Redefining Fascia: A Mechanobiological Hub and Stem Cell Reservoir in Regeneration—A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
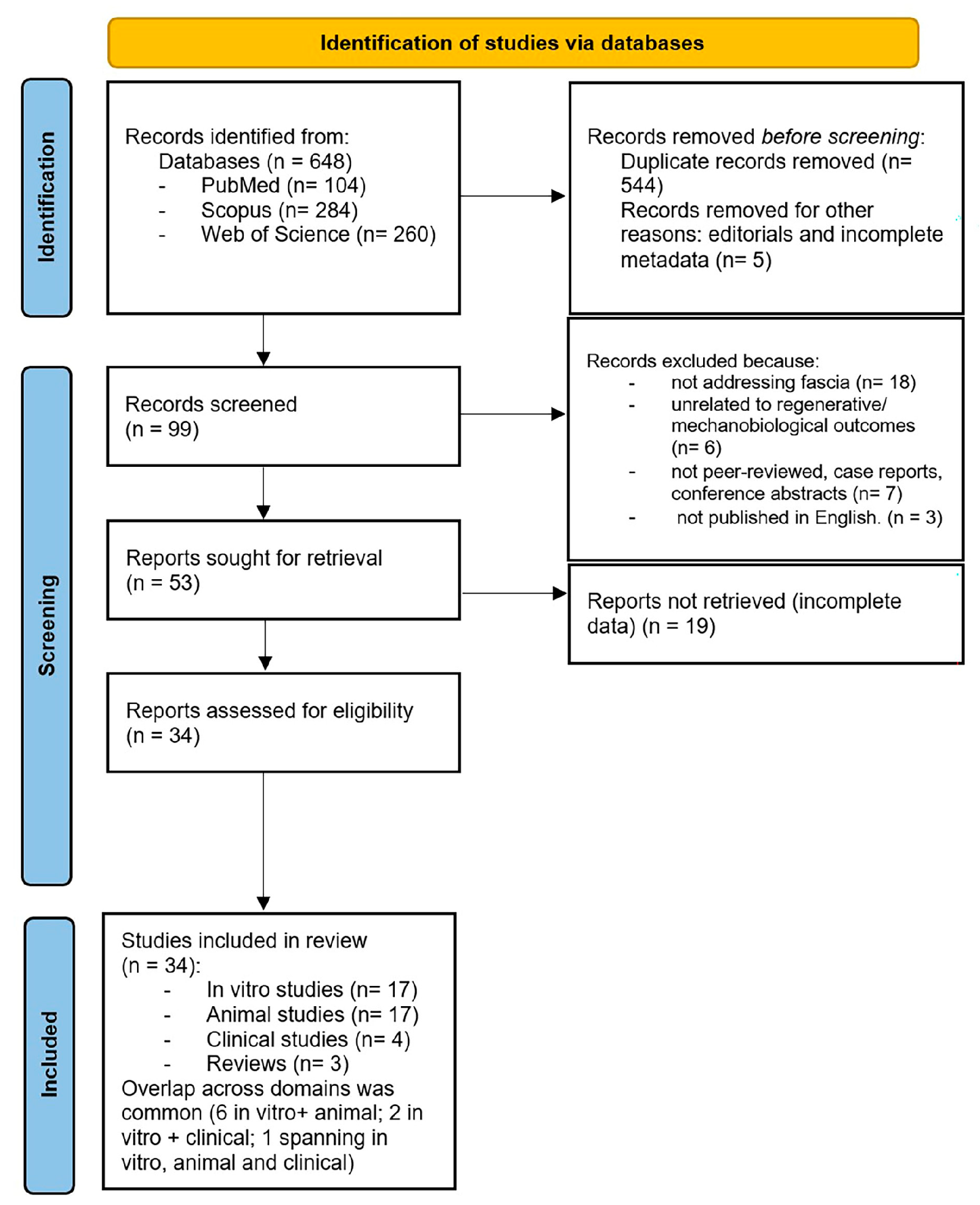
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Extraction
2.2. Risk of Bias
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
3.1.1. In Vitro Evidence on Fascia-Derived Progenitors
3.1.2. Animal Studies
3.1.3. Clinical Studies
3.1.4. Reviews and Conceptual Papers
3.2. Risk of Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| FAPs | Fibro-adipogenic progenitors |
| MSCs | Mesenchymal stem cells |
| ASCs | Adipose-derived stem cells |
References
- Fede, C.; Pirri, C.; Fan, C.; Petrelli, L.; Guidolin, D.; De Caro, R.; Stecco, C. A Closer Look at the Cellular and Molecular Components of the Deep/Muscular Fasciae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Slater, A.M.; Barclay, S.J.; Granfar, R.M.S.; Pratt, R.L. Fascia as a regulatory system in health and disease. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1458385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wilke, J.; Krause, F.; Vogt, L.; Banzer, W. What Is Evidence-Based About Myofascial Chains: A Systematic Review. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 97, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, R.L. Hyaluronan and the Fascial Frontier. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Benjamin, M. The fascia of the limbs and back—A review. J. Anat. 2009, 214, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pirri, C.; Petrelli, L.; Fede, C.; Guidolin, D.; Tiengo, C.; De Caro, R.; Stecco, C. Blood supply to the superficial fascia of the abdomen: An anatomical study. Clin. Anat. 2023, 36, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Rodriguez, V.; Fede, C.; Pirri, C.; Petrelli, L.; Loro-Ferrer, J.F.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, D.; De Caro, R.; Stecco, C. Fascial Innervation: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Joe, A.W.; Yi, L.; Natarajan, A.; Le Grand, F.; So, L.; Wang, J.; Rudnicki, M.A.; Rossi, F.M. Muscle injury activates resident fibro/adipogenic progenitors that facilitate myogenesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Uezumi, A.; Fukada, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Takeda, S.; Tsuchida, K. Mesenchymal progenitors distinct from satellite cells contribute to ectopic fat cell formation in skeletal muscle. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa-Gallegos, D.; Jiang, D.; Christ, S.; Ramesh, P.; Ye, H.; Wannemacher, J.; Kalgudde Gopal, S.; Yu, Q.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A.; et al. Patch repair of deep wounds by mobilized fascia. Nature 2019, 576, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.K.; Tuan, R.S. Mechanoactive tenogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng. Part A 2008, 14, 1615–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Rinkevich, Y. Furnishing Wound Repair by the Subcutaneous Fascia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pirri, C.; Caroccia, B.; Angelini, A.; Piazza, M.; Petrelli, L.; Caputo, I.; Montemurro, C.; Ruggieri, P.; De Caro, R.; Stecco, C. A New Player in the Mechanobiology of Deep Fascia: Yes-Associated Protein (YAP). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pirri, C.; Pirri, N.; Macchi, V.; Porzionato, A.; De Caro, R.; Özçakar, L.; Stecco, C. Ultrasonography of the Fasciae and Common Pathologies: The Game Changer. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Atilano, L.; Martin, N.; Ignacio Martin, J.; Iglesias, G.; Mendiola, J.; Bully, P.; Aiyegbusi, A.; Manuel Rodriguez-Palomo, J.; Andia, I. Ultrasound-Guided Subfascial Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections Versus Enthesis Needling for Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2024, 12, 23259671241249123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ye, H.; Rinkevich, Y. Fascia Layer-A Novel Target for the Application of Biomaterials in Skin Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, e1–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OHAT Risk of Bias Rating Tool for Human and Animal Studies; Office of Health Assessment and Translation, National Toxicology Program: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2015.
