Neurochemical Remodelling of the Enteric Nervous System Neurons in the Porcine Jejunum Following Low-Dose Glyphosate Exposure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
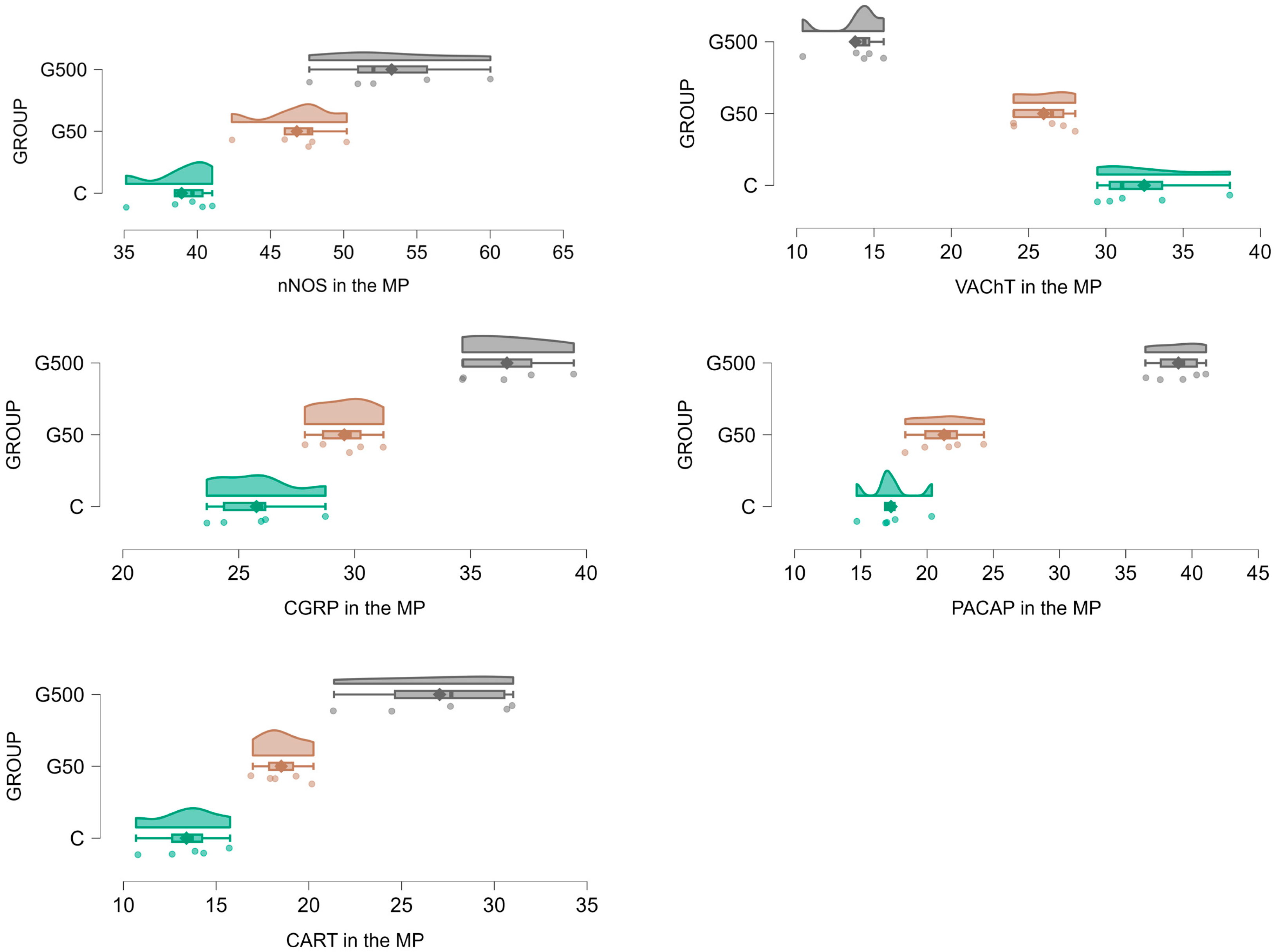
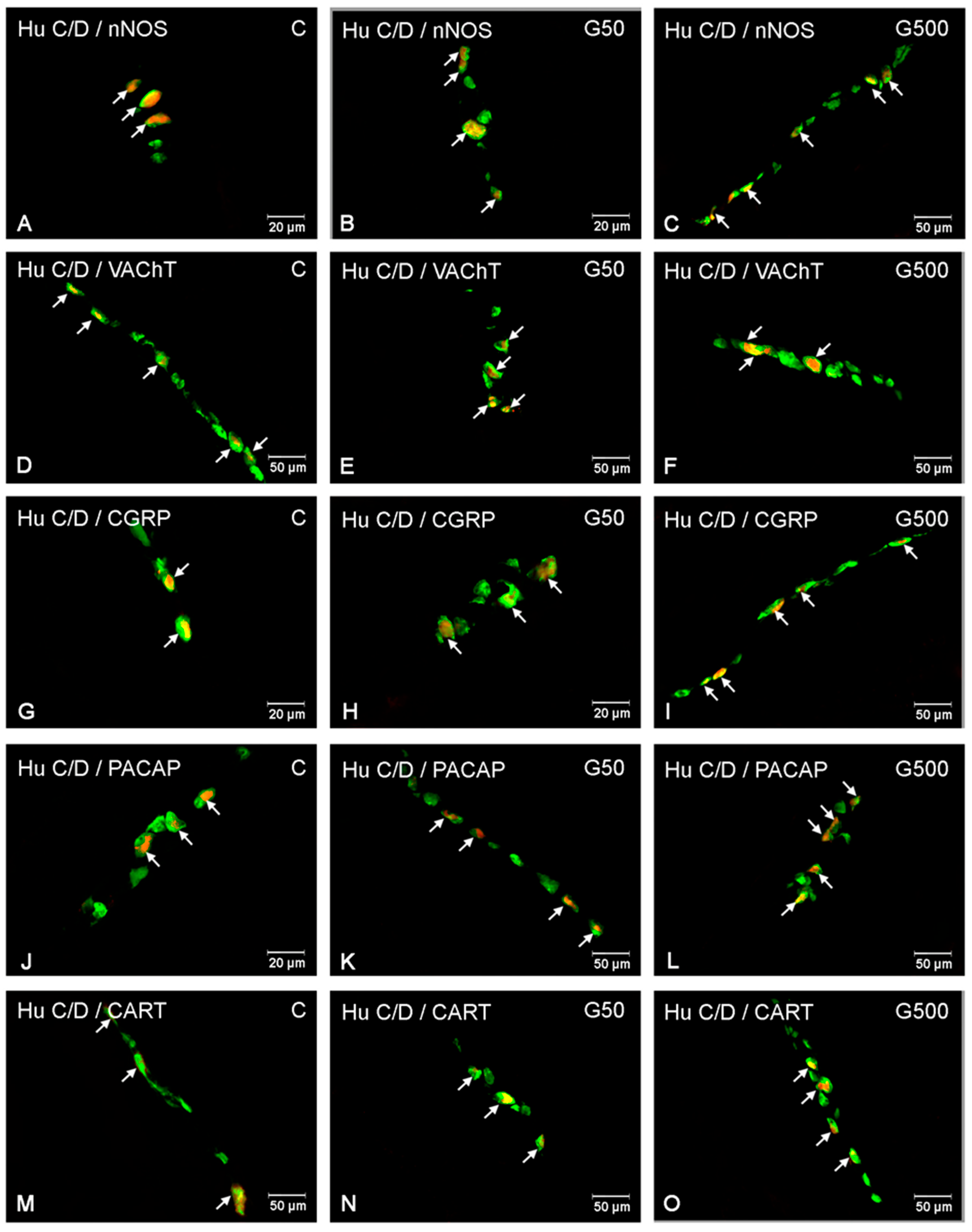
2.1. The Myenteric Plexus (MP)
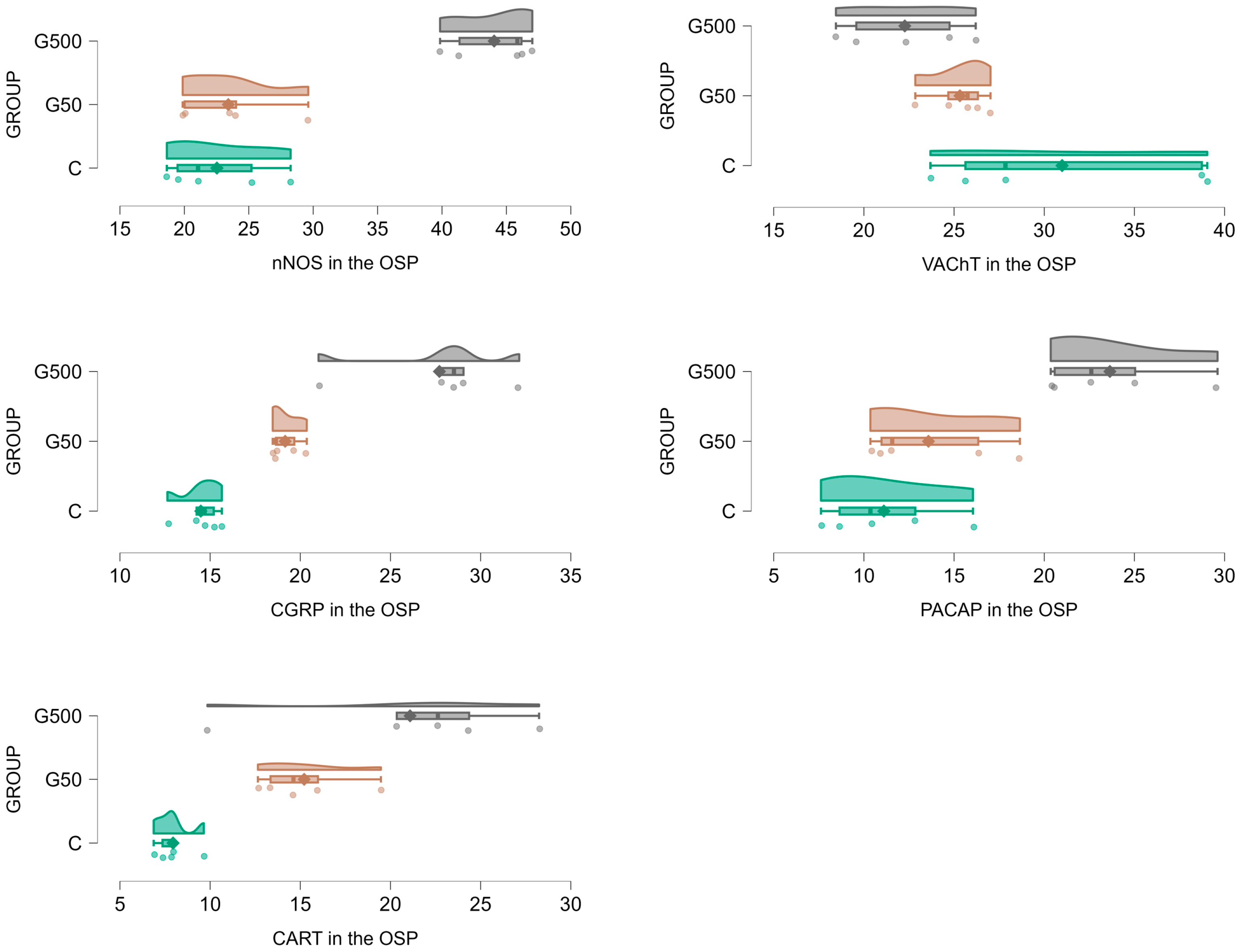
2.2. The Outer Submucosal Plexus (OSP)
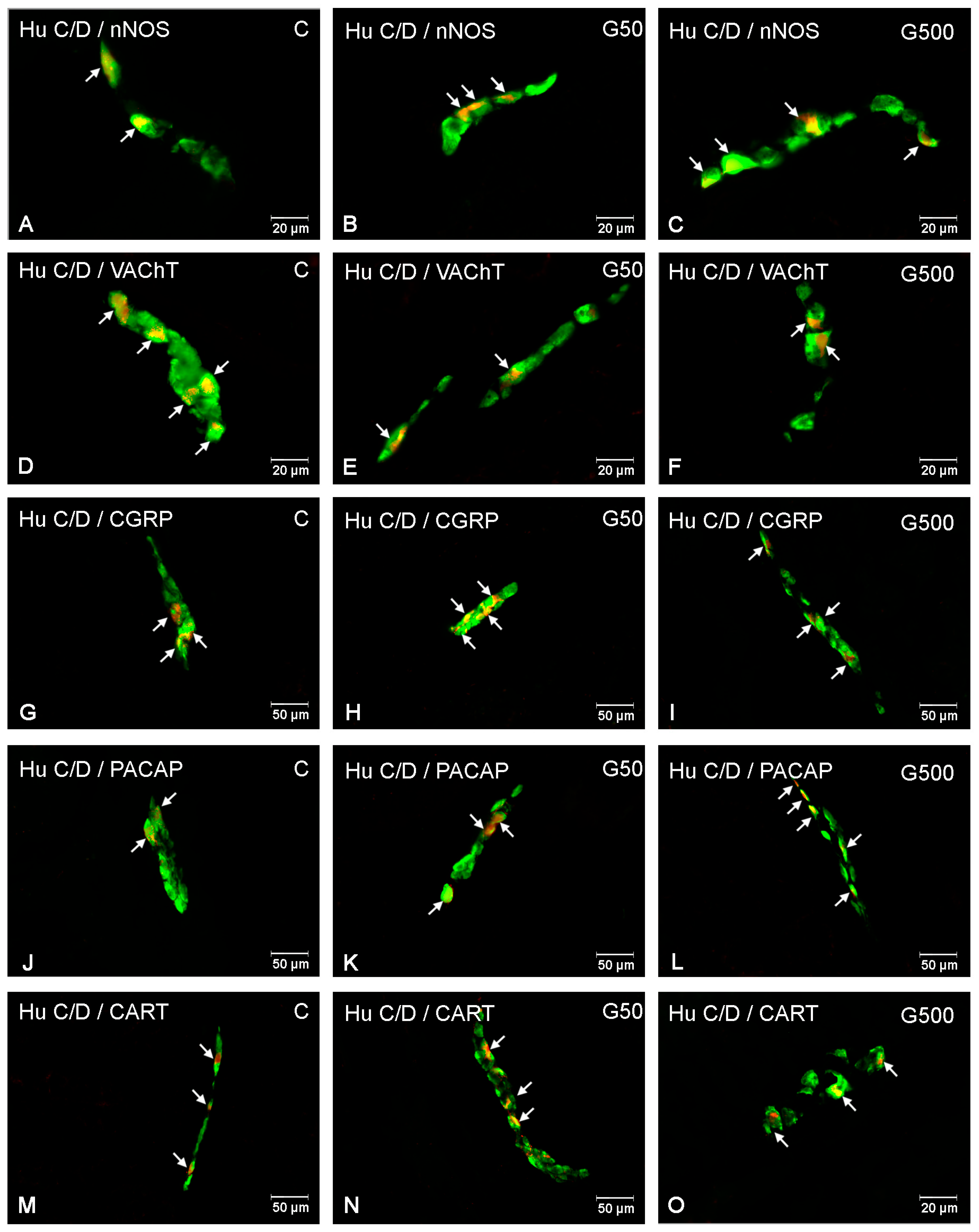
2.3. The Inner Submucosal Plexus (ISP)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Treatment
4.2. Tissue Sampling
4.3. Cutting and Immunofluorescence Staining
4.4. Microscopic Analysis and Counting
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Furness, J.B. The enteric nervous system and neurogastroenterology. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palus, K.; Obremski, K.; Bulc, M.; Całka, J. The impact of low and high doses of acrylamide on the intramural neurons of the porcine ileum. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 132, 110673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaroni, C.; De Ponti, F.; Cosentino, M.; Lecchini, S.; Frigo, G. Plasticity in the enteric nervous system. Gastroenterology 1999, 117, 1438–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, J.B. Integrated neural and endocrine control of gastrointestinal function. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 891, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabouridis, P.S.; Pachnis, V. Emerging roles of gut microbiota and the immune system in the development of the enteric nervous system. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymańska, K.; Gonkowski, S. Neurochemical characterization of the enteric neurons within the porcine jejunum in physiological conditions and under the influence of bisphenol A (BPA). Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 31, e13580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bist, P.; Choudhary, S. Impact of Heavy Metal Toxicity on the Gut Microbiota and Its Relationship with Metabolites and Future Probiotics Strategy: A Review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 5328–5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palus, K.; Chmielewska-Krzesińska, M.; Jana, B.; Całka, J. Glyphosate-induced changes in the expression of galanin and GALR1, GALR2 and GALR3 receptors in the porcine small intestine wall. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałęcka, I.; Całka, J. Oral Exposure to Microplastics Affects the Neurochemical Plasticity of Reactive Neurons in the Porcine Jejunum. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palus, K.; Całka, J. Influence of Acrylamide Administration on the Neurochemical Characteristics of Enteric Nervous System (ENS) Neurons in the Porcine Duodenum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpiesiuk, A.; Palus, K. Pituitary Adenylate Cyclase-Activating Polypeptide (PACAP) in Physiological and Pathological Processes within the Gastrointestinal Tract: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.; Lyford, G.; Gores, G.; Farrugia, G. Nitric oxide in gastrointestinal health and disease. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvidsson, U.; Riedl, M.; Elde, R.; Meister, B. Vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT) protein: A novel and unique marker for cholinergic neurons in the central and peripheral nervous systems. J. Comp. Neurol. 1997, 378, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowska, K.; Gonkowski, S. The Influence of Inflammation and Nerve Damage on the Neurochemical Characterization of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide-Like Immunoreactive (CGRP-LI) Neurons in the Enteric Nervous System of the Porcine Descending Colon. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palus, K.; Makowska, K.; Całka, J. Acrylamide-induced alterations in the cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated peptide transcript (CART)-like immunoreactivity within the enteric nervous system of the porcine small intestines. Ann. Anat. 2018, 219, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bruggen, A.H.C.; He, M.M.; Shin, K.; Mai, V.; Jeong, K.C.; Finckh, M.R.; Morris, J.G., Jr. Environmental and health effects of the herbicide glyphosate. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anadón, A.