Abstract
The P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) is a ligand-gated, non-selective cation channel activated by extracellular ATP, a key danger signal in the cellular stress response. Due to its roles in inflammation and neurological disorders, it is an attractive therapeutic target. However, clinical trials of P2X7R antagonists have failed to show clinical efficacy. This review explores whether receptor polymorphisms, alternative splicing, and membrane composition contribute to these clinical trial failures. Genotyping of trial participants is highly recommended prior to enrolment, and in vitro functional studies should be wary of the membrane composition of cells expressing P2X7R. While the P2X7R shows promising therapeutic potential, there remain large gaps in research particularly in characterising haplotypes and alternatively spliced hetero- or homotrimers of the receptor. This results in the development and testing of agents without considering the genetic variability of the receptor, which we propose to be a large contributor to the lack of clinical success. We also summarise characteristics of the receptor and recent structural findings to discuss how computational approaches may help overcome these challenges of variability. Precision targeting of the receptor in disease states is warranted, and a collaborative approach covering multiple facets of the receptor will facilitate this.
1. Introduction
ATP is a key molecule in living cells, serving as an energy source for numerous enzymatic processes, including RNA and DNA synthesis. Although ATP primarily exists intracellularly, it has been established that ATP and its metabolites also play important roles in extracellular signalling. Cell death or disruption to cell membrane integrity leads to the release of significant amounts of ATP into the extracellular space, elevating its concentration above normal physiological levels. In this context, extracellular ATP acts as a danger signal, or “damage-associated molecular pattern” (DAMP) [1]. ATP, therefore, serves a dual role, first as an essential intracellular energy source and secondly as a potent extracellular signalling molecule during cellular stress or damage.
Extracellular ATP is detected by the transmembrane purinergic P2 receptors, which can be subdivided into two classes: P2X and P2Y. P2X receptors are trimeric, ligand-gated cation channels whereas P2Y receptors are G-protein coupled receptors. A subtype of the P2X receptors, the P2X7 receptor (P2X7R), is a key responder to ATP acting as a DAMP. The P2X7R is expressed in most immune cells and cells present in the central nervous system such as astrocytes and microglia [2]. This expression pattern, combined with its role in sensing cellular stress and the production of inflammatory cytokines including interleukin-1β (IL-1β) [3,4] and IL-18 [5,6], places the P2X7R at the centre of inflammation and disease processes. The receptor is well established as a driver of NOD-, LRR-, and pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation and has been reported to interact with other membrane proteins and complexes, including pannexin-1, caveolin 1, lipid rafts, and transmembrane protein 16F (TMEM16F) [7]. Research has been focused on the P2X7R due to its involvement in inflammation, cancers, as well as neurological and immune system disorders [2,8,9,10,11,12,13]. For example, the P2X7R has been implicated in affecting the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) [14]. A study found increased levels of the P2X7R in the plasma of COVID-19 patients which was positively correlated with disease severity [15], and a systematic review investigating the involvement of purinergic signalling in the treatment of COVID-19 suggested the P2X7R as a potential therapeutic target [16].
The P2X7R can function as a pattern recognition receptor that detects extracellular ATP as a DAMP. Of all the purinergic receptors, it has the lowest affinity to ATP and requires activation by elevated ATP levels [10]. Another defining feature is its ability to open a non-selective pore distinct from regular channel function, allowing for the flux of larger molecules and resulting in eventual cell death [11,17]. In this review, we have used the standard P2X7R nomenclature to refer to “channel function” as cation flux across the membrane, and “pore function” as the flux of larger molecules. It is important to distinguish between these terms to avoid confusion, and we advise against using “pore” to describe channel function. Although initially described for the P2X7R, other subtypes (including P2X2 and P2X4) have also shown pore-forming characteristics [18]. The mechanism of pore formation remains controversial and will only be discussed briefly. Significantly, unlike other P2X family members, the P2X7R does not typically exhibit desensitisation under sustained ATP exposure, which is the gradual reduction in inward current during sustained or repeated ATP application [17].
In vitro studies show that P2X7R antagonism blocks the release of inflammatory cytokines from immune cells [5,19,20]. This can lead to downstream effects such as reducing tumour growth [21,22,23], decreasing osteoclast formation [24], and preventing neuron degeneration [25]. In animal models of disease, antagonists show promise as mediators of neuropathic pain or inflammation [3,26,27,28,29,30]. Considering its involvement in inflammatory pathways and associations with various disease states, the P2X7R has become an attractive target for drug development and remains an active area of research [31,32]. However, in human clinical trials, P2X7R antagonists have failed to meet efficacy endpoints, and it is intriguing to ask why that could be. Multiple contributing factors are likely to be responsible for this failure. Ion channels often exhibit distinct functional outcomes depending on which inhibitory site is targeted, differences that are frequently influenced by the channel’s conformational state (open or closed) [33], and the structural specificity of the binding site [34,35,36]. In the case of the P2X7R, targeting orthosteric, allosteric, or modulatory sites can result in varied effects, including full channel blockade, selective inhibition of pore formation, modulation of cytokine release, and altered receptor sensitivity.
Clinical translation is also complicated due to species-specific differences in pharmacology and binding sites. Furthermore, the receptor possesses a high degree of genetic variations [37] such as single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and alternative splicing, all of which can impact receptor structure and drug responsiveness. Genetic variations may ultimately result in altered protein function or surface expression. In this review, the structure of the P2X7R and its gating mechanism will be described including key ATP-binding residues, followed by an in-depth analysis of functionally relevant P2RX7 SNPs and haplotypes. A focused review on alternative splicing, which can substantially alter P2X7R structure and function, has been recently conducted [38] and will also be discussed in this review. The aim of this review is to shed light on the impact of mutated states of P2X7Rs. Additionally, breakthroughs in structural biology have enabled the structure of an almost complete rat P2X7R (rP2X7R) to be determined by cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) [39,40,41]. Most recently, the human P2X7R (hP2X7R) has also been resolved in both the open and closed states [31]. Together with previous and ongoing site-directed mutagenesis studies, these studies provide mechanistic insights that will assist in drug discovery and provide the basis for a personalised medicine approach, enabling customised treatment for patients based on their P2X7 genetic makeup and the presence of alternatively spliced subunits.
2. Structural Insights and Gating Mechanisms
2.1. Subunit Structure
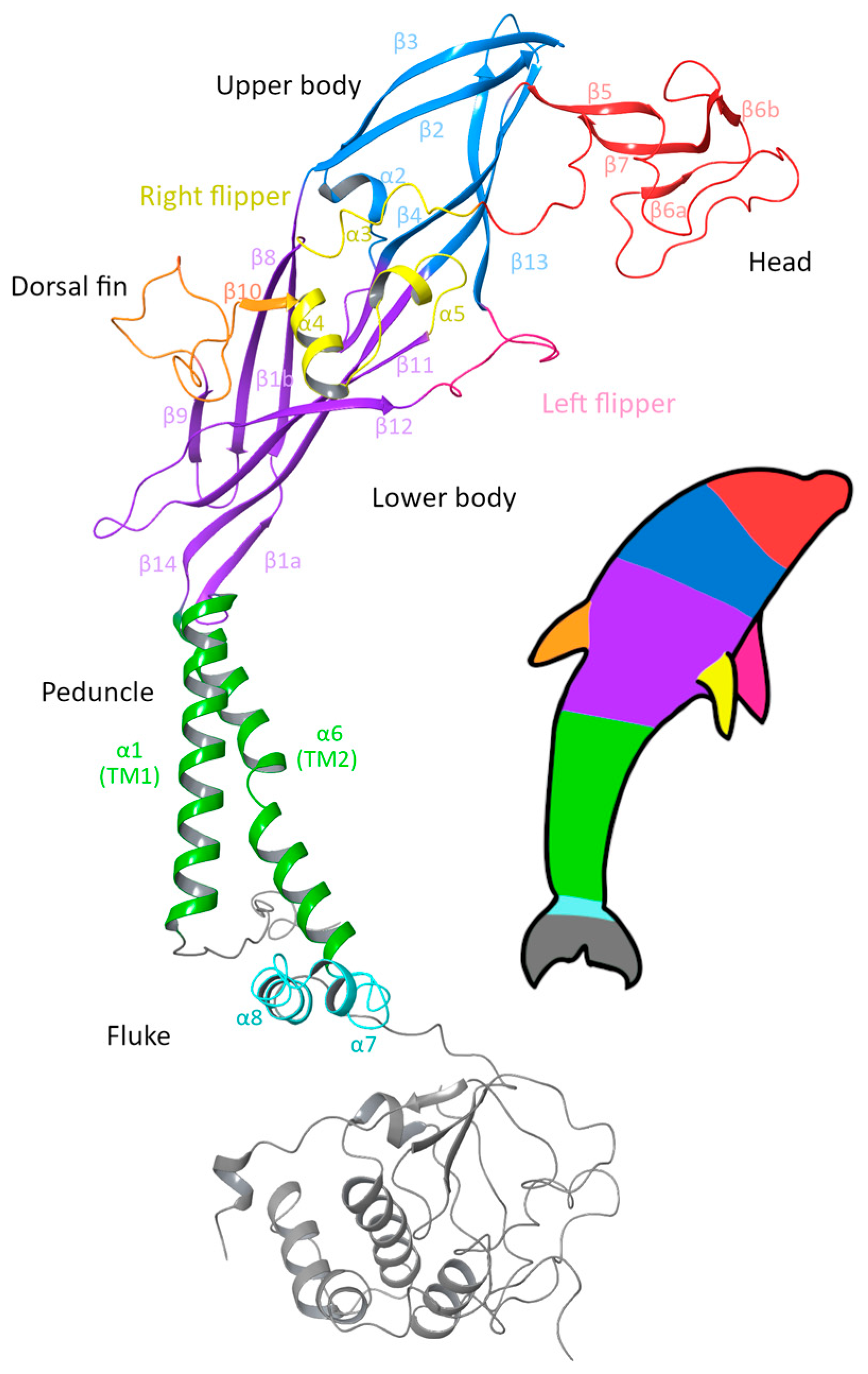
The P2X7R is composed of three subunits, which intertwine across both the extracellular and intracellular domains to form a trimeric receptor. The canonical (wild-type) human subunit is composed of 595 amino acids; beginning at the short intracellular N-terminal (M1–N25), the subunit contains two transmembrane (TM) domains, TM1 (Y26–V46) and TM2 (V335–I355), with a large extracellular domain between the two TM domains (S47–V334) and ends with a long intracellular C-terminal domain (D356–Y595). Visually, P2X subunits have been described as having a dolphin-like shape, consisting of a rigid body region with structurally flexible branching domains representing the head, dorsal fin, and left and right flippers of the dolphin [42,43]. In the original dolphin model that was developed from the structurally similar P2X4R, the tail represented the two transmembrane domains, and this description has remained for the P2X7R [34,43]. However, with the recent structures of the full-length rP2X7R being available, we suggest an updated P2X7R dolphin model (Figure 1) in which the body of the dolphin represents the extracellular domain, while the peduncle is the TM domain, and the fluke represents the large C-terminal domain.
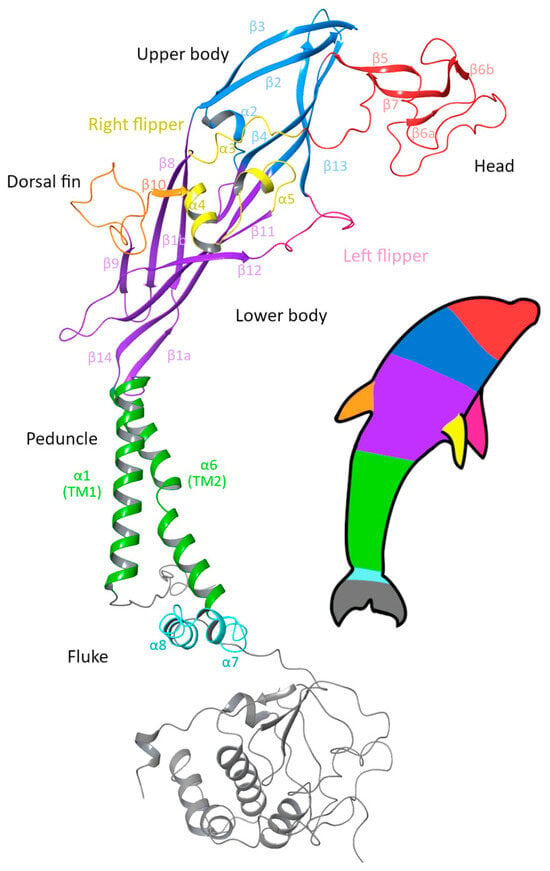
Figure 1.
Ribbon diagram of a single subunit of the P2X7 receptor (P2X7A) with the updated dolphin representation to reflect the new structural findings of the intracellular domain. The head region (red), upper body (blue) and lower body (purple) form the extracellular domain, together with the dorsal fin (orange), right flipper (yellow) and left flipper (pink). The peduncle (green) corresponds to the two transmembrane helices, which link to the fluke corresponding to the C-cys anchor (cyan) and the cytoplasmic ballast (grey) that form the intracellular domain. Figure generated using Maestro 14.0 [44] with PDB ID 6U9W [39].