- Hooijmans, C.R.; Rovers, M.M.; de Vries, R.B.; Leenaars, M.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M.; Langendam, M.W. SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hung, M.J.; Wen, M.C.; Huang, Y.T.; Chen, G.D.; Chou, M.M.; Yang, V.C. Fascia tissue engineering with human adipose-derived stem cells in a murine model: Implications for pelvic floor reconstruction. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2014, 113, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, X.; Dong, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, B.; Li, H.; Sun, X.; Xia, L.; Zhang, D.; et al. Cytological and functional characteristics of fascia adipocytes in rats: A unique population of adipocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, K.; Edwards, S.L.; Tan, K.S.; White, J.F.; Kandel, S.; Ramshaw, J.A.M.; Gargett, C.E.; Werkmeister, J.A. Induction of endometrial mesenchymal stem cells into tissue-forming cells suitable for fascial repair. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 5012–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, P.; Caves, J.; Dai, E.; Siraj, L.; Liu, L.; Chaudhuri, O.; Haller, C.A.; Mooney, D.J.; Chaikof, E.L. Engineered composite fascia for stem cell therapy in tissue repair applications. Acta Biomater. 2015, 26, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lo, T.S.; Chen, Y.P.; Harun, F.; Shaw, S.W.; Lin, Y.H. The properties of absorbable scaffold harvested with human amniotic fluid stem cells on rat model: An innovation for pelvic reconstruction surgery. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hindocha, S.; Iqbal, S.A.; Farhatullah, S.; Paus, R.; Bayat, A. Characterization of stem cells in Dupuytren’s disease. Br. J. Surg. 2011, 98, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Hu, X.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Wang, J.W.; Nie, J.Y.; Yang, J.M.; Yi, Y.Y. Extracellular Vesicles Isolated from Hypoxia-Preconditioned Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Promote Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α-Mediated Neovascularization of Random Skin Flap in Rats. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2022, 89, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, G.W.; Moon, C.; Song, A.; Vijayakumar, K.A.; Ang, M.J.; Jang, C.H. Effect of Growth Factor-Loaded Acellular Dermal Matrix/MSCs on Regeneration of Chronic Tympanic Membrane Perforations in Rats. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Di Taranto, G.; Cicione, C.; Visconti, G.; Isgrò, M.A.; Barba, M.; Di Stasio, E.; Stigliano, E.; Bernardini, C.; Michetti, F.; Salgarello, M.; et al. Qualitative and quantitative differences of adipose-derived stromal cells from superficial and deep subcutaneous lipoaspirates: A matter of fat. Cytotherapy 2015, 17, 1076–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, S.A.; Hayton, M.J.; Watson, J.S.; Szczypa, P.; Bayat, A. First identification of resident and circulating fibrocytes in Dupuytren’s disease shown to be inhibited by serum amyloid P and Xiapex. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Roman, S.; Mangir, N.; Bissoli, J.; Chapple, C.R.; MacNeil, S. Biodegradable scaffolds designed to mimic fascia-like properties for the treatment of pelvic organ prolapse and stress urinary incontinence. J. Biomater. Appl. 2016, 30, 1578–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, L.S.; Côrtes, I.; Montenegro, B.; Claudio-da-Silva, C.; Bouschbacher, M.; Jobeili, L.; Auxenfans, C.; Sigaudo-Roussel, D. A novel conjunctive microenvironment derived from human subcutaneous adipose tissue contributes to physiology of its superficial layer. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ishiuchi, N.; Nakashima, A.; Maeda, S.; Miura, Y.; Miyasako, K.; Sasaki, K.; Uchiki, T.; Sasaki, A.; Nagamatsu, S.; Nakao, N.; et al. Comparison of therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cells derived from superficial and deep subcutaneous adipose tissues. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2023, 14, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, J.; Nie, D.; Rocha, J.L.; Hogan, M.V.; Wang, J.H. Characterization of the structure, cells, and cellular mechanobiological response of human plantar fascia. J. Tissue Eng. 2018, 9, 2041731418801103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wan, L.; Jiang, D.; Correa-Gallegos, D.; Ramesh, P.; Zhao, J.; Ye, H.; Zhu, S.; Wannemacher, J.; Volz, T.; Rinkevich, Y. Connexin43 gap junction drives fascia mobilization and repair of deep skin wounds. Matrix Biol. 2021, 97, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa-Gallegos, D.; Ye, H.; Dasgupta, B.; Sardogan, A.; Kadri, S.; Kandi, R.; Dai, R.; Lin, Y.; Kopplin, R.; Shenai, D.S.; et al. CD201+ fascia progenitors choreograph injury repair. Nature 2023, 623, 792–802, Erratum in Nature 2024, 625, E4. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06928-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, G.; Long, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Gao, B.; Qin, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Song, B.; Cui, Z.; Liu, Z.; et al. Fascia-derived stem cells enhance fat graft retention by promoting vascularization through the HMOX1-HIF-1α pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2025, 16, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jiang, D.; Christ, S.; Correa-Gallegos, D.; Ramesh, P.; Kalgudde Gopal, S.; Wannemacher, J.; Mayr, C.H.; Lupperger, V.; Yu, Q.; Ye, H.; et al. Injury triggers fascia fibroblast collective cell migration to drive scar formation through N-cadherin. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rajendran, V.; Ramesh, P.; Dai, R.; Kalgudde Gopal, S.; Ye, H.; Machens, H.G.; Adler, H.; Jiang, D.; Rinkevich, Y. Therapeutic Silencing of p120 in Fascia Fibroblasts Ameliorates Tissue Repair. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 143, 854–863.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almet, A.A.; Liu, Y.; Nie, Q.; Plikus, M.V. Integrated Single-Cell Analysis Reveals Spatially and Temporally Dynamic Heterogeneity in Fibroblast States during Wound Healing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2025, 145, 645–659.e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Camargo, C.P.; Nicolas, G.; de Thomaz, B.A.S.; de Sousa Santos, D.L.; Furuya, T.K.; Alves, M.J.F.; Uno, M.; Altran, S.C.; Gemperli, R. Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy and Adipocyte Stem Cell on the Viability of Degloving Injury: A Murine Model. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2025, 49, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marie, H.; Zhang, Y.; Heffner, J.; Dorion, H.A.; Fagan, D.L. Biomechanical and elastographic analysis of mesenchymal stromal cell treated tissue following surgery. J. Biomech. Eng. 2010, 132, 074503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Jin, K.; Feng, X.; Ye, J.; Gao, C. Regeneration of different types of tissues depends on the interplay of stem cells-laden constructs and microenvironments in vivo. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 94, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakkoli Tabassi, K.; Tafazoli, N.; Hamidi Alamdari, D.; Soltani, S. Penile Enhancement Using Biodegradable Scaffolds Covered with Platelet-rich Plasma-Fibrin Glue, Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Micropenis. Urol. J. 2024, 21, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.S.; Lee, B.C.; Park, J.E.; Choi, H.K.; Choi, S.J.; Soh, K.S. Primo vascular system in human umbilical cord and placenta. J. Acupunct. Meridian Stud. 2014, 7, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, G.R.; Viterbo, F.; Deffune, E.; Custódio, M.A.D. Stem cells in end-to-side neurorrhaphy. Experimental study in rats. Acta Cir. Bras. 2021, 35, e351207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Herold, C.; Reimers, K.; Allmeling, C.; Rennekampff, H.O.; Vogt, P.M. A normothermic perfusion bioreactor to preserve viability of rat groin flaps extracorporally. Transplant. Proc. 2009, 41, 4382–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, S.A.; Manning, C.; Syed, F.; Kolluru, V.; Hayton, M.; Watson, S.; Bayat, A. Identification of mesenchymal stem cells in perinodular fat and skin in Dupuytren’s disease: A potential source of myofibroblasts with implications for pathogenesis and therapy. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 21, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Correa-Gallegos, D.; Rinkevich, Y. Cutting into wound repair. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 5034–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, Y.; Qu, R.; Dai, J. Experimental biological research on stem cells in fascia tissue. J. Acupunct. Meridian Stud. 2013, 6, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Li, Z.; Ma, S.; Chen, W.; Wan, Z.; Zhu, L.; Li, L.; Wang, D. Identification of pro-fibrotic cellular subpopulations in fascia of gluteal muscle contracture using single-cell RNA sequencing. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Authors | Fascia Type | Cell Type | Primary Outcomes | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hung et al., 2014 [20] | Pelvic fascia | ASCs | Collagen I/III, elastin | ASCs enhanced ECM deposition and scaffold remodeling |
| Zhang et al., 2020 [21] | Subcutaneous fascia | Fascia adipocytes | Morphology, inflammatory profile | Fascia adipocytes identified as a distinct, pro-inflammatory, low-lipid cell type |
| Su et al., 2014 [22] | Fascial scaffold | Endometrial MSCs | Differentiation, ECM | Differentiated into fibroblastic and smooth muscle phenotypes producing ECM |
| Ayala et al., 2015 [23] | Abdominal fascia | ASCs | Vascularization, biomechanics | Composite fascia improved angiogenesis and tensile strength |
| Lo et al., 2024 [24] | Pelvic fascia | Amniotic fluid SCs | Tensile properties | Scaffold seeded with AFSCs enhanced tensile resistance and biocompatibility |
| Hindocha et al., 2011 [25] | Palmar fascia | Resident stem cells | Cell identification | Resident stem cells identified in Dupuytren’s fascia |
