Mechanisms of Arsenic Interaction in Bacillus subtilis and Related Species with Biotechnological Potential
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Arsenic Toxicity and Cellular Interactions
2.1. Chemical Forms and Public Health Impact
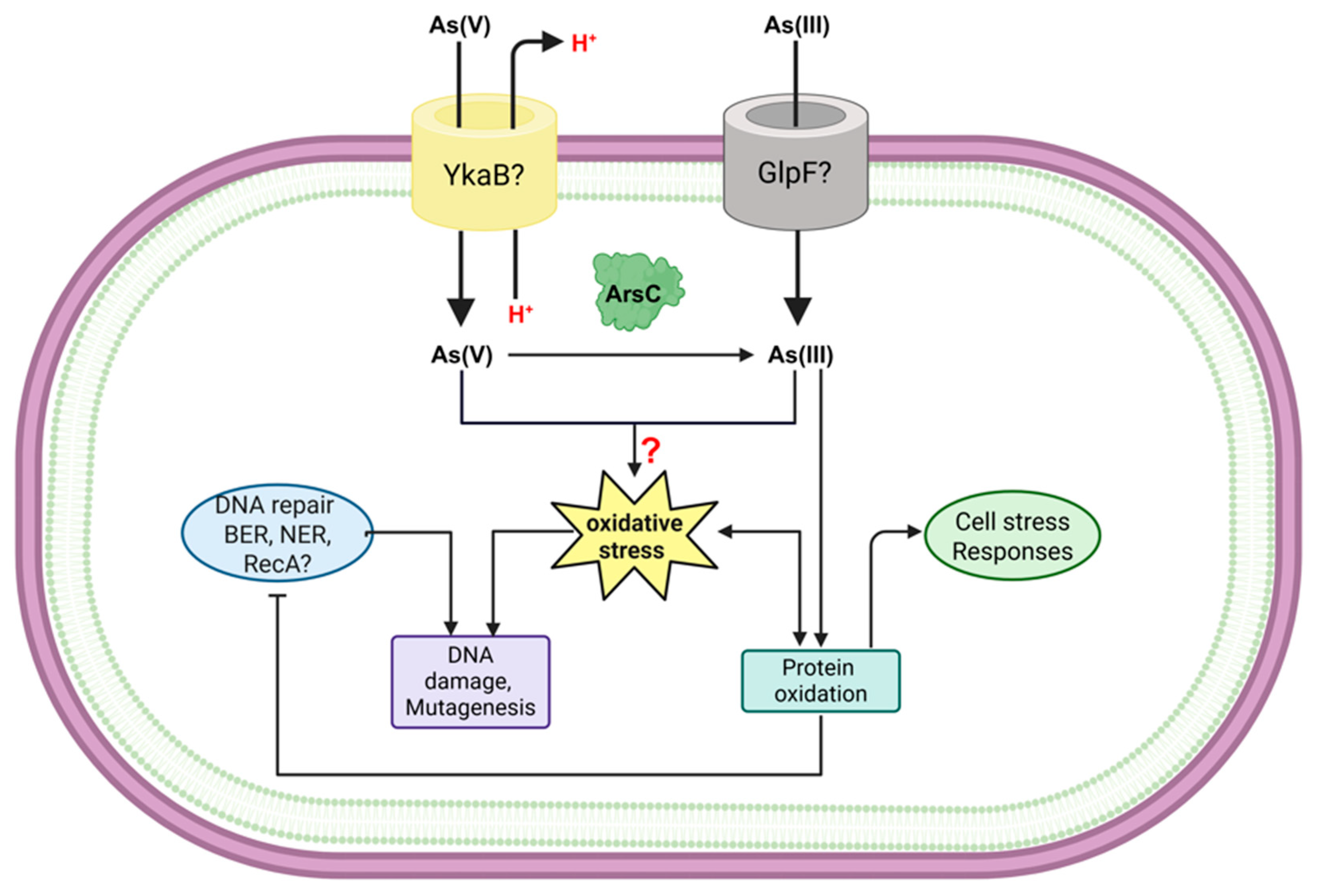
2.2. Mechanisms of Toxicity and Detoxification of Arsenic
2.3. The First Line of Defense: Extracellular Detoxification
2.3.1. Cell Surface Immobilization
2.3.2. Transformation of As by Extracellular Enzymes
2.4. Gateways to Toxicity: Cellular Uptake Pathways
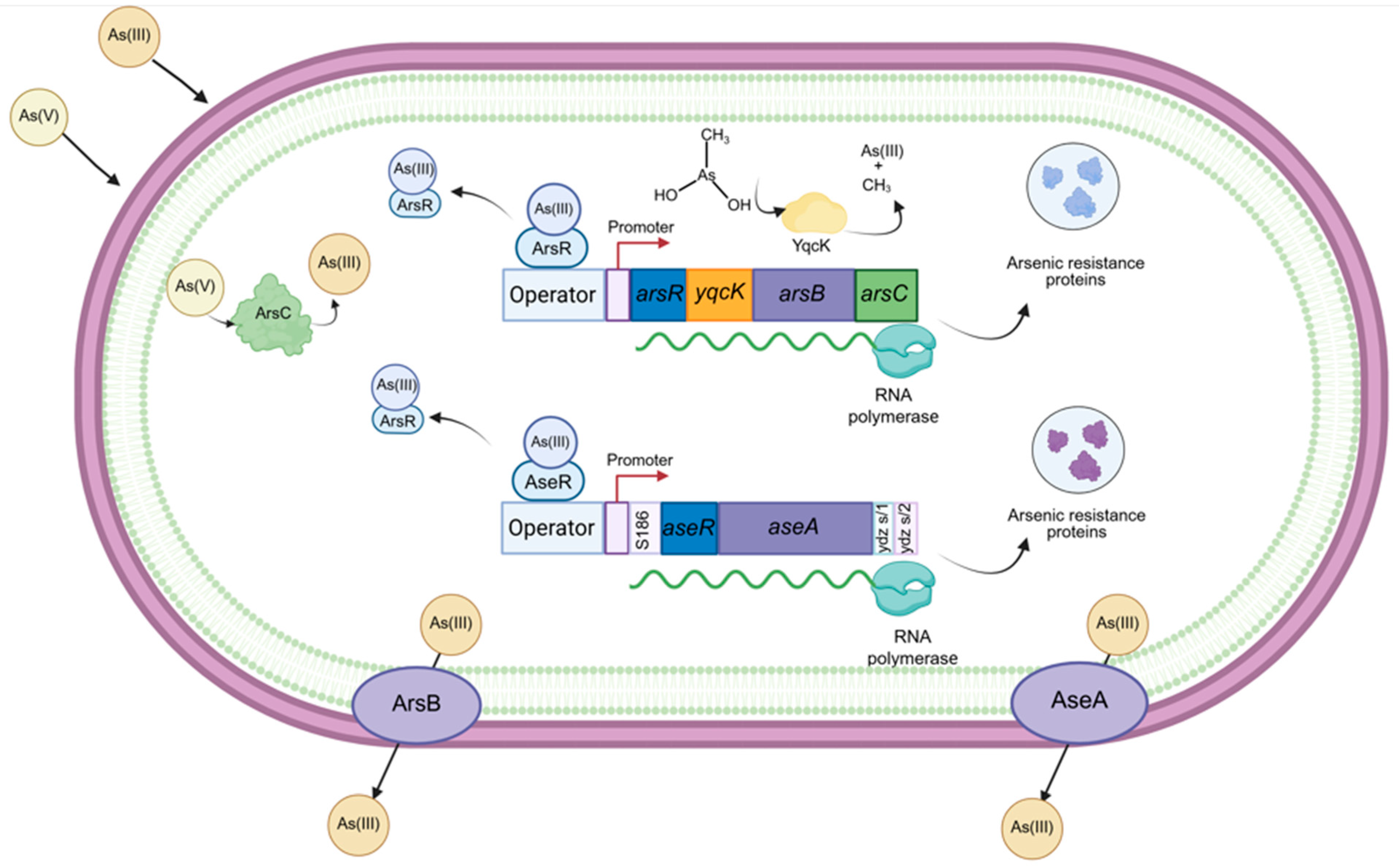
3. Molecular Arsenic Resistance Mechanisms in Bacillus subtilis
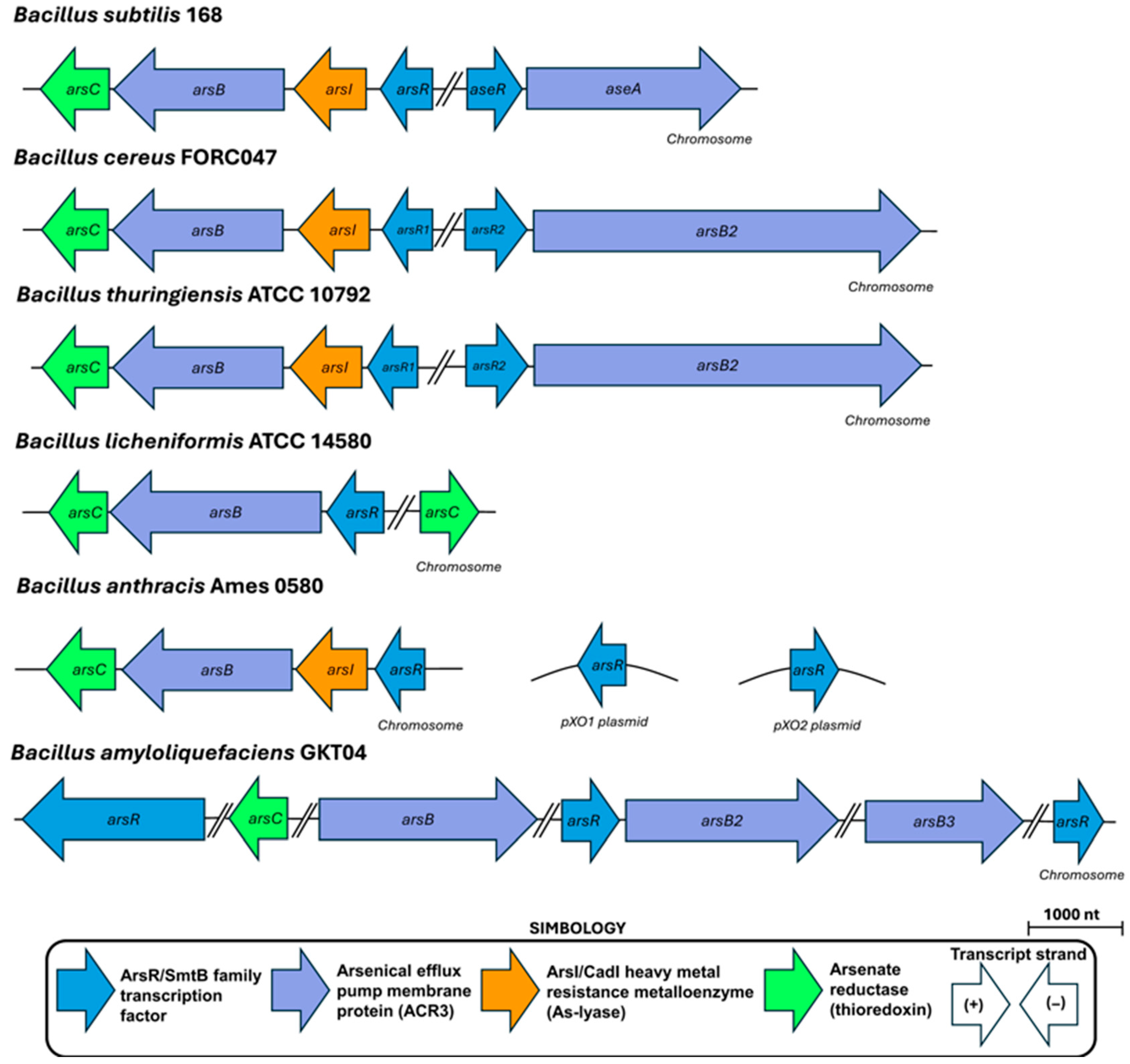
3.1. The B. subtilis Ars Operon: A Phage-Derived Genetic Island
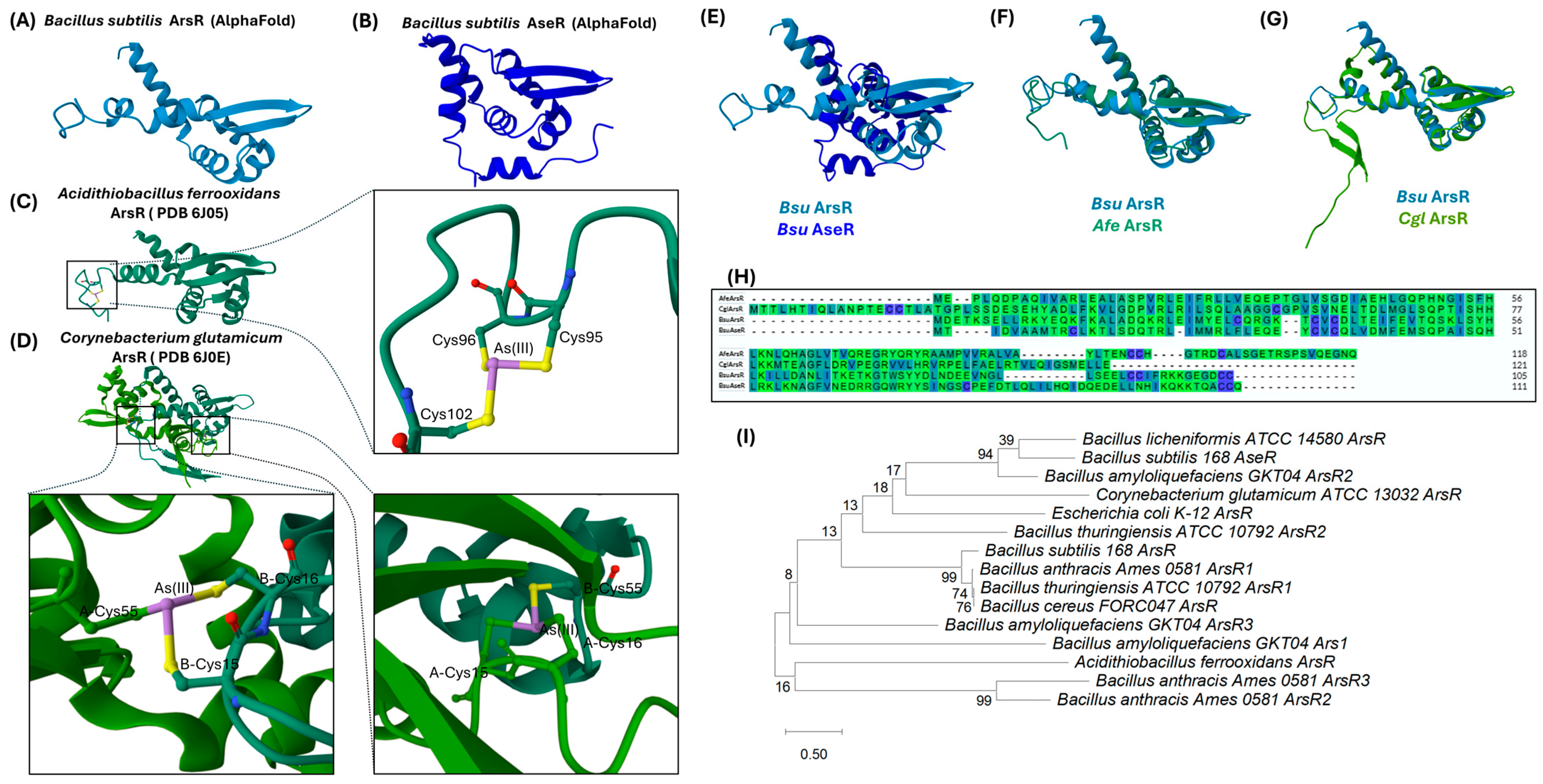
3.1.1. ArsR: The Metalloid-Sensing Repressor
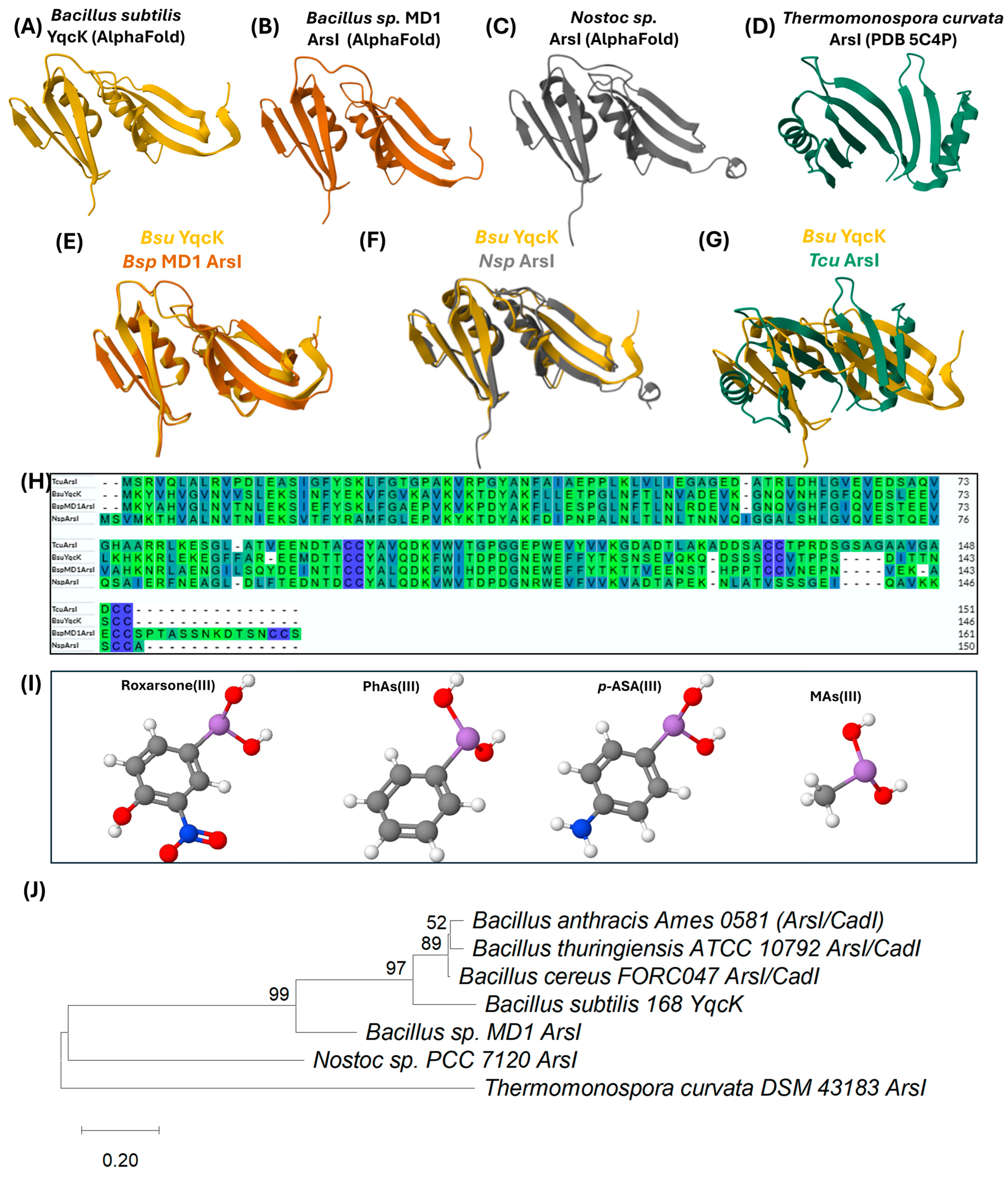
3.1.2. ArsI: The Organoarsenical Lyase
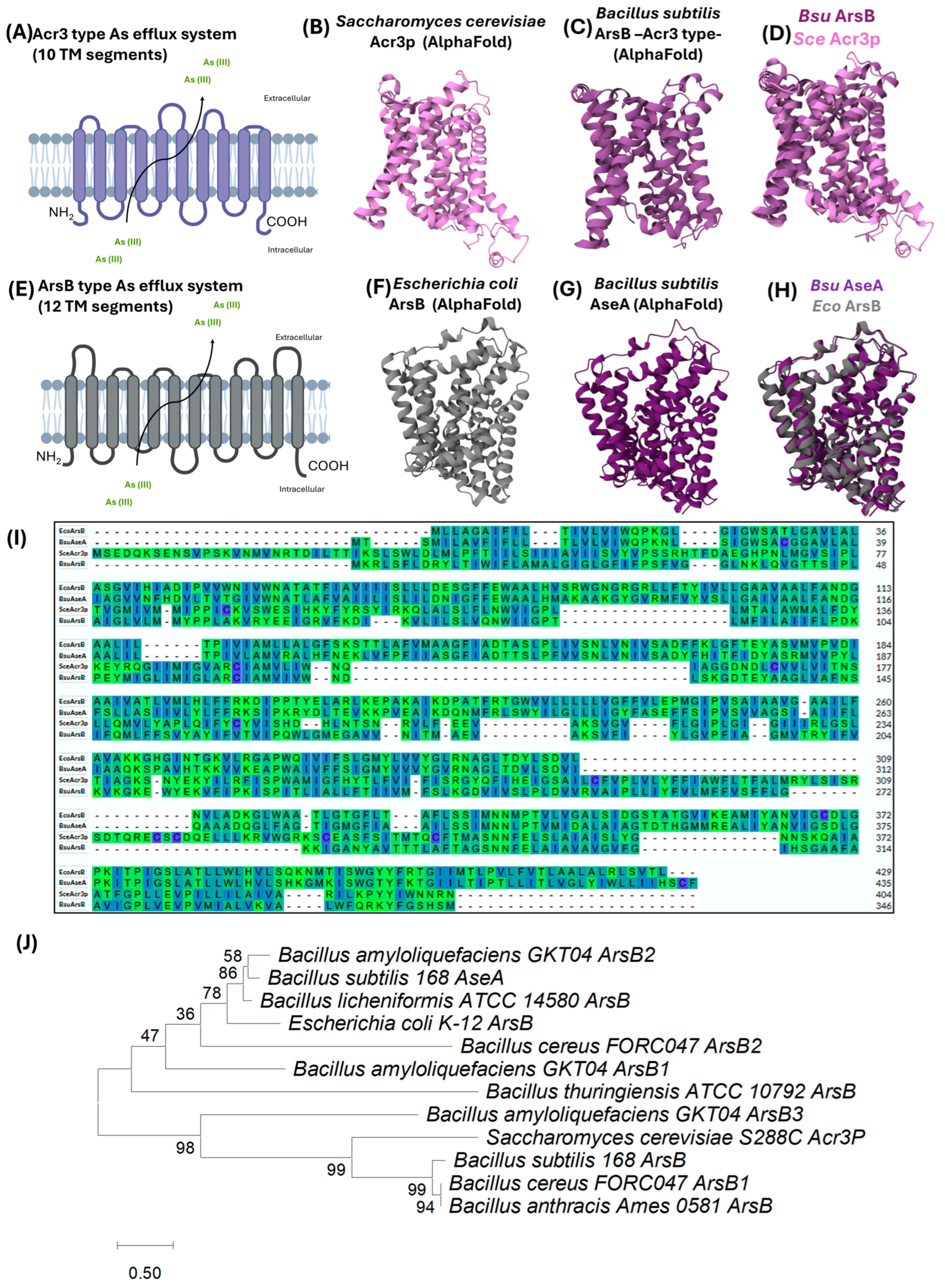
3.1.3. ArsB: The Acr3-Type Efflux Pump
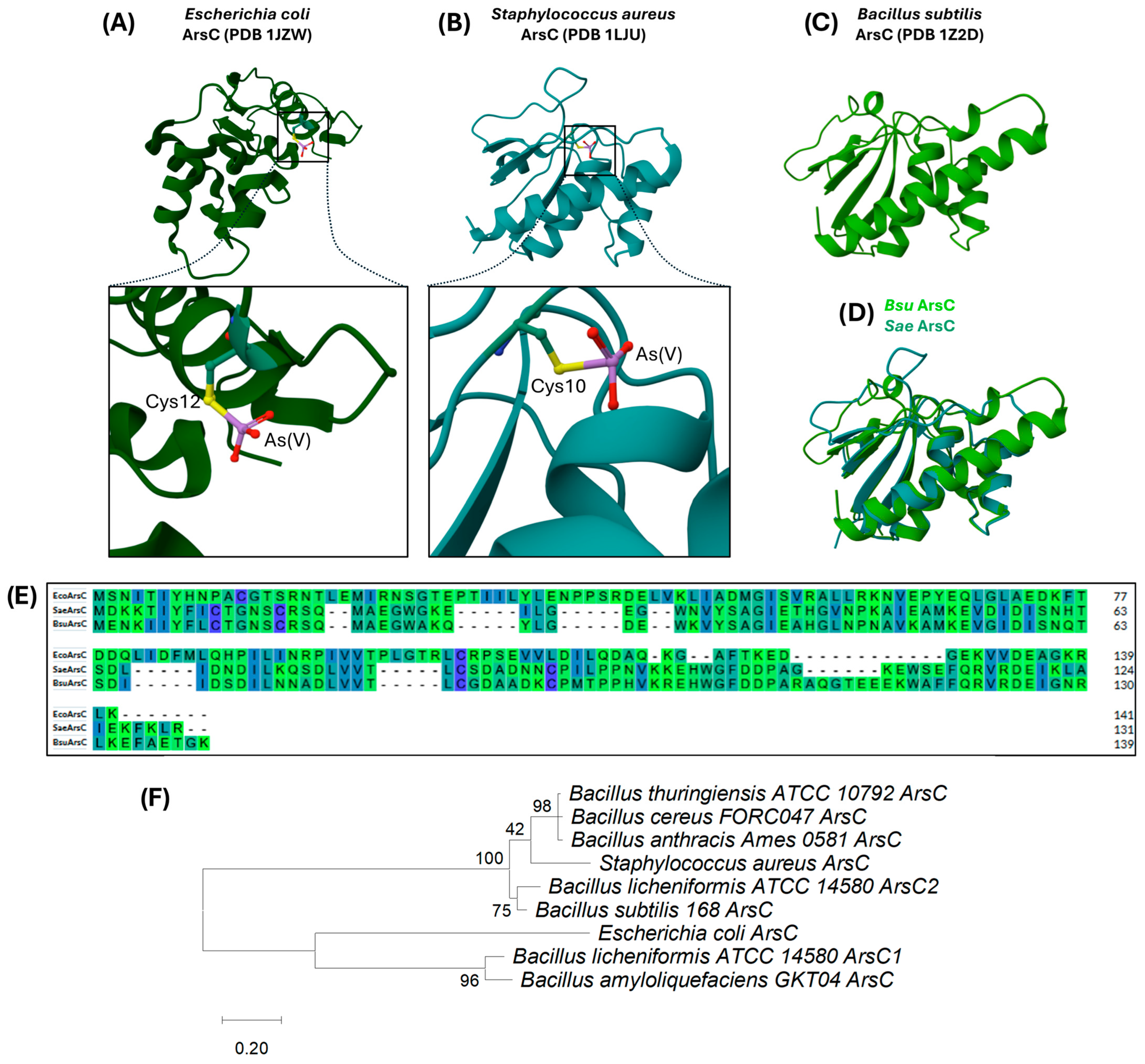
3.1.4. ArsC: The Arsenate Reductase
3.2. The Ase Operon: A Chromosomal Arsenic Resistance System
3.2.1. AseR: A Second Layer of Regulation
3.2.2. AseA: An ArsB-Type Efflux Pump
3.3. Beyond Core Operons: Additional Genetic Determinants
| As Resistance Proteins | Possible Genes with Homology in B. subtilis | Similarity (%) | Description | Gene Function Evidence | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ArsH | yhdA | 25.41% | NADPH-dependent FMN oxidoreductase | Experimental | [21,115,116,123] |
| ArsM | ydaC | 28.70% | similar to N-methyltransferase | Putative | [21,90,117] |
| ArsN | - | - | [114] | ||
| ArsJ | - | - | [103,118] | ||
| ArsP | ycgR | 23.55% | membrane protein similar to permease | Putative | [90,119] |
| ArsO | czcO | 27.48% | flavin-containing monooxygenase, facilitates cation export via CzcD | Experimental | [103,121,124] |
| ArsT | yumC | 26.88% | ferredoxin/flavodoxin-NAD(P) oxidoreductase | Experimental | [122,125] |
| ArsK | - | - | [103,120] |
3.4. Overcoming Genetic Damage: DNA Repair and Stress Responses
4. Bacillus Species Resistant to Arsenic: From Environmental Strains to Biotechnological Tools
4.1. Environmental Isolates of Arsenic-Resistant Bacillus
| Isolation Site Contaminated with Arsenic | Identified Species | References |
|---|---|---|
| Aquifers contaminated with arsenic | ||
| West Bengal, India | Bacillus indicus sp. nov. | [138] |
| West Bengal, India | Bacillus arsenicus sp. nov. | [139] |
| Brahmaputra River basin, India | Bacillus sp. IIIJ3-1 | [56] |
| Groundwater wells of Hazrapara and Ghoshpara locality of Beldanga, Murshidabad (Distt.), West Bengal, India | Bacillus sp. | [135] |
| Well water, Taif City, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia | Bacillus fusiformis strain EA2, Bacillus cereus strains EA4, EA5 y EA6 | [140] |
| Water bodies | ||
| Spring of water in Qorveh county, Kurdistan province, Iran | Bacillus flexus A-12 | [59] |
| Geothermal systems of Araró, Mexico | Bacillus altitudinis ZAP62, Bacillus paralicheniformis ZAP17 | [111] |
| Surface and groundwater samples, Rautahat District of Nepal | Bacillus smithii, Bacillus cereus | [141] |
| Lake and lagoon sediments | ||
| Lake Oliveri–Tindari lake sediments, Italy | Bacillus sp. | [142] |
| Sediments of the Orbetello Lagoon, Italy | Bacillus sp. ORAs2 | [143] |
| Sediments of Mono Lake, California | Bacillus arsenicoselenatis, sp. nov., Bacillus selenitireducens, sp. nov. | [55] |
| Sediments of Mono Lake, California | Bacillus beveridgei sp. nov. | [144] |
| Aquifer sediments of Datong Basin | Bacillus cereus strain XZM002 | [145] |
| Soils | ||
| Soil from Alkaline Crater Lake, Lonar, Maharastra, India | Bacillus firmus L-148 | [57] |
| Soil from Alps, Italy | Bacillus sp. | [146] |
| Agricultural soil and mining origin soil, Guanajuato, Mexico | Bacillus simplex, Bacillus simplex strain LRV34, Bacillus muralis strain HlS3200905, Bacillus simplex strain Md1-25, Bacillus megaterium strain LB11, Bacillus sp. strain Whitaker B12, Bacillus megaterium strain 1S7 | [134] |
| Soil from Beijing, China | Bacillus idriensis | [147] |
| Soil of the Panki thermal power plant, Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh, India | Bacillus cereus AG27 | [133,135] |
| Soil of Miyazaki Prefecture, Japan | Bacillus megaterium strain UM-123 | [148] |
| Soil of Unnao district of Uttar Pradesh (India) | B. megaterium and B. pumilus | [149] |
| Soil of Uttar Pradesh, India | B. subtilis | [69] |
| Soil of Shanxi Province in Northwest China | Bacillus thuringiensis sp. IAM | [150] |
| Soils from cattle dip sites | Bacillus sp. CDB3 | [151] |
| Golf course flooring, Florida, United States of America | Bacillus sp. MD1 | [91] |
| Industrial and domestic effluents | ||
| Industrial effluent treatment plant, Vapi, India | Bacillus sp. DJ-1 | [152] |
| Industrial wastewater from the chemical industry in Sheikhupura, Pakistan | Bacillus licheniformis | [58] |
| Wastewater from outskirts of Lahore, Pakistan | Bacillus subtilis L24, Bacillus safensis L26 and Bacillus subtilis T23 | [153] |
| Sediment from an effluent drain from a glass-manufacturing plant | Bacillus selenatarsenatis sp. nov. | [154] |
| Tannery effluents of Savar, Bangladesh | Bacillus anthracis | [155] |
| Mines | ||
| Sediment from mining site, Hokkaido, Japan | Bacillus cereus, Bacillus pumilus, | [156] |
| Ore sample, Bundugurang opencast uranium mine, India | Bacillus altitudinis 41KF2a | [157] |
| Acid mine drainage site in Sabah, Malaysia | Bacillus thuringiensis | [158] |
| Soil samples from a gold mining area, Paracatu, Minas Gerais, Brazil | Bacillus cereus (P2Ic, P1C1Ib) | [132] |
| Desertic ecosystems | ||
| Mongolian desert soil | Bacillus safensis MS11 | [159] |
| Rizosphere | ||
| Rhizosphere of the plant Prosopis laevigata from Villa de la Paz, located in the mining district of Santa María, in the State of San Luis Potosi, Mexico | Bacillus megaterium Jz11, Bacillus aryabhattai B8W22, Bacillus simplex 98AIA, Bacillus axarquiensis, Bacillus malacitensis CECT, Bacillus subtilis CYBS15, Bacillus vallismortis DSM 11,031, Bacillus endophyticus 70BC7, Bacillus niacini IFO15566, | [137] |
| Rhizosphere of Amaranthus viridis, Bihar Sharif, India | Bacillus licheniformis DAS-2 | [41] |
| Rhizosphere of Pteris vittata L. in Hanyuan, Sichuan, China | Bacillus indicus, Bacillus cereus, Bacillus muralis, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus megaterium, Bacillus sp. | [136] |
| Rhizospheric soil samples from the Baruipur district, West Bengal, India | Bacillus flexus NM02 | [160] |
| Other sites | ||
