Unveiling Berberine’s Therapeutic Mechanisms Against Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Integrated Computational Biology and Machine Learning Approaches: AURKA and CDK1 as Principal Targets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
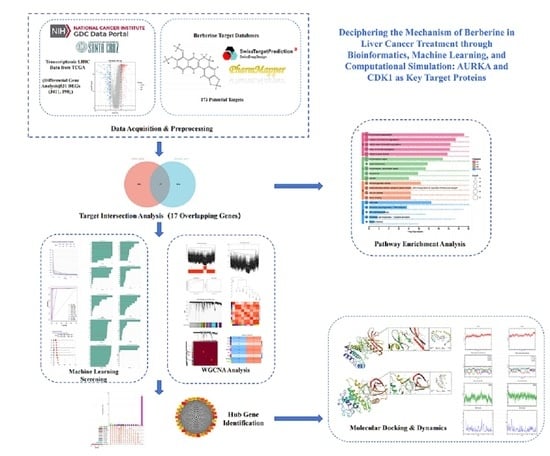
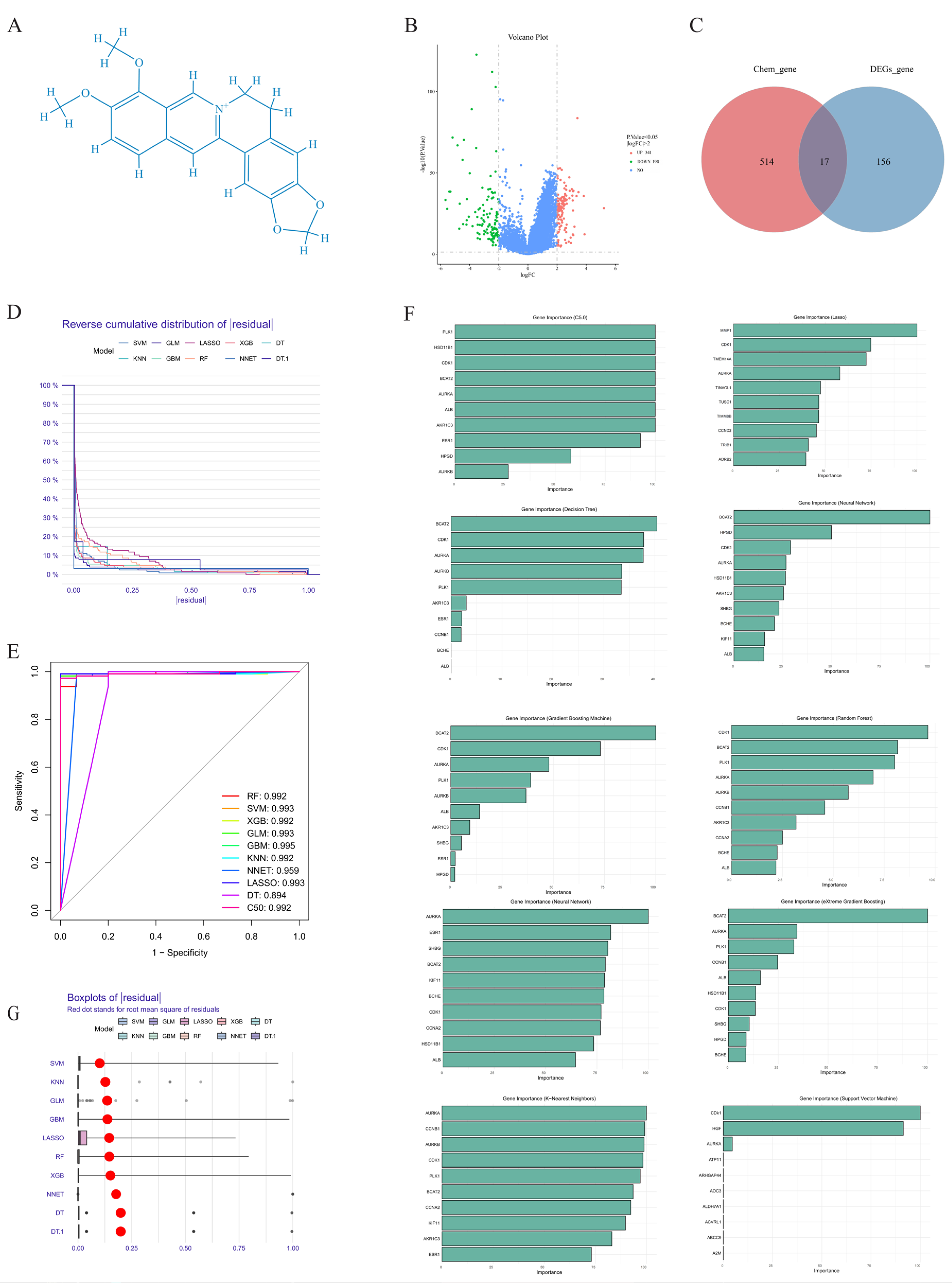
2.1. Prediction of Biological Targets of Berberine in Liver Cancer Treatment
2.2. Core Target Proteins Screened by Machine Learning
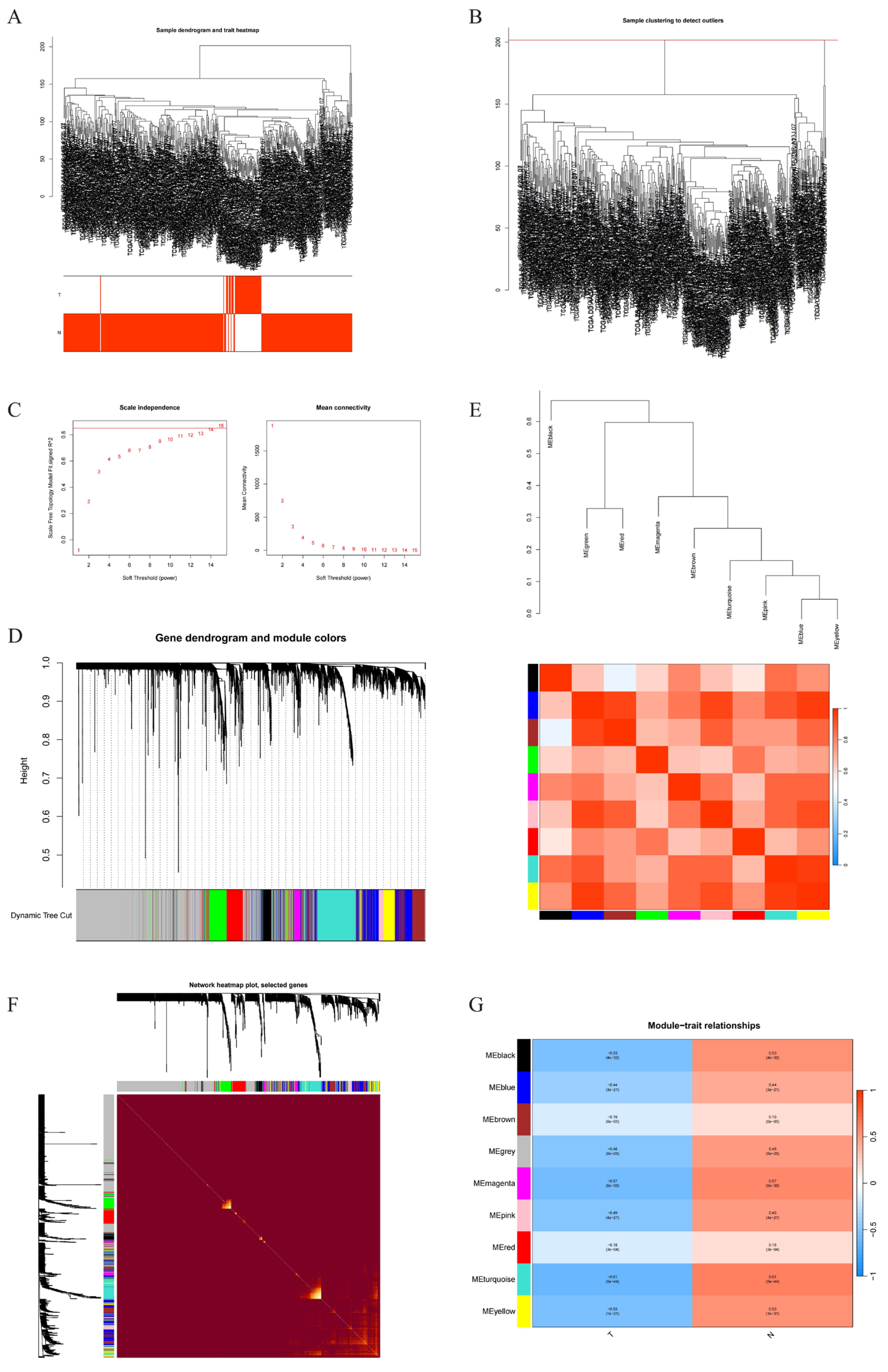
2.3. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Construction
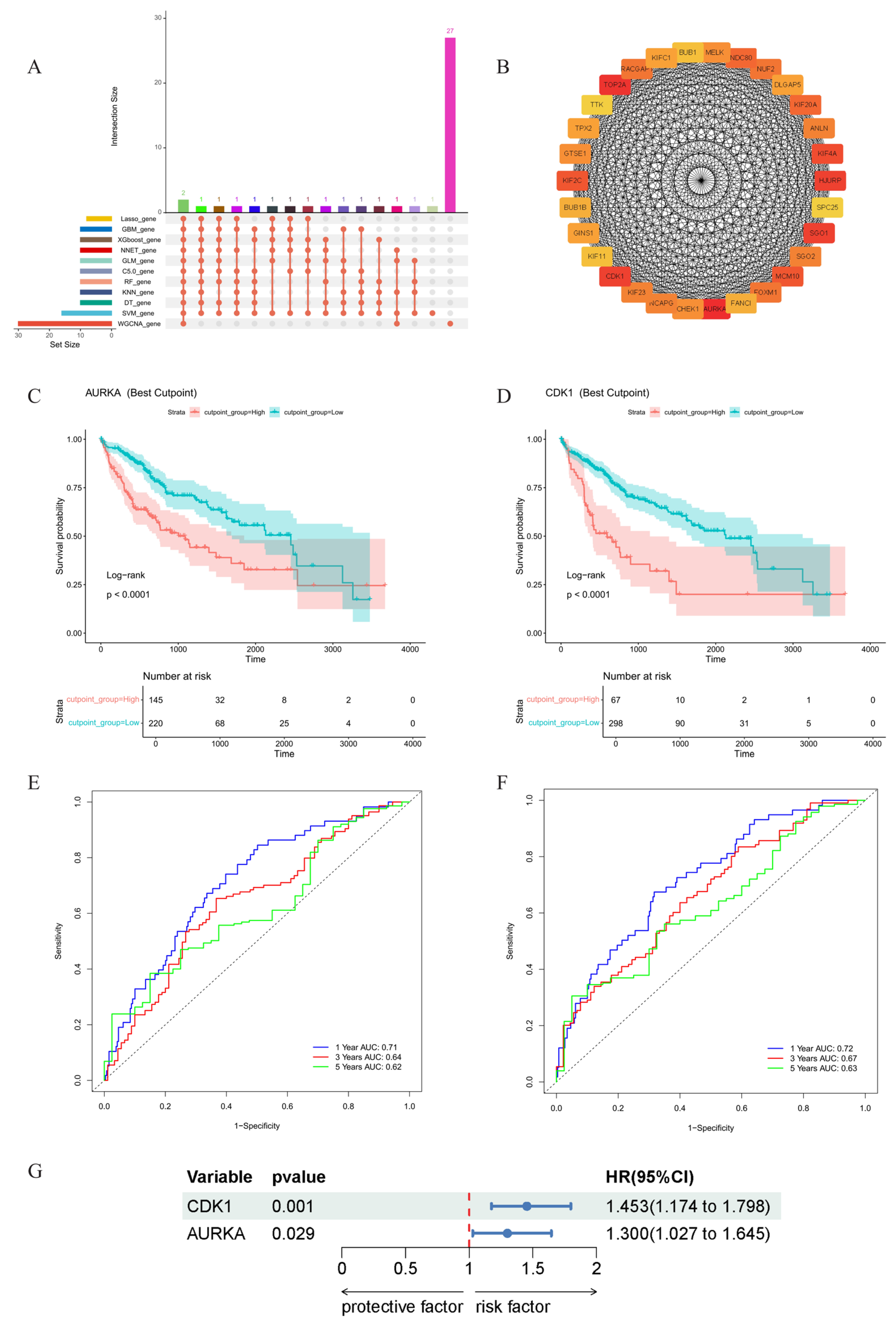
2.4. Core Gene Screening and Clinical Survival Prognosis Analysis
2.5. Molecular Docking Results
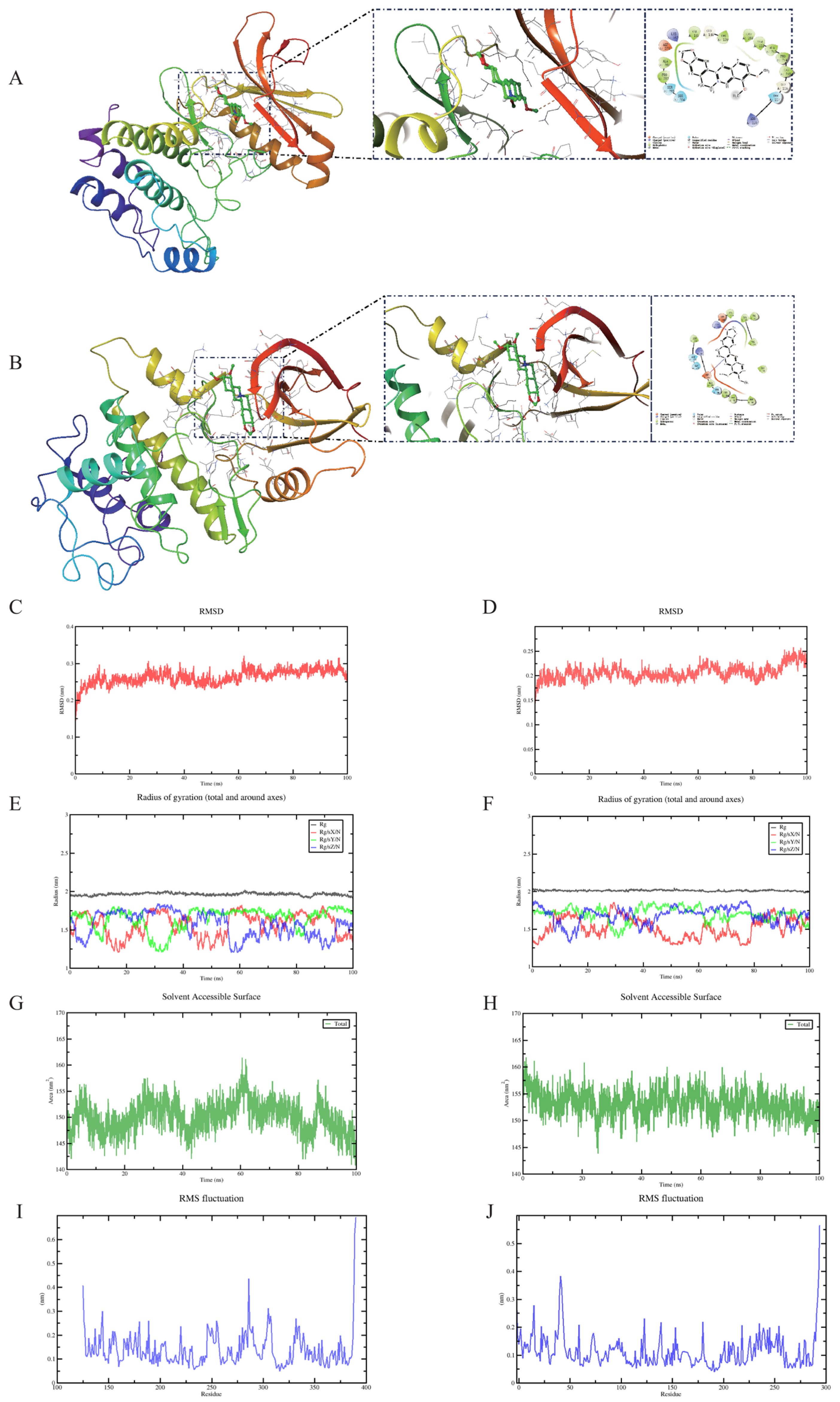
2.6. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Protein-Ligand Complexes
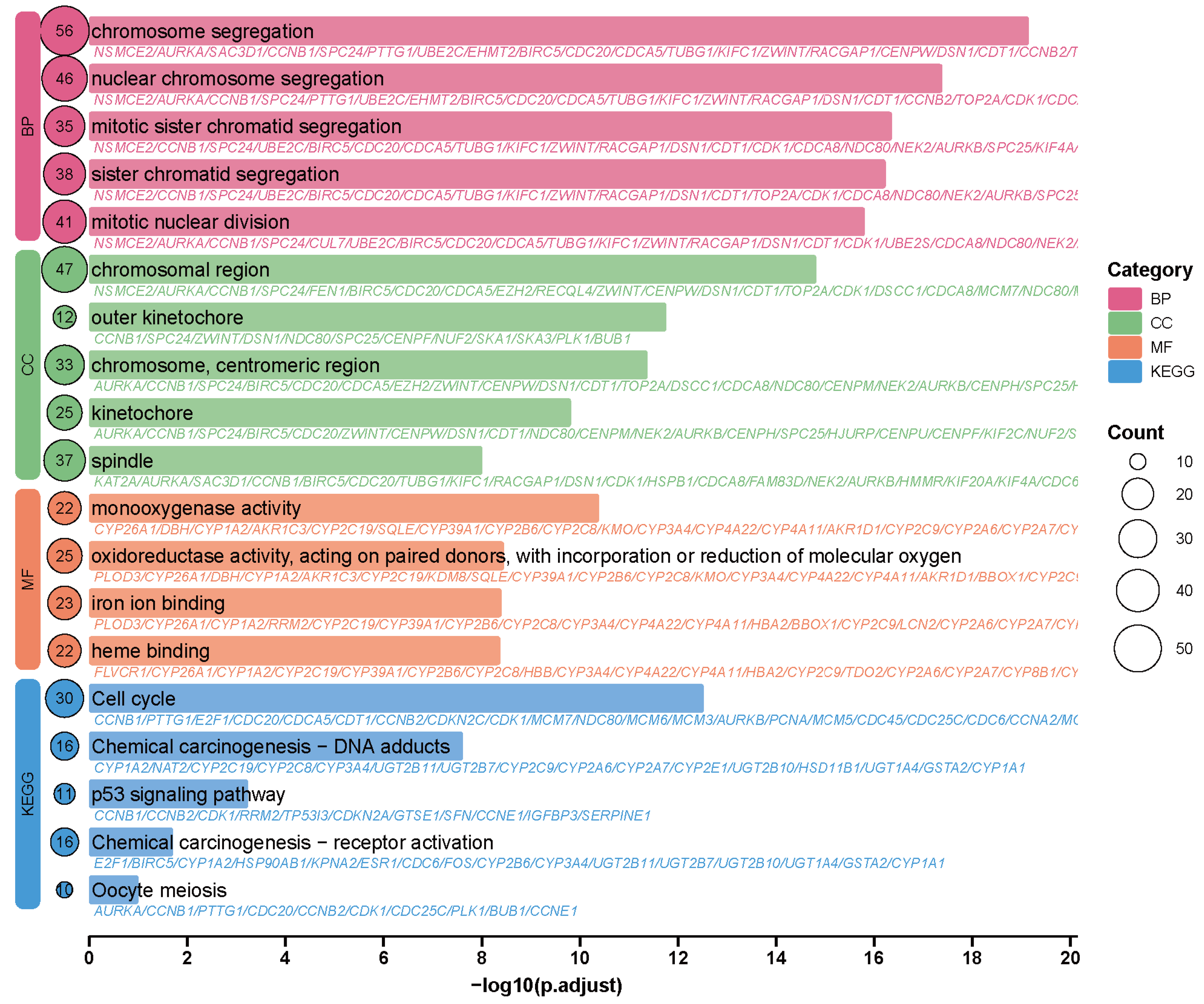
2.7. GO and KEGG Analysis Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Platforms and Software Tools
4.2. Data Sources
4.3. Analysis Methods and Workflow
4.3.1. Differential Gene Analysis
4.3.2. Potential Targets of Berberine Against Liver Cancer
4.3.3. Screening Key Targets of Berberine Against Liver Cancer Through Machine Learning
4.3.4. Construction of Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network to Identify Key Genes
4.3.5. Core Gene Screening and Clinical Survival Prognosis Analysis
4.3.6. Molecular Docking
4.3.7. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
4.3.8. GO and KEGG Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rumgay, H.; Arnold, M.; Ferlay, J.; Lesi, O.; Cabasag, C.J.; Vignat, J.; Laversanne, M.; McGlynn, K.A.; Soerjomataram, I. Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to 2040. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 1598–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Pinyol, R.; Yarchoan, M.; Singal, A.G.; Marron, T.U.; Schwartz, M.; Pikarsky, E.; Kudo, M.; Finn, R.S. Adjuvant and neoadjuvant immunotherapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 21, 294–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, N.; Cai, Y.; Li, F.; Ye, H.; Tang, W.; Song, P.; Cheng, N. The clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma worldwide: A concise review and comparison of current guidelines: 2022 update. Biosci. Trends 2022, 16, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Sheng, J.; Li, G.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Yao, X.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, R. Effects of Berberine and Its Derivatives on Cancer: A Systems Pharmacology Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 10, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Cao, J.; Wei, J.; Deng, J.; Hou, X.; Hao, E.; Du, Z.; Zou, L.; Li, P. Antiproliferative activity of berberine in HepG2 cells via inducing apoptosis and arresting cell cycle. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 12115–12126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, G.; Das, S.; Bola Sadashiva, S.R. Berberine, a natural alkaloid sensitizes human hepatocarcinoma to ionizing radiation by blocking autophagy and cell cycle arrest resulting in senescence. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 1893–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnoi, K.; Ke, R.; Saini, K.S.; Viswakarma, N.; Nair, R.S.; Das, S.; Chen, Z.; Rana, A.; Rana, B. Berberine Represses β-Catenin Translation Involving 4E-BPs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 99, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Yu, G.; Lin, J.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Q.; Gu, C.; Yang, T.; Liu, S.; Yang, H. Berberine Sensitizes Human Hepatoma Cells to Regorafenib via Modulating Expression of Circular RNAs. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 632201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Liu, G. Berberine-10-hydroxy camptothecine-loaded lipid microsphere for the synergistic treatment of liver cancer by inhibiting topoisomerase and HIF-1α. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, K.; Zhao, H.; Chen, B.; Ye, Q.; Yue, J. CDK1-PLK1/SGOL2/ANLN pathway mediating abnormal cell division in cell cycle may be a critical process in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 1236–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Wang, S.; Jiang, N.; Li, J.J. Cyclin B1/CDK1-regulated mitochondrial bioenergetics in cell cycle progression and tumor resistance. Cancer Lett. 2019, 443, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, P.; Jiang, G.; Meng, Q.; Liu, W.; Wu, X. Long non-coding RNA taurine-upregulated gene 1 promotes cells proliferation, migration and invasion while represses apoptosis, and upregulates AURKA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 3199–3207. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Fei, C.; Chen, T.; Yin, X.; Zhang, L.; Ren, Z. ID1 overexpression promotes HCC progression by amplifying the AURKA/Myc signaling pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 57, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wang, J.; Zou, S.; Xu, R.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Wen, X.; Deng, S.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Cinobufagin Triggers Defects in Spindle Formation and Cap-Dependent Translation in Liver Cancer Cells by Inhibiting the AURKA-mTOR-eIF4E Axis. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020, 48, 651–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.N.; Xu, Z.W.; Xu, R.C.; Fang, T.; Wang, F.M. The mechanism study of ouabain in inhibiting the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting the laser kinase signaling pathway. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2020, 100, 3014–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, X.T. AI and machine learning in bioinformatics and biomedicine. Methods 2025, 236, 26–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Yang, K.; Han, Y.; Zhang, L. Review on the Application of Machine Learning Algorithms in the Sequence Data Mining of DNA. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goecks, J.; Jalili, V.; Heiser, L.M.; Gray, J.W. How Machine Learning Will Transform Biomedicine. Cell 2020, 181, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Pu, K.; Wu, X. Identifying novel biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma by weighted gene co-expression network analysis. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 11418–11431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinzi, L.; Rastelli, G. Molecular Docking: Shifting Paradigms in Drug Discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vivo, M.; Masetti, M.; Bottegoni, G.; Cavalli, A. Role of Molecular Dynamics and Related Methods in Drug Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 4035–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lupala, C.S.; Liu, H.; Lin, X. Identification of Drug Binding Sites and Action Mechanisms with Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 2268–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, B.; Yu, H.Y.; Duan, T.Q.; Pan, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, R.Q.; Masroor, M.; Huang, J.F. Cell cycle kinases (AUKA, CDK1, PLK1) are prognostic biomarkers and correlated with tumor-infiltrating leukocytes in HBV related HCC. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 11845–11861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.A.; Chu, K.B.; Moon, E.K.; Quan, F.S. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor-Induced CDKN2B and CDKN2D Contribute to G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest Incurred by Oxidative Stress in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells via Forkhead Box M1 Suppression. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 5086–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, O.; Kan, M.; Zhang, M.; Shao, D.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, S. Berberine induces apoptosis by suppressing the arachidonic acid metabolic pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 4572–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisetti, L.; Garcia, C.J.C.; Saponaro, A.A.; Tiribelli, C.; Pascut, D. The role of Aurora kinase A in hepatocellular carcinoma: Unveiling the intriguing functions of a key but still underexplored factor in liver cancer. Cell Prolif. 2024, 57, e13641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Huang, N. Berberine induces selective apoptosis through the AMPK-mediated mitochondrial/caspase pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 8, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, P.; Babaei, A.; Zamanian, N.; Eshtivani, E.N. Berberine’s impact on health: Comprehensive biological, pharmacological, and nutritional perspectives. Metab. Open 2025, 28, 100399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.; Yang, H.; Li, T.; Luo, J.; Zhou, L.; Chen, R.; Han, L.; Lin, Y. Molecular mechanisms, targets and clinical potential of berberine in regulating metabolism: A review focussing on databases and molecular docking studies. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1368950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Yi, X.; Yu, Z.; Xue, K.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, E.; He, P.; Zeng, Q. Berberine sensitizes liver cancer cells to sorafenib by inducing SETDB1/NQO1/p53-dependent ferroptosis and genomic instability. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2025, 1007, 178211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; He, M.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, H.; Xiong, Y.; Shan, M.; Liu, D.; Guo, Z.; Kou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Berberine increases the killing effect of pirarubicin on HCC cells by inhibiting ATG4B-autophagy pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2024, 439, 