Audiovestibular Dysfunction in Hyper-IgE Syndrome: A Systematic Review of Characteristics, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Registration
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
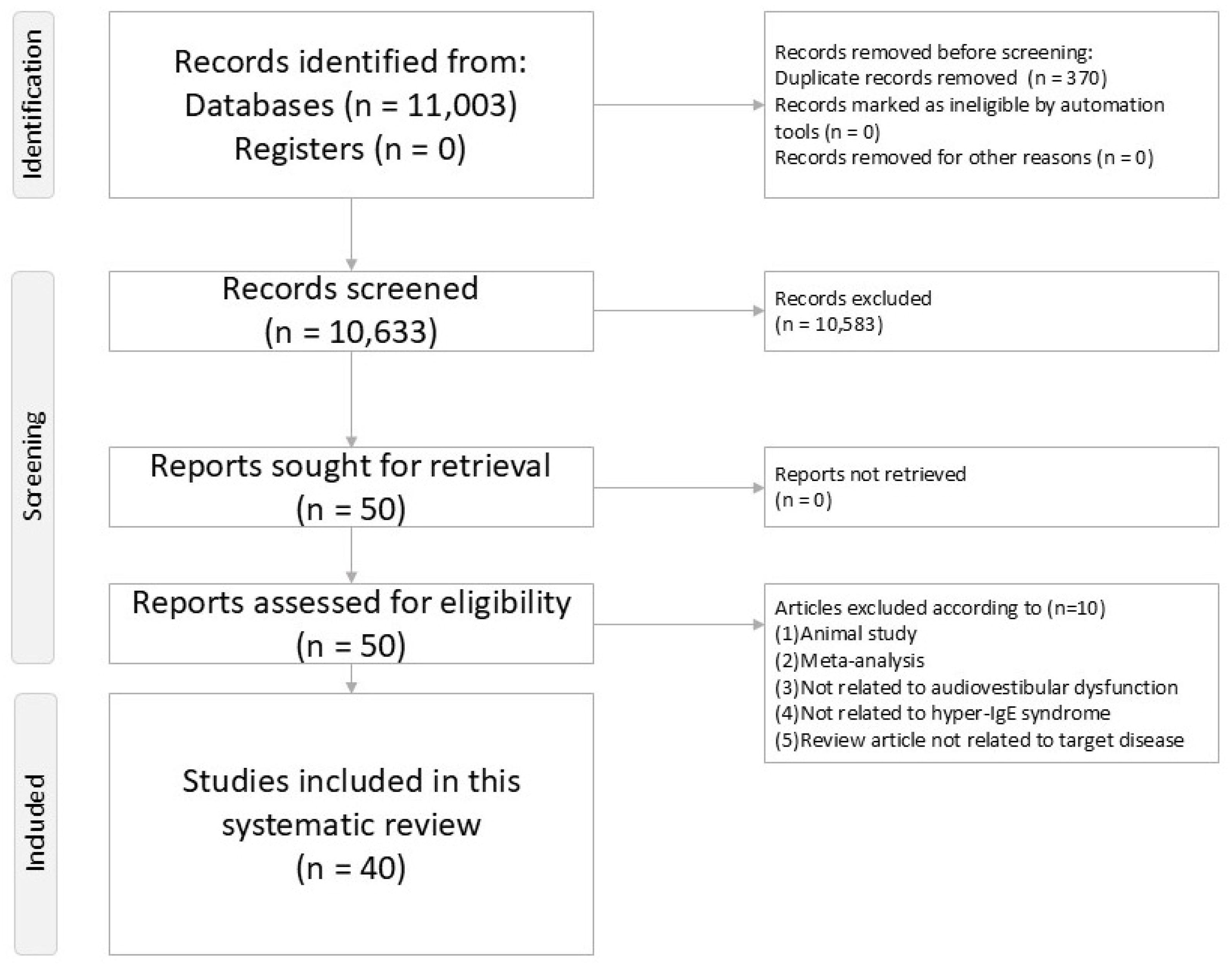
2.4. Screening and Selection
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Quality Assessment
2.7. Data Synthesis
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Characteristics and Epidemiology
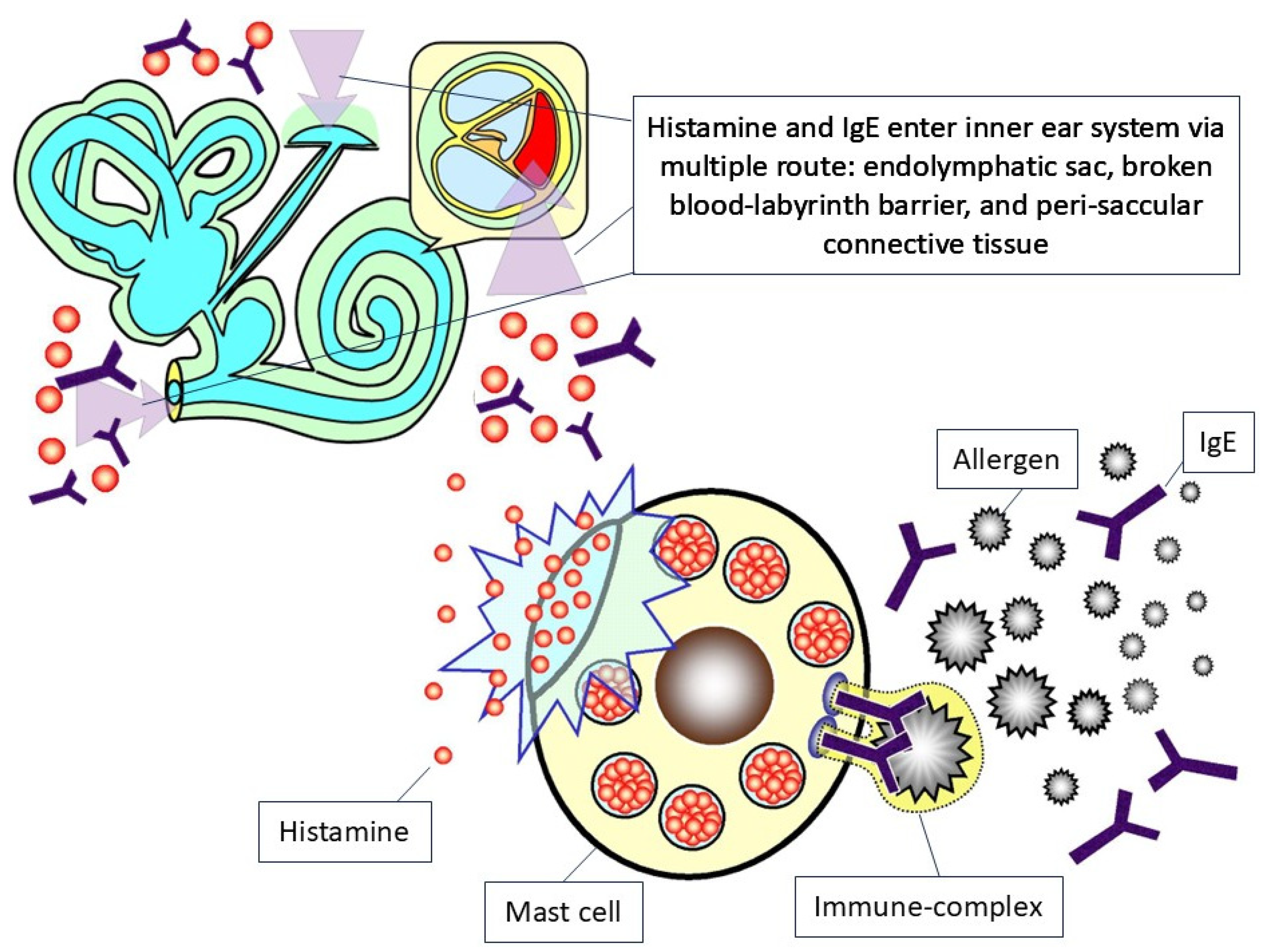
3.3. Pathophysiology
3.4. Diagnostic Approaches
3.5. Treatment
3.6. Prognosis
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Recommendations
4.2. Strengths and Limitations
4.3. Clinical Implications
4.4. Future Directions
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Freeman, A.F.; Holland, S.M. The hyper-IgE syndromes. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2008, 28, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.D.; Schaller, J.; Wedgwood, R.J. Job′s Syndrome. Recurrent, “cold”, staphylococcal abscesses. Lancet 1966, 1, 1013–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, R.H.; Wray, B.B.; Belmaker, E.Z. Extreme hyperimmunoglobulinemia E and undue susceptibility to infection. Pediatrics 1972, 49, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafsi, W.; Yarrarapu, S.N.S. Job Syndrome. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Salehi, M.; Neshati, Z.; Ahanchian, H.; Tafrishi, R.; Pasdar, A.; Safi, M.; Karimiani, E.G. Hyper IgE Syndromes: Understanding, Management, and Future Perspectives: A Narrative Review. Health Sci. Rep. 2025, 8, e70497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derebery, M.J.; Rao, V.S.; Siglock, T.J.; Linthicum, F.H.; Nelson, R.A. Meniere′s disease: An immune complex-mediated illness? Laryngoscope 1991, 101, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keles, E.; Sapmaz, E.; Godekmerdan, A. The role of allergy in the etiopathogenesis of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 270, 1795–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Lyu, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, J.; Song, Y.; Fan, Z.; Li, X.; Li, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, H. Bidirectional Transport of IgE by CD23 in the Inner Ear of Patients with Meniere′s Disease. J. Immunol. 