Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Isoflavone Synthase (IFS) Gene Family, and Analysis of GgARF4-GgIFS9 Regulatory Module in Glycyrrhiza glabra
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Classification of IFS Gene Family Members
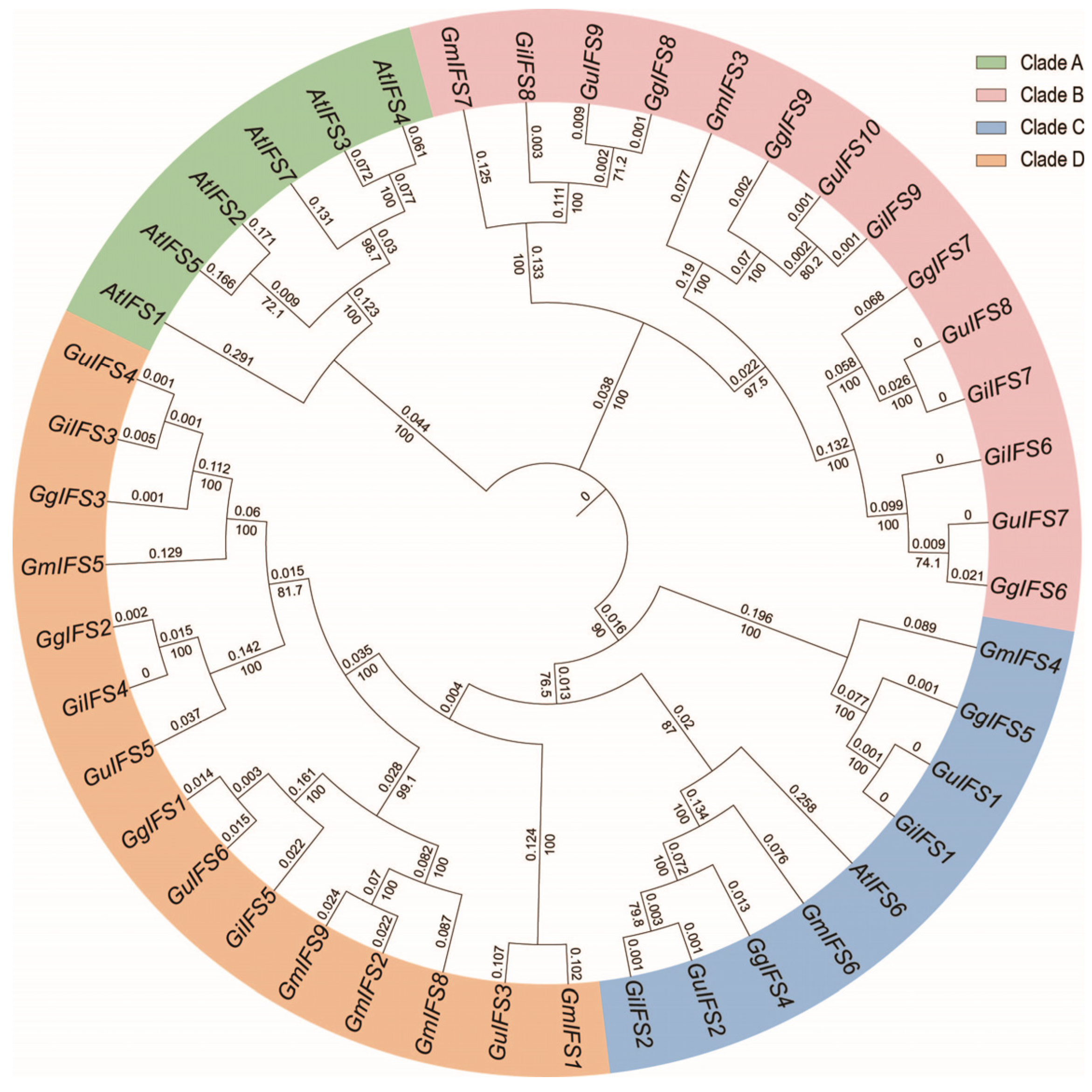
2.2. Phylogenetic Relations of the IFS Gene Family
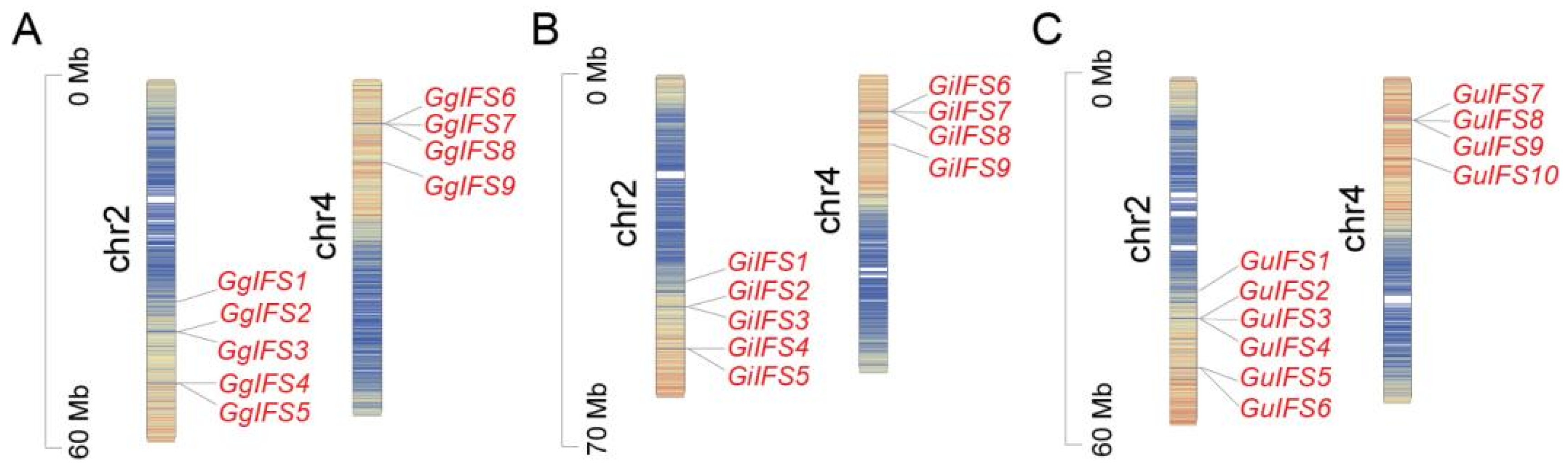
2.3. Chromosome Location of IFS Genes in Three Glycyrrhiza Species
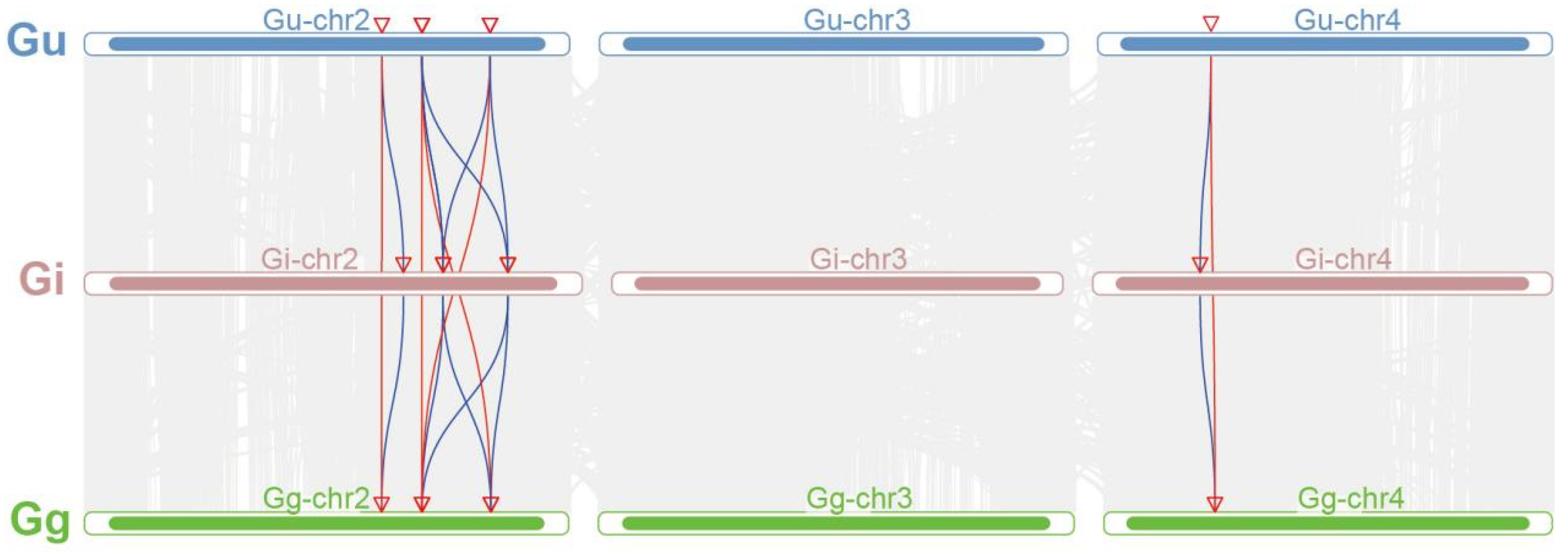
2.4. Analysis of Collinearity Relationships Among IFS Gene Families in Three Glycyrrhiza Species
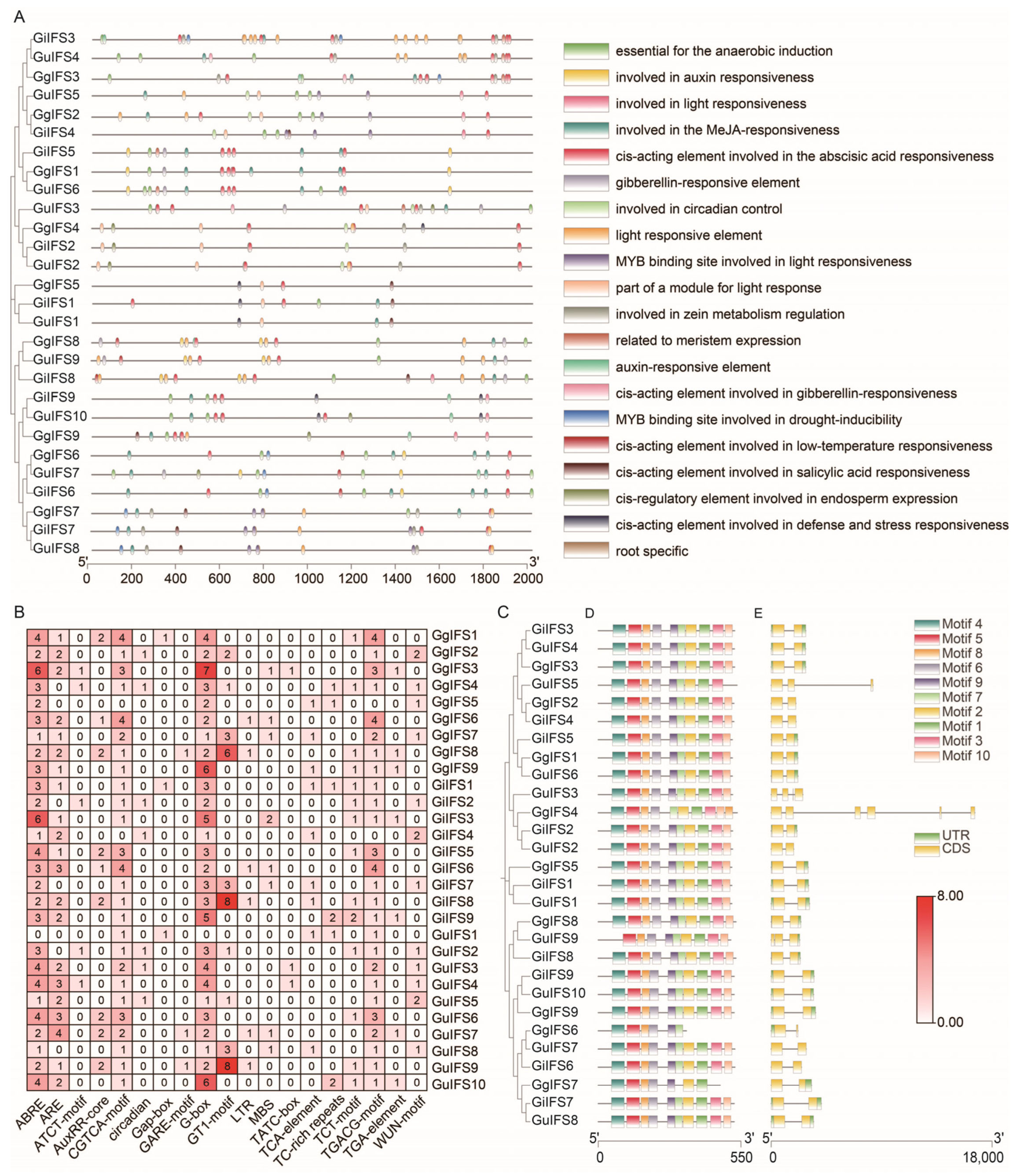
2.5. Analysis of Promoter Cis-Acting Elements, Conserved Motifs and Gene Structures of IFS Gene Family
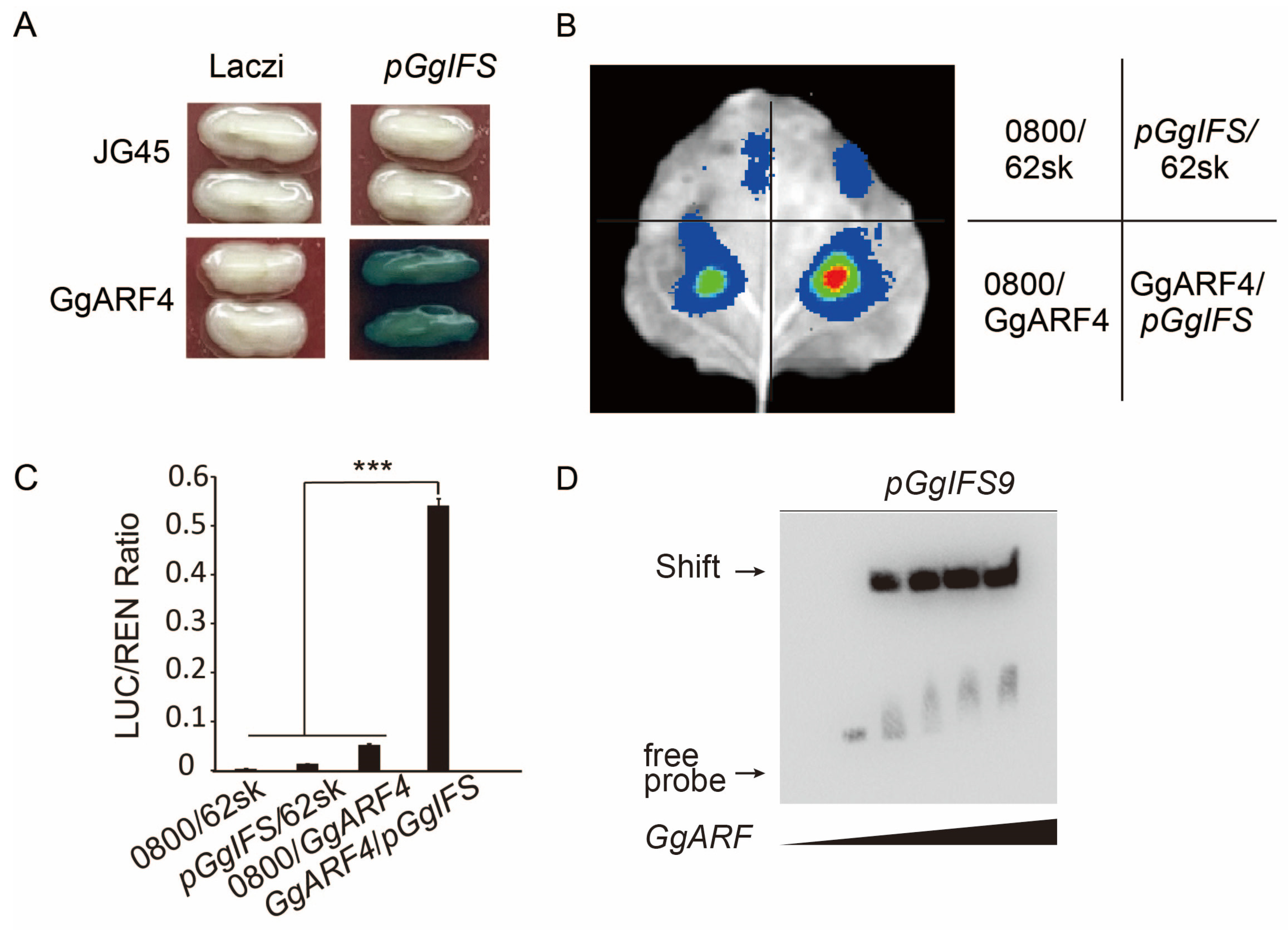
2.6. The GgARF4 Protein Positively Regulates Isoflavone Synthase GgIFS9 in G. glabra
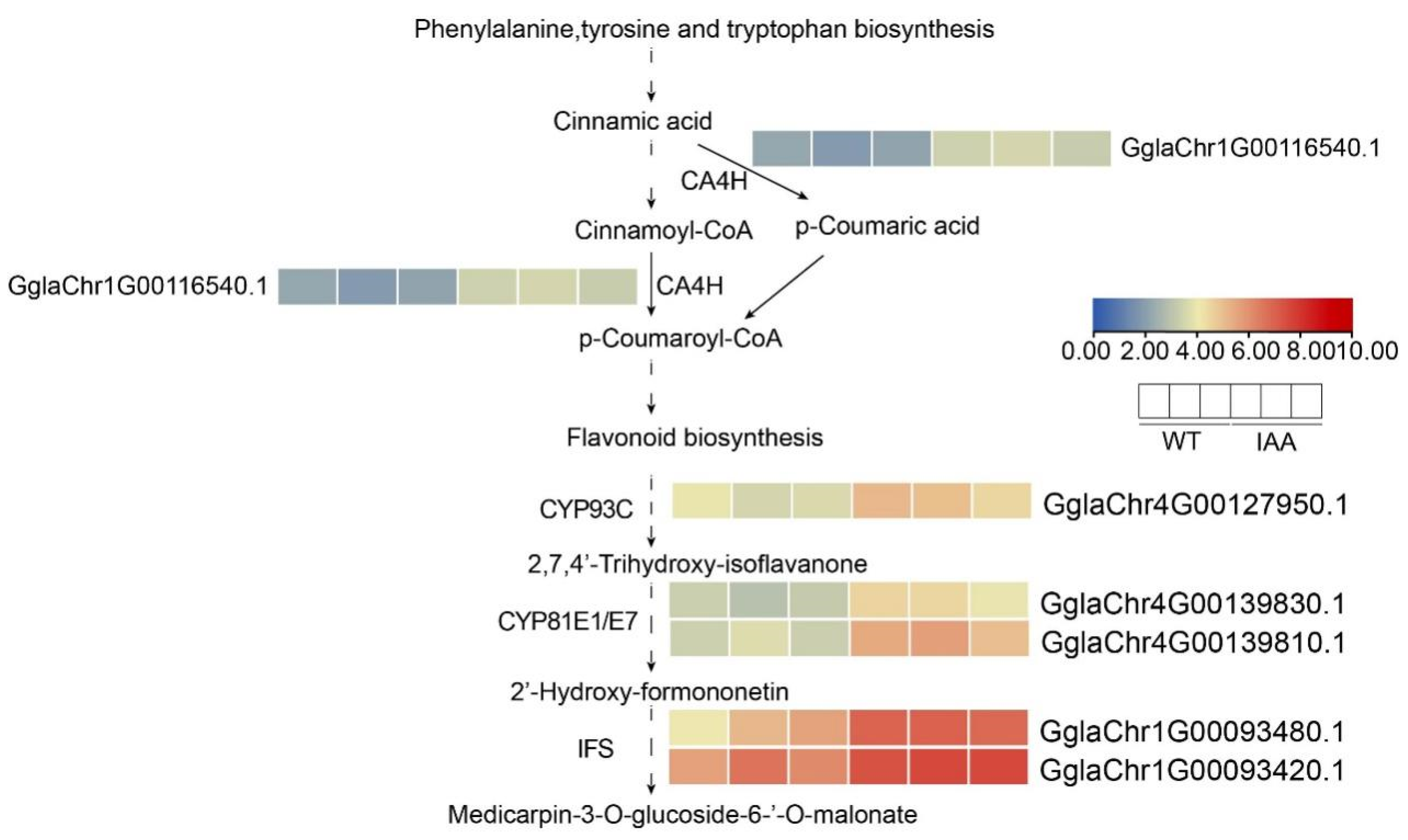
2.7. Transcriptome Sequencing Analysis and qRT-PCR Analysis of GgIFS Genes After IAA Treatment
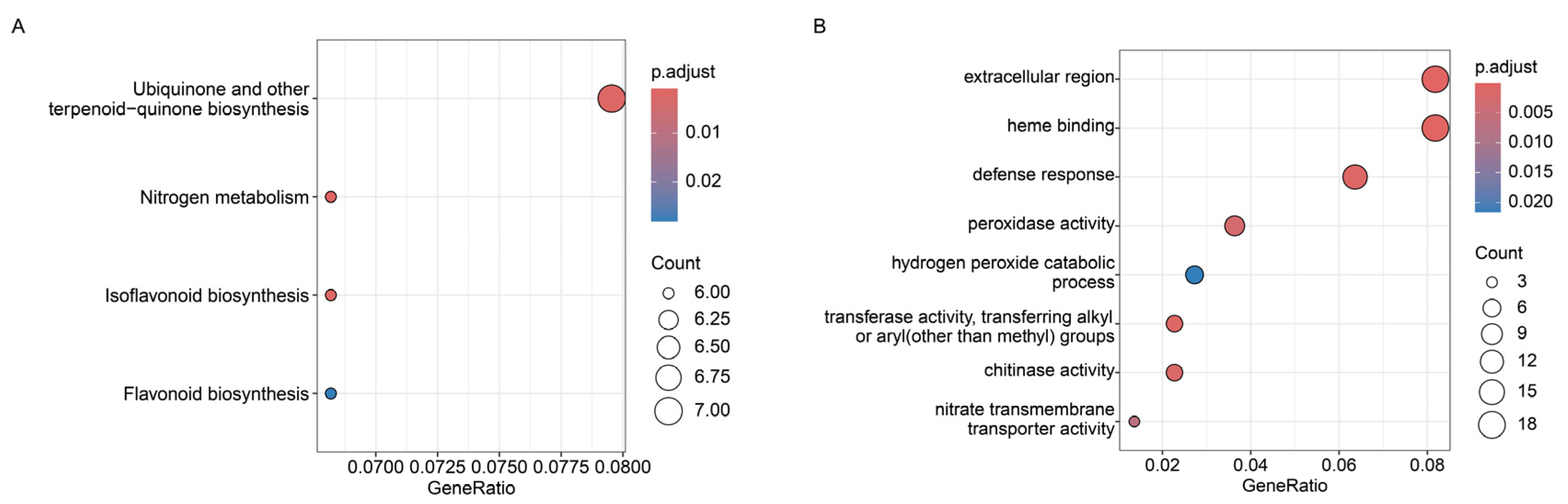
2.8. Expression Pattern of Up-Regulated Genes in the Transcriptome After IAA Treatment
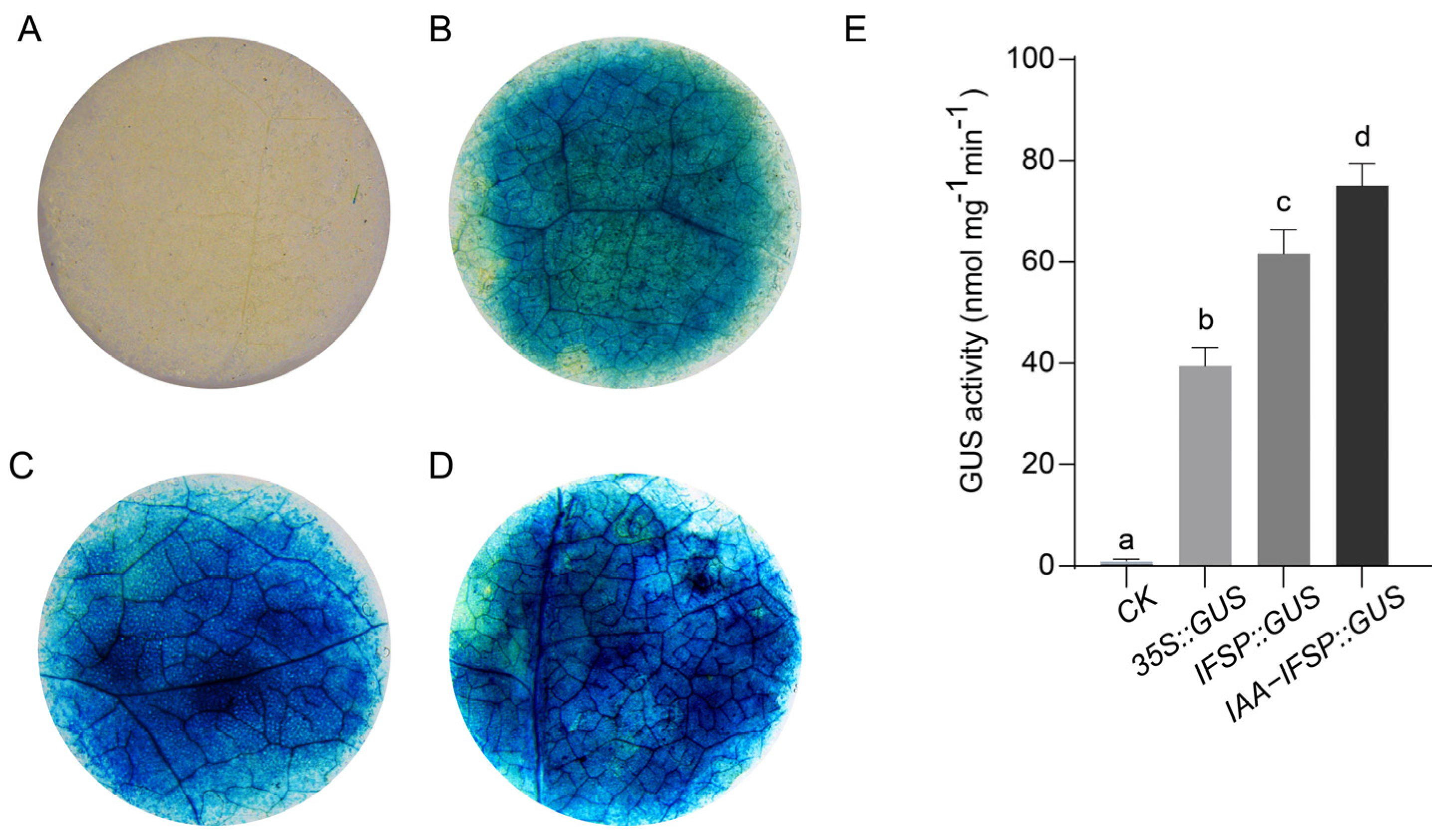
2.9. GUS Staining and GUS Activity of the GgIFS9 Promoter After IAA Treatment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification and Characterization of IFS Genes
4.2. Phylogenetic Tree Construction
4.3. Chromosome Distribution of IFS Genes in Three Glycyrrhiza Species
4.4. Gene Structure and Motif Analysis of the IFS Gene Family Members in Three Glycyrrhiza Species
4.5. The Analysis of IFS Promoter Genes in Three Glycyrrhiza Species
4.6. Synteny and Duplication Analysis
4.7. Yeast Library Screening and Y1H Assay
4.8. In Vivo Dual-Luciferase Assay
4.9. EMSA
4.10. RNA-Seq Analysis and qRT-PCR Analysis of GgIFS Genes