2.2. Gating Mechanism
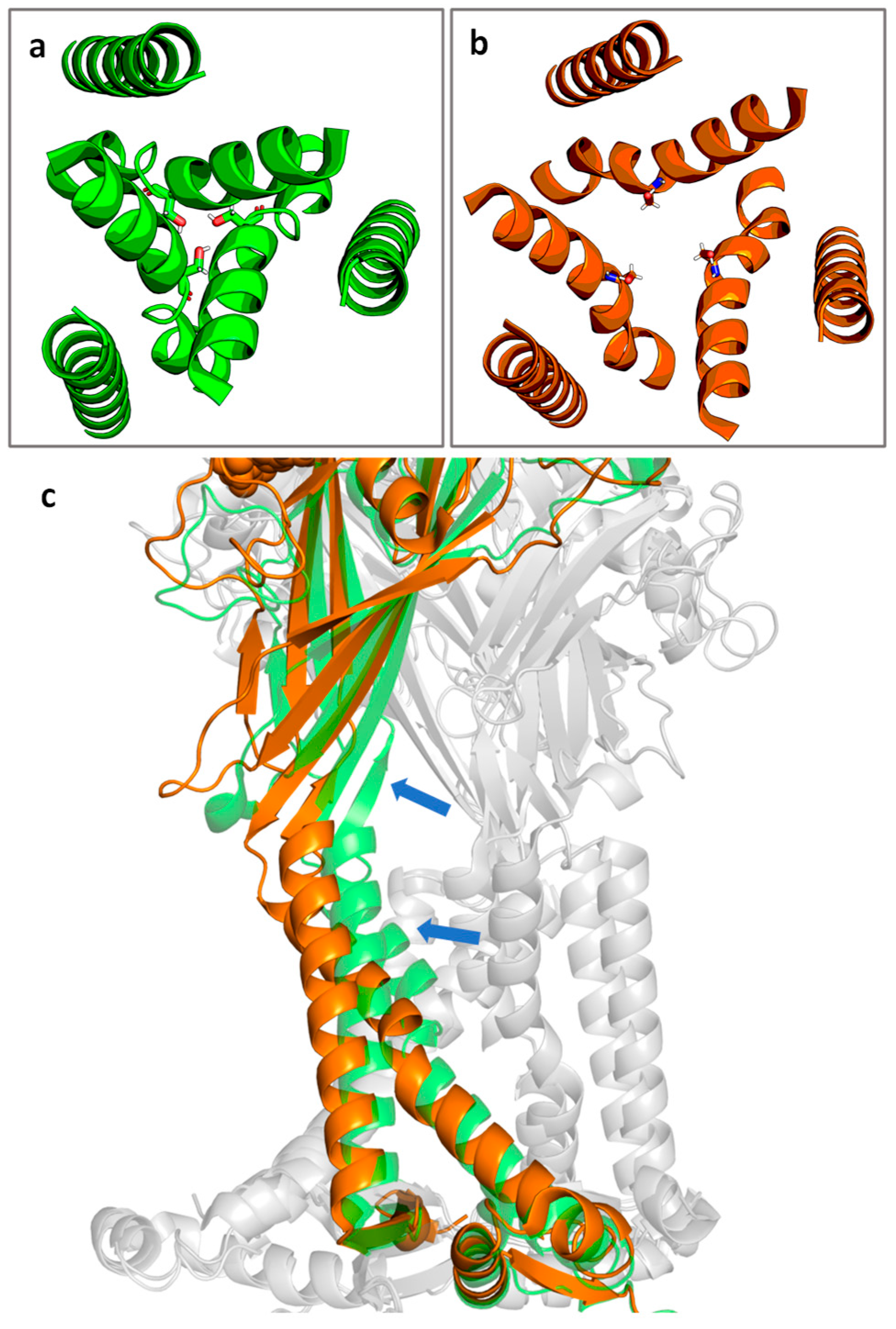
The P2X7R is gated by extracellular ATP. Channel opening results from movement of the TM gate which consists of residues S339 to S342, with the key residue S342 contributing to the narrowest part of the channel (Figure 2a,b) [39]. After agonist binding, the binding pocket undergoes a conformational change. The β strands of the extracellular domain flex outward, pulling the TM2 domains away from the channel lining and opening the channel (Figure 2c) [39].
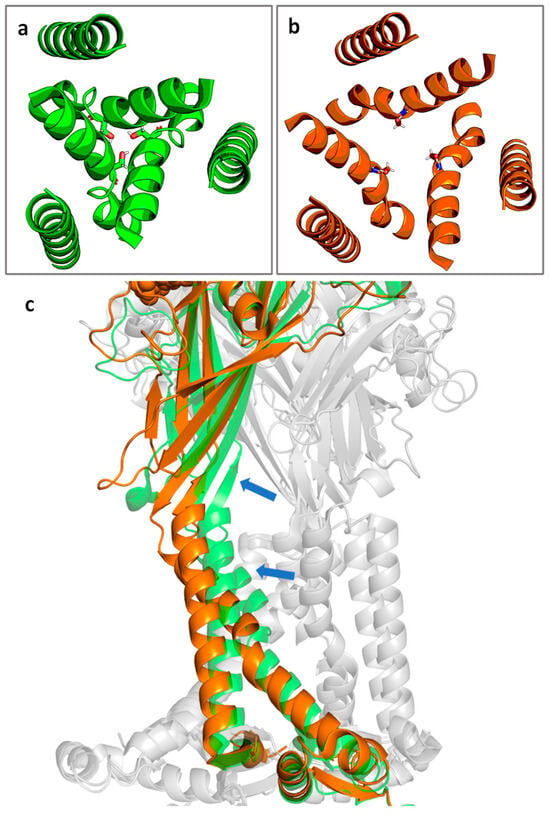
Figure 2.
Cartoon representation of the top-down view of the P2X7R channel in the (a) closed state and (b) the ATP-bound open state with S342 shown in stick representation. (c) The transition from closed (green) to open (orange) state of a single subunit. Blue arrows indicate the approximate direction of motion. Non-highlighted subunits are shown in grey for context. Figure generated using PyMOL [45] with PDB IDs 6U9V (closed state) and 6U9W (open state) [39].
In contrast to channel function, pore formation is poorly understood. Aspects of pore formation have been reviewed by North in 2002 [17], Di Virgilio et al. in 2018 [46], and Cevoli et al. in 2023 [47]. Functional studies often assess pore permeability using an assay that measures uptake of dyes or large cationic molecules, such as YOPRO-1 and ethidium, into the cell [48,49,50]. Pore formation can be reversible if ATP is quickly removed or degraded shortly after P2X7R activation, although this depends on cellular context [17,46,51]. However, prolonged activation often makes pore formation irreversible and eventually result in cell death, commonly due to necrosis from membrane disruption or apoptosis depending on context [17,46,52]. The mechanism underlying pore formation remains controversial. Currently, there are two hypotheses to explain this phenomenon. The first theory postulates that the receptor may itself become intrinsically permeable to large cations, supported by recent studies, but this remains a point of contention [46,53,54,55]. On the other hand, the second hypothesis suggests that receptor activation triggers a secondary protein such as pannexin-1 or other membrane hemichannels that interact with the P2X7R during prolonged activation [18,56]. Although it has been established that the P2X7R is involved in the activation of other proteins, it is unclear whether this results in the observed flux of large cations [57]. These two hypotheses are not mutually exclusive and both pathways may contribute to large cation transport.
3. The ATP Binding Site
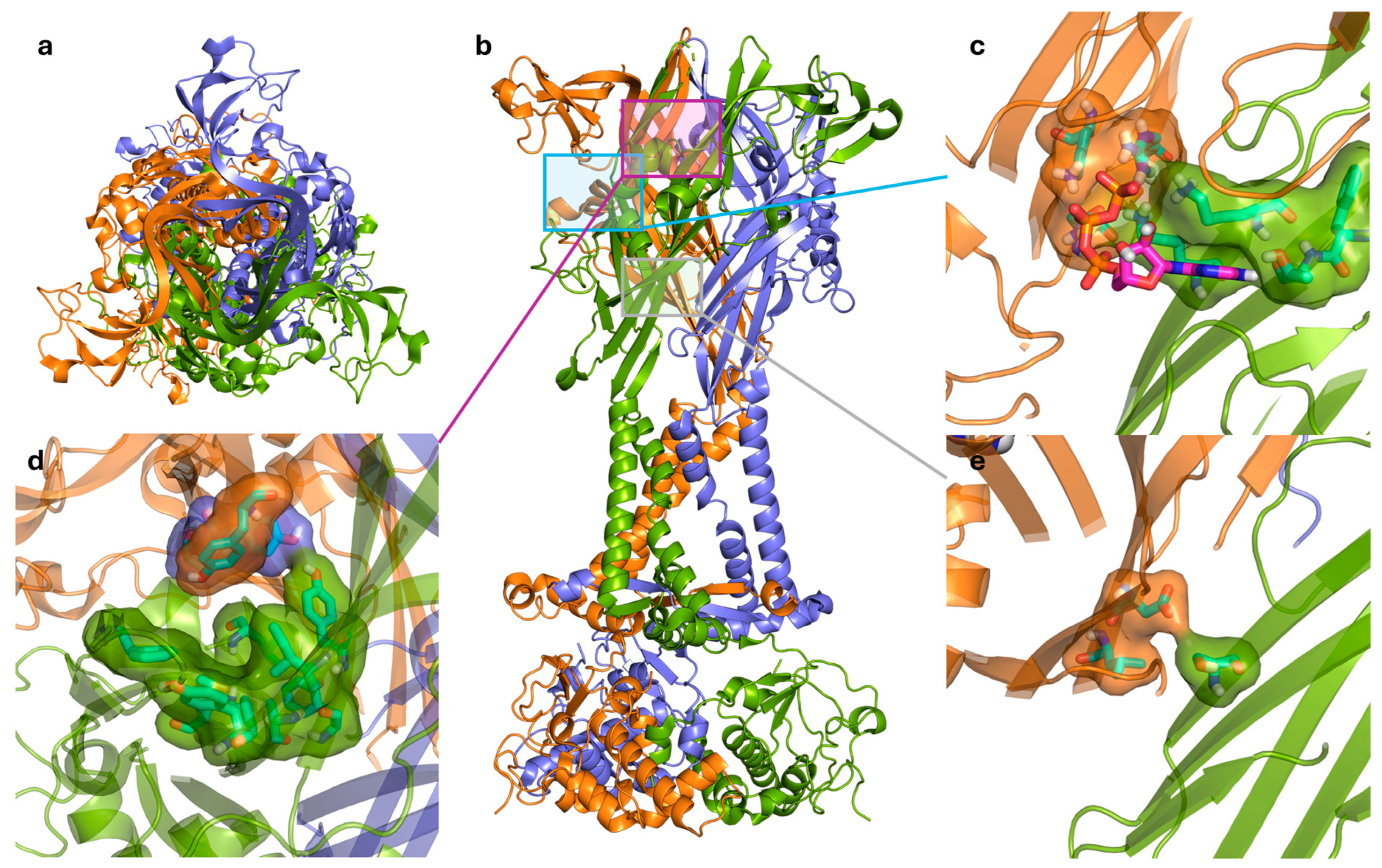
The ATP-binding site of the P2X7R has been reviewed by Jiang et al. in 2021 (Figure 3a–c) [58]. Before the determination of the receptor structure, comprehensive mutagenesis studies were conducted to identify key residues important for receptor activation [58]. By comparing known ATP-binding residues in other P2X receptors and studying highly conserved residues across different species, key residues in the hP2X7R were elucidated. The crystal structure of the zebrafish P2X4R (zfP2X4R) was used to identify eight key residues that form an inter-subunit binding site [43]. The location of this site is consistent with earlier mutagenesis studies that predicted an inter-subunit binding site [59,60]. The zfP2X4R and rP2X7R ATP-binding sites correspond to the following residues in hP2X7R: K64, K66, F188, and T189 from one subunit and N292, F293, R294, and K311 from the adjacent subunit (Figure 3c) [39,43,61]. In terms of pharmacology, ATP potency and efficacy differ between species and assays, with BzATP generally more potent than ATP at both receptors [62]. In dye uptake assays, which is a surrogate marker for pore formation, hP2X7R demonstrated greater sensitivity and greater dye uptake compared to the rP2X7R [62], which highlights a key species-specific difference. This difference is critical when using rodent models to study hP2X7R function and screening targeted therapies. Recent cryo-EM work identified that the hP2X7R has a species-specific interaction with ATP via residues L191, I214, and Y288 [31].
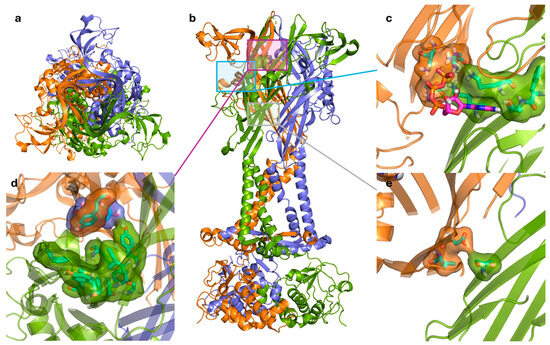
Figure 3.
(a) Top view of the trimeric P2X7R in the open state showing the three subunits colored green, orange, and blue. (b) Side view of the receptor illustrating the transmembrane and extracellular domains, with boxed regions indicating the (c) ATP-binding site with the ATP molecule, the (d) central negative allosteric modulator binding site, and the (e) proposed positive allosteric modulator binding site. Ligands and interacting residues are shown in stick and surface representations, emphasizing key hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic contacts. Figure generated using PyMOL [45] with PDB IDs 6U9W (open state), 8TR5 (closed state), and 8TR6 (closed state with negative allosteric modulator A438079 bound) [39,40,41].
4. Allosteric Modulation and Binding Sites
4.1. Negative Allosteric Modulators
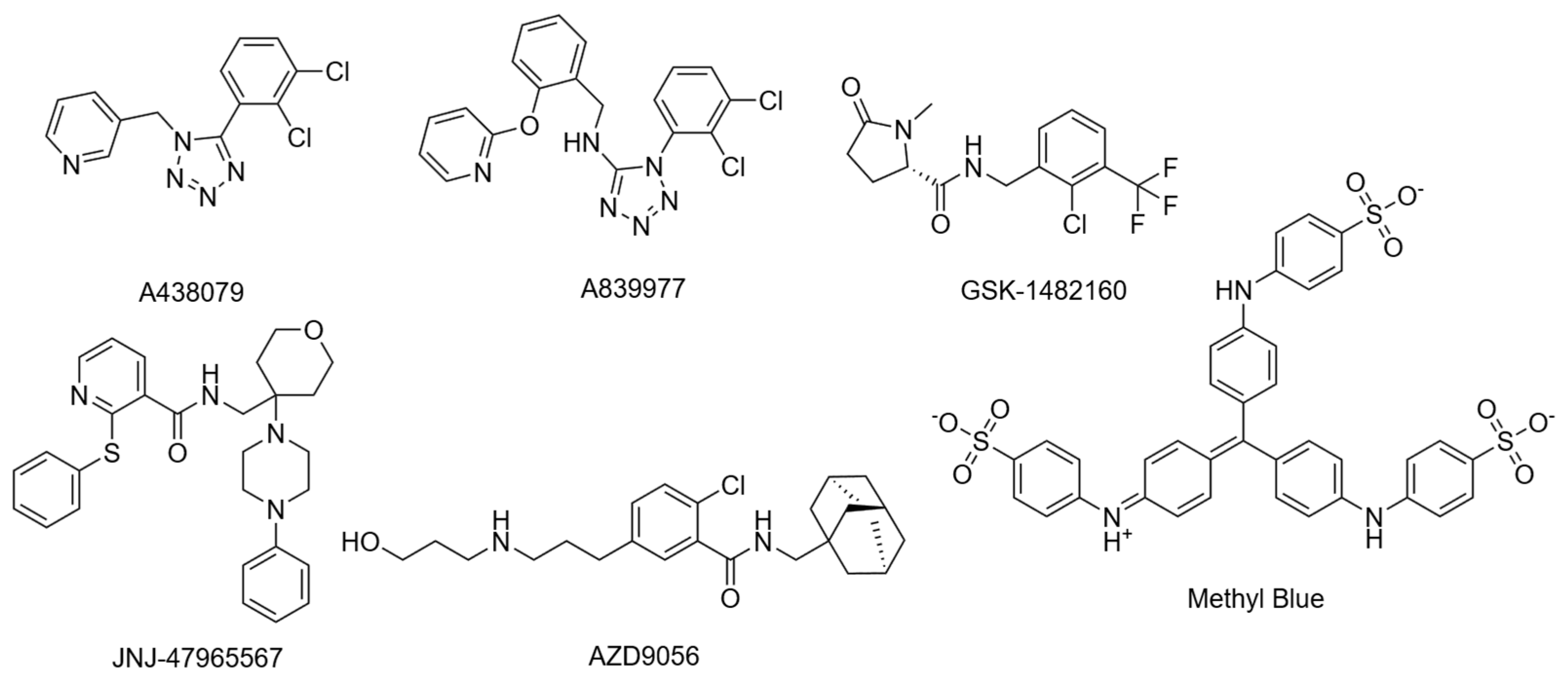
Cryo-EM structures were recently resolved for the rP2X7R with six noncompetitive negative allosteric modulators (NAMs): A438079, A839977, AZD9056, GSK1482160, JNJ47965567, and methyl blue (Figure 4) [41]. The study observed an inter-subunit hydrophobic pocket that is distinct from the orthosteric ATP-binding site [41]. All structurally characterised NAMs bound to the inter-subunit hydrophobic pocket, consisting of residues F88, L95, F103, M105, Y108, F293, Y295, Y298, I310, and A312 of the rP2X7R (Figure 3d) [41]. Hydrogen bonding with residues D92 and K297 was also observed; however, this was highly variable between NAMs due to their chemical diversity [41]. The cryo-EM mapping of this pocket was in agreement with earlier mutational, functional, and structural studies, which identified amino acid residues involved in NAM binding [34,41,63]. Seven of the ten listed residues are conserved in the hP2X7R, with the three differing residues being F95, F108, and V312. Structural analysis showed that this hydrophobic pocket usually shrinks upon ATP binding, and NAMs prevent this conformational change, consequently inhibiting receptor function [34,41]. Importantly, the study by Oken et al. also noted that NAMs bind within the extracellular domain pocket, and direct contacts are absent in TM and intracellular domains [41]. There are some differences in antagonist characteristics between species. For example, the P2X7R antagonist Brilliant Blue G (BBG) is more potent in blocking calcium uptake in the rat receptor than the human receptor [62]. On the other hand, BBG can block the dye uptake of both species [62]. It was observed that residue F95 of the hP2X7R was important in forming pi-stacking interactions that the rP2X7R did not have [64]. However, they also noted that this change does not completely account for the differences in antagonistic effect, which warrants further investigation [64]. Cryo-EM studies suggest that V312 in the hP2X7R occupies more space, and alters the conformation of Y295, providing a structural basis for species-specific differences. These variations in allosteric sites are important to consider, as they can affect a drug’s translation to human studies. For a comprehensive structural analysis of these conformational states, readers are referred to the work by Oken et al. [31].
