S.; Fregola, S.; Gallo, A.; Loria, A.; Muraca, L.; Raimondo, L.; Velcean, L.; et al. Efficacy of a Low-Dose Diosmin Therapy on Improving Symptoms and Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Venous Disease: Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioli, A. Chronic venous disorders: Pharmacological and clinical aspects of micronized purified flavonoid fraction. Phlebolymphology 2016, 23, 57–120. [Google Scholar]
- Senra Barros, B.; Kakkos, S.K.; De Maeseneer, M.; Nicolaides, A.N. Chronic venous disease: From symptoms to microcirculation. Int. Angiol. 2019, 38, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Combarieu, E.; Falzoni, M.; Fuzzati, N.; Gattesco, F.; Giori, A.; Lovati, M.; Pace, R. Identification of Ruscus steroidal saponins by HPLC-MS analysis. Fitoterapia 2002, 73, 583–596, Erratum in Fitoterapia 2003, 74, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawien, A.; Bouskela, E.; Allaert, F.A.; Nicolaïdes, A.N. The place of Ruscus extract, hesperidin methyl chalcone, and vitamin C in the management of chronic venous disease. Int. Angiol. 2017, 36, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaides, A.; Kakkos, S.; Eklof, B.; Perrin, M.; Nelzen, O.; Neglen, P.; Partsch, H.; Rybak, Z. Management of chronic venous disorders of the lower limbs—Guidelines according to scientific evidence. Int. Angiol. 2018, 37, 181–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanek, T. The clinical efficacy of Ruscus Aesculatus extract: Is there enough evidence to update the pharmacotherapy guidelines for chronic venous disease? Phlebol. Rev. 2017, 25, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, H.R. Bromelain: Biochemistry, pharmacology and medical use. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varilla, C.; Marcone, M.; Paiva, L.; Baptista, J. Bromelain, a Group of Pineapple Proteolytic Complex Enzymes (Ananas comosus) and Their Possible Therapeutic and Clinical Effects. A Summary. Foods 2020, 10, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, P.; Nikhade, P.; Patel, A.; Mankar, N.; Sedani, S. Bromelain: A Potent Phytomedicine. Cureus 2022, 14, e27876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harasstani, O.A.; Moin, S.; Tham, C.L.; Liew, C.Y.; Ismail, N.; Rajajendram, R.; Harith, H.H.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Mohamad, A.S.; Sulaiman, M.R.; et al. Flavonoid combinations cause synergistic inhibition of proinflammatory mediator secretion from lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Inflamm. Res. 2010, 59, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abohashem, R.S.; Ahmed, H.H.; Sayed, A.H.; Effat, H. Primary Protection of Diosmin against Doxorubicin Cardiotoxicity via Inhibiting Oxido-Inflammatory Stress and Apoptosis in Rats. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 82, 1353–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñiz-Alquicira, A.X.; Zapata-Arenas, A.; Bustamante-García, R.; Gómez-Martínez, A.E.; Carballo-Villalobos, A.I. Role of carbonic anhydrase in the anti-inflammatory mechanism of diosmin and hesperidin in rats. Vet. Mex. 2025, 12, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-S.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, K.-A. A Comparative Study of Hesperetin, Hesperidin and Hesperidin Glucoside: Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antibacterial Activities In Vitro. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, R.E.; Ali, D.E.; El-Shiekh, R.A.; El-Alfy, A.N.; Hafeez, M.S.; Reda, A.M.; Fayek, N.M. Therapeutic applications of natural products in the management of venous diseases: A comprehensive review. Inflammopharmacology 2025, 33, 1673–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woroń, J. Drugs containing extracts from Ruscus in chronic renal disease therapy—What’s new we know about their effects? Pol. Przegl. Chir. 2022, 94, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocera, R.; Eletto, D.; Santoro, V.; Parisi, V.; Bellone, M.L.; Izzo, M.; Tosco, A.; Dal Piaz, F.; Donadio, G.; De Tommasi, N. Design of an Herbal Preparation Composed by a Combination of Ruscus aculeatus L. and Vitis vinifera L. Extracts, Magnolol and Diosmetin to Address Chronic Venous Diseases through an Anti-Inflammatory Effect and AP-1 Modulation. Plants 2023, 12, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.B.; Lee, J.T.; Park, H.R.; Kim, J.B. Medicinal Effects of Bromelain (Ananas comosus) Targeting Oral Environment as an Anti-oxidant and Anti-inflammatory Agent. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 6, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshi, G.D.; Rangwala, Z.S.; Chauhan, A.R. Systemic enzyme therapy in chronic venous disease: A review. Int. