4.1. Chemistry
Commercially available solvents and reagents were utilized as received without any additional purification. NMR spectra were recorded with an Avance III HD 400 MHz Bruker BioSpin (Bruker Corporation, Billerica, MA, USA) for 1H-NMR (400 MHz) and 13C-NMR (101 MHz) or an Avance III HD 500 MHz Bruker BioSpin (Bruker Corporation, Billerica, MA, USA) for 1H-NMR (500 MHz) and 13C-NMR (126 MHz) MestreNova 14.3.0 (Mestrelab Research S.L., Santiago de Compostela, Spain) was utilized for data analysis and the respective chemical shifts (δ) were referenced to the deuterated solvent peak (DMSO-d6: δH = 2.50 ppm, δC = 39.52 ppm; CD2Cl2: δH = 5.32 ppm, δC = 53.84 ppm; CDCl3: δH = 7.26 ppm, δC = 77.16 ppm). Coupling constants (J) were reported in Hertz (Hz), and multiplicities were given as: s (singlet), d (doublet), t (triplet), q (quartet), or m (multiplet). While the compounds are numbered according to IUPAC guidelines, the respective hierarchy of NMR signal assignments (denoted with apostrophes) were simplified by following the sequence in which the compounds were synthesized. Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) was employed for reaction monitoring, using 0.2 mm silica gel coated POLYGRAM® SIL G/UV254 polyester plates (Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany), and visualized under UV light at 254 nm. Flash column chromatography was carried out using SiO2 60 (0.040–0.063 mm, 230–400 mesh ASTM) from Merk (Darmstadt, Germany). Infrared spectroscopy (IR) was performed on a Perkin Elmer FT-IR BXII/1000 spectrometer (Waltham, USA), paired with a DuraSamp IR II Diamond ATR sensor (Smiths Detection, London, UK). The IR spectra were recorded over the range of 4000 to 650 cm−1, and significant absorption bands were noted in cm−1. High-resolution mass spectrometry (HR-MS) was conducted using either a Jeol Mstation 700 (Akishima, Japan) or a JMS GCmate II Jeol (Akishima, Japan) for electron impact ionization (EI). Electrospray ionization (ESI) HR-MS was performed using a Thermo Finnigan LTQ (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Melting points were determined with a Büchi B-540 melting point meter (Fawil, Switzerland). The purity of compounds was assessed using an HP Agilent 1100 HPLC system (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) with a Zorbax Eclipse Plus® C18 5 µm (4.6 × 150 mm) column (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA), using acetonitrile/water (method 1), or acetonitrile/phosphate buffer pH = 5 (method 2) as mobile phases.
General Procedure: Nitrobenzene reduction: To a stirred solution of the appropriate nitrobenzene derivative (1.0 equivalent) in EtOH with a concentration of 0.010 M were added iron powder (5.0 equivalents) and 0.30 M aq. NH4Cl (5.0 equivalents) at 50 °C. The reaction mixture was refluxed at 90 °C for 2 h. Afterwards, the solids were removed by filtration and the filtrate was concentrated in vacuo. The crude product was used for the next step without further purification.
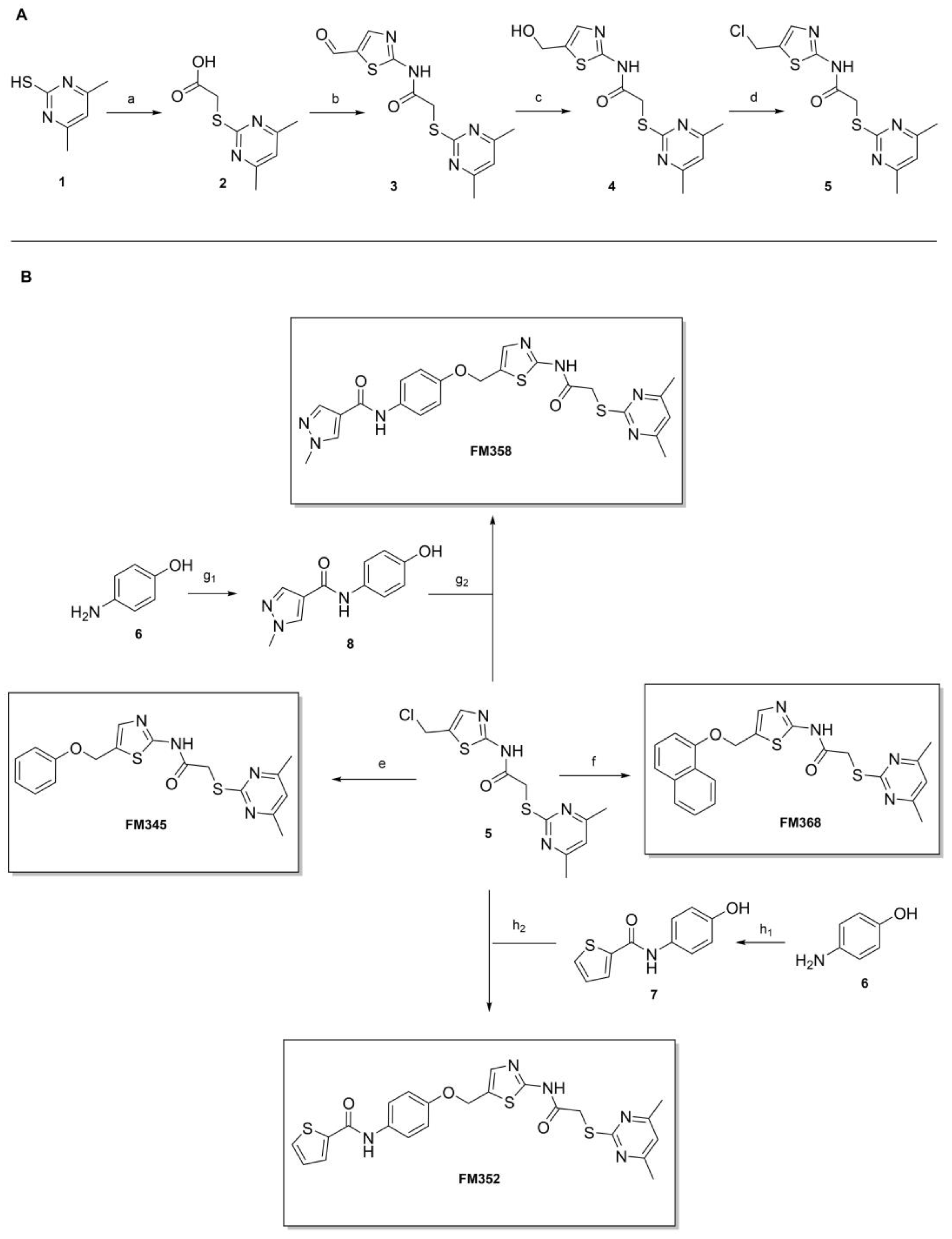
