Emerging Applications of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy in Oligometastatic Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
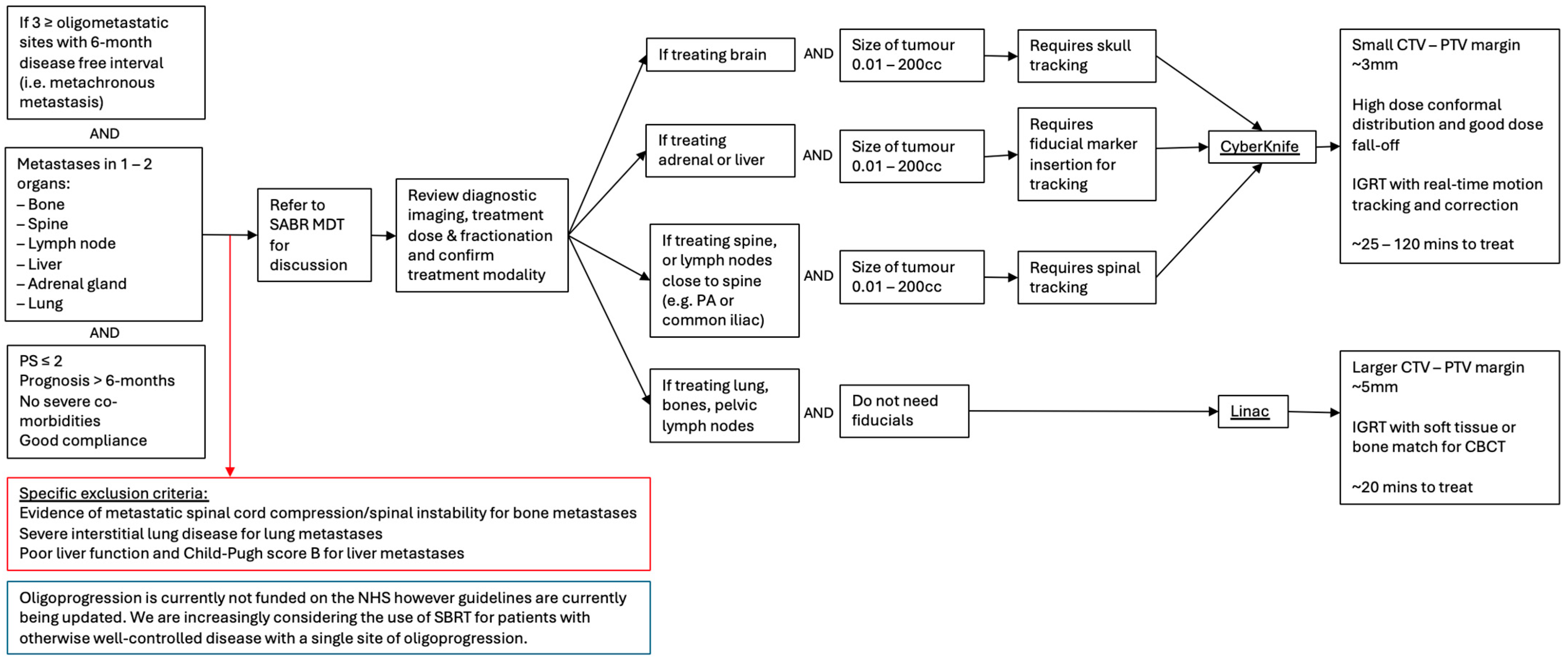
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Current Outlook
| Trial Name (Author) | Study Type | Control Arm | Primaries, Number of Patients, (Number of Colorectal Patients), and Lesion Location | Dosage Regimen | Progression-Free Survival | Overall Survival | Local Control | Toxicity Rates | Summary of Published Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase II prospective trial on SBRT for unresectable liver oligometastases from colorectal cancer (Scorsetti, 2015) [41] | Phase II prospective | Not reported | Inoperable colorectal liver metastases (n = 42 CRC) | A dose of 75 Gy in three consecutive fractions of 25 Gy | Median PFS: 12 months | Median OS: 29.2 months 1 yr: 85.2% 3 yr: 31.3% 5 yr: 18% | 2 yr actuarial LC rate: 91% | 78% grade 2 toxicity. No grade 3+ toxicity, RILD, or bile duct stenosis observed. | SBRT is a feasible alternative to surgery in inoperable tumours with good overall survival (29.2 months) and local control (91%). |
| Phase II study of individualised SABR of liver mets (Hong, 2017) [46] | Phase II single-arm, single institution | Not reported | Liver metastases from solid tumours, n = 89 (n = 34 CRC) | 30–50 Gy in five fractions (based on effective volume of liver irradiated) | Cohort median PFS: 3.7 months 1 yr: 24.7% 3 yr: 9.2% | Cohort median survival: 18.1 months 1 yr: 66.3% 2 yr: 35.9% 3 yr: 20.8% | Colorectal-specific 1 year LC: 58.8% 3 yr LC: 44.7% | 87.6% experienced radiation-related toxicity, most commonly fatigue (68.5%), dermatitis (47.2%), and abdominal pain (23.6%). No grade 3+ toxicity observed. | CRC primary tumours had lower LC rates, but PFS and OS were comparable. TP53 and KRAS associated with poor prognosis. |
| Phase I dose escalation study and phase II study on SBRT for CRC hepatic mets (McPartlin, 2017) [47] | Phase I and phase II | Not reported | Colorectal liver metastases (n = 60 CRC) | Prescription dose of 33 to 57 Gy in six fractions | Median PFS: 10.8 months | Median OS: 16 months 1 yr: 63% 2 yr: 26% 4 yr: 9% | 1 yr: 50% 2 yr: 32% 4 yr: 26% | Mostly well tolerated; one case of grade 3 nausea, two cases of grade 3 thrombocytopenia (one resolved, one fatal). No grade 3+ liver toxicity, RILD, or late gastrointestinal complications. | Treatment is safe and may be associated with long term cure. Local control is better with higher SBRT dose. |
| Multicentre phase II on safety and feasibility of SABR for patients with oligometastatic cancer (Sutera, 2018) [48] | Multicentre prospective phase II | None described | Oligometastatic cancer; lung, colorectal, head and neck, etc., n = 147 (n = 31 CRC) Multiple lesion locations including lung, lymph node, bone, and liver | Depended on lesion size and location | Colorectal median (distant) PFS: 10.4 months Cohort (local) 1 yr PFS: 91% Cohort (local) 5 yr PFS: 75% | Colorectal median OS: 54.4 months | “excellent”, no values reported | Acute grade ≥ 2: 7.5%, grade ≥ 3: 2.0%. Late grade ≥ 2: 1.4%, grade ≥ 3: 1.4%. Grade 4 small bowel obstruction (n = 1). No significant quality-of-life decline. | High overall survival rates and a respectable progression free survival, with “excellent” local control. |
| SABR-COMET (Palma, 2020) [18] | Phase II Randomised | Standard of care (palliative systemic therapy) | Oligometastatic cancer; breast, colorectal, lung, prostate, etc., n = 99 (n = 18 CRC) Multiple lesion locations including lung, bone, liver, and adrenal | Allowable doses ranged from 30 to 60 Gy in 3–8 fractions | Cohort Median PFS: 5.4 months vs. 11.6 months 5-year PFS: 0% vs. 17.3% | Cohort Median OS: 28 months vs. 50 months 5-year OS: 17.7% vs. 42.3% | Cohort overall long-term LC rate: 46% vs. 63% | Grade ≥ 2 adverse events occurred in 29% (19/66) of the SABR arm vs. 9% (3/33) in the control arm (p = 0.03). Treatment-related deaths occurred in 4.5% (3/66) of SABR patients. | SABR improved overall survival by median 22 months. |
| ORCHESTRA trial (Gootjes, 2020) [20] | Phase II randomised | Chemotherapy standard of care | Oligometastatic colorectal cancer (n = 88 CRC) Multiple lesion locations including liver, lung, and lymph node | Tumour debulking, using SABR, resection, or thermal ablation, was added alongside chemotherapy; six radiotherapy sessions delivered | Not explicitly reported, focus on chemotherapy compatibility | Not specified (data collection still underway) | High, but variable across metastatic sites | SAEs in 50% of patients; grade ≥ 3 surgical complications in 24%, plus one possible SABR-related death from pneumonitis. | Local interventions like SABR did not interfere with chemotherapy. Stable disease control reported. |
| SABR-5 trial (Baker, 2022) [40] | Single arm phase II | None described | Oligometastatic cancer; prostate, colorectal, breast, lung, renal cell carcinoma, n = 381 (n = 63 CRC) Multiple lesion locations including bone, lung, lymph node, liver, and adrenal | 24–60 Gy in 2–8 fractions | Cohort median PFS: 15 months 1 yr PFS: 56% 3 yr PFS: 31% | Cohort median OS: not reached 3 yr OS: 71% | Cohort 1 yr LC: 93% 3 yr: 87% | Grade 2+ toxicity: 18.6%, grade 3+: 4.2%, grade 4: 0%, grade 5: 0.3%. One possible SABR-related death due to biliary stenosis and infection. | Low rates of local failure, high median PFS, no specific colorectal data. |
| SABR-COMET-3 | Phase III randomised (ongoing) | Standard of care (results pending) | Pending results | Pending results | Pending results | Pending results | Pending results | ||
| SABR-COMET-10 | Phase III randomised (ongoing) | Standard of care (results pending) | Pending results | Pending results | Pending results | Pending results | Pending results | ||
| Alliance (A022101/NRG-GI009) | Phase III randomised (ongoing) | Systemic therapy alone (results pending) | Pending results | Pending results | Pending results | Pending results | Pending results |
2.2. Advancements in Patient Selection and Prognosis
2.2.1. Anatomical Factors
2.2.2. Genomics
2.2.3. Clinical Factors
2.2.4. Biomarkers
2.3. Optimising SABR
2.3.1. Magnetic Resonance-Guided SABR
2.3.2. Proton-Based SABR
2.4. Synergy with SABR
2.4.1. Immunotherapy
