Comprehensive Transcriptomic Analysis of the Molecular Mechanisms Conferring Resistance to Rice Blast in the Elite Restorer Line Fuhui2165
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Rice Blast Resistance Phenotypes
2.2. RNA Sequencing and Alignment
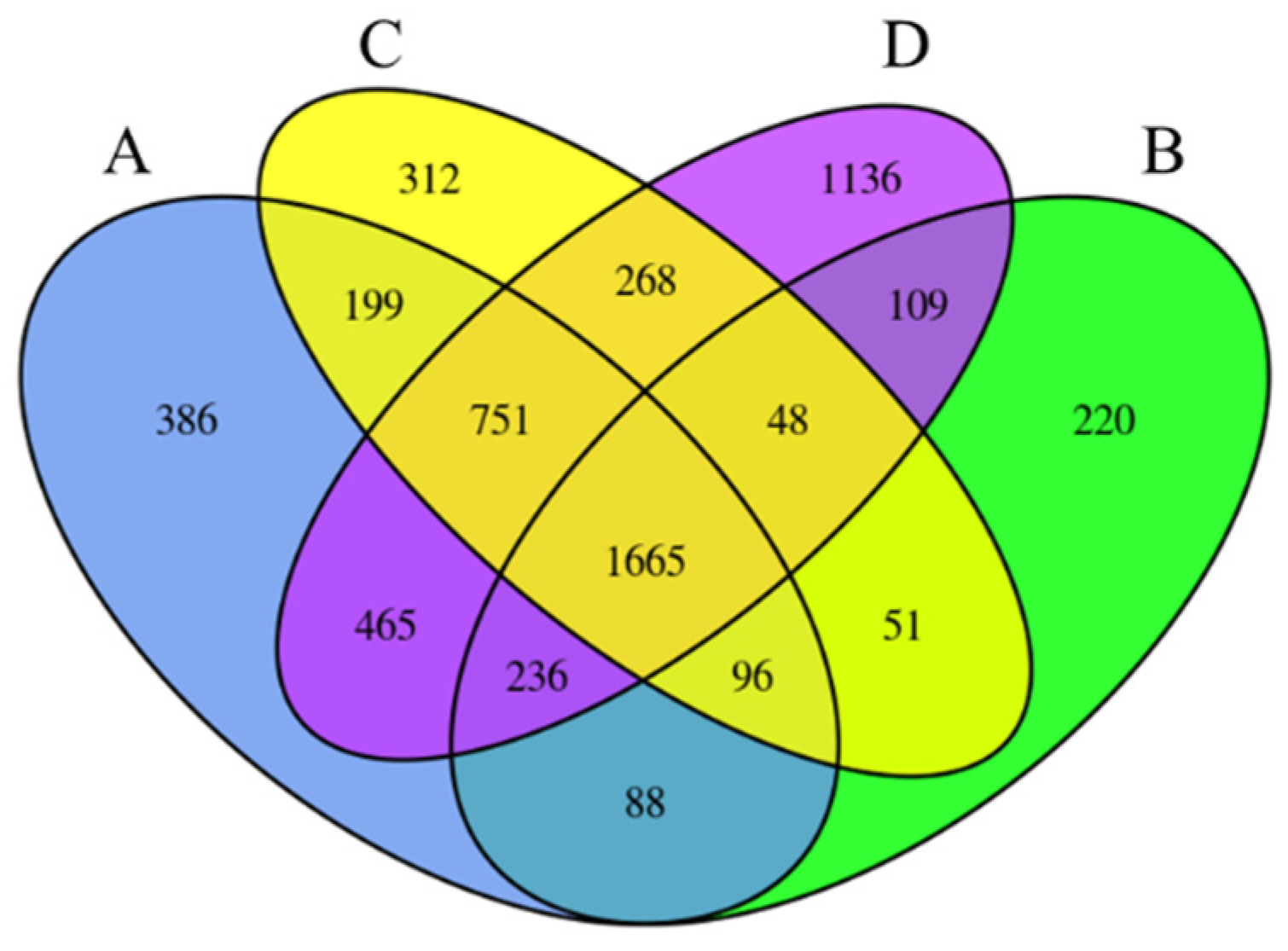
2.3. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) by RNA-Seq
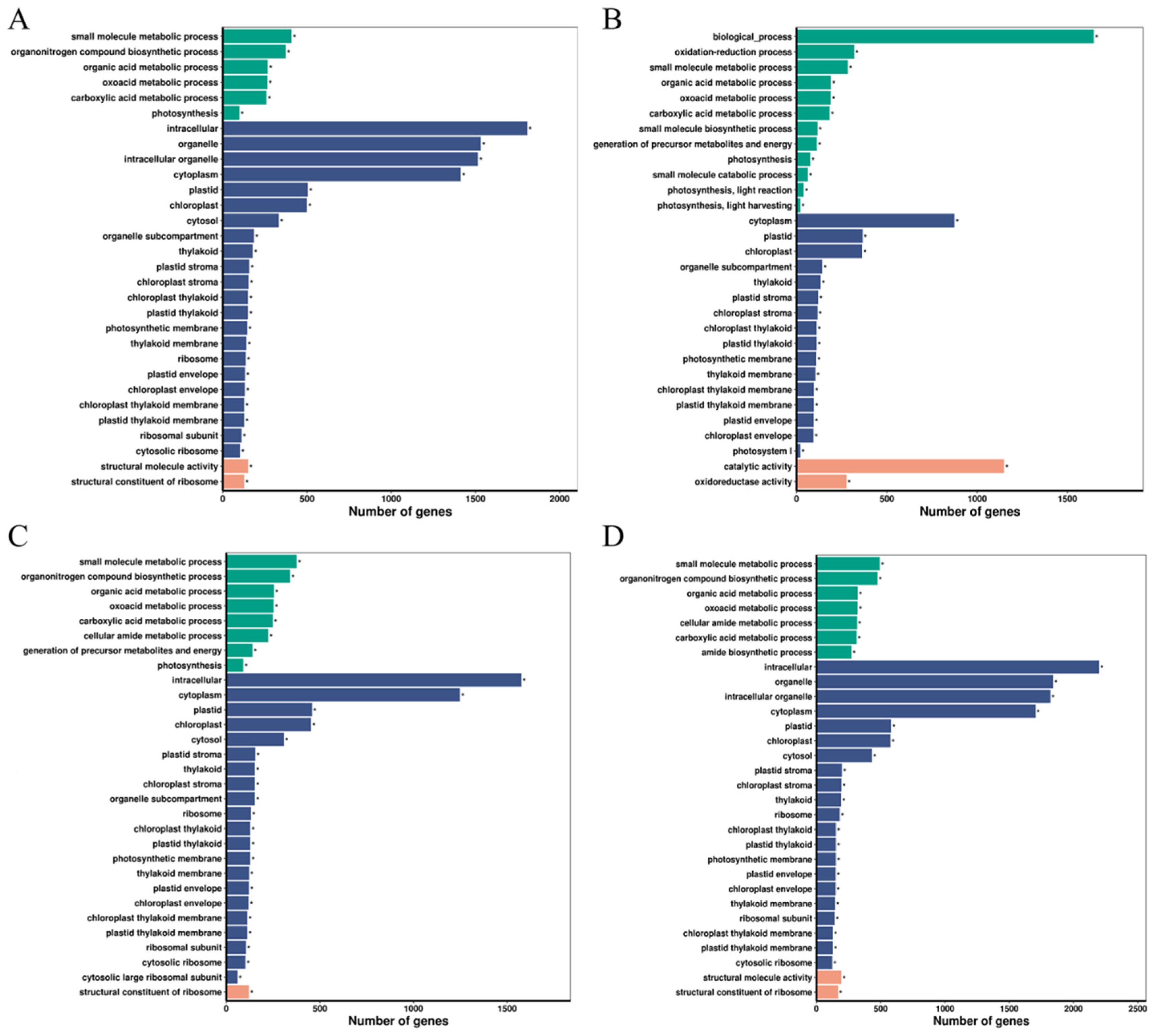
2.4. Functional Classification via Gene Ontology (GO) Analysis
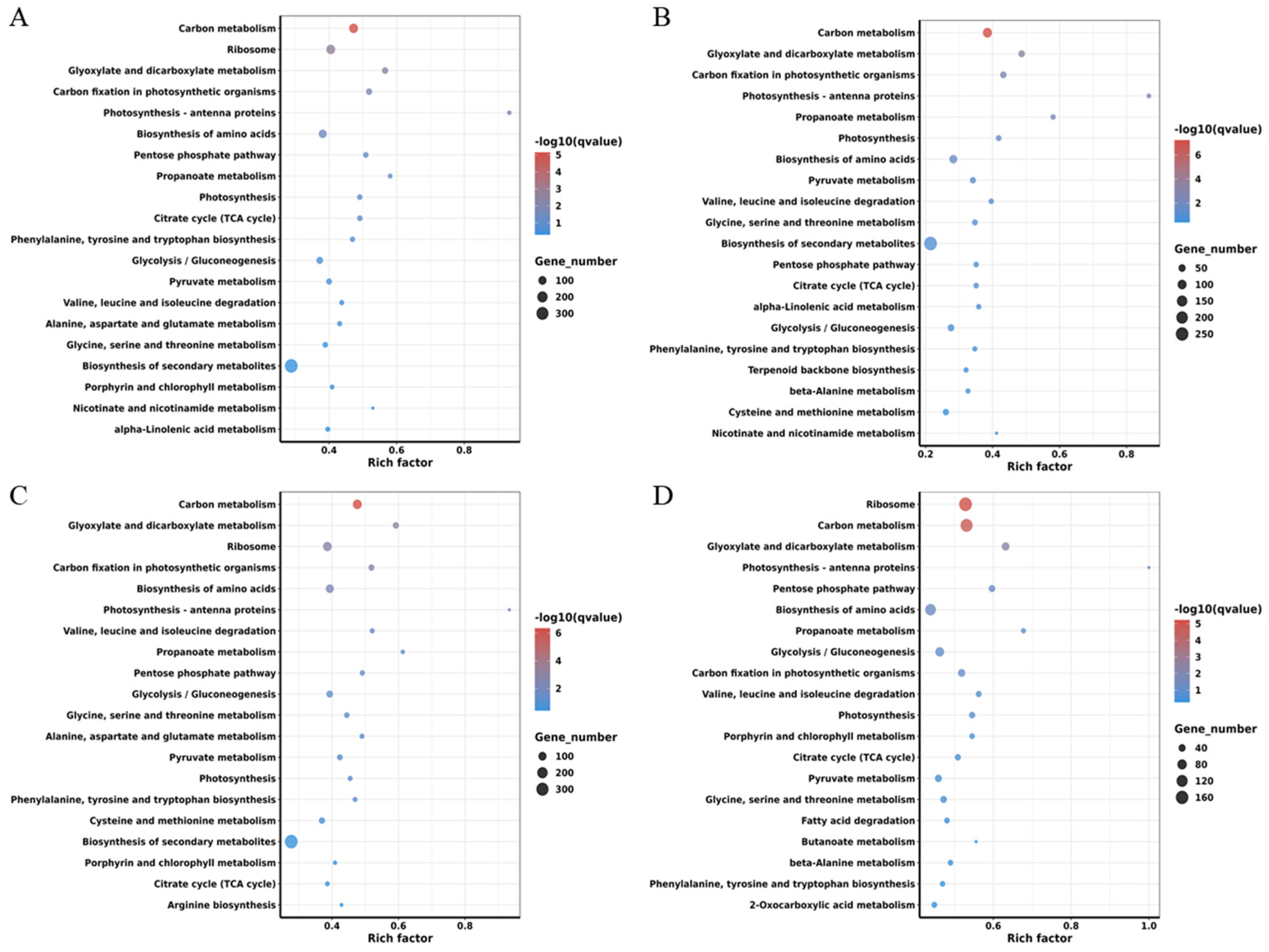
2.5. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Pathway Mapping
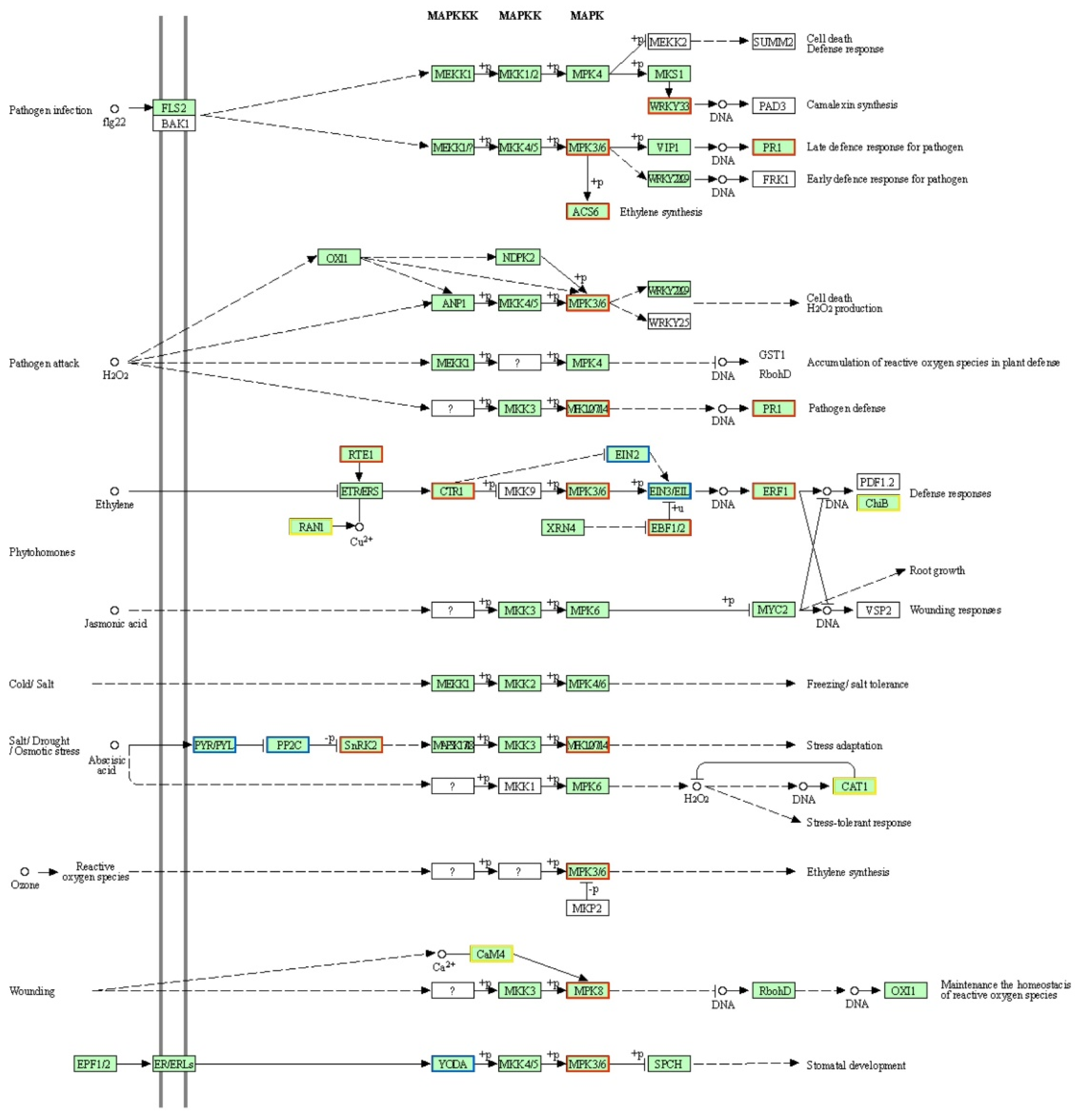
2.6. Analysis of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Signaling Pathway
2.7. Analysis of Plant Hormone Signal Transduction Pathway
2.8. Analysis of the Unique DEGs in FH2165 and HHSM
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials, Growth Conditions, and Treatments
4.2. RNA Isolation and Library Preparation
4.3. Sequencing Quality Control and Read Alignment
4.4. Differentially Expressed Genes Screening and Functional Annotation
4.5. Validation of RNA-Seq by qRT-PCR
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oliveira-Garcia, E.; Yan, X.; Oses-Ruiz, M.; de Paula, S.; Talbot, N.J. Effector-triggered susceptibility by the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. New Phytol. 2024, 241, 1007–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Liu, X.; Lin, F.; Lu, J. Casein kinase 2 mediates degradation of transcription factor Pcf1 during appressorium formation in the rice blast fungus. J. Fungi. 2022, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudin, M.; Le Naour-Vernet, M.; Gladieux, P.; Tharreau, D.; Lebrun, M.H.; Lambou, K.; Leys, M.; Fournier, E.; Césari, S.; Kroj, T. Pyricularia oryzae: Lab star and field scourge. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2024, 25, e13449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asif, N.; Lin, F.; Li, L.; Zhu, X.; Nawaz, S. Regulation of autophagy machinery in Magnaporthe oryzae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.Y.; Liang, S.; Zhu, X.M.; Liu, X.H.; Lin, F.C. Recent advances in effector research of Magnaporthe oryzae. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younas, M.U.; Qasim, M.; Ahmad, I.; Feng, Z.; Iqbal, R.; Abdelbacki, A.M.M.; Rajput, N.; Jiang, X.; Rao, B.; Zuo, S. Allelic variation in rice blast resistance: A pathway to sustainable disease management. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Gupta, R.; Min, C.W.; Kwon, S.W.; Wang, Y.; Je, B.I.; Kim, Y.J.; Jeon, J.S.; Agrawal, G.K.; Rakwal, R.; et al. Proteomics of rice-Magnaporthe oryzae interaction: What have we learned so far? Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Zhao, H.; Li, J.; Gong, Y.; Li, X. The devastating rice blast airborne pathogen Magnaporthe Oryzae—A review on genes studied with mutant analysis. Pathogens 2023, 12, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.Y.; Mao, Y.Y.; Hong, Y.H.; Zhou, P.; Hu, R.H.; Zhang, F.T.; Tu, S.H. Molecular basis analysis of important agronomic traits of Fuhui2165 based on high-density gene chips. J. Sichuan Agric. Univ. 2024, 42, 499–505, (Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, W.; Zhu, X.; Zou, C.; Yin, J.; Chern, M.; Zhou, X.; Ying, H.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Identification and characterization of rice blast resistance gene Pid4 by a combination of transcriptomic profiling and genome analysis. J. Genet Genom. 2018, 45, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, O.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Wen, J.; Ding, J.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Wang, Y. Comparative transcriptome and genome analysis between susceptible Zhefang rice variety Diantun 502 and its resistance variety Diantun 506 upon Magnaporthe oryzae infection. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yang, Z.; Yang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, T.; Huang, R.; Li, G. Genomic and transcriptomic analyses of the elite rice variety Huizhan provide insight into disease resistance and heat tolerance. Genomics 2024, 116, 110915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Bao, J.; Li, L.; Shen, Z.; Wang, J.; Daskalov, A.; Zhu, X.; Lin, F. Integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis reveals the regulation network of CEBiP in rice defense against Magnaporthe oryzae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devanna, B.N.; Jain, P.; Solanke, A.U.; Das, A.; Thakur, S.; Singh, P.K.; Kumari, M.; Dubey, H.; Jaswal, R.; Pawar, D.; et al. Understanding the dynamics of blast resistance in rice-Magnaporthe oryzae interactions. J. Fungi. 2022, 8, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangol, S.; Nguyen, N.K.; Singh, R.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Lee, H.G.; Hwang, B.K.; Jwa, N.S. Mitogen-activated protein kinase OsMEK2 and OsMPK1 signaling is required for ferroptotic cell death in rice-Magnaporthe oryzae interactions. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 710794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedi, A.; Hwarari, D.; Dzinyela, R.; Ni, S.; Yang, L. A close-up of regulatory networks and signaling pathways of MKK5 in biotic and abiotic stresses. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2025, 45, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Ravindran, P.; Kumar, P.P. Plant hormone-mediated regulation of stress responses. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, K.T.; Inoue, Y.; Vu, B.V.; Nguyen, H.H.; Nakayashiki, T.; Ikeda, K.; Nakayashiki, H. MoSET1 (Histone H3K4 methyltransferase in Magnaporthe oryzae) regulates global gene expression during infection-related morphogenesis. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005385, Correction in PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005752. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Xing, J.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wei, Z.; Xu, J.; Yu, F.; Deng, H. Phosphorylation of CPR5 by the receptor-like kinase FLR2 promotes mRNA poly(A) tail processing and immunity to Magnaporthe oryzae in rice. Plant Commun. 2025, 6, 101347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, M.; Kleinwort, K.J.H.; Degroote, R.L.; Wiedemann, C.; Kremmer, E.; Hauck, S.M.; Deeg, C.A. Interaction of septin 7 and DOCK8 in equine lymphocytes reveals novel insights into signaling pathways associated with autoimmunity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallie, D.R. The role of L-ascorbic acid recycling in responding to environmental stress and in promoting plant growth. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.; Qiu, J.; Tao, Z. Every coin has two sides: Reactive oxygen species during rice-Magnaporthe oryzae interaction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Dai, P.; Cao, Z.; Dong, J. Purine metabolism in plant pathogenic fungi. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1352354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coneva, V.; Simopoulos, C.; Casaretto, J.A.; El-Kereamy, A.; Guevara, D.R.; Cohn, J.; Zhu, T.; Guo, L.; Alexander, D.C.; Bi, Y.M.; et al. Metabolic and co-expression network-based analyses associated with nitrate response in rice. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Chen, H.; Du, P.; Miao, X.; Huang, S.; Cheng, D.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Z. Inhibition mechanism of rhizoctonia solani by pectin-coated iron metal-organic framework nanoparticles and evidence of an induced defense response in rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 474, 134807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.; Dubey, H.; Singh, P.K.; Solanke, A.U.; Singh, A.K.; Sharma, T.R. Deciphering signalling network in broad spectrum near isogenic lines of rice resistant to Magnaporthe oryzae. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Huang, F.; Lu, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.Q.; Yang, D. SPR9 encodes a 60 S ribosomal protein that modulates panicle spreading and affects resistance to false smut in rice (Oryza sativa. L). BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Yang, C.; Abubakar, Y.S.; Chen, X.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, J. The small GTPase FgRab1 plays indispensable roles in the vegetative growth, vesicle fusion, autophagy and pathogenicity of Fusarium graminearum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Nguyen, N.K.; Hwang, B.K.; Jwa, N.S. The NIN-like protein OsNLP2 negatively regulates ferroptotic cell death and immune responses to Magnaporthe oryzae in rice. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Liu, Q.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Lou, X.; Cheng, S.; Cao, L. The OsMPK15 negatively regulates Magnaporthe oryza and Xoo disease resistance via SA and JA signaling pathway in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, J.; Duan, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, G.; Jin, L. Transcriptome profiling reveals effects of drought stress on gene expression in diploid potato genotype P3-198. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayral, P.; Melo-Ferreira, J.; Glémin, S.; Bierne, N.; Carneiro, M.; Nabholz, B.; Lourenco, J.M.; Alves, P.C.; Ballenghien, M.; Faivre, N.; et al. Reference-free population genomics from next-generation transcriptome data and the vertebrate-invertebrate gap. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Han, R.; Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Deng, C.; Zhao, M.; Li, J.; Hou, Q.; Zhong, Q.; Shao, D. Transcriptomics integrated with metabolomics unveil carotenoids accumulation and correlated gene regulation in white and yellow-fleshed turnip (Brassica rapa ssp. rapa). Genes 2022, 13, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Meng, X.; Song, X.; Zhang, D.; Kou, L.; Zhang, J.; Jing, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, H.; Huang, X.; et al. Chilling-induced phosphorylation of IPA1 by OsSAPK6 activates chilling tolerance responses in rice. Cell Discov. 2022, 8, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, A.; Piya, S.; Fernandez, J.C.; Chervin, C.; Hewezi, T.; Binder, B.M. Ethylene receptors signal via a noncanonical pathway to regulate abscisic acid responses. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 910–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widhianata, H.; Basunanda, P.; Supriyadi, S.; Taryono, T. Transcriptional comparison of new hybrid progenies and clone-cultivars of tea (Camellia sinensis L.) associated to catechins content. Plants 2022, 11, 1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.D.; Wakefield, M.J.; Smyth, G.K.; Oshlack, A. Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: Accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Cai, T.; Olyarchuk, J.G.; Wei, L. Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3787–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Ding, Q.; Wang, W.; Pan, Y.; Tan, C.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Ye, N.; et al. Targeted deletion of the first intron of the Wxb allele via CRISPR/Cas9 significantly increases grain amylose content in rice. Rice 2022, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample | Raw Reads | Clean Reads | Q20 | Q30 | GC Content | Uniquely Mapped |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FHMO_0 | 51,407,562 | 47,124,988 | 98.21% | 94.65% | 49.35% | 43,535,238 (92.38%) |