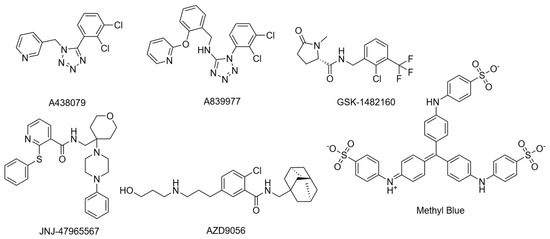
Figure 4.
Structures of NAMs used to determine the NAM binding site.
Cholesterol is another potential NAM that has a site distinct from the previous NAMs. Cholesterol and other steroid-like molecules have received little attention, and consequently their binding site is not known precisely. This presents a gap in research into the role of cholesterol inhibition on the P2X7R. Inhibition by cholesterol is dependent on a few factors, which are discussed in the section Membrane composition and receptor function.
4.2. Positive Allosteric Modulators
In contrast to NAMs, positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) have received relatively little attention despite their potential therapeutic applications and have been thoroughly reviewed by Stokes et al. [65]. PAMs can increase the effective or maximal response of a receptor (Type I), increase the receptor’s sensitivity to agonists (Type II), or a mixture of both (Mixed Type I/II). For the P2X7R, this leads to further activation of inflammatory or cell death pathways which may be beneficial for enhancing immune protection against pathogens [66], or for encouraging tumour death [65,67]. For instance, disease states where there are increased levels of extracellular ATP [68] or overexpression of the P2X7R [69] at affected sites may see therapeutic potential from PAMs. However, given the wide expression of the receptor, positive modulation is a challenge because activating P2X7R in non-diseased cells could drive inflammation or cytotoxicity, which may explain why PAMs remain understudied. Furthermore, the precise binding sites of many identified PAMs are unknown [70]. Among these, ginsenosides have been studied in greater detail using ligand docking and site directed mutagenesis to identify potential binding sites [70]. The proposed binding site of ginsenosides is distinct from that of NAMs, involving residues S60 of one subunit, and residues D318 and L320 of the neighbouring subunit [70]. This site is located between the lower body regions of two subunits and is only accessible when the P2X7R is in the open state (Figure 3e). Bidula et al. propose that PAM binding either stabilises the open state or facilitates the conformational changes associated with ATP binding [70]. Ivermectin is another recognised PAM and is thought to bind to the TM helices of the P2X4R [71,72]. Although primarily investigated in the P2X4R, ivermectin has shown activity in the hP2X7R, but not in rat or mouse P2X7Rs [65,73], and therefore species-specific interactions also complicate PAM development. Regardless, the widespread involvement of the P2X7R in disease states mean that PAMs have therapeutic potential, and their development still requires further research. Avoiding off-target effects via the use of antibody–drug conjugates and the potential for PAMs to restore function at loss-of-function mutant receptors have yet to be investigated. Alternatively, it may be beneficial to develop a P2X7R PAM to be used in conjunction with other cell-killing treatments. In this case, target-specific cell death is encouraged by further activation of the P2X7R, resulting in lower effective concentrations for both compounds. For example, a dysfunctional P2X7R variant that is chemotherapy-resistant (discussed in the section on P2X7B and alternative splicing heterotrimerisation) may become more susceptible to chemotherapy when receptor function is restored via PAM binding. Although variant-specific binding pockets have not yet been resolved, identifying these sites could guide drug design and the development of targeted modulators.
5. Membrane Composition and Receptor Function
The plasma membrane consists of many components in addition to the phospholipid bilayer, including lipids and proteins that enable essential cellular functions. It has been proposed that areas of the membrane can organise into domains enriched in sphingolipids and cholesterol, known as lipid rafts [74,75]. Lipid rafts act as platforms for signalling molecules and receptors to associate [76,77]. For a membrane protein such as the P2X7R, it is logical to consider how membrane composition, including cholesterol and lipid rafts, may affect receptor function.
The Lipid Environment Critically Impacts P2X7R Activity
A study by Karasawa et al. on the panda P2X7R (pdP2X7) demonstrated the significance of membrane composition for P2X7R activity [55]. P2X7R constructs lacking either the N-terminal domain (ΔN, residues 1–22); the C-terminal domain (ΔC, from residue 360 onwards); and pdP2X7-ΔNC, a combination of the previous two constructs, were expressed in HEK293 cells and studied. These truncated receptors showed significantly reduced dye uptake, suggesting that these domains are important for pore formation in HEK293 cells [55].
However, when pdP2X7-ΔNC was reconstituted in liposomes composed of only 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (POPE) and 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1′-rac-glycerol) (POPG), both small cation and large dye uptake were preserved, suggesting that not one or the other terminal domain was strictly required for pore function in simplified lipid environments [55]. Subsequent experiments altered the lipid compositions of the liposomes, including POPE, POPG, 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (POPC), 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-L-serine (POPS), sphingomyelin (SM) and cholesterol. These revealed that cholesterol has a dominant inhibitory role, while POPG and SM have a facilitatory role in dye uptake, and therefore pore formation [55]. Cholesterol inhibited pdP2X7-ΔNC in a dose-dependent manner, probably through directly interacting with the TM domain rather than indirect effects on bilayer rigidity [55]. A cholesterol depletion model using truncated receptor constructs was employed to identify the regions of the receptor that affected P2X7R’s sensitivity to membrane cholesterol. The pdP2X7-ΔC and pdP2X7-ΔNC constructs were not potentiated by cholesterol depletion, suggesting a loss of cholesterol sensitivity. In contrast, pdP2X7-ΔN had increased dye uptake upon cholesterol depletion, similar to the full-length receptor [55]. Notably, adding back the cysteine-rich region (C362 to C379) from the C-terminal domain to the pdP2X7-ΔNC construct restored cholesterol-mediated inhibition [55]. Mutation analysis then identified residues C362 and C363 as key (although not essential) residues in overcoming cholesterol-mediated inhibition [55]. The cysteine-rich region is located just beyond the second TM domain. Other studies in the past have shown cholesterol inhibition of the P2X7R [78] and the potential importance of the cysteine-rich region [78,79]. This region is subject to palmitoylation [55,80], a posttranslational modification in which fatty acids are covalently attached to cysteine residues. Cryo-EM structures and biochemical evidence suggest that palmitoylation anchors P2X7R to the membrane, stabilising the open state and preventing desensitisation, which is a key feature distinguishing the P2X7R from other P2X family members [39]. In addition, palmitoylation may promote association with lipid rafts, as a lack of palmitoylation reduces cell surface expression [80]. Interestingly, Karasawa et al. found similar surface expression of full-length pdP2X7R and truncated constructs in HEK293 cells [55], suggesting raft association rather than surface abundance may be the key determinate of modulating function. Finally, the recently resolved closed state structure of hP2X7R includes co-resolved cholesterol molecules, however their physiological importance remains uncertain [31]. Importantly, cholesterol has not been observed in P2X7R structures of other species.
Consequently, experimental and cellular membrane compositions must be considered when evaluating P2X7R activity. The association with lipid rafts is another factor to consider when studying different cells that will have their own lipid environments [78]. For example, truncated receptors lacking the cysteine-rich C-terminus may have reduced or no channel activity in cholesterol rich membranes (such as HEK293 cells), as a result of cholesterol inhibiting P2X7R function [55].
6. Genetic Variability: Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of the P2X7R
6.1. SNPs Complicate Drug Development
Among the P2X family, the P2RX7 gene is subject to the highest degree of genetic variation. Schäfer et al. found that when considering minor allele frequencies (MAFs) of at least 0.5%, the human P2RX7 gene contained sixteen coding SNPs, while the rest of the P2X family collectively contained only seven [81]. As a consequence, P2RX7 SNPs have received considerable attention.
In this review, we summarise the coding SNPs of the hP2X7R (Table 1 and Supplementary Table S1), aiming to highlight the complexity this creates for designing new drugs that therapeutically target the receptor. Although technically inaccurate, we refer to SNPs by their amino acid substitutions rather than nucleotide changes as this has more relevance to protein structure. Some SNPs are relatively frequent, and cause moderate changes in receptor function or expression, such as H155Y, R270H and A348T, which have MAFs > 25% [81,82]. The aforementioned SNPs tend to be well studied, however other rarer SNPs with more extreme effects on receptor function such as the SNP leading to R307Q—which causes a profound loss of channel and pore function [83]—have also been studied in great detail. Many SNPs show population-specific frequency differences, which complicates uniform therapeutic efficacy [81]. For instance, A348T has an overall MAF of approximately 31%, but ranges from 14% in the East Asian population to 46% in the African population [81]. Similarly, R270H MAF can range from 9% in the South Asian population to 40% in the East Asian population [81].
6.2. P2RX7 SNPs, Functional Effects and Disease Associations
P2RX7 SNPs have been repeatedly reported to be associated with several disease states; however, such associations are usually population specific, and sometimes not replicated. For example, the E186K mutation, a loss-of-function SNP located close to the ATP-binding site, has been associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, an inherited form of heart failure in young people [84]. The loss-of-function mutation R307Q in some cohorts has been associated with protection against development of multiple sclerosis [85]. V76A and I568N, both loss-of-function SNPs, have been associated with an increased risk of gout [86]. V76A has also been associated with another inflammatory condition, multiple sclerosis [87], although the same V76A appears to have a protective effect in sepsis and pneumonia [88]. This highlights the potential conflicting associations of SNPs.
H155Y and R270H are considered relatively weak gain-of-function SNPs [82,89] and have been associated with an increased risk of major depressive disorder (MDD) [90,91] and chronic pain [92]. Interestingly, R270H has also been associated with a decreased risk of chronic pain, which may have resulted from studying different pain types and phenotyping methods [93]. Functional studies suggest H155Y increases surface expression of the receptor rather than improvements in receptor function [94], although some studies vary [89]. In any case, synergism between H155Y, R270H, and A348T has been proposed [82]. A348T is located in the TM2 domain—the region critical for channel gating—which may explain its effect on P2X7R function [82,94]. A348T has been associated with an increased risk of gout [95] and a decreased risk of hepatocellular cancer [96]. The E496A substitution, which decreases function, has been associated with increased tuberculosis risk in two meta-analyses from 2010 and 2013 [97,98]. However, a more recent meta-analysis suggests that this association is limited to Asian populations [99].
6.3. P2RX7 SNPs in Mental Health Disorders
P2RX7 SNPs have been extensively studied in mental health conditions, in particular MDD and bipolar disorder, as reviewed by Andrejew et al. [11], which was initiated by two pioneering genetic studies [100,101]. However, these links have been challenged. A meta-analysis conducted in 2014 found no association between Q460R and mood disorders [102], while another meta-analysis conducted in 2018 confirmed an association with MDD [103]. A 2019 study found no individual SNP was significantly associated with MDD but identified a risk-associated haplotype consisting of A348T~Q460R~rs1653625-A [104]. The last mutation, rs1653625 is a 3′ untranslated region (3′UTR) SNP that increased P2X7R expression by altering microRNA binding [104]. The link between P2RX7 SNPs and bipolar disorder remains unconfirmed [101,103,105,106,107,108,109].
6.4. P2RX7 SNPs in Cancer
P2RX7 missense mutations have been studied across a range of cancers, including pancreatic, papillary thyroid, breast, hepatocellular, and blood cancers [96,110,111,112,113,114,115]. Of these, chronic lymphocyte leukaemia (CLL) has been extensively studied [116]. E496A has been shown to increase the risk of CLL but has also been shown to improve the overall survival of CLL patients [113,114]. This difference could be attributed to variations in the role of the receptor at different stages of the disease [114]. However, other studies have failed to show an association between E496A and CLL [117,118,119], and a meta-analysis published in 2021 found no significant association between E496A and overall cancer risk [120]. The relevance of mutations in the risk of developing pancreatic cancer is also an interesting case, as studied by Magni et al. [110]. The study found two relevant mutations: G150R, causing a loss of channel and pore function, and R276H, which showed regular channel function but reduced pore function. While the G150R variants had a decreased risk of developing pancreatic cancer, R276H variants had an increased risk of developing pancreatic cancer [110]. This difference may be due to downstream signalling pathways, which are not well understood.
Although individual SNPs can confer significant changes in P2X7R function or expression, whether those changes lead to clinical effects, including symptoms or disease outcomes, depends on the specific biological or environmental context. Missense mutations can be associated with either protective or risk-increasing effects despite having similar effects on receptor function. This section focused on non-synonymous SNPs; however, synonymous SNPs have the potential to ‘silently’ alter protein expression and adds another aspect of variation to consider [121,122]. Additionally, SNPs located within introns should also be considered as they may give rise to spliced isoforms, as discussed in the section Splice Variants of the P2X7R.

Table 1.