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; Martínez, M.A.; Castellano, V.J.; Martínez, M.; Martin, M.T.; Nozal, M.J.; Bernal, J.L. Toxicokinetics of glyphosate and its metabolite aminomethyl phosphonic acid in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 190, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, M.; Mele, E.; Viggiano, A.; Nori, S.L.; Meccariello, R.; Santoro, A. Pleiotropic outcomes of glyphosate exposure: From organ damage to effects on inflammation, cancer, reproduction and development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costas-Ferreira, C.; Durán, R.; Faro, L.R.F. Toxic Effects of Glyphosate on the Nervous System: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattani, D.; de Liz Oliveira Cavalli, V.L.; Heinz Rieg, C.E.; Domingues, J.T.; Dal-Cim, T.; Tasca, C.I.; Mena Barreto Silva, F.R.; Zamoner, A. Mechanisms underlying the neurotoxicity induced by glyphosate-based herbicide in immature rat hippocampus: Involvement of glutamate excitotoxicity. Toxicology 2014, 320, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portier, C.J.; Armstrong, B.K.; Baguley, B.C.; Baur, X.; Belyaev, I.; Belle, R.; Belpoggi, F.; Biggeri, A.; Bosland, M.C.; Bruzzi, P.; et al. Differences in the carcinogenic evaluation of glyphosate between the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2016, 70, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, K.; Tessema, R.A.; Budnik, L.T.; Adam, B. Comparative cyto- and genotoxicity assessment of glyphosate and glyphosate-based herbicides in human peripheral white blood cells. Environ. Res. 2019, 179 Pt B, 108851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peillex, C.; Pelletier, M. The impact and toxicity of glyphosate and glyphosate-based herbicides on health and immunity. J. Immunotoxicol. 2020, 17, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignácio, A.D.C.; Guerra, A.M.D.R.; de Souza-Silva, T.G.; Carmo, M.A.V.D.; Paula, H.A.A. Effects of glyphosate exposure on intestinal microbiota, metabolism and microstructure: A systematic review. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 7757–7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda-Ruzafa, L.; Cruz, F.; Roman, P.; Cardona, D. Gut microbiota and neurological effects of glyphosate. Neurotoxicology 2019, 75, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Fu, H.; Zhou, R.; Yang, Z.; Bai, G.; Shi, B. Toxic effects of glyphosate on intestinal morphology, antioxidant capacity and barrier function in weaned piglets. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 187, 109846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palus, K.; Bulc, M.; Całka, J. Glyphosate affects the neurochemical phenotype of the intramural neurons in the duodenum in the pig. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2023, 35, e14507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kararli, T.T. Comparison of the gastrointestinal anatomy, physiology, and biochemistry of humans and commonly used laboratory animals. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1995, 16, 351–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, C.J.; Gallegos, C.E.; Raisman-Vozari, R.; Minetti, A. Behavioral impairments following repeated intranasal glyphosate-based herbicide administration in mice. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2017, 64, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, Y.; O’Dell, K.A.; Zorumski, C.F. The herbicide glyphosate inhibits hippocampal long-term potentiation and learning through activation of pro-inflammatory signaling. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.A.; Ares, I.; Rodríguez, J.L.; Martínez, M.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; Anadón, A. Neurotransmitter changes in rat brain regions following glyphosate exposure. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiantia, G.; Comai, D.; Hidisoglu, E.; Gurgone, A.; Franchino, C.; Carabelli, V.; Marcantoni, A.; Giustetto, M. Glyphosate impairs both structure and function of GABAergic synapses in hippocampal neurons. Neuropharmacology 2025, 262, 110183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astiz, M.; de Alaniz, M.J.; Marra, C.A. Antioxidant defense system in rats simultaneously intoxicated with agrochemicals. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 28, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Tang, J.; Ren, X.; Li, C. Glyphosate exposure induces inflammatory responses in the small intestine and alters gut microbial composition in rats. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Shangguan, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Sultan, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, X. Negative impacts of microcystin-LR and glyphosate on zebrafish intestine: Linked with gut microbiota and microRNAs? Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panza, S.B.; Vargas, R.; Balbo, S.L.; Bonfleur, M.L.; Granzotto, D.C.T.; Sant’Ana, D.M.G.; Nogueira-Melo, G.A. Perinatal exposure to low doses of glyphosate-based herbicide combined with a high-fat diet in adulthood causes changes in the jejunums of mice. Life Sci. 2021, 275, 119350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Martín, R.D.; Valencia-Hernández, J.D.; Betancourt-Lozano, M.; Yáñez-Rivera, B. Changes in microtubule stability in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos after glyphosate exposure. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, D.; Xie, J.; Wang, J. Neuroprotective Effects of Brain-Gut Peptides: A Potential Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease. Neurosci. Bull. 2019, 35, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Hu, S.; Yang, M.; Pan, H.; Zhu, S. CART peptide promotes the survival of hippocampal neurons by upregulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 347, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, V.; Mancuso, C.; Calvani, M.; Rizzarelli, E.; Butterfield, D.A.; Stella, A.M. Nitric oxide in the central nervous system: Neuroprotection versus neurotoxicity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y. The regulatory role of nitric oxide in proinflammatory cytokine expression during the induction and resolution of inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 88, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrecht, N.; Burchert, M.; Respondek, M.; Müller, K.M.; Peskar, B.M. Role of calcitonin gene-related peptide and nitric oxide in the gastroprotective effect of capsaicin in the rat. Gastroenterology 1993, 104, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rytel, L.; Gonkowski, I.; Grzegorzewski, W.; Wojtkiewicz, J. Chemically-Induced Inflammation Changes the Number of Nitrergic Nervous Structures in the Muscular Layer of the Porcine Descending Colon. Animals 2021, 11, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulc, M.; Całka, J.; Palus, K. Effect of Streptozotocin-Inducted Diabetes on the Pathophysiology of Enteric Neurons in the Small Intestine Based on the Porcine Diabetes Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costas-Ferreira, C.; Durán, R.; Faro, L.R.F. Evaluation of the potential role of glutamatergic, cholinergic, and nitrergic systems in the dopamine release induced by the pesticide glyphosate in rat striatum. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2024, 44, 1489–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowska, K.; Gonkowski, S. Changes Caused by Bisphenols in the Chemical Coding of Neurons of the Enteric Nervous System of Mouse Stomach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandpal, M.; Indari, O.; Baral, B.; Jakhmola, S.; Tiwari, D.; Bhandari, V.; Pandey, R.K.; Bala, K.; Sonawane, A.; Jha, H.C. Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota from the Perspective of the Gut-Brain Axis: Role in the Provocation of Neurological Disorders. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, J.S.; Mak, W.Q.; Tan, L.K.S.; Ng, C.X.; Chan, H.H.; Yeow, S.H.; Foo, J.B.; Ong, Y.S.; How, C.W.; Khaw, K.Y. Microbiota-gut-brain axis and its therapeutic applications in neurodegenerative diseases. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2024, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesnage, R.; Calatayud, M.; Duysburgh, C.; Marzorati, M.; Antoniou, M.N. Alterations in infant gut microbiome composition and metabolism after exposure to glyphosate and Roundup and/or a spore-based formulation using the SHIME technology. Gut Microbiome 2022, 3, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bombardi, C.; Rambaldi, A.M.; Galiazzo, G.; Giancola, F.; Graïc, J.M.; Salamanca, G.; Cozzi, B.; Chiocchetti, R. Nitrergic and Substance P Immunoreactive Neurons in the Enteric Nervous System of the Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) Intestine. Animals 2021, 11, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercurio, P.; Flores, F.; Mueller, J.F.; Carter, S.; Negri, A.P. Glyphosate persistence in seawater. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feltracco, M.; Barbaro, E.; Morabito, E.; Zangrando, R.; Piazza, R.; Barbante, C.; Gambaro, A. Assessing glyphosate in water, marine particulate matter, and sediments in the Lagoon of Venice. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 16383–16391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palus, K.; Bulc, M.; Całka, J. Changes in Somatostatin-Like Immunoreactivity in the Sympathetic Neurons Projecting to the Prepyloric Area of the Porcine Stomach Induced by Selected Pathological Conditions. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9037476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Primary antibody | ||||