| FHMO_24 | 50,904,432 | 47,060,074 | 98.18% | 94.56% | 48.15% | 43,296,564 (92.00%) |
| HHMO_0 | 49,472,538 | 44,541,728 | 98.20% | 94.67% | 49.11% | 40,984,592 (92.01%) |
| HHMO_24 | 51,106,482 | 46,917,842 | 98.15% | 94.51% | 48.26% | 42,758,974 (91.14%) |
| MHMO_0 | 48,331,684 | 44,533,256 | 98.25% | 94.78% | 49.20% | 41,411,002 (92.99%) |
| MHMO_24 | 49,630,466 | 45,871,454 | 98.24% | 94.76% | 48.25% | 42,282,068 (92.18%) |
| SHMO_0 | 46,636,886 | 41,370,362 | 98.27% | 94.83% | 49.66% | 38,016,724 (91.89%) |
| SHMO_24 | 47,496,244 | 43,262,282 | 98.24% | 94.71% | 48.57% | 39,659,960 (91.67%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Mao, Y.; Hong, Y.; Zheng, F.; Hu, R.; Tu, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, P. Comprehensive Transcriptomic Analysis of the Molecular Mechanisms Conferring Resistance to Rice Blast in the Elite Restorer Line Fuhui2165. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010164
Zhang S, Mao Y, Hong Y, Zheng F, Hu R, Tu S, Zhang F, Zhou P. Comprehensive Transcriptomic Analysis of the Molecular Mechanisms Conferring Resistance to Rice Blast in the Elite Restorer Line Fuhui2165. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010164
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shuijin, Yinyin Mao, Yonghe Hong, Feiyan Zheng, Ronghua Hu, Shihang Tu, Fantao Zhang, and Peng Zhou. 2025. "Comprehensive Transcriptomic Analysis of the Molecular Mechanisms Conferring Resistance to Rice Blast in the Elite Restorer Line Fuhui2165" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010164
APA StyleZhang, S., Mao, Y., Hong, Y., Zheng, F., Hu, R., Tu, S., Zhang, F., & Zhou, P. (2025). Comprehensive Transcriptomic Analysis of the Molecular Mechanisms Conferring Resistance to Rice Blast in the Elite Restorer Line Fuhui2165. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010164





