Molecular and Clinical Considerations for Anesthesia in the Aging Brain
Abstract
1. Introduction
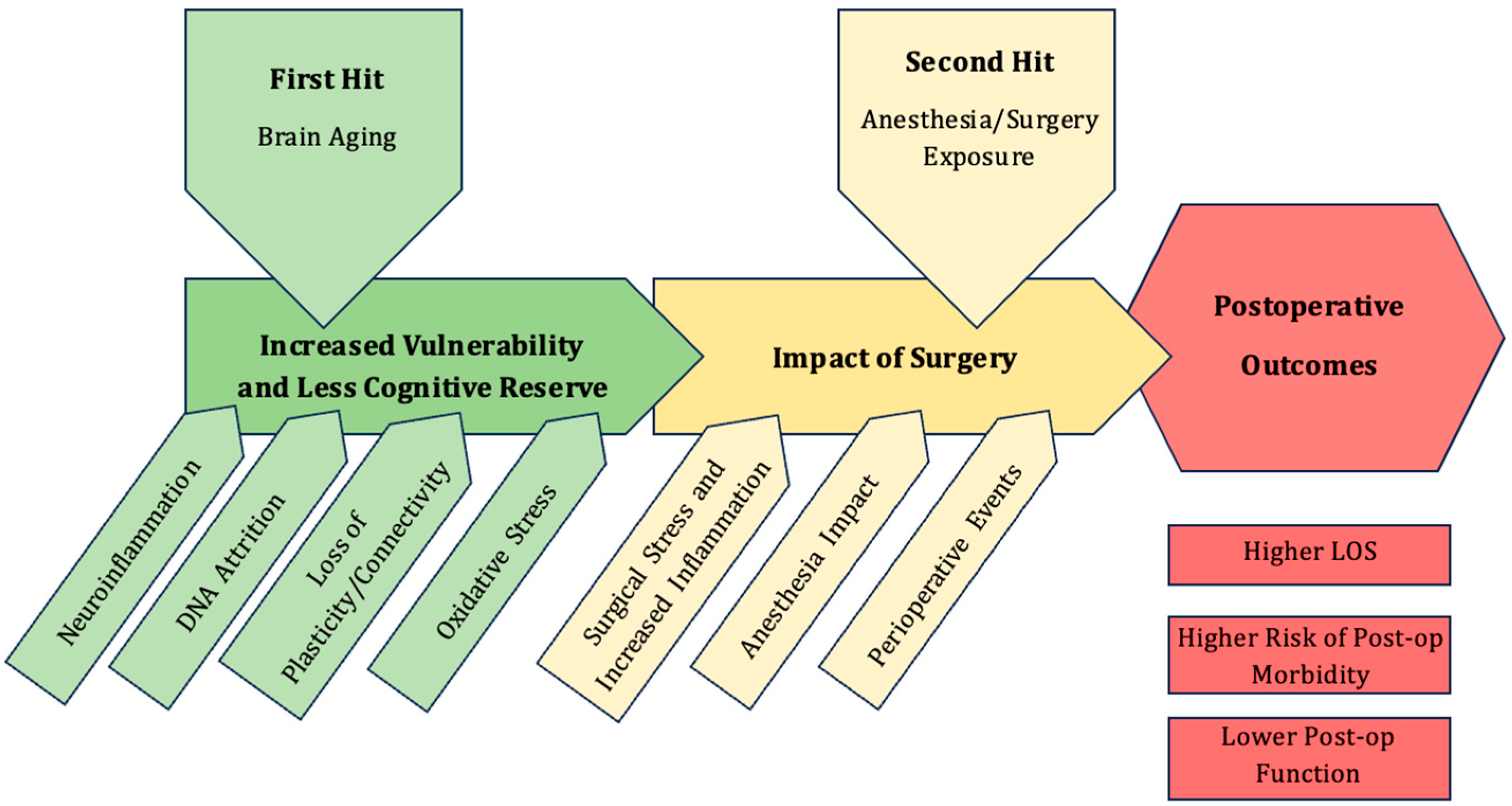
2. Postoperative Neurocognitive Disorders
2.1. Timeline of PNDs
2.2. Epidemiology of PNDs
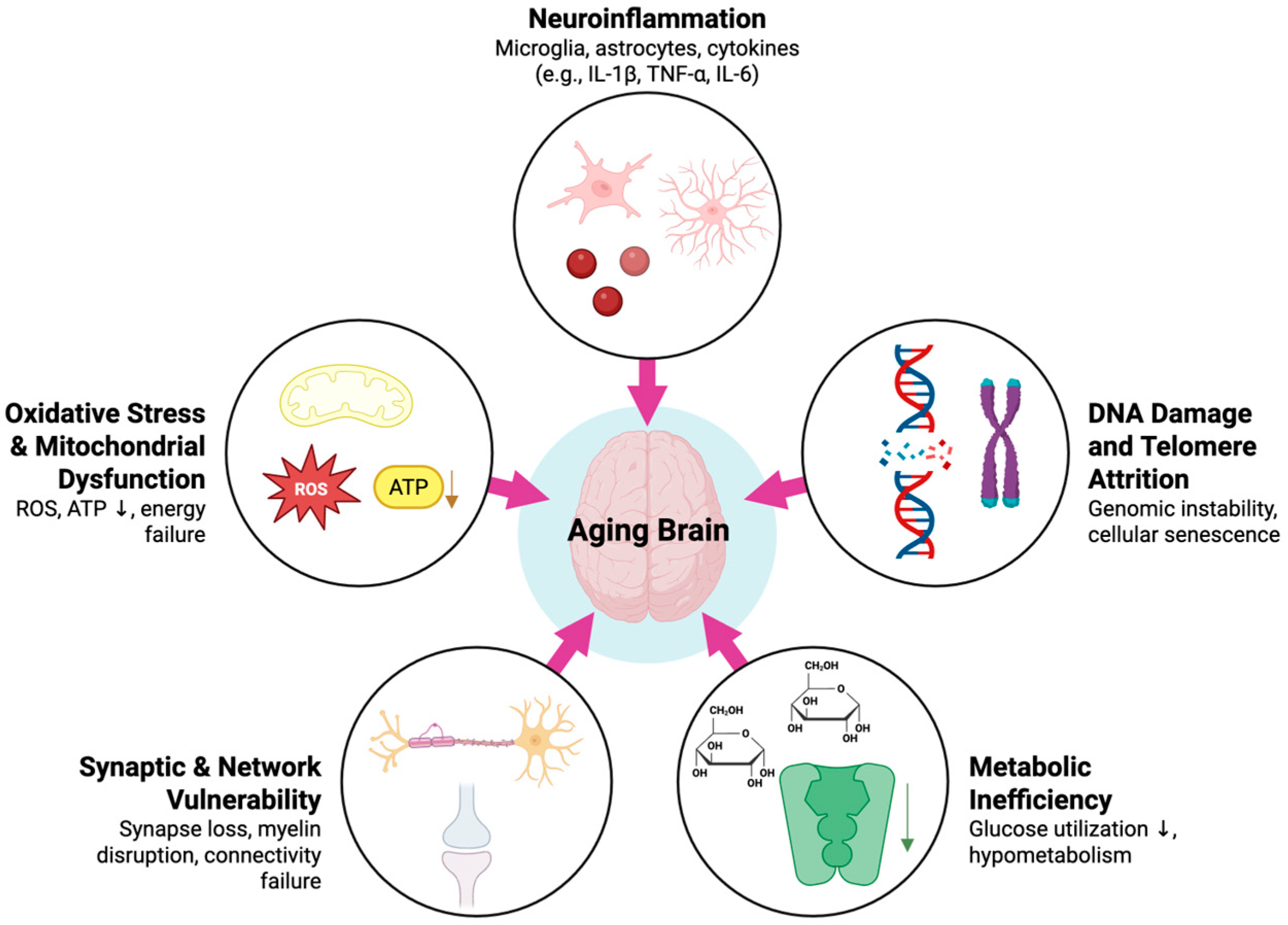
3. Molecular Biology Basis for Brain Aging
3.1. Aging and Neuroinflammation
3.2. DNA Damage and Telomere Attrition
3.3. Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
3.4. Metabolic Change
3.5. Synaptic Architecture and Neurotransmission
4. Effect of Anesthesia on the Aging Brain
4.1. Anesthesia and Neuroinflammation
4.2. Mitochondrial Impact
4.3. Synaptic Function and Neuroplasticity
4.4. Anesthetic Effects on RNA
4.5. Anesthetic Choice and PNDs
4.6. Anesthesia and the Glymphatic System
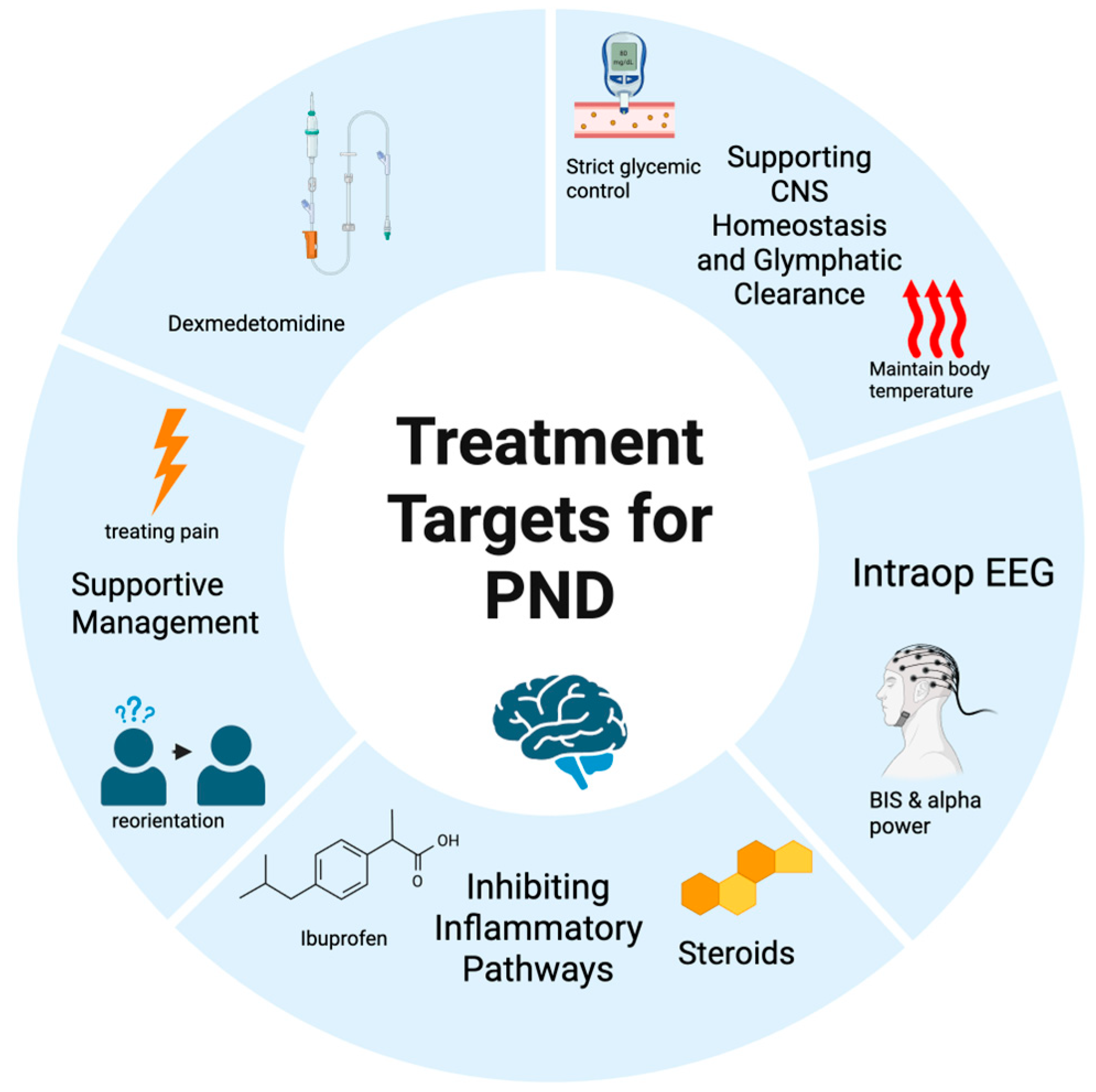
5. Molecular and Clinical Targets for PND Management
5.1. The Molecular Cascade of Neuroinflammation
5.2. Dexmedetomidine
5.3. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
5.4. The Role of EEG Guidance
5.5. Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AQP4 | Aquaporin-4 |
| BBB | Blood–Brain Barrier |
| BDNF | Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor |
| BER | Base Excision Repair |
| BIM | Bcl2l11 |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| dNCR | Delayed Neurocognitive Recovery |
| IL | Interleukin |
| lncRNAs | Long Noncoding RNAs |
| LTP | Long-term Potentiation |
| MMP9 | Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 |
| NCD | Neurocognitive Dysfunction |
| NSAIDs | Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin E2 |
| PND | Postoperative Neurocognitive Disorders |
| POCD | Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction |
| POD | Postoperative Delirium |
| PSD-95 | Postsynaptic Density Protein-95 |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| Sancr | Sevoflurane Associated Noncoding RNA |
| SIRT1 | Sirtuin 1 |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha |
References
- National Institute on Aging; National Institutes of Health; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Global Health and Aging. Available online: https://www.nia.nih.gov/sites/default/files/2017-06/global_health_aging.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- International Surgical Outcomes Study Group. Global patient outcomes after elective surgery: Prospective cohort study in 27 low-, middle- and high-income countries. Br. J. Anaesth. 2016, 117, 601–609.
- Dilmen, O.K.; Meco, B.C.; Evered, L.A.; Radtke, F.M. Postoperative neurocognitive disorders: A clinical guide. J. Clin. Anesth. 2024, 92, 111320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witlox, J.; Eurelings, L.S.; de Jonghe, J.F.; Kalisvaart, K.J.; Eikelenboom, P.; van Gool, W.A. Delirium in elderly patients and the risk of postdischarge mortality, institutionalization, and dementia: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2010, 304, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodier, E.A.; Cibelli, M. Postoperative cognitive dysfunction in clinical practice. BJA Educ. 2021, 21, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.M.; Marcantonio, E.R.; Inouye, S.K.; Kiely, D.K.; Rudolph, J.L.; Fearing, M.A.; Jones, R.N. Phenomenological subtypes of delirium in older persons: Patterns, prevalence, and prognosis. Psychosomatics 2009, 50, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, C.G.; Boncyk, C.S.; Culley, D.J.; Fleisher, L.A.; Leung, J.M.; McDonagh, D.L.; Gan, T.J.; McEvoy, M.D.; Miller, T.E.; Workgroup, P.Q.I.P. American Society for Enhanced Recovery and Perioperative Quality Initiative Joint Consensus Statement on Postoperative Delirium Prevention. Anesth. Analg. 2020, 130, 1572–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilevskis, E.E.; Han, J.H.; Hughes, C.G.; Ely, E.W. Epidemiology and risk factors for delirium across hospital settings. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2012, 26, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ely, E.W.; Inouye, S.K.; Bernard, G.R.; Gordon, S.; Francis, J.; May, L.; Truman, B.; Speroff, T.; Gautam, S.; Margolin, R.; et al. Delirium in mechanically ventilated patients: Validity and reliability of the confusion assessment method for the intensive care unit (CAM-ICU). JAMA 2001, 286, 2703–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Weed, H.G.; He, X.; Agrawal, A.; Ozer, E.; Schuller, D.E. Alcohol-related predictors of delirium after major head and neck cancer surgery. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 138, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olin, K.; Eriksdotter-Jönhagen, M.; Jansson, A.; Herrington, M.K.; Kristiansson, M.; Permert, J. Postoperative delirium in elderly patients after major abdominal surgery. Br. J. Surg. 2005, 92, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, D.L.; Wang, D.X.; Li, L.H.; Shan, G.J.; Li, J.; Yu, Q.J.; Shi, C.X. High serum cortisol level is associated with increased risk of delirium after coronary artery bypass graft surgery: A prospective cohort study. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koebrugge, B.; van Wensen, R.J.; Bosscha, K.; Dautzenberg, P.L.; Koning, O.H. Delirium after emergency/elective open and endovascular aortoiliac surgery at a surgical ward with a high-standard delirium care protocol. Vascular 2010, 18, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noimark, D. Predicting the onset of delirium in the post-operative patient. Age Ageing 2009, 38, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Fang, P.; Zhu, W.; Guo, J.; Li, L.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ma, S.; Mei, B.; et al. The Association of Preoperative Diabetes With Postoperative Delirium in Older Patients Undergoing Major Orthopedic Surgery: A Prospective Matched Cohort Study. Anesth. Analg. 2024, 138, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Song, Y.; Shi, W.; Mi, W.; Lou, J.; Liu, J. Association between combinations of preoperative comorbidities and postoperative delirium in older patients: A matched cohort study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2025, 25, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansaloni, L.; Catena, F.; Chattat, R.; Fortuna, D.; Franceschi, C.; Mascitti, P.; Melotti, R.M. Risk factors and incidence of postoperative delirium in elderly patients after elective and emergency surgery. Br. J. Surg. 2010, 97, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouquet, A.; Cudennec, T.; Benoist, S.; Moulias, S.; Beauchet, A.; Penna, C.; Teillet, L.; Nordlinger, B. Impaired mobility, ASA status and administration of tramadol are risk factors for postoperative delirium in patients aged 75 years or more after major abdominal surgery. Ann. Surg. 2010, 251, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.B.; Mears, S.C.; Rosenberg, P.B.; Leoutsakos, J.M.; Gottschalk, A.; Sieber, F.E. Predisposing factors for postoperative delirium after hip fracture repair in individuals with and without dementia. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2011, 59, 2306–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, R.C.; Osse, R.J.; Tulen, J.H.; Kappetein, A.P.; Bogers, A.J. Preoperative and operative predictors of delirium after cardiac surgery in elderly patients. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2012, 41, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucerius, J.; Gummert, J.F.; Borger, M.A.; Walther, T.; Doll, N.; Falk, V.; Schmitt, D.V.; Mohr, F.W. Predictors of delirium after cardiac surgery delirium: Effect of beating-heart (off-pump) surgery. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2004, 127, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.M.; Arciniegas, D.B.; Grigsby, J.; McCarthy, M.; McDonald, G.O.; Moritz, T.E.; Shroyer, A.L.; Sethi, G.K.; Henderson, W.G.; London, M.J.; et al. Predictors of cognitive decline following coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2004, 77, 597–603; discussion 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepousé, C.; Lautner, C.A.; Liu, L.; Gomis, P.; Leon, A. Emergence delirium in adults in the post-anaesthesia care unit. Br. J. Anaesth. 2006, 96, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radtke, F.M.; Franck, M.; Hagemann, L.; Seeling, M.; Wernecke, K.D.; Spies, C.D. Risk factors for inadequate emergence after anesthesia: Emergence delirium and hypoactive emergence. Minerva. Anestesiol. 2010, 76, 394–403. [Google Scholar]
- Taipale, P.G.; Ratner, P.A.; Galdas, P.M.; Jillings, C.; Manning, D.; Fernandes, C.; Gallaher, J. The association between nurse-administered midazolam following cardiac surgery and incident delirium: An observational study. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2012, 49, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, J.; Devereaux, P.J.; Lee, S.F.; D’Aragon, F.; Avidan, M.S.; Whitlock, R.P.; Mazer, C.D.; Rousseau-Saine, N.; Rajamohan, R.R.; Pryor, K.O.; et al. Benzodiazepine-Free Cardiac Anesthesia for Reduction of Postoperative Delirium: A Cluster Randomized Crossover Trial. JAMA Surg. 2025, 160, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.; Belley-Côté, E.P.; Young, J.; He, H.; Saud, H.; D’Aragon, F.; Um, K.; Alhazzani, W.; Piticaru, J.; Hedden, M.; et al. Effect of perioperative benzodiazepine use on intraoperative awareness and postoperative delirium: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials and observational studies. Br. J. Anaesth. 