| Wu et al., 2022 [26] | Fascial flap | ASC-derived EVs | Angiogenesis, flap survival | EVs improved HIF-1α signaling and flap survival |
| Cho et al., 2021 [27] | Fascial repair model | MSCs + GFs | ECM deposition, healing | GF-loaded scaffolds improved fascial healing in vitro |
| Di Taranto et al., 2015 [28] | Subcutaneous fascia | ASCs | Stemness, differentiation | Significant heterogeneity between superficial and deep fascia ASCs |
| Iqbal et al., 2014 [29] | Palmar fascia | MSCs | Stem cell identification | First identification of resident/circulating MSCs in Dupuytren’s fascia |
| Roman et al., 2016 [30] | Pelvic fascia | MSCs | Biocompatibility, scaffold design | Scaffold mimicked fascia mechanics and supported cell growth |
| Baptista et al., 2021 [31] | Fascial constructs | MSCs | Adhesion, ECM phenotype | Microenvironment promoted adhesion and regenerative phenotypes |
| Ishiuchi et al., 2023 [32] | Fascial scaffolds | MSCs | ECM deposition | MSCs in fascial scaffolds deposited more ECM than dermal constructs |
| Zhang et al., 2018 [33] | Thoracolumbar fascia | Fibroblasts | Histology, mechanics | Described collagen organization, cellularity, and mechanical properties |
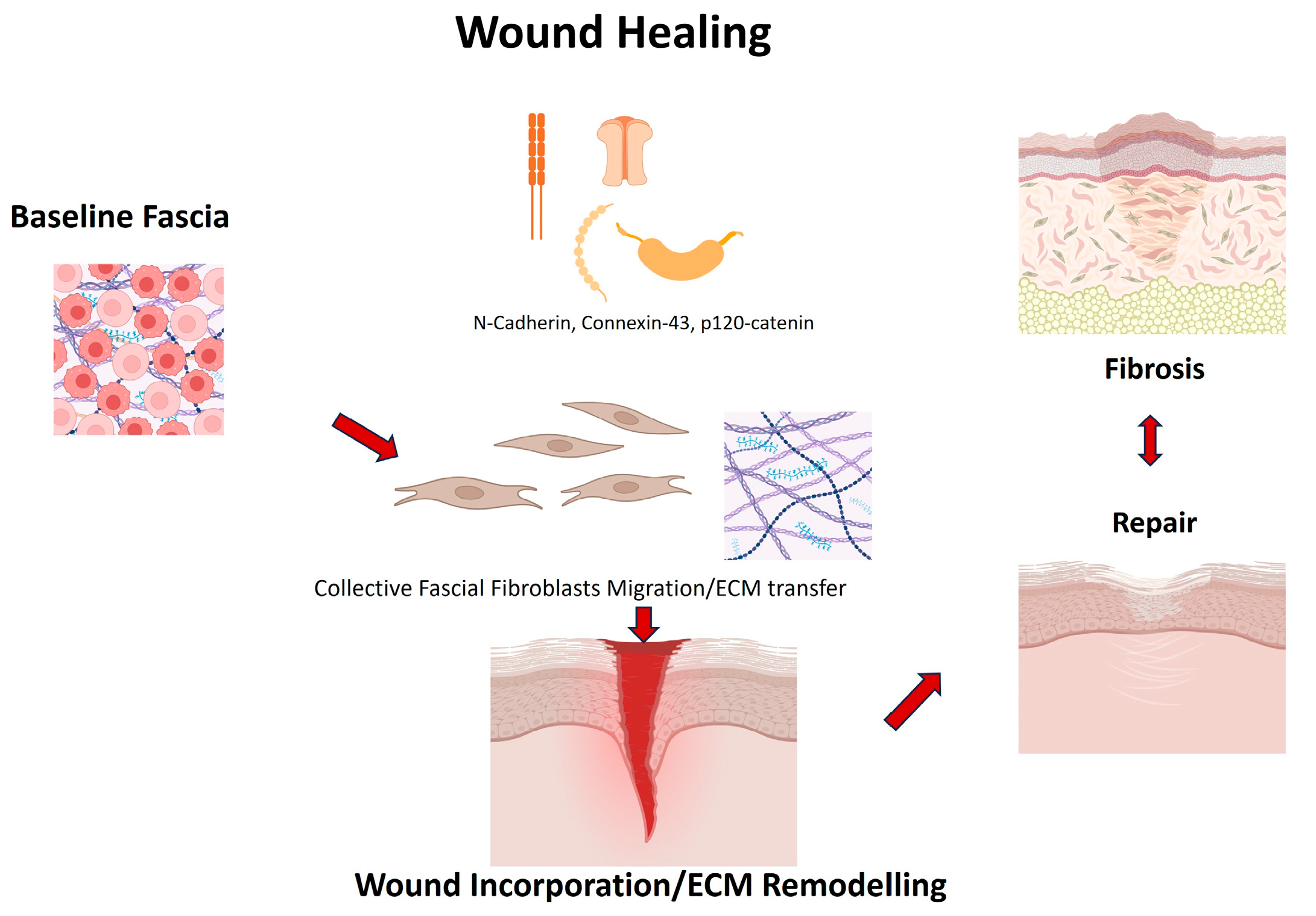
| Wan et al., 2021 [34] | Subcutaneous fascia (back skin, mouse and human) | Subcutaneous fascia (back skin, mouse and human) | Cx43 expression, calcium oscillations, fascia fibroblast migration, matrix mobilization, scar size and composition | Cx43 is upregulated in fascia EPFs after injury; gap junction communication sustains collective migration and fascia matrix mobilization into wounds; inhibition of Cx43 (2-APB, GAP27) or calcium signaling reduces fascia mobilization and scar formation. |
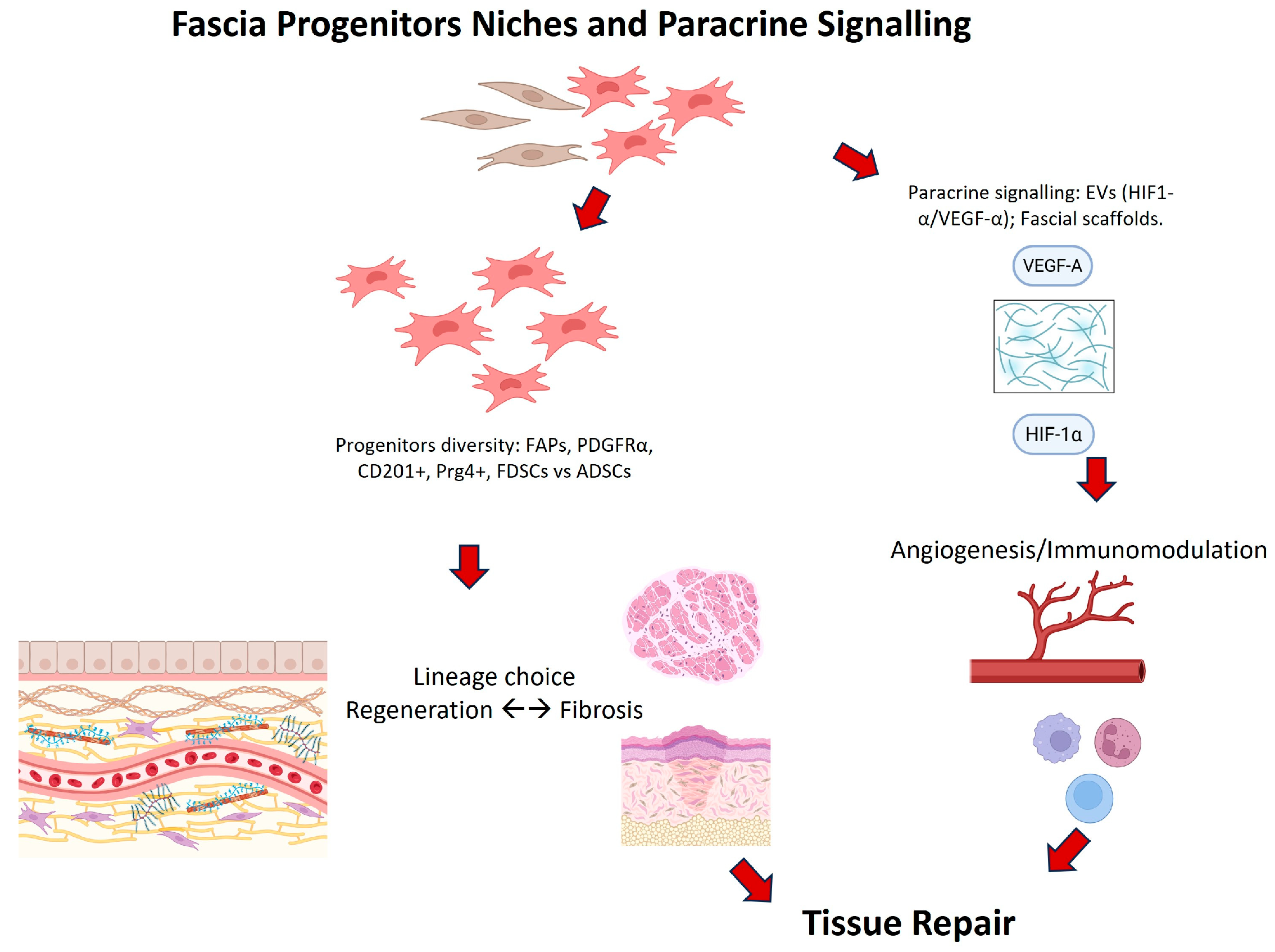
| Correa-Gallegos et al., 2023 [35] | Subcutaneous fascia | CD201+ progenitors | Lineage tracing, fibroblast transition | CD201+ progenitors sequentially generate fibroblasts and myofibroblasts |
| Chen et al., 2025 [36] | Human superficial fascia | Fascia-derived stem cells (FDSC) | Transcriptomics, angiogenesis, graft retention | FDSCs expressed higher HMOX1, HIF-1α, and VEGFa; promoted angiogenesis and improved graft retention |
| Authors | Fascia Type | Cell Type | Primary Outcomes | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correa-Gallegos et al. [10] | Subcutaneous fascia | Fibroblasts | Wound closure, ECM | Fascia fibroblasts mobilize as pre-assembled ECM patches |
| Jiang et al. [37] | Subcutaneous fascia | Fibroblasts | Scar size, migration | N-cadherin essential for collective migration |
| Wan et al. [34] | Subcutaneous fascia | Fibroblasts | Migration, calcium signaling | Connexin43 regulates collective migration |
| Rajendran et al. [38] | Subcutaneous fascia | Fibroblasts | ECM transfer, scarring | p120 controls supracellular organization in fascia fibroblasts |
| Correa-Gallegos et al. [35] | Subcutaneous fascia | CD201+ progenitors | Lineage tracing | CD201+ cells sequentially generate fibroblasts/myofibroblasts |
| Joe et al. [8] | Muscle fascia | FAPs | Myogenesis, fibrosis | FAPs aid myogenesis but drive fibrosis if dysregulated |
| Uezumi et al. [9] | Muscle fascia | PDGFRα+ progenitors | Adipogenesis | PDGFRα+ progenitors cause ectopic fat |
| Almet et al. [39] | Subcutaneous/deep fascia in murine back skin | Fascia Fibroblasts | scRNA-seq, spatial transcriptomics | Identified dynamic fibroblast states during wound healing; fascia fibroblasts contribute to transient upper and lower scar compartments |