2.4.2. The Abscopal Effect
2.4.3. AI and Machine Learning
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Term |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AMP-224 | PD-L2 Fc Fusion Protein |
| ATM | Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated (gene) |
| AURKB | Aurora B Kinase |
| BED | Biologically Effective Dose |
| BED10 | Biologically Effective Dose using an α/β ratio of 10 |
| BRCA1/2 | Breast Cancer Genes 1 and 2 |
| CD | Cluster of Differentiation |
| CD274 | Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) |
| CEA | Carcinoembryonic Antigen |
| CRC | Colorectal Cancer |
| ctDNA | Circulating Tumour DNA |
| CTV | Clinical Target Volume |
| dMMR | Deficient Mismatch Repair |
| DAMP | Damage-Associated Molecular Pattern |
| EMT | Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition |
| ERE | Electron Return Effect |
| ESMO | European Society for Medical Oncology |
| EU | European Union |
| FFCLP | Freedom From Local–Regional Progression |
| GITR | Glucocorticoid-Induced TNF Receptor |
| GNL | Gradient Non-Linearity |
| GSK-3β | Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Beta |
| GTV | Gross Tumour Volume |
| Gy | Gray (unit of radiation dose) |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| HIF-1α | Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 Alpha |
| HMGB1 | High-Mobility Group Box 1 |
| HR (repair) | Homologous Recombination (DNA repair pathway) |
| ICD | Immunogenic Cell Death |
| ICB | Immune Checkpoint Blockade |
| IL-2 | Interleukin-2 |
| IL6R | Interleukin-6 Receptor |
| IV | Intravenous |
| KRAS | Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog |
| LC | Local Control |
| LET | Linear Energy Transfer |
| M5A-IL2 | Immunocytokine targeting CEA linked to IL-2 |
| MDT | Multidisciplinary Team |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MLC | Multi-Leaf Collimator |
| MMR | Mismatch Repair |
| MRIgRT | Magnetic Resonance Image-guided Radiotherapy |
| MRgSBRT | Magnetic Resonance-guided Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy |
| MR-Linac | Magnetic Resonance Linear Accelerator |
| MSI-H | Microsatellite Instability-High |
| NHEJ | Non-Homologous End Joining (DNA repair pathway) |
| OAR | Organ at Risk |
| OER | Oxygen Enhancement Ratio |
| ORCHESTRA | Optimal Treatment for Patients with Oligometastatic Colorectal Cancer |
| OS | Overall Survival |
| PFS | Progression-Free Survival |
| PI3K/AKT | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B Pathway |
| PKC | Protein Kinase C |
| PTV | Planning Target Volume |
| RILD | Radiation-Induced Liver Disease |
| RNA-seq | RNA Sequencing |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| RSI | Radiosensitivity Index |
| SABR | Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy |
| SAE | Serious Adverse Event |
| SBRT | Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy |
| SRS | Stereotactic Radiosurgery |
| STING | Stimulator of Interferon Genes |
| TAAs | Tumour-Associated Antigens |
| TGFβ | Transforming Growth Factor Beta |
| TNT | Total Neoadjuvant Therapy |
| TP53 | Tumour Protein 53 |
| UK | United Kingdom |
| US | United States |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424, Erratum in CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, M.D.; Wang, K.; Wang, L.; Polychronidis, G.; Berstad, P.; Hjartåker, A.; Fang, Z.; Ogino, S.; Chan, A.T.; Song, M. Colorectal Cancer Incidence and Mortality After Negative Colonoscopy Screening Results. JAMA Oncol. 2025, 11, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, E.; Tanis, P.J.; Vleugels, J.L.A.; Kasi, P.M.; Wallace, M.B. Colorectal Cancer. Lancet 2019, 394, 1467–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santucci, C.; Mignozzi, S.; Levi, F.; Malvezzi, M.; Boffetta, P.; Negri, E.; Vecchia, C.L. European Cancer Mortality Predictions for the Year 2025 with Focus on Breast Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2025, 36, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riihimäki, M.; Hemminki, A.; Sundquist, J.; Hemminki, K. Patterns of Metastasis in Colon and Rectal Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeineddine, F.A.; Zeineddine, M.A.; Yousef, A.; Gu, Y.; Chowdhury, S.; Dasari, A.; Huey, R.W.; Johnson, B.; Kee, B.; Lee, M.S.; et al. Survival Improvement for Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer over Twenty Years. npj Precis. Oncol. 2023, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañellas-Socias, A.; Sancho, E.; Batlle, E. Mechanisms of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 21, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biller, L.H.; Schrag, D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2021, 325, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellman, S.; Weichselbaum, R.R. Oligometastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmanabhan, C.; Nussbaum, D.P.; D’Angelica, M. Surgical Management of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2025, 39, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinak, C.T.; Schwartz, P.B.; Basree, M.M.; Hurst, N.; Bassetti, M.; Kratz, J.D.; Uboha, N.V. Treatment of Oligometastatic GI Cancers. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2024, 44, e430152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carconi, C.; Cerreti, M.; Roberto, M.; Arrivi, G.; D’Ambrosio, G.; De Felice, F.; Di Civita, M.A.; Iafrate, F.; Lucatelli, P.; Magliocca, F.M.; et al. The Management of Oligometastatic Disease in Colorectal Cancer: Present Strategies and Future Perspectives. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2023, 186, 103990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupferthaler, A. Local Treatment Strategies in Oligometastatic Colorectal Cancer. Memo Mag. Eur. Med. Oncol. 2025, 18, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suydam, C.R.; Schlussel, A.T. Management of Oligometastatic Colorectal Cancer. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2024, 104, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sattar, H.; Okondo, E.; Hassan-Dinif, J.; Jaafari, A.M.; Augustine, A.; Galante, J.R.; Metawe, M.; Mikropoulos, C.; Adeleke, S. The Curative Potential of Stereotactic Radiotherapy in Oligometastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Narrative Review. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2025, 14, 17188–17288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, A.; Sanuki, N.; Kunieda, E. Role of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Oligometastasis from Colorectal Cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SABR Consortium. SABR Consortium Guidelines 2019, Version 6.1.0. 2019. Available online: https://www.sabr.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/SABRconsortium-guidelines-2019-v6.1.0.pdf (accessed on 16 October 2025).