4.11. β-Glucuronidase (GUS) Staining and GUS Activity
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Nomura, T.; Fukai, T.; Akiyama, T. Chemistry of phenolic compounds of licorice (Glycyrrhiza species) and their estrogenic and cytotoxic activities. Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-B.; Wu, Y.; Wang, S.; Yi, L.; Qiu, R.; Zhou, H. Chemical constituents and chemotaxonomic study of Glycyrrhiza glabra L. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2020, 92, 104130. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Tian, X.; He, X.; Yang, Z.; Fang, W. Exogenous melatonin stimulated isoflavone biosynthesis in NaCl-stressed germinating soybean (Glycine max L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 185, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.T.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.H.; Sun, G.Z.; Yang, W.Y.; Liu, J. Effects of drought stress on biosynthesis of isoflavones in soybean seedling. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 3927–3934. [Google Scholar]
- Lozovaya, V.V.; Lygin, A.V.; Ulanov, A.V.; Nelson, R.L.; Dayde, J.; Widholm, J.M. Effect of Temperature and Soil Moisture Status during Seed Development on Soybean Seed Isoflavone Concentration and Composition. Crop Sci. 2005, 45, 1934–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhao, H.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, L.; Alotaibi, S.H.; Zhang, Y. Anti-human Glioma Cancer Potentials of Neobavaisoflavone as Natural Antioxidant Compound and Its Inhibition Profiles for Acetylcholinesterase and Butyrylcholinesterase Enzymes with Molecular Modeling and Spin Density Distributions Studies. J. Oleo Sci. 2022, 71, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Biersack, B.; Li, Y.; Bao, B.; Kong, D.; Ali, A.; Banerjee, S.; Sarkar, F.H. Perspectives on the role of isoflavones in prostate cancer. AAPS J. 2013, 15, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.Z.; Du, G.J.; Qi, L.W.; Calway, T.; He, T.C.; Du, W.; Yuan, C.S. Genistein induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via ATM/p53-dependent pathway in human colon cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Yang, W.; Bosland, M.C. Soy isoflavones and prostate cancer: A review of molecular mechanisms. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 140, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, S. Mechanisms of Action of Isoflavones in Cancer Prevention. In Bioactive Compounds and Cancer; Nutrition and Health; Milner, J.A., Romagnolo, D.F., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 633–670. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; An, Y.; Lv, C.; Ma, W.; Xi, Y.; Xiao, R. Dietary soybean isoflavones in Alzheimer’s disease prevention. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 27, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schreiner, M.; Mewis, I.; Huyskens-Keil, S.; Jansen, M.A.K.; Zrenner, R.; Winkler, J.B.; Krumbein, A. UV-B-Induced Secondary Plant Metabolites—Potential Benefits for Plant and Human Health. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2012, 31, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, S.; Sharma, I.; Kaur, N.; Pati, P.K. Auxin: A master regulator in plant root development. Plant Cell Rep. 2013, 32, 741–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Han, S.; Qi, Y. Advances in structure and function of auxin response factor in plants. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2023, 65, 617–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yin, F.