2-((4,6-Dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)thio)acetic acid (2). 4,6-Dimethylpyrimidine-2-thiol (1) (3.80 g, 27.1 mmol, 1.00 eq) and chloroacetic acid (3.07 g, 32.5 mmol, 1.20 eq) were suspended in acetonitrile (25 mL) at room temperature. After addition of NEt3 (15.1 mL, 108 mmol, 4.00 eq), the reaction mixture was stirred for 24 h. After evaporating the solvent, the crude product was purified via flash column chromatography (DCM/MeOH/AcOH 100:1:1) to yield thioether 2 as a light-beige solid (4.33 g, 21.8 mmol, 81%); m.p. 128 °C; IR (ATR) ṽ/cm−1 3474, 2942, 2534, 1924, 1716, 1584, 1538, 1309, 1267, 1208, 1172, 984, 862, 791, 661; δH (400 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 12.73 (s, 1H, COOH), 6.97 (s, 1H, 5-H), 3.90 (s, 2H, CH2), 2.33 (s, 6H, 4-CH3, 6-CH3). δC (101 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 170.2 (COOH), 169.0 (C-2), 167.0 (C-4, C-6), 116.0 (C-5), 32.9 (CH2), 23.3 (4-CH3, 6-CH3); HRMS (ESI): m/z = [M−H]− calculated for C8H9N2O2S−: 197.0390; found: 197.0390.
2-((4,6-Dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(5-formylthiazol-2-yl)acetamide (3). Carboxylic acid 2 (1.55 g, 7.80 mmol, 1.00 eq) was dissolved in DMF (5 mL) and added to a previously prepared solution of 2-aminothiazole-5-carbaldehyde (1.00 g, 7.80 mmol, 1.00 eq), DMAP (0.477 g, 3.90 mmol, 0.50 eq) and EDC·HCl (1.83 g, 9.36 mmol, 1.20 eq) in 5 mL DMF. After stirring for 16 h at room temperature, the reaction mixture was diluted with water (400 mL) and extracted with EtOAc (3 × 100 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over sodium sulfate. After evaporating the solvent, the crude product was purified via flash column chromatography (DCM/MeOH 100:1) to yield aldehyde 3 as a pale yellow solid (1.11 g, 3.61 mmol, 46%); m.p. 191–193 °C; IR (ATR) ṽ/cm−1 2924, 2137, 1688, 1664, 1586, 1555, 1516, 1427, 1385, 1311, 1268, 1234, 1173, 1123, 977, 872, 819, 733; δH (400 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 13.02 (s, 1H, NHCO), 9.96 (s, 1H, CHO), 8.44 (s, 1H, 4′-H), 6.97 (s, 1H, 5-H), 4.18 (s, 2H, CH2), 2.28 (s, 6H, 4-CH3, 6-CH3). δC (101 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 184.1 (CHO), 168.7 (C-2), 168.4 (NHCO), 167.1 (C-4, C-6), 164.0 (C-2′), 150.7 (C-4′) 132.1 (C-5′), 116.2 (C-5), 34.4 (CH2), 23.2 (4-CH3, 6-CH3); HRMS (ESI): m/z = [M−H]− calculated for C12H11N4O2S2−: 307.0329; found: 307.0330.
2-((4,6-Dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(5-(hydroxymethyl)thiazol-2-yl)acetamide (4). To a stirred solution of aldehyde 3 (550 mg, 1.78 mmol) in dry MeOH (20 mL) was added NaBH4 (101 mg, 2.68 mmol) at 0 °C. The reaction mixture was stirred at 0 °C for 3 h under N2 atmosphere. Water (15 mL) was then added, and the reaction mixture was stirred for another 10 min. The suspension was vacuum filtered, and the obtained solid washed with water (1 × 50 mL) and acetone (1 × 50 mL) to give alcohol 4 as a white solid (553 mg, 1.78 mmol, quantitative); m.p. 250–252 °C; IR (ATR) ṽ/cm−1 3284, 2917, 1696, 1588, 1537, 1323, 1273, 1262, 1161, 1037, 971, 843, 834, 788, 717; δH (400 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 12.22 (s, 1H, NHCO), 7.28 (d, J = 1.0 Hz, 1H, 4′-H), 6.96 (s, 1H, 5-H), 5.35 (t, J = 5.7 Hz, 1H, OH), 4.57 (dd, J = 5.7, 0.9 Hz, 2H, CH2OH), 4.11 (s, 2H, CH2S), 2.30 (s, 6H, 4-CH3, 6-CH3). δC (101 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 168.9 (C-2), 167.0 (C-4, C-6), 166.9 (NHCO), 157.5 (C-2′), 134.5 (C-4′) 133.1 (C-5′), 116.1 (C-5), 55.7 (CH2OH), 34.1 (CH2S), 23.3 (4-CH3, 6-CH3); HRMS (ESI): m/z = [M−H]− calculated for C12H13N4O2S2−: 309.0485; found: 309.0486.