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2021, 9, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Ling, J.; Lin, H.; Chen, J. Use of Caco-2 cell monolayers to study drug absorption and metabolism. In Optimization in Drug Discovery: In Vitro Methods, 1st ed.; Yan, Z., Caldwell, G., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes-Pinto, D.; Bastianetto, P.; Cavalcanti Braga Lyra, L.; Kikuchi, R.; Kabnick, L. Endovenous laser ablation of the great saphenous vein comparing 1920-nm and 1470-nm diode laser. Int. Angiol. 2016, 35, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pfisterer, L.; König, G.; Hecker, M.; Korff, T. Pathogenesis of varicose veins—Lessons from biomechanics. Vasa 2014, 43, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.J.; Wu, Z.Y.; Nie, X.W.; Bian, J.S. Role of endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: The link between inflammation and hydrogen sulfide. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 10, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makó, V.; Czúcz, J.; Weiszhár, Z.; Herczenik, E.; Matkó, J.; Prohászka, Z.; Cervenak, L. Proinflammatory activation pattern of human umbilical vein endothelial cells induced by IL-1β, TNF-α, and LPS. Cytom. Part A 2010, 77, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcaro, G.; Dugall, M.; Luzzi, R.; Corsi, M.; Ledda, A.; Ricci, A.; Pellegrini, L.; Cesarone, M.R.; Hosoi, M.; Errichi, B.M.; et al. Management of Varicose Veins and Chronic Venous Insufficiency in a Comparative Registry with Nine Venoactive Products in Comparison with Stockings. Int. J. Angiol. 2017, 26, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergan, J.J.; Rattner, Z. Endovenous therapy--2005. Acta Chir Belg 2005, 105, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Moon, K.M.; Kim, C.Y. Tight Junction in the Intestinal Epithelium: Its Association with Diseases and Regulation by Phytochemicals. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 2645465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, X.W.; Zheng, H.Z.; Wang, R.; Chen, H.; Xiao, J.X.; Zheng, B.; Liu, S.L.; Ding, Y.T. Ameliorative Effects of Peptides Derived from Oyster (Crassostrea gigas) on Immunomodulatory Function and Gut Microbiota Structure in Cyclophosphamide-Treated Mice. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerges, S.H.; Wahdan, S.A.; Elsherbiny, D.A.; El-Demerdash, E. Pharmacology of diosmin, a citrus flavone glycoside: An updated review. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2022, 47, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maria das Graças, C.; Cyrino, F.Z.; de Carvalho, J.J.; Blanc-Guillemaud, V.; Bouskela, E. Protective effects of micronized purified flavonoid fraction (MPFF) on a novel experimental model of chronic venous hypertension. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2018, 55, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaschek, W. Natural products as lead compounds for sodium glucose cotrans-porter (SGLT) inhibitors. Planta Medica 2017, 83, 985–993. [Google Scholar]
- Kerimi, A.; Gauer, J.S.; Crabbe, S.; Cheah, J.W.; Lau, J.; Walsh, R.; Cancalon, P.F.; Williamson, G. Effect of the flavonoid hesperidin on glucose and fructose transport, sucrase activity and glycaemic response to orange juice in a crossover trial on healthy volunteers. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 121, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdiya, R.; Banu, Z.; Rahman, A. Hesperidin: A Comprehensive review of its health benefits and therapeutic potential. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 13, 1835. [Google Scholar]
- Raffetto, J.D.; Mannello, F. Pathophysiology of chronic venous disease. Int. Angiol. 2014, 33, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, N.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Qiu, Y.; Gong, Y.; Yin, L.; Qiu, Q.; Wu, X. Diosmin alleviates retinal edema by protecting the blood-retinal barrier and reducing retinal vascular permeability during ischemia/reperfusion injury. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyers, C.M.; Miller, F.J. Endothelial dysfunction in chronic inflammatory diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 11324–11349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, Q.; Sun, G. Interaction between traditional Chinese medicine and anticoagulant/antiplatelet drugs. Curr. Drug Metab. 2019, 20, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, E.; Guex, J.J.; Puskas, A.; Scuderi, A.; Fernandez Quesada, F.; Coordinators, V. Epidemiology of chronic venous disorders in geographically diverse populations: Results from the Vein Consult Program. Int. Angiol. J. Int. Union Angiol. 2012, 31, 105–115. [Google Scholar]
