Discovery of Blood-Based Proteins That Mark Benzo[a]pyrene Modulation of Autoimmunity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
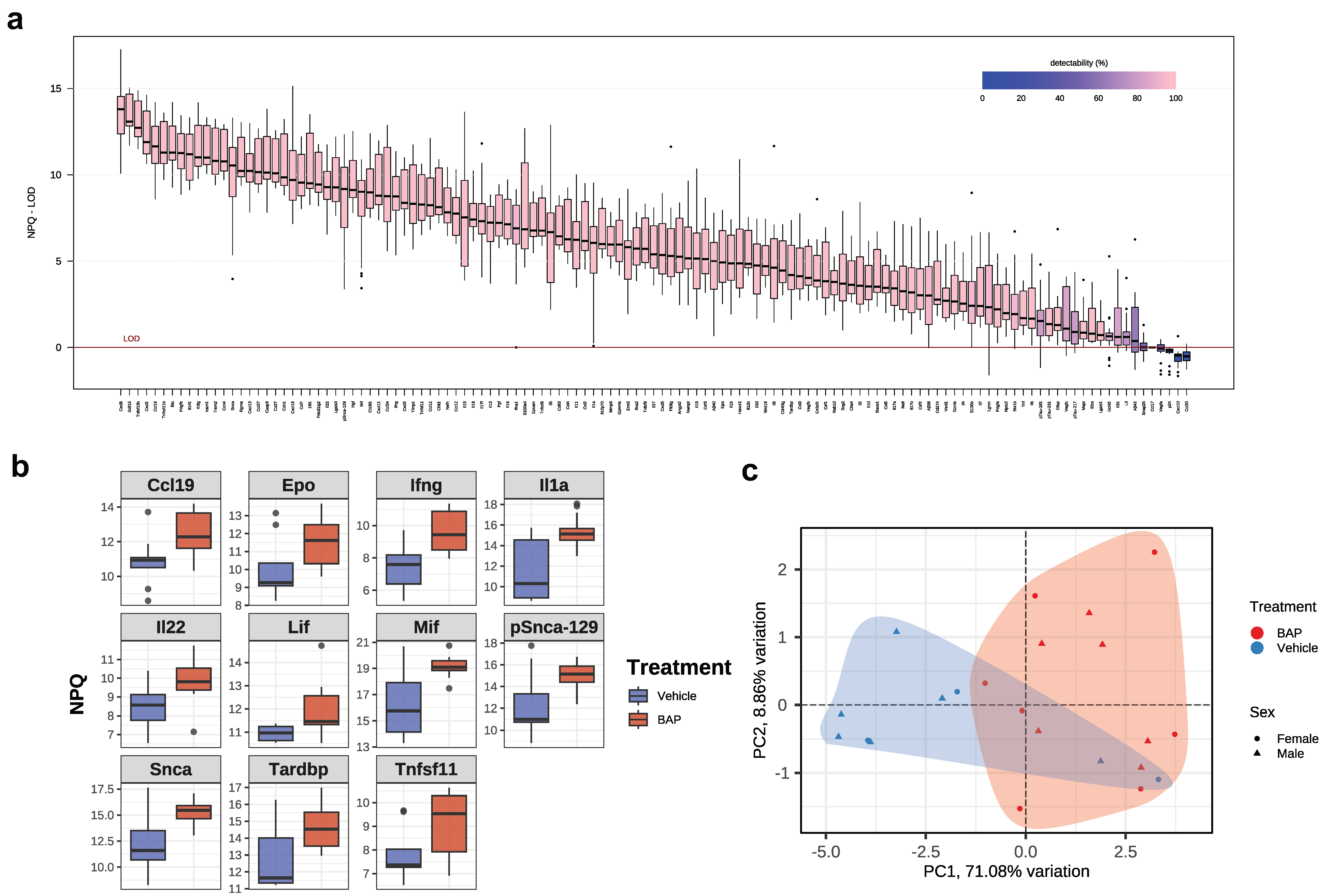
2.1. Characteristics of Murine Model Used and Cytokine Profiling
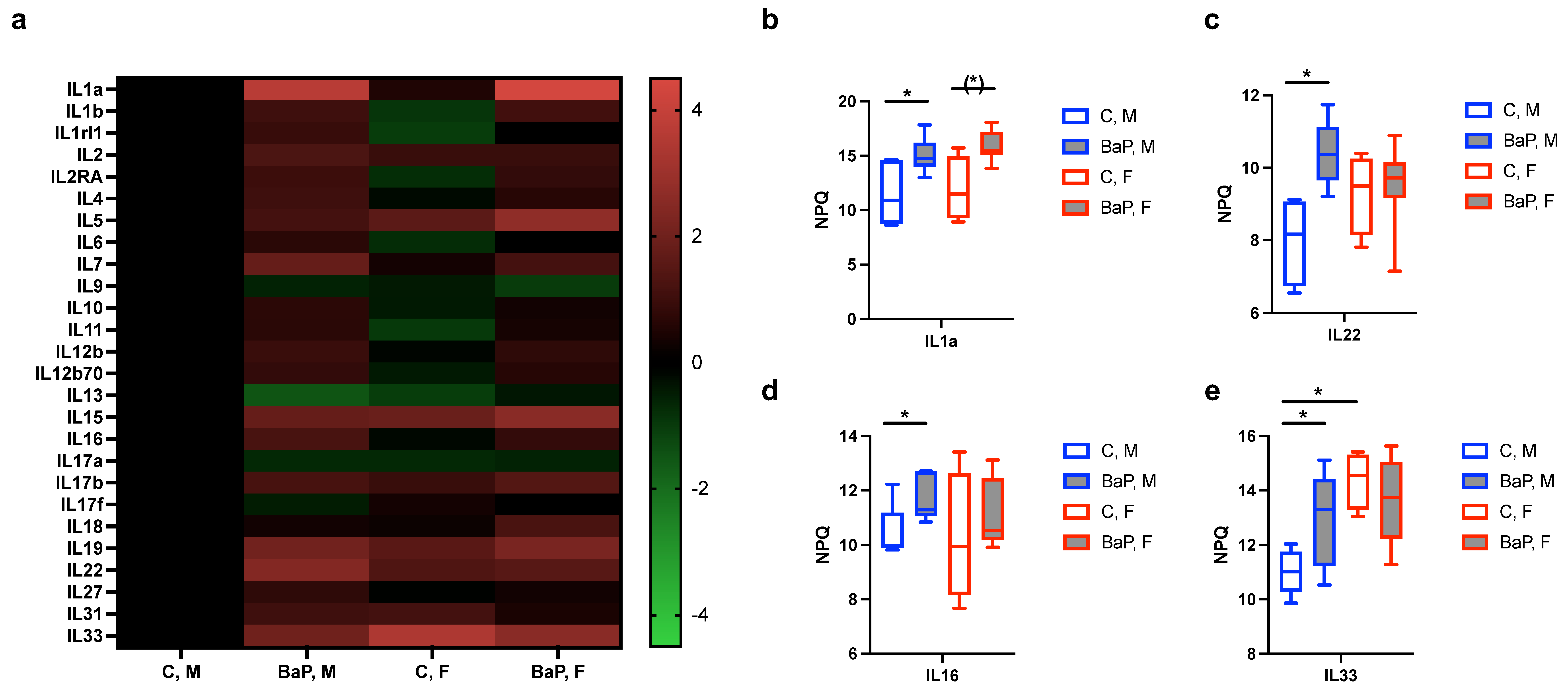
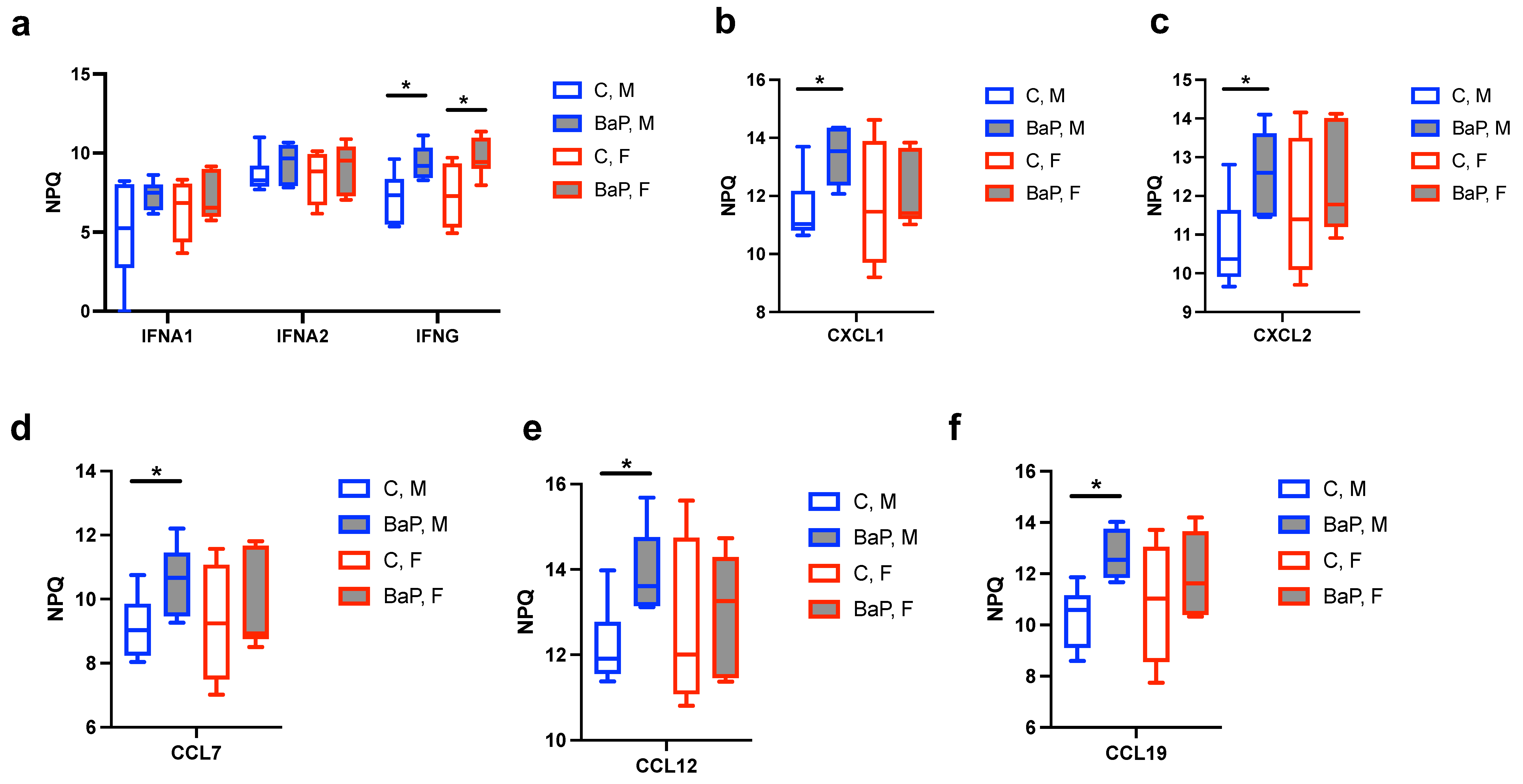
2.2. Serum Cytokines Regulated by BaP
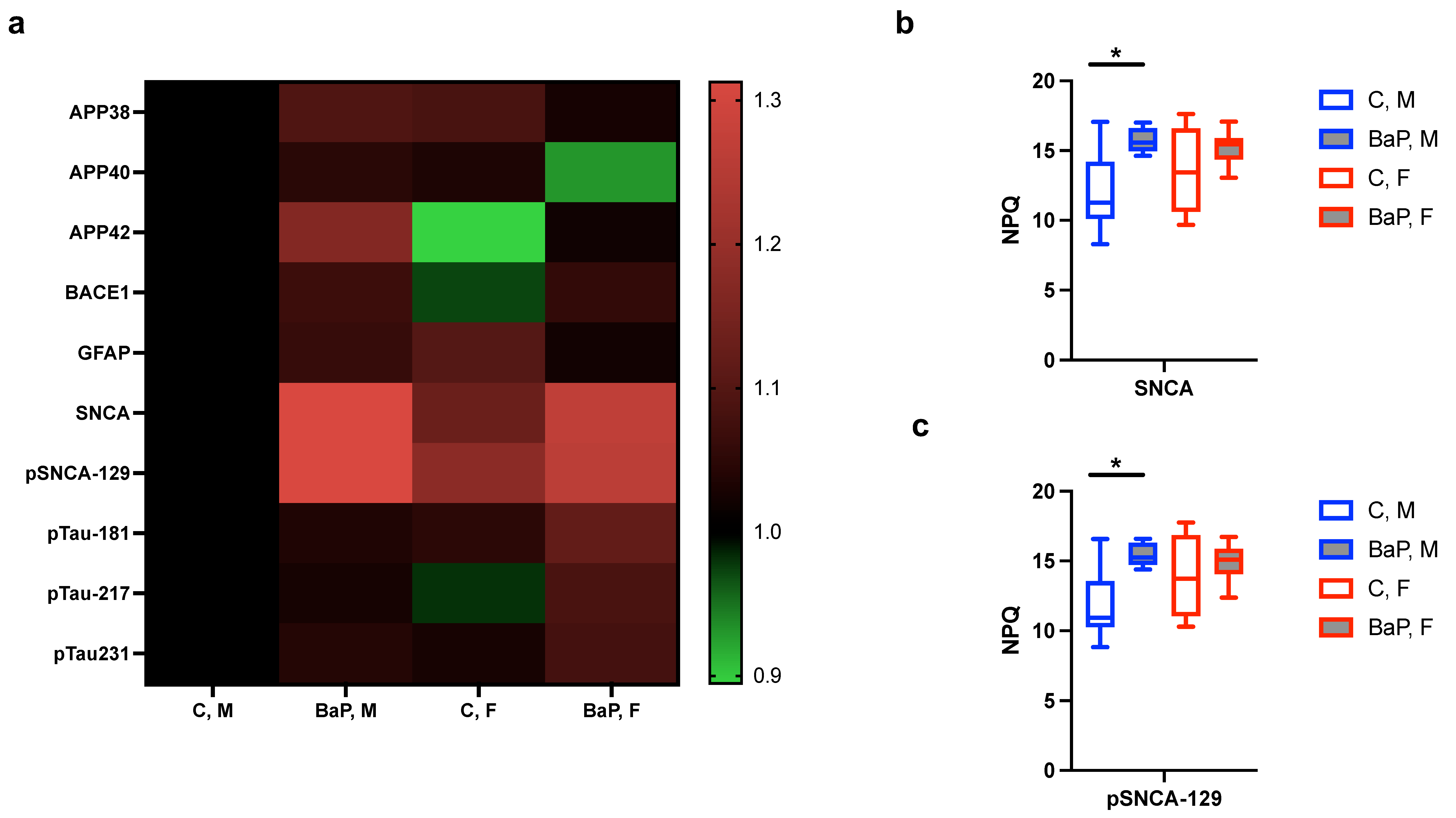
2.3. Blood-Based Markers of Neurological Disorders in the BaP-MRL Model
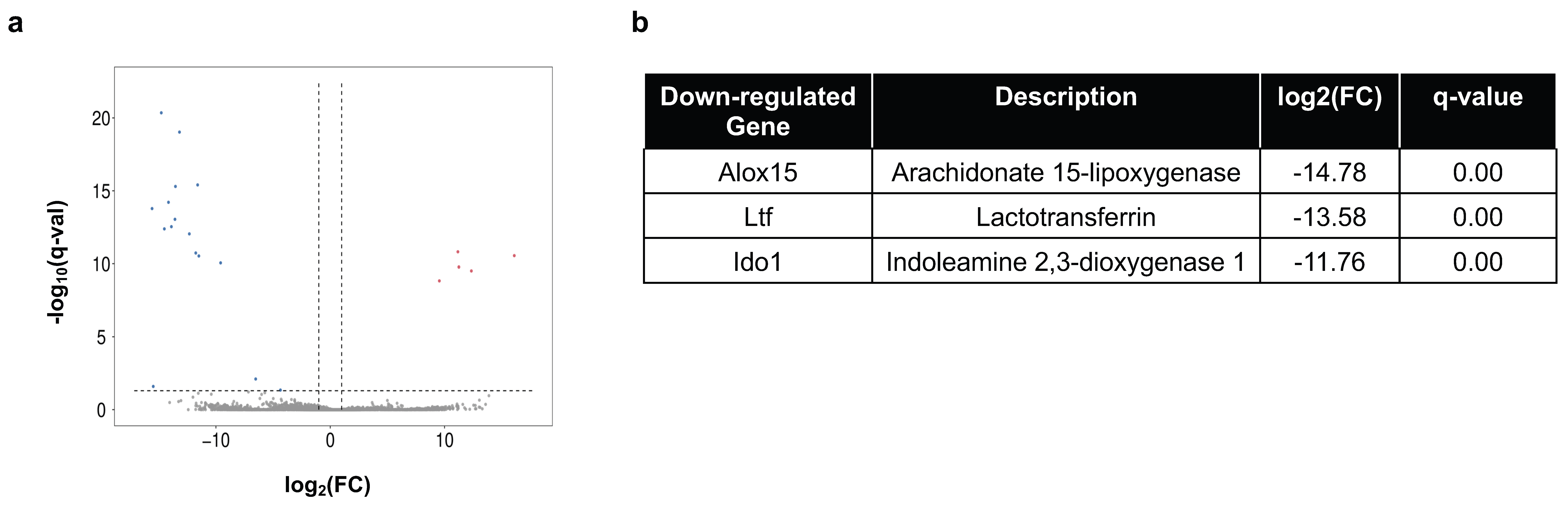
2.4. Immune Gene Expression in Peripheral Organs
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. NULISASeq
4.3. Transcriptomic Analysis
4.4. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
| IL1a: | ACGGCTGAGTTTCAGTGAGACC |
| CACTCTGGTAGGTGTAAGGTGC | |
| IL6: | TACCACTTCACAAGTCGGAGGC |
| CTGCAAGTGCATCATCGTTGTTC | |
| IL15: | GTAGGTCTCCCTAAAACACAGAGGC |
| TCCAGGAGAAAGCAGTTCATTGC | |
| IL18: | GACAGCCTGTGTTCGAGGATATG |
| TGTTCTTACAGGAGAGGGTAGAC | |
| IL33: | CTACGCATGAGACTCCGTTCTG |
| AGAATCCCGTGGATAGGCAGAG |
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collison, J. Autoimmunity: The ABCs of autoimmune disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costenbader, K.H.; Gay, S.; Alarcon-Riquelme, M.E.; Iaccarino, L.; Doria, A. Genes, epigenetic regulation and environmental factors: Which is the most relevant in developing autoimmune diseases? Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.; Wang, H. Environmental Exposures and Autoimmune Diseases: Contribution of Gut Microbiome. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, F.W. The increasing prevalence of autoimmunity and autoimmune diseases: An urgent call to action for improved understanding, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2023, 80, 102266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.N.; Xu, Z.; Wu, G.C.; Mao, Y.M.; Liu, L.N.; Qian, W.; Dan, Y.L.; Tao, S.S.; Zhang, Q.; Sam, N.B.; et al. Emerging role of air pollution in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvani, N.; Caricchio, R.; Tucci, M.; Sobel, E.S.; Silvestris, F.; Tartaglia, P.; Richards, H.B. Induction of apoptosis by the hydrocarbon oil pristane: Implications for pristane-induced lupus. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 4777–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, W.H.; Lee, P.Y.; Weinstein, J.S.; Satoh, M.; Lu, L. Induction of autoimmunity by pristane and other naturally occurring hydrocarbons. Trends Immunol. 2009, 30, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe, W.; Allsopp, P.J.; Watson, G.E.; Magee, P.J.; Strain, J.J.; Armstrong, D.J.; Ball, E.; McSorley, E.M. Mercury as an environmental stimulus in the development of autoimmunity—A systematic review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, K.M.; Cauvi, D.M.; Toomey, C.B.; Hultman, P.; Kono, D.H. Mercury-induced inflammation and autoimmunity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 129299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, K.M.; Escalante, G.M.; Huang, H.; Haraldsson, K.M.; Hultman, P.; Christy, J.M.; Pawar, R.D.; Mayeux, J.M.; Gonzalez-Quintial, R.; Baccala, R.; et al. Induction of Systemic Autoimmunity by a Xenobiotic Requires Endosomal TLR Trafficking and Signaling from the Late Endosome and Endolysosome but Not Type I IFN. