Utility of Serum HBV RNA Measurement During Nucleoside/Nucleotide Analog Therapy in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Comparison of Initial Values Between the ETV and TAF Groups
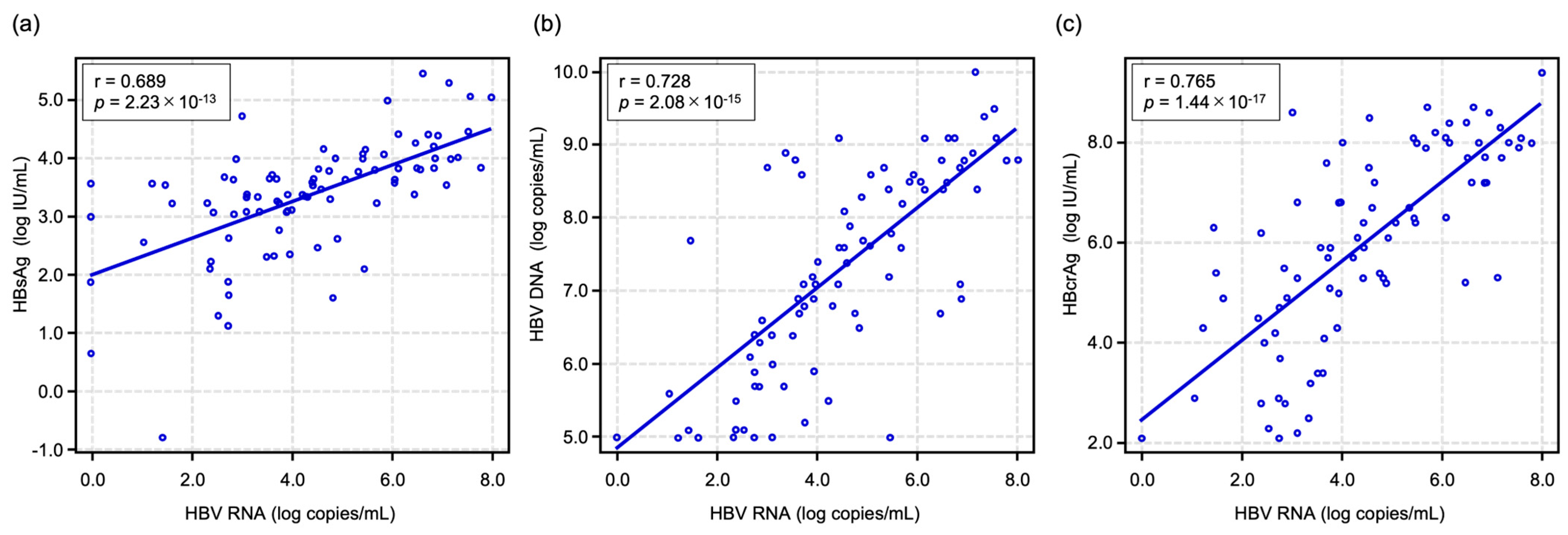
2.2. Correlations Between HBV RNA Level and Other HBV-Related Markers at Baseline
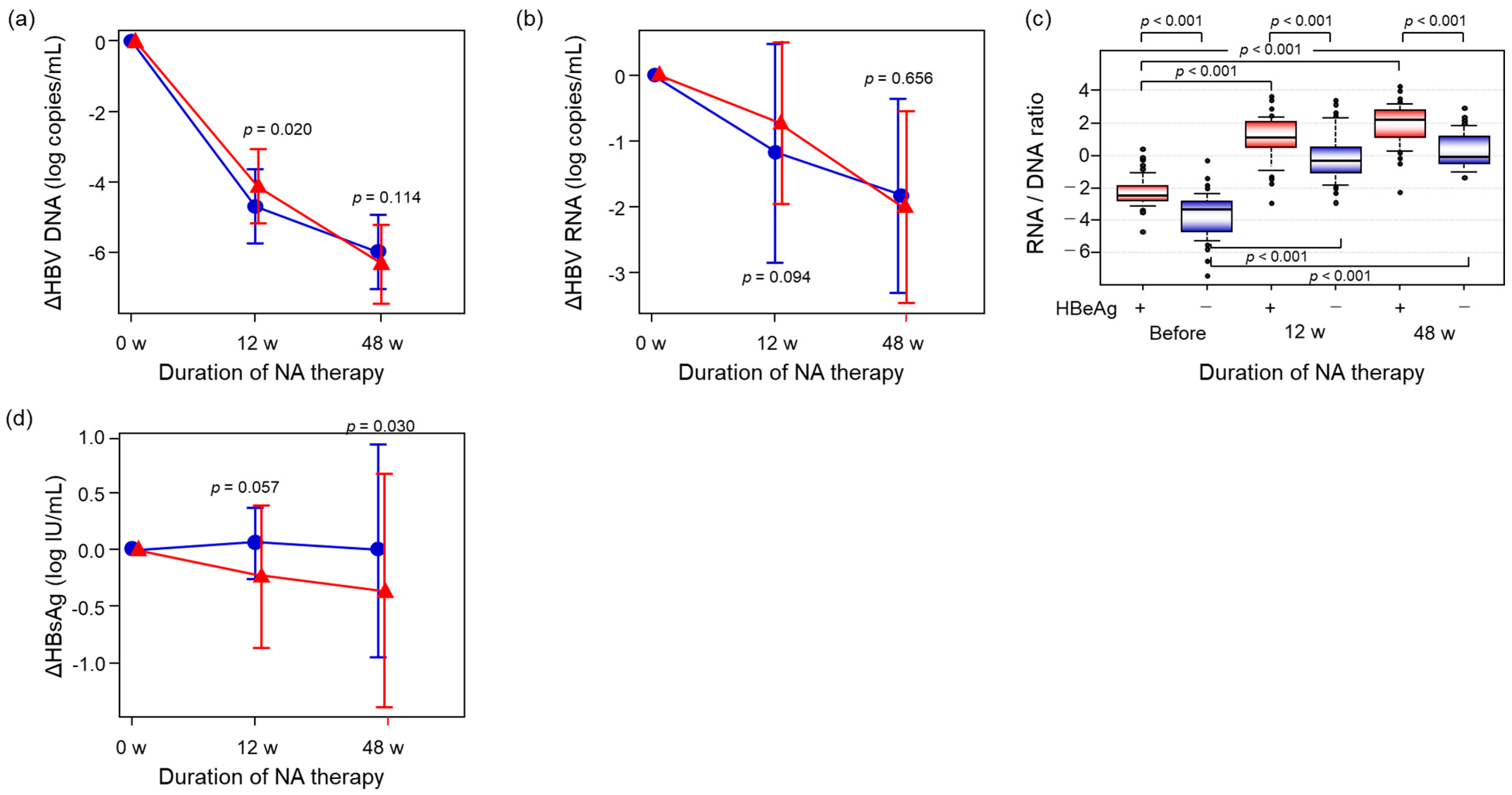
2.3. Comparison of the Alterations of HBV-Related Markers Between HBeAg-Positive and -Negative Patients During NA Therapy
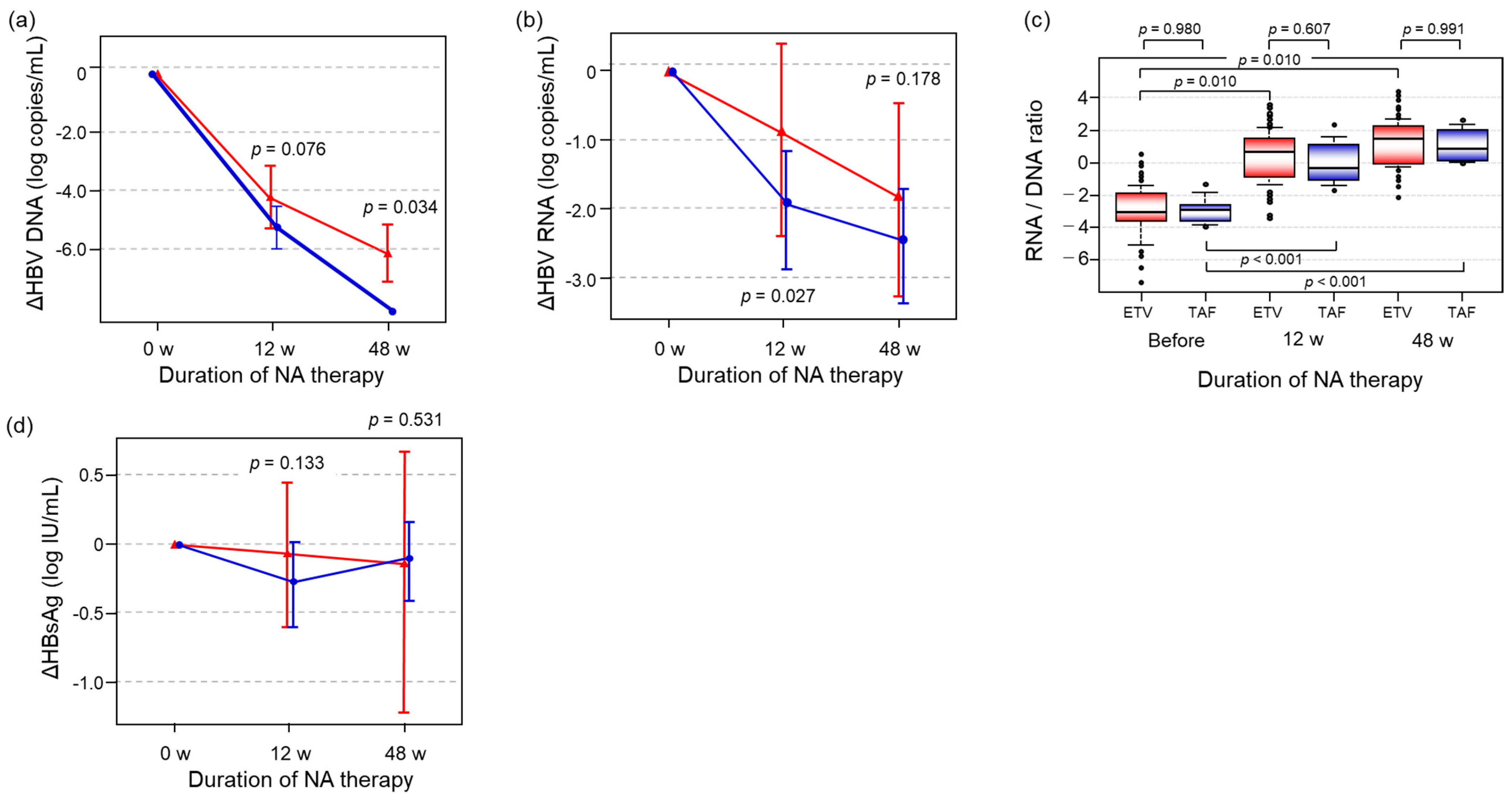
2.4. Differences in the Alterations of HBV-Related Markers Between the ETV and TAF Groups
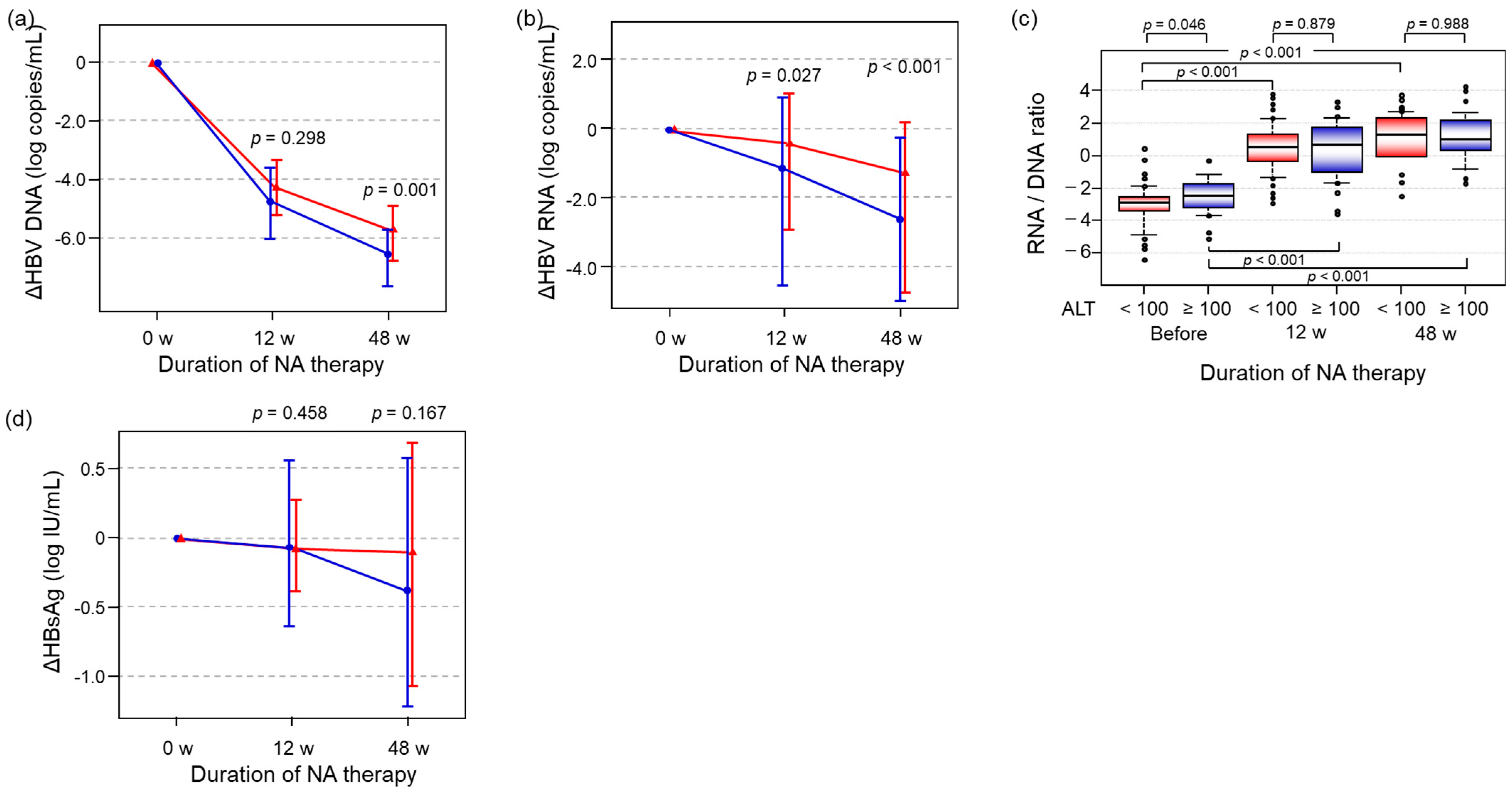
2.5. The Impact of ALT Level on the Alteration of HBV-Related Markers During NA Therapy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Determination of Liver Fibrosis Stage
4.3. Quantification of HBV RNA Level
4.4. Measurement of Other HBV-Related Markers
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HBV | hepatitis B virus |
| HBsAg | hepatitis B surface antigen |
| HBeAg | hepatitis B e antigen |
| HBcrAg | hepatitis B core-related antigen |
| cccDNA | covalently closed circular DNA |
| CHB | chronic hepatitis B |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| NA | nucleotide/nucleoside analog |
| ETV | entecavir |
| TAF | tenofovir alafenamide |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
References
- WHO. Global Hepatitis Report 2024: Action for Access in Low- and Middle-Income Countries; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; p. 242. [Google Scholar]
- Iloeje, U.H.; Yang, H.I.; Chen, C.J. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B: What exactly has REVEAL revealed? Liver Int. 2012, 32, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brechot, C.; Gozuacik, D.; Murakami, Y.; Paterlini-Brechot, P. Molecular bases for the development of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Semin. Cancer Biol. 2000, 10, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, S.; Jin, Y.; Mu, X.; Guo, Z.; Qiao, S.