Stanniocalcin2, A Promising New Target for Identifying Patients with Stroke/Ictus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
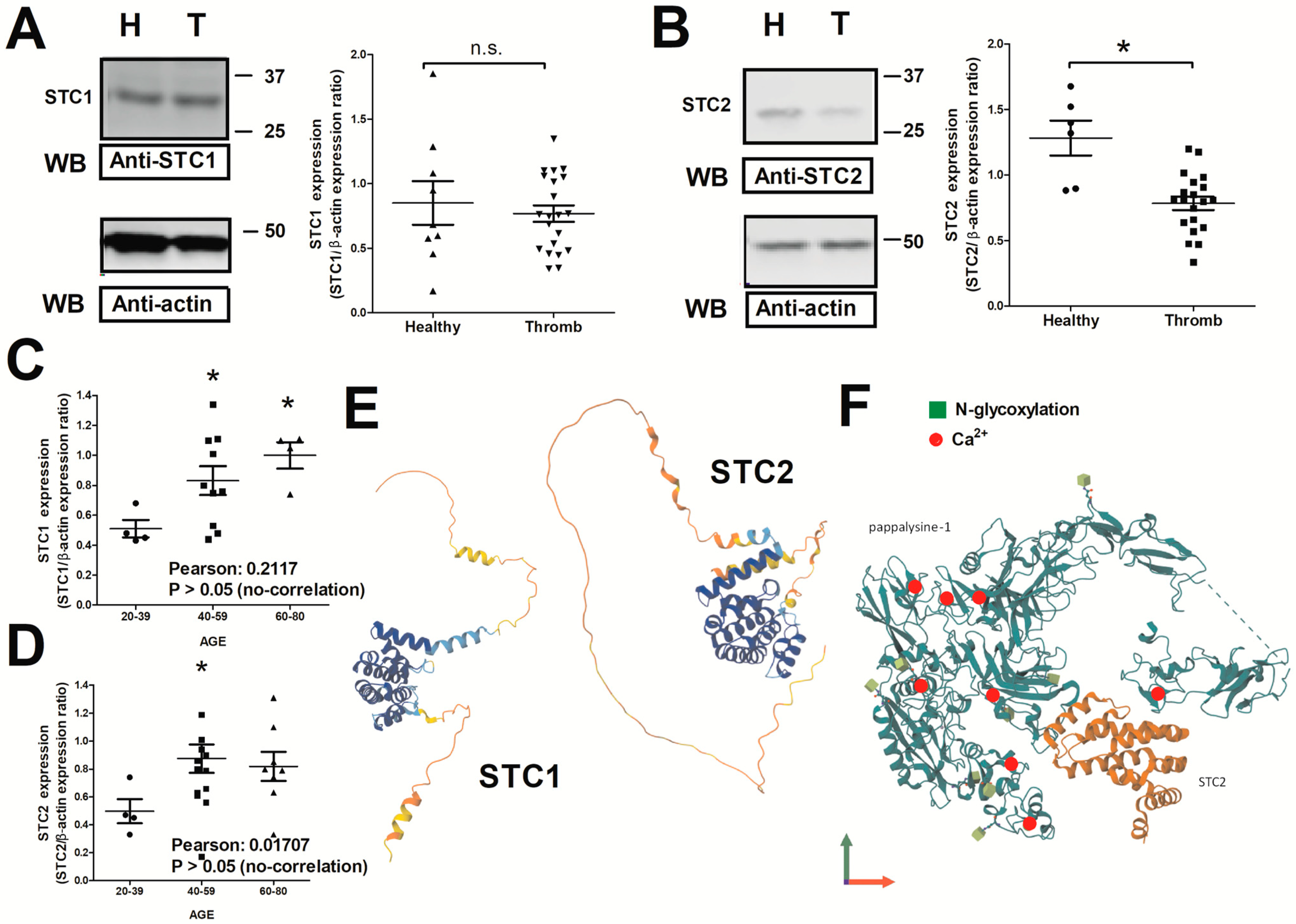
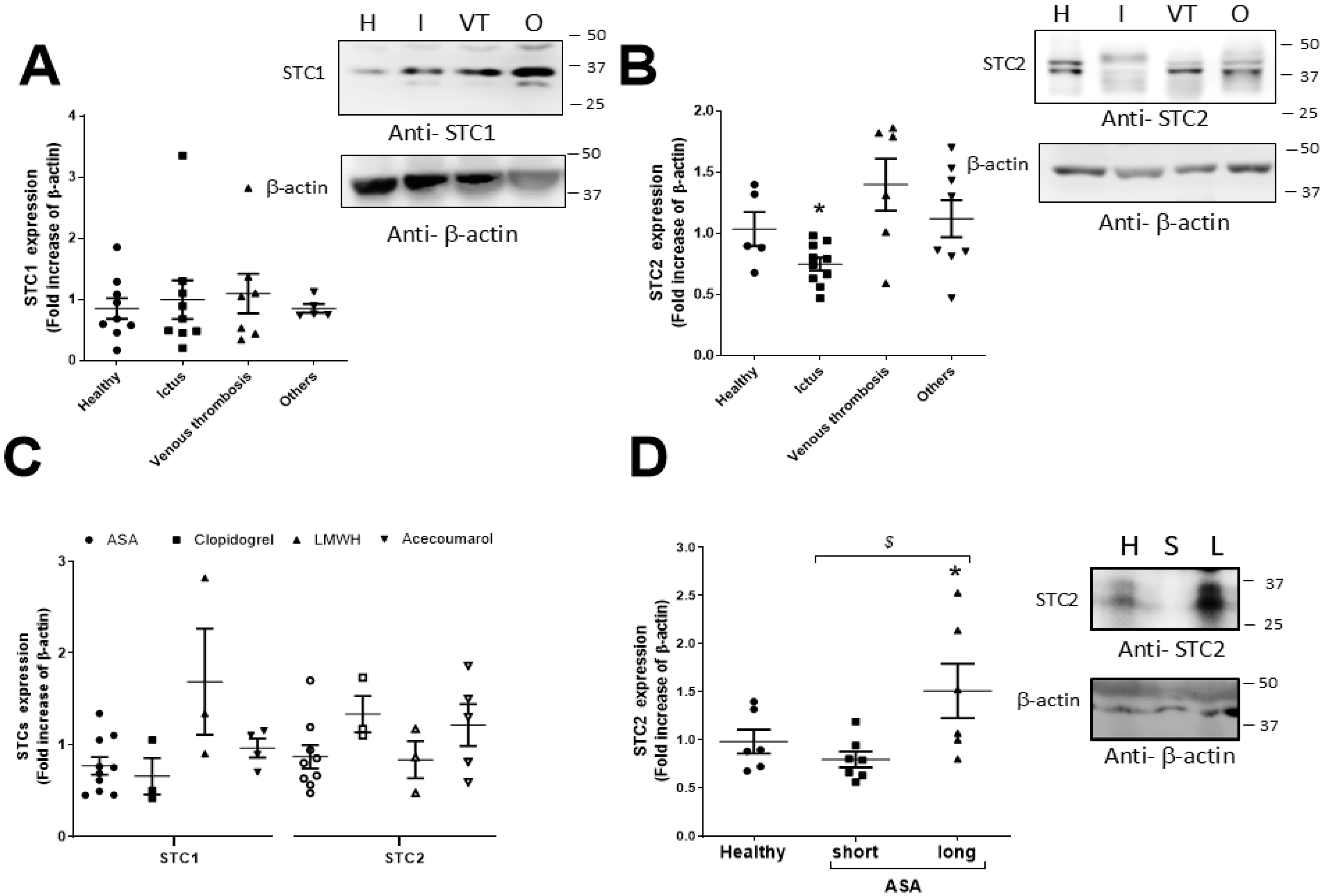
2.1. Expression of STC1 and STC2 in Thrombotic Patients
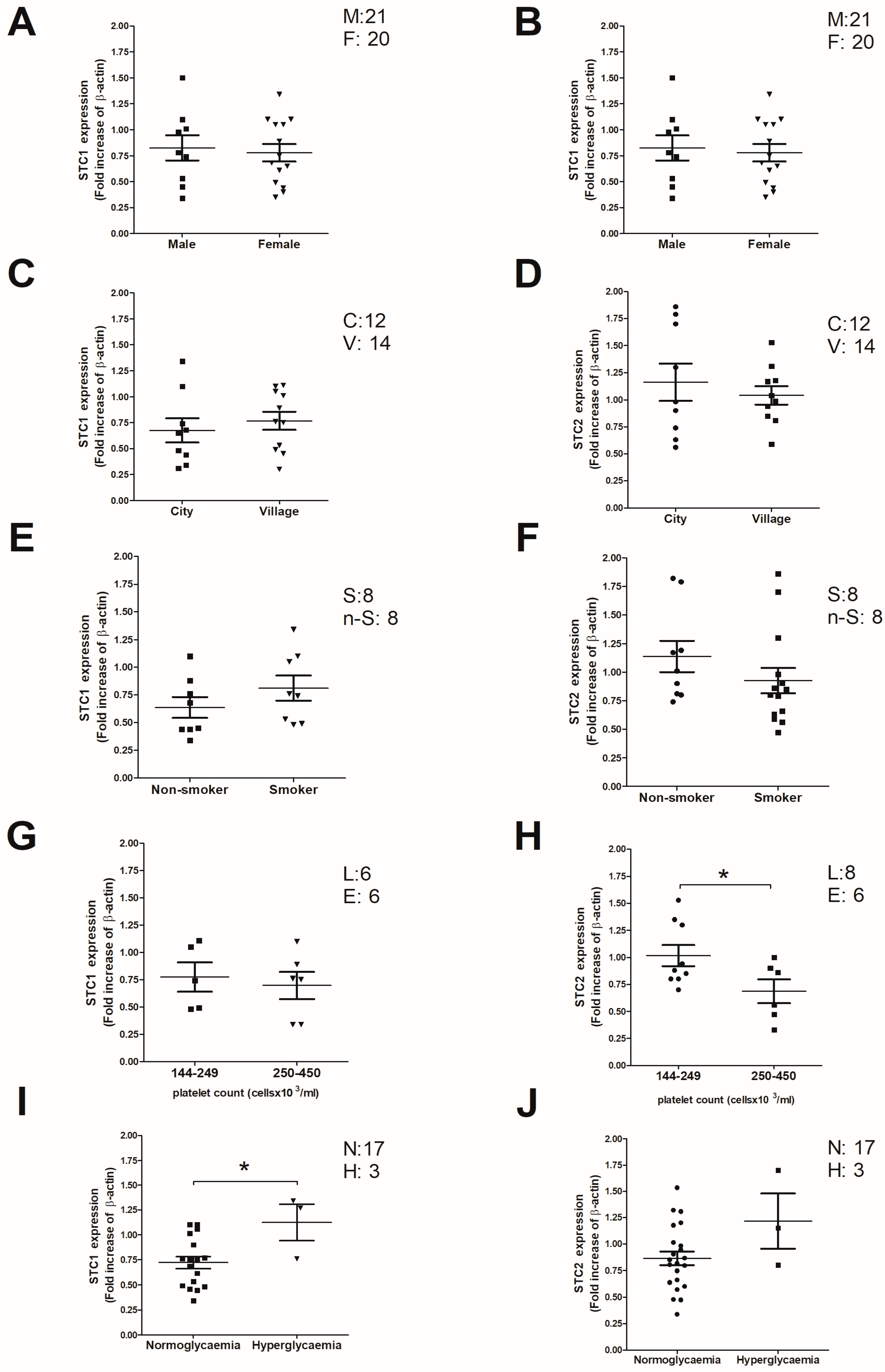
2.2. Analysis of Clinical and Demographic Variables That May Correlate with the STC2 Expression Values in Thrombotic Patients
2.3. Analysis of STC2 Post-Translational Modification by Phosphorylation in Patients Suffering from Stroke
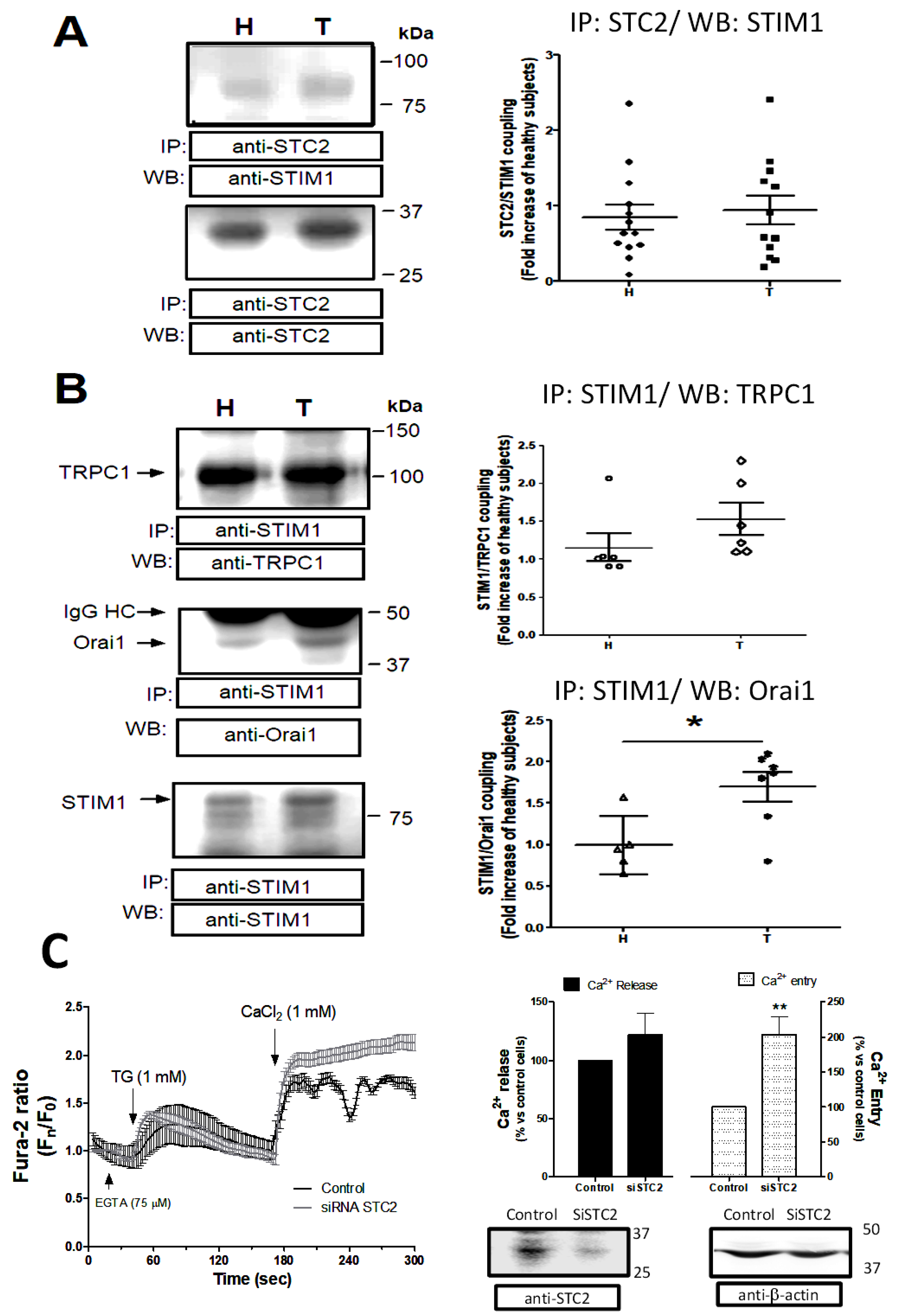
2.4. Regulation of the Capacitative Ca2+ Channels by STC2 in Patients Suffering from Stroke
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients: Healthy Subjects and Mice
4.2. Blood Sampling and Conservation
4.3. Cell Culture and Glycosylation Analysis of STC2
4.4. Preparation of Platelet Protein Samples for Immunoprecipitation and Western Blotting
4.5. ”In Silico” Analysis of the Proteins
4.6. Ca2+ Homeostasis Evaluation
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| STC | Stanniocalcin |
| ASA | Acetyl salicylic acid |
| STIM | Stromal interaction molecule |
| Orai | ORAI calcium release-activated calcium modulator |
| SOCE | Store-operated Ca2+ entry |
| TRPC | Transient receptor potential channel |
| [Ca2+]i | Intracellular calcium concentration |
| SARAF | Store-operated calcium entry-associated regulatory factor (TMEM66) |
| PAPP-A | Pregnancy associated plasma protein-A |
| LMWH | Low-molecular-weight heparin |
| PKA | Protein kinase A |
| PKC | Protein kinase C |
| Ser | Serine |
| Thr | Threonine |
| Tyr | Tyrosine |
| HIF-1 | Hypoxia-induced factor 1 |
| PRP | Platelet-rich plasma |
| PPP | Platelet-poor plasma |
| TBST | Tris-buffered saline with Tween® 20 Detergent |
References
- World Health Organization. The Top 10 Causes of Death. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Chang, J.C. Novel Classification of Thrombotic Disorders Based on Molecular Hemostasis and Thrombogenesis Producing Primary and Secondary Phenotypes of Thrombosis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jy, W.; Ahn, Y.S.; Shanbaky, N.; Fernandez, L.F.; Harrington, W.J.; Haynes, D.H. Abnormal