Molecular Crosstalk of Vitamin D3 with cGAS–STING and BDNF Pathways in a Rat Model of Chronic Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Result
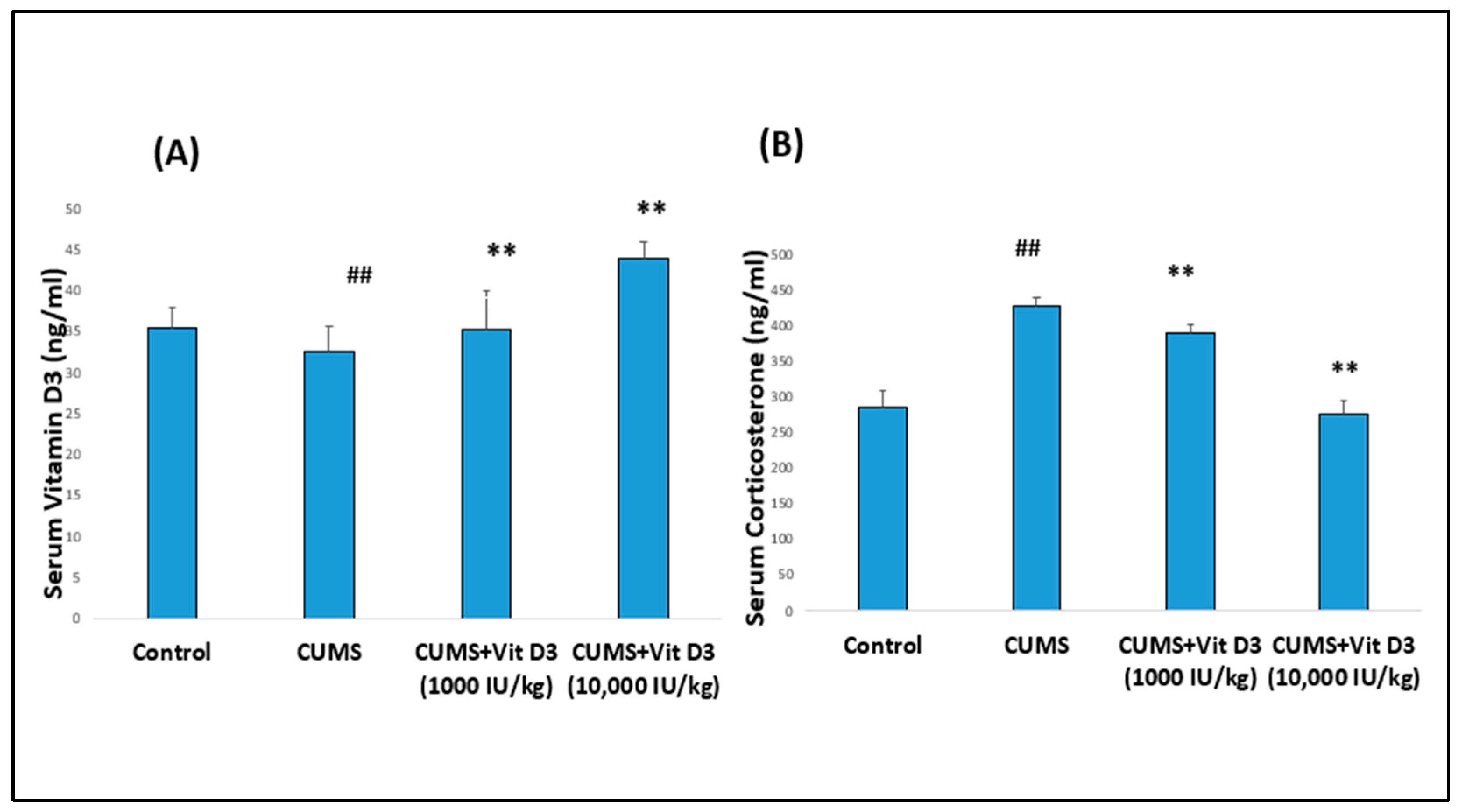
2.1. Body Weight Changes, Serum Vitamin D3, and Corticosterone Levels in Different Groups
2.2. Vitamin D3 Attenuates CUMS-Induced Activation of the cGAS–STING Pathway in the Hippocampus
2.3. Vitamin D3 Suppresses CUMS-Induced Upregulation of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in the Hippocampus
2.4. Vitamin D3 Reduces Microglial Activation Marked by Iba1 Expression in CUMS-Exposed Rats
2.5. Vitamin D Receptor (VDR) Expression Is Modulated in Response to CUMS and Vitamin D3
2.6. Vitamin D3 Restores BDNF Expression in the Hippocampus
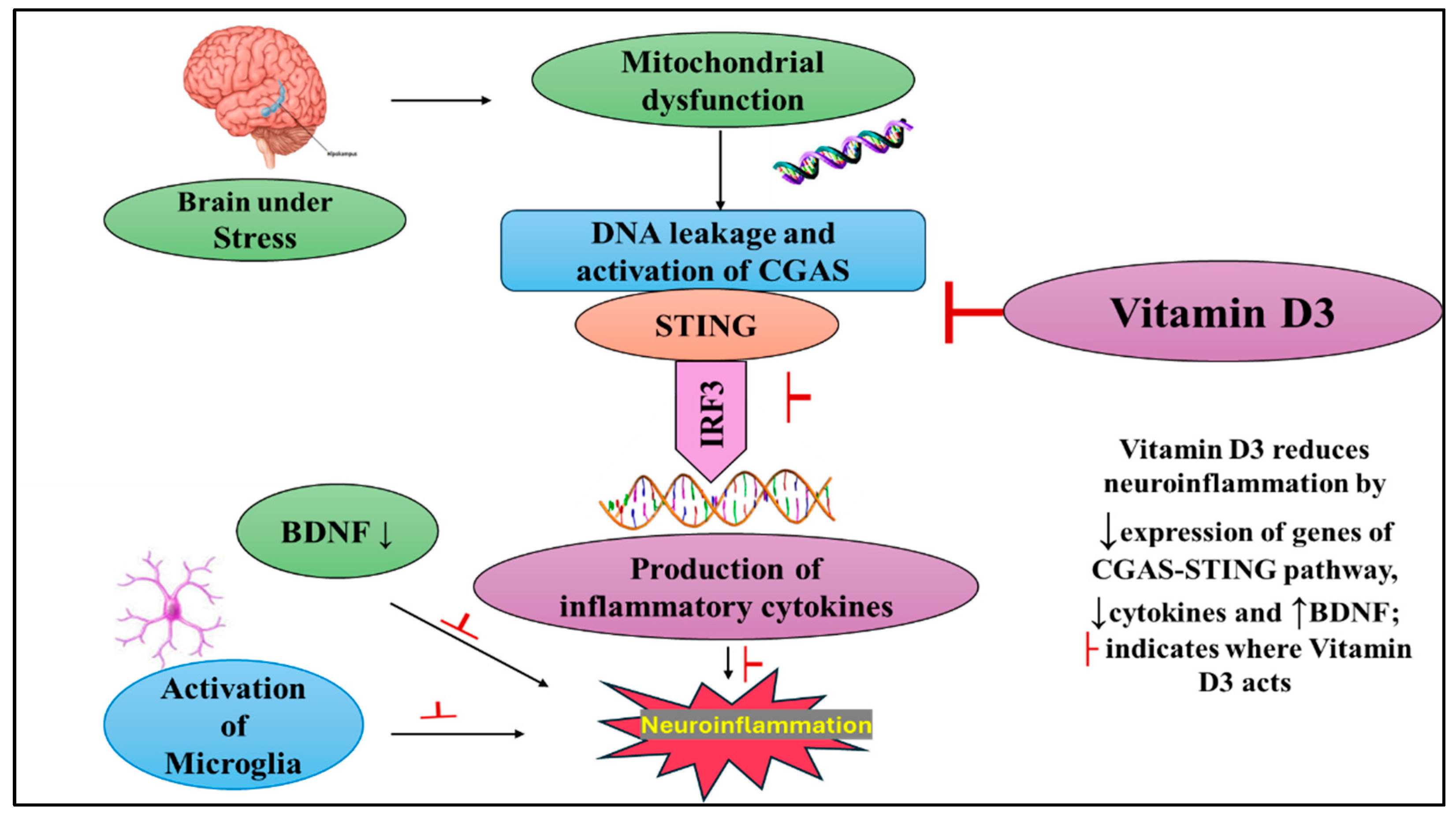
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals, Study Design, and Ethics
4.1.1. Animal Groups
4.1.2. Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress (CUMS) Induction: Protocol
4.1.3. Vitamin D3 Administration
4.2. Body Weight Measurement
4.3. Sample Collection
4.4. Serum Analysis
4.4.1. Serum Vitamin D3
4.4.2. Serum Corticosterone
4.5. Gene Expression Analysis by Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.5.1. Tissue Source
4.5.2. RNA Extraction
4.5.3. Reverse Transcription
4.5.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CUMS | Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress |
| cGAS | Cyclic GMP–AMP Synthase |
| STING | Stimulator of Interferon Genes |
| TBK1 | TANK-binding kinase 1 |
| IRF3 | Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-Gamma |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-kappa B |
References
- Rehm, J.; Shield, K.D. Global Burden of Disease and the Impact of Mental and Addictive Disorders. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2019, 21, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Yu, W.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xia, M.; Li, B. Major Depressive Disorder: Hypothesis, Mechanism, Prevention and Treatment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.; Li, X.; Qiang, M.; Zeng, G.; He, Q.; Liu, X.; et al. Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Induces Anxiety-like Behavior in Female C57BL/6N Mice, Accompanied by Alterations in Inflammation and the Kynurenine Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism. Front. Neurosci. 2025, 19, 1556744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markov, D.D.; Novosadova, E.V. Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Model of Depression: Possible Sources of Poor Reproducibility and Latent Variables. Biology 2022, 11, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, T.; Shively, C.A.; Li, X.; Jiang, X.; Neigh, G.N.; Yin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, L.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, M.; et al. Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Produces Depressive-like Behavior, Hypercortisolemia, and Metabolic Dysfunction in Adolescent Cynomolgus Monkeys. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 9, Erratum in Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 126. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-021-01251-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numakawa, T.; Kajihara, R. The Role of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor as an Essential Mediator in Neuronal Functions and the Therapeutic Potential of Its Mimetics for Neuroprotection in Neurologic and Psychiatric Disorders. Molecules 2025, 30, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sălcudean, A.; Bodo, C.-R.; Popovici, R.-A.; Cozma, M.-M.; Păcurar, M.; Crăciun, R.-E.; Crisan, A.-I.; Enatescu, V.-R.; Marinescu, I.; Cimpian, D.-M.; et al. Neuroinflammation—A Crucial Factor in the Pathophysiology of Depression—A Comprehensive Review. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Li, L.; Luo, J. Brain Endothelial Cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase (cGAS)–Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING) Signaling Pathway in Aging and Neurodegeneration. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 20, 2005–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xue, L.; Xiao, J.; Li, P.; Xue, W.; Li, C.; Guo, H.; Chen, Y. The Effect of the Cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase-Stimulator of Interferon Genes Signaling Pathway on Organ Inflammatory Injury and Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1033982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Li, J.; Feng, Z. Significance of the cGAS-STING Pathway in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourtzi, N.; Sertedaki, A.; Charmandari, E. Glucocorticoid Signaling and Epigenetic Alterations in Stress-Related Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Li, K.; Zou, W.; Wang, L. The Central Role of Microglia in Major Depressive Disorder and Its Potential as a Therapeutic Target. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2025, 19, 1598178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopperton, K.E.; Mohammad, D.; Trépanier, M.O.; Giuliano, V.; Bazinet, R.P. Markers of Microglia in Post-Mortem Brain Samples from Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Jiang, J.; Tan, Y.; Chen, S. Microglia in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Mechanism and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, S.; Manohar, K.; Shariff, A.; Kinattingal, N.; Wani, S.U.D.; Alshehri, S.; Imam, M.T.; Shakeel, F.; Krishna, K.L. Omega-3 Fatty Acids Supplementation in the Treatment of Depression: An Observational Study. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.L.; Hassan, S.T.; Jamil, S.; Fatima, W.; Fatima, M. Nutritional Interventions in Depression: The Role of Vitamin D and Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Neuropsychiatric Health. Clin. Nutr. 2025, 45, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ramadhan, F.R.; Abulmeaty, M.M.A.; Alquraishi, M.; Razak, S.; Alhussain, M.H. Effect of Vitamin D3 on Depressive Behaviors of Rats Exposed to Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlGhamdi, S.A. Effectiveness of Vitamin D on Neurological and Mental Disorders. Diseases 2024, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasoń, W.; Jantas, D.; Leśkiewicz, M.; Regulska, M.; Basta-Kaim, A. The Vitamin D Receptor as a Potential Target for the Treatment of Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases Such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases: A Narrative Review. Cells 2023, 12, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, S.J.; Lee, H.; Ahn, Y.M. Serum Vitamin D Concentrations Are Associated With Depressive Symptoms in Men: The Sixth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2014. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzek, D.; Kołota, A.; Lachowicz, K.; Skolmowska, D.; Stachoń, M.; Głąbska, D. Association between Vitamin D Supplementation and Mental Health in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Ma, B.; Xiao, M.; Ren, Q.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, Z. Vitamin D Modified DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice via STING Signaling Pathway. Biology 2025, 14, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, V.; Kar, S.K.; Suthar, N.; Nebhinani, N. Vitamin D and Depression: A Critical Appraisal of the Evidence and Future Directions. Indian J. Psychol. Med. 2020, 42, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anaswaradev, A.; Joseph, A. Association between Depression and Vitamin D3 among the People Attending Private Clinic in Ernakulam, Kerala, India. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2025, 14, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Wang, Y.; Xie, H.; Li, R.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, B.; Du, J. 1,25(OH)2D3 Blocks IFNβ Production through Regulating STING in Epithelial Layer of Oral Lichen Planus. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 3751–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Sun, A.; Lin, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, X. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation from Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Mice Donors Affects Anxiety-like and Depression-like Behavior in Recipient Mice via the Gut Microbiota-Inflammation-Brain Axis. Stress 2019, 22, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.G.; Elias, E.; Orozco, A.; Robinson, S.A.; Manners, M.T. Chronic Stress-Induced Neuroinflammation: Relevance of Rodent Models to Human Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Rong, P. Mechanisms Underlying Antidepressant Effect of Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation on CUMS Model Rats Based on Hippocampal α7nAchR/NF-κB Signal Pathway. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Wu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, W.; Wan, C.; Yuan, N.; Chen, J.; Hao, W.; Mo, X.; Guo, X.; et al. Roles of Microglia in Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Depression and Their Therapeutics. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1193053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Li, W.; Chen, P.; Wang, L.; Bao, X.; Huang, R.; Liu, G.; Chen, X. Microglial NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Neuroinflammation and Therapeutic Strategies in Depression. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 19, 1890–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-M.; Hu, T.; Zhou, X.