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, X.; Yao, Y.; Ge, F.; Wang, W. Transcriptomics integrated with targeted metabolomics reveals endogenous hormone changes in tuberous root expansion of Pueraria. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Diao, R.; Wu, Z.; Wan, S.; Yang, S.; Li, X. Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analyses Reveal the Roles of Flavonoids and Auxin on Peanut Nodulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnafgui, W.; Hajlaoui, H.; Rizzo, V.; Muratore, G.; Eleuch, A. Priming with EDTA, IAA and Fe alleviates Pb toxicity in Trigonella Foneum graecum L. growth: Phytochemicals and secondary metabolites. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 356, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Feng, Y.; Rui, W.; Shi, Z.; Wu, L. Bioactive components of Glycyrrhiza uralensis mediate drug functions and properties through regulation of CYP450 enzymes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Křížová, L.; Dadáková, K.; Kašparovská, J.; Kašparovský, T. Isoflavones. Molecules 2019, 24, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakora, F.D.; Phillips, D.A. Diverse functions of isoflavonoids in legumes transcend anti-microbial definitions of phytoalexins. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 1996, 49, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Huang, Y.; Fau-Tang, Y.; Tang, Y. Genetic and metabolic engineering of isoflavonoid biosynthesis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 1293–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.G.; Kim, S.Y.; Song, H.S.; Lee, C.; Hur, H.G.; Kim, S.I.; Ahn, J.H. Cloning and expression of the isoflavone synthase gene (IFS-Tp) from Trifolium