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 3739–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, C.G.; Santos, A.S.E.; Lerro, C.C.; DellaValle, C.T.; Ward, M.H.; Alavanja, M.C.; Berndt, S.I.; Beane Freeman, L.E.; Sandler, D.P.; Hofmann, J.N. Lifetime Pesticide Use and Antinuclear Antibodies in Male Farmers From the Agricultural Health Study. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobel, E.S.; Gianini, J.; Butfiloski, E.J.; Croker, B.P.; Schiffenbauer, J.; Roberts, S.M. Acceleration of autoimmunity by organochlorine pesticides in (NZB × NZW)F1 mice. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Sobel, E.S.; Butfiloski, E.J.; Roberts, S.M. Comparison of chlordecone and estradiol effects on splenic T-cells in (NZBxNZW)F(1) mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 183, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freemer, M.M.; King, T.E., Jr.; Criswell, L.A. Association of smoking with dsDNA autoantibody production in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perricone, C.; Ceccarelli, F.; Massaro, L.; Alessandri, C.; Spinelli, F.R.; Marocchi, E.; Miranda, F.; Truglia, S.; Valesini, G.; Conti, F. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus with or without Anti-Dsdna Antibodies: Not So Different. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1085–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speyer, C.B.; Costenbader, K.H. Cigarette smoking and the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reizer, E.; Csizmadia, I.G.; Palotas, A.B.; Viskolcz, B.; Fiser, B. Formation Mechanism of Benzo(a)pyrene: One of the Most Carcinogenic Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH). Molecules 2019, 24, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.L.; Ye, Z.M.; Ling, Y.X.; Cai, S.F.; Xu, J.L.; Fan, C.H.; Zhong, Y.H.; Shen, Q.; Li, Y.J. Relationship between polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and rheumatoid arthritis in US general population, NHANES 2003–2012. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, M.M.; Studenski, S. Clinical prognostic factors in lupus nephritis. The importance of hypertension and smoking. Arch. Intern. Med. 1992, 152, 2082–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaussy, N.O.; Sibbitt, W., Jr.; Bankhurst, A.D.; Qualls, C.R. Cigarette smoking and disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, C.R.; Chung, W.T.; Chen, W.T.; Lee, R.Y.; Hwang, B.F. Long-term exposure to traffic-related air pollution and systemic lupus erythematosus in Taiwan: A cohort study. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seise, I.; Pilz, Z.A.; Kusi, M.Y.; Bogan, B.; McHale, B.J.; Gato, W.E. Dietary ingestion of 2-aminoanthracene (2AA) and the risk for type-1 diabetes (T1D). J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2020, 55, 1638–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukowska, B.; Mokra, K.; Michalowicz, J. Benzo[a]pyrene—Environmental occurrence, human exposure, and mechanisms of toxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, M.L.; Sokol, C.L.; Eaton-Bassiri, A.; Seo, S.; Madaio, M.P.; Erikson, J. Fas/Fas ligand deficiency results in altered localization of anti-double-stranded DNA B cells and dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 2370–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theofilopoulos, A.N.; Dixon, F.J. Murine models of systemic lupus erythematosus. Adv. Immunol. 1985, 37, 269–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Kennicott, K.; Liang, Y. Benzo[a]pyrene Exposure Reduces Cell-Type Diversity and Stimulates Sex-Biased Damage Pathways in End Organs of Lupus-Prone Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernatsky, S.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Urowitz, M.B.; Hanly, J.G.; Gordon, C.; Petri, M.A.; Ginzler, E.M.; Wallace, D.J.; Bae, S.C.; Romero-Diaz, J.; et al. Cancer Risk in a Large Inception Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Cohort: Effects of Demographic Characteristics, Smoking, and Medications. Arthritis Care Res. 2021, 73, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Beer, J.C.; Hao, Q.; Ariyapala, I.S.; Sahajan, A.; Komarov, A.; Cha, K.; Moua, M.; Qiu, X.; Xu, X.; et al. NULISA: A proteomic liquid biopsy platform with attomolar sensitivity and high multiplexing. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.M.; Chen, W.S.; Sheu, J.J.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, J.H.; Chang, C.C. Autoimmune rheumatic diseases increase dementia risk in middle-aged patients: A nationwide cohort study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0186475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, K.L., Jr.; Holsapple, M.P. Direct suppression of in vitro antibody production by mouse spleen cells by the carcinogen benzo(a)pyrene but not by the noncarcinogenic congener benzo(e)pyrene. Cancer Res. 1984, 44, 3388–3393. [Google Scholar]
- Burchiel, S.W.; Luster, M.I. Signaling by environmental polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in human lymphocytes. Clin. Immunol. 2001, 98, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Driscoll, C.A.; Owens, L.A.; Gallo, M.E.; Hoffmann, E.J.; Afrazi, A.; Han, M.; Fechner, J.H.; Schauer, J.J.; Bradfield, C.A.; Mezrich, J.D. Differential effects of diesel exhaust particles on T cell differentiation and autoimmune disease. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozier, Y.C.; Barbhaiya, M.; Castro-Webb, N.; Conte, C.; Tedeschi, S.K.; Leatherwood, C.; Costenbader, K.H.; Rosenberg, L. Relationship of Cigarette Smoking and Alcohol Consumption to Incidence of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in a Prospective Cohort Study of Black Women. Arthritis Care Res. 2019, 71, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, J.A.; Singh, S.K.; Goswami, D.G.; Braucher, L.N.; Wright, H.N.; Noland, E.L.; Agarwal, R.; Tewari-Singh, N. Exposure