N-(5-(Chloromethyl)thiazol-2-yl)-2-((4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)thio)acetamide (5). Primary alcohol 4 (358 mg, 1.15 mmol, 1.00 eq) was suspended in anhydrous DCM (15 mL) under nitrogen atmosphere and SOCl2 (101 µL, 1.38 mmol, 1.20 eq) was added dropwise, while stirring at room temperature. After 18 h, n-hexane (5 mL) was added to the reaction mixture and the precipitate was collected by filtration. Subsequently the product was washed with n-hexane/DCM (1:1, 3 × 20 mL) to yield chloromethyl compound 5 as a white solid (378 mg, 1.15 mmol, quantitative yield); m.p. 226–233 °C (decomposition); IR (ATR) ṽ/cm−1 3270, 2421, 1720, 1624, 1602, 1582, 1540, 1417, 1370, 1333, 1307, 1268, 1158, 876, 849, 716, 703, 695; δH (400 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 12.46 (s, 1H, NHCO), 7.53 (s, 1H, 3′-H), 6.96 (s, 1H, 5-H), 5.03 (s, 2H, CH2S), 4.13 (s, 2H, CH2Cl), 2.29 (s, 6H, 4-CH3, 6-CH3). δC (101 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 168.8 (C-2), 167.4 (NHCO), 167.0 (C-4, C-6), 159.2 (C-2′), 138.2 (C-3′), 128.0 (C-4′), 116.2 (C-5), 38.7 (CH2Cl), 34.1 (CH2S), 23.2 (4-CH3, 6-CH3). HRMS (ESI): m/z = [M-Cl+H2O-2H]− calculated for C12H13N4O2S2−: 309.0485; found: 309.0483.
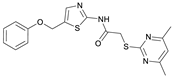
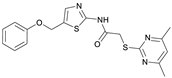
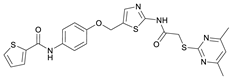
2-((4,6-Dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(5-(phenoxymethyl)thiazol-2-yl)acetamide (FM345). Chloromethyl compound 5 (154 mg, 0.468 mmol, 1.00 eq) and sodium phenolate (54.4 mg, 0.468 mmol, 1.00 eq) were suspended in anhydrous DCM (20 mL) under nitrogen atmosphere and the reaction mixture was stirred for 24 h at room temperature. Following TLC monitoring, an additional equivalent of sodium phenolate (54.4 mg, 0.468 mmol, 1.00 eq) was added to complete the reaction. After 2 h, the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure. NaOH solution (aq., 2 M, 50 mL) was added to the residue and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (4 × 75 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over sodium sulfate. After evaporating the solvent, the crude product was purified by flash column chromatography (DCM/MeOH 100:1) to yield FM345 as a white solid (33.0 mg, 0.0854 mmol, 18%); m.p. 160–163 °C; IR (ATR) ṽ/cm−1 2916, 2159, 1688, 1583, 1539, 1496, 1384, 1312, 1270, 1238, 1171, 1139, 1008, 966, 883, 803, 749, 733, 687; δH (500 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 12.38 (s, 1H, NHCO), 7.54 (s, 1H, 4′-H), 7.33–7.25 (m, 2H, 3″-H, 5″-H), 7.03–6.98 (m, 2H, 2″-H, 5″-H), 6.98–6.91 (m, 2H, 4″-H, 5-H), 5.25 (s, 2H, CH2O), 4.11 (s, 2H, CH2S), 2.28 (s, 6H, 4-CH3, 6-CH3). δC (126 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 168.9 (C-2), 167.2 (NHCO), 167.0 (C-4, C-6), 158.6 (C-2′), 157.7 (C-1″), 137.7 (C-4′), 129.5 (C-3″, C-5″), 126.6 (C-5′), 121.0 (C-4′), 116.1 (C-5), 115.0 (C-2″, C-6″), 61.8 (CH2O), 34.1 (CH2S), 23.2 (4-CH3, 6-CH3). HRMS (ESI): m/z = [M+H]+ calculated for C18H19N4O2S2+: 387.0944; found: 387.0944; Purity (HPLC): >99% (210 nm), >99% (254 nm), (method 1).
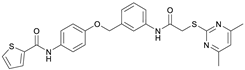
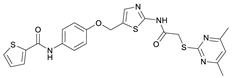
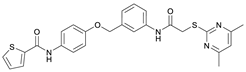
N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)thiophene-2-carboxamide (7). At room temperature, 4-aminophenol (6) (9.38 g, 86.0 mmol, 1.00 eq) was dissolved in DMF (30 mL) and pyridine (7.41 mL, 91.7 mmol, 1.07 eq) was added. The stirred mixture was cooled to 0 °C, and 2-thiophenecarbonyl chloride (9.78 mL, 91.4 mmol, 1.06 eq) was added dropwise. After 1.5 h the reaction mixture was diluted with water (300 mL) and extracted with EtOAc (4 × 100 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over sodium sulfate and concentrated in vacuo to obtain a viscous oil. The addition of DCM/hexanes (5 mL, 9:1) to the viscous oil induced the crystallization process. The obtained crystals were collected by filtration and washed with DCM/hexanes (9:1, 3 × 50 mL) to yield amide 7 as a white-pink solid (13.0 g, 59.1 mmol, 69%); m.p. 192–195 °C; IR (ATR) ṽ/cm−1 3109, 1620, 1598, 1539, 1505, 1438, 1355, 1314, 1264, 1245, 1221, 1173, 1095, 884, 8299, 765, 739, 712. δH (400 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 10.01 (s, 1H, NHCO), 9.27 (s, 1H, OH), 7.96 (dd, J = 3.8, 1.1 Hz, 1H, 3′-H), 7.81 (dd, J = 5.0, 1.2 Hz, 1H, 5′-H), 7.50–7.44 (m, 2H, 2-H, 6-H), 7.20 (dd, J = 5.0, 3.7 Hz, 1H, 4′-H), 6.77–6.72 (m, 2H, 3-H, 5-H). δC (101 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 159.4 (NHCO), 153.8 (C-4), 140.4 (C-2′), 131.3 (C-5′), 130.1 (C-1′), 128.5 (C-3′), 128.0 (C-4′), 122.4 (C-2, C-6), 115.0 (C-3, C-5). HRMS (ESI): m/z = [M−H]− calculated for C11H8NO2S−: 218.0281; found: 218.0280.
