Molecular Signature in Focal Cortical Dysplasia: A Systematic Review of RNA and Protein Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Design
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
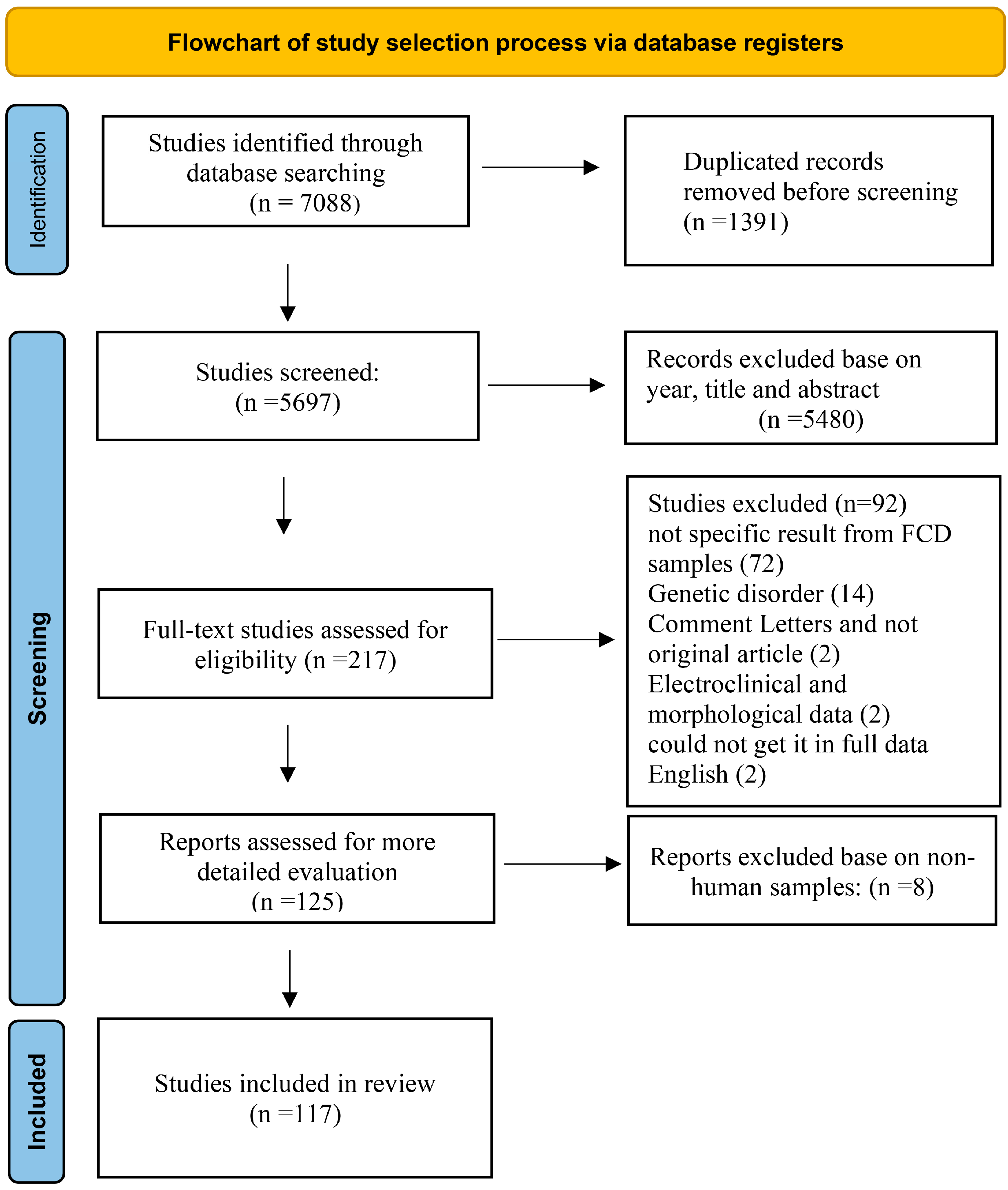
2.3. Study Selection Workflow
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Statistical and Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Overview of Reviewed Studies Across FCD Subtypes
3.2. Human-Specific Dysregulated miRNAs in FCD
3.3. Dysregulated RNA Expression in Human FCD
3.4. Protein-Level Alterations in FCD Subtypes
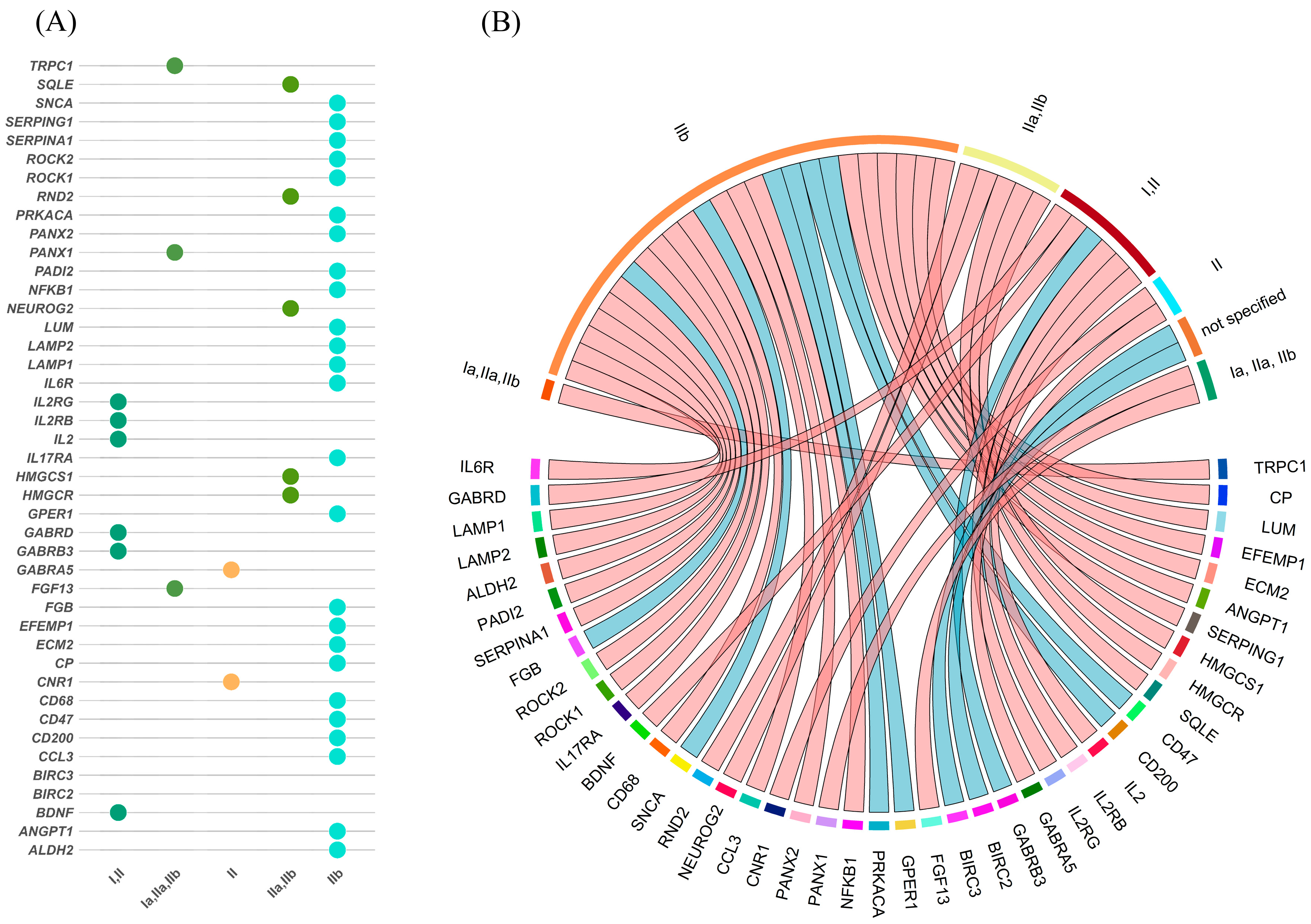
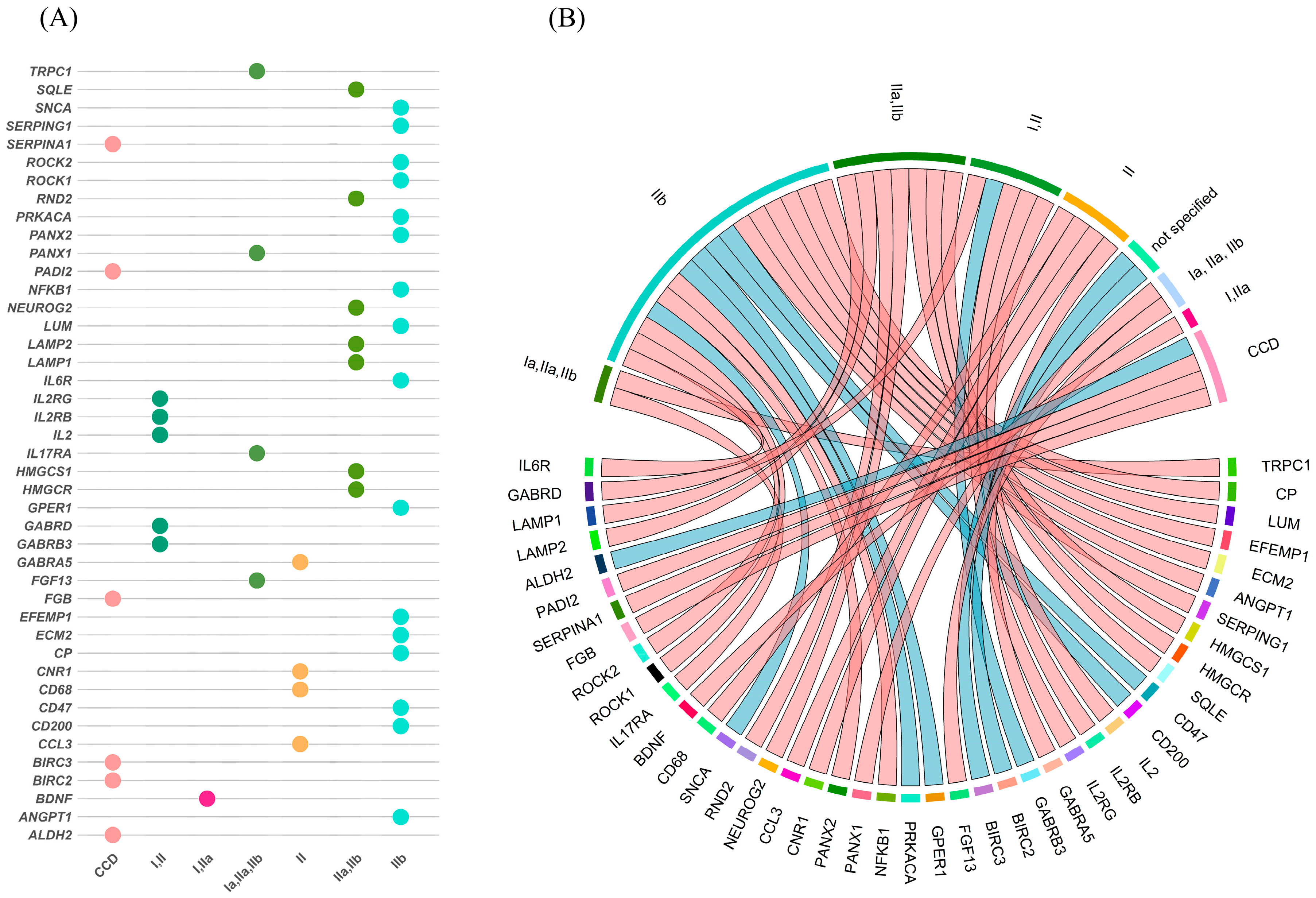
3.5. Overlap Between mRNA and Protein Expression Across FCD Subtypes
3.6. Subtype-Specific Molecular Profiles
4. Discussion
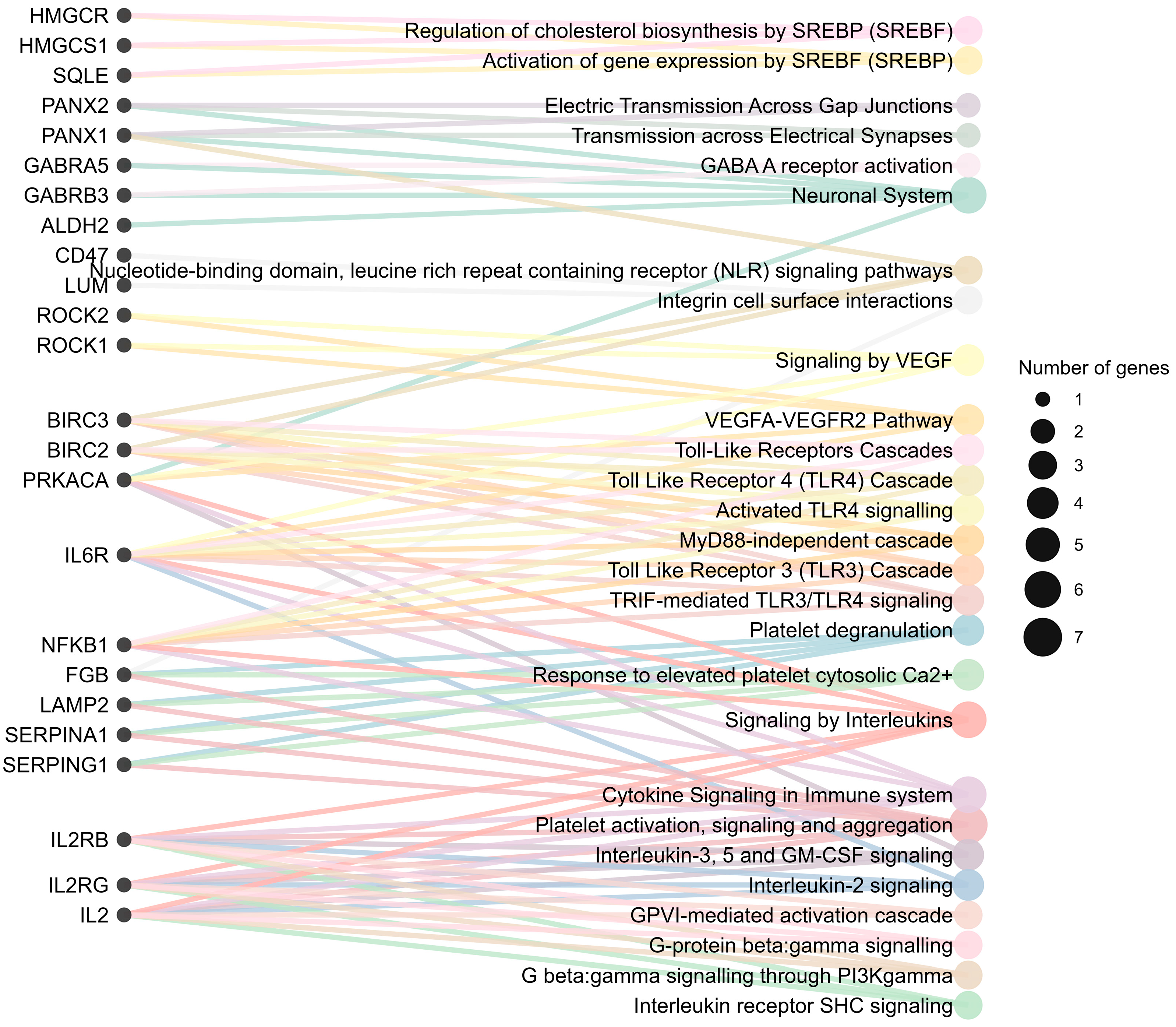
4.1. Molecular Pathways Enriched in FCD
4.1.1. Inflammation and Immune-Mediated Mechanisms
4.1.2. Neuronal and Synaptic Dysfunction
4.1.3. Cytoskeletal Remodeling and Cell Migration
4.1.4. Metabolic Dysregulation
4.2. Crosstalk Between Inflammation, Metabolism, and mTOR in FCD
4.2.1. Inflammatory Pathways and mTOR Activation
4.2.2. Neuronal Signaling and Synaptic Dysfunction
4.2.3. Extracellular Matrix and Angiogenesis
4.3. Integration of miRNA–Target Interactions in FCD
4.4. Clinical Implications
4.5. FCD Type-Specific Insights
4.6. Age-Related Molecular Heterogeneity in FCD
4.7. Region- and Compartment-Related Molecular Heterogeneity in FCD
4.8. Integration with Recent Single-Cell and Spatial Transcriptomic Studies
4.9. Limitations
4.9.1. Biological and Methodological Heterogeneity
4.9.2. Variability in Sample Type and Preservation
4.9.3. Publication Bias and Incomplete Reporting
4.9.4. Reliance on Histopathological Diagnosis
5. Conclusions
State of the Field and Future Research and Recommendations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FCD | Focal cortical dysplasia |
| CCD | Childhood cortical dysplasia |
| ILAE | International League Against Epilepsy |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| PROSPERO | International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews |
| iPSCs | Induced pluripotent stem cells |
| mTOR | Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| Akt | Protein kinase B |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| RNA-Seq | RNA sequencing |
| PCR | Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| RT-PCR | real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| WB | Western blot |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| LC–MS/MS | liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| ISH | In situ hybridization |
| DL-IF | Double-label immunofluorescence |
| iTRAQ | Multiplexed Isobaric Tagging Technology for Relative Quantitation |
| HGNC | HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee |
| UniProtKB | Universal Protein Knowledgebase |
| gProfiler | Gene Enrichment Profiler |
| MOGHE | mild malformation of cortical development with oligodendroglial hyperplasia in epilepsy |
| LITT | laser interstitial thermal therapy |
| SEEG-RFTC | stereo-EEG-guided radiofrequency thermocoagulation |
| EEG | electroencephalography |
References
- Kasper, B.S. Taylor’s Focal Cortical Dysplasia Revisited: History, Original Specimens and Impact. Free Neuropathol. 2021, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellock, J.M.; Hrachovy, R.; Shinnar, S.; Baram, T.Z.; Bettis, D.; Dlugos, D.J.; Gaillard, W.D.; Gibson, P.A.; Holmes, G.L.; Nordli, D.R.; et al. Infantile Spasms: A U.S. Consensus Report. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 2175–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najm, I.; Lal, D.; Alonso Vanegas, M.; Cendes, F.; Lopes-Cendes, I.; Palmini, A.; Paglioli, E.; Sarnat, H.B.; Walsh, C.A.; Wiebe, S.; et al. The ILAE Consensus Classification of Focal Cortical Dysplasia: An Update Proposed by an Ad Hoc Task Force of the ILAE Diagnostic Methods Commission. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 1899–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veersema, T.J.; Ferrier, C.H.; van Eijsden, P.; Gosselaar, P.H.; Aronica, E.; Visser, F.; Zwanenburg, J.M.; de Kort, G.A.P.; Hendrikse, J.; Luijten, P.R.; et al. Seven Tesla MRI Improves Detection of Focal Cortical Dysplasia in Patients with Refractory Focal Epilepsy. Epilepsia Open 2017, 2, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosa, A.N.V.; Gupta, A. Outcome after Epilepsy Surgery for Cortical Dysplasia in Children. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2014, 30, 1905–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral, T.; Von Lehe, M.; Podlogar, M.; Clusmann, H.; Süßmann, P.; Kurthen, M.; Becker, A.; Urbach, H.; Schramm, J. Focal Cortical Dysplasia: Long Term Seizure Outcome after Surgical Treatment. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, G.L.; Streetman, D.R.; Fricker, J.G.; Bui, N.E.; Yang, C.; Patel, N.A.; Brown, N.J.; Shahrestani, S.; Rangel, I.C.; Singh, R.; et al. Focal Cortical Dysplasia as a Cause of Epilepsy: The Current Evidence of Associated Genes and Future Therapeutic Treatments. Interdiscip. Neurosurg. 2022, 30, 101635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; François, R.; Henry, L.; Müller, K.; Vaughan, D. dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation. R package version 1.1.4. 2025. Available online: https://dplyr.tidyverse.org (accessed on 6 October 2025).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruford, E.A.; Braschi, B.; Denny, P.; Jones, T.E.M.; Seal, R.L.; Tweedie, S. HGNC: The Worldwide Authority on Human Gene Nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D945–D951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consortium, T.U. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res 2023, 51, D523–D530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, G.; Rosen, N.; Plaschkes, I.; Zimmerman, S.; Twik, M.; Fishilevich, S.; Nudel, R.; Iny-Stein, T.; Rappaport, N.; Mituyama, T.; et al. The GeneCards Suite: From Gene Data Mining to Disease Genome Sequence Analyses. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 54, 1.30.1–1.30.33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolberg, L.; Raudvere, U.; Kuzmin, I.; Vilo, J.; Peterson, H. Gprofiler2: An R Package for Gene List Functional Enrichment Analysis and Namespace Conversion Toolset g:Profiler. F1000Research 2020, 9, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, Y.; Kechris, K.J.; Tabakoff, B.; Hoffman, P.; Radcliffe, R.A.; Bowler, R.; Mahaffey, S.; Rossi, S.; Calin, G.A. The MultiMiR R Package and Database: Integration of MicroRNA–Target Interactions along with Their Disease and Drug Associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, e133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.Y.; Tan, C.M.; Kou, Y.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Meirelles, G.V.; Clark, N.R.; Ma’ayan, A. Enrichr: Interactive and Collaborative HTML5 Gene List Enrichment Analysis Tool. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. [Google Scholar]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An Information Aesthetic for Comparative Genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, N.; Zu, G.; Zhou, T.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Tan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Luo, X.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Aberrant Expression of MiR-323a-5p in Patients with Refractory Epilepsy Caused by Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2017, 21, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Tan, Z.; Che, N.; Ji, A.; Luo, X.; Sun, X.; Li, X.; Yang, K.; Wang, G.; et al. Serum MicroRNA-4521 Is a Potential Biomarker for Focal Cortical Dysplasia with Refractory Epilepsy. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avansini, S.H.; Torres, F.R.; Vieira, A.S.; Dogini, D.B.; Rogerio, F.; Coan, A.C.; Morita, M.E.; Guerreiro, M.M.; Yasuda, C.L.; Secolin, R.; et al. Dysregulation of NEUROG2 Plays a Key Role in Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Park, A.K.; Lee, E.S.; Park, W.Y.; Park, S.H.; Choi, J.W.; Phi, J.H.; Wang, K.C.; Kim, S.K. MiRNA Expression Analysis in Cortical Dysplasia: Regulation of MTOR and LIS1 Pathway. Epilepsy Res. 2014, 108, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, C.Q.; Li, T.F.; Guan, Y.G.; Zhou, J.; Qi, X.L.; Yang, Y.T.; Deng, J.H.; Xu, Z.Q.D.; Luan, G.M. Analysis of Altered Micro RNA Expression Profiles in Focal Cortical Dysplasia IIB. J. Child Neurol. 2016, 31, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, A.; Zurolo, E.; Prabowo, A.; Fluiter, K.; Spliet, W.G.M.; van Rijen, P.C.; Gorter, J.A.; Aronica, E. MicroRNA-146a: A Key Regulator of Astrocyte-Mediated Inflammatory Response. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.; Dixit, A.B.; Paul, D.; Tripathi, M.; Sarkar, C.; Chandra, P.S.; Banerjee, J. Comparative Analysis of Cytokine/Chemokine Regulatory Networks in Patients with Hippocampal Sclerosis (HS) and Focal Cortical Dysplasia (FCD). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.D.; Pan, H.Y.; Huang, J.B.; Liu, X.P.; Li, J.H.; Ho, C.J.; Tsai, M.H.; Yang, J.L.; Chen, S.F.; Chen, N.C.; et al. Circulating Micrornas from Serum Exosomes May Serve as a Putative Biomarker in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Cells 2020, 9, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurolo, E.; Iyer, A.; Maroso, M.; Carbonell, C.; Anink, J.J.; Ravizza, T.; Fluiter, K.; Spliet, W.G.M.; Van Rijen, P.C.; Vezzani, A.; et al. Activation of Toll-like Receptor, RAGE and HMGB1 Signalling in Malformations of Cortical Development. Brain 2011, 134, 1015–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinowic, D.R.; Majolo, F.; Zanirati, G.G.; Plentz, I.; Neto, E.P.; Palmini, A.L.F.; Machado, D.C.; Da Costa, J.C. Analysis of Genes Involved in Cell Proliferation, Adhesion, and Control of Apoptosis during Embryonic Neurogenesis in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (IPSCs) from Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 155, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, T.S.; Ciriminna, G.; Arena, A.; Anink, J.J.; Korotkov, A.; Jansen, F.E.; van Hecke, W.; Spliet, W.G.; van Rijen, P.C.; Baayen, J.C.; et al. Chronic Activation of Anti-Oxidant Pathways and Iron Accumulation in Epileptogenic Malformations. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2020, 46, 546–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Rincón, D.; Díaz-Alonso, J.; Paraíso-Luna, J.; Ortega, Z.; Aguareles, J.; De Salas-Quiroga, A.; Jou, C.; De Prada, I.; Martínez-Cerdeño, V.; Aronica, E.; et al. Contribution of Altered Endocannabinoid System to Overactive MTORC1 Signaling in Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Tripathi, M.; Doddamani, R.; Sharma, M.C.; Lalwani, S.; Sarat Chandra, P.; Banerjee Dixit, A.; Banerjee, J. Correlation of Age at Seizure Onset with GABAA Receptor Subunit and Chloride Co-Transporter Configuration in Focal Cortical Dysplasia (FCD). Neurosci. Lett. 2023, 796, 137065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Chen, X.; He, J.J.; Wei, Y.J.; Zang, Z.L.; Liu, S.Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, C.Q. Down-Regulated Expression of Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1a in Cortical Lesions of Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 53, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, K.; Yang, X.; Shen, K.; Yang, L.; Ruan, R.; Shi, X.; Wang, M.; Zhu, G.; Yang, M.; et al. Downregulated GPR30 Expression in the Epileptogenic Foci of Female Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type IIb and Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Is Correlated with 18F-FDG PET-CT Values. Brain Pathol. 2021, 31, 346–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.J.; Zhang, C.Q.; Chen, X.; Wei, Y.J.; Li, S.; Liu, S.Y.; Zang, Z.L.; He, J.J.; Guo, W.; Yang, H. Downregulation of CD47 and CD200 in Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type IIb and Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Zheng, D.; Shu, H.; Guo, W.; Zhao, B.; Shen, K.; Wei, Y.J.; et al. Expression Patterns of TRPC1 in Cortical Lesions from Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 57, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Zheng, D.-H.; Sun, F.-J.; Yang, J.-Y.; Zang, Z.-L.; Liu, S.-Y.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, C.-Q.; Yang, H. Expression and Cellular Distribution of the Interleukin 2 Signaling System in Cortical Lesions From Patients With Focal Cortical Dysplasia. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 73, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.H.; Guo, W.; Sun, F.J.; Xu, G.Z.; Zang, Z.L.; Shu, H.F.; Yang, H. Expression of TRPC6 and BDNF in Cortical Lesions from Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 75, 718–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zang, Z.; He, J.; Chen, X.; Yu, S.; Pei, Y.; Hou, Z.; An, N.; Yang, H.; Zhang, C.; et al. Expression of Pannexin 1 and 2 in Cortical Lesions from Intractable Epilepsy Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 6883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Dai, L.; Zhu, G.; Yang, X.L.; He, Z.; Li, Y.H.; Yang, H.; Zhang, C.Q.; Shen, K.F.; et al. Expression Profiles of α-Synuclein in Cortical Lesions of Patients with FCD IIb and TSC, and FCD Rats. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1255097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.J.; Guo, W.; Sun, F.J.; Fu, W.L.; Zheng, D.H.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Zang, Z.L.; Zhang, C.Q.; Liu, S.Y.; et al. Increased Expression and Cellular Localization of P2X7R in Cortical Lesions of Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 75, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Yue, J.; Shen, K.; He, J.; Zhu, G.; Liu, S.; Zhang, C.; Yang, H. Increased Expression of Fibroblast Growth Factor 13 in Cortical Lesions of the Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Brain Res. Bull. 2021, 168, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Dixit, A.B.; Dey, S.; Tripathi, M.; Doddamani, R.; Sharma, M.C.; Lalwani, S.; Gurjar, H.K.; Chandra, P.S.; Banerjee, J. Increased Levels of A4-Containing GABAA Receptors in Focal Cortical Dysplasia: A Possible Cause of Benzodiazepine Resistance. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 148, 105084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Liu, M.; Wang, H.; Dong, Y.; Ji, T.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Cai, L.; Wu, Y. Upregulation of HMGB1-TLR4 Inflammatory Pathway in Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type II. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baybis, M.; Yu, J.; Lee, A.; Golden, J.A.; Weiner, H.; McKhann, G.; Aronica, E.; Crino, P.B. MTOR Cascade Activation Distinguishes Tubers from Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 56, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmer, T.S.; Broekaart, D.W.M.; Luinenburg, M.; Mijnsbergen, C.; Anink, J.J.; Sim, N.S.; Michailidou, I.; Jansen, F.E.; van Rijen, P.C.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Balloon Cells Promote Immune System Activation in Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type 2b. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2021, 47, 826–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.F.; Scerif, F.; Picker, S.R.; Stone, T.J.; Pickles, J.C.; Moulding, D.A.; Avery, A.; Virasami, A.; Fairchild, A.R.; Tisdall, M.; et al. Identifying Cellular Signalling Molecules in Developmental Disorders of the Brain: Evidence from Focal Cortical Dysplasia and Tuberous Sclerosis. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2021, 47, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, I.C.; Kandratavicius, L.; Messias, L.A.; Athié, M.C.P.; Assis-Mendonça, G.R.; Alvim, M.K.M.; Ghizoni, E.; Tedeschi, H.; Yasuda, C.L.; Cendes, F.; et al. Identifying Cellular Markers of Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type II with Cell-Type Deconvolution and Single-Cell Signatures. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchin, M.M.; Haas, C.A.; Sarnat, H.B.; Rogerio, F.; Mcp, A.; Jvg, T.; Ad, S.; PAORdA, A.; Mkm, A. Transcriptome Analyses of the Cortex and White Matter of Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type II: Insights into Pathophysiology and Tissue Characterization. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1023950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfano, V.; Romagnolo, A.; Mills, J.D.; Cifelli, P.; Gaeta, A.; Morano, A.; Mühlebner, A.; Aronica, E.; Palma, E.; Ruffolo, G. Unexpected Effect of IL-1β on the Function of GABAA Receptors in Pediatric Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungberg, M.C.; Bhattacharjee, M.B.; Lu, Y.; Armstrong, D.L.; Yoshor, D.; Swann, J.W.; Sheldon, M.; D’Arcangelo, G. Activation of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin in Cytomegalic Neurons of Human Cortical Dysplasia. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 60, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu-Okabe, C.; Tanaka, M.; Matsuda, K.; Mihara, T.; Okabe, A.; Sato, K.; Inoue, Y.; Fujiwara, T.; Yagi, K.; Fukuda, A. KCC2 Was Downregulated in Small Neurons Localized in Epileptogenic Human Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Epilepsy Res. 2011, 93, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, S.; Saito, T.; Nakagawa, E.; Arai, A.; Otsuki, T.; Sasaki, M.; Goto, Y.i.; Itoh, M. Abnormal Maturation of Non-Dysmorphic Neurons in Focal Cortical Dysplasia: Immunohistochemical Considerations. Seizure 2010, 19, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Yun-Lin, L.; Yong-Ling, L.; Wei-Wei, Z.; Yue-Shan, P. Alteration of GABAergic Neurons and Abnormality of NKCC1/KCC2 in Focal Cortical Dysplasia (FCD) Type Ⅱ Lesions. Epilepsy Res. 2023, 194, 107180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munakata, M.; Watanabe, M.; Otsuki, T.; Nakama, H.; Arima, K.; Itoh, M.; Nabekura, J.; Iinuma, K.; Tsuchiya, S. Altered Distribution of KCC2 in Cortical Dysplasia in Patients with Intractable Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2007, 48, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, M.; Martinian, L.; Sen, A.; Squier, W.; Harding, B.N.; Cross, J.H.; Harkness, W.; Mcevoy, A.; Sisodiya, S.M. An Investigation of the Expression of G 1-Phase Cell Cycle Proteins in Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type IIB. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 66, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchukhidze, G.; Wieselthaler-Hölzl, A.; Drexel, M.; Unterberger, I.; Luef, G.; Ortler, M.; Becker, A.J.; Trinka, E.; Sperk, G. Calcium-Binding Proteins in Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, A.; Prabowo, A.; Anink, J.; Spliet, W.G.M.; Van Rijen, P.C.; Aronica, E. Cell Injury and Premature Neurodegeneration in Focal Malformations of Cortical Development. Brain Pathol. 2014, 24, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, K.; Duan, Z.; Zhou, J.; Li, L.; Zhai, F.; Dong, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, Z.; Bian, Y.; Qi, X.; et al. Clinical and Immunohistochemical Characteristics of Type II and Type I Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 76415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knerlich-Lukoschus, F.; Connolly, M.B.; Hendson, G.; Steinbok, P.; Dunham, C. Clinical, Imaging, and Immunohistochemical Characteristics of Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type II Extratemporal Epilepsies in Children: Analyses of an Institutional Case Series. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2017, 19, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamecnik, J.; Krsek, P.; Druga, R.; Marusic, P.; Benes, V.; Tichy, M.; Komarek, V. Densities of Parvalbumin-Immunoreactive Neurons in Non-Malformed Hippocampal Sclerosis-Temporal Neocortex and in Cortical Dysplasias. Brain Res. Bull. 2006, 68, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamparello, P.; Baybis, M.; Pollard, J.; Hol, E.M.; Eisenstat, D.D.; Aronica, E.; Crino, P.B. Developmental Lineage of Cell Types in Cortical Dysplasia with Balloon Cells. Brain 2007, 130, 2267–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medici, V.; Rossini, L.; Deleo, F.; Tringali, G.; Tassi, L.; Cardinale, F.; Bramerio, M.; de Curtis, M.; Garbelli, R.; Spreafico, R. Different Parvalbumin and GABA Expression in Human Epileptogenic Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Epilepsia 2016, 57, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Zhang, C.Q.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.K.; Yue, J.; An, N.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.Y.; Yang, H. Differential Expression Hallmarks of Interneurons in Different Types of Focal Cortical Dysplasia. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 70, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Scheppingen, J.; Broekaart, D.W.M.; Scholl, T.; Zuidberg, M.R.J.; Anink, J.J.; Spliet, W.G.; van Rijen, P.C.; Czech, T.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Feucht, M.; et al. Dysregulation of the (Immuno)Proteasome Pathway in Malformations of Cortical Development. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.K.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.Q.; Liang, C.; Wei, Y.J.; Yue, J.; Liu, S.Y.; Yang, H. Elevated Expression of TRPC4 in Cortical Lesions of Focal Cortical Dysplasia II and Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 62, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, A.; Zurolo, E.; Spliet, W.G.M.; Van Rijen, P.C.; Baayen, J.C.; Gorter, J.A.; Aronica, E. Evaluation of the Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Type i and Type II Focal Cortical Dysplasias. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 1763–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronica, E.; Gorter, J.A.; Jansen, G.H.; Van Veelen, C.W.M.; Van Rijen, P.C.; Ramkema, M.; Troost, D. Expression and Cell Distribution of Group I and Group II Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Subtypes in Taylor-Type Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Epilepsia 2003, 44, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ak, H.; Ay, B.; Tanriverdi, T.; Sanus, G.Z.; Is, M.; Sar, M.; Oz, B.; Ozkara, C.; Ozyurt, E.; Uzan, M. Expression and Cellular Distribution of Multidrug Resistance-Related Proteins in Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Seizure 2007, 16, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitovskaya, D.; Zabrodskaya, Y.; Parshakov, P.; Sokolova, T.; Kudlay, D.; Starshinova, A.; Samochernykh, K. Expression of Cytoskeletal Proteins (GFAP, Vimentin), Proapoptotic Protein (Caspase-3) and Protective Protein (S100) in the Epileptic Focus in Adults and Children with Drug-Resistant Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Associated with Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.; Tilelli, C.; Bingaman, W.; Najm, I. Expression of Neural Stem Cell Surface Marker CD133 in Balloon Cells of Human Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 1716–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlain, W.A.; Prayson, R.A. Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type II (Malformations of Cortical Development) Aberrantly Expresses Apoptotic Proteins. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2008, 16, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.W.; Reeves, C.; van der Pijl, R.; Thom, M. Glial Regenerative Cell Types in the Superficial Cortex in Cortical Dysplasia Subtypes. Epilepsy Res. 2021, 169, 106529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.W.; Min, B.W.; Kim, Y.; Jeong, E.H.; Park, C.S.; Woo, Y.J.