| Antigen | Host species | Cat No. | Dilution | Supplier |
| Hu C/D | mouse | A-21271 | 1:1000 | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA |
| PACAP | guinea pig | T-5039 | 1:3000 | Peninsula, San Carlos, CA, USA |
| CGRP | rabbit | MAB317 | 1:4000 | Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA |
| CART | rabbit | H-003-61 | 1:8000 | Phoenix Pharmaceuticals, Burlingame, CA, USA |
| nNOS | rabbit | AB5380 | 1:2000 | Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA |
| VAChT | rabbit | H-V007 | 1:2000 | Phoenix Pharmaceuticals, Burlingame, CA, USA |
| Secondary antibodies | ||||
| Reagents | Cat No. | Dilution | Supplier | |
| Alexa Fluor 488 donkey anti- mouse IgG | A21202 | 1:1000 | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA | |
| Alexa Fluor 546 donkey anti- guinea pig IgG | A11074 | 1:1000 | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA | |
| Alexa Fluor 546 goat anti- rabbit IgG | A11010 | 1:1000 | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palus, K.; Karpiesiuk, A.; Jana, B. Neurochemical Remodelling of the Enteric Nervous System Neurons in the Porcine Jejunum Following Low-Dose Glyphosate Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9840. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209840
Palus K, Karpiesiuk A, Jana B. Neurochemical Remodelling of the Enteric Nervous System Neurons in the Porcine Jejunum Following Low-Dose Glyphosate Exposure. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):9840. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209840
Chicago/Turabian StylePalus, Katarzyna, Aleksandra Karpiesiuk, and Barbara Jana. 2025. "Neurochemical Remodelling of the Enteric Nervous System Neurons in the Porcine Jejunum Following Low-Dose Glyphosate Exposure" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 9840. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209840
APA StylePalus, K., Karpiesiuk, A., & Jana, B. (2025). Neurochemical Remodelling of the Enteric Nervous System Neurons in the Porcine Jejunum Following Low-Dose Glyphosate Exposure. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 9840. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209840