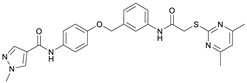
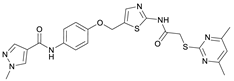
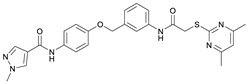
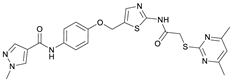
N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide (8). DIPEA (3.80 mL, 22.0 mmol, 3.00 eq) and HATU (2.26 g, 5.95 mmol, 1.50 eq) were added to a solution of 1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid (925 mg, 7.33 mmol, 1.00 eq) in anhydrous THF (15 mL) and the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1 h. 4-Aminophenol (6) (800 mg, 7.33 mmol, 1.00 eq) was added and the reaction mixture was stirred for another 3 h. Then the mixture was diluted with water (150 mL) and extracted with DCM (4 × 100 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over sodium sulfate. After evaporating the solvent, the crude product was purified by flash column chromatography (hexanes/EtOAc 2:8) to yield amide 8 as a white solid (171 mg, 0.787 mmol, 11%); m.p. 227–230 °C; IR (ATR) ṽ/cm−1 3347, 2926, 1641, 1601, 1558, 1509, 1430, 1388, 1308, 1273, 1201, 1151, 1099, 1005, 841, 812, 749, 703. δH (400 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 9.57 (s, 1H, NHCO), 9.18 (s, 1H, OH), 8.24 (s, 1H, 5′-H), 7.96 (s, 1H, 3′-H), 7.48–7.40 (m, 2H, 2-H, 6-H), 6.75–6.67 (m, 2H, 3-H, 5-H), 3.87 (s, 3H, CH3). δC (101 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 160.0 (NHCO), 153.4 (C-4), 138.6 (C-3′), 132.3 (C-5′), 130.6 (C-1), 121.9 (C-2, C-6), 118.7 (C-4′), 114.0 (C-3, C-5), 38.8 (CH3). HRMS (ESI): m/z = [M+H]+ calculated for C11H12N3O2+: 218.0924; found: 218.0928.
N-(4-((2-(2-((4,6-Dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)thio)acetamido)thiazol-5-yl)methoxy)phenyl)thiophene-2-carboxamide (FM352). Under nitrogen atmosphere, phenol 7 (268 mg, 1.22 mmol, 1.00 eq) was dissolved in anhydrous methanol (2 mL) and sodium methanolate (25% (w/w) in MeOH, 272 µL, 1.22 mmol, 1.00 eq) was added at room temperature. The reaction mixture was stirred for 2 min, subsequently the solvent was evaporated. The residue was dried under high vacuum to yield sodium 4-(thiophene-2-carboxamido)phenolate in quantitative yield, which was used without further purification for the next step. Chloromethyl compound 5 (123 mg, 0.374 mmol, 1.00 eq) and the previously prepared sodium 4-(thiophene-2-carboxamido)phenolate (90.2 mg, 0.374 mmol, 1.00 eq) were suspended in anhydrous DCM (15 mL) and the reaction mixture was stirred for 18 h at room temperature. Following TLC monitoring, an additional equivalent of sodium 4-(thiophene-2-carboxamido)phenolate (90.2 mg, 0.374 mmol, 1.00 eq) was added to complete the reaction. After 2 h, NaOH solution (aq., 2 M, 50 mL) was added, and the mixture was extracted with DCM (3 × 50 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over sodium sulfate. After evaporating the solvent, the crude product was purified by flash column chromatography (DCM/MeOH 100:1) to yield FM352 as a white solid (31.5 mg, 0.0616 mmol, 17%); m.p. 176–179 °C; IR (ATR) ṽ/cm−1 2923, 2164, 1700, 1635, 1578, 1512, 1422, 1323, 1265, 1229, 1159, 1010, 845, 734; δH (500 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 12.38 (s, 1H, 2′-NHCO), 10.11 (s, 1H, 4″-NHCO), 7.97 (d, J = 3.7 Hz, 1H, 3‴-H), 7.83 (d, J = 4.9 Hz, 1H, 5‴-H), 7.63–7.57 (m, 2H, 3″-H, 5″-H), 7.55 (s, 1H, 4′-H), 7.21 (t, J = 4.3 Hz, 1H, 4‴-H), 7.03–6.98 (m, 2H, 2″-H, 6″-H), 6.95 (s, 1H, 5-H), 5.25 (s, 2H, CH2O), 4.12 (s, 2H, CH2S), 2.28 (s, 6H, 4-CH3, 6-CH3). δC (126 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 168.9 (C-2), 167.2 (2′-NHCO), 167.0 (C-4, C-6), 159.6 (4″-NHCO), 158.6 (C-2′), 154.0 (C-1″), 140.2 (C-2‴), 137.8 (C-4′), 132.2 (C-4″), 131.5 (C-5‴), 128.8 (C-3‴), 128.0 (C-4‴), 126.6 (C-5′), 121.9 (C-3″, C-5″), 116.1 (C-5), 115.1 (C-2″, C-6″), 62.1 (CH2O), 34.1 (CH2S), 23.2 (4-CH3, 6-CH3). HRMS (ESI): m/z = [M−H]− calculated for C23H20N5O3S3−: 510.0734; found: 510.0733. Purity (HPLC): >99% (210 nm), >99% (254 nm), (method 1).
N-(4-((2-(2-((4,6-Dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)thio)acetamido)thiazol-5-yl)methoxy)-phenyl)-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide (FM358). Under nitrogen atmosphere, phenol 8 (294 mg, 1.35 mmol, 1.00 eq) was dissolved in anhydrous methanol (2 mL) and sodium methanolate (25% (w/w) in MeOH, 302 µL, 1.35 mmol, 1.00 eq) was added at room temperature. The reaction mixture was stirred for 2 min, subsequently the solvent was evaporated. The residue was dried under high vacuum to yield sodium 4-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamido)phenolate in quantitative yield, which was used without further purification for the next step. Under nitrogen atmosphere, chloromethyl compound 5 (150 mg, 0.456 mmol, 1.00 eq) and the previously prepared sodium 4-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamido)phenolate (109 mg, 0.456 mmol, 1.00 eq) were suspended in anhydrous DCM (15 mL) and the reaction mixture was stirred for 18 h at room temperature. Following TLC monitoring, an additional equivalent of sodium 4-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamido)phenolate (0.456 mmol, 109 mg, 1.00 eq) was added to complete the reaction. After 2 h, MeOH (1 mL) was added, and the reaction mixture was concentrated in vacuo. The crude product was purified by flash column chromatography (DCM/MeOH/AcOH 100:3:0.5) to yield FM358 as a white solid (87.1 mg, 0.171 mmol, 38%); m.p. 188–191 °C; IR (ATR) ṽ/cm−1 3285, 2923, 1692, 1640, 1578, 1559, 1512, 1489, 1438, 1413, 1378, 1325, 1268, 1226, 1172, 1158, 1007, 977, 870, 845, 820, 779, 757, 717; δH (500 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 12.37 (s, 1H, 2′-NHCO), 9.68 (s, 1H, 4″-NHCO), 8.26 (s, 1H, 4‴-H), 7.97 (s, 1H, 2‴-H), 7.60–7.58 (m, 2H, 3″-H, 5″-H), 7.53 (s, 1H, 4′-H), 6.98 (m, 2H, 2″-H), 6.95 (s, 1H, 5-H) 5.23 (s, 2H, CH2O), 4.11 (s, 2H, CH2S), 3.88 (s, 3H, NCH3), 2.28 (s, 6H, 4-CH3, 6-CH3). δC (126 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 168.9 (C-2), 167.2 (2’-NHCO), 167.0 (C-4, C-6), 160.1 (4″-NHCO), 158.8 (C-2’), 153.6 (C-1″), 138.7 (C-2‴), 137.7 (C-4’), 132.7 (C-4″), 132.5 (C-4‴), 126.6 (C-5’), 121.4 (C-3″, C-5″), 118.6 (C-3‴), 116.1 (C-5‴), 115.1 (C-2‴, C-6‴), 62.2 (CH2O), 38.8 (NCH3), 34.2 (CH2S), 23.2 (4-CH3, 6-CH3); HRMS (ESI): m/z = [M−H]− calculated for C23H22N7O3S2−: 508.1231; found: 508.1231; Purity (HPLC): >99% (210 nm), >99% (254 nm), (method 1).