| Surface of used polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottle fragments | Bacillus sp. EIKU23 | [161] |
| Sludge of a sewage treatment plant, Taiwan, China | Bacillus cereus OSBH5 | [162] |
| Mangrove sediment, Matang Mangrove Forest, Perak, Malaysia | Bacillus sp. CCB-MMP212 | [163] |
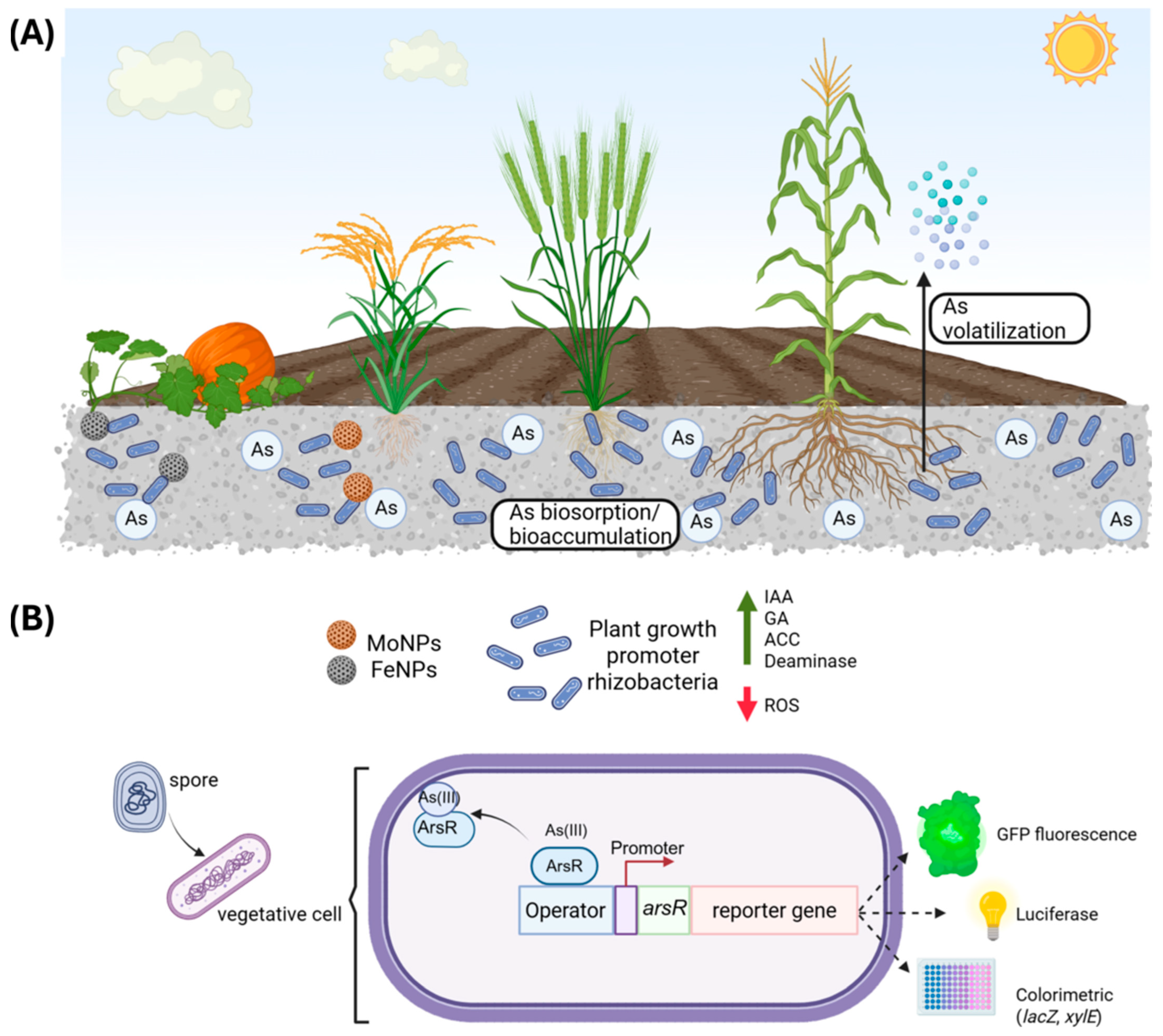
4.2. Harnessing Bacillus for Bioremediation and Sustainable Agriculture
4.3. Engineering Biosensors: Precision Detection of Arsenic
5. Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Errington, J.; van der Aart, L.T. Microbe Profile: Bacillus subtilis: Model Organism for Cellular Development, and Industrial Workhorse. Microbiology 2020, 166, 425–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunst, F.; Ogasawara, N.; Moszer, I.; Albertini, A.M.; Alloni, G.; Azevedo, V.; Bertero, M.G.; Bessières, P.; Bolotin, A.; Borchert, S.; et al. The Complete Genome Sequence of the Gram-Positive Bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Nature 1997, 390, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, A.M.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. Ecology and Genomics of Bacillus subtilis. Trends Microbiol. 2008, 16, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saier, M.H., Jr.; Goldman, S.R.; Maile, R.R.; Moreno, M.S.; Weyler, W.; Yang, N.; Paulsen, I.T. Transport Capabilities Encoded within the Bacillus subtilis Genome. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 4, 37–67. [Google Scholar]
- Alcaraz, L.D.; Moreno-Hagelsieb, G.; Eguiarte, L.E.; Souza, V.; Herrera-Estrella, L.; Olmedo, G. Understanding the Evolutionary Relationships and Major Traits of Bacillus through Comparative Genomics. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, A.P.; Price, N.P.J.; Ehrhardt, C.; Sewzey, J.L.; Bannan, J.D. Phylogeny and Molecular Taxonomy of the Bacillus subtilis Species Complex and Description of Bacillus subtilis subsp. inaquosorum subsp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2429–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeigler, D.R.; Prágai, Z.; Rodriguez, S.; Chevreux, B.; Muffler, A.; Albert, T.; Bai, R.; Wyss, M.; Perkins, J.B. The Origins of 168, W23, and Other Bacillus subtilis Legacy Strains. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 6983–6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, D.J. Sulfide Mineralogy and Geochemistry: Introduction and Overview. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2006, 61, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, I.; Vithanage, M.; Bundschuh, J.; Maity, J.P.; Bhattacharya, P. Natural Arsenic in Global Groundwaters: Distribution and Geochemical Triggers for Mobilization. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2016, 2, 68–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Lauria, G.; Catalano, A.; Carocci, A.; Sinicropi, M.S. Arsenic: A Review on a Great Health Issue Worldwide. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, P.; Liu, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; Ge, Y. Review of Arsenic Speciation, Toxicity and Metabolism in Microalgae. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura-Lima, J.; Bogo, M.R.; Monserrat, J.M. Arsenic Toxicity in Mammals and Aquatic Animals: A Comparative Biochemical Approach. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Sohn, M. Aquatic Arsenic: Toxicity, Speciation, Transformations, and Remediation. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 743–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.F. Arsenic Toxicity and Potential Mechanisms of Action. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 133, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.; Wang, Q.Q.; Naranmandura, H. Molecular Mechanisms of Arsenic Toxicity. In Advances in Molecular Toxicology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Sevak, P.; Pushkar, B. Arsenic Pollution Cycle, Toxicity and Sustainable Remediation Technologies: A Comprehensive Review and Bibliometric Analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 119504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Udensi, U.K.; Pacurari, M.; Stevens, J.J.; Patlolla, A.K.; Noubissi, F.; Kumar, S. State of the Science Review of the Health Effects of Inorganic Arsenic: Perspectives for Future Research. Environ. Toxicol. 2019, 34, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervantes, C.; Ji, G.; Ramirez, J.; Silver, S. Resistance to Arsenic Compounds in Microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1994, 15, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, R.; Rosen, B.P.; Phung, L.T.; Silver, S. Microbial Arsenic: From Geocycles to Genes and Enzymes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 26, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Rosen, B.P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Franke, S.; Rensing, C. Arsenic Detoxification and Evolution of Trimethylarsine Gas by a Microbial Arsenite S-Adenosylmethionine Methyltransferase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2075–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.C.; Rosen, B.P. New Mechanisms of Bacterial Arsenic Resistance. Biomed. J. 2016, 39, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgante, V.; Mirete, S.; de Figueras, C.G.; Postigo Cacho, M.; González-Pastor, J.E. Exploring the Diversity of Arsenic Resistance Genes from Acid Mine Drainage Microorganisms. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 1910–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Yoshinaga, M.; Zhao, F.J.; Rosen, B.P. Earth Abides Arsenic Biotransformations. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2014, 42, 443–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.; Hur, H.G.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Byappanahalli, M.N.; Yan, T.; Ishii, S. Environmental Escherichia coli: Ecology and Public Health Implications—A Review. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Fekih, I.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.P.; Zhao, Y.; Alwathnani, H.A.; Saquib, Q.; Rensing, C.; Cervantes, C. Distribution of Arsenic Resistance Genes in Prokaryotes. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni Dhubhghaill, O.M.; Sadler, P.J. The Structure and Reactivity of Arsenic Compounds: Biological Activity and Drug Design. In Bioinorganic Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Kalia, K.; Joshi, D.N. Detoxification of Arsenic. In Handbook of Toxicology of Chemical Warfare Agents; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Garbinski, L.D.; Rosen, B.P.; Chen, J. Pathways of Arsenic Uptake and Efflux. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, M.C.; Bertin, P.N.; Heipieper, H.J.; Arsène-Ploetze, F. Bacterial Metabolism of Environmental Arsenic—Mechanisms and Biotechnological Applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 3827–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Francisco, P.; Martín-González, A.; Rodriguez-Martín, D.; Díaz, S. Interactions with Arsenic: Mechanisms of Toxicity and Cellular Resistance in Eukaryotic Microorganisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróbel, M.; Śliwakowski, W.; Kowalczyk, P.; Kramkowski, K.; Dobrzyński, J. Bioremediation of Heavy Metals by the Genus Bacillus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S. Microbial Biodegradation and Bioremediation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dadwal, A.; Mishra, V. Review on Biosorption of Arsenic From Contaminated Water. Clean 2017, 45, 1600364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Chen, M.L.; Liu, L.H.; Wang, J.H.; Dasgupta, P.K. Iron(III) Modification of Bacillus subtilis Membranes Provides Record Sorption Capacity for Arsenic and Endows Unusual Selectivity for As(V). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2251–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, A.K.; Patel, R.K.; Mahapatra, S.S.; Mishra, P.C. Biosorption of Arsenic (III) from Aqueous Solution by Living Cells of Bacillus cereus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 1281–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Bahari, Z.; Ali Hamood Altowayti, W.; Ibrahim, Z.; Jaafar, J.; Shahir, S. Biosorption of As (III) by Non-Living Biomass of an Arsenic-Hypertolerant Bacillus cereus Strain SZ2 Isolated from a Gold Mining Environment: Equilibrium and Kinetic Study. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 171, 2247–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, P.K.; Pramanik, K.; Mahapatra, K.; Mondal, S.; Ghosh, S.K.; Ghosh, A.; Maiti, T.K. Plant Growth-Promoting Bacillus cereus MCC3402 Facilitates Rice Seedling Growth under Arsenic-Spiked Soil. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2024, 61, 103405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altowayti, W.A.H.; Algaifi, H.A.; Bakar, S.A.; Shahir, S. The Adsorptive Removal of As (III) Using Biomass of Arsenic Resistant Bacillus thuringiensis Strain WS3: Characteristics and Modelling Studies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 172, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Nie, Z.W.; Wang, R.; He, L.Y.; Sheng, X.F. Metal(Loid)-Resistant Bacillus megaterium H3 Reduces Arsenic Uptake in Rice (Oryza sativa Nanjing 5055) at Different Growth Stages in Arsenic-Contaminated Soil. Geoderma 2020, 375, 114510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanò, A.; Zammuto, V.; Macrì, A.; Agostino, E.; Nicolò, M.S.; Scala, A.; Trombetta, D.; Smeriglio, A.; Ingegneri, M.; Caccamo, M.T.; et al. Arsenic Adsorption and Toxicity Reduction of An Exopolysaccharide Produced by Bacillus licheniformis B3-15 of Shallow Hydrothermal Vent Origin. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripti, K. Shardendu PH Modulates Arsenic Toxicity in Bacillus licheniformis DAS-2. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 130, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripti, K.; Shardendu, S. Efficiency of Arsenic Remediation from Growth Medium through Bacillus licheniformis Modulated by Phosphate (PO4)3− and Nitrate (NO3)− Enrichment. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 4081–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Gupta, A.; Srivastava, S. Bacterial Consortium (Priestia endophytica NDAS01F, Bacillus licheniformis NDSA24R, and Priestia flexa NDAS28R) and Thiourea Mediated Amelioration of Arsenic Stress and Growth Improvement of Oryza sativa L. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 195, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Hazra, A.; Das, S.; Sengupta, C. Groundwater Inhabited Bacillus and Paenibacillus Strains Alleviate Arsenic-Induced Phytotoxicity of Rice Plant. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2020, 22, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, H.; Mishra, S.K.; Prasad, V.; Chauhan, P.S. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Modulate Sugar Metabolism to Mitigate Arsenic Toxicity in Oryza sativa L. Var Saryu-52. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 137070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadrasnia, A.; Usman, M.M.; Abutawila, Z.; Omar, R.; Ismail, S.; Abdullah, R. Biotechnological Remediation of Arsenate from Aqueous Solution Using a Novel Bacterial Strain: Isotherm, Kinetics and Thermodynamic Studies. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2019, 17, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabiraj, A.; Halder, U.; Panja, A.S.; Chitikineni, A.; Varshney, R.K.; Bandopadhyay, R. Detailed Genomic and Biochemical Characterization and Plant Growth Promoting Properties of an Arsenic-Tolerant Isolate of Bacillus pacificus from Contaminated Groundwater of West Bengal, India. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2023, 52, 102825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podder, M.S.; Majumder, C.B. Kinetic, Mechanistic and Thermodynamic Studies of Removal of Arsenic Using Bacillus arsenicus MTCC 4380 Immobilized on Surface of Granular Activated Carbon/MnFe2O4 Composite. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 2–3, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atikpo, E.; Agori, J.E.; Peretomode, M.T.; Micheal, A.; Ofonedu, E.C. Kinetic Study of Biosorption of Arsenic from Soil Using Microorganisms. Niger. J. Technol. 2019, 38, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia-Brunet, F.; Crouzet, C.; Burnol, A.; Coulon, S.; Morin, D.; Joulian, C. Precipitation of Arsenic Sulphide from Acidic Water in a Fixed-Film Bioreactor. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3923–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZHANG, X.; JIA, Y.; WANG, X.; XU, L. Phylogenetic Analysis and Arsenate Reduction Effect of the Arsenic-Reducing Bacteria Enriched from Contaminated Soils at an Abandoned Smelter Site. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Kang, F.; Qu, X.; Fu, H.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Tao, S.; Zhu, D. Role of Extracellular Polymeric Substances in Microbial Reduction of Arsenate to Arsenite by Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6185–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, G.L.; Williams, J.; Hille, R. The Purification and Characterization of Arsenite Oxidase from Alcaligenes faecalis, a Molybdenum-Containing Hydroxylase. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 23674–23682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrun, E.; Brugna, M.; Baymann, F.; Muller, D.; Lièvremont, D.; Lett, M.C.; Nitschke, W. Arsenite Oxidase, an Ancient Bioenergetic Enzyme. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Switzer Blum, J.; Burns Bindi, A.; Buzzelli, J.; Stolz, J.F.; Oremland, R.S. Bacillus arsenicoselenatis, sp. nov., and Bacillus selenitireducens, sp. nov.: Two Haloalkaliphiles from Mono Lake, California That Respire Oxyanions of Selenium and Arsenic. Arch. Microbiol. 1998, 171, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Mohapatra, B.; Satyanarayana, T.; Sar, P. Molecular and Taxonomic Characterization of Arsenic (As) Transforming Bacillus sp. Strain IIIJ3-1 Isolated from As-Contaminated Groundwater of Brahmaputra River Basin, India. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagade, A.; Nandre, V.; Paul, D.; Patil, Y.; Sharma, N.; Giri, A.; Kodam, K. Characterisation of Hyper Tolerant Bacillus firmus L-148 for Arsenic Oxidation. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, S.; Sultan, S.; Rehman, A. Characterization of Multiple Metal Resistant Bacillus licheniformis and Its Potential Use in Arsenic Contaminated Industrial Wastewater. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebeli, M.A.; Maleki, A.; Amoozegar, M.A.; Kalantar, E.; Izanloo, H.; Gharibi, F. Bacillus flexus Strain As-12, a New Arsenic Transformer Bacterium Isolated from Contaminated Water Resources. Chemosphere 2017, 169, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, R.L.; Malamy, M.H. Arsenate Resistant Mutants of Escherichia coli and Phosphate Transport. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1970, 40, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willsky, G.R.; Malamy, M.H. Effect of Arsenate on Inorganic Phosphate Transport in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1980, 144, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfasi, H.; Friedberg, D.; Friedberg, I. Phosphate Transport in Arsenate-Resistant Mutants of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. J. Bacteriol. 1979, 137, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, J.F.; Liras, P. Molecular Mechanisms of Phosphate Sensing, Transport and Signalling in Streptomyces and Related Actinobacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Qin, D.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Rensing, C.; Mcdermott, T.R.; Wang, G. Fate of Arsenate Following Arsenite Oxidation in Agrobacterium tumefaciens GW4. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 1926–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.; Kazy, S.K.; Sar, P. Studies on Arsenic Transforming Groundwater Bacteria and Their Role in Arsenic Release from Subsurface Sediment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 8645–8662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Hulett, F.M. The Pst Operon of Bacillus subtilis Has a Phosphate-Regulated Promoter and Is Involved in Phosphate Transport but Not in Regulation of the Pho Regulon. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 2534–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.L.; Liu, Z.; Rosen, B.P. As(III) and Sb(III) Uptake by GlpF and Efflux by ArsB in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 18334–18341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaltonen, E. Prokaryotic Arsenic Resistance: Studies in Bacillus subtilis. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Cell and Organism Biology, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2008. Volume 35. [Google Scholar]
- Vishnoi, N.; Dixit, S.; Singh, D.P. Surface Binding and Intracellular Uptake of Arsenic in Bacteria Isolated from Arsenic Contaminated Site. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, A.; Pasini, P.; Daunert, S. Construction of Spores for Portable Bacterial Whole-Cell Biosensing Systems. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 9391–9397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-García, L.I.; Alarcón-Herrera, M.T.; Ayala-García, V.M.; Barraza-Salas, M.; Salas-Pacheco, J.M.; Díaz-Valles, J.F.; Pedraza-Reyes, M. Design of a Whole-Cell Biosensor Based on Bacillus subtilis Spores and the Green Fluorescent Protein to Monitor Arsenic. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0043223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Kobayashi, Y. The Ars Operon in the Skin Element of Bacillus subtilis Confers Resistance to Arsenate and Arsenite. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.M.; Gaballa, A.; Hui, M.; Ye, R.W.; Helmann, J.D. Genetic and Physiological Responses of Bacillus subtilis to Metal Ion Stress. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 57, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemaru, K.I.; Mizuno, M.; Sato, T.; Takeuchi, M.; Kobayashi, Y. Complete Nucleotide Sequence of a Skin Element Excised by DNA Rearrangement during Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology 1995, 141, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, M.; Masuda, S.; Takemaru, K.I.; Hosono, S.; Sato, T.; Takeuchi, M.; Kobayashi, Y. Systematic Sequencing of the 283 Kb 210–232 Region of the Bacillus subtilis Genome Containing the Skin Element and Many Sporulation Genes. Microbiology 1996, 142, 3103–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Yoshikawa, M.; Imamura, D.; Abe, K.; Eichenberger, P.; Sato, T. Compatibility of Site-Specific Recombination Units between Mobile Genetic Elements. iScience 2020, 23, 100805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, S.; Sethi, D.; Kasivisweswaran, S.; Ramya, L.; Priyadarshini, R.; Yennamalli, R.M. Structural and Functional Mapping of Ars Gene Cluster in Deinococcus indicus DR1. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvie, D.R.; Andreini, C.; Cavallaro, G.; Meng, W.; Connolly, B.A.; Yoshida, K.I.; Fujita, Y.; Harwood, C.R.; Radford, D.S.; Tottey, S.; et al. Predicting Metals Sensed by ArsR-SmtB Repressors: Allosteric Interference by a Non-Effector Metal. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 1341–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Nadar, V.S.; Rosen, B.P. A Novel MAs(III)-Selective ArsR Transcriptional Repressor. Mol. Microbiol. 2017, 106, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Silver, S. Regulation and Expression of the Arsenic Resistance Operon from Staphylococcus aureus Plasmid PI258. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 3684–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capdevila, D.A.; Rondón, J.J.; Edmonds, K.A.; Rocchio, J.S.; Dujovne, M.V.; Giedroc, D.P. Bacterial Metallostasis: Metal Sensing, Metalloproteome Remodeling, and Metal Trafficking. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 13574–13659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Rosen, B.P. Metalloregulated Expression of the Ars Operon*. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busenlehner, L.S.; Pennella, M.A.; Giedroc, D.P. The SmtB/ArsR Family of Metalloregulatory Transcriptional Repressors: Structural Insights into Prokaryotic Metal Resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly Accurate Protein Structure Prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, J.; Magana, P.; Nair, S.; Tsenkov, M.; Bertoni, D.; Pidruchna, I.; Lima Afonso, M.Q.; Midlik, A.; Paramval, U.; Žídek, A.; et al. AlphaFold Protein Structure Database and 3D-Beacons: New Data and Capabilities. J. Mol. Biol. 2025, 437, 168967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabaharan, C.; Kandavelu, P.; Packianathan, C.; Rosen, B.P.; Thiyagarajan, S. Structures of Two ArsR As(III)-Responsive Transcriptional Repressors: Implications for the Mechanism of Derepression. J. Struct. Biol. 2019, 207, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez, E.; Thiyagarajan, S.; Cook, J.D.; Stemmler, T.L.; Gil, J.A.; Mateos, L.M.; Rosen, B.P. Evolution of Metal(Loid) Binding Sites in Transcriptional Regulators. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25706–25714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Fu, H.L.; Ye, J.; Bencze, K.Z.; Stemmler, T.L.; Rawlings, D.E.; Rosen, B.P. Convergent Evolution of a New Arsenic Binding Site in the ArsR/SmtB Family of Metalloregulators. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 34346–34355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Dong, J.; Scott, R.A.; Ksenzenko, M.Y.; Rosen, B.P. The Role of Arsenic-Thiol Interactions in Metalloregulation of the Ars Operon. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 9291–9297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedreira, T.; Elfmann, C.; Stülke, J. The Current State of SubtiWiki, the Database for the Model Organism Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D875–D882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshinaga, M.; Rosen, B.P. A C·As Lyase for Degradation of Environmental Organoarsenical Herbicides and Animal Husbandry Growth Promoters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7701–7706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadar, V.S.; Kandavelu, P.; Sankaran, B.; Rosen, B.P.; Yoshinaga, M. The ArsI C-As Lyase: Elucidating the Catalytic Mechanism of Degradation of Organoarsenicals. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2022, 232, 111836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawitwar, S.S.; Nadar, V.S.; Kandegedara, A.; Stemmler, T.L.; Rosen, B.P.; Yoshinaga, M. Biochemical Characterization of ArsI: A Novel C-As Lyase for Degradation of Environmental Organoarsenicals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11115–11125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcón, T.; Llorens, E.; Poch, M. Remoción de Arsénico Del Agua Para Consumo Humano En Latinoamérica; CIMAV: Chihuahua, Mexico, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nadar, V.S.; Yoshinaga, M.; Rosen, B.P. Structure of the ArsI C-As Lyase with Bound Substrate Roxarsone and Mutational Studies of Active Site Residues: Elucidating the Catalytic Mechanism of Degradation of Organoarsenicals. In Arsenic in the Environment: Bridging Science to Practice for Sustainable Development As2021; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Ye, J.; Xue, X.M.; Zhu, Y.G. Arsenic Demethylation by a C·As Lyase in Cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. PCC 7120. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14350–14358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaltonen, E.K.J.; Silow, M. Transmembrane Topology of the Acr3 Family Arsenite Transporter from Bacillus subtilis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2008, 1778, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Shi, L.D.; Li, J.; Xiao, X.; Shao, Z.; Dong, X. Unexpected Genetic and Microbial Diversity for Arsenic Cycling in Deep Sea Cold Seep Sediments. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2023, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIaszczyk-Dziubinska, E.; Migocka, M.; Wysocki, R. Acr3p Is a Plasma Membrane Antiporter That Catalyzes As(III)/H+ and Sb(III)/H+ Exchange in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2011, 1808, 1855–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Shang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Su, D.; Wang, W.; Li, C.; Ma, C.; Yang, C. Structural Basis for the Arsenite Binding and Translocation of Acr3 Antiporter with NhaA Folding Pattern. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Hederstedt, L.; Li, J.P.; Su, X.D. Preparation and Crystallization of a Bacillus subtilis Arsenate Reductase. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2001, 57, 1718–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Zheng, F.; Yu, M.; Shabala, S.; Song, W.Y. Comparative Analysis of Arsenic Transport and Tolerance Mechanisms: Evolution from Prokaryote to Higher Plants. Cells 2022, 11, 2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Xue, X.M.; Kappler, A.; Rosen, B.P.; Meharg, A.A. Linking Genes to Microbial Biogeochemical Cycling: Lessons from Arsenic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7326–7339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, D.; Fujita, K.; Sakuma, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Ohashi, Y.; Ohshima, H.; Tomita, M.; Itaya, M. Comparative Analysis of Physical Maps of Four Bacillus subtilis (Natto) Genomes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 6247–6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andres, J.; Bertin, P.N. The Microbial Genomics of Arsenic. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 40, 299–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajees, A.A.; Yang, J.; Rosen, B.P. The ArsD as(III) Metallochaperone. BioMetals 2011, 24, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Kennedy, S.P.; Fasiludeen, S.; Rensing, C.; DasSarma, S. Arsenic Resistance in Halobacterium sp. Strain NRC-1 Examined by Using an Improved Gene Knockout System. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 3187–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musingarimi, W.; Tuffin, M.; Cowan, D. Characterisation of the Arsenic Resistance Genes in Bacillus sp. UWC Isolated from Maturing Fly Ash Acid Mine Drainage Neutralised Solids. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2010, 106, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.; Hara, T.O.; Tian, F.; Singh, B. Review of Analytical Techniques for Arsenic Detection and Determination in Drinking Water. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2022, 2, 171–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Bu, R.; Zhao, T.; Wu, K. Sensitive and Specific Whole-Cell Biosensor for Arsenic Detection. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e00694-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, A.; Valencia-Marín, M.F.; Chávez-Avila, S.; Ramírez-Díaz, M.I.; de los Santos-Villalobos, S.; Meza-Carmen, V.; del Carmen Orozco-Mosqueda, M.; Santoyo, G. Genome Mining, Phylogenetic, and Functional Analysis of Arsenic (As) Resistance Operons in Bacillus Strains, Isolated from As-Rich Hot Spring Microbial Mats. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 264, 127158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.F.; Yang, J.; Rosen, B.P. ArsD: An As(III) Metallochaperone for the ArsAB As(III)-Translocating ATPase. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2007, 39, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Rosen, B.P. Metalloregulatory Properties of the ArsD Repressor. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 14257–14262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.S.; Ranjan, R.; Purohit, H.J.; Kalia, V.C.; Sharma, R. Identification of Genes Conferring Arsenic Resistance to Escherichia coli from an Effluent Treatment Plant Sludge Metagenomic Library. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 67, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Bhattacharjee, H.; Rosen, B.P. ArsH Is an Organoarsenical Oxidase That Confers Resistance to Trivalent Forms of the Herbicide Monosodium Methylarsenate and the Poultry Growth Promoter Roxarsone. Mol. Microbiol. 2015, 96, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-García, L.I.; Zapata, B.L.; Ramírez-Ramírez, N.; Huchin-Mian, J.P.; Robleto, E.A.; Ayala-Garcia, V.M.; Pedraza-Reyesa, M. Novel Biochemical Properties and Physiological Role of the Flavin Mononucleotide Oxidoreductase YhdA from Bacillus subtilis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01688-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, W.; Wong, M.T.; Luo, F.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Liu, X.; Edwards, E.A.; Tang, X.; Xu, J. Arsenic Methylation and Its Relationship to Abundance and Diversity of ArsM Genes in Composting Manure. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep42198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yoshinaga, M.; Garbinski, L.D.; Rosen, B.P. Synergistic Interaction of Glyceraldehydes-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase and ArsJ, a Novel Organoarsenical Efflux Permease, Confers Arsenate Resistance. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 100, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Madegowda, M.; Bhattacharjee, H.; Rosen, B.P. ArsP: A Methylarsenite Efflux Permease. Mol. Microbiol. 2015, 98, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Li, C.; Rensing, C.; Dai, X.; Fan, X.; Wang, G. Efflux Transporter ArsK Is Responsible for Bacterial Resistance to Arsenite, Antimonite, Trivalent Roxarsone, and Methylarsenite. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01842-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chen, S.; Xiao, X.; Huang, X.; You, D.; Zhou, X.; Deng, Z. ArsRBOCT Arsenic Resistance System Encoded by Linear Plasmid PHZ227 in Streptomyces sp. Strain FR-008. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 3738–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Scifleet, J.; Yu, X.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, R. Function of ArsATorf7orf8 of Bacillus sp. CDB3 in Arsenic Resistance. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deller, S.; Sollner, S.; Trenker-El-Toukhy, R.; Jelesarov, I.; Gübitz, G.M.; Macheroux, P. Characterization of a Thermostable NADPH:FMN Oxidoreductase from the Mesophilic Bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 7083–7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guffanti, A.A.; Wei, Y.; Rood, S.V.; Krulwich, T.A. An Antiport Mechanism for a Member of the Cation Diffusion Facilitator Family: Divalent Cations Efflux in Exchange for K+ and H+. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 45, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, D.; Kamino, K.; Inoue, K.; Sakurai, H. Purification and Characterization of Ferredoxin-NADP+ Reductase Encoded by Bacillus subtilis YumC. Arch. Microbiol. 2004, 182, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossman, T.G.; Meyn, M.S.; Troll, W. Effects of Arsenite on DNA Repair in Escherichia coli. Environ. Health Perspect. 1977, 19, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Escobar, F.; Leyva-Sánchez, H.C.; Ramírez-Ramírez, N.; Obregón-Herrera, A.; Pedraza-Reyes, M. Roles of Bacillus subtilis RecA, Nucleotide Excision Repair, and Translesion Synthesis Polymerases in Counteracting Cr(VI)-Promoted DNA Damage. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Escobar, F.; Gutiérrez-Corona, J.F.; Pedraza-Reyes, M. Role of Bacillus subtilis Error Prevention Oxidized Guanine System in Counteracting Hexavalent Chromium-Promoted Oxidative DNA Damage. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5493–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Xie, X.; Su, C. Response of Growth and Superoxide Dismutase to Enhanced Arsenic in Two Bacillus Species. Ecotoxicology 2014, 23, 1922–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, S.; Xie, Z.; Mehmood, S.; Nawaz, A.; Ditta, A.; Mahmood, Q. Insights into Conventional and Recent Technologies for Arsenic Bioremediation: A Systematic Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 18870–18892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmik, S.; Prajapati, S.C.; Kumar, S.; Priyanka, K.; Saxena, R. Bioremediation of Arsenic Metal from Water and Soil by Bacillus Species-A Review. J. Integr. Sci. Technol. 2025, 13, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, N.C.; Faria, M.C.S.; Pedron, T.; Batista, B.L.; Mesquita, J.P.; Bomfeti, C.A.; Rodrigues, J.L. Isolation and Characterization of Bacteria from a Brazilian Gold Mining Area with a Capacity of Arsenic Bioaccumulation. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Saluja, B.; Gupta, A.; Marla, S.S.; Goel, R. Validation of Arsenic Resistance in Bacillus cereus Strain AG27 by Comparative Protein Modeling of ArsC Gene Product. Protein J. 2011, 30, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Pérez, M.E.; Saldaña-Robles, A.; Zanor, G.A.; Ibarra, J.E.; Del Rincón-Castro, M.C. Microbiomes in Agricultural and Mining Soils Contaminated with Arsenic in Guanajuato, Mexico. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saluja, B.; Gupta, A.; Goel, R. Mechanism of Arsenic Resistance Prevalent in Bacillus Species Isolated from Soil and Ground Water Sources of India. Ekologija 2011, 57, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, K.; Xiang, Q.; Yu, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Q. Genetic Diversity and Characterization of Arsenic-Resistant Endophytic Bacteria Isolated from Pteris vittata, an Arsenic Hyperaccumulator. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román-Ponce, B.; Ramos-Garza, J.; Arroyo-Herrera, I.; Maldonado-Hernández, J.; Bahena-Osorio, Y.; Vásquez-Murrieta, M.S.; Wang, E.T. Mechanism of Arsenic Resistance in Endophytic Bacteria Isolated from Endemic Plant of Mine Tailings and Their Arsenophore Production. Arch. Microbiol. 2018, 200, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, K.; Prabagaran, S.R.; Sengupta, S.; Shivaji, S. Bacillus indicus sp. nov., an Arsenic-Resistant Bacterium Isolated from an Aquifer in West Bengal, India. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaji, S.; Suresh, K.; Chaturvedi, P.; Dube, S.; Sengupta, S. Bacillus arsenicus sp. nov., an Arsenic-Resistant Bacterium Isolated from a Siderite Concretion in West Bengal, India. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.A.H.; Farag, A.G. Arsenic Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Different Bacillus and Lysinibacillus Species. Bioremediat J. 2015, 19, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, S.; Pradhan, B.; Smith, L.; Shrestha, J.; Tuladhar, S. Isolation and Characterization of Aerobic Culturable Arsenic-Resistant Bacteria from Surfacewater and Groundwater of Rautahat District, Nepal. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 95, S250–S255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruta, M.; Pepi, M.; Gaggi, C.; Bernardini, E.; Focardi, S.; Magaldi, E.; Gasperini, S.; Volterrani, M.; Zanini, A.; Focardi, S.E. As(V)-Reduction to As(III) by Arsenic-Resistant Bacillus spp. Bacterial Strains Isolated from Low-Contaminated Sediments of the Oliveri-Tindari Lagoon, Italy. Chem. Ecol. 2011, 27, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepi, M.; Heipieper, H.J.; Fischer, J.; Ruta, M.; Volterrani, M.; Focardi, S.E. Membrane Fatty Acids Adaptive Profile in the Simultaneous Presence of Arsenic and Toluene in Bacillus sp. ORAs2 and Pseudomonas sp. ORAs5 Strains. Extremophiles 2008, 12, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baesman, S.M.; Stolz, J.F.; Kulp, T.R.; Oremland, R.S. Enrichment and Isolation of Bacillus beveridgei sp. nov., a Facultative Anaerobic Haloalkaliphile from Mono Lake, California, That Respires Oxyanions of Tellurium, Selenium, and Arsenic. Extremophiles 2009, 13, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Wang, Y.; Duan, M.; Xie, X.; Su, C. Arsenic Release by Indigenous Bacteria Bacillus cereus from Aquifer Sediments at Datong Basin, Northern China. Front. Earth Sci. 2011, 5, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepi, M.; Protano, G.; Ruta, M.; Nicolardi, V.; Bernardini, E.; Focardi, S.E.; Gaggi, C. Arsenic-Resistant Pseudomonas spp. and Bacillus sp. Bacterial Strains Reducing As(V) to As(III), Isolated from Alps Soils, Italy. Folia Microbiol. 2011, 56, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, F.; Chen, J.; Sun, G. Arsenic Removal from Contaminated Soil via Biovolatilization by Genetically Engineered Bacteria under Laboratory Conditions. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyatake, M.; Hayashi, S. Characteristics of Arsenic Removal from Aqueous Solution by Bacillus megaterium Strain UM-123. J. Environ. Biotechnol. 2009, 9, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Vishnoi, N.; Dixit, S.; Singh, D.P. Differential Pattern of Arsenic Binding by the Cell Wall in Two Arsenite Tolerant Bacillus Strains Isolated from Arsenic Contaminated Soil. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 62, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Du, J.; Zhuang, G.; Jing, C. Bacillus sp. SXB and Pantoea sp. IMH, Aerobic As(V)-Reducing Bacteria Isolated from Arsenic-Contaminated Soil. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, B.K.; Bhat, S.; Mikheenko, I.P.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Luo, X.; Chen, H.; van Zwieten, L.; Lilley, R.M.C.; Zhang, R. The Characteristics of Rhizosphere Microbes Associated with Plants in Arsenic-Contaminated Soils from Cattle Dip Sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 378, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, D.N.; Flora, S.J.S.; Kalia, K. Bacillus sp. Strain DJ-1, Potent Arsenic Hypertolerant Bacterium Isolated from the Industrial Effluent of India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 1500–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qamar, N.; Rehman, Y.; Hasnain, S. Arsenic-Resistant and Plant Growth-Promoting Firmicutes and γ-Proteobacteria Species from Industrially Polluted Irrigation Water and Corresponding Cropland. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, S.; Yamashita, M.; Fujimoto, N.; Kuroda, M.; Kashiwa, M.; Sei, K.; Fujita, M.; Ike, M. Bacillus selenatarsenatis sp. nov., a Selenate- and Arsenate-Reducing Bacterium Isolated from the Effluent Drain of a Glass-Manufacturing Plant. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 1060–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, F.; Jabeen, I.; Keya, C.A.; Shuvo, S.R. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Comparative Analysis of Heavy Metals Tolerant Bacillus anthracis FHq Strain Isolated from Tannery Effluents in Bangladesh. AIMS Microbiol. 2022, 8, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, C.E.; Omine, K. Characterization of Boron Resistant and Accumulating Bacteria Lysinibacillus fusiformis M1, Bacillus cereus M2, Bacillus cereus M3, Bacillus pumilus M4 Isolated from Former Mining Site, Hokkaido, Japan. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2012, 47, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakat, K.; Chakraborty, A.; Islam, E. Characterization of Arsenic Oxidation and Uranium Bioremediation Potential of Arsenic Resistant Bacteria Isolated from Uranium Ore. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 12907–12919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yik, L.Y.; Chin, G.J.W.L.; Budiman, C.; Joseph, C.G.; Musta, B.; Rodrigues, K.F. Adaptive Strategies of Bacillus thuringiensis Isolated from Acid Mine Drainage Site in Sabah, Malaysia. Indian. J. Microbiol. 