- Bouskela, E. Effects of Ruscus extract on the microcirculation are mediated by muscarinic receptors. In Proceedings of the 16th Annual European Venous Forum, 16th Annual European Venous Forum, St. Petersburg, Russia, 2–4 July 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, M.; Conti, V.; Damato, A.; Ambrosio, M.; Puca, A.A.; Sciarretta, S.; Frati, G.; Vecchione, C.; Carrizzo, A. Targeting nitric oxide with natural derived compounds as a therapeutic strategy in vascular diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 7364138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totzeck, M.; Rassaf, T. Dietary Flavonoids as Modulators of NO Bioavailability in Acute and Chronic Cardiovascular Diseases. In Nitrite and Nitrate in Human Health and Disease; Bryan, N., Loscalzo, J., Eds.; Nutrition and Health; Humana Press: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliu, E.; Brailoiu, G.C.; Mallilankaraman, K.; Wang, H.; Madesh, M.; Undieh, A.S. Intracellular endothelin type B receptor-driven Ca2+ signal elicits nitric oxide production in endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 41023–41031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, N.; Förstermann, U.; Li, H. Implication of eNOS uncoupling in cardio-vascular disease. React. Oxyg. Species 2017, 3, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, M.P.; Boesen, E.I.; Pollock, D.M. Contrasting actions of endothelin ETA and ETB receptors in cardiovascular disease. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 47, 731–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostov, K. The causal relationship between endothelin-1 and hypertension: Focusing on endothelial dysfunction, arterial stiffness, vascular remodeling, and blood pressure regulation. Life 2011, 11, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrashev, H.; Abrasheva, D.; Nikolov, N.; Ananiev, J.; Georgieva, E. A Sys-tematic Review of Endothelial Dysfunction in Chronic Venous Disease—Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Shear Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldo, M.; Wójciak-Kosior, M.; Sowa, I.; Kocki, J.; Bogucki, J.; Zubilewicz, T.; Karakuła, W.; Bogucka-Kocka, A. Monitoring of Endostatin, TNF-a VEGFs, MMP-9, and Cathepsin-L during Three Months of Diosmin Treatment in Patients with Chronic Venous Disease (CVD). Acta Angiol. 2019, 25, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoffersson, G.; Vågesjö, E.; Vandooren, J.; Lidén, M.; Massena, S.; Reinert, R.B.; Brissova, M.; Powers, A.C.; Opdenakker, G.; Phillipson, M. VEGF-A recruits a proangiogenic MMP-9-delivering neutrophil subset that induces angiogenesis in transplanted hypoxic tissue. Blood 2012, 120, 4653–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q. Research Progress of Flavonoids Regulating Endothelial Function. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwozdzinski, L.; Bernasinska-Slomczewska, J.; Hikisz, P.; Wiktorowska-Owczarek, A.; Kowalczyk, E.; Pieniazek, A. The Effect of Diosmin, Escin, and Bromelain on Human Endothelial Cells Derived from the Umbilical Vein and the Varicose Vein—A Preliminary Study. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreca, M.M.; Raimondo, S.; Conigliaro, A.; Siragusa, S.; Napolitano, M.; Alessandro, R.; Corrado, C. The Combination of Natural Compounds Escin–Bromelain–Ginkgo Biloba–Sage Miltiorrhiza (EBGS) Reduces Platelet Adhesion to TNFα-Activated Vascular Endothelium through FAK Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanscheidt, W.; Jost, V.; Wolna, P.; Lücker, P.W.; Müller, A.; Theurer, C.; Patz, B.; Grützner, K.I. Efficacy and safety of a butcher’s broom preparation (Ruscus aculeatus L. extract) compared to placebo in patients suffering from chronic venous insufficiency. Arzneimittelforschung 2002, 52, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakkos, S.K.; Allaert, F.A. Efficacy of Ruscus extract, HMC and vitamin C, constituents of Cyclo 3 fort®, on improving individual venous symptoms and edema: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trials. Int. Angiol. 2017, 36, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, D.F.P.; Da Silva, F.R.P.; Vasconcelos, A.C.C.G.; Alves, E.H.P.; Junior, P.V.D.O.; De Oliveira, J.S. Bromelain: A potential strategy for the adjuvant treatment of periodontitis. Dent. Hypotheses 2016, 7, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, A.; Kramer, J.; de Souza Cristiane, C.; Lehr, C.M. In vitro–in vivo correlation: Shades on some non-conventional dosage forms. Dissolut. Technol. 