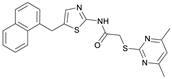
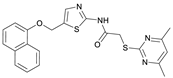
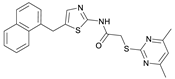
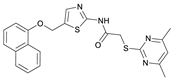
2-((4,6-Dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(5-((naphthalen-1-yloxy)methyl)thiazol-2-yl)acetamide (FM368). Under nitrogen atmosphere, naphthalen-1-ol (377 mg, 2.61 mmol, 1.00 eq) was dissolved in anhydrous methanol (2 mL) and sodium methanolate (25% (w/w) in MeOH, 583 µL, 2.61 mmol, 1.00 eq) was added at room temperature. The reaction mixture was stirred for 2 min, subsequently the solvent was evaporated. The residue was dried under high vacuum to yield sodium 1-naphtholate in quantitative yield, which was used without further purification for the next step. Under nitrogen atmosphere chloromethyl compound 5 (150 mg, 0.456 mmol, 1.00 eq) and the previously prepared sodium 1-naphtholate (75.8 mg, 0.456 mmol, 1.00 eq) were suspended in anhydrous acetone (5 mL) and the reaction mixture was stirred for 3 h at room temperature. Following TLC monitoring, an additional equivalent of sodium 1-naptholate (75.8 mg, 0.456 mmol, 1.00 eq) was added to complete the reaction. After 2 h, water (50 mL) was added to the reaction mixture and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (3 × 100 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over sodium sulfate. After evaporating the solvent in vacuo, the crude product was purified by flash column chromatography (DCM/MeOH 100:0.5) to yield FM368 as a white solid (28.0 mg, 0.0641 mmol, 14%); m.p. 181–183 °C; IR (ATR) ṽ/cm−1 2907, 1697, 1580, 1552, 1506, 1437, 1396, 1367, 1320, 1264, 1241, 1163, 1099, 1065, 1018, 975, 891, 874, 859, 834, 778, 768, 717; δH (500 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 12.42 (s, 1H; NHCO), 8.09 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H, 8″-H), 7.87 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, 5″-H), 7.63 (s, 1H, 4’-H), 7.55–7.40 (m, 4H, 3″-H, 4″-H, 6″-H, 7″-H), 7.14 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H, 2″-H), 6.95 (s, 1H, 5-H), 5.47 (s, 2H, CH2O), 4.13 (s, 2H, CH2S), 2.29 (s, 6H, 4-CH3, 6-CH3). δC (126 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 168.9 (C-2), 167.2 (NHCO), 167.0 (C-4, C-6), 158.7 (C-2’), 153.1 (C-1″), 137.6 (C-4’), 134.1 (C-4a″), 127.5 (C-5″), 126.7 (C-5’), 126.5 (C-3″), 126.1 (C-6″), 125.5 (C-7″), 125.0 (C-8a″), 121.4 (C-8″), 120.5 (C-4″), 116.1 (C-5), 106.1 (C-2″), 62.6 (CH2O), 34.1 (CH2S), 23.2 (4-CH3, 6-CH3); HRMS (EI): m/z = [M]•+ calculated for C22H20N4O2S2•+: 436.1028; found: 436.1032; Purity (HPLC): >99% (210 nm), >99% (254 nm), (method 2).