- Palma, D.A.; Olson, R.; Harrow, S.; Gaede, S.; Louie, A.V.; Haasbeek, C.; Mulroy, L.; Lock, M.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Yaremko, B.P.; et al. Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for the Comprehensive Treatment of Oligometastatic Cancers: Long-Term Results of the SABR-COMET Phase II Randomized Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2830–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.; Lechner, L.; Liu, M.; Chang, J.S.; Cruz-Lim, E.M.; Mou, B.; Jiang, W.; Bergman, A.; Schellenberg, D.; Alexander, A.; et al. Upfront Versus Delayed Systemic Therapy in Patients With Oligometastatic Cancer Treated With SABR in the Phase 2 SABR-5 Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2024, 118, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gootjes, E.C.; van der Stok, E.P.; Buffart, T.E.; Bakkerus, L.; Labots, M.; Zonderhuis, B.M.; Tuynman, J.B.; Meijerink, M.R.; van de Ven, P.M.; Haasbeek, C.J.A.; et al. Safety and Feasibility of Additional Tumor Debulking to First-Line Palliative Combination Chemotherapy for Patients with Multiorgan Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Oncologist 2020, 25, e1195–e1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinj, R.; Bondiau, P.-Y.; François, E.; Gérard, J.-P.; Naghavi, A.O.; Leysalle, A.; Chamorey, E.; Evesque, L.; Padovani, B.; Ianessi, A.; et al. Radiosensitivity of Colon and Rectal Lung Oligometastasis Treated With Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2017, 16, e211–e220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkley, M.S.; Trakul, N.; Jacobs, L.R.; von Eyben, R.; Le, Q.-T.; Maxim, P.G.; Loo, B.W.; Shultz, D.B.; Diehn, M. Colorectal Histology Is Associated With an Increased Risk of Local Failure in Lung Metastases Treated With Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 92, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.A.; Fulp, W.J.; Berglund, A.E.; Hoffe, S.E.; Dilling, T.J.; Eschrich, S.A.; Shridhar, R.; Torres-Roca, J.F. Differences between Colon Cancer Primaries and Metastases Utilizing a Molecular Assay for Tumor Radiosensitivity Suggest Implications for Potential Oligometastatic SBRT Patient Selection. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 92, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, H.; Uemoto, K.; Suzuki, O.; Yamada, K.; Masai, N.; Tatsumi, D.; Shiomi, H.; Oh, R.-J. Effect of Primary Tumor Location and Tumor Size on the Response to Radiotherapy for Liver Metastases from Colorectal Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comito, T.; Cozzi, L.; Clerici, E.; Campisi, M.C.; Liardo, R.L.E.; Navarria, P.; Ascolese, A.; Tozzi, A.; Iftode, C.; De Rose, F.; et al. Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SABR) in Inoperable Oligometastatic Disease from Colorectal Cancer: A Safe and Effective Approach. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernando-Requejo, O.; Chen, X.; López, M.; Sánchez, E.; García, J.; García, P.; Alonso, R.; Montero, A.; Ciervide, R.; Álvarez, B.; et al. Real-World Effectiveness and Safety of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Liver Metastases with Different Respiratory Motion Management Techniques. Strahlenther. Und Onkol. 2023, 199, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargett, M.; Haddad, C.; Kneebone, A.; Booth, J.T.; Hardcastle, N. Clinical Impact of Removing Respiratory Motion during Liver SABR. Radiat. Oncol. Lond. Engl. 2019, 14, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamsiz, H.; Sager, O.; Uysal, B.; Dincoglan, F.; Demiral, S.; Colak, O.; Ozcan, F.; Dirican, B.; Beyzadeoglu, M. Active Breathing Control Guided Stereotactic Body Ablative Radiotherapy for Management of Liver Metastases from Colorectal Cancer. Acta Gastro-Enterol. Belg. 2022, 85, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, Y.A.; Speir, D.B.; Burrell, W.E.; Wang, C.J.; Wu, H.T. Efficacy of a Thermoplastic Mask and Pneumatic Abdominal Compression Device for Immobilization in Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy of Spine Metastases. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2025, 26, e14577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, Y.A.; Wang, C.J.; Speir, D.B.; Burrell, W.E.; Palomeque, C.D.; Henry, J.C.; Rodrigues, M.M.; Jacobs, T.D.; Broekhoven, B.L.; Dugas, J.P.; et al. Patient Positional Uncertainty and Margin Reduction in Lung Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy Using Pneumatic Abdominal Compression. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 15, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Cathail, S.M.; Smith, T.; Owens, R.; Zeniou, A.; Tsang, Y.; Holyoake, D.L.P.; Murray, L.; Harrison, M.; Hawkins, M.A. Superior Outcomes of Nodal Metastases Compared to Visceral Sites in Oligometastatic Colorectal Cancer Treated with Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 151, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Fan, Y. Combined KRAS and TP53 Mutation in Patients with Colorectal Cancer Enhance Chemoresistance to Promote Postoperative Recurrence and Metastasis. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, D.; Teriaca, M.A.; Dominici, L.; Franzese, C.; Scorsetti, M. Knowing When to Use Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy in Oligometastatic Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 7009–7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdemir, E.Y.; Herrera, R.; Gurdikyan, S.; Hodgson, L.C.; Yarlagadda, S.; Kaiser, A.; Press, R.H.; Mittauer, K.E.; Bassiri-Gharb, N.; Tolakanahalli, R.; et al. Stereotactic Magnetic Resonance Guided Adaptive Radiation Therapy for Infradiaphragmatic Oligometastatic Disease: Disrupting the One-Size-Fits-All Paradigm. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2025, 122, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romesser, P.B.; Tyagi, N.; Crane, C.H. Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Guided Adaptive Radiotherapy for Colorectal Liver Metastases. Cancers 2021, 13, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugurluer, G.; Mustafayev, T.Z.; Gungor, G.; Atalar, B.; Abacioglu, U.; Sengoz, M.; Agaoglu, F.; Demir, G.; Ozyar, E. Stereotactic MR-Guided Online Adaptive Radiation Therapy (SMART) for the Treatment of Liver Metastases in Oligometastatic Patients: Initial Clinical Experience. Radiat. Oncol. J. 2021, 39, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaito, S.; Marvaso, G.; Ortiz, R.; Crellin, A.; Aznar, M.C.; Indelicato, D.J.; Pan, S.; Whitfield, G.; Alongi, F.; Jereczek-Fossa, B.A.; et al. Proton Beam Therapy in the Oligometastatic/Oligorecurrent Setting: Is There a Role? A Literature Review. Cancers 2023, 15, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, W.; Wu, R.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, F. Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy Combined with Fruquintinib and Tislelizumab in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Updated Findings from a Single-Arm, Prospective Phase II Trial (RIFLE). J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, e15570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, J.; Han, D.; Ma, X. Artificial Intelligence Applications in the Treatment of Colorectal Cancer: A Narrative Review. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2024, 18, 11795549231220320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.; Jiang, W.; Mou, B.; Lund, C.R.; Liu, M.; Bergman, A.M.; Schellenberg, D.; Alexander, A.S.; Carolan, H.; Atrchian, S.; et al. Progression-Free Survival and Local Control After SABR for up to 5 Oligometastases: An Analysis From the Population-Based Phase 2 SABR-5 Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 114, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorsetti, M.; Comito, T.; Tozzi, A.; Navarria, P.; Fogliata, A.; Clerici, E.; Mancosu, P.; Reggiori, G.; Rimassa, L.; Torzilli, G.; et al. Final Results of a Phase II Trial for Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Patients with Inoperable Liver Metastases from Colorectal Cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Jücker, M. The Role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling in Tumor Radioresistance and Advances in Inhibitor Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.; Shim, H.S.; Yang, A.J.; Lee, J.J.B.; Yoon, H.I.; Ahn, J.B.; Chang, J.S. Increased Radiosensitivity of Solid Tumors Harboring ATM and BRCA1/2 Mutations. Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 54, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Fan, C.; Luo, B.; Zhang, J.; Jensen, L.D.; Burman, J.; Jönsson, C.; Ljusberg, A.; Larsson, P.; Zhao, Z.; et al. APR-246 Enhances Colorectal Cancer Sensitivity to Radiotherapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2023, 22, 947–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, S.-B.; Cheng, Y.-K.; Zhang, L.; Zou, Y.-F.; Chen, P.; Deng, Y.-H.; Huang, Y.; Peng, J.-H.; Wu, X.-J.; Lan, P. Association of Mismatch Repair Status with Survival and Response to Neoadjuvant Chemo(Radio)Therapy in Rectal Cancer. npj Precis. Oncol. 2020, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, T.S.; Wo, J.Y.; Borger, D.R.; Yeap, B.Y.; McDonnell, E.I.; Willers, H.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Kwak, E.L.; Allen, J.N.; Clark, J.W.; et al. Phase II Study of Proton-Based Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Liver Metastases: Importance of Tumor Genotype. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPartlin, A.; Swaminath, A.; Wang, R.; Pintilie, M.; Brierley, J.; Kim, J.; Ringash, J.; Wong, R.; Dinniwell, R.; Craig, T.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Phase 1 and 2 Studies of SBRT for Hepatic Colorectal Metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 99, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutera, P.; Clump, D.A.; Kalash, R.; D’Ambrosio, D.; Mihai, A.; Wang, H.; Petro, D.P.; Burton, S.A.; Heron, D.E. Initial Results of a Multicenter Phase 2 Trial of Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy for Oligometastatic Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 103, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrelli, F.; Comito, T.; Barni, S.; Pancera, G.; Scorsetti, M.; Ghidini, A. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases: A Systematic Review. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 129, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Acqua, V.; Surgo, A.; Kraja, F.; Kobiela, J.; Zerella, M.A.; Spychalski, P.; Gandini, S.; Francia, C.M.; Ciardo, D.; Fodor, C.; et al. Stereotactic Radiation Therapy in Oligometastatic Colorectal Cancer: Outcome of 102 Patients and 150 Lesions. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2019, 36, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingu, K.; Matsushita, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Umezawa, R.; Ishikawa, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Katagiri, Y.; Takeda, K.; Kadoya, N. Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Pulmonary Oligometastases From Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1533033818794936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Wang, D.; Tian, D.H.; Wilson-Smith, A.; Huang, J.; Rimner, A. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Colorectal Pulmonary Metastases. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 5187–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Cervantes, A.; Adam, R.; Sobrero, A.; Van Krieken, J.H.; Aderka, D.; Aranda Aguilar, E.; Bardelli, A.; Benson, A.; Bodoky, G.; et al. ESMO Consensus Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1386–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO). Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) Model Policy; Version 6.1.0; American Society for Radiation Oncology: Arlington, VA, USA, 2019; Available online: https://www.astro.org/ASTRO/media/ASTRO/Daily%20Practice/PDFs/ASTROSBRTModelPolicy.pdf (accessed on 22 October 2025).