Non-synonymous SNPs in the hP2X7R that have been found to have disease associations, indicating their MAF, resultant amino acid change, and functional effects. Associations marked below are those reported in individual studies; several have negative or non-replicated results in other cohorts, as noted.
Table 1.
Non-synonymous SNPs in the hP2X7R that have been found to have disease associations, indicating their MAF, resultant amino acid change, and functional effects. Associations marked below are those reported in individual studies; several have negative or non-replicated results in other cohorts, as noted.
| rsID | MAF * | Amino Acid Change | Functional Effect [Reference] | Disease Association [Reference] | Lack of Significant Disease Association # [Reference] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs17525809 | 0.05 (0.02–0.07) | V76A | Partial loss of pore function [82] Partial loss of ion channel and pore function [123] | Decreased risk of pneumonia and sepsis [88] Increased risk of gout [86] and MS a [87] | Anxiety [124], IS b [125], MM c [126], pancreatic cancer [110] |
| rs28360447 | 0.01 (0.00–0.02) | G150R | Complete loss of pore function [82] Complete loss of ion channel and pore function [92,123] Complete loss of ion channel function and significantly reduced pore function [110] | Decreased risk of pancreatic cancer [110] Decreased BMD d [127] | MM c [126], schizophrenia [128] |
| rs208294 | 0.46 (0.35–0.71) | H155Y | Gain of pore function [82] Gain of ion channel function and increased rate of dye uptake [123] Gain of ion channel function but no significant effect on pore function [92] | Potential protective effect against Alzheimer’s disease [129] Increased risk of alcoholism [90], anxiety [90], chronic pain as PMP e [93], HHV-6A infection f [130], MDD g [90], SLE h with a history of pericarditis [131] | BMD d [132], chronic pain in OA i [93], IS b [125], MM c [126], PTC j [112], RA k [133], schizophrenia [128], SLE h [133], TB l [99] |
| rs28360451 | <0.01 (<0.01) | E186K | Complete loss of ion channel and pore function [123] | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy [84] | - |
| rs7958311 | 0.29 (0.05–0.45) | R270H | Loss of pore function [82] No significant change in pore function [123] Gain of ion channel function but loss of pore function [92] | Decreased risk of chronic pain [93] Increased risk of chronic pelvic pain [92], fibromyalgia [92], IBS m [92], MDD g with previous stress exposure [91] | Pancreatic cancer [110], TB l [99] |
| rs7958316 | 0.01 (0.00–0.02) | R276H | Complete loss of pore function [82] Normal channel function but reduced pore function [110] Loss of ion channel and pore function [92] | Increased risk of gout [86], pancreatic cancer [110] | Anxiety [124] |
| rs28360457 | <0.01 (0.00–0.01) | R307Q | Complete loss of ion channel and pore function [83,92] | Decreased risk of MS a [85] Higher rate of bone loss in post-menopausal women [132,134] Increased risk of hepatocellular cancer [96] | BMD d [127], MM c [126], pancreatic cancer [110], RA k [133], schizophrenia [128], SLE h [133], disease severity in MS a [135] |
| rs1718119 | 0.31 (0.10–0.46) | A348T | Gain of ion channel and pore function [123] No significant effect on ion channel and pore function [92] | Decreased risk of hepatocellular cancer [96] Increased risk of gout [95], toxoplasmosis [136] Synergistic effect with Q460R, causing increased disease severity in relapse-remitting MS a [135] | Anxiety [124], BD n [107], chronic pain as PMP e and OA i [93], IS b [125], MDD g [104], MM g [126], pancreatic cancer [110], Schizophrenia [128], TB l [99] |
| rs2230911 | 0.14 (0.08–0.31) | T357S | Partial loss of ion channel and pore function [92,123] | Increased risk of pneumonia [88] | Hepatocellular cancer [96], MDD g [104], MM c [126], pancreatic cancer [110], RA k [133], Schizophrenia [128], SLE h [133], TB l [99], toxoplasmosis [136], disease severity in MS a [135] |
| rs2230912 | 0.07 (0.00–0.18) | Q460R | Partial loss of pore function [82] No effect [123] Gain of ion channel function but no effect on pore function [92] | Increased risk of anxiety [90], BD n development [101,105], MDD g [90,103] Synergistic effect with A348T, causing increased disease severity in relapse-remitting MS a [135] | BD n [106,107,108,109], chronic pain in PMP e and OA i [93], MDD g [102,106,107,108], MM c [126], ocular toxoplasmosis [136,137], pancreatic cancer [110], schizophrenia [128] |
| rs3751143 | 0.19 (0.10–0.29) | E496A | Partial loss of ion channel and pore function [92,123] | Decreased BMD d [127] Decreased risk of IS b [125] Increased risk of BD n [138], breast cancer [111], CLL o [113], follicular subtype of PTC j [112], hepatocellular cancer [96], ocular toxoplasmosis [137], Parkinson’s disease [139], TB l [97,98,140] Synergistic protective effect with H155Y against Alzheimer’s disease [129] Increased survival in CLL o [114] | Anxiety [124], BMD d [132], cancer [120], chronic pain in PMP e and OA i [93], CLL o [117,118], MDD g [104], MM c [126], pancreatic cancer [110], PTC j [112], RA k [133], Schizophrenia [128], SLE h [133], toxoplasmosis [136], disease severity in MS a [135] |
| rs1653624 | 0.01 (0.00–0.02) | I568N | Complete loss of ion channel and pore function [123] Partial loss of ion channel and pore function [92] | Higher rate of bone loss in post-menopausal women [134] Increased risk of gout [86] | BMD d [127,132], MM c [126], pancreatic cancer [110], schizophrenia [128] |
* MAF: average minor allele frequency (Only >0.5% reported) in sample of 1000 Genomes Project, rounded to 2 decimal places [81]. Ranges are acquired from the Allele Frequency Aggregator (ALFA) [141] from dbSNP (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/snp/docs/gsr/alfa/ (accessed on 16 April 2025)) [142,143,144]. # The list is not comprehensive; rather, it is intended to show that the lack of an association is still an important result to consider. a MS: multiple sclerosis, b IS: ischaemic stroke, c MM: multiple myeloma, d BMD: bone mineral density, e PMP: post-mastectomy, f HHV-6A: human herpesvirus 6A, g MDD: major depressive disorder, pain, h SLE: systemic lupus erythematosus, i OA: osteoarthritis, j PTC: papillary thyroid cancer, k RA: rheumatoid arthritis, l TB: tuberculosis, m IBS: irritable bowel syndrome, n BD: bipolar disorder, o CLL: chronic lymphocyte leukaemia.
7. Haplotypes and Functional Predictions
Rather than acting alone, SNPs often occur in haplotype blocks that co-influence P2X7R function by combining opposing or synergistic effects (e.g., gain and loss of function). Considering the frequency of P2RX7 SNPs, a shift in focus from attributing disease to a single SNP toward a haplotype or haplotype pair may give clearer associations between P2X7R function and disease [82,134,145]. Jørgensen et al. have created a comprehensive resource of haplotypes detected in their study, and we have summarised these haplotypes together with the corresponding amino acid substitutions and frequencies (Table 2) [134]. The haplotype frequencies suggest that the most frequent haplotypes differ from the RefSeq wild-type haplotype (H) 2, which is in fact relatively rare, with a frequency of 5.3% (Table 2) [134]. Instead, there are multiple commonly expressed haplotypes, many of which contain two or more coding SNPs distinct from the wild type. In fact, this high degree of diversity has been observed previously in a different cohort; however, the haplotypes were grouped more broadly [82]. Although haplotypes have been identified, the resulting functions of some haplotypes have not been investigated or experimentally validated, and this remains as a gap in current research. The population-specific frequency differences in SNPs complicate the study of haplotypes. While the study by Jørgensen et al. is comprehensive, the dataset is constructed from a Danish cohort [134]. Haplotype frequencies may vary in different populations such as the South Asian or African population. Furthermore, certain populations may express haplotypes that are otherwise not present in other populations. For instance, the SNP P430R has an MAF of less than 1% in the European population, but greater than 10% in the African population [141]. More work is needed to identify the variability of haplotype frequencies between populations.

Table 2.
P2X7 variants derived from common haplotype blocks as determined by Jørgensen et al. [134]. The table is organised with respect to the 4-SNP haplotype block predicted by Stokes et al., involving residues A348, T357, Q460, and E496 [82]. The wild-type H2 has been shaded grey and refers to the base sequence described in RefSeq Accession number NM_002562.6 [146,147]. Bolded residues highlight differences from the wild-type H2.
Haplotypes May Better Explain Disease Associations
The consideration of haplotypes is important, as it avoids the confounding effects that would otherwise be present when analysing individual SNPs. This is especially so for the hP2X7R, which has a degree of polymorphism such that most individuals are expected to co-express two different copies of the hP2X7R [81]. For instance, a patient expressing P2X7-H9 would present with the loss-of-function V76A and gain-of-function A348T substitutions. The overall function of the receptor is predicted to increase [134], but the patient would still be considered a part of V76A mutants during genetic analyses. A more comprehensive example in a similar situation can be seen in P2X7-H14 and P2X7-H15. While Q460R confers a relatively small change in function, the variant is also likely to contain an A348T mutation, which causes an increase in channel and pore function. The overall result is the expression of a receptor with increased channel and pore function, leading to elevated secretion of the proinflammatory cytokine IL-1β [82]. Without considering haplotypes, Q460R may be attributed to disease states when it is more accurately described as part of the P2X7-H14 and P2X7-H15 haplotypes.
Can haplotype analysis translate to a disease association? This was hinted at previously, where a haplotype consisting of A348T~Q460R~rs1653625-A, corresponding to P2X7-H14/H15, was associated with increased MDD severity [104]. A more recent study conducted by Guerini et al. in 2022 supports this sentiment, showing that a haplotype corresponding to P2X7-H14/H15 resulted in increased disease severity in relapse-remitting multiple sclerosis, while the complementary haplotype (A348 and Q460) was shown to be protective against disease severity [135]. Haplotype-based analysis may provide clearer associations with disease phenotypes and should be prioritised in future research and clinical design. Similar with disease associations in SNPs, haplotype associations will require replication, especially in different populations, where large variations in SNPs will also likely lead to variations in expressed haplotypes.
8. Splice Variants and Alternatively Spliced Heterotrimers
8.1. Splice Variants
Alternative splicing is another important consideration for the P2X7R, as it can lead to deletion or inclusion of whole exons, resulting in the expression of subunits that are distinct from the wild type. Multiple splice variants of P2X7R exist and these variants can form homotrimers or heterotrimers with wild-type subunits, sometimes enhancing or reducing functionality. Their roles in disease progression and therapeutic resistance, such as in leukaemia, are underexplored.
The alternatively spliced isoforms have been reviewed [38], and their structures predicted by AlphaFold [148]. The nomenclature used to refer to splice variants in this review follows that of Cheewatrakoolpong et al. who employed alphabetical ordering to distinguish variants (Table 3) [149]. The study compared splice variants P2X7B and P2X7H against the wild type, P2X7A, in terms of expression, ion channel function, and pore formation [149]. P2X7B lacks the long C-terminus of the receptor (Δ-C) that has been replaced by a shortened sequence, while P2X7H lacks the TM1 domain (ΔTM-1) [149]. P2X7B was found to retain ion channel function; however, it reduced agonist sensitivity and resulted in a significant impairment in pore formation [149]. In contrast, P2X7H showed no activity in response to the agonist BzATP, suggesting that P2X7H is a non-functional receptor. Interestingly, P2X7B has been reported as highly expressed in some tissues and may represent a predominant isoform in some physiological contexts [149].
If cells expressing the P2X7R do not exhibit pore formation, it is advisable to assess which isoforms are being expressed before drawing conclusions. Other variants (C, D, E, F, and G) could not to be analysed at the time due to difficulties developing appropriate reagents to perform gene expression studies [149]. P2X7E was later characterised as a non-functional receptor [150]. Additionally, other variants have been identified, but most of these remain uncharacterised, presenting a gap in current research.

Table 3.
Splice variants of the hP2X7R, their functional differences, and Genbank accession number unless otherwise stated [151,152]. The variant P2X7I results in a null allele [153]. P2X7K has been identified in the rat and mouse but not in the human [154].
Table 3.
Splice variants of the hP2X7R, their functional differences, and Genbank accession number unless otherwise stated [151,152]. The variant P2X7I results in a null allele [153]. P2X7K has been identified in the rat and mouse but not in the human [154].
| Variant Name | Suggested Effects [Reference] a | NCBI Accession Number |
|---|---|---|
| P2X7A | Normal function [149,155] | Y09561.1 (RefSeq: NM_002562.6) |
| P2X7B | Reduced agonist sensitivity, but similar channel function to P2X7A homotrimers [149,156] Significant reduction in pore formation [149,156] Little change to antagonist sensitivity [149,156] Heterotrimer formation with P2X7A [156] | AY847298.1 |
| P2X7C | N/I [149] | AY847299.1 |
| P2X7D | N/I [149] | AY847300.1 |
| P2X7E | Deletion of ATP-binding site No surface expression, leading to a non-functional receptor [149,150] | AY847301.1 |
| P2X7F | N/I [149] | AY847302.1 |
| P2X7G | N/I [149] | AY847303.1 |
| P2X7H | Non-functional receptor [149] | AY847304.1 |
| P2X7J | Deficient pore formation Reduced channel function Heterotrimer formation with P2X7A [155] | DQ399293.1 |
| P2X7L | Loss of channel and pore function due to deletion of ATP-binding site Heterotrimer formation with P2X7A [150] | MK465687.1 |
| P2X7M b (ΔE2) | N/I [89] | - |
| P2X7N | N/I [150] | MK465688.1 |
| P2X7O | N/I [150] | MK465689.1 |
| P2X7P | N/I [150] | MK465690.1 |
| P2X7Q | N/I [150] | MK465691.1 |
| Variant 4 (V4) | N/I [157] | - (RefSeq [146]: NR_033950.2) |
| Variant 7 (V7) | N/I [157] | - (RefSeq [146]: NR_033953.2) |
a N/I = not investigated, b as suggested by De Salis et al. [38].
8.2. P2X7B and Alternative Splicing Heterotrimerisation
An added complication is that of heterotrimerisation. Heteromers, or heterotrimers for the P2X7R may refer to the formation of P2X7Rs composed of different isoforms or as receptors formed between different P2X subunits. We will use the term alternatively spliced (AS) heterotrimers to distinguish the two forms. For example, mixtures of P2X7A and P2X7B isoforms can associate in four different ways—homotrimeric forms P2X7A and P2X7B, and AS heterotrimeric forms P2X7A/(P2X7B)2 and (P2X7A)2/P2X7B. A study analysed P2X7B in detail and found similar changes in terms of expression, ion channel function, agonist response, and pore formation [156]. However, the study also considers AS heterotrimeric constructs of P2X7A and P2X7B, finding that heterotrimers can form between the variants, called P2X7A/(P2X7B)2 and (P2X7A)2/P2X7B heterotrimers. Unexpectedly, preliminary data suggested these heterotrimers may exhibit increased pore formation compared to homotrimers of P2X7A and P2X7B, though this remains as preliminary evidence requiring replication [156]. The study hypothesised that P2X7B was better for growth promotion compared to P2X7A, since channel function was retained, but pore formation, which has been linked to cell cytotoxicity, had been abolished [156]. Therefore, it was suggested that the cell’s response to extracellular ATP depended on the expression of P2X7A and P2X7B, noting that this dichotomy is unique to the P2X7R [156].