-N.; Zhang, T.; Guo, J.-H.; Wang, M.-Y.; Wu, Y.-L.; Su, W.-J.; Jiang, C.-L. The Involvement of NLRP3 Inflammasome in CUMS-Induced AD-like Pathological Changes and Related Cognitive Decline in Mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 112. Available online: https://jneuroinflammation.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12974-023-02791-0?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 9 September 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Tao, C.; Gao, X.; Wang, L.; Jiang, F.; Wang, C.; Fang, K.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Ge, J. BDNF-Related Imbalance of Copine 6 and Synaptic Plasticity Markers Couples With Depression-Like Behavior and Immune Activation in CUMS Rats. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Liang, L. Vitamin D3/Vitamin D Receptor Signaling Mitigates Symptoms of Post-Stroke Depression in Mice by Upregulating Hippocampal BDNF Expression. Neurosci. Res. 2021, 170, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Xu, L.; Qu, C.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J. Resveratrol Prevents Cognitive Deficits Induced by Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress: Sirt1/miR-134 Signalling Pathway Regulates CREB/BDNF Expression in Hippocampus In Vivo and In Vitro. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 349, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, D.; Lv, C.; Cao, L.; Yao, D.; Wu, Y.; Long, M.; Liu, N.; Jiang, P. Curcumin Attenuates Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress-Induced Depressive-Like Behaviors via Restoring Changes in Oxidative Stress and the Activation of Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Rats. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 9268083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducottet, C.; Griebel, G.; Belzung, C. Effects of the Selective Nonpeptide Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Receptor 1 Antagonist Antalarmin in the Chronic Mild Stress Model of Depression in Mice. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 27, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, D.; Elshopakey, G.E.; Albukhari, T.A.; Almehmadi, S.J.; Refaat, B.; Risha, E.F.; Mahgoub, H.A.; El-Boshy, M.E.; Abdelhamid, F.M. Vitamin D3 alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats by inhibiting hepatic oxidative stress and inflammation via the SREBP-1-c/ PPARα-NF-κB/IR-S2 signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1164512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BaSalamah, M.A.; Abdelghany, A.H.; El-Boshy, M.; Ahmad, J.; Idris, S.; Refaat, B. Vitamin D alleviates lead induced renal and testicular injuries by immunomodulatory and antioxidant mechanisms in rats. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhtiari-Dovvombaygi, H.; Izadi, S.; Zare Moghaddam, M.; Hashemzehi, M.; Hosseini, M.; Azhdari-Zarmehri, H.; Dinpanah, H.; Beheshti, F. Beneficial Effects of Vitamin D on Anxiety and Depression-like Behaviors Induced by Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress by Suppression of Brain Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in Rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2021, 394, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari-Zaer, A.; Hosseini, M.; Salmani, H.; Arab, Z.; Zareian, P. Vitamin D3 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive impairment in rats by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress. Life Sci. 2020, 253, 117703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Cage tilting at 45° for 24 h | Food deprivation for 24 h | Shaking the cage at 150 rpm for 1 h | Wet bedding for 24 h |
| Day 2 | Shaking the cage at 150 rpm for 1 h | Wet bedding for 24 h | Cage tilting at 45° for 24 h | Food deprivation for 24 h |
| Day 3 | Wet bedding for 24 h | Shaking the cage at 150 rpm for 1 h | Wet bedding for 24 h | Cage tilting at 45° for 24 h |
| Day 4 | Water deprivation for 24 h | Cage tilting at 45° for 24 h | Water deprivation for 24 h | Shaking the cage at 150 rpm for 1 h |
| Day 5 | Continuous light exposure for 24 h | Continuous light exposure for 24 h | Continuous light exposure for 24 h | Continuous light exposure for 24 h |
| Day 6 | Continuous light exposure for 24 h | Continuous light exposure for 24 h | Continuous light exposure for 24 h | Continuous light exposure for 24 h |
| Day 7 | Food deprivation for 24 h | Water deprivation for 24 h | Food deprivation for 24 h | Water deprivation for 24 h |
| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| CGAS | F-AAGATCCGCGTAGAAGGACGA |
| R-CTCCACGGTGACATCTGTATCT | |
| STING | F-TAGCACTTCACATAGCCTCGC |
| R-GAATGTGGGACTCATCTGGAG | |
| TBK1 | F-GCACATCAGGAAGGCACTCA |
| R-CTTGTAGAGGAACTGACCCTAG | |
| IRF3 | F-TTCAGGATCCCATGGAAGCATG |
| R-TTATTGGAGCAGCTGAGCTGG | |
| BDNF | F-AGGGAAATCTCCTGAGCCGA |
| R-TAATCCAATTTGCACGCCGC | |
| IFN-γ | F-ATTCATGAGCATCGCCAAGTTC |
| R-ATACTGCCTGCCTGAAGCTCTTGT | |
| TNF-α | F-AGATGTGGAACTGGCAGAGG |
| R-CCCATTTGGGAACTTCTCCT | |
| IL-6 | F-AGTTGCCTTCTTGGGACTGA |
| R-ACAGTGCATCATCGCTGTTC | |
| NF-κB | F-ACGATCTGTTTCCCCTCATCT |
| R-TGCTTCTCTCCCCAGGAATA | |
| Iba 1 | F-CCTGTATGGCTTTCCCATCAC |
| R-ATTAGAAGGTCCTCGGTCCCA | |
| VDR | F-GCCCCTCATAAAGTTCCAGGTG |
| R-GGATAGGCGGTCCTGAATGG | |
| GADPH | F-TGCACCACCAACTGCTTAGC |
| R-GGATGCAGGGATGATGATGTTCT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alrashed, M.M.; Tabassum, H.; Aldisi, D.; Abulmeaty, M.M.A. Molecular Crosstalk of Vitamin D3 with cGAS–STING and BDNF Pathways in a Rat Model of Chronic Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110436
Alrashed MM, Tabassum H, Aldisi D, Abulmeaty MMA. Molecular Crosstalk of Vitamin D3 with cGAS–STING and BDNF Pathways in a Rat Model of Chronic Stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110436
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlrashed, May M., Hajera Tabassum, Dara Aldisi, and Mahmoud M. A. Abulmeaty. 2025. "Molecular Crosstalk of Vitamin D3 with cGAS–STING and BDNF Pathways in a Rat Model of Chronic Stress" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110436
APA StyleAlrashed, M. M., Tabassum, H., Aldisi, D., & Abulmeaty, M. M. A. (2025). Molecular Crosstalk of Vitamin D3 with cGAS–STING and BDNF Pathways in a Rat Model of Chronic Stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110436