to Environmental Pollutant Benzo[a]pyrene Exacerbates Skin Inflammation in a Mouse Psoriatic Model. Faseb J. 2020, 34, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booker, C.D.; White, K.L., Jr. Benzo(a)pyrene-induced anemia and splenomegaly in NZB/WF1 mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, W.H.; Kroese, E.D.; Vos, J.G.; Van Loveren, H. Detection of immunotoxicity of benzo[a]pyrene in a subacute toxicity study after oral exposure in rats. Toxicol. Sci. 1999, 50, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melani, R.D.; Gerbasi, V.R.; Anderson, L.C.; Sikora, J.W.; Toby, T.K.; Hutton, J.E.; Butcher, D.S.; Negrao, F.; Seckler, H.S.; Srzentic, K.; et al. The Blood Proteoform Atlas: A reference map of proteoforms in human hematopoietic cells. Science 2022, 375, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, M.; Eriksson, A.; Tran, B.; Assarsson, E.; Fredriksson, S. Homogeneous antibody-based proximity extension assays provide sensitive and specific detection of low-abundant proteins in human blood. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeyer, C.M.; Adler, M.; Wacker, R. Immuno-PCR: High sensitivity detection of proteins by nucleic acid amplification. Trends Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Lafferty, T.K.; Sehrawat, A.; Chen, Y.; Ferreira, P.C.L.; Bellaver, B.; Povala, G.; Kamboh, M.I.; Klunk, W.E.; Cohen, A.D.; et al. Multi-analyte proteomic analysis identifies blood-based neuroinflammation, cerebrovascular and synaptic biomarkers in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2024, 19, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairweather, D.; Frisancho-Kiss, S.; Rose, N.R. Sex differences in autoimmune disease from a pathological perspective. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, E.N. The X-files in immunity: Sex-based differences predispose immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.L.; Flanagan, K.L. Sex differences in immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schett, G.; Dayer, J.M.; Manger, B. Interleukin-1 function and role in rheumatic disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdis, M.; Burgler, S.; Crameri, R.; Eiwegger, T.; Fujita, H.; Gomez, E.; Klunker, S.; Meyer, N.; O’Mahony, L.; Palomares, O.; et al. Interleukins, from 1 to 37, and interferon-gamma: Receptors, functions, and roles in diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 701–721.E70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, G.; Colafrancesco, S.; Emmi, G.; Imazio, M.; Lopalco, G.; Maggio, M.C.; Sota, J.; Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin 1alpha: A comprehensive review on the role of IL-1alpha in the pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zheng, S.G. Interleukin-22: A likely target for treatment of autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathy, N.L.; Scheuer, W.; Lanzendorfer, M.; Honold, K.; Ambrosius, D.; Norley, S.; Kurth, R. Interleukin-16 