Another study found that the expression of P2X7B is linked to chemotherapy resistance and relapse in acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) patients overexpressing P2X7B [158]. The chemotherapeutic agent daunorubicin (DNR) causes cell death and the release of ATP into the extracellular microenvironment. AML cells expressing high levels of either P2X7A or P2X7B were treated with DNR and it was found that DNR toxicity was increased in cells with high P2X7A expression, while cells expressing high levels of P2X7B were protected from DNR-dependent death [158]. Furthermore, when DNR was combined with the P2X7R NAM AZ10606120 in an in vivo mouse model, it was found that coadministration was more efficacious than single treatment using either agent in reducing leukaemia growth [158]. Treatment with DNR kills cells with a higher expression of P2X7A, while application of a P2X7R inhibitor blocks cell proliferation induced by the DNR-resistant P2X7B [158]. This indicates the therapeutic potential of modulating the P2X7R as well as the contribution of splice variant expression in disease states.
8.3. Splice Variants Are Not Well Characterised
The formation of heterotrimers between P2X7 splice variants has not been widely studied. A major barrier to investigating AS heterotrimers is the difficulty in detecting and distinguishing different splice variants. Without the ability to detect the different AS heterotrimers, it is difficult to understand their expression and physiological effects compared to the receptor made up of three wild-type subunits. Additionally, the relevance of isoforms and AS heterotrimers in disease states remain largely unexplored. The existence of at least 17 human splice variants, some of which have not been studied in detail, suggests that there are many possible heterotrimeric P2X7R combinations with unknown physiological roles. In the context of drug development, attempting to design a modulator to inhibit pore formation may be futile if pore formation is absent. Conversely, heterotrimers with increased agonist sensitivity or pore formation may have therapeutic potential, depending on their pattern of expression.
A significant obstacle to this research is the lack of in vitro techniques to control receptor stoichiometry when expressing splice forms in model systems. Other fields, such as GABAA and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor research, have benefitted from techniques that concatenate subunits, enabling control over receptor assembly [159,160]. Concatenation studies have not yet been conducted between P2X7 splice variants. Alternatively, deep learning models such as AlphaFold have enabled the modelling of heterotrimeric assemblies of P2X7R [148]. When molecular dynamic simulations were used to assess these generated models, the heterotrimers were found to be structurally stable [148]. However, further experimental and computational studies are needed to support these predictions and the structural and functional outcomes of splice variants and heterotrimers.
9. Clinical Failures and Therapeutic Barriers
9.1. Clinical Trials and the Polymorphous P2X7R
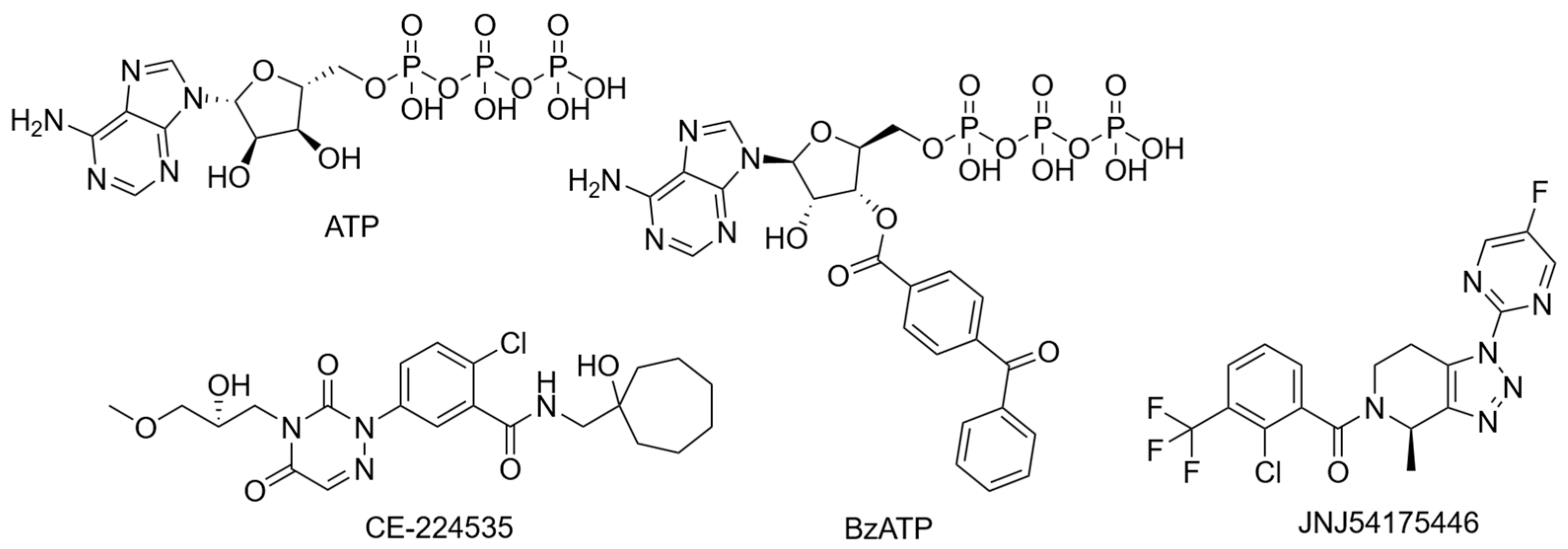
The preceding sections highlight the individual variability of the P2X7R and its subunits, but in combination, this variability underscores the complexity of studying the receptor. Despite strong preclinical rationale, several P2X7R antagonists have been tested, and all have failed to prove efficacy in clinical trials. Two benzamide antagonists, AZD9056 (Figure 4) and CE-224,535 (Figure 5), have been evaluated in phase IIa and IIb randomised clinical trials for their efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis resistant to conventional treatments [161,162]. Both compounds failed to demonstrate significant efficacy compared to placebo [161,162]. More specifically, AZD9056 was shown to be effective in a phase IIa trial, with significant improvements in markers of rheumatoid arthritis severity: however, this did not translate in a phase IIb trial [161]. Clinical failure was attributed to the complex pathogenesis of the condition, suggesting P2X7R antagonism alone may be insufficient to manage inflammation [161,162]. AZD9056 was also evaluated as ineffective in a phase IIa randomised clinical trial in patients with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease [163]. While more patients treated with AZD9056 responded to treatment positively compared to placebo, the difference was not statistically significant [163]. Another placebo-controlled, randomised clinical trial was conducted to assess the safety and tolerability of the triazolopyridine P2X7R antagonist JNJ-54175446 (Figure 5) in patients with MDD and under acute sleep deprivation, serving as a proxy for aggravated neuroinflammation [164]. Although JNJ-54175446 was found to show targeted engagement and was safe and tolerable, clinical efficacy on mood remains inconclusive [164]. Despite proving pharmacological activity in ex vivo models [164,165], levels of IL-1β in peripheral blood after JNJ-57417446 remain unchanged compared to placebo, suggesting other potential pathways leading to IL-1β release [164].
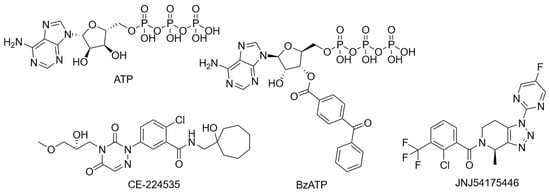
Figure 5.
Structures of frequently used agonists (ATP and BzATP) as well as antagonists used in clinical trials.
Variability in SNPs, splice variant expression, and membrane composition likely underlies inconsistent responses. While no mutations can be clearly linked to the disease states studied in P2X7 clinical trials, none of these trials conducted subgroup analyses based on the genetic background of the study populations. Furthermore, testing was not performed to confirm the receptor’s expression or functionality, including calcium flux or dye uptake. Drugs targeting the channel or pore may be ineffective in receptors already compromised by mutation. Therefore, genotyping and isoform profiling should be standard in clinical studies of P2X7Rs. Secondary markers of activity such as IL-1β levels may also be informative but may not be representative of P2X7R function. Stratifying the population by receptor function and genotypes will allow for more direct links between a compound and its efficacy. A demonstration of this can be seen in a phase I clinical trial that tests topical non-functional P2X7 (nfP2X7)-targeted antibodies for the treatment of basal cell carcinoma [166]. While it is too early to determine efficacy, target specificity appears to play an important role, especially so for the variable P2X7R.
The frequencies of SNPs can vary significantly between ethnicities, complicating the development of universally effective therapeutics [81]. For example, NAMs that inhibit channel function and pore formation may have reduced efficacy in receptors with SNPs that already impair these functions. While individual SNPs can significantly alter P2X7R function, their correlation with disease risk, such as MDD or bipolar disorder, can remain unclear. Focusing on haplotypes or haplotype pairs may give clearer associations between P2X7R function and disease, though this area is still relatively understudied. This same recommendation applies to clinical studies, where participant genotyping should be performed prior to enrolling in trials. In addition, splice variant heterotrimers will also alter outcomes, and there remains a pressing need to further explore how alternative splicing is regulated in different disease states and environments.
9.2. The P2X7R Has Potential as a Diagnostic or Prognostic Marker
A lot of attention has been focused on the P2X7R as a drug target; however, the receptor’s expression can also be used as a biomarker. In COVID-19, increased levels of detectable P2X7Rs served as markers of disease severity [15] and unfavourable clinical outcomes [167]. An in vitro model of tuberculosis showed that P2X7R expression levels distinctly worsened the outcome of severe forms of tuberculosis [168]. In cancers, nfP2X7 have been shown to be useful as an early diagnostic marker [169] and as a prognostic marker [22,170,171]. Several brain-penetrant radio-labelled ligands have been developed and used in human studies, highlighting the receptor’s potential as a biomarker [172,173,174,175]. For instance, these radio-labelled ligands have been used to highlight the P2X7R as a biomarker for epilepsy [176]. While P2X7R expression is promising as a biomarker, the impact of receptor mutations remains comparatively unexplored, likely due to challenges in isoform identification and the lack of haplotype studies.
10. Forward-Looking: Potential of In Silico Studies in the P2X7R
New Structural Insights Now Enable Computational Investigations
Structural determination of the rP2X7R has resolved the TM and intracellular domains of the receptor that were previously uncharacterised [39]. Further cryo-EM studies have produced full-length cryo-EM structures at higher resolutions, enabling identification of structural water molecules, particularly within the TM domain, and suggesting a bound sodium ion in the channel [40,41]. Several agonists and antagonists have also been co-resolved with the rP2X7R (Table 4) [39,40,41]. These structures will provide a good foundation for in silico studies, although some regions remain unresolved that will require additional modelling. For most structures, the missing regions include the N-terminus (M1–C5), a loop in the upper body (N74–T81), and a large intracellular loop (S443–R471). Additionally, structures of splice variants of the receptor have been predicted through deep learning methods, presenting opportunities for further study [148].

Table 4.
Available structures of the P2X7R from PDB (http://www.rcsb.org/ (accessed on 25 March 2025)) [177] and their sequence identity to the hP2X7R determined by BLAST (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi (accessed on 16 April 2025)) [178]. Resolution has been rounded to 1 decimal place.
In silico techniques such as ligand docking and molecular dynamics simulations will greatly benefit from the newly resolved P2X7R structures. These advances will enable the modelling of features of the receptor that have not been able to be explored, including splice variants, functional dependence on membrane composition, and the effects of SNPs on binding and receptor conformation. For example, SNPs resulting in E186K and L191P, both located near the ATP-binding site, may affect ATP binding and loss of P2X7R function [84,123]. Similarly, the R276H mutation, located close to the PAM binding site, abolishes P2X7R-dependent dye uptake [82]. Furthermore, splice variants can be computationally assembled as AS homo- or heterotrimers, allowing the modelling of stoichiometries that are difficult to resolve experimentally. Complex conditions involving combinations of SNPs and AS heterotrimers can now be simulated, making it possible to study the resultant conformational changes. Given the extensive in vitro and in vivo data now available, along with multiple resolved P2X7R structures, in silico approaches are highly encouraged to support and refine future studies. Although a few studies have explored P2X7R using molecular docking [63,70,181] and molecular dynamics simulations [31,181], these have mainly focused on analysing ligand binding. Similar computational approaches in other receptors have defined membrane cholesterol interactions [182,183], effects of mutations on protein structure [184], and mechanistic insights of ligand binding [185], showing the value of such techniques in P2X7R research.
Historically, many studies have been conducted on the non-human receptor. With current modelling techniques, a homology model of the hP2X7R can be generated using the cryo-EM structure as a template. Notably, rat and hP2X7Rs share approximately 80% identity and conserve key residues, supporting the validity of homology modelling, although subtle species-specific pharmacological differences remain.
11. Conclusions
The polymorphic nature of the P2X7R and splice isoform variants has likely contributed to the clinical failure of antagonists. A detailed understanding of receptor biology, including genetic, structural, and membrane influences, is essential for therapeutic progress. In silico tools and genotyped clinical trials represent the next steps toward realising the therapeutic potential of the P2X7R.
This review has outlined the mutations of the P2X7R and their functional implications. Without a comprehensive understanding of the receptor’s genetic variability, developing agents to alter the function of this receptor will remain challenging. Considering the large number of SNPs that alter the function of the P2X7R, the presence of the less-sensitive splice variant P2X7B, and various haplotype combinations, it is important to account for these genetic factors when designing compounds and planning clinical trials. Drug development efforts should consider binding modes in the context of SNPs that affect ligand binding. Future clinical trials would benefit from genotyping participants and/or measuring isoform expression to enable stratified analyses based on the predicted P2X7R function. Moreover, understanding how antagonists interact with AS heterotrimers is critical, but the identification of splice variants and heterotrimers remains a large gap in the field. In silico techniques have the potential to resolve heterotrimeric structures, but they remain underutilised. Although the P2X7R is a highly attractive target, many characteristics remain poorly understood, which likely contributes to the lack of clinical success, to date.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms262110265/s1.