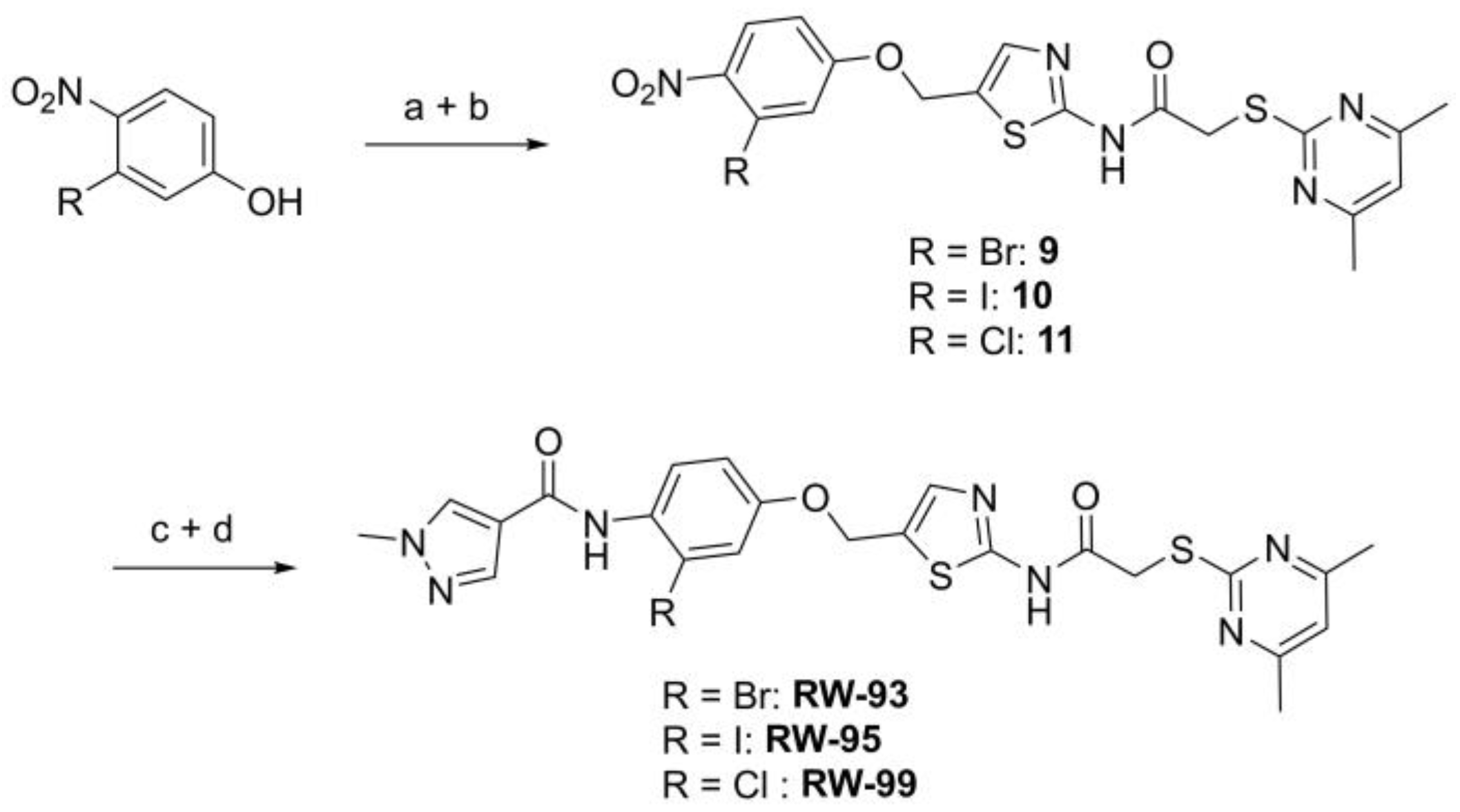
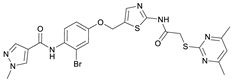
N-(5-((3-Bromo-4-nitrophenoxy)methyl)thiazol-2-yl)-2-((4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)thio)acetamide (9). To a stirred solution of 3-bromo-4-nitrophenol (150 mg, 0.667 mmol) in dry MeOH (3 mL) was added sodium methanolate 25% (w/w) in MeOH (0.153 mL, 0.667 mmol). The solution was stirred at room temperature for 5 min, then concentrated in vacuo to give sodium 3-bromo-4-nitrophenolate as an orange solid, which was used for the next step without further purification. Chloromethyl compound 5 (80.0 mg, 0.243 mmol) and sodium 3-bromo-4-nitrophenolate (158 mg, 0.730 mmol) were dissolved in dry DCM (7 mL) and stirred at room temperature for 3 h under N2 atmosphere. The reaction mixture was then diluted with DCM (50 mL) and washed with 2M NaOH (3 × 50 mL). The organic phase was then dried using a phase separation paper, concentrated in vacuo and purified by flash column chromatography (DCM/MeOH 98:2) to give ether 9 as a pale-yellow solid (45.9 mg, 0.0899 mmol, 37%); m.p. 175 °C; IR (ATR) ṽ/cm−1 2923, 1742, 1666, 1578, 1555, 1518, 1477, 1432, 1372, 1340, 1318, 1267, 1217, 1170, 1153, 1137, 1000, 979, 965, 809, 746, 721; δH (400 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 12.44 (s, 1H, CONH), 8.06 (d, J = 9.1 Hz, 1H, 5″-H), 7.61 (s, 1H, 4’-H), 7.55 (d, J = 2.6 Hz, 1H, 2″-H), 7.23 (dd, J = 9.1, 2.7 Hz, 1H, 6″-H), 6.95 (d, J = 0.6 Hz, 1H, 5-H), 5.46–5.43 (m, 2H, OCH2), 4.12 (s, 2H, SCH2), 2.28 (s, 6H, 4-CH3 and 6-CH3). δC (126 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 168.9 (C-2), 167.3 (CONH), 167.0 (C-4 and C-6), 161.0 (C-1″), 159.1 (C-2’), 142.6 (C-4″), 138.8 (C-4’), 127.9 (C-5″), 125.1 (C-5’), 120.6 (C-2″), 116.1 (C-5), 115.5 (C-3″), 115.2 (C-6″), 63.1 (OCH2), 34.1 (SCH2), 23.2 (4-CH3 and 6-CH3). HRMS (ESI): m/z = [M+H]+ calculated for C18H17BrN5O4S2+: 509.9905; found: 509.9895.
2-((4,6-Dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(5-((3-iodo-4-nitrophenoxy)methyl)thiazol-2-yl)acetamide (10). To a stirred solution of 3-iodo-4-nitrophenol (220 mg, 0.805 mmol) in dry MeOH (3 mL) was added sodium methanolate 25% (w/w) in MeOH (0.179 mL, 0.805 mmol). The solution was stirred at room temperature for 5 min, then concentrated in vacuo to give sodium 3-iodo-4-nitrophenolate as an orange solid, which was used for the next step without further purification. Chloromethyl compound 5 (143 mg, 0.434 mmol) and sodium 3-iodo-4-nitrophenolate (177 mg, 0.650 mmol) were dissolved in dry DCM (7 mL) and stirred at room temperature for 3 h under N2 atmosphere. The reaction mixture was then diluted with DCM (50 mL) and washed with 2M NaOH (3 × 50 mL). The organic phase was then dried using a phase separation paper, concentrated in vacuo and purified by flash column chromatography (DCM/MeOH 98:2) to give ether 10 as a pale-yellowsolid (93.3 mg, 0.167 mmol, 39%); m.p. 81 °C; IR (ATR) ṽ/cm−1 2920, 1688, 1574, 1515, 1337, 1315, 1265, 1222, 1165, 988, 868, 815, 747; δH (400 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 12.43 (s, 1H, CONH), 7.99 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H, 5′-H), 7.72 (d, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H, 2′-H), 7.60 (s, 1H, 4-H), 7.23 (dd, J = 9.1, 2.7 Hz, 1H, 6′-H), 6.95 (s, 1H, 5″-H), 5.43–5.42 (m, 2H, OCH2), 4.12 (s, 2H, SCH2), 2.28 (s, 6H, 4″-CH3 and 6″-CH3). δC (101 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 168.9 (C-2″), 167.3 (CONH), 167.0 (C-4″ and C-6″), 160.6 (C-1′), 159.1 (C-2), 146.0 (C-4′), 138.7 (C-4), 127.3 (C-2′ or C-5′), 127.1 (C-2′ or C-5′), 125.2 (C-5), 116.1 (C-5″), 115.5 (C-6′), 90.2 (C-3′), 62.9 (OCH2), 34.1 (SCH2), 23.2 (4″-CH3 and 6″-CH3); HRMS (ESI): m/z = [M+H]+ calculated for C18H17IN5O4S2+: 557.9761; found: 557.9755.
