Active Peptides Derived from Snail Mucus Promoted Wound Healing by Enhancing Endothelial Cell Proliferation and Angiogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
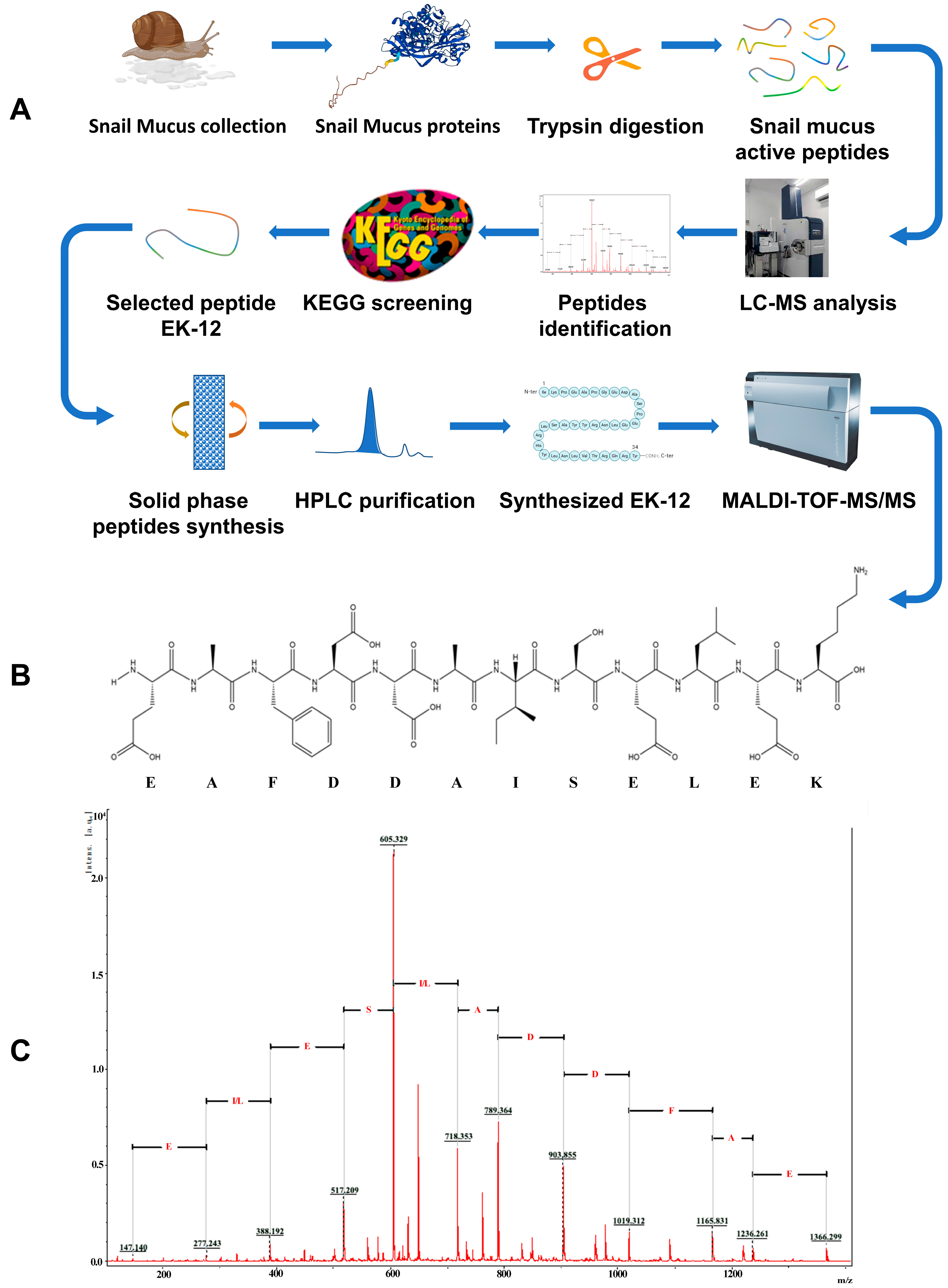
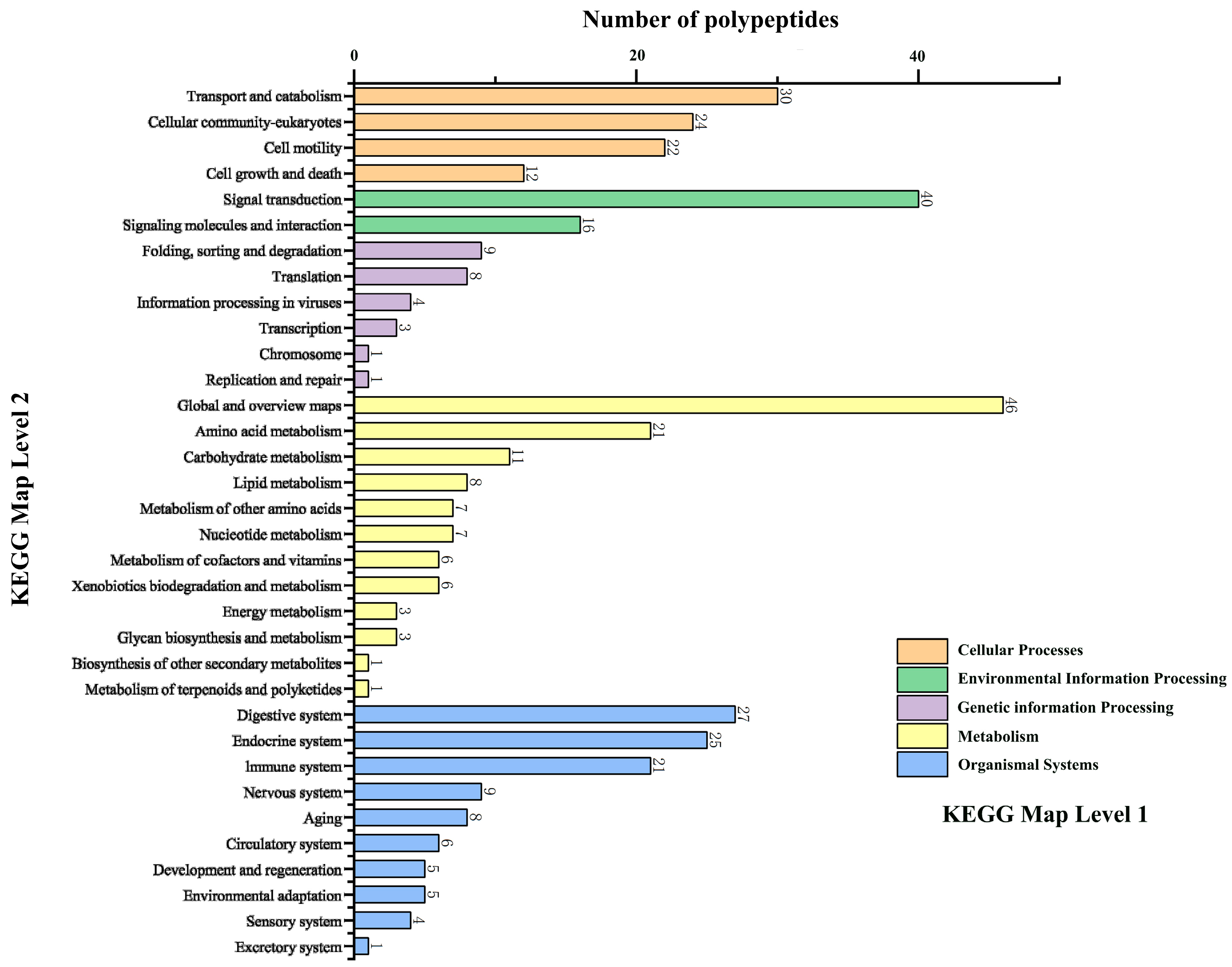
2.1. Screening and Synthesis of SMAPs
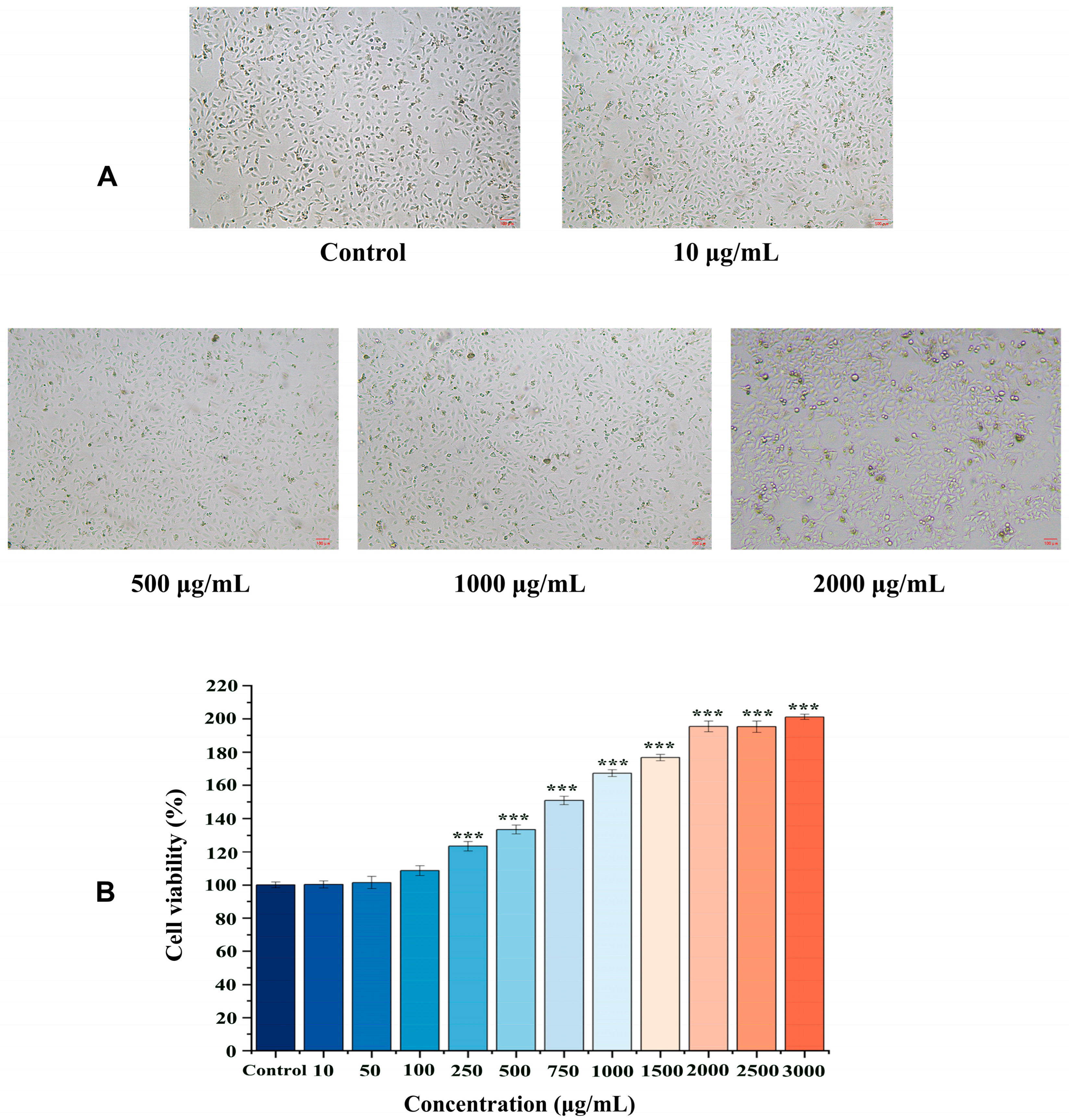
2.2. Effects of EK-12 on Cell Proliferation
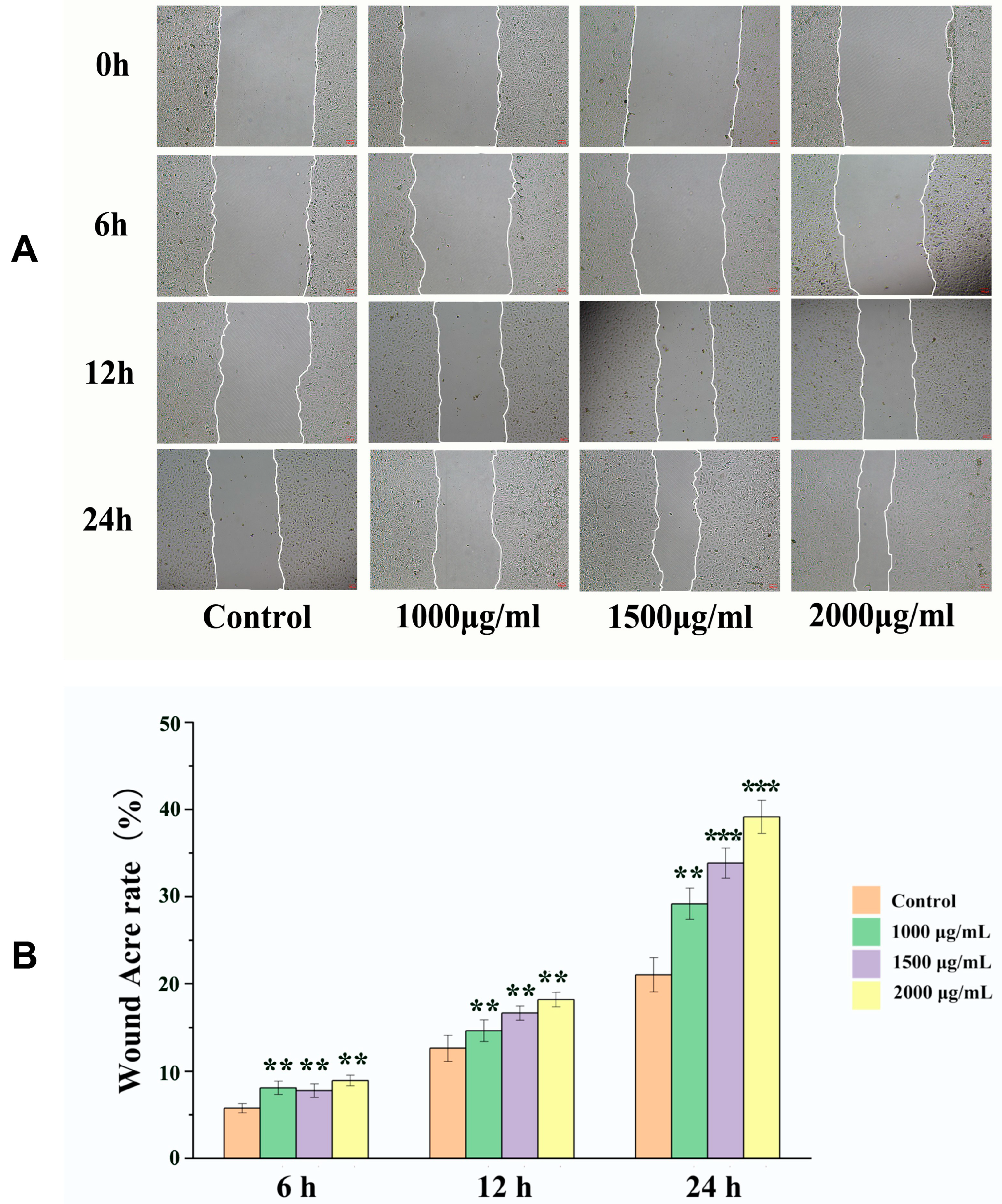
2.3. Effects of EK-12 on Cell Migration
2.4. Effects of EK-12 on Tube Formation Capacity
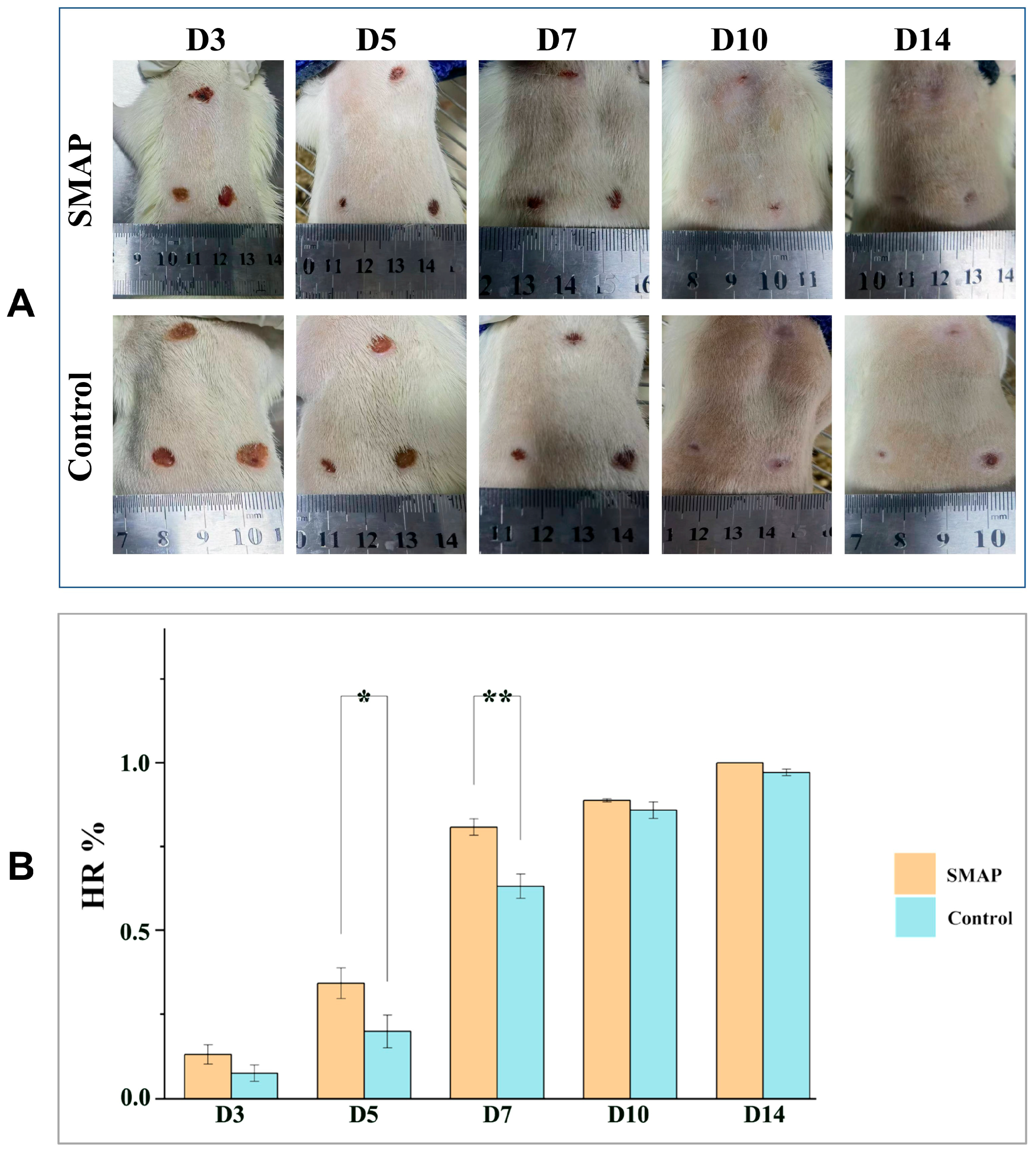
2.5. Effects of EK-12 on Wound Healing and Angiogenesis
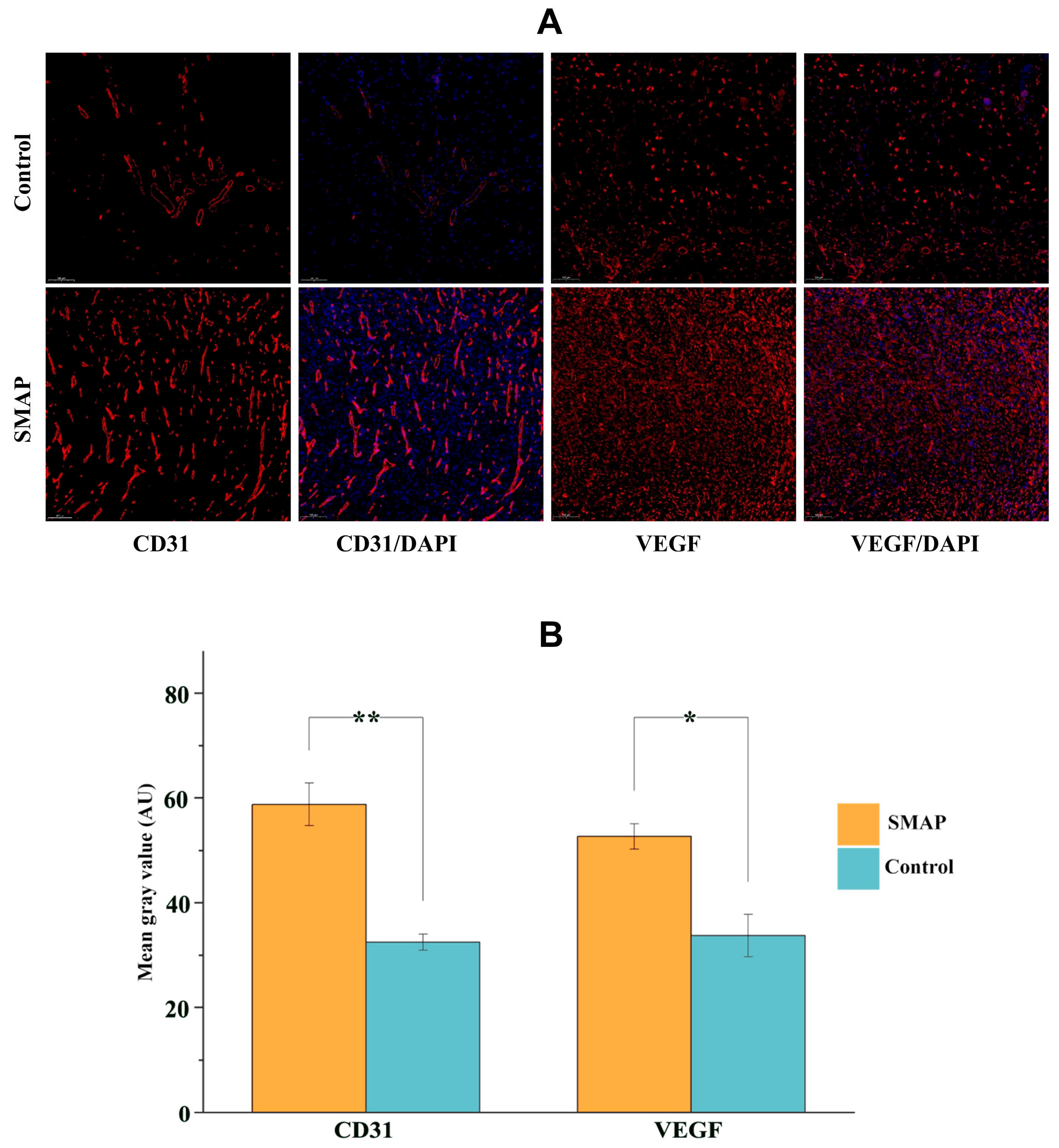
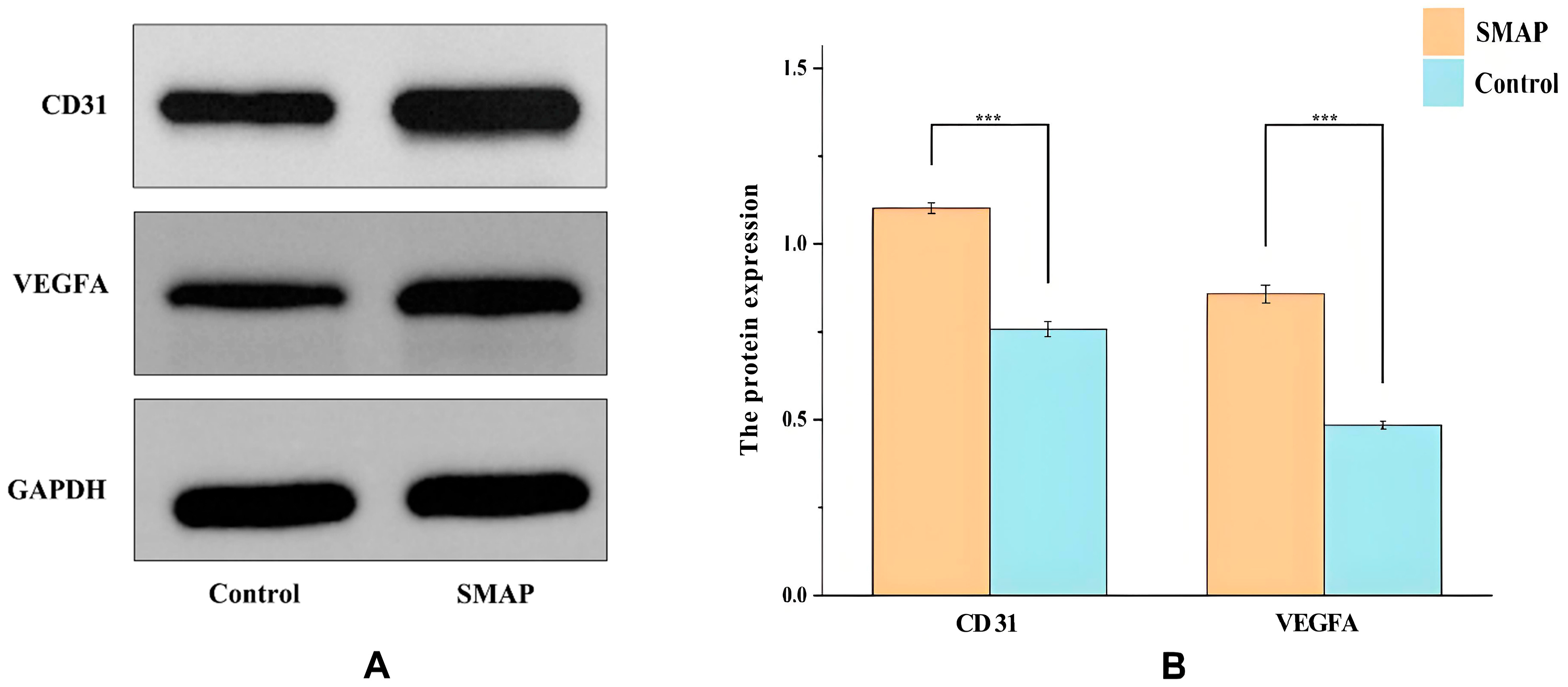
2.6. Expression of VEGFA and CD31 in Wound Tissues
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Snail Mucus Lyophilized Powder
4.2. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Snail Mucus
4.3. Screening and Synthesis of SMAPs
4.4. Cell Culture and Proliferation Assay
4.5. Cell Scratch Test
4.6. Tube Formation Assay
4.7. Pro-Wound-Healing Assay of SMAPs
4.8. Histopathological Examination
4.9. Detection of VEGF and CD31 Protein Expression Using Western Blotting
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCA | Bicinchoninic Acid |
| CCK-8 | Cell Counting Kit-8 |