2022, 208, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, P.T.; Chen, T.Y.; Lui, C.C.; Chen, Y.W.; Chen, J.J. Tinnitus Associated with Mild Osteomyelitis of the Temporal Bone Reversed after Conservative Antibiotic Treatment: A Case Series. Medicina 2022, 58, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, Y.W.; Chen, T.Y.; Zeng, B.Y.; Tseng, P.T. Audiovestibular Dysfunction Related to Anti-Phospholipid Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, Y.W.; Chen, T.Y.; Zeng, B.S.; Tseng, P.T. Audiovestibular Dysfunction in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, Y.W.; Chen, T.Y.; Zeng, B.S.; Tseng, P.T. Audiological Features in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, T.Y.; Liang, C.S.; Chen, Y.W.; Zeng, B.Y.; Tseng, P.T. Audiovestibular Dysfunction in Patients with Hashimoto′s Disease: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maihoub, S.; Mavrogeni, P.; Molnar, V.; Molnar, A. Tinnitus and Its Comorbidities: A Comprehensive Analysis of Their Relationships. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.; Georgalas, C.; Papesch, M. Co-morbidity of migraine and Meniere’s disease—Is allergy the link? J. Laryngol. Otol. 2005, 119, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minegishi, Y. Hyper-IgE syndrome, 2021 update. Allergol. Int. 2021, 70, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagli, M.; Goksu, N.; Eryilmaz, A.; Mocan Kuzey, G.; Bayazit, Y.; Gun, B.D.; Gocer, C. Expression of histamine receptors (H(1), H(2), and H(3)) in the rabbit endolymphatic sac: An immunohistochemical study. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2008, 29, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altermatt, H.J.; Gebbers, J.O.; Muller, C.; Arnold, W.; Laissue, J.A. Human endolymphatic sac: Evidence for a role in inner ear immune defence. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 1990, 52, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, S.R.; Mabry, R.L.; Roland, P.S.; Shoup, A.G.; Mabry, C.S. Electrocochleographic changes after intranasal allergen challenge: A possible diagnostic tool in patients with Meniere′s disease. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 1999, 121, 283–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toubi, E.; Ben-David, J.; Kessel, A.; Halas, K.; Sabo, E.; Luntz, M. Immune-mediated disorders associated with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2004, 113, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keles, E.; Godekmerdan, A.; Kalidag, T.; Kaygusuz, I.; Yalcin, S.; Cengiz Alpay, H.; Aral, M. Meniere′s disease and allergy: Allergens and cytokines. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2004, 118, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, K.; Bai, L.; Du, L. High level of IgE in acute low-tone sensorineural hearing loss: A predictor for recurrence and Meniere Disease transformation. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2021, 42, 102856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruckenstein, M.J. Immunologic aspects of Meniere′s disease. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 1999, 20, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahni, D.; Verma, P.; Bhagat, S.; Sharma, V. Hearing Assessment in Patients of Allergic Rhinitis: A Study on 200 Subjects. Indian. J. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2022, 74, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derebery, M.J.; Berliner, K.I. Prevalence of allergy in Meniere′s disease. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2000, 123, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasisi, A.O.; Abdullahi, M. The inner ear in patients with nasal allergy. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2008, 100, 903–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derebery, M.J. Allergic management of Meniere′s disease: An outcome study. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2000, 122, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O′Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. Available online: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 12 June 2024).