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Q.; Cui, X. The role of the hepatitis B virus genome and its integration in the hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1469016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wei, W.; Hou, F.; Xu, H.; Cui, X. The integration model of hepatitis B virus genome in hepatocellular carcinoma cells based on high-throughput long-read sequencing. Genomics 2022, 114, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Saigo, K.; Takashima, H.; Minami, M.; Okanoue, T.; Brechot, C.; Paterlini-Brechot, P. Large scaled analysis of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA integration in HBV related hepatocellular carcinomas. Gut 2005, 54, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conjeevaram, H.S.; Lok, A.S. Management of chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2003, 38 (Suppl. 1), S90–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumada, H.; Okanoue, T.; Onji, M.; Moriwaki, H.; Izumi, N.; Tanaka, E.; Chayama, K.; Sakisaka, S.; Takehara, T.; Oketani, M.; et al. Guidelines for the treatment of chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis due to hepatitis B virus infection for the fiscal year 2008 in Japan. Hepatol Res 2010, 40, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Suh, D.J.; Lim, Y.S.; Jung, S.W.; Kim, K.M.; Lee, H.C.; Chung, Y.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Yoo, W.; Kim, S.O. Increased risk of adefovir resistance in patients with lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B after 48 weeks of adefovir dipivoxil monotherapy. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magri, A.; Harris, J.M.; D’Arienzo, V.; Minisini, R.; Juhling, F.; Wing, P.A.C.; Rapetti, R.; Leutner, M.; Testoni, B.; Baumert, T.F.; et al. Inflammatory Gene Expression Associates with Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA- but Not Integrant-Derived Transcripts in HBeAg Negative Disease. Viruses 2022, 14, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, M.A.; Calabrese, D.; Suslov, A.; Terracciano, L.M.; Heim, M.H.; Wieland, S. Ubiquitous expression of HBsAg from integrated HBV DNA in patients with low viral load. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Chang, J.; Rijnbrand, R.; Lam, A.M.; Sofia, M.J.; Cuconati, A.; Guo, J.T. Pregenomic RNA Launch Hepatitis B Virus Replication System Facilitates the Mechanistic Study of Antiviral Agents and Drug-Resistant Variants on Covalently Closed Circular DNA Synthesis. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0115022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Cheng, J.; Tang, L.; Hu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, T.; Chang, J.; Guo, J.T. Virological Basis for the Cure of Chronic Hepatitis B. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 659–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, T.M.; Guo, H.; Guo, J.T. Molecular virology of hepatitis B virus for clinicians. Clin. Liver Dis. 2007, 11, 685–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Seeger, C. Hepadnavirus Genome Replication and Persistence. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a021386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, T.; Noguchi, C.; Hiraga, N.; Mori, N.; Tsuge, M.; Imamura, M.; Takahashi, S.; Kawakami, Y.; Fujimoto, Y.; Ochi, H.; et al. Serum HBV RNA is a predictor of early emergence of the YMDD mutant in patients treated with lamivudine. Hepatology 2007, 45, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.W.; Chayama, K.; Tsuge, M.; Takahashi, S.; Hatakeyama, T.; Abe, H.; Hu, J.T.; Liu, C.J.; Lai, M.Y.; Chen, D.S.; et al. Differential effects of interferon and lamivudine on serum HBV RNA inhibition in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Antivir. Ther. 2010, 15, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Wang, S.F.; Chang, T.E.; Breitkreutz, R.; Hennig, H.; Takegoshi, K.; Edler, L.; Schroder, C.H. Circulating hepatitis B virus nucleic acids in chronic infection: Representation of differently polyadenylated viral transcripts during progression to nonreplicative stages. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 2005–2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Hacker, H.J.; Tokus, M.; Bock, T.; Schroder, C.H. Patterns of circulating hepatitis B virus serum nucleic acids during lamivudine therapy. J. Med. Virol. 2003, 71, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuge, M.; Murakami, E.; Imamura, M.; Abe, H.; Miki, D.; Hiraga, N.; Takahashi, S.; Ochi, H.; Nelson Hayes, C.; Ginba, H.; et al. Serum HBV RNA and HBeAg are useful markers for the safe discontinuation of nucleotide analogue treatments in chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 1188–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giersch, K.; Allweiss, L.; Volz, T.; Dandri, M.; Lutgehetmann, M. Serum HBV pgRNA as a clinical marker for cccDNA activity. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 460–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, B.; Valdes, J.D.; Sun, J.; Guo, H. Serum Hepatitis B Virus RNA: A New Potential Biomarker for Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1816–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, M.; Fujino, H.; Tsuge, M.; Yamaoka, K.; Fujii, Y.; Uchikawa, S.; Ono, A.; Murakami, E.; Kawaoka, T.; Miki, D.; et al. Usefulness of serum HBV RNA levels for predicting antiviral response to entecavir treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Gastroenterol. 2025, 60, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testoni, B.; Lebosse, F.; Scholtes, C.; Berby, F.; Miaglia, C.; Subic, M.; Loglio, A.; Facchetti, F.; Lampertico, P.; Levrero, M.; et al. Serum hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg) correlates with covalently closed circular DNA transcriptional activity in chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Chen, R.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F.; Xu, D.; Lu, F. Serum HBV DNA plus RNA shows superiority in reflecting the activity of intrahepatic cccDNA in treatment-naive HBV-infected individuals. J. Clin. Virol. 2018, 99–100, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanaka, M.; Nishino, K.; Kawamoto, H.; Haruma, K. Hepatitis B: Who should be treated?-managing patients with chronic hepatitis B during the immune-tolerant and immunoactive phases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 7497–7508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Yang, H.I.; Su, J.; Jen, C.L.; You, S.L.; Lu, S.N.; Huang, G.T.; Iloeje, U.H.; Group, R.-H.S. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA 2006, 295, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iloeje, U.H.; Yang, H.I.; Su, J.; Jen, C.L.; You, S.L.; Chen, C.J.; Risk Evaluation of Viral Load Elevation and Associated Liver Disease/Cancer-In HBV (the REVEAL-HBV) Study Group. Predicting cirrhosis risk based on the level of circulating hepatitis B viral load. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Pan, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, F.; Jiang, C.; Fan, T.