Author Contributions
J.S.Y.C. and T.B. conceptualised the study. J.S.Y.C. conducted the literature search, data extraction, and prepared the figures and tables. J.S.Y.C. and T.B. drafted the manuscript. K.K.S., T.B. and S.J.F. jointly supervised the work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
J.S.Y.C. was funded by the Australian Government Research Training Programme Scholarship.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Denning, N.-L.; Aziz, M.; Gurien, S.D.; Wang, P. DAMPs and NETs in Sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G.; Knight, G.E. The potential of P2X7 receptors as a therapeutic target, including inflammation and tumour progression. Purinergic Signal. 2018, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solle, M.; Labasi, J.; Perregaux, D.G.; Stam, E.; Petrushova, N.; Koller, B.H.; Griffiths, R.J.; Gabel, C.A. Altered Cytokine Production in Mice Lacking P2X7 Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluyter, R.; Shemon, A.N.; Wiley, J.S. Glu496 to Ala Polymorphism in the P2X7 Receptor Impairs ATP-Induced IL-1β Release from Human Monocytes. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 3399–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, V.B.; Hart, J.; Wewers, M.D. ATP-stimulated release of interleukin (IL)-1beta and IL-18 requires priming by lipopolysaccharide and is independent of caspase-1 cleavage. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 3820–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluyter, R.; Dalitz, J.G.; Wiley, J.S. P2X7 receptor polymorphism impairs extracellular adenosine 5′-triphosphate-induced interleukin-18 release from human monocytes. Genes Immun. 2004, 5, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, R.; Krautloher, A.; Ramírez-Fernández, A.; Nicke, A. P2X7 Interactions and Signaling—Making Head or Tail of It. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelegrin, P. P2X7 receptor and the NLRP3 inflammasome: Partners in crime. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 187, 114385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, H.; Gao, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Z. P2X7 receptor mediates NLRP3 inflammasome activation in depression and diabetes. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, J.; Koch-Nolte, F.; Dahl, G. Purine Release, Metabolism, and Signaling in the Inflammatory Response. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 37, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrejew, R.; Oliveira-Giacomelli, Á.; Ribeiro, D.E.; Glaser, T.; Arnaud-Sampaio, V.F.; Lameu, C.; Ulrich, H. The P2X7 Receptor: Central Hub of Brain Diseases. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Wang, C.; Jia, F.; Wu, H.; Hao, H.; Jing, S. P2X7 receptor as a key player in pathological pain: Insights into Neuropathic, inflammatory, and cancer pain. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1585545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Song, X.; Mou, Y.; Yang, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Ren, C.; Song, X. New insights into pathogenisis and therapies of P2X7R in Parkinson’s disease. npj Park. Dis. 2025, 11, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, D.E.; Oliveira-Giacomelli, Á.; Glaser, T.; Arnaud-Sampaio, V.F.; Andrejew, R.; Dieckmann, L.; Baranova, J.; Lameu, C.; Ratajczak, M.Z.; Ulrich, H. Hyperactivation of P2X7 receptors as a culprit of COVID-19 neuropathology. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 1044–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Villalba, J.; Hurtado-Navarro, L.; Penin-Franch, A.; Molina-Lopez, C.; Martinez-Alarcon, L.; Angosto-Bazarra, D.; Baroja-Mazo, A.; Pelegrin, P. Soluble P2X7 Receptor Is Elevated in the Plasma of COVID-19 Patients and Correlates with Disease Severity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 894470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korb, V.G.; Schultz, I.C.; Beckenkamp, L.R.; Wink, M.R. A Systematic Review of the Role of Purinergic Signalling Pathway in the Treatment of COVID-19. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, R.A. Molecular Physiology of P2X Receptors. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 1013–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peverini, L.; Beudez, J.; Dunning, K.; Chataigneau, T.; Grutter, T. New Insights Into Permeation of Large Cations Through ATP-Gated P2X Receptors. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalafalla, M.G.; Woods, L.T.; Camden, J.M.; Khan, A.A.; Limesand, K.H.; Petris, M.J.; Erb, L.; Weisman, G.A. P2X7 receptor antagonism prevents IL-1β release from salivary epithelial cells and reduces inflammation in a mouse model of autoimmune exocrinopathy. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 16626–16637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamin, L.S.; Braganhol, E.; Figueiró, F.; Casali, E.A.; Zanin, R.F.; Sévigny, J.; Battastini, A.M. Involvement of purinergic system in the release of cytokines by macrophages exposed to glioma-conditioned medium. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, L.K.; Drill, M.; Jayakrishnan, P.C.; Sequeira, R.P.; Galea, E.; Todaro, M.; Sanfilippo, P.G.; Hunn, M.; Williams, D.A.; O’Brien, T.J.; et al. P2X7 receptor antagonism by AZ10606120 significantly reduced in vitro tumour growth in human glioblastoma. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoroso, F.; Capece, M.; Rotondo, A.; Cangelosi, D.; Ferracin, M.; Franceschini, A.; Raffaghello, L.; Pistoia, V.; Varesio, L.; Adinolfi, E. The P2X7 receptor is a key modulator of the PI3K/GSK3β/VEGF signaling network: Evidence in experimental neuroblastoma. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5240–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannuzzo, A.; Saccomano, M.; Napp, J.; Ellegaard, M.; Alves, F.; Novak, I. Targeting of the P2X7 receptor in pancreatic cancer and stellate cells. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 2540–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Buckley, K.A.; Bowers, K.; Furber, M.; Gallagher, J.A.; Gartland, A. The effects of P2X7 receptor antagonists on the formation and function of human osteoclasts in vitro. Purinergic Signal. 2010, 6, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, M.R.; Menezes, A.P.; Nunes, A.C.; Pliássova, A.; Rolo, A.P.; Palmeira, C.M.; Cunha, R.A.; Canas, P.M.; Andrade, G.M. The P2X7 receptor antagonist Brilliant Blue G attenuates contralateral rotations in a rat model of Parkinsonism through a combined control of synaptotoxicity, neurotoxicity and gliosis. Neuropharmacology 2014, 81, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, T.; Gomez-Villafuertes, R.; Tanaka, K.; Mesuret, G.; Sanz-Rodriguez, A.; Garcia-Huerta, P.; Miras-Portugal, M.T.; Henshall, D.C.; Diaz-Hernandez, M. Seizure suppression and neuroprotection by targeting the purinergic P2X7 receptor during status epilepticus in mice. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 1616–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, M.; Ota, K.T.; Li, X.-Y.; Sakaue, F.; Li, N.; Dutheil, S.; Banasr, M.; Duric, V.; Yamanashi, T.; Kaneko, K.; et al. Psychological Stress Activates the Inflammasome via Release of Adenosine Triphosphate and Stimulation of the Purinergic Type 2X7 Receptor. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 80, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honore, P.; Donnelly-Roberts, D.; Namovic, M.T.; Hsieh, G.; Zhu, C.Z.; Mikusa, J.P.; Hernandez, G.; Zhong, C.; Gauvin, D.M.; Chandran, P.; et al. A-740003 [N-(1-{[(cyanoimino)(5-quinolinylamino) methyl]amino}-2,2-dimethylpropyl)-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acetamide], a Novel and Selective P2X7 Receptor Antagonist, Dose-Dependently Reduces Neuropathic Pain in the Rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 319, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andó, R.D.; Méhész, B.; Gyires, K.; Illes, P.; Sperlágh, B. A comparative analysis of the activity of ligands acting at P2X and P2Y receptor subtypes in models of neuropathic, acute and inflammatory pain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 159, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savio, L.E.B.; de Andrade Mello, P.; da Silva, C.G.; Coutinho-Silva, R. The P2X7 Receptor in Inflammatory Diseases: Angel or Demon? Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, A.C.; Turcu, A.L.; Tzortzini, E.; Georgiou, K.; Nagel, J.; Westermann, F.G.; Barniol-Xicota, M.; Seidler, J.; Kim, G.-R.; Lee, S.-D.; et al. A polycyclic scaffold identified by structure-based drug design effectively inhibits the human P2X7 receptor. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 8283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinotsuka, N.; Shimizu, H.; Komatsu, T.; Ito, A.; Yoshikawa, S.; Takashima, T.; Sugiura, A.; Moriguchi, Y.; Ohno, Y.; Yamasawa, M.; et al. AK1780, a selective P2X7 receptor antagonist with high central nervous system penetration, exhibits analgesic effect in rat neuropathic pain model. J. Pain. 2025, 31, 105380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcangeli, A.; Becchetti, A. New Trends in Cancer Therapy: Targeting Ion Channels and Transporters. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 1202–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasawa, A.; Kawate, T. Structural basis for subtype-specific inhibition of the P2X7 receptor. eLife 2016, 5, e22153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.H. Inhibition of P2X(7) receptors by divalent cations: Old action and new insight. Eur. Biophys. J. 2009, 38, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicke, A. The P2X7 Receptor: Methods and Protocols, 1st ed.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2022; Volume 2510, p. 394. [Google Scholar]
- Fuller, S.J.; Stokes, L.; Skarratt, K.K.; Gu, B.J.; Wiley, J.S. Genetics of the P2X7 receptor and human disease. Purinergic Signal. 2009, 5, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Salis, S.K.F.; Li, L.; Chen, Z.; Lam, K.W.; Skarratt, K.K.; Balle, T.; Fuller, S.J. Alternatively Spliced Isoforms of the P2X7 Receptor: Structure, Function and Disease Associations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, A.E.; Yoshioka, C.; Mansoor, S.E. Full-Length P2X7 Structures Reveal How Palmitoylation Prevents Channel Desensitization. Cell 2019, 179, 659–670.e613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, A.C.; Lisi, N.E.; Krishnamurthy, I.; McCarthy, A.E.; Godsey, M.H.; Glasfeld, A.; Mansoor, S.E. High-affinity agonism at the P2X7 receptor is mediated by three residues outside the orthosteric pocket. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, A.C.; Ditter, I.A.; Lisi, N.E.; Krishnamurthy, I.; Godsey, M.H.; Mansoor, S.E. P2X7 receptors exhibit at least three modes of allosteric antagonism. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eado5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habermacher, C.; Dunning, K.; Chataigneau, T.; Grutter, T. Molecular structure and function of P2X receptors. Neuropharmacology 2016, 104, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawate, T.; Michel, J.C.; Birdsong, W.T.; Gouaux, E. Crystal structure of the ATP-gated P2X4 ion channel in the closed state. Nature 2009, 460, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger, L. Maestro, Schrödinger Release 2024-2; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2024.
- Schrödinger, L. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.3; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2019.
- Di Virgilio, F.; Schmalzing, G.; Markwardt, F. The Elusive P2X7 Macropore. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cevoli, F.; Arnould, B.; Peralta, F.A.; Grutter, T. Untangling Macropore Formation and Current Facilitation in P2X7. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surprenant, A.; Rassendren, F.; Kawashima, E.; North, R.A.; Buell, G. The Cytolytic P2z Receptor for Extracellular ATP Identified as a P2X receptor (P2X7). Science 1996, 272, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jursik, C.; Sluyter, R.; Georgiou, J.G.; Fuller, S.J.; Wiley, J.S.; Gu, B.J. A quantitative method for routine measurement of cell surface P2X7 receptor function in leucocyte subsets by two-colour time-resolved flow cytometry. J. Immunol. Methods 2007, 325, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.J.; Avula, P.; Wiley, J.S. Assays to Measure Purinoceptor Pore Dilation. In Purinergic Signaling: Methods and Protocols, 1st ed.; Pelegrín, P., Ed.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 323–334. [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg, T.H.; Newman, A.S.; Swanson, J.A.; Silverstein, S.C. ATP4- permeabilizes the plasma membrane of mouse macrophages to fluorescent dyes. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 8884–8888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammas, D.A.; Stober, C.; Harvey, C.J.; Kendrick, N.; Panchalingam, S.; Kumararatne, D.S. ATP-Induced Killing of Mycobacteria by Human Macrophages Is Mediated by Purinergic P2Z(P2X7) Receptors. Immunity 1997, 7, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Toombes, G.E.S.; Silberberg, S.D.; Swartz, K.J. Physical basis of apparent pore dilation of ATP-activated P2X receptor channels. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1577–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harkat, M.; Peverini, L.; Cerdan, A.H.; Dunning, K.; Beudez, J.; Martz, A.; Calimet, N.; Specht, A.; Cecchini, M.; Chataigneau, T.; et al. On the permeation of large organic cations through the pore of ATP-gated P2X receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3786–E3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasawa, A.; Michalski, K.; Mikhelzon, P.; Kawate, T. The P2X7 receptor forms a dye-permeable pore independent of its intracellular domain but dependent on membrane lipid composition. eLife 2017, 6, e31186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.A.; de Melo Reis, R.A.; de Souza, C.A.M.; de Freitas, M.S.; Teixeira, P.C.N.; Neto Moreira Ferreira, D.; Xavier, R.F. The P2X7 receptor: Shifting from a low- to a high-conductance channel—An enigmatic phenomenon? Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2014, 1838, 2578–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugur, M.; Ugur, Ö. A Mechanism-Based Approach to P2X7 Receptor Action. Mol. Pharmacol. 2019, 95, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.-H.; Caseley, E.A.; Muench, S.P.; Roger, S. Structural basis for the functional properties of the P2X7 receptor for extracellular ATP. Purinergic Signal. 2021, 17, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, L.E.; Jiang, L.H.; North, R.A. New structure enlivens interest in P2X receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 31, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, W.J.; Jiang, L.-H.; Surprenant, A.; North, R.A. Role of Ectodomain Lysines in the Subunits of the Heteromeric P2X2/3 Receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 70, 1159–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D480–D489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly-Roberts, D.L.; Namovic, M.T.; Han, P.; Jarvis, M.F. Mammalian P2X7 receptor pharmacology: Comparison of recombinant mouse, rat and human P2X7 receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin Dayel, A.; Evans, R.J.; Schmid, R. Mapping the Site of Action of Human P2X7 Receptor Antagonists AZ11645373, Brilliant Blue G, KN-62, Calmidazolium, and ZINC58368839 to the Intersubunit Allosteric Pocket. Mol. Pharmacol. 2019, 96, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caseley, E.A.; Muench, S.P.; Baldwin, S.A.; Simmons, K.; Fishwick, C.W.; Jiang, L.H. Docking of competitive inhibitors to the P2X7 receptor family reveals key differences responsible for changes in response between rat and human. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3164–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, L.; Bidula, S.; Bibič, L.; Allum, E. To Inhibit or Enhance? Is There a Benefit to Positive Allosteric Modulation of P2X Receptors? Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darville, T.; Welter-Stahl, L.; Cruz, C.; Sater, A.A.; Andrews, C.W., Jr.; Ojcius, D.M. Effect of the Purinergic Receptor P2X7 on Chlamydia Infection in Cervical Epithelial Cells and Vaginally Infected Mice. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 3707–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvestrini, V.; Orecchioni, S.; Talarico, G.; Reggiani, F.; Mazzetti, C.; Bertolini, F.; Orioli, E.; Adinolfi, E.; Di Virgilio, F.; Pezzi, A.; et al. Extracellular ATP induces apoptosis through P2X7R activation in acute myeloid leukemia cells but not in normal hematopoietic stem cells. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 5895–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegatti, P.; Raffaghello, L.; Bianchi, G.; Piccardi, F.; Pistoia, V.; Di Virgilio, F. Increased Level of Extracellular ATP at Tumor Sites: In Vivo Imaging with Plasma Membrane Luciferase. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, S.; Jelassi, B.; Couillin, I.; Pelegrin, P.; Besson, P.; Jiang, L.H. Understanding the roles of the P2X7 receptor in solid tumour progression and therapeutic perspectives. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2015, 1848, 2584–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidula, S.M.; Cromer, B.A.; Walpole, S.; Angulo, J.; Stokes, L. Mapping a novel positive allosteric modulator binding site in the central vestibule region of human P2X7. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silberberg, S.D.; Li, M.; Swartz, K.J. Ivermectin Interaction with Transmembrane Helices Reveals Widespread Rearrangements during Opening of P2X Receptor Channels. Neuron 2007, 54, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popova, M.; Trudell, J.; Li, K.; Alkana, R.; Davies, D.; Asatryan, L. Tryptophan 46 is a site for ethanol and ivermectin action in P2X4 receptors. Purinergic Signal. 2013, 9, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nörenberg, W.; Sobottka, H.; Hempel, C.; Plötz, T.; Fischer, W.; Schmalzing, G.; Schaefer, M. Positive allosteric modulation by ivermectin of human but not murine P2X7 receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, K.; Ikonen, E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature 1997, 387, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgin, E.; Levental, I.; Mayor, S.; Eggeling, C. The mystery of membrane organization: Composition, regulation and roles of lipid rafts. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, V.; Bakovic, M. Lipid rafts in health and disease. Biol. Cell 2007, 99, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savio, L.E.B.; de Andrade Mello, P.; Santos, S.A.C.S.; de Sousa, J.C.; Oliveira, S.D.S.; Minshall, R.D.; Kurtenbach, E.; Wu, Y.; Longhi, M.S.; Robson, S.C.; et al. P2X7 receptor activation increases expression of caveolin-1 and formation of macrophage lipid rafts, thereby boosting CD39 activity. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133, jcs237560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, L.E.; Shridar, M.; Smith, P.; Murrell-Lagnado, R.D. Plasma Membrane Cholesterol as a Regulator of Human and Rodent P2X7 Receptor Activation and Sensitization. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 31983–31994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allsopp, R.C.; Evans, R.J. Contribution of the Juxtatransmembrane Intracellular Regions to the Time Course and Permeation of ATP-gated P2X7 Receptor Ion Channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 14556–14566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonnord, P.; Delarasse, C.; Auger, R.; Benihoud, K.; Prigent, M.; Cuif, M.H.; Lamaze, C.; Kanellopoulos, J.M. Palmitoylation of the P2X7 receptor, an ATP-gated channel, controls its expression and association with lipid rafts. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, W.; Stähler, T.; Pinto Espinoza, C.; Danquah, W.; Knop, J.H.; Rissiek, B.; Haag, F.; Koch-Nolte, F. Origin, distribution, and function of three frequent coding polymorphisms in the gene for the human P2X7 ion channel. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1033135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, L.; Fuller, S.J.; Sluyter, R.; Skarratt, K.K.; Gu, B.J.; Wiley, J.S. Two haplotypes of the P2X7 receptor containing the Ala-348 to Thr polymorphism exhibit a gain-of-function effect and enhanced interleukin-1β secretion. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 2916–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, B.J.; Sluyter, R.; Skarratt, K.K.; Shemon, A.N.; Dao-Ung, L.P.; Fuller, S.J.; Barden, J.A.; Clarke, A.L.; Petrou, S.; Wiley, J.S. An Arg307 to Gln polymorphism within the ATP-binding site causes loss of function of the human P2X7 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 31287–31295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Raza, A.; Das, S.; Kapoor, M.; Jayarajan, R.; Verma, A.; Shamsudheen, K.V.; Murry, B.; Seth, S.; Bhargava, B.; et al. Loss of function mutation in the P2X7, a ligand-gated ion channel gene associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Purinergic Signal. 2019, 15, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, B.J.; Field, J.; Dutertre, S.; Ou, A.; Kilpatrick, T.J.; Lechner-Scott, J.; Scott, R.; Lea, R.; Taylor, B.V.; Stankovich, J.; et al. A rare P2X7 variant Arg307Gln with absent pore formation function protects against neuroinflammation in multiple sclerosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 5644–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.H.; Cheng, M.; Tang, J.P.; Dai, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.P.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.L. Single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with P2X7R function regulate the onset of gouty arthritis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyanguren-Desez, O.; Rodríguez-Antigüedad, A.; Villoslada, P.; Domercq, M.; Alberdi, E.; Matute, C. Gain-of-function of P2X7 receptor gene variants in multiple sclerosis. Cell Calcium 2011, 50, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guggemos, J.; Fuller, S.J.; Skarratt, K.K.; Mayer, B.; Schneider, E.M. Loss-of-function/gain-of-function polymorphisms of the ATP sensitive P2X7R influence sepsis, septic shock, pneumonia, and survival outcomes. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1352789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Chu, J.; Singh, S.; Salter, R.D. Identification and characterization of a novel variant of the human P2X7 receptor resulting in gain of function. Purinergic Signal. 2010, 6, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soronen, P.; Mantere, O.; Melartin, T.; Suominen, K.; Vuorilehto, M.; Rytsälä, H.; Arvilommi, P.; Holma, I.; Holma, M.; Jylhä, P.; et al. P2RX7 gene is associated consistently with mood disorders and predicts clinical outcome in three clinical cohorts. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2011, 156, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonda, X.; Hullam, G.; Antal, P.; Eszlari, N.; Petschner, P.; Hökfelt, T.G.; Anderson, I.M.; Deakin, J.F.W.; Juhasz, G.; Bagdy, G. Significance of risk polymorphisms for depression depends on stress exposure. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorina-Lichtenwalter, K.; Ase, A.R.; Verma, V.; Parra, A.I.M.; Komarova, S.; Khadra, A.; Séguéla, P.; Diatchenko, L. Characterization of Common Genetic Variants in P2RX7 and Their Contribution to Chronic Pain Conditions. J. Pain 2024, 25, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorge, R.E.; Trang, T.; Dorfman, R.; Smith, S.B.; Beggs, S.; Ritchie, J.; Austin, J.S.; Zaykin, D.V.; Vander Meulen, H.; Costigan, M.; et al. Genetically determined P2X7 receptor pore formation regulates variability in chronic pain sensitivity. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, H.J.; Baldwin, J.M.; Goli, G.R.; Johnson, B.; Zou, J.; Sivaprasadarao, A.; Baldwin, S.A.; Jiang, L.-H. Residues 155 and 348 Contribute to the Determination of P2X7 Receptor Function via Distinct Mechanisms Revealed by Single-nucleotide Polymorphisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 8176–8187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-Y.; Fang, X.; Ma, Y.; Pan, X.-Y.; Dai, X.-J.; Li, X.-M.; Li, X.-L.; Wang, Y.-P.; Tao, J.-H.; Li, X.-P. The functional change of the P2X7R containing the Ala348 to Thr polymorphism is associated with the pathogenesis of gout. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Yu, J.; Han, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Liang, P. Association Between P2RX7 Gene and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Susceptibility: A Case-Control Study in a Chinese Han Population. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 1916–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Sun, L.; Yan, H.; Jiao, W.; Miao, Q.; Feng, W.; Wu, X.; Gu, Y.; Jiao, A.; Guo, Y.; et al. Metaanalysis of P2X7 gene polymorphisms and tuberculosis susceptibility. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areeshi, M.Y.; Mandal, R.K.; Panda, A.K.; Haque, S. Association of P2X7 A1513C (rs3751143) Gene Polymorphism with Risk of Tuberculosis: Evidence from a Meta-Analysis. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomarkers 2013, 17, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, M.; Sarani, H.; Moazeni-Roodi, A.; Naderi, M.; Hashemi, M. Association between P2X7 Polymorphisms and Susceptibility to Tuberculosis: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies. Medicina 2019, 55, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucae, S.; Salyakina, D.; Barden, N.; Harvey, M.; Gagne, B.; Labbe, M.; Binder, E.B.; Uhr, M.; Paez-Pereda, M.; Sillaber, I.; et al. P2RX7, a gene coding for a purinergic ligand-gated ion channel, is associated with major depressive disorder. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 2438–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barden, N.; Harvey, M.; Gagné, B.; Shink, E.; Tremblay, M.; Raymond, C.; Labbé, M.; Villeneuve, A.; Rochette, D.; Bordeleau, L.; et al. Analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms in genes in the chromosome 12Q24.31 region points to P2RX7 as a susceptibility gene to bipolar affective disorder. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2006, 141B, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.P.; Zhang, B.; Li, W.; Liu, J. Lack of Association of P2RX7 Gene rs2230912 Polymorphism with Mood Disorders: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czamara, D.; Müller-Myhsok, B.; Lucae, S. The P2RX7 polymorphism rs2230912 is associated with depression: A meta-analysis. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 82, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vereczkei, A.; Abdul-Rahman, O.; Halmai, Z.; Nagy, G.; Szekely, A.; Somogyi, A.; Faludi, G.; Nemoda, Z. Association of purinergic receptor P2RX7 gene polymorphisms with depression symptoms. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 92, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuillin, A.; Bass, N.J.; Choudhury, K.; Puri, V.; Kosmin, M.; Lawrence, J.; Curtis, D.; Gurling, H.M. Case-control studies show that a non-conservative amino-acid change from a glutamine to arginine in the P2RX7 purinergic receptor protein is associated with both bipolar- and unipolar-affective disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigoroiu-Serbanescu, M.; Herms, S.; Mühleisen, T.W.; Georgi, A.; Diaconu, C.C.; Strohmaier, J.; Czerski, P.; Hauser, J.; Leszczynska-Rodziewicz, A.; Jamra, R.A.; et al. Variation in P2RX7 candidate gene (rs2230912) is not associated with bipolar I disorder and unipolar major depression in four European samples. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2009, 150B, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, E.K.; Grozeva, D.; Raybould, R.; Elvidge, G.; Macgregor, S.; Craig, I.; Farmer, A.; McGuffin, P.; Forty, L.; Jones, L.; et al. P2RX7: A bipolar and unipolar disorder candidate susceptibility gene? Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2009, 150B, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halmai, Z.; Dome, P.; Vereczkei, A.; Abdul-Rahman, O.; Szekely, A.; Gonda, X.; Faludi, G.; Sasvari-Szekely, M.; Nemoda, Z. Associations between depression severity and purinergic receptor P2RX7 gene polymorphisms. J. Affect. Disord. 2013, 150, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backlund, L.; Nikamo, P.; Hukic, D.S.; Ek, I.R.; Träskman-Bendz, L.; Landén, M.; Edman, G.; Schalling, M.; Frisén, L.; Osby, U. Cognitive manic symptoms associated with the P2RX7 gene in bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 2011, 13, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magni, L.; Yu, H.; Christensen, N.M.; Poulsen, M.H.; Frueh, A.; Deshar, G.; Johansen, A.Z.; Johansen, J.S.; Pless, S.A.; Jørgensen, N.R.; et al. Human P2X7 receptor variants Gly150Arg and Arg276His polymorphisms have differential effects on risk association and cellular functions in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2024, 24, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiringhelli, F.; Apetoh, L.; Tesniere, A.; Aymeric, L.; Ma, Y.; Ortiz, C.; Vermaelen, K.; Panaretakis, T.; Mignot, G.; Ullrich, E.; et al. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in dendritic cells induces IL-1Β-dependent adaptive immunity against tumors. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardano, A.; Falzoni, S.; Caraccio, N.; Polini, A.; Tognini, S.; Solini, A.; Berti, P.; Di Virgilio, F.; Monzani, F. 1513A>C Polymorphism in the P2X7 Receptor Gene in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer: Correlation with Histological Variants and Clinical Parameters. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, J.S.; Dao-Ung, L.P.; Gu, B.J.; Sluyter, R.; Shemon, A.N.; Li, C.; Taper, J.; Gallo, J.; Manoharan, A. A loss-of-function polymorphic mutation in the cytolytic P2X7 receptor gene and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: A molecular study. Lancet 2002, 359, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thunberg, U.; Tobin, G.; Johnson, A.; Söderberg, O.; Padyukov, L.; Hultdin, M.; Klareskog, L.; Enblad, G.; Sundström, C.; Roos, G.; et al. Polymorphism in the P2X7 receptor gene and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Lancet 2002, 360, 1935–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegoraro, A.; Grignolo, M.; Ruo, L.; Ricci, L.; Adinolfi, E. P2X7 Variants in Pathophysiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchi, E.; Pegoraro, A.; Adinolfi, E. P2X7 Receptor in Hematological Malignancies. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 645605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starczynski, J.; Pepper, C.; Pratt, G.; Hooper, L.; Thomas, A.; Hoy, T.; Milligan, D.; Bentley, P.; Fegan, C. The P2X7 receptor gene polymorphism 1513 A-->C has no effect on clinical prognostic markers, in vitro sensitivity to fludarabine, Bcl-2 family protein expression or survival in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 123, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Ibbotson, R.E.; Orchard, J.A.; Gardiner, A.C.; Seear, R.V.; Chase, A.J.; Oscier, D.G.; Cross, N.C. P2X7 polymorphism and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: Lack of correlation with incidence, survival and abnormalities of chromosome 12. Leukemia 2003, 17, 2097–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nückel, H.; Frey, U.H.; Dürig, J.; Dührsen, U.; Siffert, W. 1513A/C polymorphism in the P2X7 receptor gene in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Absence of correlation with clinical outcome. Eur. J. Haematol. 2004, 72, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.J.; Chen, J.Y.; Guan, Y.; Liu, D.C.; Cao, Z.C.; Kong, J.; Wu, Z.S.; Wu, W.Y. Predicted the P2RX7 rs3751143 polymorphism is associated with cancer risk: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20193877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, R.; Sauna, Z.E.; Ambudkar, S.V.; Gottesman, M.M.; Kimchi-Sarfaty, C. Silent (synonymous) SNPs: Should we care about them? Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 578, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, C.; Cui, Q. A Large-Scale Analysis of the Relationship of Synonymous SNPs Changing MicroRNA Regulation with Functionality and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 23545–23555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, S.; Mei, Z.Z.; Baldwin, J.M.; Dong, L.; Bradley, H.; Baldwin, S.A.; Surprenant, A.; Jiang, L.H. Single nucleotide polymorphisms that were identified in affective mood disorders affect ATP-activated P2X7 receptor functions. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2010, 44, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erhardt, A.; Lucae, S.; Unschuld, P.G.; Ising, M.; Kern, N.; Salyakina, D.; Lieb, R.; Uhr, M.; Binder, E.B.; Keck, M.E.; et al. Association of polymorphisms in P2RX7 and CaMKKb with anxiety disorders. J. Affect. Disord. 2007, 101, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gidlöf, O.; Smith, J.G.; Melander, O.; Lövkvist, H.; Hedblad, B.; Engström, G.; Nilsson, P.; Carlson, J.; Berglund, G.; Olsson, S.; et al. A Common Missense Variant in the ATP Receptor P2X7 Is Associated with Reduced Risk of Cardiovascular Events. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangsted, A.J.; Klausen, T.W.; Gimsing, P.; Abildgaard, N.; Andersen, N.F.; Gang, A.O.; Holmström, M.; Gregersen, H.; Vogel, U.; Schwarz, P.; et al. Genetic variants in the P2RX7 gene are associated with risk of multiple myeloma. Eur. J. Haematol. 2014, 93, 172–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husted, L.B.; Harsløf, T.; Stenkjær, L.; Carstens, M.; Jørgensen, N.R.; Langdahl, B.L. Functional polymorphisms in the P2X7 receptor gene are associated with osteoporosis. Osteoporos. Int. 2013, 24, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.; Jakobsen, K.D.; Fenger, M.; Nielsen, J.; Krane, K.; Fink-Jensen, A.; Lublin, H.; Ullum, H.; Timm, S.; Wang, A.G.; et al. Variation in the purinergic P2RX7 receptor gene and schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2008, 104, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, J.M.; Falzoni, S.; Rizzo, R.; Cipollone, F.; Zuliani, G.; Di Virgilio, F. Possible protective role of the 489C>T P2X7R polymorphism in Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 60, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegoraro, A.; Bortolotti, D.; Marci, R.; Caselli, E.; Falzoni, S.; De Marchi, E.; Di Virgilio, F.; Rizzo, R.; Adinolfi, E. The P2X7 Receptor 489C>T Gain of Function Polymorphism Favors HHV-6A Infection and Associates with Female Idiopathic Infertility. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Yu, F.; Ye, C.; Huang, X.; Lei, X.; Dai, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y. The presence of P2RX7 single nuclear polymorphism is associated with a gain of function in P2X7 receptor and inflammasome activation in SLE complicated with pericarditis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gartland, A.; Skarratt, K.K.; Hocking, L.J.; Parsons, C.; Stokes, L.; Jørgensen, N.R.; Fraser, W.D.; Reid, D.M.; Gallagher, J.A.; Wiley, J.S. Polymorphisms in the P2X7 receptor gene are associated with low lumbar spine bone mineral density and accelerated bone loss in post-menopausal women. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 20, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portales-Cervantes, L.; Niño-Moreno, P.; Salgado-Bustamante, M.; García-Hernández, M.H.; Baranda-Candido, L.; Reynaga-Hernández, E.; Barajas-López, C.; González-Amaro, R.; Portales-Pérez, D.P. The His155Tyr (489C>T) single nucleotide polymorphism of P2RX7 gene confers an enhanced function of P2X7 receptor in immune cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Cell. Immunol. 2012, 276, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, N.R.; Husted, L.B.; Skarratt, K.K.; Stokes, L.; Tofteng, C.L.; Kvist, T.; Jensen, J.-E.B.; Eiken, P.; Brixen, K.; Fuller, S.; et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the P2X7 receptor gene are associated with post-menopausal bone loss and vertebral fractures. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 20, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerini, F.R.; Agliardi, C.; Bolognesi, E.; Zanzottera, M.; Caputo, D.; Pasanisi, M.B.; Rovaris, M.; Clerici, M. Two Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the Purinergic Receptor P2X7 Gene Are Associated with Disease Severity in Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamieson, S.E.; Peixoto-Rangel, A.L.; Hargrave, A.C.; Roubaix, L.A.; Mui, E.J.; Boulter, N.R.; Miller, E.N.; Fuller, S.J.; Wiley, J.S.; Castellucci, L.; et al. Evidence for associations between the purinergic receptor P2X7 (P2RX7) and toxoplasmosis. Genes Immun. 2010, 11, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naranjo-Galvis, C.A.; McLeod, R.; Gómez-Marín, J.E.; de-la-Torre, A.; Rocha-Roa, C.; Cardona, N.; Sepúlveda-Arias, J.C. Genetic Variations in the Purinergic P2X7 Receptor Are Associated with the Immune Response to Ocular Toxoplasmosis in Colombia. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubert, C.; Andrejew, R.; Jacintho Moritz, C.E.; Dietrich, F.; Vasconcelos-Moreno, M.P.; dos Santos, B.T.M.Q.; Fijtman, A.; Kauer-Sant’Anna, M.; Kapczinski, F.; da Silva Magalhães, P.V.; et al. Bipolar disorder and 1513A>C P2RX7 polymorphism frequency. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 694, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Han, X.; Li, Y.; Zou, H.; Xie, A. Association of P2X7 receptor gene polymorphisms with sporadic Parkinson’s disease in a Han Chinese population. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 546, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.M.; Boulter, N.R.; Fuller, S.J.; Zakrzewski, A.M.; Lees, M.P.; Saunders, B.M.; Wiley, J.S.; Smith, N.C. The role of the P2X7 receptor in infectious diseases. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information; U.S. National Library of Medicine. ALFA: Allele Frequency Aggregator. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/snp/docs/gsr/alfa/ (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- Sherry, S.T.; Ward, M.H.; Kholodov, M.; Baker, J.; Phan, L.; Smigielski, E.M.; Sirotkin, K. dbSNP: The NCBI database of genetic variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Villamarin, R.; Hefferon, T.; Ramanathan, A.; Kattman, B. The evolution of dbSNP: 25 years of impact in genomic research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D925–D931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US); National Center for Biotechnology Information. dbSNP. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/snp/ (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- Jørgensen, N.R. Role of the purinergic P2X receptors in osteoclast pathophysiology. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2019, 47, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, N.A.; Wright, M.W.; Brister, J.R.; Ciufo, S.; Haddad, D.; McVeigh, R.; Rajput, B.; Robbertse, B.; Smith-White, B.; Ako-Adjei, D.; et al. Reference sequence (RefSeq) database at NCBI: Current status, taxonomic expansion, and functional annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D733–D745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US); National Center for Biotechnology Information. RefSeq. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/refseq/ (accessed on 8 September 2025).
- De Salis, S.K.F.; Chen, J.Z.; Skarratt, K.K.; Fuller, S.J.; Balle, T. Deep learning structural insights into heterotrimeric alternatively spliced P2X7 receptors. Purinergic Signal. 2024, 20, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheewatrakoolpong, B.; Gilchrest, H.; Anthes, J.C.; Greenfeder, S. Identification and characterization of splice variants of the human P2X7 ATP channel. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 332, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarratt, K.K.; Gu, B.J.; Lovelace, M.D.; Milligan, C.J.; Stokes, L.; Glover, R.; Petrou, S.; Wiley, J.S.; Fuller, S.J. A P2RX7 single nucleotide polymorphism haplotype promotes exon 7 and 8 skipping and disrupts receptor function. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 3884–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, D.A.; Cavanaugh, M.; Clark, K.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D36–D42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US); National Center for Biotechnology Information. GenBank. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/ (accessed on 8 September 2025).
- Sluyter, R.; Stokes, L. Significance of P2X7 Receptor Variants to Human Health and Disease. Recent Pat. DNA Gene Seq. 2011, 5, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicke, A.; Kuan, Y.H.; Masin, M.; Rettinger, J.; Marquez-Klaka, B.; Bender, O.; Górecki, D.C.; Murrell-Lagnado, R.D.; Soto, F. A Functional P2X7 Splice Variant with an Alternative Transmembrane Domain 1 Escapes Gene Inactivation in P2X7 Knock-out Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 25813–25822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.H.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, L.; Gorodeski, G.I. A Truncated P2X7 Receptor Variant (P2X7-j) Endogenously Expressed in Cervical Cancer Cells Antagonizes the Full-length P2X7 Receptor through Hetero-oligomerization. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 17228–17237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adinolfi, E.; Cirillo, M.; Woltersdorf, R.; Falzoni, S.; Chiozzi, P.; Pellegatti, P.; Callegari, M.G.; Sandonà, D.; Markwardt, F.; Schmalzing, G.; et al. Trophic activity of a naturally occurring truncated isoform of the P2X7 receptor. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 3393–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Ni, H.; Zhang, L.; Xing, Y.; Fan, J.; Li, P.; Li, T.; Jia, R.; Ge, S.; Zhang, H.; et al. P2RX7-V3 is a novel oncogene that promotes tumorigenesis in uveal melanoma. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 13533–13543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegoraro, A.; Orioli, E.; De Marchi, E.; Salvestrini, V.; Milani, A.; Di Virgilio, F.; Curti, A.; Adinolfi, E. Differential sensitivity of acute myeloid leukemia cells to daunorubicin depends on P2X7A versus P2X7B receptor expression. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, V.W.Y.; Chua, H.C.; Kowal, N.M.; Chebib, M.; Balle, T.; Ahring, P.K. Concatenated γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors revisited: Finding order in chaos. J. Gen. Physiol. 2019, 151, 798–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, V.W.Y.; Kusay, A.S.; Balle, T.; Ahring, P.K. Heterologous expression of concatenated nicotinic ACh receptors: Pros and cons of subunit concatenation and recommendations for construct designs. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 4275–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keystone, E.C.; Wang, M.M.; Layton, M.; Hollis, S.; McInnes, I.B. Clinical evaluation of the efficacy of the P2X7 purinergic receptor antagonist AZD9056 on the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in patients with active disease despite treatment with methotrexate or sulphasalazine. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, T.C.; Bloom, B.J.; Wei, N.; Ishaq, S.; Park, W.; Wang, X.; Gupta, P.; Mebus, C.A. Efficacy and Safety of CE-224,535, an Antagonist of P2X7 Receptor, in Treatment of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Inadequately Controlled by Methotrexate. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eser, A.; Colombel, J.-F.; Rutgeerts, P.; Vermeire, S.; Vogelsang, H.; Braddock, M.; Persson, T.; Reinisch, W. Safety and Efficacy of an Oral Inhibitor of the Purinergic Receptor P2X7 in Adult Patients with Moderately to Severely Active Crohn’s Disease: A Randomized Placebo-controlled, Double-blind, Phase IIa Study. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2247–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recourt, K.; de Boer, P.; van der Ark, P.; Benes, H.; van Gerven, J.M.A.; Ceusters, M.; van Nueten, L.; Drevets, W.C.; Bhatacharya, A.; Browning, M.; et al. Characterization of the central nervous system penetrant and selective purine P2X7 receptor antagonist JNJ-54175446 in patients with major depressive disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recourt, K.; van der Aart, J.; Jacobs, G.; de Kam, M.; Drevets, W.; van Nueten, L.; Kanhai, K.; Siebenga, P.; Zuiker, R.; Ravenstijn, P.; et al. Characterisation of the pharmacodynamic effects of the P2X7 receptor antagonist JNJ-54175446 using an oral dexamphetamine challenge model in healthy males in a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multiple ascending dose trial. J. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 34, 1030–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, S.M.; Gidley Baird, A.; Glazer, S.; Barden, J.A.; Glazer, A.; Teh, L.C.; King, J. A phase I clinical trial demonstrates that nfP2X7-targeted antibodies provide a novel, safe and tolerable topical therapy for basal cell carcinoma. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vultaggio-Poma, V.; Sanz, J.M.; Amico, A.; Violi, A.; Ghisellini, S.; Pizzicotti, S.; Passaro, A.; Papi, A.; Libanore, M.; Di Virgilio, F.; et al. The shed P2X7 receptor is an index of adverse clinical outcome in COVID-19 patients. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1182454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, E.P.; Ribeiro, S.C.M.; Lanes, V.R.; Almeida, F.M.; de Andrade, M.R.M.; Bomfim, C.C.B.; Salles, É.M.; Bortoluci, K.R.; Coutinho-Silva, R.; Hirata, M.H.; et al. Pulmonary Infection with Hypervirulent Mycobacteria Reveals a Crucial Role for the P2X7 Receptor in Aggressive Forms of Tuberculosis. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slater, M.; Danieletto, S.; Gidley-Baird, A.; Teh, L.C.; Barden, J.A. Early prostate cancer detected using expression of non-functional cytolytic P2X7 receptors. Histopathology 2004, 44, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, L.; An, H.; Chang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J. P2X7 receptor predicts postoperative cancer-specific survival of patients with clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, S.M.; Oliphant, C.J.; Hassan, S.; Peille, A.L.; Bronsert, P.; Falzoni, S.; Di Virgilio, F.; McNulty, S.; Lara, R. ATP in the tumour microenvironment drives expression of nfP2X7, a key mediator of cancer cell survival. Oncogene 2019, 38, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Isaak, A.; Junker, A. Spotlight on P2X7 Receptor PET Imaging: A Bright Target or a Failing Star? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Weehaeghe, D.; Koole, M.; Schmidt, M.E.; Deman, S.; Jacobs, A.H.; Souche, E.; Serdons, K.; Sunaert, S.; Bormans, G.; Vandenberghe, W.; et al. [11C]JNJ54173717, a novel P2X7 receptor radioligand as marker for neuroinflammation: Human biodistribution, dosimetry, brain kinetic modelling and quantification of brain P2X7 receptors in patients with Parkinson’s disease and healthy volunteers. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 2051–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koole, M.; Schmidt, M.E.; Hijzen, A.; Ravenstijn, P.; Vandermeulen, C.; Van Weehaeghe, D.; Serdons, K.; Celen, S.; Bormans, G.; Ceusters, M.; et al. 18F-JNJ-64413739, a Novel PET Ligand for the P2X7 Ion Channel: Radiation Dosimetry, Kinetic Modeling, Test-Retest Variability, and Occupancy of the P2X7 Antagonist JNJ-54175446. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagens, M.H.J.; Golla, S.S.V.; Janssen, B.; Vugts, D.J.; Beaino, W.; Windhorst, A.D.; O’Brien-Brown, J.; Kassiou, M.; Schuit, R.C.; Schwarte, L.A.; et al. The P2X7 receptor tracer [11C]SMW139 as an in vivo marker of neuroinflammation in multiple sclerosis: A first-in man study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, T. The P2X7 Receptor as a Mechanistic Biomarker for Epilepsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasuya, G.; Yamaura, T.; Ma, X.B.; Nakamura, R.; Takemoto, M.; Nagumo, H.; Tanaka, E.; Dohmae, N.; Nakane, T.; Yu, Y.; et al. Structural insights into the competitive inhibition of the ATP-gated P2X receptor channel. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.; Yue, C.-X.; Jin, F.; Wang, Y.; Ichikawa, M.; Yu, Y.; Guo, C.-R.; Hattori, M. Structural insights into the orthosteric inhibition of P2X receptors by non-ATP analog antagonists. eLife 2024, 12, RP92829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, E.G.; Faria, R.X.; Rodrigues, C.R.; Bello, M.L. Molecular dynamic simulations of full-length human purinergic receptor subtype P2X7 bonded to potent inhibitors. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 152, 105454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frangos, Z.J.; Wilson, K.A.; Aitken, H.M.; Cantwell Chater, R.; Vandenberg, R.J.; O’Mara, M.L. Membrane cholesterol regulates inhibition and substrate transport by the glycine transporter, GlyT2. Life Sci. Alliance 2023, 6, e202201708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakany, F.; Kovacs, T.; Panyi, G.; Varga, Z. Direct and indirect cholesterol effects on membrane proteins with special focus on potassium channels. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutho, B.; Samsri, S.; Pornsuwan, S. Structural Dynamics of the Precatalytic State of Human Cytochrome c upon T28C, G34C, and A50C Mutations: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Perspective. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 15229–15238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazeri, G.; Povinelli, A.P.R.; Lima, M.d.F.; Cornélio, M.L. Detailed Characterization of the Cooperative Binding of Piperine with Heat Shock Protein 70 by Molecular Biophysical Approaches. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).