pratense. Mol. Cells 2003, 15, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.; Yu, O.; Lau, S.M.; O’Keefe, D.P.; Odell, J.; Fader, G.; McGonigle, B. Identification and expression of isoflavone synthase, the key enzyme for biosynthesis of isoflavones in legumes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 208–212, Erratum in Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overkamp, S.; Hein, F.; Barz, W. Cloning and characterization of eight cytochrome P450 cDNAs from chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) cell suspension cultures. Plant Sci. 2000, 155, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Shimada, N.; Akashi, T.; Aoki, T.; Ayabe, S. Induction of isoflavonoid pathway in the model legume Lotus japonicus: Molecular characterization of enzymes involved in phytoalexin biosynthesis. Plant Sci. 2000, 160, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, C.L.; Gijzen, M.; Qutob, D.; Dixon, R.A. Molecular characterization of the enzyme catalyzing the aryl migration reaction of isoflavonoid biosynthesis in soybean. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1999, 367, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajid, M.; Stone, S.R.; Kaur, P. Phylogenetic Analysis and Protein Modelling of Isoflavonoid Synthase Highlights Key Catalytic Sites towards Realising New Bioengineering Endeavours. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M. Too many transcription factors: Positive and negative interactions. New Biol. 1990, 2, 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.Y.; Yin, Q.G.; Liu, J.Y.; Jiang, W.B.; Di, S.K.; Pang, Y.Z. GmMYB58 and GmMYB205 are seed-specific activators for isoflavonoid biosynthesis in Glycine max. Plant Cell Rep. 2017, 36, 1889–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.L. Functional