2018, 58, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, C.E.; Omine, K. Arsenic, Boron and Salt Resistant Bacillus safensis MS11 Isolated from Mongolia Desert Soil. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 2267–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwa, N.; Singh, N.; Srivastava, S.; Saxena, G.; Pandey, V.; Singh, N. Characterizing the Hypertolerance Potential of Two Indigenous Bacterial Strains (Bacillus flexus and Acinetobacter junii) and Their Efficacy in Arsenic Bioremediation. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.A.; Basak, N.; Islam, E. Uranium and Arsenic Bioremediation Potential of Plastic Associated Multi-Metal Tolerant Bacillus sp. EIKU23. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2024, 5, 100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, J.P.; Kar, S.; Liu, J.H.; Jean, J.S.; Chen, C.Y.; Bundschuh, J.; Santra, S.C.; Liu, C.C. The Potential for Reductive Mobilization of Arsenic [As(V) to As(III)] by OSBH 2 (Pseudomonas stutzeri) and OSBH 5 (Bacillus cereus) in an Oil-Contaminated Site. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2011, 46, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azami, N.A.; Lau, N.S.; Furusawa, G. Genome Sequence Data of Bacillus sp. CCB-MMP212 Isolated from Malaysian Mangrove: A Potential Strain in Arsenic Resistance with ArsI, C•As Lyase. Data Brief. 2022, 45, 108597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulaki, E.G.; Tjamos, S.E. Bacillus Species: Factories of Plant Protective Volatile Organic Compounds. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxad037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quach, N.T.; Vu, T.H.N.; Nguyen, N.A.; Nguyen, V.T.; Bui, T.L.; Ky, S.C.; Le, T.L.; Hoang, H.; Ngo, C.C.; Le, T.T.M.; et al. Phenotypic Features and Analysis of Genes Supporting Probiotic Action Unravel Underlying Perspectives of Bacillus velezensis VTX9 as a Potential Feed Additive for Swine. Ann. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaghabee, F.M.F.; Rokana, N.; Gulhane, R.D.; Sharma, C.; Panwar, H. Bacillus as Potential Probiotics: Status, Concerns, and Future Perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Wan, J.; Wang, X.; Peng, C.; Wang, G.; Liang, W.; Zhang, W. Mixed Bacteria-Loaded Biochar for the Immobilization of Arsenic, Lead, and Cadmium in a Polluted Soil System: Effects and Mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 152112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalca, L.; Zanchi, R.; Corsini, A.; Colombo, M.; Romagnoli, C.; Canzi, E.; Andreoni, V. Arsenic-Resistant Bacteria Associated with Roots of the Wild Cirsium arvense (L.) Plant from an Arsenic Polluted Soil, and Screening of Potential Plant Growth-Promoting Characteristics. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 33, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Noman, M.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Ijaz, U.; Nazir, M.M.; ALHaithloul, H.A.S.; Alghanem, S.M.; Abdulmajeed, A.M.; Li, B. Green Molybdenum Nanoparticles-Mediated Bio-Stimulation of Bacillus sp. Strain ZH16 Improved the Wheat Growth by Managing in Planta Nutrients Supply, Ionic Homeostasis and Arsenic Accumulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, T.; Shah, A.A.; Akram, W.; Yasin, N.A. Synergistic Ameliorative Effect of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Bacillus subtilis S4 against Arsenic Toxicity in Cucurbita Moschata: Polyamines, Antioxidants, and Physiochemical Studies. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2020, 22, 1408–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bist, V.; Anand, V.; Srivastava, S.; Kaur, J.; Naseem, M.; Mishra, S.; Srivastava, P.K.; Tripathi, R.D.; Srivastava, S. Alleviative Mechanisms of Silicon Solubilizing Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Mediated Diminution of Arsenic Toxicity in Rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 428, 128170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Ashraf, H.; Huang, S.; Ramzan, M.; Saba, R.; Baqir, M.; Salmen, S.H.; Alharbi, S.A.; Hareem, M. Unveiling the Efficacy of Bacillus faecalis and Composted Biochar in Alleviating Arsenic Toxicity in Maize. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Chen, C.; Shen, Q.; Rosen, B.P.; Zhao, F.J. Genetically Engineering Bacillus subtilis with a Heat-Resistant Arsenite Methyltransferase for Bioremediation of Arsenic-Contaminated Organic Waste. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 6718–6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicke, N.; Radford, D.S.; French, C.E. A Simple Chromogenic Whole-Cell Arsenic Biosensor Based on Bacillus subtilis. bioRxiv 2018, 395178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.; Wang, X.; Montgomery, L.; Elfick, A.; French, C.E. Novel Approaches to Biosensors for Detection of Arsenic in Drinking Water. Desalination 2009, 248, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, A.; Pasini, P.; Daunert, S. Integration of Spore-Based Genetically Engineered Whole-Cell Sensing Systems into Portable Centrifugal Microfluidic Platforms. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, A.; Pasini, P.; Sangal, A.; Daunert, S. Packaging Sensing Cells in Spores for Long-Term Preservation of Sensors: A Tool for Biomedical and Environmental Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6098–6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valenzuela-García, L.I.; Alarcón-Herrera, M.T.; Cisneros-Lozano, E.; Pedraza-Reyes, M.; Ayala-García, V.M. Mechanisms of Arsenic Interaction in Bacillus subtilis and Related Species with Biotechnological Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110277
Valenzuela-García LI, Alarcón-Herrera MT, Cisneros-Lozano E, Pedraza-Reyes M, Ayala-García VM. Mechanisms of Arsenic Interaction in Bacillus subtilis and Related Species with Biotechnological Potential. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110277
Chicago/Turabian StyleValenzuela-García, Luz I., María Teresa Alarcón-Herrera, Elizabeth Cisneros-Lozano, Mario Pedraza-Reyes, and Víctor M. Ayala-García. 2025. "Mechanisms of Arsenic Interaction in Bacillus subtilis and Related Species with Biotechnological Potential" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110277
APA StyleValenzuela-García, L. I., Alarcón-Herrera, M. T., Cisneros-Lozano, E., Pedraza-Reyes, M., & Ayala-García, V. M. (2025). Mechanisms of Arsenic Interaction in Bacillus subtilis and Related Species with Biotechnological Potential. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110277