114094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.S.; Tan, H.Y.; Zhang, C.; Chan, Y.T.; Zhang, Z.J.; Man, K.; Yuen, M.F.; Wang, N.; Feng, Y. Berberine suppresses metastasis and recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting circulating tumour cells: Abridged secondary publication. Hong Kong Med. J. 2022, 28 (Suppl. 6), 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Rastaghi, S.; Saki, A.; Tabesh, H. Modifying the false discovery rate procedure based on the information theory under arbitrary correlation structure and its performance in high-dimensional genomic data. BMC Bioinform. 2024, 25, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Murphy, D. Application of ggplot2 to Pharmacometric Graphics. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2013, 2, e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, N. Bioinformatics screening the novel and promising targets of curcumin in hepatocellular carcinoma chemotherapy and prognosis. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, M.; Salimi, H.; Eskandari, S.; Nezafat, N. Identification of potential biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma: A network-based approach. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2022, 28, 100864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libbrecht, M.W.; Noble, W.S. Machine learning applications in genetics and genomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.G.; Dos Santos, R.N.; Oliva, G.; Andricopulo, A.D. Molecular docking and structure-based drug design strategies. Molecules 2015, 20, 13384–13421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, A.; Coote, M.L.; Barakat, K. Molecular dynamics-driven drug discovery: Leaping forward with confidence. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 249–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: A web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Platform/Software Name | URL | Date of Visit |
|---|---|---|