| Camargo et al. [40] | Murine fascia | ASCs | Viability | HBOT + ASCs improved fascial survival |
| Wu S. et al. [26] | Fascial flap | ASC-derived EVs | Angiogenesis, viability | EVs enhanced HIF-1α and vascularization |
| Marie et al. [41] | Fascial tissue | MSCs | Elasticity, mechanics | MSCs improved fascial biomechanics |
| Dai et al. [42] | Fascial environment | MSCs | Integration | Better integration in fascia-rich sites |
| Tavakkoli Tabassi et al. [43] | Fascial scaffolds | MSCs | Repair outcomes | MSCs + PRP improved fascial integration |
| Lee et al. [44] | Umbilical fascia | Endothelial-like | Anatomy | Identified novel vascular structures with fascia |
| Hindocha S. et al. [25] | Palmar fascia | Progenitors | Stemness | Progenitors identified in diseased fascia |
| Di Taranto et al. [28] | Subcutaneous fascia | ASCs | Stemness | Regional ASC heterogeneity in fascia |
| Pavia et al. [45] | Muscle fascia (autologous, used to wrap neurorrhaphy) | Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (autologous, uncultured) | Peripheral nerve regeneration, muscle reinnervation, functional recovery (peroneal functional index) | ESN wrapped with fascia and platelet gel carrying ADSCs improved functional recovery and nerve fiber counts, reaching values comparable to controls; fascia served as scaffold to retain stem cells and support regeneration |
| Authors | D1 Cell Source Characterization | D2 Biological Replicates | D3 Controls | D4 Blinded Assessment | D5 Data Completeness | D6 Statistics | D7 Outcome Validity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hung et al. [20] | High | Unclear | High | Low | High | Unclear | Low |
| Zhang et al. [21] | High | Unclear | High | Low | High | High | Unclear |
| Su et al. [22] | High | Unclear | High | Low | High | High | Unclear |
| Ayala et al. [23] | High | Unclear | High | Low | High | Unclear | Unclear |
| Lo et al. [24] | High | Unclear | High | Low | High | High | Unclear |
| Hindocha et al. [25] | High | Unclear | High | Low | High | High | Unclear |
| Wu et al. [26] | High | Unclear | High | Low | High | High | Unclear |
| Cho et al. [27] | High | Unclear | High | Low | High | High | High |
| Di Taranto et al. [28] | High | High | High | Low | High | High | High |
| Iqbal et al. [29] | High | Unclear | High | Low | High | High | Unclear |
| Roman et al. [30] | High | Unclear | High | Low | High | High | Unclear |
| Baptista et al. [31] | High | High | High | Low | High | High | High |
| Ishiuchi et al. [32] | High | High | High | Low | High | High | High |
| Zhang et al. [33] | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear |
| Wan et al. [34] | High | Unclear | High | Low | High | High | Unclear |
| Correa-Gallegos et al. [35] | High | Unclear | High | Low | High | High | High |
| Chen et al. [36] | High | High | High | Low | High | High | High |
| Authors | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | D9 | D10 | D11 | D12 | D13 | D14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correa-Gallegos et al. [10] | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Some concerns |
| Jiang et al. [37] | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Some concerns |
| Wan et al. [34] | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Some concerns |