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, M.C. Immunohistochemical Analysis of Developmental Neural Antigen Expression in the Balloon Cells of Focal Cortical Dysplasia. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 18, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, K.; Middeldorp, J.; Spliet, W.G.M.; Razavi, F.; van Rijen, P.C.; Baayen, J.C.; Hol, E.M.; Aronica, E. Immunohistochemical Characterization of the Out-of Frame Splice Variants GFAP Δ164/Δexon 6 in Focal Lesions Associated with Chronic Epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2010, 90, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, C.; Miyata, H.; Ueda, M.; Ohama, E.; Vinters, H.V.; Ohno, K. Immunohistochemical Expression of Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF)-2 in Epilepsy-Associated Malformations of Cortical Development (MCDs). Neuropathology 2008, 28, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, M.; Sugiura, C.; Ohno, K.; Kakita, A.; Hori, A.; Ohama, E.; Vinters, H.V.; Miyata, H. Immunohistochemical Expression of Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 in Developing Human Cerebrum and Epilepsy-Associated Malformations of Cortical Development. Neuropathology 2011, 31, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, H.; Chiang, A.C.Y.; Vinters, H.V. Insulin Signaling Pathways in Cortical Dysplasia and TSC-Tubers: Tissue Microarray Analysis. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 56, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, J.M.; Rousset, O.G.; Guiot, M.C.; Hall, J.A.; Reader, A.J.; Soucy, J.P.; Rosa-Neto, P.; Kobayashi, E. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Type 5 (MGluR5) Cortical Abnormalities in Focal Cortical Dysplasia Identified in Vivo with [11C]ABP688 Positron-Emission Tomography (PET) Imaging. Cereb. Cortex 2016, 26, 4170–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crino, P.B. Molecular Pathogenesis of Focal Cortical Dysplasia and Hemimegalencephaly. J. Child. Neurol. 2005, 20, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, L.; Garbelli, R.; Gnatkovsky, V.; Didato, G.; Villani, F.; Spreafico, R.; Deleo, F.; Lo Russo, G.; Tringali, G.; Gozzo, F.; et al. Seizure Activity per Se Does Not Induce Tissue Damage Markers in Human Neocortical Focal Epilepsy. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjivassiliou, G.; Martinian, L.; Squier, W.; Blumcke, I.; Aronica, E.; Sisodiya, S.M.; Thom, M. The Application of Cortical Layer Markers in the Evaluation of Cortical Dysplasias in Epilepsy. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 120, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulu, M.O.; Tanriverdi, T.; Oz, B.; Biceroglu, H.; Isler, C.; Eraslan, B.S.; Ozkara, C.; Ozyurt, E.; Uzan, M. The Expression of Astroglial Glutamate Transporters in Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia: An Immunohistochemical Study. Acta Neurochir. 2010, 152, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, P.J.; Sater, R.; French, J.; Baltuch, G.; Crino, P.B. Transcription of Intermediate Filament Genes Is Enhanced in Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Acta Neuropathol. 2001, 102, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, K.; Sharma, M.C.; Kakkar, A.; Malgulwar, P.B.; Pathak, P.; Suri, V.; Sarkar, C.; Chandra, S.P.; Faruq, M. MTOR Pathway Activation in Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2020, 46, 151523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Gao, Q.; Tang, C.; Deng, J.; Xiong, Z.; Kong, X.; Guan, Y.; et al. Aberrant Adenosine Signaling in Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 4396–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Deng, J.; Liu, C.; Luo, H.; Guan, Y.; Zhou, J.; Qi, X.; Li, T.; Xu, Z.D.; Luan, G.-M. Altered Expression of Neuropeptide Y Receptors Caused by Focal Cortical Dysplasia in Human Intractable Epilepsy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 15329–15338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talos, D.M.; Sun, H.; Kosaras, B.; Joseph, A.; Folkerth, R.D.; Poduri, A.; Madsen, J.R.; Black, P.M.; Jensen, F.E. Altered Inhibition in Tuberous Sclerosis and Type IIb Cortical Dysplasia. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, K.; Troost, D.; Spliet, W.G.M.; Van Rijen, P.C.; Gorter, J.A.; Aronica, E. Cellular Distribution of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A (VEGFA) and B (VEGFB) and VEGF Receptors 1 and 2 in Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type IIB. Acta Neuropathol. 2008, 115, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Lin, Y.; Kang, D.; Chen, F.; Lin, K.; Su, X. Distribution and Expression of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, Nerve Growth Factor, and Neurotrophic Factor-3 in Refractory Epilepsyassociated Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Clin. Neuropathol. 2017, 36, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, K.; Lucassen, P.J.; Spliet, W.G.M.; Vreugdenhil, E.; van Rijen, P.C.; Troost, D.; Jansen, F.E.; Aronica, E. Doublecortin-like (DCL) Expression in Focal Cortical Dysplasia and Cortical Tubers. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 2629–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, B.; Yue, J.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Yang, H. Down-Regulated Expression of Liver X Receptor Beta in Cortical Lesions of Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 60, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronica, E.; Boer, K.; Doorn, K.J.; Zurolo, E.; Spliet, W.G.M.; van Rijen, P.C.; Baayen, J.C.; Gorter, J.A.; Jeromin, A. Expression and Localization of Voltage Dependent Potassium Channel Kv4.2 in Epilepsy Associated Focal Lesions. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 36, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.Q.; An, N.; Liu, S.Y.; Zheng, D.H.; Yang, H. Expression of TRPC3 in Cortical Lesions from Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 724, 134880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.-F.; Zhang, C.-Q.; Yin, Q.; An, N.; Liu, S.-Y.; Yang, H. Expression of the Interleukin 6 System in Cortical Lesions From Patients with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex and Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type IIb. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 69, 838–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.-X.; Li, S.; Shu, H.-F.; Zhang, C.-Q.; Liu, S.-Y.; Yang, H. Expression of the Nogo-A System in Cortical Lesions of Pediatric Patients with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex and Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type IIb. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 71, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toering, S.T.; Boer, K.; De Groot, M.; Troost, D.; Heimans, J.J.; Spliet, W.G.M.; Van Rijen, P.C.; Jansen, F.E.; Gorter, J.A.; Reijneveld, J.C.; et al. Expression Patterns of Synaptic Vesicle Protein 2A in Focal Cortical Dysplasia and TSC-Cortical Tubers. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, T.; Teaw, S.; Nguyen, L.H.; Hsieh, L.S.; Gong, X.; Burns, L.H.; Bordey, A. Filamin A Inhibition Reduces Seizure Activity in a Mouse Model of Focal Cortical Malformations. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaay0289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, Z.; Najm, I.; Nemes, A.; Pinheiro-Martins, A.P.; Alexopoulos, A.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.; Bingaman, W. Growth-Associated Protein 43 and Progressive Epilepsy in Cortical Dysplasia. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2014, 1, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Lai, H.; Cheng, L.; Li, D.; Yu, T.; Yan, X.; Xu, C.; et al. Imbalance between the Function of Na+-K+-2Cl and K+-Cl Impairs Cl− Homeostasis in Human Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 954167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholl, T.; Mühlebner, A.; Ricken, G.; Gruber, V.; Fabing, A.; Samueli, S.; Gröppel, G.; Dorfer, C.; Czech, T.; Hainfellner, J.A.; et al. Impaired Oligodendroglial Turnover Is Associated with Myelin Pathology in Focal Cortical Dysplasia and Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. Brain Pathol. 