2023, 131, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evered, L.; Silbert, B.; Knopman, D.S.; Scott, D.A.; DeKosky, S.T.; Rasmussen, L.S.; Oh, E.S.; Crosby, G.; Berger, M.; Eckenhoff, R.G.; et al. Recommendations for the Nomenclature of Cognitive Change Associated with Anaesthesia and Surgery-2018. Anesthesiology 2018, 129, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, M.G.; Markofski, M.M.; Carrillo, A.E. Elevated Inflammatory Status and Increased Risk of Chronic Disease in Chronological Aging: Inflamm-aging or Inflamm-inactivity? Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webers, A.; Heneka, M.T.; Gleeson, P.A. The role of innate immune responses and neuroinflammation in amyloid accumulation and progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Immunol. Cell. Biol. 2020, 98, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikodemova, M.; Small, A.L.; Kimyon, R.S.; Watters, J.J. Age-dependent differences in microglial responses to systemic inflammation are evident as early as middle age. Physiol. Genom. 2016, 48, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, A.; Encinas, J.M.; Deudero, J.J.; Chancey, J.H.; Enikolopov, G.; Overstreet-Wadiche, L.S.; Tsirka, S.E.; Maletic-Savatic, M. Microglia shape adult hippocampal neurogenesis through apoptosis-coupled phagocytosis. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 7, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, K.; Ogawa, M.; Yoshida, M. Effects of ageing on microglia in the normal rat brain: Immunohistochemical observations. Neuroreport 1994, 5, 1224–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, L.E.; Liddelow, S.A.; Chakraborty, C.; Münch, A.E.; Heiman, M.; Barres, B.A. Normal aging induces A1-like astrocyte reactivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1896–E1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niraula, A.; Sheridan, J.F.; Godbout, J.P. Microglia Priming with Aging and Stress. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M.; Dragunow, M. The human side of microglia. Trends Neurosci. 2014, 37, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Munster, B.C.; Korevaar, J.C.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Levi, M.; Wiersinga, W.J.; De Rooij, S.E. Time-course of cytokines during delirium in elderly patients with hip fractures. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2008, 56, 1704–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, K.; Kinoshita, H.; Kumagai, G.; Takekawa, D.; Nitobe, Y.; Asari, T.; Wada, K.; Kushikata, T.; Ishibashi, Y.; Hirota, K. Association between preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, uric acid, and postoperative delirium in elderly patients undergoing degenerative spine surgery. J. Anesth. 2024, 38, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cape, E.; Hall, R.J.; van Munster, B.C.; de Vries, A.; Howie, S.E.; Pearson, A.; Middleton, S.D.; Gillies, F.; Armstrong, I.R.; White, T.O.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid markers of neuroinflammation in delirium: A role for interleukin-1β in delirium after hip fracture. J. Psychosom. Res. 2014, 77, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, F.; Hinz, R.; Gentleman, S.; Hampshire, A.; Dani, M.; Brooks, D.J.; Edison, P. Neuroinflammation is independently associated with brain network dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malpetti, M.; Kievit, R.A.; Passamonti, L.; Jones, P.S.; Tsvetanov, K.A.; Rittman, T.; Mak, E.; Nicastro, N.; Bevan-Jones, W.R.; Su, L.; et al. Microglial activation and tau burden predict cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2020, 143, 1588–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passamonti, L.; Tsvetanov, K.A.; Jones, P.S.; Bevan-Jones, W.R.; Arnold, R.; Borchert, R.J.; Mak, E.; Su, L.; O’Brien, J.T.; Rowe, J.B. Neuroinflammation and Functional Connectivity in Alzheimer’s Disease: Interactive Influences on Cognitive Performance. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 7218–7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, E.; Boonekamp, J. Does oxidative stress shorten telomeres in vivo? A meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 85, 101854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmos, A.B.; Duarte, R.R.R.; Smeeth, D.M.; Hedges, E.C.; Nixon, D.F.; Thuret, S.; Powell, T.R. Telomere length and human hippocampal neurogenesis. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 2239–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, L.; Swartz, K.R.; Bruemmer, D.; Eum, S.Y.; Huang, W.; Seelbach, M.; Choi, Y.J.; Hennig, B.; Toborek, M. Deficiency of telomerase activity aggravates the blood-brain barrier disruption and neuroinflammatory responses in a model of experimental stroke. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 88, 2859–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linghui, D.; Shi, Q.; Chi, C.; Xiaolei, L.; Lixing, Z.; Zhiliang, Z.; Birong, D. The Association Between Leukocyte Telomere Length and Cognitive Performance Among the American Elderly. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 527658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Pan, Y.; Kao, S.Y.; Li, C.; Kohane, I.; Chan, J.; Yankner, B.A. Gene regulation and DNA damage in the ageing human brain. Nature 2004, 429, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbunova, V.; Seluanov, A.; Mao, Z.; Hine, C. Changes in DNA repair during aging. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7466–7474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbunova, V.; Seluanov, A. DNA double strand break repair, aging and the chromatin connection. Mutat. Res. 2016, 788, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautrup, S.; Myrup Holst, C.; Yde, A.; Asmussen, S.; Thinggaard, V.; Larsen, K.; Laursen, L.S.; Richner, M.; Vaegter, C.B.; Prieto, G.A.; et al. The role of aging and brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling in expression of base excision repair genes in the human brain. Aging Cell 2023, 22, e13905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionescu-Tucker, A.; Cotman, C.W. Emerging roles of oxidative stress in brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2021, 107, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tönnies, E.; Trushina, E. Oxidative Stress, Synaptic Dysfunction, and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 57, 1105–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkov, A.A. The role of mitochondria in reactive oxygen species metabolism and signaling. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1147, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, R.; Perluigi, M.; Butterfield, D.A. Protein oxidation and lipid peroxidation in brain of subjects with Alzheimer’s disease: Insights into mechanism of neurodegeneration from redox proteomics. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2006, 8, 2021–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P.; Arumugam, T.V. Hallmarks of Brain Aging: Adaptive and Pathological Modification by Metabolic States. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1176–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, H.J. Normal Aging Induces Changes in the Brain and Neurodegeneration Progress: Review of the Structural, Biochemical, Metabolic, Cellular, and Molecular Changes. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 931536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Ji, J.; Rabow, Z.; Shen, T.; Folz, J.; Brydges, C.R.; Fan, S.; Lu, X.; Mehta, S.; Showalter, M.R.; et al. A metabolome atlas of the aging mouse brain. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, C.A.; Hudon, C.; Croteau, E.; Fortier, M.; St-Pierre, V.; Vandenberghe, C.; Nugent, S.; Tremblay, S.; Paquet, N.; Lepage, M.; et al. Links Between Metabolic and Structural Changes in the Brain of Cognitively Normal Older Adults: A 4-Year Longitudinal Follow-Up. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, J.H.; Baxter, M.G. The ageing cortical synapse: Hallmarks and implications for cognitive decline. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, S.N.; Barnes, C.A. Neural plasticity in the ageing brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez Colmenares, A.; Thomas, M.L.; Anderson, C.; Arciniegas, D.B.; Calhoun, V.; Choi, I.Y.; Kramer, A.F.; Li, K.; Lee, J.; Lee, P.; et al. Testing the structural disconnection hypothesis: Myelin content correlates with memory in healthy aging. Neurobiol. Aging 2024, 141, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, R.F.; Nagano, S. Crosstalk between Oxidative Stress and Aging in Neurodegeneration Disorders. Cells 2023, 12, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; Xue, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Gu, X.; Dong, Y.; Qiu, P. Neuroinflammation: The central enabler of postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrando, N.; Monaco, C.; Ma, D.; Foxwell, B.M.; Feldmann, M.; Maze, M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha triggers a cytokine cascade yielding postoperative cognitive decline. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20518–20522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovens, I.B.; Schoemaker, R.G.; van der Zee, E.A.; Heineman, E.; Izaks, G.J.; van Leeuwen, B.L. Thinking through postoperative cognitive dysfunction: How to bridge the gap between clinical and pre-clinical perspectives. Brain Behav. Immun. 