| Rajendran et al. [38] | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Some concerns |
| Correa-Gallegos et al. [35] | High | Low | High | Unclear | Low | Low | High | Low | Low | High | High | Low | High | Some concerns |
| Joe et al. [8] | Unclear | Low | High | Unclear | Low | Low | High | Low | Some concerns | Unclear | Low | Low | High | Some concerns |
| Uezumi et al. [9] | Unclear | Low | High | Unclear | Low | Low | High | Low | Some concerns | Unclear | Low | Low | High | Some concerns |
| Almet et al. [39] | Low | Low | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | High | Low | Some concerns | Low | Unclear | Low | High | Some concerns |
| Camargo et al. [40] | High | Unclear | High | Unclear | Low | Unclear | High | Low | Low | High | Low | Unclear | High | Some concerns |
| Wu S. et al. [26] | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Some concerns |
| Marie et al. [41] | Unclear | Low | High | Unclear | Low | Low | High | Some concerns | High | Unclear | High | Low | High | Some concerns |
| Dai et al. [42] | Unclear | Low | High | Unclear | Low | Low | High | Some concerns | Low | High | Low | Low | High | Some concerns |
| Tavakkoli Tabassi et al. [43] | Unclear | Low | Unclear | NA | Low | Low | High | Some concerns | High | Unclear | Low | High | High | Some concerns |
| Lee et al. [44] | Low | Low | High | NA | NA | Low | High | Some concerns | High | Low | Low | Low | High | Some concerns |
| Hindocha S. et al. [25] | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Some concerns |
| Di Taranto et al. [28] | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Some concerns |
| Pavia et al. [45] | High | Unclear | High | Unclear | Low | Unclear | High | Low | Low | High | Low | Unclear | High | Some concerns |
| Authors | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | D9 | D10 | D11 | D12 | Overall RoB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atilano L. et al. [15] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Moderate | Low | Low | Low | Low | Moderate | Low | Low | Low |
| Herold C. et al. [46] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Moderate | Low | Low | Low | Low | Moderate | Low | Low | Low |
| Hindocha S. et al. [25] | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Low | Low | Moderate | High | NA | NA | Moderate | High | Moderate | High |
| Iqbal SA et al. [47] | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Serious |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pirri, C.; Pirri, N.; Petrelli, L.; De Caro, R.; Stecco, C. Redefining Fascia: A Mechanobiological Hub and Stem Cell Reservoir in Regeneration—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010166
Pirri C, Pirri N, Petrelli L, De Caro R, Stecco C. Redefining Fascia: A Mechanobiological Hub and Stem Cell Reservoir in Regeneration—A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010166
Chicago/Turabian StylePirri, Carmelo, Nina Pirri, Lucia Petrelli, Raffaele De Caro, and Carla Stecco. 2025. "Redefining Fascia: A Mechanobiological Hub and Stem Cell Reservoir in Regeneration—A Systematic Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010166
APA StylePirri, C., Pirri, N., Petrelli, L., De Caro, R., & Stecco, C. (2025). Redefining Fascia: A Mechanobiological Hub and Stem Cell Reservoir in Regeneration—A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010166