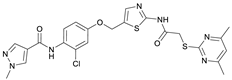
N-(5-((3-Chloro-4-nitrophenoxy)methyl)thiazol-2-yl)-2-((4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)thio)acetamide (11). To a stirred solution of 3-chloro-4-nitrophenol (141 mg, 0.805 mmol) in dry MeOH (3 mL) was added sodium methanolate 25% (w/w) in MeOH (0.179 mL, 0.805 mmol). The solution was stirred at room temperature for 5 min, then concentrated in vacuo to give sodium 3-chloro-4-nitrophenolate as an orange solid, which was used for the next step without further purification. Chloromethyl compound 5 (143 mg, 0.434 mmol) and sodium 3-chloro-4-nitrophenolate (116 mg, 0.652 mmol) were dissolved in dry DCM (7 mL) and stirred at room temperature for 3 h under N2 atmosphere. The reaction mixture was then diluted with DCM (50 mL) and washed with 2M NaOH (3 × 50 mL). The organic phase was then dried using a phase separation paper, concentrated in vacuo and purified by flash column chromatography (DCM/MeOH 98:2) to give ether 11 as a pale-yellow solid (96.6 mg, 0.207 mmol, 48%); m.p. 225 °C; IR (ATR) ṽ/cm−1 2924, 1666, 1583, 1556, 1516, 1481, 1433, 1373, 1640, 1321, 1267, 1219, 1171, 1155, 1138, 1037, 985, 964, 891, 825, 808, 747, 721; δH (400 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 12.44 (s, 1H, CONH), 8.10 (d, J = 9.1 Hz, 1H, 5″-H), 7.62 (s, 1H, 4‘-H), 7.43 (d, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H, 2″-H), 7.20 (dd, J = 9.2, 2.7 Hz, 1H, 6″-H), 6.95 (s, 1H, 5-H), 5.45 (d, J = 0.7 Hz, 2H, OCH2), 4.12 (s, 2H, SCH2), 2.28 (s, 6H, 4-CH3 and 6-CH3). δC (101 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 168.9 (C-2), 167.3 (CONH), 167.0 (C-4 and C-6), 161.3 (C-1″), 159.1 (C-2′), 140.6 (C-4″), 138.8 (C-4’), 128.1 (C-5″), 127.7 (C-3″), 125.0 (C-5′), 117.5 (C-2″), 116.1 (C-5), 114.9 (C-6″), 63.2 (OCH2), 34.1 (SCH2), 23.2 (4-CH3 and 6-CH3). HRMS (ESI): m/z = [M+Na]+ calculated for C18H16ClN5O4S2Na+: 488.0230; found: 488.0218.
N-(2-Bromo-4-((2-(2-((4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)thio)acetamido)thiazol-5-yl)-methoxy)phenyl)-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide (RW-93). 1-Methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid (3.00 g, 23.8 mmol) was treated with thionyl chloride (10 mL, 136 mmol) and the mixture stirred at 80 °C for 2 h. The excess thionyl chloride was then removed in vacuo to give 1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonyl chloride as a thick white suspension which solidified to a white solid upon standing at room temperature. Reduction of nitrobenzene 9 (46.0 mg, 90.1 µmol) was performed according to General Procedure: Nitrobenzene reduction. The obtained crude amine was dissolved in dry DCM (1 mL). 1-Methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonyl chloride (26.2 mg, 0.181 mmol) and pyridine (3.66 µL, 45.3 µmol) were added into the reaction mixture and the solution was stirred at room temperature for 1 h. The reaction mixture was then concentrated in vacuo and the crude product was purified by flash column chromatography (DCM/MeOH 98:2) to give RW-93 as a white solid (19.7 mg, 33.5 µmol, 37% over two steps); m.p. 185 °C; elemental analysis found: C, 46.9; H, 3.9; N, 16.1; S, 10.9%; calc. for C23H22BrN7O3S2: C, 46.9; H, 3.8; N, 16.65; S, 10.9%; IR (ATR) ṽ/cm−1 3418, 2918, 1689, 1675, 1581, 1532, 1411, 1392, 1314, 1293, 1278, 1265, 1223, 1165, 1124, 1047, 1003, 982, 870, 845, 807, 743; δH (400 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 12.39 (s, 1H, 2″-NHCO), 9.49 (s, 1H, 4-CONH), 8.25 (s, 1H, 5-H), 7.96 (s, 1H, 3-H), 7.56 (s, 1H, 4″-H), 7.37–7.33 (m, 2H, 3’-H and 6’-H), 7.05 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.8 Hz, 1H, 5’-H), 6.96 (s, 1H, 5‴-H), 5.31 (s, 2H, OCH2), 4.12 (s, 2H, SCH2), 3.88 (s, 3H, NCH3), 2.29 (s, 6H, 4‴-CH3 and 6‴-CH3). δC (101 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 168.9 (C-2‴), 167.0 (2″-NHCO, C-4‴ and C-6‴), 160.7 (4-CONH), 158.9 (C-2″) 156.2 (C-4’), 138.8 (C-3), 138.1 (C-4″), 132.6 (C-5), 129.8 (C-3’), 129.6 (C-1’), 126.0 (C-5″), 118.6 (C-6’), 117.9 (C-4), 116.1 (C-5‴), 115.0 (C-5’), 62.5 (OCH2), 38.8 (NCH3), 34.2 (SCH2), 23.2 (4‴-CH3 and 6‴-CH3). HRMS (ESI): m/z = [M+H]+ calculated for C23H23BrN7O3S2+: 588.0482; found: 588.0480.