- Lee, B.M.; Kim, H.E.; Yang, Y.H.; Yang, S.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Choi, S.H.; Koom, W.S.; Park, B.J.; Chang, J.S. Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy Versus Surgery in Patients with Pulmonary Metastases from Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2025, 57, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jethwa, K.R.; Jang, S.; Mullikin, T.C.; Harmsen, W.S.; Petersen, M.M.; Olivier, K.R.; Park, S.S.; Neben-Wittich, M.A.; Hubbard, J.M.; Sandhyavenu, H.; et al. Association of Tumor Genomic Factors and Efficacy for Metastasis-Directed Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Oligometastatic Colorectal Cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 146, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.M.; Ma, B.; Taylor, D.L.; Griffith, L.; Wells, A. Liver Metastases: Microenvironments and Ex-Vivo Models. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 241, 1639–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Kuo, L.-M.; Chang, Y.; Wu, W.; Goldbach, C.; Ross, M.A.; Stolz, D.B.; Chen, L.; Fung, J.J.; Lu, L.; et al. In Vivo Immune Modulatory Activity of Hepatic Stellate Cells in Mice. Hepatology 2006, 44, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, T. Molecular Mechanisms of Tumor Resistance to Radiotherapy. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Sun, F.; Chen, D.; Yu, J. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Liver Metastasis in Hypofractionated Radiotherapy-Resistant Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 120, S222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kwon, J.H.; Lee, J.-O.; Bang, S.-M.; Park, K.U.; Kim, D.-W.; Kang, S.-B.; et al. Different Metastatic Pattern According to the KRAS Mutational Status and Site-Specific Discordance of KRAS Status in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Baère, T.; Aupérin, A.; Deschamps, F.; Chevallier, P.; Gaubert, Y.; Boige, V.; Fonck, M.; Escudier, B.; Palussiére, J. Radiofrequency Ablation Is a Valid Treatment Option for Lung Metastases: Experience in 566 Patients with 1037 Metastases. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frattini, M.; Balestra, D.; Suardi, S.; Oggionni, M.; Alberici, P.; Radice, P.; Costa, A.; Daidone, M.G.; Leo, E.; Pilotti, S.; et al. Different Genetic Features Associated with Colon and Rectal Carcinogenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 4015–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-H.; Yan, Y.-Y.; Zeng, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Ni, K.-M.; Yu, X.-R.; Shi, J.-M.; Li, H.-L.; Wang, J.-F.; Yuan, Z.-Y.; et al. The Efficacy and Safety of Neoadjuvant and Adjuvant Chemo(Radio)Therapy Combined with Surgery in Patients with Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer Harboring Defective Mismatch Repair System: A Large-Scale Multicenter Propensity Score Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1626438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, C.; Walch, H.S.; Mueller, K.D.; Boe, L.A.; Ilica, A.T.; Strong, J.; Eichholz, J.E.; Yu, K.K.H.; Wilcox, J.A.; Manca, P.; et al. Clinicogenomic Predictors of Survival and Intracranial Progression after Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Colorectal Cancer Brain Metastases. J. Neurosurg. 2025, 142, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cengel, K.A.; Voong, K.R.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Maggiorella, L.; Brunner, T.B.; Stanbridge, E.; Kao, G.D.; McKenna, W.G.; Bernhard, E.J. Oncogenic K-Ras Signals through Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Wild-Type H-Ras to Promote Radiation Survival in Pancreatic and Colorectal Carcinoma Cells. Neoplasia 2007, 9, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, E.T.; Molloy, C.; Gough, M.; Kryza, T.; Samuel, S.G.; Tucker, A.; Bhatia, M.; Ferguson, G.; Heyman, R.; Vora, S.; et al. Inhibition of Aurora B Kinase (AURKB) Enhances the Effectiveness of 5-Fluorouracil Chemotherapy against Colorectal Cancer Cells. Br. J. Cancer 2024, 130, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Park, J.-E.; Lee, W.H.; Kwon, Y.B.; Seu, Y.-B.; Kim, K.S. Novel Amidine Derivative K1586 Sensitizes Colorectal Cancer Cells to Ionizing Radiation by Inducing Chk1 Instability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekers, N.H.; Olivo Pimentel, V.; Yaromina, A.; Lieuwes, N.G.; Biemans, R.; Zegers, C.M.L.; Germeraad, W.T.V.; Van Limbergen, E.J.; Neri, D.; Dubois, L.J.; et al. The Immunocytokine L19-IL2: An Interplay between Radiotherapy and Long-Lasting Systemic Anti-Tumour Immune Responses. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1414119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Limbergen, E.J.; Hoeben, A.; Lieverse, R.I.Y.; Houben, R.; Overhof, C.; Postma, A.; Zindler, J.; Verhelst, F.; Dubois, L.J.; De Ruysscher, D.; et al. Toxicity of L19-Interleukin 2 Combined with Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy: A Phase 1 Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 109, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Proof of Concept through a Randomised Phase II Study: A Combination of Immunotherapy and Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy as a Curative Treatment for Limited Metastatic Lung Cancer. Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/733008 (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Zhao, Y.; Tang, Y.; Jin, J. Phase II Study of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) in Patients with Lung and/or Liver Oligometastases from Colorectal Cancer (CRC): KRAS Gene Status and Metastatic Site Matter. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 114, e438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klement, R.J.; Guckenberger, M.; Alheid, H.; Allgäuer, M.; Becker, G.; Blanck, O.; Boda-Heggemann, J.; Brunner, T.; Duma, M.; Gerum, S.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Oligo-Metastatic Liver Disease–Influence of Pre-Treatment Chemotherapy and Histology on Local Tumor Control. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 123, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Peng, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 71, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boysen, A.K.; Pallisgaard, N.; Andersen, C.S.A.; Spindler, K.