| The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) | https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/ | Accessed 8 July 2025 |
| UCSC Xena Data Platform | https://xena.ucsc.edu/ | Accessed 8 July 2025 |
| GeneCards Database | https://www.genecards.org/ | Accessed 10 July 2025 |
| PubChem Database | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ | Accessed 8 July 2025 |
| Cytoscape 3.10.3 | https://cytoscape.org/ | Accessed 10 July 2025 |
| PharmMapper Database | https://www.lilab-ecust.cn/pharmmapper/ | Accessed 8 July 2025 |
| SwissTargetPrediction Database | http://swisstargetprediction.ch/ | Accessed 8 July 2025 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Liu, H.; Wan, L. Unveiling Berberine’s Therapeutic Mechanisms Against Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Integrated Computational Biology and Machine Learning Approaches: AURKA and CDK1 as Principal Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110309
Wu Y, Hu Y, Liu H, Wan L. Unveiling Berberine’s Therapeutic Mechanisms Against Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Integrated Computational Biology and Machine Learning Approaches: AURKA and CDK1 as Principal Targets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110309
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yuyang, Yanmei Hu, Haicui Liu, and Li Wan. 2025. "Unveiling Berberine’s Therapeutic Mechanisms Against Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Integrated Computational Biology and Machine Learning Approaches: AURKA and CDK1 as Principal Targets" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110309
APA StyleWu, Y., Hu, Y., Liu, H., & Wan, L. (2025). Unveiling Berberine’s Therapeutic Mechanisms Against Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Integrated Computational Biology and Machine Learning Approaches: AURKA and CDK1 as Principal Targets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10309. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110309