stimulates the expression and production of pro-inflammatory cytokines by human monocytes. Immunology 2000, 100, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molofsky, A.B.; Savage, A.K.; Locksley, R.M. Interleukin-33 in Tissue Homeostasis, Injury, and Inflammation. Immunity 2015, 42, 1005–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojdani, A.; Pollard, K.M.; Campbell, A.W. Environmental triggers and autoimmunity. Autoimmune Dis. 2014, 2014, 798029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.Y.; Schwarz, H. CD137/CD137 ligand signalling regulates the immune balance: A potential target for novel immunotherapy of autoimmune diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 112, 102499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawant, K.V.; Poluri, K.M.; Dutta, A.K.; Sepuru, K.M.; Troshkina, A.; Garofalo, R.P.; Rajarathnam, K. Chemokine CXCL1 mediated neutrophil recruitment: Role of glycosaminoglycan interactions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Gao, Y.; Ding, P.; Wu, T.; Ji, G. The role of CXCL family members in different diseases. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salanga, C.L.; Dyer, D.P.; Kiselar, J.G.; Gupta, S.; Chance, M.R.; Handel, T.M. Multiple glycosaminoglycan-binding epitopes of monocyte chemoattractant protein-3/CCL7 enable it to function as a non-oligomerizing chemokine. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 14896–14912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Rocha, N.P.; Salem, H.; Diniz, B.S.; Teixeira, A.L. The association between systemic lupus erythematosus and dementia A meta-analysis. Dement. Neuropsychol. 2018, 12, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagold, S.; Casas Parera, I. The prevalence of neuropsychiatric syndromes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Neurology 2002, 58, 1867, author reply 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcolea, D.; Beeri, M.S.; Rojas, J.C.; Gardner, R.C.; Lleo, A. Blood Biomarkers in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Implications for the Clinical Neurologist. Neurology 2023, 101, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allenspach, E.; Torgerson, T.R. Autoimmunity and Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders. J. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 36 (Suppl. S1), 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costagliola, G.; Cappelli, S.; Consolini, R. Autoimmunity in Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders: An Updated Review on Pathogenic and Clinical Implications. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutte, B.C.; Mitros, J.P.; Bartlett, J.A.; Walters, J.D.; Jia, H.P.; Welsh, M.J.; Casavant, T.L.; McCray, P.B., Jr. Discovery of five conserved beta -defensin gene clusters using a computational search strategy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2129–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte-Delgado, N.P.; Segura, K.; Gomez, O.; Pulido, S.; Tovar-Sanchez, C.; Bello-Gualtero, J.M.; Fernandez-Avila, D.G.; Amado-Garzon, S.B.; Romero-Sanchez, C.; Cacciatore, S.; et