calcium handling by platelets in thrombotic disorders. Circ. Res. 1987, 60, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicari, A.M.; Monzani, M.L.; Pellegatta, F.; Ronchi, P.; Galli, L.; Folli, F. Platelet calcium homeostasis is abnormal in patients with severe arteriosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. J. Vasc. Biol. 1994, 14, 1420–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.J.; Salido, G.M.; Pariente, J.A.; Rosado, J.A. Interaction of STIM1 with endogenously expressed human canonical TRP1 upon depletion of intracellular Ca2+ stores. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 28254–28264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbidi, H.; Jardin, I.; Woodard, G.E.; Lopez, J.J.; Berna-Erro, A.; Salido, G.M.; Rosado, J.A. STIM1 and STIM2 Are Located in the Acidic Ca2+ Stores and Associates with Orai1 upon Depletion of the Acidic Stores in Human Platelets. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 12257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berna-Erro, A.; Galan, C.; Dionisio, N.; Gomez, L.J.; Salido, G.M.; Rosado, J.A. Capacitative and non-capacitative signaling complexes in human platelets. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 1242–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misceo, D.; Holmgren, A.; Louch, W.E.; Holme, P.A.; Mizobuchi, M.; Morales, R.J.; De Paula, A.M.; Stray-Pedersen, A.; Lyle, R.; Dalhus, B.; et al. A dominant STIM1 mutation causes Stormorken syndrome. Hum. Mutat. 2014, 35, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrner, M.; Stadlbauer, M.; Muik, M.; Rathner, P.; Stathopulos, P.; Ikura, M.; Müller, N.; Romanin, C. A dual mechanism promotes switching of the Stormorken STIM1 R304W mutant into the activated state. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berna-Erro, A.; Jardín, I.; Smani, T.; Rosado, J.A.; Berna-Erro, A.; Jardín, I.; Smani, T.; Rosado, J.A. Regulation of Platelet Function by Orai, STIM and TRP. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 898, 157–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarran, L.; Lopez, J.J.; Jardin, I.; Sanchez-Collado, J.; Berna-Erro, A.; Smani, T.; Camello, P.J.; Salido, G.M.; Rosado, J.A. EFHB is a Novel Cytosolic Ca2+ Sensor That Modulates STIM1-SARAF Interaction. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 51, 1164–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berna-Erro, A.; Granados, M.P.; Teruel-Montoya, R.; Ferrer-Marin, F.; Delgado, E.; Corbacho, A.J.; Fenández, E.; Vazquez-Godoy, M.T.; Tapia, J.A.; Redondo, P.C. SARAF overexpression impairs thrombin-induced Ca2+ homeostasis in neonatal platelets. Br. J. Haematol. 2024, 204, 988–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berna-Erro, A.; Ramesh, G.; Delgado, E.; Corbacho, A.J.; Ferrer-Marín, F.; Teruel, R.; Granados, M.P.; Rosado, J.A.; Redondo, P.C. CAPN1 (Calpain1)-Dependent Cleavage of STIM1 (Stromal Interaction Molecule 1) Results in an Enhanced SOCE (Store-Operated Calcium Entry) in Human Neonatal Platelets. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2023, 43, e151–e170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israels, S.J.; Cheang, T.; Roberston, C.; Ward, E.M.M.M.; McNicol, A. Impaired signal transduction in neonatal platelets. Pediatr. Res. 1999, 45, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelman, B.; Setty, B.N.Y.; Chen, D.; Amin-Hanjani, S.; Stuart, M.J. Impaired Mobilization of Intracellular Calcium in Neonatal Platelets. Pediatr. Res. 1996, 39, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uçar, T.; Gurman, C.; Arsan, S.; Kemahli, S. Platelet aggregation in term and preterm newborns. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2005, 22, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiger, W.; Ito, D.; Swetlik, C.; Oh-hora, M.; Villereal, M.L.; Thinakaran, G. Stanniocalcin 2 is a negative modulator of store-operated calcium entry. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 3710–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.C.M.; Reddel, R.R. Identification of a second stanniocalcin cDNA in mouse and human: Stanniocalcin 2. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1998, 141, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, Q.; Li, D.; Lv, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z. The significance of Stanniocalcin 2 in malignancies and mechanisms. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 7276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, E.; Gómez-Gordo, L.; Cantonero, C.; Bermejo, N.; Pérez-Gómez, J.; Granados, M.P.; Salido, G.M.; Dionisio, J.A.R.; Liberal, P.C.R. Stanniocalcin 2 regulates non-capacitative Ca2+ entry and aggregation in mouse platelets. Front. Physiol. 2018, 23, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.J.; Jardín, I.; Cantonero Chamorro, C.; Duran, M.L.; Tarancón Rubio, M.J.; Reyes Panadero, M.; Jiménez, F.; Montero, R.; González, M.J.; Martínez, M.; et al. Involvement of stanniocalcins in the deregulation of glycaemia in obese mice and type 2 diabetic patients. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gude, M.F.; Hjortebjerg, R.; Bjerre, M.; Charles, M.H.; Witte, D.R.; Sandbæk, A.; Frystyk, J. The STC2–PAPP-A–IGFBP4–IGF1 axis and its associations to mortality and CVD in T2D. Endocr. Connect. 2023, 12, e220451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridar, J.; Mafi, A.; Judge, R.A.; Xu, J.; Kong, K.A.; Wang, J.C.K.; Stoll, V.S.; Koukos, G.; Simon, R.J.; Eaton, D.; et al. Cryo-EM structure of human PAPP-A2 and mechanism of substrate recognition. Commun. Chem. 2023, 6, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauer, R.L.; Whitaker, D.J. Thrombocytopenia: Evaluation and Management. Am. Fam. Physician 2022, 106, 288–298. [Google Scholar]
- Law, A.Y.S.; Wong, C.K.C. Stanniocalcin-2 is a HIF-1 target gene that promotes cell proliferation in hypoxia. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Westberg, J.A.; Andersson, L.C. Stanniocalcin 2, forms a complex with heme oxygenase 1, binds hemin and is a heat shock protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 421, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amemiya, Y.; Marra, L.E.; Reyhani, N.; Youson, J.H. Stanniocalcin from an ancient teleost: A monomeric form of the hormone and a possible extracorpuscular distribution. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2002, 188, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, G.F.; Hampong, M.; Park, C.M.; Copp, D.H. Purification, characterization, and bioassay of teleocalcin, a glycoprotein from salmon corpuscles of Stannius. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1986, 63, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafeber, F.P.J.G.; Perry, S.F. Experimental hypercalcemia induces hypocalcin release and inhibits branchial Ca+ influx in freshwater trout. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1988, 72, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.T.; Hu, R.; Shao, C.J.; Feng, Y.; Yang, X.L.; Xie, Y.P.; Shi, J.X.; Li, J.S.; Li, X.M. Stanniocalcin-1 secreted by human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells regulates interleukin-10 expression via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in alveolar macrophages. Cytokine 2023, 162, 156114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, G. Stanniocalcin1 (STC1) Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Invasion of Cervical Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Jiang, B.; Liu, J.; Ding, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, R.; Peng, L.; Qin, C.; Fang, S.; Li, G.; et al. STC1 promotes cell apoptosis via NF-κB phospho-P65 Ser536 in cervical cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 46249–46261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zeng, X.; He, Y.; Wang, X.; Liang, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, H.; Xu, N.; Liang, S.; et al. STC2 promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer cells through AKT-ERK signaling pathways. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 71400–71416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjaer, A.S.L.; Sehgal, S.; Wu, Y.; Iyer, P.; Winn, V.D. Placental Expression of Stanniocalcin 2 (STC2) in Healthy and Preeclamptic Pregnancies. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 228, S93–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhao, D.; Bao, L.J. Stanniocalcin 1 alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis of myocardial cells. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 4309–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ceunynck, K.; Peters, C.G.; Jain, A.; Higgins, S.J.; Aisiku, O.; Fitch-Tewfik, J.L.; Chaudhry, S.A.; Dockendorff, C.; Parikh, S.M.; Ingber, D.E.; et al. PAR1 agonists stimulate APC-like endothelial cytoprotection and confer resistance to thromboinflammatory injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E982–E991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Antoniak, S. New Insights in the Pathology of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Basic Transl. Sci. 2024, 9, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, A.R.; Wolska, N.; Vara, D.; Mailer, R.K.; Schröder, K.; Pula, G. Diabetes and Thrombosis: A Central Role for Vascular Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Huang, N.K.; Lin, Y.C.; Chang, W.C.; Huang, W.C. Aspirin and Sulindac act via different mechanisms to inhibit store-operated calcium channel: Implications for colorectal cancer metastasis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, A.Y.; Hébert, R.L.; Nasrallah, R.; Langenbach, R.; Wong, C.K.C.; Wagner, G.F. Cyclooxygenase-2 mediates induction of the renal stanniocalcin-1 gene by arginine vasopressin. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 381, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.H.; Oh, J.Y. The Effect of miR-146a on the Gene Expression of Immunoregulatory Cytokines in Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, B.; Santhanam, S.; Azadian, M.; Swaminathan, V.; Lee, A.G.; McConnell, K.W.; Levinson, A.; Song, S.; Patel, J.J.; Gardner, E.E.; et al. Electrical modulation of transplanted stem cells improves functional recovery in a rodent model of stroke. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, D.; Walker, J.R.; Thompson, C.S.; Moroz, I.; Lin, W.; Veselits, M.L.; Hakim, A.M.; Fienberg, A.A.; Thinakaran, G. Characterization of Stanniocalcin 2, a Novel Target of the Mammalian Unfolded Protein Response with Cytoprotective Properties. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 9456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozpedek, W.; Pytel, D.; Mucha, B.; Leszczynska, H.; Diehl, J.A.; Majsterek, I. The Role of the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP Signaling Pathway in Tumor Progression During Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Curr. Mol. Med. 2016, 16, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, I.; Milevskiy, M.J.G.; Chalmers, S.B.; Yapa, K.T.D.S.; Robitaille, M.; Henry, C.; Baillie, G.J.; Thompson, E.W.; Roberts-Thomson, S.J.; Monteith, G.R. ORAI1 