Analysis of Soybean bHLH Transcription Factors GmbHLH3 and GmPIF1; Jilin University: Changchun, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, S.; Li, R.; Xia, S.; Liu, Y.; Jin, D.; Xie, X.; Dhanbhadel, S.; Zhai, L.; Wang, J.; Li, X. Soybean CCA1-like MYB transcription factor GmMYB133 modulates isoflavonoid biosynthesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 507, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Lei, C.; Lu, W. Expression Analysis of IFSI Gene in Isoflavonoids Pathway in Soybean. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin. 2013, 28, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: A revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, A.W.; Bartel, B. Auxin: Regulation, action, and interaction. Ann. Bot. 2005, 95, 707–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Xia, Y.; Su, X.; Pang, Y. ARF2 positively regulates flavonols and proanthocyanidins biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 2022, 256, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Wang, N.; Xu, H.F.; Jiang, S.H.; Fang, H.C.; Su, M.Y.; ZHANG, Z.Y.; Zhang, T.L.; Chen, X.S. Auxin regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis through the Aux/IAA-ARF signaling pathway in apple. Hortic. Res. 2018, 5, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.R.; Ramirez, M.V.; Miller, N.D.; Vallabhaneni, P.; Keith Ray, W.; Helm, R.F.; Winkel, B.S.J.; Muday, G.K. Auxin and ethylene induce flavonol accumulation through distinct transcriptional networks. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 144–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, F. The regulatory network composed of phytohormones, transcription factors and non-coding RNAs is involved in the flavonoids biosynthesis of fruits. Hortic. Plant J. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Chen, X. Research progress of fruit color development in apple (Malus domestica Borkh.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 162, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.P.; Zhang, X.W.; Liu, Y.J.; Wang, X.F.; You, C.X.; Hao, Y.J. ABI5 regulates ABA-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis by modulating the MYB1-bHLH3 complex in apple. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 1460–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Hernandez, M.; Berardini, T.Z.; Chen, G.; Crist, D.; Doyle, A.; Huala, E.; Knee, E.; Lambrecht, M.; Miller, N.; Mueller, L.; et al. TAIR: A resource for integrated Arabidopsis data. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2002, 2, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.D.; Mistry, J.; Schuster-Böckler, B.; Grffiths-Jones, S.; Hollich, V.; Lassmann, T.; Moxon, S.; Marshall, M.; Khanna, A.; Durbin, R.; et al. Pfam: Clans, web tools and services. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D247–D251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.C.; Shen, H.B. A new method for predicting the subcellular localization of eukaryotic proteins with both single and multiple sites: Euk-mPLoc 2.0. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, B.; Gao, S.; Lercher, M.J. Evolview v3: A webserver for visualization, annotation, and management of phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W270–W275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.; Frank, M.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Bi, C.; Wu, G.; Wei, S.; Dai, X.; Yin, T.; Ye, N. VGSC: A Web-Based Vector Graph Toolkit of Genome Synteny and Collinearity. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 7823429, Erratum in BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 2150291. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.K.; Mangalam, A.K.; Dwivedi, S.; Naik, S. Primer premier: Program for design of degenerate primers from a protein sequence. Biotechniques 1998, 24, 318–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Q.; Hu, X.; Cui, S.; Gao, J.; Zeng, L.; Li, Z.; Kuang, S.; Chen, X.; Xie, Q.; Li, Z.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Isoflavone Synthase (IFS) Gene Family, and Analysis of GgARF4-GgIFS9 Regulatory Module in Glycyrrhiza glabra. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110435
Xu Q, Hu X, Cui S, Gao J, Zeng L, Li Z, Kuang S, Chen X, Xie Q, Li Z, et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Isoflavone Synthase (IFS) Gene Family, and Analysis of GgARF4-GgIFS9 Regulatory Module in Glycyrrhiza glabra. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110435
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Qing, Xiangxiang Hu, Shiyan Cui, Jianguo Gao, Lijie Zeng, Ziqi Li, Sheng Kuang, Xifeng Chen, Quanliang Xie, Zihan Li, and et al. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Isoflavone Synthase (IFS) Gene Family, and Analysis of GgARF4-GgIFS9 Regulatory Module in Glycyrrhiza glabra" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110435
APA StyleXu, Q., Hu, X., Cui, S., Gao, J., Zeng, L., Li, Z., Kuang, S., Chen, X., Xie, Q., Li, Z., Li, H., Wang, F., Shi, S., & Xie, S. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Isoflavone Synthase (IFS) Gene Family, and Analysis of GgARF4-GgIFS9 Regulatory Module in Glycyrrhiza glabra. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110435