| CD31 | Cluster of Differentiation 31 |
| CM | Cell migration rate |
| DAPI | 4′,6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole |
| EC | Endothelial cells |
| ECL | Enhanced Chemiluminescence |
| ECM | Endothelial Cell Medium |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase |
| HPLC | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| HR | Healing rate |
| HRP | Horseradish Peroxidase |
| HUVECs | Human umbilical vein endothelial cells |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 Beta |
| IL-8 | Interleukin-8 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| MAPK/ERK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase/Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
| MS/MS | Tandem mass spectrometry |
| PI3K/AKT | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene Fluoride |
| SMAP | Snail mucus active peptides |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| VEGFA | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A |
References
- Zhang, H.; Lin, X.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y. Developing natural polymers for skin wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 33, 355–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Pintado, M.; Tavaria, F.K. A systematic review of natural products for skin applications: Targeting inflammation, wound healing, and photo-aging. Phytomedicine 2023, 115, 154824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G.; Sun, J.; Gu, T.; Ain, N.U.; Zhang, X.; Li, D. Extraction, structure, pharmacological activities and applications of polysaccharides and proteins isolated from snail mucus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 128878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, M.; Cerullo, A.R.; Parziale, J.; Achrak, E.; Sultana, S.; Ferd, J.; Samad, S.; Deng, W.; Braunschweig, A.B.; Holford, M. Advancing Discovery of Snail Mucins Function and Application. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 734023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Gao, D.; Song, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, L.; Tao, M.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, L.; Luo, L.; Zhou, A.; et al. A natural biological adhesive from snail mucus for wound repair. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.C.; Venkatraman, G.; Vellasamy, K.M.; Abdul-Rahman, P.S.; Karsani, S.A. A Scoping Review of Snail Antibacterial Peptides and Proteins: From Natural Defence to Translational Prospects. Probiot. Antimicrob. Proteins 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Yao, Z.; Gu, T.