2012, 26, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Dong, H.Q.; Liu, Y.H.; Ji, M.H.; Zhang, X.; Dai, H.Y.; Sun, Z.C.; Liu, L.; Zhou, J.; Sha, H.H.; et al. Laparotomy-Induced Peripheral Inflammation Activates NR2B Receptors on the Brain Mast Cells and Results in Neuroinflammation in a Vagus Nerve-Dependent Manner. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 771156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaper, S.D.; Facci, L.; Zusso, M.; Giusti, P. Neuroinflammation, Mast Cells, and Glia: Dangerous Liaisons. Neuroscientist 2017, 23, 478–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Hu, X.D.; He, Z.Q.; Liu, Y.; Gui, Y.K.; Zhu, S.H.; Da, X.; Liu, Y.N.; Liu, L.X.; Shen, Q.Y.; et al. Anesthesia/surgery activate MMP9 leading to blood-brain barrier disruption, triggering neuroinflammation and POD-like behavior in aged mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 135, 112290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Han, L.; Wang, Y.; Deng, D.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, L.; Chen, X. Prolonged anesthesia induces neuroinflammation and complement-mediated microglial synaptic elimination involved in neurocognitive dysfunction and anxiety-like behaviors. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, M.R.; Najafi, A.R.; Koike, M.A.; Dagher, N.N.; Spangenberg, E.E.; Rice, R.A.; Kitazawa, M.; Matusow, B.; Nguyen, H.; West, B.L.; et al. Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor signaling is necessary for microglia viability, unmasking a microglia progenitor cell in the adult brain. Neuron 2014, 82, 380–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, B.A.; Kalarickal, P.L.; Maybrier, H.R.; Muench, M.R.; Dearth, D.; Chen, Y.; Escallier, K.E.; Ben Abdallah, A.; Lin, N.; Avidan, M.S. Intraoperative Electroencephalogram Suppression Predicts Postoperative Delirium. Anesth. Analg. 2016, 122, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flippo, K.H.; Strack, S. Mitochondrial dynamics in neuronal injury, development and plasticity. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro-Pérez, J.; Rodrigo, R. Contribution of oxidative stress in the mechanisms of postoperative complications and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Redox Rep. 2021, 26, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorov, A.; Lehto, A.; Klein, J. Inhibition of mitochondrial respiration by general anesthetic drugs. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2023, 396, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Chen, L.; Ye, J.; Chen, C.; Zhou, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, M. Surgery/Anesthesia disturbs mitochondrial fission/fusion dynamics in the brain of aged mice with postoperative delirium. Aging 2020, 12, 844–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, M.; Leunig, A.; Han, S.; Peterka, D.S.; Yuste, R. Prolonged anesthesia alters brain synaptic architecture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2023676118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, G.; Xie, Z.; Dong, Y. Anesthesia/Surgery Induces Cognitive Impairment in Female Alzheimer’s Disease Transgenic Mice. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 57, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci-D’Amato, L.; Speranza, L.; Volpicelli, F. Neurotrophic Factor BDNF, Physiological Functions and Therapeutic Potential in Depression, Neurodegeneration and Brain Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.F.; Chen, C.; Lin, J.T.; Jiao, X.H.; Dong, W.; Wan, J.; Liu, Q.; Qiu, Y.K.; Sun, A.; Liu, Y.Q.; et al. Impaired synaptic plasticity and decreased glutamatergic neuron excitability induced by SIRT1/BDNF downregulation in the hippocampal CA1 region are involved in postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2024, 29, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herskovits, A.Z.; Guarente, L. SIRT1 in neurodevelopment and brain senescence. Neuron 2014, 81, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, W.Y.; Mao, Y.W.; Graff, J.; Guan, J.S.; Pan, L.; Mak, G.; Kim, D.; Su, S.C.; Tsai, L.H. A novel pathway regulates memory and plasticity via SIRT1 and miR-134. Nature 2010, 466, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, V.V.; Maday, S. Compartment-specific dynamics and functions of autophagy in neurons. Dev. Neurobiol. 2018, 78, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, H.; Tao, X.; Ni, Y.; Pei, D.; Kang, S.; Yan, W.; Lu, J. Role of mTOR-Regulated Autophagy in Synaptic Plasticity Related Proteins Downregulation and the Reference Memory Deficits Induced by Anesthesia/Surgery in Aged Mice. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 628541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, M.; Amit, I.; Garber, M.; French, C.; Lin, M.F.; Feldser, D.; Huarte, M.; Zuk, O.; Carey, B.W.; Cassady, J.P.; et al. Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature 2009, 458, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapranov, P.; Cheng, J.; Dike, S.; Nix, D.A.; Duttagupta, R.; Willingham, A.T.; Stadler, P.F.; Hertel, J.; Hackermuller, J.; Hofacker, I.L.; et al. RNA maps reveal new RNA classes and a possible function for pervasive transcription. Science 2007, 316, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, C.; Jiang, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Z.; Ou, H.; Jiang, T.; Liang, W.; et al. LncRNA-AC006129.1 reactivates a SOCS3-mediated anti-inflammatory response through DNA methylation-mediated CIC downregulation in schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 4511–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Zuo, X.; Deng, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Ji, A. Roles of long noncoding RNAs in brain development, functional diversification and neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res. Bull. 2013, 97, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Zheng, Y.; Suo, Z.; Zhang, M.; Xu, W.; Wang, L.; Ge, D.; Qu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, H.; et al. The role of lncRNAs related ceRNA regulatory network in multiple hippocampal pathological processes during the development of perioperative neurocognitive disorders. PeerJ 2024, 12, e17775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, D.; Prasanth, K.V.; Tripathi, V.; Colasse, S.; Nakamura, T.; Xuan, Z.; Zhang, M.Q.; Sedel, F.; Jourdren, L.; Coulpier, F.; et al. A long nuclear-retained non-coding RNA regulates synaptogenesis by modulating gene expression. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 3082–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, K.; Jana, N.R.; Mukhopadhyay, D. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 protects against Abeta(1-42) induced toxicity by regulating the expression of receptor tyrosine kinase EPHA2 via quenching miR-200a/26a/26b in Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci. 2022, 302, 120652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, X.; Lu, D.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; He, W.; Feng, X. Aberrantly expressed long noncoding RNAs are involved in sevoflurane-induced developing hippocampal neuronal apoptosis: A microarray related study. Metab. Brain Dis. 2016, 31, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putcha, G.V.; Moulder, K.L.; Golden, J.P.; Bouillet, P.; Adams, J.A.; Strasser, A.; Johnson, E.M. Induction of BIM, a proapoptotic BH3-only BCL-2 family member, is critical for neuronal apoptosis. Neuron 2001, 29, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Li, H.; Shi, C.; Qian, M.; Yang, N.; Wang, L.; Gao, X.; Ni, C. lncRNAs Are Involved in Sevoflurane Anesthesia-Related Brain Function Modulation through Affecting Mitochondrial Function and Aging Process. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 8841511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearn, M.L.; Hu, Y.; Niesman, I.R.; Patel, H.H.; Drummond, J.C.; Roth, D.M.; Akassoglou, K.; Patel, P.M.; Head, B.P. Propofol neurotoxicity is mediated by p75 neurotrophin receptor activation. Anesthesiology 2012, 116, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanlander, A.V.; Okun, J.G.; de Jaeger, A.; Smet, J.; De Latter, E.; De Paepe, B.; Dacremont, G.; Wuyts, B.; Vanheel, B.; De Paepe, P.; et al. Possible pathogenic mechanism of propofol infusion syndrome involves coenzyme q. Anesthesiology 2015, 122, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radtke, F.M.; Franck, M.; Lorenz, M.; Luetz, A.; Heymann, A.; Wernecke, K.D.; Spies, C.D. Remifentanil reduces the incidence of post-operative delirium. J. Int. Med. Res. 2010, 38, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, A.D.; Chernobylsky, D.J.; Thakur, P.; Siddaiah, H.; Kaye, R.J.; Eng, L.K.; Harbell, M.W.; Lajaunie, J.; Cornett, E.M. Dexmedetomidine in Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) Protocols for Postoperative Pain. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2020, 24, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Du, X.; Yu, D.; Yang, Y.; Ma, G.; Jia, X.; Cheng, L. Sufentanil alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting inflammation and protecting the blood-brain barrier in rats. Eur. J. Histochem. 2022, 66, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Sun, Y.; He, W. Comparative effects of fentanyl versus sufentanil on cerebral oxygen saturation and postoperative cognitive function in elderly patients undergoing open surgery. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 31, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, J.; Yuan, L.; Wu, J.; Jiang, C.; Daniels, J.; Mehta, R.L.; Wang, M.; Yeung, J.; Jackson, T.; et al. Effect of Regional vs General Anesthesia on Incidence of Postoperative Delirium in Older Patients Undergoing Hip Fracture Surgery: The RAGA Randomized Trial. JAMA 2022, 327, 50–58, Correction in JAMA 2022, 327, 1188. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2022.3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.Y.; Yang, T.X.; Chong, D.Y.; So, E.H. Neuraxial versus general anesthesia in elderly patients undergoing hip fracture surgery and the incidence of postoperative delirium: A systematic review and stratified meta-analysis. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023, 23, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliff, J.J.; Wang, M.; Liao, Y.; Plogg, B.A.; Peng, W.; Gundersen, G.A.; Benveniste, H.; Vates, G.E.; Deane, R.; Goldman, S.A.; et al. A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid beta. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 147ra111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedergaard, M. Neuroscience. Garbage truck of the brain. Science 2013, 340, 1529–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; He, X.; Cai, J.; Li, Q. Functional aspects of the brain lymphatic drainage system in aging and neurodegenerative diseases. J. Biomed. Res. 2024, 38, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Han, Y.; Lv, P.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Z.; Peng, L.; Liu, S.; Ma, Z.; Xia, T.; Zhang, B.; et al. Long-term isoflurane anesthesia induces cognitive deficits via AQP4 depolarization mediated blunted glymphatic inflammatory proteins clearance. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2024, 44, 1450–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, X.; Cheng, L.; Ren, W.; Wen, G.; Wu, X.; Lou, H.; Ren, X.; Lu, L.; Hermenean, A.; et al. Dexmedetomidine improves the circulatory dysfunction of the glymphatic system induced by sevoflurane through the PI3K/AKT/DeltaFosB/AQP4 pathway in young mice. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hablitz, L.M.; Vinitsky, H.S.; Sun, Q.; Staeger, F.F.; Sigurdsson, B.; Mortensen, K.N.; Lilius, T.O.; Nedergaard, M. Increased glymphatic influx is correlated with high EEG delta power and low heart rate in mice under anesthesia. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, J.; Sorg, C.; Muller, L.; Zistler, F.; Neumaier, V.; Bonhoeffer, M.; Ranft, A.; Golkowski, D.; Priller, J.; Zimmer, C.; et al. Impaired Macroscopic Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow by Sevoflurane in Humans during and after Anesthesia. Anesthesiology 2025, 142, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, A.; Luo, T.; Hsieh, B.; Edge, C.J.; Gridley, M.; Wong, R.T.C.; Constandinou, T.G.; Wisden, W.; Franks, N.P. Brain clearance is reduced during sleep and anesthesia. Nat. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 1046–1056, Correction in Nat. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, V.H.; Cunningham, C.; Holmes, C. Systemic infections and inflammation affect chronic neurodegeneration. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benveniste, H.; Lee, H.; Ding, F.; Sun, Q.; Al-Bizri, E.; Makaryus, R.; Probst, S.; Nedergaard, M.; Stein, E.A.; Lu, H. Anesthesia with Dexmedetomidine and Low-dose Isoflurane Increases Solute Transport via the Glymphatic Pathway in Rat Brain When Compared with High-dose Isoflurane. Anesthesiology 2017, 127, 976–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fultz, N.E.; Bonmassar, G.; Setsompop, K.; Stickgold, R.A.; Rosen, B.R.; Polimeni, J.R.; Lewis, L.D. Coupled electrophysiological, hemodynamic, and cerebrospinal fluid oscillations in human sleep. Science 2019, 366, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Li, Z.; He, J.; Fu, W. Dexmedetomidine for the prevention of postoperative delirium in elderly patients undergoing noncardiac surgery: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Ren, Z.; Gao, J.; He, X.; Li, Q. Dexmedetomidine for the prevention of postoperative delirium in patients undergoing cardiac surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. BMC Anesthesiol. 2025, 25, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.E.; Mart, M.F.; Cunningham, C.; Shehabi, Y.; Girard, T.D.; MacLullich, A.M.J.; Slooter, A.J.C.; Ely, E.W. Delirium. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The American Geriatrics Society Expert Panel on Postoperative Delirium in Older Adults. American Geriatrics Society abstracted clinical practice guideline for postoperative delirium in older adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2015, 63, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad Mosallam, M.; Said Elgebaly, A.; Mohye Eldin Abu Elyazed, M.; Ramadan Naser, S. Effect of dexmedetomidine infusion on incidence of postoperative delirium in elderly patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty: Randomised controlled double-blinded trial. Int. J. Med. Anesthesiol. 2024, 7, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Meng, Z.T.; Wu, X.H.; Cui, F.; Li, H.L.; Wang, D.X.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, S.N.; Maze, M.; Ma, D. Dexmedetomidine for prevention of delirium in elderly patients after non-cardiac surgery: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 1893–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehabi, Y.; Howe, B.D.; Bellomo, R.; Arabi, Y.M.; Bailey, M.; Bass, F.E.; Bin Kadiman, S.; McArthur, C.J.; Murray, L.; Reade, M.C.; et al. Early Sedation with Dexmedetomidine in Critically Ill Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2506–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Na, H.-S.; Ryu, J.-H.; Shin, H.-J. The effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on postoperative delirium: A meta-analysis. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2024, 77, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, H.; Saito, J.; Kushikata, T.; Oyama, T.; Takekawa, D.; Hashiba, E.; Sawa, T.; Hirota, K. The Perioperative Frontal Relative Ratio of the Alpha Power of Electroencephalography for Predicting Postoperative Delirium After Highly Invasive Surgery: A Prospective Observational Study. Anesth. Analg. 2023, 137, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hight, D.; Ehrhardt, A.; Lersch, F.; Luedi, M.M.; Stuber, F.; Kaiser, H.A. Lower alpha frequency of intraoperative frontal EEG is associated with postoperative delirium: A secondary propensity-matched analysis. J. Clin. Anesth. 2024, 93, 111343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, K.K.; Britt-Spells, A.M.; Sands, L.P.; Leung, J.M. Processed Electroencephalogram Monitoring and Postoperative Delirium: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Anesthesiology 2018, 129, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildes, T.S.; Mickle, A.M.; Ben Abdallah, A.; Maybrier, H.R.; Oberhaus, J.; Budelier, T.P.; Kronzer, A.; McKinnon, S.L.; Park, D.; Torres, B.A.; et al. Effect of Electroencephalography-Guided Anesthetic Administration on Postoperative Delirium Among Older Adults Undergoing Major Surgery: The ENGAGES Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 321, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswamy, S.M.; Weerink, M.A.S.; Struys, M.; Nagaraj, S.B. Dexmedetomidine-induced deep sedation mimics non-rapid eye movement stage 3 sleep: Large-scale validation using machine learning. Sleep 2021, 44, zsaa167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzone, M.J.; Chapin, B.; Walker, J.; Santana, M.; Wang, Y.; Amini, S.; Kimmet, F.; Perera, E.; Rubinos, C.; Arias, F.; et al. Electroencephalographic Measures of Delirium in the Perioperative Setting: A Systematic Review. Anesth. Analg. 2025, 140, 1127–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, L.; Gao, M.; Guo, W.; Ma, Y. Dexmedetomidine reduces postoperative delirium after joint replacement in elderly patients with mild cognitive impairment. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 28, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.S.; Meng, F.G.; Rong, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.W.; Liu, H.Q. Dexmedetomidine and the glymphatic system: A new perspective in managing postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1648308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tawfik, G.-A.; Lu, M.; De La Hoz, M.; Crugnola, W.; Jin, Z.; Moller, D. Molecular and Clinical Considerations for Anesthesia in the Aging Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110272
Tawfik G-A, Lu M, De La Hoz M, Crugnola W, Jin Z, Moller D. Molecular and Clinical Considerations for Anesthesia in the Aging Brain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110272
Chicago/Turabian StyleTawfik, George-Abraam, Michael Lu, Marc De La Hoz, William Crugnola, Zhaosheng Jin, and Daryn Moller. 2025. "Molecular and Clinical Considerations for Anesthesia in the Aging Brain" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110272
APA StyleTawfik, G.-A., Lu, M., De La Hoz, M., Crugnola, W., Jin, Z., & Moller, D. (2025). Molecular and Clinical Considerations for Anesthesia in the Aging Brain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110272