2015, 22, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójciak, M.; Feldo, M.; Borowski, G.; Kubrak, T.; Płachno, B.J.; Sowa, I. Antioxidant Potential of Diosmin and Diosmetin against Oxidative Stress in Endothelial Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 8232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbruch, M.; Nunes, C.; Gama, R.; Kaufman, R.; Gama, G.; Suchmacher Neto, M.; Nigri, R.; Cytrynbaum, N.; Brauer Oliveira, L.; Bertaina, I.; et al. Is nonmicronized diosmin 600 mg as effective as micronized diosmin 900 mg plus hesperidin 100 mg on chronic venous disease symptoms? Results of a noninferiority study. Int. J. Vasc. Med. 2020, 2020, 4237204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusuma, H.S.W.; Tiono, H.; Onggowidjaja, P.; Obeng, S.S.; Widowati, W.; Wahyuni, C.D.; Rizal, R. Anti-inflammatory Activities of Pineapple (Ananas comosus) Core Extract in Lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264. 7 Cell Line. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Emerging Issues in Technology, Engineering and Science, Bandung, Indonesia, 14–15 February 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galla, R.; Grisenti, P.; Farghali, M.; Saccuman, L.; Ferraboschi, P.; Uberti, F. Ovotransferrin Supplementation Improves the Iron Absorption: An In Vitro Gastro-Intestinal Model. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uberti, F.; Morsanuto, V.; Ruga, S.; Galla, R.; Farghali, M.; Notte, F.; Bozzo, C.; Magnani, C.; Nardone, A.; Molinari, C. Study of Magnesium Formulations on Intestinal Cells to Influence Myometrium Cell Relaxation. Nutrients 2020, 12, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceriotti, L.; Meloni, M. La valutazione dell’assorbimento intestinale in vitro. L’integratore Nutr. 2014, 17, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Q.; Li, D.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, W.; Zhou, G.; Wen, J. Enhanced uptake and transport of (+)-catechin and (−)-epigallocatechin gallate in niosomal formulation by human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 2157–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Song, J.; Shi, X.; Miao, S.; Li, Y.; Wen, A. Absorption and metabolism characteristics of rutin in caco-2 cells. Sci. World J. 2013, 13, 382350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uberti, F.; Lattuada, D.; Morsanuto, V.; Nava, U.; Bolis, G.; Vacca, G.; Squarzanti, D.F.; Cisari, C.; Molinari, C. Vitamin D protects human endothelial cells from oxidative stress through the autophagic and survival pathways. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felice, F.; Belardinelli, E.; Frullini, A.; Santoni, T.; Imbalzano, E.; Di Stefano, R. Effect of aminaphtone on in vitro vascular permeability and capillary-like maintenance. Phlebology 2018, 33, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uberti, F.; Morsanuto, V.; Ghirlanda, S.; Molinari, C. Iron Absorption from Three Commercially Available Supplements in Gastrointestinal Cell Lines. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fda.Gov. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/117974/download (accessed on 4 June 2024).
- Ema.Eu. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-m9-biopharmaceutics-classification-system-based-biowaivers-step-2b-first-version_en.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2024).
- Ema.europa.eu. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-m9-biopharmaceutics-classification-system-based-biowaivers-step-5_en.pdf (accessed on 18 June 2025).
- Song, P.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, J.; Cui, X. Mechanism of the intestinal absorption of six flavonoids from Zizyphi spinosi semen across caco-2 cell monolayer model. Curr. Drug Metab. 2020, 21, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Breemen, R.B.; Li, Y. Caco-2 cell permeability assays to measure drug absorption. Expert. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2005, 1, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Z.; Ye, Z.; Hauck, C.; Murphy, P.A.; Mc Coy, J.A.; Widrlechne, M.P.; Reddy, M.B.; Hendrich, S. Permeability of rosmarinic acid in Prunella vulgaris and ursolic acid in Salvia officinalis extracts across Caco-2 cell monolayers. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sánchez, A.; Borrás-Linares, I.; Barrajón-Catalán, E.; Arráez-Román, D.; González-Álvarez, I.; Ibáñez, E.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Bermejo, M.; Micol, V. Evaluation of the intestinal permeability of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) extract polyphenols and terpenoids in Caco-2 cell monolayers. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.C.; Peng, C.C.; Chang, C.H.; Huang, S.H.; Chyau, C.C. Extraction of Antioxidant Components from Bidens pilosa Flowers and Their Uptake by Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells. Molecules 2013, 18, 1582–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galkin, A.; Tammela, P. Natural Product–Drug Interactions and Their Evaluation Using a Caco-2 Cell Culture Model. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2023, 18, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, S.; Alvarez, S.; Majumder, K. Transport of Dietary Anti-Inflammatory Peptide, γ-Glutamyl Valine (γ-EV), across the Intestinal Caco-2 Monolayer. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, Y.; Hagiwara, K.; Shimizu, M. Transepithelial transport of fluorescein in Caco-2 cell monolayers and use of such transport in in vitro evaluation of phenolic acid availability. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 2449–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsanuto, V.; Galla, R.; Molinari, C.; Uberti, F. A New Palmitoylethanolamide form Combined with Antioxidant Molecules to Improve Its Effectivess on Neuronal Aging. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galla, R.; Ruga, S.; Aprile, S.; Ferrari, S.; Brovero, A.; Grosa, G.; Molinari, C.; Uberti, F. New Hyaluronic Acid from Plant Origin to Improve Joint Protection-An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-García, D.; Juarez-Moreno, K.; Calderón-Osuna, I.; Navarro, P.; Hirata, G.A. Nanotoxicological study of downconversion Y2O3: Eu3+ luminescent nanoparticles functionalized with folic acid for cancer cells bioimaging. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2020, 108, 2396–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.P.; Bayir, H.; Belousov, V.; Chang, C.J.; Davies, K.J.A.; Davies, M.J.; Dick, T.P.; Finkel, T.; Forman, H.J.; Janssen-Heininger, Y.; et al. Guidelines for measuring reactive oxygen species and oxidative damage in cells and in vivo. Nat. Metab. 2022, 4, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uberti, F.; Trotta, F.; Cavalli, R.; Galla, R.; Caldera, F.; Ferrari, S.; Mulè, S.; Brovero, A.; Molinari, C.; Pagliaro, P.; et al. Enhancing Vitamin D3 Efficacy: Insights from Complexation with Cyclodextrin Nanosponges and Its Impact on Gut-Brain Axes in Physiology and IBS Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X. Role of glucose metabolism and ATP in maintaining PINK1 levels during Parkin-mediated mitochondrial damage responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Galla, R.; Mulè, S.; Uberti, F. Analysis of the Beneficial Effects of Probiotics on the Gut-Prostate Axis Using Prostatic Co-Culture Model. Foods 2024, 13, 3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulè, S.; Ferrari, S.; Rosso, G.; Galla, R.; Battaglia, S.; Curti, V.; Molinari, C.; Uberti, F. The Combined Effect of Green Tea, Saffron, Resveratrol, and Citicoline against Neurodegeneration Induced by Oxidative Stress in an. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2024, 2024, 7465045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, T.; Iwasaki, K.; Matsuoka, M.; Morioka, Y.; Matsubara, S.; Kondo, E.; Iwasaki, N. The alterations in nerve growth factor concentration in plasma and synovial fluid before and after total knee arthroplasty. Sci rep 2024, 14, 8943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galla, R.; Ferrari, S.; Miletto, I.; Mulè, S.; Uberti, F. In Vitro Neuroprotective Effects of a Mixed Extract of Bilberry, Centella asiatica, Hericium erinaceus, and Palmitoylethanolamide. Foods 2025, 14, 2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Tested Dosage |
|---|---|
| 90:10 mixture of Diosmin/Hesperidin | 500 mg |
| Bromelain 2500 GDU/g | 75 mg |
| Ruscus aculeatus L. | 37.5 mg |
| Ananas comosus L. | 5 mg |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galla, R.; Mulè, S.; Ferrari, S.; Molinari, C.; Uberti, F. Combined Effects of Diosmin, Hesperidin, Ruscus aculeatus, Ananas comosus, and Bromelain on Endothelial Function and Gut Barrier Integrity In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10538. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110538
Galla R, Mulè S, Ferrari S, Molinari C, Uberti F. Combined Effects of Diosmin, Hesperidin, Ruscus aculeatus, Ananas comosus, and Bromelain on Endothelial Function and Gut Barrier Integrity In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10538. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110538
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalla, Rebecca, Simone Mulè, Sara Ferrari, Claudio Molinari, and Francesca Uberti. 2025. "Combined Effects of Diosmin, Hesperidin, Ruscus aculeatus, Ananas comosus, and Bromelain on Endothelial Function and Gut Barrier Integrity In Vitro" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10538. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110538
APA StyleGalla, R., Mulè, S., Ferrari, S., Molinari, C., & Uberti, F. (2025). Combined Effects of Diosmin, Hesperidin, Ruscus aculeatus, Ananas comosus, and Bromelain on Endothelial Function and Gut Barrier Integrity In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10538. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110538