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, D. Study of the ability of polysaccharides isolated from Zizania latifolia to promote wound healing in mice via in vitro screening and in vivo evaluation. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Baassiri, M.G.; Dosh, L.; Haidar, H.; Gerges, A.; Baassiri, S.; Leone, A.; Rappa, F.; Jurjus, A. Nerve growth factor and burn wound healing: Update of molecular interactions with skin cells. Burns 2023, 49, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Teng, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, A. Modulation of macrophages by a phillyrin-loaded thermosensitive hydrogel promotes skin wound healing in mice. Cytokine 2024, 177, 156556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, P.; Faizan, M.; Porwal, M.; Sharma, H.; Sachan, N. An Overview and Review of Growth Factors in Wound Healing: Emerging Trends and Innovations. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2025; Epub ahead of printing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorg, H.; Sorg, C.G.G. Skin wound healing: Of players, patterns, and processes. Eur. Surg. Res. 2023, 64, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Yao, C.; Shui, Y.; Li, S.; Yan, H. Research progress on the mechanism of angiogenesis in wound repair and regeneration. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1284981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, A.; Gallorini, M.; Feghali, N.; Sampò, S.; Cataldi, A.; Zara, S. Snail slime extracted by a cruelty-free method preserves viability and controls inflammation occurrence: A focus on fibroblasts. Molecules 2023, 28, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Deng, T.; Luo, L.; Lin, L.; Yang, L.; Tian, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wu, M. Bionic sulfated glycosaminoglycan-based hydrogel inspired by snail mucus promotes diabetic chronic wound healing via regulating macrophage polarization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281, 135708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasari, N.; Jiang, A.; Skochdopole, A.; Chung, J.; Reece, E.M.; Vorstenbosch, J.; Winocour, S. Updates in diabetic wound healing, inflammation, and scarring. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2021, 35, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Cai, H.A.; Zhang, M.S.; Liao, R.Y.; Huang, X.; Hu, F.D. Ginsenoside Rg1 promoted the wound healing in diabetic foot ulcers via miR-489-3p/Sirt1 axis. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 147, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y.; Tian, Y.; Guo, R.; Shi, J.; Kwak, K.J.; Tong, Y.; Estania, A.P.; Hsu, W.H.; Liu, Y.; Hu, S.; et al. Extracellular vesicle-mediated VEGF-A mRNA delivery rescues ischaemic injury with low immunogenicity. Eur. Heart J. 2025, 46, 1662–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Huang, J.; Shi, J.; Shi, L.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, H. Ruyi Jinhuang Powder accelerated diabetic ulcer wound healing by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway of fibroblasts in vivo and in vitro. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 293 (Suppl. C), 115321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Zhang, J.; Meng, X.; Wang, F.; Tang, W.; Liu, Y.; Fu, L.; Liang, F.; Mo, Z. Inhibition of microRNA-139-5p improves fibroblasts viability and enhances wound repair in diabetic rats through AP-1 (c-Fos/c-Jun). Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2025, 18, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, M.; Gao, Y.; Qin, X.; Zhang, T.; Cui, W.; Mao, C.; Xiao, D.; Lin, Y. Tetrahedral framework nucleic acids promote scarless healing of cutaneous wounds via the AKT-signaling pathway. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.K.H.M.; Edirisinghe, S.L.; Zoysa, M.D.; Whang, I. Octopus minor Antimicrobial Peptide-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles Accelerate Dermal Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, C.H.; Chang, L.; Ho, C.Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Liu, Y.C.; Huang, W.Y.; Wang, Y.N.; Wang, W.H.; Wang, T.W. Immunomodulatory hydrogel orchestrates pro-regenerative response of macrophages and angiogenesis for chronic wound healing. Biomaterials 2024, 314, 122848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandel, S.; Kumaragurubaran, R.; Giri, H.; Dixit, M. Isolation and Culture of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVECs). Methods Mol. Biol. 2024, 2711, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shou, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Liang, Y.; Yang, C.; Xiao, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Shu, J.; Tian, X.; et al. Exosomal miR-301a-3p from esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells promotes angiogenesis by inducing M2 polarization of macrophages via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.L. MicroRNA-9 inhibits retinal neovascularization in rats with diabetic retinopathy by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor A. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 120, 8032–8043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, K.; Hu, B.; Huang, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, X. Active Peptides Derived from Snail Mucus Promoted Wound Healing by Enhancing Endothelial Cell Proliferation and Angiogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110341
Li G, Shi Y, Zhu J, Zhu K, Hu B, Huang X, Sun Y, Li D, Zhang X. Active Peptides Derived from Snail Mucus Promoted Wound Healing by Enhancing Endothelial Cell Proliferation and Angiogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110341
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guanqiang, Yucheng Shi, Junmei Zhu, Kehan Zhu, Bo Hu, Xianchen Huang, Yuan Sun, Duxin Li, and Xicheng Zhang. 2025. "Active Peptides Derived from Snail Mucus Promoted Wound Healing by Enhancing Endothelial Cell Proliferation and Angiogenesis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110341
APA StyleLi, G., Shi, Y., Zhu, J., Zhu, K., Hu, B., Huang, X., Sun, Y., Li, D., & Zhang, X. (2025). Active Peptides Derived from Snail Mucus Promoted Wound Healing by Enhancing Endothelial Cell Proliferation and Angiogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110341