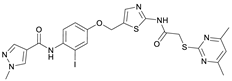
N-(4-((2-(2-((4,6-Dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)thio)acetamido)thiazol-5-yl)methoxy)-2-iodophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide (RW-95). 1-Methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid (3.00 g, 23.8 mmol) was treated with thionyl chloride (10 mL, 136 mmol) and the mixture stirred at 80 °C for 2 h. The excess thionyl chloride was then removed in vacuo to give 1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonyl chloride as a thick white suspension which solidified to a white solid upon standing at room temperature. Reduction of nitrobenzene 10 (83.0 mg, 0.149 mmol) was performed according to General Procedure: Nitrobenzene reduction. The obtained crude primary amine was dissolved in dry DCM (1.5 mL). 1-Methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonyl chloride (43.0 mg, 0.298 mmol) and pyridine (6.02 µL, 74.4 µmol) were added into the reaction mixture and the solution was stirred at room temperature for 1 h. The reaction mixture was then concentrated in vacuo and the crude product was purified via flash column chromatography (DCM/MeOH 98:2) to give RW-95 as a white solid (37.0 mg, 58.2 µmol, 39% over two steps); m.p. 202 °C; elemental analysis: found: C, 43.3; H, 3.5; N, 15.2; S, 10.1%; calc. for C23H22IN7O3S2: C, 43.5; H, 3.5; N, 15.4; S, 10.1%; IR (ATR) ṽ/cm−1 3396, 3175, 3139, 2918, 1697, 1671, 1580, 1553, 1525, 1433, 1386, 1327, 1309, 1276, 1268, 1217, 1206, 1168, 1151, 991, 984, 855, 815, 777, 745, 732; δH (500 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 12.40 (s, 1H, 2″-NHCO), 9.48 (s, 1H, 4-CONH), 8.25 (s, 1H, 5-H), 7.96 (s, 1H, 3-H), 7.56 (s, 1H, 4″-H), 7.53 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, 1H, 3’-H), 7.25 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H, 6’-H), 7.07 (dd, J = 8.7, 2.8 Hz, 1H, 5’-H), 6.96 (s, 1H, 5‴-H), 5.30 (s, 2H, OCH2), 4.12 (s, 2H, SCH2), 3.88 (s, 3H, NCH3), 2.29 (s, 6H, 4‴-CH3 and 6‴-CH3). δC (126 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 168.9 (C-2‴), 167.2 (2″-NHCO), 167.0 (C-4‴ and C-6‴), 160.7 (4-CONH), 158.8 (C-2″), 156.2 (C-4’), 138.8 (C-3), 138.1 (C-4″), 133.0 (C-1’), 132.5 (C-5), 129.1 (C-6’), 126.1 (C-5″), 124.5 (C-3’), 118.1 (C-4), 116.1 (C-5‴), 115.6 (C-5’), 99.6 (C-2’), 62.4 (OCH2), 38.8 (NCH3), 34.1 (SCH2), 23.2 (4‴-CH3 and 6‴-CH3); HRMS (ESI): m/z = [M+H]+ calculated for C23H23IN7O3S2+: 636.0343; found: 636.0336.
N-(2-Chloro-4-((2-(2-((4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)thio)acetamido)thiazol-5-yl)methoxy)phenyl)-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide (RW-99). 1-Methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid (3.00 g, 23.8 mmol) was treated with thionyl chloride (10 mL, 136 mmol) and the mixture stirred at 80 °C for 2 h. The excess thionyl chloride was then removed in vacuo to give 1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonyl chloride as a thick white suspension which solidified to a white solid upon standing at room temperature. Reduction of nitrobenzene 9 (80.0 mg, 0.172 mmol) was performed according to General Procedure: Nitrobenzene reduction. The obtained crude amine was dissolved in dry DCM (1.5 mL). 1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonyl chloride (49.7 mg, 0.344 mmol) and pyridine (6.96 µL, 86.0 µmol) were added into the reaction mixture and the solution was stirred at room temperature for 1 h. The reaction mixture was then concentrated in vacuo and the crude product was purified via flash column chromatography (DCM/MeOH 98:2) to give RW-99 as a white solid (35.8 mg, 65.8 µmol, 38% over two steps); m.p. 195 °C; elemental analysis: found: C, 50.5; H, 4.1; N, 17.6; S, 11.7; Cl, 6.9%; calc: for C23H22ClN7O3S2: C, 50.8; H, 4.1; N, 18.0; S, 11.8; Cl, 6.5%; IR (ATR) ṽ/cm−1 2918, 1679, 1582, 1555, 1535, 1394, 1315, 1295, 1281, 1267, 1224, 1167, 1050, 1003, 900, 869, 845, 809, 743; δH (400 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 12.40 (s, 1H, 2″-NHCO), 9.51 (s, 1H, 4-CONH), 8.26 (s, 1H, 5-H), 7.96 (s, 1H, 3-H), 7.57 (s, 1H, 4″-H), 7.39 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H, 6’-H), 7.22 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, 1H, 3’-H), 7.01 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.8 Hz, 1H, 5’-H), 6.96 (s, 1H, 5‴-H), 5.31 (s, 2H, OCH2), 4.12 (s, 2H, SCH2), 3.88 (s, 3H, NCH3), 2.29 (s, 6H, 4‴-CH3 and 6‴-CH3). δC (101 MHz; (CD3)2SO) 168.9 (C-2‴), 167.2 (2″-NHCO), 167.0 (C-4‴ and C-6‴), 160.7 (4-CONH), 158.8 (C-2″), 156.0 (C-4’), 138.8 (C-3), 138.1 (C-4″), 132.6 (C-5), 130.4 (C-2’), 129.6 (C-6’), 128.1 (C-1’), 126.1 (C-5″), 117.8 (C-4), 116.1 (C-5‴), 115.6 (C-3’), 114.4 (C-5’), 62.5 (OCH2), 38.8 (NCH3), 34.1 (SCH2), 23.2 (4‴-CH3 and 6‴-CH3). HRMS (ESI): m/z = [M+Na]+ calculated for C23H22ClN7O3S2Na+: 566.0812; found: 566.0798.