- Grimbacher, B.; Schaffer, A.A.; Holland, S.M.; Davis, J.; Gallin, J.I.; Malech, H.L.; Atkinson, T.P.; Belohradsky, B.H.; Buckley, R.H.; Cossu, F.; et al. Genetic linkage of hyper-IgE syndrome to chromosome 4. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1999, 65, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, T.; Tashrifwala, F.A.A.; Rangwala, U.S.; Hameed, R. Hyper-IgE syndrome: A case report. Ann. Med. Surg. (Lond.) 2024, 86, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, H.; Mohebbi, M.; Mehravaran, S.; Mazloumi, M.; Jahanbani-Ardakani, H.; Abtahi, S.H. Hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome: Genetics, immunopathogenesis, clinical findings, and treatment modalities. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2017, 22, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlYafie, R.; Velayutham, D.; van Panhuys, N.; Jithesh, P.V. The genetics of hyper IgE syndromes. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1516068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutanto, H.; Adytia, G.J.; Fetarayani, D. Hyper IgE Syndrome: Bridging the Gap Between Immunodeficiency, Atopy, and Allergic Diseases. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2025, 25, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaakoubi, R.; Mekki, N.; Ben-Mustapha, I.; Ben-Khemis, L.; Bouaziz, A.; Ben Fraj, I.; Ammar, J.; Hamzaoui, A.; Turki, H.; Boussofara, L.; et al. Diagnostic challenge in a series of eleven patients with hyper IgE syndromes. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1057679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachover-Roth, I.; Lagovsky, I.; Shtorch-Asor, A.; Confino-Cohen, R.; Reinstein, E.; Garty, B.Z. Hyper IgE Syndrome in an Isolated Population in Israel. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 829239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakol, M.; Sharafian, S.; Salari, F.; Shokri, S. A Review on Hyper-IgE Syndromes, Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis and Therapeutic Approaches. Immunol. Genet. J. 2019, 2, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, R.; Kakaje, A. Hyper IgE syndrome (Job syndrome) in Syria: A case report. Oxf. Med. Case Rep. 2020, 2020, omaa106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.Y.; Iyer, V.N.; Boyce, T.G.; Hagan, J.B.; Park, M.A.; Abraham, R.S. Elevated serum immunoglobulin E (IgE): When to suspect hyper-IgE syndrome-A 10-year pediatric tertiary care center experience. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2009, 30, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, A.F.; Holland, S.M. Clinical manifestations, etiology, and pathogenesis of the hyper-IgE syndromes. Pediatr. Res. 2009, 65, 32R–37R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, A.; Yoshino, H.; Yuasa, T. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy in a patient with hyperIgEaemia. J. Neurol. Sci. 2005, 231, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, E.D.; Puck, J.M.; Holland, S.M.; Schmitt, M.; Weiss, M.; Frosch, M.; Bergmann, M.; Davis, J.; Belohradsky, B.H.; Grimbacher, B. Autosomal recessive hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome: A distinct disease entity. J. Pediatr. 2004, 144, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, S.M.; DeLeo, F.R.; Elloumi, H.Z.; Hsu, A.P.; Uzel, G.; Brodsky, N.; Freeman, A.F.; Demidowich, A.; Davis, J.; Turner, M.L.; et al. STAT3 mutations in the hyper-IgE syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1608–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilifis, C.; Freeman, A.F.; Gennery, A.R. STAT3 Hyper-IgE Syndrome-an Update and Unanswered Questions. J. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 41, 864–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilzadeh, M.; Soleymani, A.A.; Mozafar, S.; Tariverdi, N.; Fatemi, S.A.; Khosrozamiri, M. Hyper IgE (Job′s) Syndrome: A Primary Immune Deficiency with Oral Manifestations. J. Dent. Sch. 2024, 42, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharehzadehshirazi, A.; Amini, A.; Rezaei, N. Hyper IgE syndromes: A clinical approach. Clin. Immunol. (Orlando Fla.) 2022, 237, 108988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, J.; Ma, L. Oral ulcerations in a patient with autosomal dominant hyper-IgE syndrome (AD-HIES). BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e236705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Mandal, A.; Seth, R. Hyper IgE syndrome: Often a missed diagnosis. Int. J. Contemp. Pediatr. 2016, 3, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.; Roman, J.; Latasa, M.; Oehling, A. Perforation of the nasal wall and hyper-IgE syndrome. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 1993, 3, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Knight, J.M.; Li, Y.D.; Ashoori, F.; Citardi, M.J.; Yao, W.C.; Corry, D.B.; Luong, A.U. Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis linked to other hyper-IgE syndromes through defective T(H)17 responses. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 154, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, K.M., Jr.; Tomita, S.; Caliman e Gurgel, J.D. Association between nasal polyposis, Dubowitz syndrome and hyper-IgE syndrome. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2008, 72, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponsford, M.J.; Klocperk, A.; Pulvirenti, F.; Dalm, V.; Milota, T.; Cinetto, F.; Chovancova, Z.; Rial, M.J.; Sediva, A.; Litzman, J.; et al. Hyper-IgE in the allergy clinic--when is it primary immunodeficiency? Allergy 2018, 73, 2122–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moin, M.; Farhoudi, A.; Movahedi, M.; Rezaei, N.; Pourpak, Z.; Yeganeh, M.; Gharagozlou, M.; Mirsaeid Ghazi, B.; Arshi, S.; Mansouri, D.; et al. The clinical and laboratory survey of Iranian patients with hyper-IgE syndrome. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 38, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devilliers, H.; Turcu, A.; Vernier, N.; Muller, G.; Bielefeld, P.; Bonniaud, P.; Besancenot, J.F. Hyper-IgE in internal medicine. Rev. Med. Interne 2018, 39, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Song, M.; Cai, S.; Luo, H.; OuYang, R.; Yang, P.; Shi, X.; Long, Y.; Chen, Y. Omalizumab for STAT3 Hyper-IgE Syndromes in Adulthood: A Case Report and Literature Review. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2022, 9, 835257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilora, F.; Petrobelli, F.; Boccioletti, V.; Pomerri, F. Moderate-dose intravenous immunoglobulin treatment of Job′s syndrome. Case report. Minerva Med. 2000, 91, 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- DeWitt, C.A.; Bishop, A.B.; Buescher, L.S.; Stone, S.P. Hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome: Two cases and a review of the literature. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 54, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, A.P.; Davis, J.; Puck, J.M.; Holland, S.M.; Freeman, A.F. STAT3 Hyper IgE Syndrome. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Chandesris, M.O.; Melki, I.; Natividad, A.; Puel, A.; Fieschi, C.; Yun, L.; Thumerelle, C.; Oksenhendler, E.; Boutboul, D.; Thomas, C.; et al. Autosomal dominant STAT3 deficiency and hyper-IgE syndrome: Molecular, cellular, and clinical features from a French national survey. Medicine 2012, 91, e1–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goussetis, E.; Peristeri, I.; Kitra, V.; Traeger-Synodinos, J.; Theodosaki, M.; Psarra, K.; Kanariou, M.; Tzortzatou-Stathopoulou, F.; Petrakou, E.; Fylaktou, I.; et al. Successful long-term immunologic reconstitution by allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation cures patients with autosomal dominant hyper-IgE syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 392–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.C.; Gallagher, J.L.; Torgerson, T.R.; Gilman, A.L. Successful haploidentical donor hematopoietic stem cell transplant and restoration of STAT3 function in an adolescent with autosomal dominant hyper-IgE syndrome. J. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 35, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagimachi, M.; Ohya, T.; Yokosuka, T.; Kajiwara, R.; Tanaka, F.; Goto, H.; Takashima, T.; Morio, T.; Yokota, S. The Potential and Limits of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for the Treatment of Autosomal Dominant Hyper-IgE Syndrome. J. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 36, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purkait, R.; Kar, S.; Bhadra, R.; Sinhamahapatra, T. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis: An uncommon presentation of hyper IgE syndrome. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. JCPSP 2014, 24 (Suppl. 3), S256–S258. [Google Scholar]
- Milner, J.D.; Sandler, N.G.; Douek, D.C. Th17 cells, Job′s syndrome and HIV: Opportunities for bacterial and fungal infections. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2010, 5, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, A.F.; Kleiner, D.E.; Nadiminti, H.; Davis, J.; Quezado, M.; Anderson, V.; Puck, J.M.; Holland, S.M. Causes of death in hyper-IgE syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 119, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uno, K.; Miyamura, K.; Kanzaki, Y.; Fukuda, H.; Masuyama, K.; Ishikawa, T. Type I allergy in the inner ear of the guinea pig. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. Suppl. 1992, 157, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadre, A.K.; Fayad, J.N.; O′Leary, M.J.; Zakhary, R.; Linthicum, F.H., Jr. Arterial supply of the human endolymphatic duct and sac. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 1993, 108, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, S.; Nakamura, M.; Katoh, H.; Miyao, T.; Shimazaki, T.; Ishii, K.; Yamane, J.; Yoshimura, A.; Iwamoto, Y.; Toyama, Y.; et al. Conditional ablation of Stat3 or Socs3 discloses a dual role for reactive astrocytes after spinal cord injury. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derebery, M.J. Allergic and immunologic aspects of Meniere′s disease. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 1996, 114, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseli, C.; Gibson, W. A comparison of three methods of using transtympanic electrocochleography for the diagnosis of Meniere′s disease: Click summating potential measurements, tone burst summating potential amplitude measurements, and biasing of the summating potential using a low frequency tone. Acta Otolaryngol. 2010, 130, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, G.W.; Lee, K.Y. Blood eosinophils and serum IgE as predictors for prognosis of interferon-gamma therapy in atopic dermatitis. Allergy 1998, 53, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsberger, M.; Porsbjerg, C.; Yde, J.; Aanæs, K. Effects on hearing and tinnitus following Dupilumab treatment of severe asthma with chronic rhinosinusitis—A case report. Rhinol. Online 2021, 4, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitre, E.; Nutman, T.B. IgE memory: Persistence of antigen-specific IgE responses years after treatment of human filarial infections. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 117, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuruvilla, M.; de la Morena, M.T. Antibiotic prophylaxis in primary immune deficiency disorders. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2013, 1, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemis, J.D. Allergic cochleovestibular disturbances. Trans. Am. Acad. Ophthalmol. Otolaryngol. 1972, 76, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar]