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Lower HBV DNA level is associated with more severe liver fibrosis in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B with normal alanine transaminase. Virol. J. 2024, 21, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buti, M.; Gane, E.; Seto, W.K.; Chan, H.L.; Chuang, W.L.; Stepanova, T.; Hui, A.J.; Lim, Y.S.; Mehta, R.; Janssen, H.L.; et al. Tenofovir alafenamide versus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for the treatment of patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A randomised, double-blind, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, 196–206, Erratum in Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.L.; Fung, S.; Seto, W.K.; Chuang, W.L.; Chen, C.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Hui, A.J.; Janssen, H.L.; Chowdhury, A.; Tsang, T.Y.; et al. Tenofovir alafenamide versus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for the treatment of HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A randomised, double-blind, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, 185–195, Erratum in Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.L.; Shouval, D.; Lok, A.S.; Chang, T.T.; Cheinquer, H.; Goodman, Z.; DeHertogh, D.; Wilber, R.; Zink, R.C.; Cross, A.; et al. Entecavir versus lamivudine for patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1011–1020, Erratum in N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, A.; Suzuki, F.; Kawamura, Y.; Sezaki, H.; Hosaka, T.; Akuta, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Saitou, S.; Arase, Y.; et al. Long-term continuous entecavir therapy in nucleos(t)ide-naive chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, K.; Tsukuda, S.; Suizu, F.; Kimura, A.; Sugiyama, M.; Watashi, K.; Noguchi, M.; Mizokami, M. Immunomodulatory Mechanism of Acyclic Nucleoside Phosphates in Treatment of Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1533–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, N.; Murayama, A.; Shiina, M.; Aly, H.H.; Iwamoto, M.; Tsukuda, S.; Watashi, K.; Tanaka, T.; Moriishi, K.; Nishitsuji, H.; et al. Anti-viral effects of interferon-lambda3 on hepatitis B virus infection in cell culture. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokuhara, A.; Tanaka, E.; Matsumoto, A.; Kimura, T.; Yamaura, T.; Orii, K.; Sun, X.; Yagi, S.; Maki, N.; Kiyosawa, K. Clinical evaluation of a new enzyme immunoassay for hepatitis B virus core-related antigen; a marker distinct from viral DNA for monitoring lamivudine treatment. J. Viral Hepat. 2003, 10, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, E.; Matsumoto, A.; Suzuki, F.; Kobayashi, M.; Mizokami, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Okanoue, T.; Minami, M.; Chayama, K.; Imamura, M.; et al. Measurement of hepatitis B virus core-related antigen is valuable for identifying patients who are at low risk of lamivudine resistance. Liver Int. 2006, 26, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Rokuhara, A.; Sakamoto, Y.; Yagi, S.; Tanaka, E.; Kiyosawa, K.; Maki, N. Sensitive enzyme immunoassay for hepatitis B virus core-related antigens and their correlation to virus load. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, K.; Fung, S.; Seto, W.K.; Lim, Y.S.; Gane, E.; Janssen, H.L.; Sharma, M.; Chuang, W.L.; Bae, H.; Yoon, K.T.; et al. A phase 3 study comparing tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) in patients with HBeAg-positive, chronic hepatitis B (CHB): Efficacy and safety results at week 96. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, S478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.T.; Lai, C.L.; Kew Yoon, S.; Lee, S.S.; Coelho, H.S.; Carrilho, F.J.; Poordad, F.; Halota, W.; Horsmans, Y.; Tsai, N.; et al. Entecavir treatment for up to 5 years in patients with hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2010, 51, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gish, R.G.; Chang, T.T.; Lai, C.L.; de Man, R.; Gadano, A.; Poordad, F.; Yang, J.; Brett-Smith, H.; Tamez, R. Loss of HBsAg antigen during treatment with entecavir or lamivudine in nucleoside-naive HBeAg-positive patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Viral Hepat. 