2017, 27, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, F.J.; Wei, Y.J.; Wang, L.K.; Zang, Z.L.; Chen, B.; Li, S.; Liu, S.Y.; Yang, H. Increased Expression of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4 in Cortical Lesions of Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2016, 22, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, V.E.; Luinenburg, M.J.; Colleselli, K.; Endmayr, V.; Anink, J.J.; Zimmer, T.S.; Jansen, F.; Gosselaar, P.; Coras, R.; Scholl, T.; et al. Increased Expression of Complement Components in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex and Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type 2B Brain Lesions. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finardi, A.; Colciaghi, F.; Castana, L.; Locatelli, D.; Marras, C.E.; Nobili, P.; Fratelli, M.; Bramerio, M.A.; Lorusso, G.; Battaglia, G.S. Long-Duration Epilepsy Affects Cell Morphology and Glutamatergic Synapses in Type IIB Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 126, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konopka, A.; Grajkowska, W.; Ziemiańska, K.; Roszkowski, M.; Daszkiewicz, P.; Rysz, A.; Marchel, A.; Koperski, Ł.; Wilczyński, G.M.; Dzwonek, J. Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in Human Intractable Epilepsy Caused by Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Epilepsy Res. 2013, 104, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Li, Y.; Lv, Y.Y.; Jiang, L. Screening and Identification of Novel Candidate Biomarkers of Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type II via Bioinformatics Analysis. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2022, 38, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, S.A.; Ali, A.M.; Tata, M.; Picker, S.R.; Anderson, G.W.; Latimer-Bowman, E.; Nicholson, S.L.; Harkness, W.; Cross, J.H.; Paine, S.M.L.; et al. MTOR-Dependent Abnormalities in Autophagy Characterize Human Malformations of Cortical Development: Evidence from Focal Cortical Dysplasia and Tuberous Sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 126, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Zhang, C.; Shi, X.; Wei, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, S.; Yang, H. Activation of Leukocyte Immunoglobulin-like Receptor B2 Signaling Pathway in Cortical Lesions of Pediatric Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type IIb and Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. Brain Dev. 2019, 41, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, G.; Gao, Q.; Zhai, F.; Zhou, J.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, T. Adenosine Kinase Expression in Cortical Dysplasia with Balloon Cells: Analysis of Developmental Lineage of Cell Types. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 74, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Aronica, E.; Boer, K.; Fällmar, D.; Kumlien, E.; Nistér, M.; Wester, K.; Pontén, F.; Smits, A. DLG3/SAP102 Protein Expression in Malformations of Cortical Development: A Study of Human Epileptic Cortex by Tissue Microarray. Epilepsy Res. 2009, 84, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srikandarajah, N.; Martinian, L.; Sisodiya, S.M.; Squier, W.; Blumcke, I.; Aronica, E.; Thom, M. Doublecortin Expression in Focal Cortical Dysplasia in Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 2619–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, H.F.; Yu, S.X.; Zhang, C.Q.; Liu, S.Y.; Wu, K.F.; Zang, Z.L.; Yang, H.; Zhou, S.W.; Yin, Q. Expression of TRPV1 in Cortical Lesions from Patients with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex and Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type IIb. Brain Dev. 2013, 35, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, C.Q.; Shu, H.F.; Yang, M.H.; Yin, Q.; Yang, H. Expression of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-4 in the Cortical Lesions of Focal Cortical Dysplasia IIb and the Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 50, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Yu, S.; Zhang, C.; Shu, H.; Liu, S.; An, N.; Yang, M.; Yin, Q.; Yang, H. Increased Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 in Cortical Lesions from Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type IIb and Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. Brain Res. 2012, 1453, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbelli, R.; de Bock, F.; Medici, V.; Rousset, M.C.; Villani, F.; Boussadia, B.; Arango-Lievano, M.; Jeanneteau, F.; Daneman, R.; Bartolomei, F.; et al. PDGFRβ+ Cells in Human and Experimental Neuro-Vascular Dysplasia and Seizures. Neuroscience 2015, 306, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.-J.; Li, S.; Shu, H.-F.; Yu, S.-X.; Liu, S.-Y.; Yin, Q.; Yang, H. The Interleukin 17 System in Cortical Lesions in Focal Cortical Dysplasias. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 72, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honke, J.; Hoffmann, L.; Coras, R.; Kobow, K.; Leu, C.; Pieper, T.; Hartlieb, T.; Bien, C.G.; Woermann, F.; Cloppenborg, T.; et al. Deep Histopathology Genotype–Phenotype Analysis of Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type II Differentiates between the GATOR1-Altered Autophagocytic Subtype IIa and MTOR-Altered Migration Deficient Subtype IIb. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2023, 11, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, L.; De Santis, D.; Cecchini, E.; Cagnoli, C.; Maderna, E.; Cartelli, D.; Morgan, B.P.; Torvell, M.; Spreafico, R.; di Giacomo, R.; et al. Dendritic Spine Loss in Epileptogenic Type II Focal Cortical Dysplasia: Role of Enhanced Classical Complement Pathway Activation. Brain Pathol. 2023, 33, e13141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, L. Differentially Expressed Proteins Underlying Childhood Cortical Dysplasia with Epilepsy Identified by ITRAQ Proteomic Profiling. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Martínez, J.A.; Ying, Z.; Prayson, R.; Bingaman, W.; Najm, I. Glutamate Clearance Mechanisms in Resected Cortical Dysplasia: Laboratory Investigation. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 114, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Nie, Q.; Li, F. Lamotrigine Decreases MRP8 and IL-7 in Rat Modelsof Intractable Epilepsy Secondary to Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 3694–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.S.; Lee, M.C.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, M.K.; Woo, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.I.; Kim, S.U. Pathophysiologic Characteristics of Balloon Cells in Cortical Dysplasia. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2008, 24, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marucci, G.; Martinoni, M.; Giulioni, M. Relationship between Focal Cortical Dysplasia and Epilepsy-Associated Low-Grade Tumors: An Immunohistochemical Study. APMIS 2013, 121, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-ΚB Signaling in Inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik, C.D.; Kim, N.D.; Alekseeva, E.; Luster, A.D. Il-17ra Signaling Amplifies Antibody-Induced Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.W.; Farooq, M.; Hwang, M.J.; Haseeb, M.; Choi, S. Autoimmune Neuroinflammatory Diseases: Role of Interleukins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.M.; Wynshaw-Boris, A. Cytoskeleton in Action: Lissencephaly, a Neuronal Migration Disorder. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2013, 2, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, T. Cholesterol Lowering: Role in Cancer Prevention and Treatment. Biol. Chem. 2015, 396, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinno, J.; Bongartz, H.; Klepsch, O.; Wundrack, N.; Poli, V.; Schaper, F.; Dittrich, A. Interleukin-6 Influences Stress-Signalling by Reducing the Expression of the MTOR-Inhibitor REDD1 in a STAT3-Dependent Manner. Cell. Signal. 2016, 28, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M. Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (MTOR) Activation in Focal Cortical Dysplasia and Related Focal Cortical Malformations. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 244, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Chapman, N.M.; Karmaus, P.W.F.; Zeng, H.; Chi, H. MTOR and Metabolic Regulation of Conventional and Regulatory T Cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 97, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, A.M.; Evangelisti, C.; Chiarini, F.; Grimaldi, C.; Cappellini, A.; Ognibene, A.; McCubrey, J.A. The Emerging Role of the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Signaling Network in Normal Myelopoiesis and Leukemogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2010, 1803, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopeikina, E.; Dukhinova, M.; Yung, A.W.Y.; Veremeyko, T.; Kuznetsova, I.S.; Lau, T.Y.B.; Levchuk, K.; Ponomarev, E.D. Platelets Promote Epileptic Seizures by Modulating Brain Serotonin Level, Enhancing Neuronal Electric Activity, and Contributing to Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress. Prog. Neurobiol. 2020, 188, 101783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schüle, M.; Butto, T.; Dewi, S.; Schlichtholz, L.; Strand, S.; Gerber, S.; Endres, K.; Schweiger, S.; Winter, J. Mtor Driven Gene Transcription Is Required for Cholesterol Production in Neurons of the Developing Cerebral Cortex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iffland, P.H.; Crino, P.B. Focal Cortical Dysplasia: Gene Mutations, Cell Signaling, and Therapeutic Implications. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2017, 12, 547–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedi, M.; Berkovic, S.F.; Macdonell, R.A.L.; Curatolo, J.M.; Marini, C.; Reutens, D.C. Intracortical Hyperexcitability in Humans with a GABAA Receptor Mutation. Cereb. Cortex 2008, 18, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsan, E.; Baulac, S. Review: Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin (MTOR) Pathway, Focal Cortical Dysplasia and Epilepsy. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2018, 44, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcher, C.; Medina, I.; Gaiarsa, J.L. Mechanism of BDNF Modulation in GABAergic Synaptic Transmission in Healthy and Disease Brains. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, S.L.; Lugo, J.N. Therapeutic Role of Targeting MTOR Signaling and Neuroinflammation in Epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2020, 161, 106282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaldirim, M.; Lang, A.; Pfeiler, S.; Fiegenbaum, P.; Kelm, M.; Bönner, F.; Gerdes, N. Modulation of MTOR Signaling in Cardiovascular Disease to Target Acute and Chronic Inflammation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 907348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeganeh, B.; Wiechec, E.; Ande, S.R.; Sharma, P.; Moghadam, A.R.; Post, M.; Freed, D.H.; Hashemi, M.; Shojaei, S.; Zeki, A.A.; et al. Targeting the Mevalonate Cascade as a New Therapeutic Approach in Heart Disease, Cancer and Pulmonary Disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 143, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson-Farley, N.N.; Patel, K.; Kim, D.; Cowen, D.S. Interaction of FGF-2 with IGF-1 and BDNF in Stimulating Akt, ERK, and Neuronal Survival in Hippocampal Cultures. Brain Res. 2007, 1154, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravizza, T.; Boer, K.; Redeker, S.; Spliet, W.G.M.; van Rijen, P.C.; Troost, D.; Vezzani, A.; Aronica, E. The IL-1β System in Epilepsy-Associated Malformations of Cortical Development. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006, 24, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, F.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Niu, J.; Wang, L.; He, Y.; Etxeberria, A.; Chan, J.R.; Xiao, L. Stage-Specific Deletion of Olig2 Conveys Opposing Functions on Differentiation and Maturation of Oligodendrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 8454–8462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansom, S.N.; Griffiths, D.S.; Faedo, A.; Kleinjan, D.J.; Ruan, Y.; Smith, J.; Van Heyningen, V.; Rubenstein, J.L.; Livesey, F.J. The Level of the Transcription Factor Pax6 Is Essential for Controlling the Balance between Neural Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Neurogenesis. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvão, I.C.; Lemoine, M.; Messias, L.A.; Araújo, P.A.O.R.A.; Geraldis, J.C.; Yasuda, C.L.; Alvim, M.K.M.; Ghizoni, E.; Tedeschi, H.; Cendes, F.; et al. Multimodal Single-Cell Profiling Reveals Neuronal Vulnerability and Pathological Cell States in Focal Cortical Dysplasia. iScience 2024, 27, 111337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldassari, S.; Klingler, E.; Teijeiro, L.G.; Doladilhe, M.; Raoux, C.; Roig-Puiggros, S.; Bizzotto, S.; Couturier, J.; Gilbert, A.; Sami, L.; et al. Single-Cell Genotyping and Transcriptomic Profiling of Mosaic Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Nat. Neurosci. 2025, 28, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzotto, S.; Talukdar, M.; Stronge, E.A.; Ramirez, R.B.; Yang, Y.; Huang, A.Y.; Hu, Q.; Hou, Y.; Hylton, N.K.; Finander, B.; et al. Cell-Type-Informed Genotyping of Mosaic Focal Epilepsies Reveals Cell-Autonomous and Non-Cell-Autonomous Disease-Associated Transcriptional Programs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2025, 122, e2509622122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, L.; Shen, C.; Fu, Y.; Wei, P.; Shan, Y.; Wu, Q.; Piao, Y.S.; Zhao, G. Spatial Transcriptomics in Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type IIb. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2024, 12, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Lei, L.; Yu, J.; Tan, H.; Sui, L.; Guo, Q.; Zhou, L. Excitatory Neurons and Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells Are Vulnerable to Focal Cortical Dysplasia Type IIIa as Suggested by Single-nucleus Multiomics. Clin. Transl. Med. 2024, 14, e70072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Sun, L.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, M.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Transcriptomic and Morphologic Vascular Aberrations Underlying FCDIIb Etiology. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



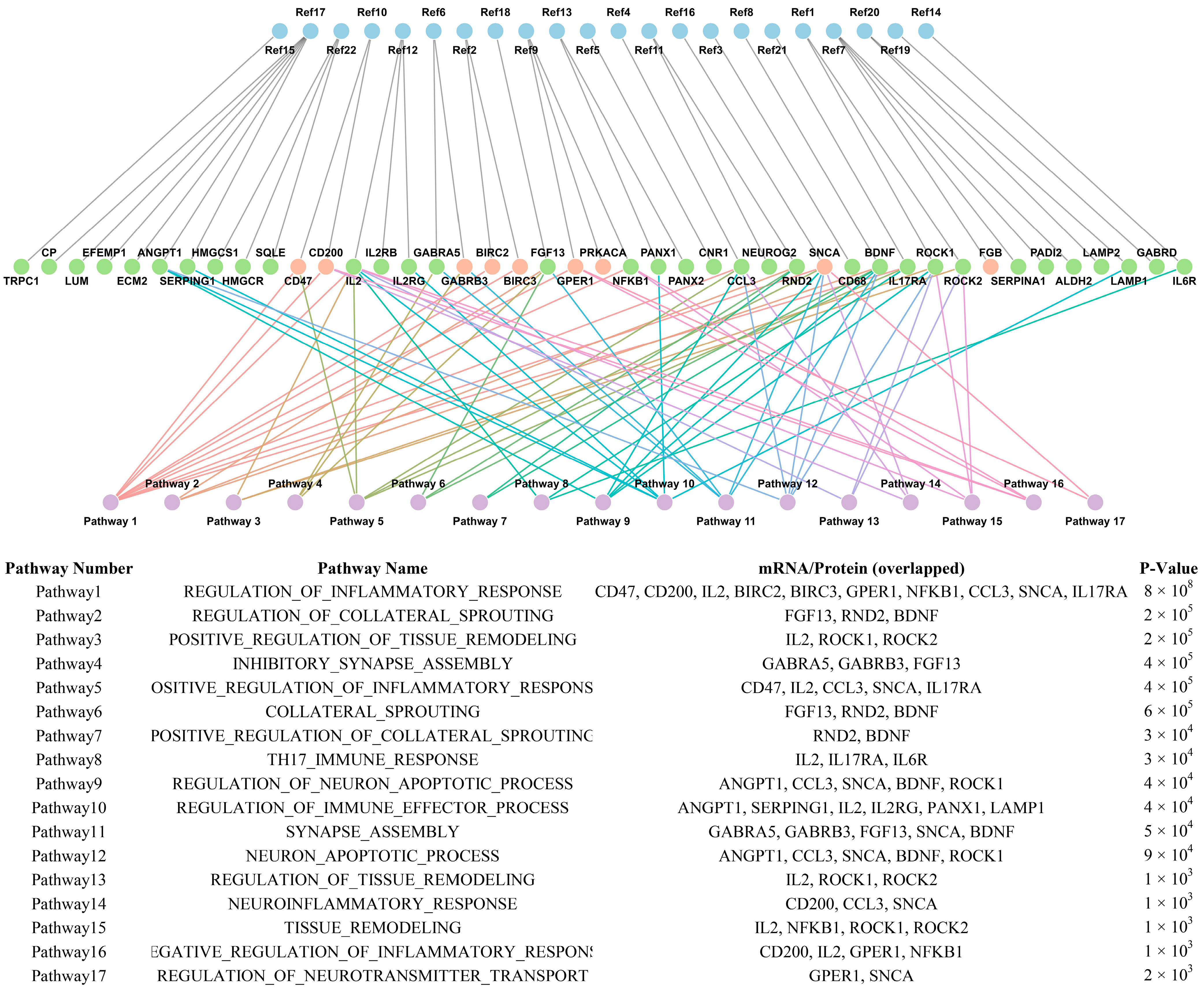
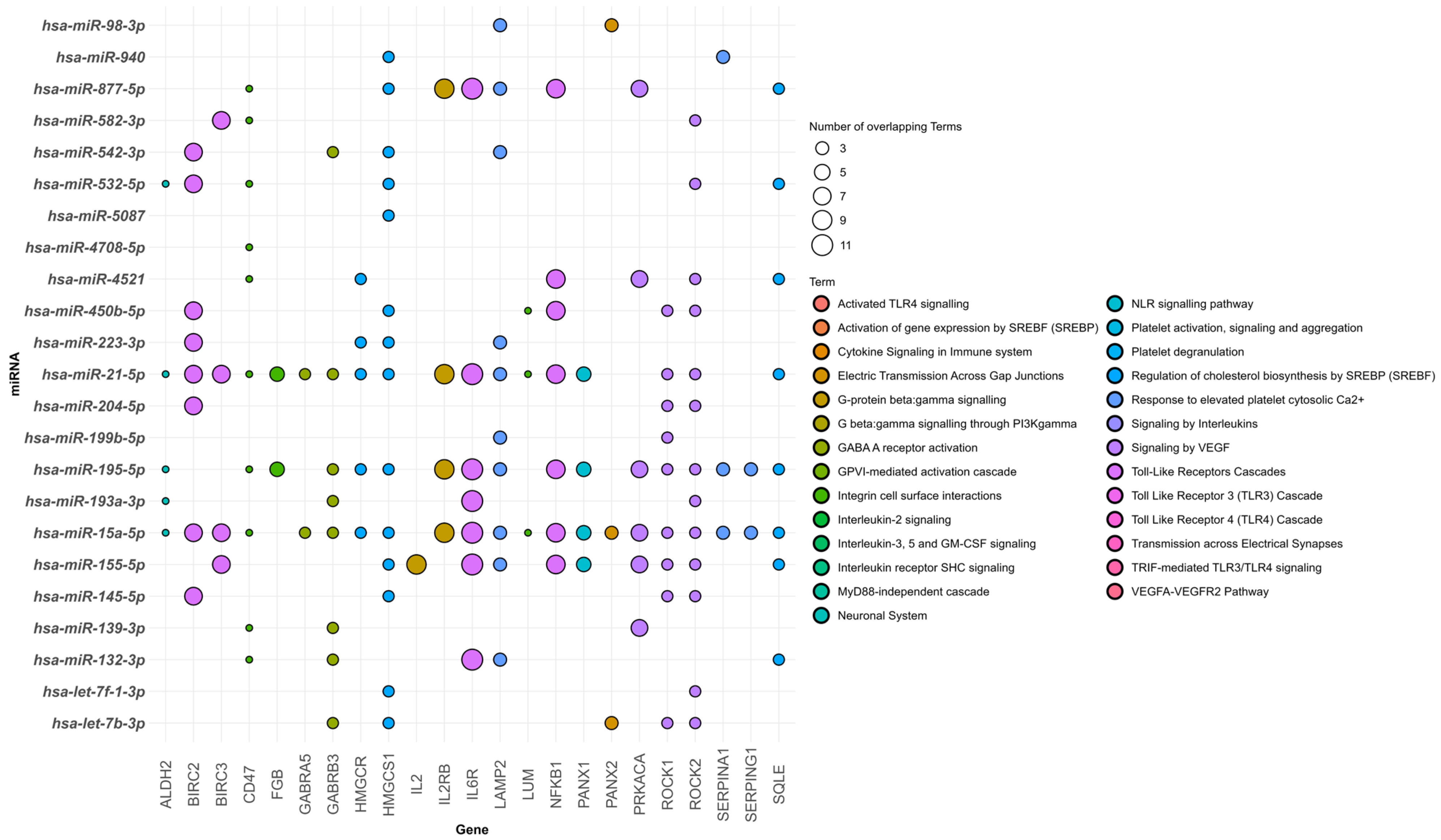
| FCD Type | Upregulated | Downregulated | Age (Year) | Sample Type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| microarray and RT-PCR techniques | |||||
| General | hsa-mir-323a-5p | - | 37–61 | Temporal cortex | [18] |
| General | hsa-miR-4521 | - | 37–61 | Temporal cortex | [19] |
| IIa, IIb | - | hsa-let-7f hsa-mir-31 hsa-mir-34a | 2–18 | Temporal and frontal cortex | [20] |
| I, II | hsa-mir-21 hsa-mir-155 hsa-mir-193a-3p hsa-mir-130b | hsa-mir-139-3p hsa-mir-877 hsa-mir-572 | 3–19 | Frontal cortex | [21] |
| IIb | hsa-miR-1825 hsa-miR-3065-3p hsa-miR-940 hsa-miR-1281 hsa-miR-5681a hsa-miR-98-3p hsa-let-7b-3p hsa-let-7f-1-3p | hsa-mir-6511b-5p hsa-mir-877-5p hsa-mir-6865-5p hsa-mir-6862-5p hsa-mir-4708-5p | 4–9 | Frontal cortex | [22] |
| RT-PCR technique | |||||
| IIb | hsa-mir-146a | - | 1–16 | Frontal and temporal cortex | [23] |
| II | hsa-mir-155-p | hsa-mir-223-3p hsa-mir-21-5p hsa-mir-204-5p hsa-mir-195-5p hsa-mir-203-3p hsa-let-7a-5p | 4–51 | cortex | [24] |
| RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) with RT-PCR validation techniques | |||||