- Roomiani, M.; Dehghani Firouzabadi, F.; Delbandi, A.A.; Ghalehbaghi, B.; Daneshi, A.; Yazdani, N.; Fazeli Delshad, B.; Asghari, A. Evaluation of Serum Immunoreactivity to Common Indigenous Iranian Inhalation and Food Allergens in Patients with Meniere′s Disease. Immunol. Investig. 2022, 51, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Nagarkar, A.N.; Bansal, S.; Vir, D.; Gupta, A.K. Audiological manifestations of allergic rhinitis. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2011, 125, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Manhas, M.; Kalsotra, P.; Kalsotra, G.; Gul, N. A Prospective Study of Audiological Manifestations in Patients of Allergic Rhinitis. Indian. J. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2022, 74, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabulut, H.; Acar, B.; Dagli, M.; Karadag, A.S.; Baysal, S.; Karasen, R.M. Investigation of hearing in patients with allergic rhinitis. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011, 10, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Howard, B.K.; Mabry, R.L.; Meyerhoff, W.L.; Mabry, C.S. Use of a screening RAST in a large neuro-otologic practice. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 1997, 117, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupinek, C.; Derfler, K.; Lee, S.; Prikoszovich, T.; Movadat, O.; Wollmann, E.; Cornelius, C.; Weber, M.; Froschl, R.; Selb, R.; et al. Extracorporeal IgE Immunoadsorption in Allergic Asthma: Safety and Efficacy. EBioMedicine 2017, 17, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.M.; Cabanski, C.R.; Scheerens, H.; Samineni, D.; Bradley, M.S.; Cochran, C.; Staubach, P.; Metz, M.; Sussman, G.; Maurer, M. A randomized trial of quilizumab in adults with refractory chronic spontaneous urticaria. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1730–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, A.; Maihoub, S.; Tamas, L.; Szirmai, A. Intratympanically administered steroid for progressive sensorineural hearing loss in Meniere′s disease. Acta Otolaryngol. 2019, 139, 982–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klokman, V.W.; Koningstein, F.N.; Dors, J.W.W.; Sanders, M.S.; Koning, S.W.; de Kleijn, D.P.V.; Jie, K.E. Blood biomarkers for the differentiation between central and peripheral vertigo in the emergency department: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2024, 31, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, F. Upadacitinib for Treatment of Hyper-IgE Syndrome. JAMA Dermatol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.J.; Yu, G.H.; Park, J.H. Hypereosinophilic syndrome presenting with bilateral ear fullness. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2019, 136, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, B.; Domarecka, E.; Kong, L.; Olze, H.; Scheffel, J.; Monino-Romero, S.; Siebenhaar, F.; Szczepek, A.J. A systematic review of the clinical evidence for an association between type I hypersensitivity and inner ear disorders. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1378276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.-J.; Hsu, C.-W.; Stubbs, B.; Chen, T.-Y.; Liang, C.-S.; Chen, Y.-W.; Zeng, B.-Y.; Tseng, P.-T. Audiovestibular Dysfunction in Hyper-IgE Syndrome: A Systematic Review of Characteristics, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209932
Chen J-J, Hsu C-W, Stubbs B, Chen T-Y, Liang C-S, Chen Y-W, Zeng B-Y, Tseng P-T. Audiovestibular Dysfunction in Hyper-IgE Syndrome: A Systematic Review of Characteristics, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):9932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209932
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jiann-Jy, Chih-Wei Hsu, Brendon Stubbs, Tien-Yu Chen, Chih-Sung Liang, Yen-Wen Chen, Bing-Yan Zeng, and Ping-Tao Tseng. 2025. "Audiovestibular Dysfunction in Hyper-IgE Syndrome: A Systematic Review of Characteristics, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 9932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209932
APA StyleChen, J.-J., Hsu, C.-W., Stubbs, B., Chen, T.-Y., Liang, C.-S., Chen, Y.-W., Zeng, B.-Y., & Tseng, P.-T. (2025). Audiovestibular Dysfunction in Hyper-IgE Syndrome: A Systematic Review of Characteristics, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 9932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209932