-L.G. Circulating Tumor DNA as a Marker of Minimal Residual Disease Following Local Treatment of Metastases from Colorectal Cancer. Acta Oncol. 2020, 59, 1424–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, A.; Fontana, E.; Nyamundanda, G.; Ragulan, C.; Patil, Y.; Mansfield, D.; Kingston, J.; Errington-Mais, F.; Bottomley, D.; von Loga, K.; et al. Differential and Longitudinal Immune Gene Patterns Associated with Reprogrammed Microenvironment and Viral Mimicry in Response to Neoadjuvant Radiotherapy in Rectal Cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001717, Correction in J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001717corr1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagendijk, J.J.W.; Raaymakers, B.W.; van Vulpen, M. The Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Linac System. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 24, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shortall, J.; Vasquez Osorio, E.; Aitkenhead, A.; Berresford, J.; Agnew, J.; Budgell, G.; Chuter, R.; McWilliam, A.; Kirkby, K.; Mackay, R.; et al. Experimental Verification the Electron Return Effect around Spherical Air Cavities for the MR-Linac Using Monte Carlo Calculation. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 2506–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sritharan, K.; Tree, A. MR-Guided Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20210800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.Z.Y.; Shan, S.; Waddington, D.; Whelan, B.; Dong, B.; Liney, G.; Keall, P. Rapid Distortion Correction Enables Accurate Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Guided Real-Time Adaptive Radiotherapy. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 25, 100414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, S.A.; Henke, L.E.; Shaverdian, N.; Mittauer, K.; Wojcieszynski, A.P.; Hullett, C.R.; Kamrava, M.; Lamb, J.; Cao, M.; Green, O.L.; et al. A Multi-Institutional Experience of MR-Guided Liver Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 4, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.C.; Morais, J.A.V.; Ganassin, R.; Oliveira, G.R.T.; Costa, F.C.; Morais, A.A.C.; Silveira, A.P.; Silva, V.C.M.; Longo, J.P.F.; Muehlmann, L.A. An Overview on Immunogenic Cell Death in Cancer Biology and Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, H. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1–Mediated Characteristic Features of Cancer Cells for Tumor Radioresistance. J. Radiat. Res. 2016, 57, i99–i105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gérard, M.; Corroyer-Dulmont, A.; Lesueur, P.; Collet, S.; Chérel, M.; Bourgeois, M.; Stefan, D.; Limkin, E.J.; Perrio, C.; Guillamo, J.-S.; et al. Hypoxia Imaging and Adaptive Radiotherapy: A State-of-the-Art Approach in the Management of Glioma. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Osmundson, E.C.; Donahue, M.J.; De Vis, J.B. Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Detect Tumor Hypoxia in Brain Malignant Disease: A Systematic Review of Validation Studies. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2025, 52, 100940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fast, M.; van de Schoot, A.; van de Lindt, T.; Carbaat, C.; van der Heide, U.; Sonke, J.-J. Tumor Trailing for Liver SBRT on the MR-Linac. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 103, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, A.R.; Szabolcs, A.; Allen, J.N.; Clark, J.W.; Wo, J.Y.; Raabe, M.; Thel, H.; Hoyos, D.; Mehta, A.; Arshad, S.; et al. Radiation Therapy Enhances Immunotherapy Response in Microsatellite-Stable Colorectal and Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma in a Phase II Trial. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, P.; Pan, Y. Case Report: The MSI-L/p-MMR Metastatic Rectal Cancer Patient Who Failed Systemic Therapy Responds to Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy after Stereotactic Body Radiation-Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 981527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Chan, C.K.; Weissman, I.L.; Kim, B.Y.S.; Hahn, S.M. Immune Priming of the Tumor Microenvironment by Radiation. Trends Cancer 2016, 2, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Liang, H.; Burnette, B.; Beckett, M.; Darga, T.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Fu, Y.-X. Irradiation and Anti–PD-L1 Treatment Synergistically Promote Antitumor Immunity in Mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2014, 124, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, A.G.; Makarova-Rusher, O.V.; Pratt, D.; Kleiner, D.E.; Fioravanti, S.; Walker, M.; Carey, S.; Figg, W.D.; Steinberg, S.M.; Anderson, V.; et al. A Pilot Study of AMP-224, a PD-L2 Fc Fusion Protein, in Combination with Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floudas, C.S.; Brar, G.; Mabry-Hrones, D.; Duffy, A.G.; Wood, B.; Levy, E.; Krishnasamy, V.; Fioravanti, S.; Bonilla, C.M.; Walker, M.; et al. A Pilot Study of the PD-1 Targeting Agent AMP-224 Combined with Low-Dose Cyclophosphamide and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2019, 18, e349–e360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.T.; Uram, J.N.; Wang, H.; Bartlett, B.R.; Kemberling, H.; Eyring, A.D.; Skora, A.D.; Luber, B.S.; Azad, N.S.; Laheru, D.; et al. PD-1 Blockade in Tumors with Mismatch-Repair Deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2509–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theelen, W.S.M.E.; Chen, D.; Verma, V.; Hobbs, B.P.; Peulen, H.M.U.; Aerts, J.G.J.V.; Bahce, I.; Niemeijer, A.L.N.; Chang, J.Y.; de Groot, P.M.; et al. Pembrolizumab with or without Radiotherapy for Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Pooled Analysis of Two Randomised Trials. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 467–475, Correction in Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altorki, N.K.; McGraw, T.E.; Borczuk, A.C.; Saxena, A.; Port, J.L.; Stiles, B.M.; Lee, B.E.; Sanfilippo, N.J.; Scheff, R.J.; Pua, B.B.; et al. Neoadjuvant Durvalumab with or without Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Patients with Early-Stage Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Single-Centre, Randomised Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, A.; Morel, D.; Texier, M.; Sun, R.; Durand-Labrunie, J.