| General | hsa-mir-194-2-5p hsa-mir-15a-5p hsa-mir-132-3p has-mir-145-5p | - | 2–22 | Serum exosomes | [25] |
| FCD Type | Upregulated | Downregulated | Age | Sample Type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT-PCR technique | |||||
| IIb | TLR2, TLR4, AGER | - | 11–26 y | Temporal, Frontal | [26] |
| IIb | - | BIRC2, PIK3CA, CTNNB1, EIF4EBP1, BIRC3 | 12–45 y | Frontal and left orbitofrontal | [27] |
| IIb | HMOX1, FTH1, ELANE, ALDH2, ELANE, FTH1 | - | 4–18 y | Frontal and temporal lobe | [28] |
| II | IL1B, IL6, CCL3, CCL4, STAT3, JUN, CCR5 | IL10 | 4–51 y | Frontal, temporal | [24] |
| II | CNR1, RPS6 | - | 3–21 y | Frontal and temporal cortex | [29] |
| I, II | GABRA1, GABRA5, GABRG2, NKCC1, GABRA4, GABRD | GABRB3 | 0–9 y and ≥10 years | Frontal and temporal cortex | [30] |
| I, II | - | ASIC1 | 4.8–7.1 y | Frontal, temporal | [31] |
| IIb | NF-ΚB1, IL6, IL1B | GPER1, PRKACA | 4–35 y | Cortex not consistently specified | [32] |
| IIb | - | CD47, CD200, SIRPA, IL4 | 1.8–9.5 y | Frontal and temporal | [33] |
| IIa, IIb | NEUROG2, RND2 | - | 2–18 y | Temporal and frontal | [20] |
| Ia, IIa, IIb | TRPC1 | - | 1.2–12 y | Frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital | [34] |
| I, II | IL2, IL2RA, IL2RB, IL2RG | - | 1–11.5 y | Frontal, Temporal, Parietal, Occipital | [35] |
| I, II | TRPC6, BDNF | - | 2–33 y | Frontal, Temporal | [36] |
| Ia, IIa, IIb, IIb | I: PANX1 II: PANX1, PANX2 | - | 1–7 y | Frontal, Temporal | [37] |
| IIb | GRIN2A, GRIN2B | SNCA | 3.5–34 y | Frontal, temporal, parietal | [38] |
| Ia, IIa, IIb | P2RX7, IL1B | - | 1–20 y | Frontal, Temporal, Parietal, Occipital | [39] |
| Ia, IIa, IIb | FGF13 | - | 1–19 y | Frontal, Temporal, Parietal, Occipital | [40] |
| I, II | I, II: GABRG2, GABRD II: GABRA4, | - | 3–32 y | Frontal, Temporal, Parietal, Occipital | [41] |
| IIa, IIb | TLR4, IL1B, TNF | - | 1–13 y | Frontal, Temporal, Parietal | [42] |
| IIb | β-actin, BF-1/FOXG1, ErbB3, CaMKII, CREB, IGF-1, IGF-2, OTX-1 and NOS | BMP-6, EGFR, TGF-βR1, TGF-βR3, TGF-β1/2, c-fos and HES1 | 1–20 y | Frontotemporal | [43] |
| RNA-Seq techniques | |||||
| IIa, IIb | HLA-DRA,HLA-A,CD68, CCL2, CCL19, NOS2, C1q, C3d | 80 genes downregulated but not validated | 2–29 y | Frontal and temporal | [44] |
| IIa, IIb | IIa, IIb: CP, LUM, TNC, MANT2, EFEMP1, ECM2, ANGPT1, SERPING1 IIb: CHI3L1, CCL2 | - | not provide | Neocortex from temporal | [45] |
| IIb | GFAP, VIM, NES, S100B, C3, SERPINA3, STAT3 | - | 1–40 y | Frontal and temporal | [46] |
| IIa, IIb | IIa and IIb: HMGCS1, HMGCR, SQLE. IIa: MTRNR2L12 IIb: GPNMB | - | 1–50 y | Frontal | [47] |
| IIb | IL1B, IL1RN, SLC12A2/NKCC1 in Pediatric not adult | - | Adult > 18 y and Pediatric < 12 y | Temporal, parietal, and frontal | [48] |
| Microarray and ISH techniques | |||||
| IIa, IIb | NEFH | - | 3–16 m | Frontal, Temporal, Parietal | [49] |
| IIa | - | KCC2 (in small dysplastic neuron) | 8–37 y | Frontal | [50] |
| Publication | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [26] | + | + | |||||
| [42] | + | + | |||||
| [48] | + | ||||||
| [28] | + | ||||||
| [24] | + | ||||||
| [39] | + | ||||||
| [32] | + | ||||||
| [46] | + | ||||||
| [43] | + | ||||||
| [41] | + | ||||||
| [30] | + | ||||||
| IL1B | TLR2 | TLR4 | ELANE | C3 | ERBB3 | GABRA4 | |
| Type | IIb | II | Mix | ||||
| Color | |||||||
| FCD Type | Up Regulated | Down Regulated | Age | Sample Type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Techniques | |||||
| I, II | ASCL1, PROX1, TUBB3 | MAP2 | 6–19 m | Parietal, frontal, temporal, occipital | [51] |
| IIa, IIb | NKCC1 | GAD67, KCC2 | 3–54 y | Parietal, frontal, temporal, occipital | [52] |
| IIb | - | KCC2 in neuropil/mislocalized to soma | 3–31 m | Frontal, temporal, parietal | [53] |
| IIb | MCM2 | GMNN, CCNE1, CCND1, CDK2, CDK4, RB1 | 1–81 y | Frontal, parietal, temporal, and multilobar lesions | [54] |
| IIb | - | BIRC2, IK3CA/B, CTNNB1, EIF4EBP1, BIRC3 | 12–45 y | Frontal and left orbitofrontal | [27] |
| IIa, IIb | HLA-I/II, CD3, CD8, CD68, TSPO, CCL2, CCL19, C1q, C3d, COX-2, and IL-17 upregulated in FCD (stronger in IIb) | - | 2–29 y | Frontal and temporal lobes | [44] |
| Ia, IIIa | PVALB, CALB1, CALB2 | - | ~25 y | Temporal | [55] |
| IIb | CASP3, CASP6, APP, TNFRSF21, SQSTM1, pS6 MAPT | - | 23–50 y | Temporal (most frequent), frontal, and some parietal | [56] |
| II | SOX2, KLF4, RPS6 | - | 2–14 y | Mostly frontal | [57] |
| IIa, IIb | IIa, IIb: GFAP, CRYAB, IIb: CD34 | - | IIa: 3 my–7 y IIb: 4.2–16 | Frontal, occipital | [58] |
| Ia, Ib, IIa, IIb | - | PVALB | 1–51 y | Temporal parietal, frontal | [59] |
| IIb | FABP7, VIM, ASCL1, SLC17A7, SLC17A6, PAX6, GFAP | SLC32A1, DLX1, DLX2 | 1–15 y | mostly temporal but also parietal, frontal, | [60] |
| I, III | - | PVALB | ~38 y | Temporal, frontal, parietal and occipital | [61] |
| IIb | VIP | PVALB | 0.4–26 y | Frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital | [62] |
| IIa, IIb | PSMB9, PSMB8, PSMB6, PSMB5 | - | 18–45 y | Frontal, temporal | [63] |
| IIa, IIb | TRPC4, PLCD1 | - | 1.5–12 y | Frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital | [64] |
| II | CD3E, CD8A, HLA-DRA, C1QA, C3, IL1B, CCL2 | - | 1–17 y | Temporal neocortex | [65] |
| IIb | GRM5, GRM1, GRM2, 3 (glia expressions) | GRM2, 3 in neuronal expressions | 1–50 y | Majority were frontal, several parietal, and temporal | [66] |
| IIa, IIb | ABCB1, ABCC1 | - | 1–51 y | Frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital | [67] |
| I, II, III | GFAP, VIM, S100, CASP3 | - | 1–45 y | Temporal lobe cortex and white matter | [68] |
| IIb | VIM, BCL2, PROM1, NES, MAP2, GFAP, TUBB3 | RBFOX3 | 1–12 y | Frontal neocortex | [69] |
| II | BCL2L1, BAX, BCL2, TP53 | - | 6 weeks–57 y | [70] | |
| I, II, III | GFAP, MCM2, PAX6, OLIG2, PDGFRB with subtype-specific differences (GFAP/PAX6 in FCDIIIa, Olig2 and GFAP/MCM2 in FCDIIIb, PDGFRβ in FCD1a | - | 3–47 y | Temporal, frontal, occipital | [71] |
| IIb | CHI3L1, CCL2 | - | not provide | neocortex from temporal lobe | [45] |
| IIb | GFAP | MAP2 | 1–40 y | Frontal and temporal lobes | [46] |
| IIb | PROM1, NES, VIM, GFAP | - | 8–55 y | Temporal, Frontal | [72] |
| IIb | GFAP+1 | - | 27.3 ± 12.7 y | Temporal, Frontal | [73] |
| IIb | FGF2 | - | 2–45 y | Temporal, Frontal | [74] |
| IIb | FGF2 | - | 11 weeks–45 y | Temporal, Frontal | [75] |
| I, II | I, II: GABRG2 GABRA4 (markedly higher in II) | - | 3–32 y | Frontal, Temporal, Parietal, Occipital. | [41] |
| I, II | I, II: RPS6, II: EIF4EBP1 | - | 10 weeks–49 y | Cortex | [76] |
| IIa | - | KCC2 (in small dysplastic neuron) | 8–37 y | Frontal | [50] |
| IIa, IIb | - | GRM5 | 19–56 y | Frontal, parietal, temporal, para hippocampal, orbitofrontal, fusiform gyrus | [77] |
| IIb | CCND1, RPS6, CTNNB1 | STAT3, EIF4EBP1, RPS6KB1 | 1–20 y | Temporal, Frontal | [78] |
| IIa, IIb | IIa, IIb: GFAP, HLA, IIb: CD3, VIM | RBFOX3 | 1–34 y | Temporal, Frontal | [79] |
| I, II | II, I: TBR1, OTX1, PAX6, MAP1B, II: ER81, NEFM | - | 1–52 y | Temporal, Frontal | [80] |
| Ia, Ib, IIa, IIb | - | SLC1A3, SLC1A2 | 2–44 y | Lateral temporal neocortex | [81] |
| II | INA, NES, NEFL, NVIM, NEFM, NEFH, PRPH | - | 15–30 y | temporal neocortex | [82] |
| IIa, IIb | IIa, IIb: HMGCS1, IIb: HMGCR, SQLE, GPNMB | - | 1–50 y | Frontal | [47] |
| IIb | RPS6 | 1–20 y | Frontal, temporal | [43] | |
| IIa, IIb | IIa, IIb: RPS6, WNT, RPS6KB1, IIb: NES, EIF4EBP1, SOX2, CD34 | CCND1, CTNNB1 Not detected | 1–33 y | Frontal and temporal | [83] |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Western Blotting (WB) Techniques | |||||
| I, II | ADA, ADK, NT5E, ADORA2A | SLC1A2 | 6–27 y | lesional cortex | [84] |
| I, II, III | NPY2R, NPY1R, NPY5R, NPY | - | 2–41 y | Temporal, Frontal, Parietal | [85] |
| IIa, IIb | IIa, IIb: SLC12A2, IIa: SLC12A5 | IIb: SLC12A5 IIa: GABRA4, IIb: GABRA1 | ~10.3 y | neocortex | [86] |
| IIb | VEGFB, VEGFA, FLT1, KDR | - | 11–31 y | Temporal lobe | [87] |