al. Cytokine profiles and their correlation with clinical and blood parameters in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Hu, X.; Yang, J.; Zhu, D.; Wu, M.; Li, X.; Bentum-Ennin, L.; Wanglai, H. IL-22, a vital cytokine in autoimmune diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2024, 218, 242–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Hu, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, X. Interleukin-22 From Type 3 Innate Lymphoid Cells Aggravates Lupus Nephritis by Promoting Macrophage Infiltration in Lupus-Prone Mice. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 584414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niewold, T.B.; Lehman, J.S.; Gunnarsson, I.; Meves, A.; Oke, V. Role of interleukin-16 in human diseases: A novel potential therapeutic target. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1524026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, A.; Rao, D.A.; Mohan, C.; Zhang, T.; Rosenberg, A.; Fenaroli, P.; Belmont, H.M.; Izmirly, P.; Clancy, R.; Trujillo, J.M.; et al. Urine Proteomics and Renal Single-Cell Transcriptomics Implicate Interleukin-16 in Lupus Nephritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. Overview of the IL-1 family in innate inflammation and acquired immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronov, E.; Dotan, S.; Krelin, Y.; Song, X.; Elkabets, M.; Carmi, Y.; Rider, P.; Cohen, I.; Romzova, M.; Kaplanov, I.; et al. Unique versus redundant functions of IL-1α and IL-1β in the tumor microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2013, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postal, M.; Vivaldo, J.F.; Fernandez-Ruiz, R.; Paredes, J.L.; Appenzeller, S.; Niewold, T.B. Type I interferon in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2020, 67, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banchereau, J.; Pascual, V. Type I interferon in systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases. Immunity 2006, 25, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Londe, A.C.; Fernandez-Ruiz, R.; Julio, P.R.; Appenzeller, S.; Niewold, T.B. Type I Interferons in Autoimmunity: Implications in Clinical Phenotypes and Treatment Response. J. Rheumatol. 2023, 50, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Banuelos, E.; Goldman, D.W.; Andrade, V.; Darrah, E.; Petri, M.; Andrade, F. Uncoupling interferons and the interferon signature explains clinical and transcriptional subsets in SLE. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, N.A.; Wu, L.C.; Burd, C.J.; Friedman, A.K.; Kaffenberger, B.H.; Rajaram, M.V.; Schlesinger, L.S.; James, H.; Shupnik, M.A.; Jarjour, W.N. Estrogen modulation of endosome-associated toll-like receptor 8: An IFNalpha-independent mechanism of sex-bias in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 151, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margutti, P.; Sorice, M.; Conti, F.; Delunardo, F.; Racaniello, M.; Alessandri, C.; Siracusano, S.; Riganòm, R.; Profumo, E.; Valesini, G.; et al. Screening of an endothelial cDNA library identifies the C-terminal region of Nedd5 as a novel autoantigen in systemic lupus erythematosus with psychiatric manifestations. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2005, 7, R896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, A.; Fadler, T.; Dorfmeister, E.; Hoffmann, A.C.; Xiang, W.; Winner, B.; Prots, I. Infiltrating T lymphocytes reduce myeloid phagocytosis activity in synucleinopathy model. J. Neuroinflammation 2016, 13, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.K.; Bae, E.J.; Jung, B.C.; Choi, M.; Shin, S.J.; Park, S.J.; Kim, J.T.; Jung, M.K.; Ulusoy, A.; Song, M.Y.; et al. Inflammation promotes synucleinopathy propagation. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 2148–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartzman-Morris, J.; Putterman, C. Gender differences in the pathogenesis and outcome of lupus and of lupus nephritis. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 604892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, C.C.; Lau, C.S.; Chan, T.M.; Wong, R.W. Clinical characteristics and outcome of southern Chinese males with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 1999, 8, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Li, Y.; Xi, H.; Niu, Z.; Chen, N.; Wang, R.; Yan, Y.; Gan, X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, W.; et al. Benzo(a)pyrene and cardiovascular diseases: An overview of pre-clinical studies focused on the underlying molecular mechanism. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 978475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Aniagu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, T. AHR-mediated DNA damage contributes to BaP-induced cardiac malformations in zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, K.M.; Christy, J.M.; Cauvi, D.M.; Kono, D.H. Environmental xenobiotic exposure and autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2017, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tao, Y.; Ji, C.; Aniagu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, T. AHR/ROS-mediated mitochondria apoptosis contributes to benzo[a]pyrene-induced heart defects and the protective effects of resveratol. Toxicology 2021, 462, 152965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Sinha, N.; Kodidela, S.; Zhou, L.; Singh, U.P.; Kumar, S. Effect of benzo(a)pyrene on oxidative stress and infalmmatory mediators in astrocytes and HIV-infected macrophages. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekpi, X.; Rissel, M.; Huc, L.; Catheline, D.; Sergent, O.; Rioux, V.; Legrand, P.; Holme, J.; Dimanche-Boitrel, M.; Lagadic-Gossmann, D. Membrane remodeling, an early event in benzo[a]pyrene-induced apoptosis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 243, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozzi, A.; Manganelli, V.; Riitano, G.; Caissutti, D.; Longo, A.; Garofalo, T.; Sorice, M.; Misasi, R. Advances in the pathophysiology of thrombosis in antiphospholipid syndrome: Molecular mechanisms and signaling through lipid rafts. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, P.W.; Ley, S.C.; Magee, A.I.; Kabouridis, P.S. The role of lipid rafts in T cell antigen receptor (TCR) signalling. Semin. Immunol. 2000, 12, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Pedrera, C.; Buendia, P.; Cuadrado, M.J.; Siendones, E.; Aguirre, M.A.; Barbarroja, N.; Montiel-Duarte, C.; Torres, A.; Khamashta, M.; Velasco, F. Antiphospholipid antibodies from patients with the antiphospholipid syndrome induce monocyte tissue factor expression through the simultaneous activation of NF-kappaB/Rel proteins via the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, and of the MEK-1/ERK pathway. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, A.L.L.; Kudruk, S.; Moratz, J.; Heflik, M.; Grill, D.; Ravoo, B.J.; Gerke, V. Membrane Binding Promotes Annexin A2 Oligomerization. Cells 2020, 9, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teschke, R.; Eickhoff, A.; Dana, G. Drug-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis: Robust Causality Assessment Using Two Different Validated and Scoring Diagnostic Algorithms. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klufio, C.A. An Introduction to Medical Statistics and Research Methodology; Woeli Pub. Services: Accra, Ghana, 2003; p. xii. 324p. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, A.; Morris, M.; Stufken, J.; Bingham, D.R. Handbook of Design and Analysis of Experiments; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2015; p. xix. 940p. [Google Scholar]
- Welham, S.J. Statistical Methods in Biology: Design and Analysis of Experiments and Regression; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA ; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2015; p. xx. 582p. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, F.; Robert, M.; Li, Y. Statistical methods and common problems in medical or biomedical science research. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 9, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bland, M. An Introduction to Medical Statistics, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2000; p. xvi. 405p. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kennicott, K.; Nie, Y.; Liang, Y. Discovery of Blood-Based Proteins That Mark Benzo[a]pyrene Modulation of Autoimmunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010242
Kennicott K, Nie Y, Liang Y. Discovery of Blood-Based Proteins That Mark Benzo[a]pyrene Modulation of Autoimmunity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010242
Chicago/Turabian StyleKennicott, Kameron, Yilin Nie, and Yun Liang. 2025. "Discovery of Blood-Based Proteins That Mark Benzo[a]pyrene Modulation of Autoimmunity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010242
APA StyleKennicott, K., Nie, Y., & Liang, Y. (2025). Discovery of Blood-Based Proteins That Mark Benzo[a]pyrene Modulation of Autoimmunity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010242