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Racadot, S.; Supiot, S.; Magné, N.; Cyrille, S.; et al. An International Phase II Trial and Immune Profiling of SBRT and Atezolizumab in Advanced Pretreated Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciscano, A.E.; Haimovitz-Friedman, A.; Lee, P.; Tran, P.T.; Tomé, W.A.; Guha, C.; Spring Kong, F.-M.; Sahgal, A.; El Naqa, I.; Rimner, A.; et al. Immunomodulatory Effects of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy: Preclinical Insights and Clinical Opportunities. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 110, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.W.; Kim, H.; Cho, H.; Kim, M.-S.; Paek, S.-H.; Park, H.-J.; Griffin, R.J.; Terezakis, S.; Cho, L.C. HIF-1α Inhibition Improves Anti-Tumor Immunity and Promotes the Efficacy of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SABR). Cancers 2022, 14, 3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, M.B.; Krishnan, S.; Hodge, J.W.; Chang, J.Y. Immunotherapy and Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (ISABR): A Curative Approach? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 13, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.Y.; Xu, X.; Shroff, G.S.; Comeaux, N.I.; Li, W.; Ahnert, J.R.; Karp, D.D.; Dumbrava, E.E.; Verma, V.; Chen, A.; et al. Phase I/II Study of BMS-986156 with Ipilimumab or Nivolumab with or without Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy in Patients with Advanced Solid Malignancies. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e009975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanpouille-Box, C.; Alard, A.; Aryankalayil, M.J.; Sarfraz, Y.; Diamond, J.M.; Schneider, R.J.; Inghirami, G.; Coleman, C.N.; Formenti, S.C.; Demaria, S. DNA Exonuclease Trex1 Regulates Radiotherapy-Induced Tumour Immunogenicity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davar, D.; Zappasodi, R. Targeting GITR in Cancer Immunotherapy – There Is No Perfect Knowledge. Oncotarget 2023, 14, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpics, M.C.; Katipally, R.R.; Partouche, J.; Cutright, D.; Pointer, K.B.; Bestvina, C.M.; Luke, J.J.; Pitroda, S.P.; Dignam, J.J.; Chmura, S.J.; et al. Predictors of Pneumonitis in Combined Thoracic Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy and Immunotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 114, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deming, D.A.; Lubner, S.J.; Uboha, N.V.; Emmerich, P.; Kraus, S.; LoConte, N.K.; Kim, D.H.; Matkowskyj, K.A.; Weber, S.; Abbott, D.; et al. Phase Ib of Pembrolizumab (Pem) in Combination with Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) for Resectable Liver Oligometastatic MMR-Proficient (pMMR) Colorectal Cancer (CRC): Final Results. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demaria, S.; Ng, B.; Devitt, M.L.; Babb, J.S.; Kawashima, N.; Liebes, L.; Formenti, S.C. Ionizing Radiation Inhibition of Distant Untreated Tumors (Abscopal Effect) Is Immune Mediated. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2004, 58, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagoglu, N.; Karaman, S.; Caglar, H.B.; Oral, E.N. Abscopal Effect of Radiotherapy in the Immunotherapy Era: Systematic Review of Reported Cases. Cureus 2019, 11, e4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuodeh, Y.; Venkat, P.; Kim, S. Systematic Review of Case Reports on the Abscopal Effect. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2016, 40, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiko, K.; Matsumura, N.; Hamanishi, J.; Horikawa, N.; Murakami, R.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yoshioka, Y.; Baba, T.; Konishi, I.; Mandai, M. IFN-γ from Lymphocytes Induces PD-L1 Expression and Promotes Progression of Ovarian Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1501–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiravand, Y.; Khodadadi, F.; Kashani, S.M.A.; Hosseini-Fard, S.R.; Hosseini, S.; Sadeghirad, H.; Ladwa, R.; O’Byrne, K.; Kulasinghe, A. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 3044–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, T.P.; Greenberg, R.A. The Abscopal Effect: A Sense of DNA Damage Is in the Air. J. Clin. Invest. 2021, 131, e148274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, D.; Siva, S.; Hanna, G.G. The Abscopal Effect of Stereotactic Radiotherapy and Immunotherapy: Fool’s Gold or El Dorado? Clin. Oncol. 2019, 31, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwa, W.; Irabor, O.C.; Schoenfeld, J.D.; Hesser, J.; Demaria, S.; Formenti, S.C. Using Immunotherapy to Boost the Abscopal Effect. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, B.; Hyde, D.; Becker, N. Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Oligometastatic Pericolonic Soft Tissue Metastases Using Daily Cone-Beam Computed Tomography-Guided Online Adaptive Radiotherapy. Cureus 2021, 16, e69937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Kang, K.; Han, C.; Wang, S.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Z. A Blind Randomized Validated Convolutional Neural Network for Auto-segmentation of Clinical Target Volume in Rectal Cancer Patients Receiving Neoadjuvant Radiotherapy. Cancer Med. 2021, 11, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira Silvério, N.; van den Wollenberg, W.; Betgen, A.; Wiersema, L.; Marijnen, C.; Peters, F.; van der Heide, U.A.; Simões, R.; Janssen, T. Evaluation of Deep Learning Clinical Target Volumes Auto-Contouring for Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Guided Online Adaptive Treatment of Rectal Cancer. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 9, 101483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Chai, F.; Wei, J.; Yue, Y.; Cheng, J.; Gu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, T.; Sheng, W.; Hong, N.; et al. Identification of Predominant Histopathological Growth Patterns of Colorectal Liver Metastasis by Multi-Habitat and Multi-Sequence Based Radiomics Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Royal College of Radiologists. Auto-Contouring in Radiotherapy: Guidance for Selection, Implementation and Monitoring. 2024. Available online: https://www.rcr.ac.uk/our-services/all-our-publications/clinical-oncology-publications/auto-contouring-in-radiotherapy/ (accessed on 16 October 2025).