and ORAI3 in breast cancer molecular subtypes and the identification of ORAI3 as a hypoxia sensitive gene and a regulator of hypoxia responses. Cancers 2019, 11, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouras, T.; Southey, M.C.; Chang, A.C.; Reddel, R.R.; Willhite, D.; Glynne, R.; Henderson, M.A.; Armes, J.E.; Venter, D.J. Stanniocalcin 2 Is an Estrogen-responsive Gene Coexpressed with the Estrogen Receptor in Human Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar]
- Tozlu, S.; Girault, I.; Vacher, S.; Vendrell, J.; Andrieu, C.; Spyratos, F.; Cohen, P.; Lidereau, R.; Bieche, I. Identification of novel genes that co-cluster with estrogen receptor alpha in breast tumor biopsy specimens, using a large-scale real-time reverse transcription-PCR approach. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2006, 13, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferroni, P.; Basili, S.; Falco, A.; Davì, G. Platelet activation in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 2, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Xiao, L.; Liu, G.; Sun, L.; He, L. STC-1 ameliorates renal injury in diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting the expression of BNIP3 through the AMPK/SIRT3 pathway. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2019, 99, 684–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzka, A.M.; Schilling, B.; Cusack, M.P.; Sahu, A.K.; Drake, P.; Fisher, S.J.; Benz, C.C.; Gibson, B.W. Phosphoprotein secretome of tumor cells as a source of candidates for breast cancer biomarkers in plasma. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 1034–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londero, A.P.; Bertozzi, S.; Cedolini, C.; Neri, S.; Bulfoni, M.; Orsaria, M.; Mariuzzi, L.; Uzzau, A.; Risaliti, A.; Barillari, G. Incidence and Risk Factors for Venous Thromboembolism in Female Patients Undergoing Breast Surgery. Cancers 2022, 14, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinek, D.A.; Chang, A.C.; Larsen, M.R.; Wang, X.; Robinson, P.J.; Reddel, R.R. Stanniocalcin 1 and 2 are secreted as phosphoproteins from human fibrosarcoma cells. Biochem. J. 2000, 2, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.C.M.; Hook, J.; Lemckert, F.A.; McDonald, M.M.