| IIb | HMOX1, NFE2L2, FTH1, FTL | - | 4–18 y | Frontal, temporal | [28] |
| I, IIa | BDNF, NGF, NTF3 | - | 6–36 y | temporal | [88] |
| IIb | DCLK1 | - | 11–41 y | Frontal, temporal | [89] |
| IIa, IIb | CTNNB1 | NR1H2, FABP7, PDGFRA, OLIG2 | 1.5–18 y | Frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital | [90] |
| II, I | - | ASIC1 | 4.8–7.1 y | Frontal, temporal | [31] |
| IIb | NF-ΚB1 | GPER1, PRKACA | 4–35 y | cortex | [32] |
| IIb | - | CD47, CD200, SIRPA | 1.8–9.5 y | Frontal and temporal | [33] |
| IIa, IIb | TRPC4, PLCD1 | - | 1.5–12 y | Frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital | [64] |
| Ia, IIa, IIb | TRPC1 | - | 1.2–12 y | Frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital | [34] |
| I, II | IL2, IL2RA, IL2RB, IL2RG | - | 1–11.5 y | Frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital | [35] |
| IIb | KCND2, P- KCND2, pERK1/2 | - | 14–41 y | Frontal, temporal, parietal | [91] |
| Ia, IIa, IIb | TRPC3 | - | <12 y | frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital | [92] |
| Ia, IIa, IIb | Ia, IIa, IIb: PANX1, IIb: PANX2 | - | 1–7 y | Frontal and temporal | [37] |
| IIb | p-STAT3, IL6, IL6R, JAK2 | - | 1.2–9 y | frontal, temporal, parietal | [93] |
| IIb | RTN4R, LINGO1, TNFRSF19, RTN4, RHOA | - | 1.2–8.5 y | frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital | [94] |
| IIb | - | SV2A | 12–40 y | frontal, temporal | [95] |
| IIb | GRIN2A, GRIN2B | SNCA | 3.5–34 y | Mainly frontal | [38] |
| IIa, IIb | FLNA, RPS6 | - | 1–14 y | frontal, temporal | [96] |
| IIa, IIb | GAP43 | - | 2.6–14 y | frontal, parietal, temporo-parieto-occipital | [97] |
| Ia, IIa, IIb, IIIa | - | KCC2 | 7–48.5 y | frontal, temporal | [98] |
| IIb | RPS6, VIM | MBP, CNP, PDGFRA | 1–18 y | frontal, parietal, temporo-parieto-occipital | [99] |
| Ia, IIa, IIb | TRPV4, PRKCA | - | 1.5–12 y | frontal, parietal, temporo-parieto-occipital | [100] |
| IIb | C3, C1q | - | 1–18 y | Frontal, temporal, occipital | [101] |
| Ia, IIa, IIb | FGF13 | - | 1–19 y | Frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital | [40] |
| IIb | GRIN2A, GRIN2B, DLG4, DLG1, SLC17A7 | - | 1–47 y | Frontal, temporal | [102] |
| IIa, IIb, III | MMP1, MMP-9, MMP8, MMP2 | - | 2.7–35 y | [103] | |
| IIa, IIb | FANCI, FANCA, BRCA2, RAD18, KEAP1 | - | Not reported | Not reported | [104] |
| IIb | LAMP2, LAMP1, SQSTM1, ATG5 | - | pediatric | Temporal neocortex | [105] |
| IHC, WB, and double-label immunofluorescence | |||||
| IIb | (DL-IF) SH3RF1, LILRB2, SHROOM3, ROCK1, ROCK2 | - | 1.7–12.5 y | Frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital | [106] |
| IIb | ADK | - | 2.42–29 y | Frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal | [107] |
| IIa, IIb | NKCC1 | NKCC2, GAD | 3–54 y | Frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital | [52] |
| IIb | DLG3, GRIN2B in postsynaptic density enriched fraction | - | 14–40 y | mostly temporal | [108] |
| Ia, IIb | DCX | - | 2–32 y | Frontal, temporal, occipital | [109] |
| IIb | TRPV1 | - | 1.5–9 y | Frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital cortex | [110] |
| IIb | - | BMP4 | 1.5–9 y | Frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital cortex | [111] |
| IIb | MMP-9 | - | 1.6–9.2 y | Frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital cortex | [112] |
| IIb | PDGFRB, CSPG4 (NG2), IBA1, GFAP | - | 1–21 y | frontal, parietal, temporal | [113] |
| I, II | II, I: TBR1, OTX1, PAX6, MAP1B, II: ER81, NEFM | - | 1–52 y | Temporal, Frontal | [80] |
| Ia, IIa, IIb | IL17RA, IL17A, TRAF3IP2, RELA | - | 1–31 y | Frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital cortex | [114] |
| IIa, IIb | TLR4, IL1B, TNFA | - | 1–13 y | Frontal, Temporal, Parietal | [42] |
| Mass Spectrometry and Other Methods (ISH, Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) | |||||
| IIb | TLR2, TLR4, AGER | - | 11–26 y | Temporal, Frontal | [26] |
| IIa, IIb | NEFH | - | 3–16 m | Frontal, Temporal, Parietal, | [49] |
| II | IL1B, IL6, CCL3, CCL4 | IL-10 | 4–51 y | Frontal, Temporal | [24] |
| II | CNR1, RPS6 | - | 3–21 y | Frontal, Temporal | [29] |
| I, II | NKCC1 GABRA4, GABRA5, GABRG2 | - | 0–9 y and ≥10 y | Frontal, Temporal | [30] |
| IIa, IIb | pS6 present | - | 1–42 y | Frontal lobe | [115] |
| IIb | C1QA/B/C, C3, AIF1, HLA-DRB1 | - | 2–57 y | temporal, frontal, parietal | [116] |
| CCD | 64 proteins, including FSCN1, CRMP1, NDRG1, DPYSL5, MAP4, FABP3 | 89 proteins, including PRDX6 and PSAP | ~7 y | neocortical tissue | [117] |
| IIa, IIb | SLC1A1 | GLUL, SLC1A2 | 12–27 y | temporal, frontal, occipital | [118] |
| General | IL7 | - | 21 y | hippocampus | [119] |
| II | NES, CD34, GFAP, VIM, NEFL, GRIN1, GRIN2A, GRIA1, GRIA3, ABCB1 | - | 10–36 y | Frontal and temporal neocortex | [120] |
| II, IIIb | II, III: CD34 II: BCL2 | - | 3–51 y | Temporal neocortex | [121] |
| Publication | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [65] | + | ||||||
| [78] | + | ||||||
| [76] | + | ||||||
| [69] | + | + | + | ||||
| [43] | + | ||||||
| [53] | |||||||
| [60] | + | + | |||||
| [73] | + | ||||||
| [72] | + | + | + | ||||
| [121] | + | ||||||
| [29] | + | ||||||
| [96] | + | ||||||
| [115] | + | ||||||
| [82] | + | ||||||
| [52] | − | ||||||
| [79] | + | + | |||||
| [120] | + | + | + | ||||
| [50] | − | ||||||
| [99] | + | + | |||||
| [71] | + | ||||||
| [58] | + | + | |||||
| [86] | − | ||||||
| [42] | + | ||||||
| [113] | + | ||||||
| [68] | + | ||||||
| [98] | − | ||||||
| [52] | − | ||||||
| [83] | + | + | + | ||||
| [24] | + | ||||||
| Protein | CD34 | GFAP | IL1B | NES | RPS6 | SLC12A5 | VIM |
| Type | IIa | IIb | II | Mix | |||
| Color |
| Overlaps | [93] | [29] | [37] | [32] | [40] | [30] | [105] | [35] | [106] | [114] | [88] | [33] | [47] | [34] | [44] | [38] | [20] | [24] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGF13 | + | |||||||||||||||||
| TRPC1 | + | |||||||||||||||||
| PANX1 | + | |||||||||||||||||
| GPER1 | − | |||||||||||||||||
| PRKACA | − | |||||||||||||||||
| CD47 | − | |||||||||||||||||
| CD200 | − | |||||||||||||||||
| SNCA | − | |||||||||||||||||
| NF-ΚB1 | + | |||||||||||||||||
| PANX2 | + | |||||||||||||||||
| ROCK1 | + | |||||||||||||||||
| ROCK2 | + | |||||||||||||||||
| IL17RA | + | |||||||||||||||||
| LAMP1 | + | |||||||||||||||||
| LAMP2 | + | |||||||||||||||||
| IL6R | + | |||||||||||||||||
| HMGCS1 | + | |||||||||||||||||
| HMGCR | + | |||||||||||||||||
| SQLE | + | |||||||||||||||||
| NEUROG2 | + | |||||||||||||||||
| RND2 | + | |||||||||||||||||
| CCL3 | + | |||||||||||||||||
| CNR1 | + | |||||||||||||||||
| GABRA5 | + | |||||||||||||||||
| CD68 | + | |||||||||||||||||
| IL2 | + | |||||||||||||||||
| IL2RB | + | |||||||||||||||||
| IL2RG | + | |||||||||||||||||
| BDNF | + | |||||||||||||||||
| GABRD | + | |||||||||||||||||
| Type | IIb | II | Mix | |||||||||||||||
| Color | ||||||||||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shakerzadeh, J.; Jaroušek, R.; Goliášová, Z.; Brázdil, M. Molecular Signature in Focal Cortical Dysplasia: A Systematic Review of RNA and Protein Data. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209909
Shakerzadeh J, Jaroušek R, Goliášová Z, Brázdil M. Molecular Signature in Focal Cortical Dysplasia: A Systematic Review of RNA and Protein Data. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):9909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209909
Chicago/Turabian StyleShakerzadeh, Jalleh, Radim Jaroušek, Zita Goliášová, and Milan Brázdil. 2025. "Molecular Signature in Focal Cortical Dysplasia: A Systematic Review of RNA and Protein Data" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 9909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209909
APA StyleShakerzadeh, J., Jaroušek, R., Goliášová, Z., & Brázdil, M. (2025). Molecular Signature in Focal Cortical Dysplasia: A Systematic Review of RNA and Protein Data. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 9909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209909