- Psoroulas, S.; Paunoiu, A.; Corradini, S.; Hörner-Rieber, J.; Tanadini-Lang, S. MR-Linac: Role of Artificial Intelligence and Automation. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2025, 201, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Yao, C.; Zhang, L.; Qi, S. Application of Artificial Intelligence in Diagnosis and Treatment of Colorectal Cancer: A Novel Prospect. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1128084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitsam, N.G.; Enke, J.S.; Vu Trung, K.; Märkl, B.; Kather, J.N. Artificial Intelligence in Colorectal Cancer: From Patient Screening over Tailoring Treatment Decisions to Identification of Novel Biomarkers. Digestion 2024, 105, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Lama, N.; Chen, M.; Amidi, E.; Ramzanpour, M.; Rahman, M.A.; Xiu, J.; Helmstetter, A.; Dickman, L.; Ribeiro, J.R.; et al. Synergistic H&E and IHC Image Analysis by AI Predicts Cancer Biomarkers and Survival Outcomes in Colorectal and Breast Cancer. Commun. Med. 2025, 5, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilla, S.; Pistilli, D.; Romano, C.; Macchia, G.; Pierro, A.; Arcelli, A.; Buwenge, M.; Morganti, A.G.; Deodato, F. CT-Based Radiomics Prediction of Complete Response after Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Patients with Lung Metastases. Strahlenther. Und Onkol. 2023, 199, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibragimov, B.; Toesca, D.A.S.; Yuan, Y.; Koong, A.C.; Chang, D.T.; Xing, L. Neural Networks for Deep Radiotherapy Dose Analysis and Prediction of Liver SBRT Outcomes. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2019, 23, 1821–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study (First Author, Year) | Alteration(s) Examined | RT Setting (Site/Modality) | Reported Impact/Association | Key Results | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jethwa et al., 2020 [56] | KRAS; TP53; combined KRAS + TP53 | Oligometastatic CRC, multi-site photon SABR (85 patients, 109 lesions) | KRAS mutations associated with reduced OS; KRAS + TP53 double mutants with highest local-failure risk | 1-year LF 44% vs. 11% (WT); OS HR 2.4 for KRAS; HR 5.7 for KRAS + TP53 | Retrospective; first dedicated genomic–SABR analysis in CRC metastases |
| Hong et al., 2017 [46] | KRAS; TP53; KRAS + TP53 | Proton-based SABR, liver metastases (89 pts; 34 CRC) | KRAS mutation strongest predictor of poor LC; all double mutants failed locally | 1 yr LC 42.9% (KRAS mut) vs. 72.1% (WT); KRAS + TP53 1 yr LC 20% | Mixed primaries but CRC-dominant subset; modest dose range (30–50 GyE/5 fx) |
| Zhao et al., 2022 [72] | KRAS mutation status | Prospective phase II, lung and/or liver SABR for oligometastatic CRC (48 pts, 60 lesions) | KRAS status identified as an independent prognostic factor for local control, along with metastatic site, PTV, and time to metastasis | 1 yr LC 88.3%, 3 yr LC 65.9%; median BED ≈ 100 Gy; no grade ≥ 3 toxicity | First prospective study to demonstrate KRAS status as a significant predictor of LC following SBRT in CRC oligometastases |
| Gui et al., 2021 [65] | TP53 (driver) ± MYC-pathway | SRS, brain metastases from CRC (123 pts) | TP53 drivers increases risk of intracranial progression; MYC alterations protective | HR 2.7 for intracranial progression with TP53 driver; HR 0.15 for MYC-pathway | Stereotactic radiosurgery data but mechanistically relevant to SABR radioresistance |
| Wang et al., 2023 [59] | dMMR/MSI-H | Rectal chemoradiotherapy (locally advanced; 119 pts) | dMMR/MSI-H tumours relatively resistant to CRT; surgery-alone outcomes superior | Adjusted analysis: CRT arm worse OS and PFS in MSI-H cohort (p < 0.05) | Conventional RT, not SABR; included for context on genotype-specific radiosensitivity |
| Trial Name | Trial Type | Progress of Trial | Population | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT06120127 | Randomised controlled phase II | Recruiting | Colorectal liver metastases with high risk of local recurrence | Postoperative chemotherapy with/without radiotherapy and immunotherapy |
| NCT06603818 | Prospective | Not yet recruiting | Microsatellite stable metastatic colorectal cancer | Tiragolumab and atezolizumab combined with radiotherapy |
| NCT06794086 | Prospective, single-arm, phase II | Recruiting | Unresectable colorectal cancer liver metastases | SBRT combined with PD-1 inhibitors |
| NCT06130826 | Phase I dose escalation study | Recruiting | Unresectable or metastatic colorectal cancer (and CEA positive breast cancer) | M5A-IL2 immunocytokine and SBRT |
| NCT06053996 | Proof of concept phase II trial | Not yet recruiting | Metastatic colorectal cancer | Ablation of hepatic and pulmonary metastases with SBRT in combination with checkpoint inhibition |
| NCT06300463 | Three-arm randomised phase II trial | Recruitment | Patients with colorectal cancer liver metastases pre-surgery | Combination immunotherapy (botensilimab/balstilimab) with or without radiation and/or TGFβ-CD73 trap |
| NCT06349044 | Randomised multicentre phase II | Recruitment | Colorectal adenocarcinoma | SBRT, Probio-M9 microbial agents and PD-1 inhibitors |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Sattar, H.; Okondo, E.; Jaafari, A.M.; Sood, I.; Hassan Dinif, J.; Lim, S.Y.; Hafkamp, C.; Chong, I.; Galante, J.R.; Adeleke, S. Emerging Applications of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy in Oligometastatic Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110302
Al-Sattar H, Okondo E, Jaafari AM, Sood I, Hassan Dinif J, Lim SY, Hafkamp C, Chong I, Galante JR, Adeleke S. Emerging Applications of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy in Oligometastatic Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110302
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Sattar, Hasan, Esele Okondo, Amir Mashia Jaafari, Inesh Sood, Jakob Hassan Dinif, Su Yin Lim, Charlotte Hafkamp, Irene Chong, Joao R. Galante, and Sola Adeleke. 2025. "Emerging Applications of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy in Oligometastatic Colorectal Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110302
APA StyleAl-Sattar, H., Okondo, E., Jaafari, A. M., Sood, I., Hassan Dinif, J., Lim, S. Y., Hafkamp, C., Chong, I., Galante, J. R., & Adeleke, S. (2025). Emerging Applications of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy in Oligometastatic Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110302