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; Hardeman, E.C.; Little, D.G.; Gunning, P.W.; Reddel, R.R. The murine stanniocalcin 2 gene is a negative regulator of postnatal growth. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 2403–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albarran, L.; Lopez, J.J.; Amor, N.B.; Martin-Cano, F.E.; Berna-Erro, A.; Smani, T.; Salido, G.M.; Rosado, J.A. Dynamic interaction of SARAF with STIM1 and Orai1 to modulate store-operated calcium entry. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palty, R.; Raveh, A.; Kaminsky, I.; Meller, R.; Reuveny, E. SARAF inactivates the store operated calcium entry machinery to prevent excess calcium refilling. Cell 2012, 149, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bermejo, N.; López, J.J.; Berna-Erro, A.; Fernández, E.; Corbacho, A.J.; Vázquez, M.T.; Granados, M.P.; Redondo, P.C. Stanniocalcin2, A Promising New Target for Identifying Patients with Stroke/Ictus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209999
Bermejo N, López JJ, Berna-Erro A, Fernández E, Corbacho AJ, Vázquez MT, Granados MP, Redondo PC. Stanniocalcin2, A Promising New Target for Identifying Patients with Stroke/Ictus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):9999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209999
Chicago/Turabian StyleBermejo, Nuria, José Javier López, Alejandro Berna-Erro, Esperanza Fernández, Antonio Jesús Corbacho, Maria Teresa Vázquez, Maria Purificación Granados, and Pedro Cosme Redondo. 2025. "Stanniocalcin2, A Promising New Target for Identifying Patients with Stroke/Ictus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 9999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209999
APA StyleBermejo, N., López, J. J., Berna-Erro, A., Fernández, E., Corbacho, A. J., Vázquez, M. T., Granados, M. P., & Redondo, P. C. (2025). Stanniocalcin2, A Promising New Target for Identifying Patients with Stroke/Ictus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 9999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209999