2010, 17, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoutendijk, R.; Reijnders, J.G.P.; Brown, A.; Zoulim, F.; Mutimer, D.; Deterding, K.; Petersen, J.; Hofmann, W.P.; Buti, M.; Santantonio, T.; et al. Entecavir Treatment for Chronic Hepatitis B: Adaptation Is Not Needed for the Majority of Naive Patients with a Partial Virological Response. Hepatology 2011, 54, 443–451, Erratum in Hepatology 2011, 54, 2281–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlendorf, V.; Bremer, B.; Sandmann, L.; Mix, C.; Tergast, T.; Cornberg, M.; Wedemeyer, H.; Deterding, K.; Maasoumy, B. Limited stability of Hepatitis B virus RNA in plasma and serum. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maasoumy, B.; Geretti, A.M.; Frontzek, A.; Austin, H.; Aretzweiler, G.; Garcia-Alvarez, M.; Leuchter, S.; Simon, C.O.; Marins, E.G.; Canchola, J.A.; et al. HBV-RNA Co-amplification May Influence HBV DNA Viral Load Determination. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 983–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, M.F.; Riveiro-Barciela, M.; Tabernero, D.; Rodriguez-Algarra, F.; Palom, A.; Sopena, S.; Rando-Segura, A.; Roade, L.; Kuchta, A.; Ferrer-Costa, R.; et al. Standardized Hepatitis B Virus RNA Quantification in Untreated and Treated Chronic Patients: A Promising Marker of Infection Follow-Up. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0214921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Factors | Overall (N = 86) | ETV Group (N = 80) | TAF Group (N = 6) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 48 (21–81) | 49 (21–81) | 40 (34–51) | 0.125 * |
| Gender (Male/Female) | 63/23 | 59/21 | 4/2 | 0.656 ** |
| Platelet count (×104/μL) | 15.9 (5.4–37.8) | 15.7 (5.4–37.8) | 19.1 (13.8–21.7) | 0.282 * |
| AST (U/L) | 57 (16–935) | 57 (16–304) | 87 (37–935) | 0.282 * |
| ALT (U/L) | 61 (13–389) | 60 (13–389) | 92 (31–314) | 0.282 * |
| HBsAg (Log IU/mL) | 3.56 (−0.78–5.46) | 3.54 (−0.78–5.46) | 3.61 (2.78–4.99) | 0.919 * |
| HBeAg (+/−) | 47/39 | 43/37 | 4/2 | 0.685 ** |
| HBV DNA (Log copies/mL) | 7.2 (5.0–10.0) | 7.2 (5.8–10.0) | 7.8 (5.0–8.6) | 0.919 * |
| HBV RNA (Log copies/mL) | 4.35 (undet.–7.96) | 4.25 (undet.–7.96) | 4.73 (1.22–6.05) | 0.872 * |
| HBV genotype (B/C/ND) | 2/69/15 | 2/64/14 | 0/5/1 | 1.000 ** |
| Fib-4 index | 2.05 (0.47–12.29) | 2.05 (0.47–9.97) | 1.85 (0.83–12.29) | 0.780 * |
| Fibrosis stage (F0-1/2/3/4/ND) | 11/24/17/4/30 | 8/22/17/3/30 | 3/2/0/1/0 | 0.007 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hiraoka, K.; Tsuge, M.; Kawahara, M.; Fujino, H.; Fujii, Y.; Ono, A.; Murakami, E.; Kawaoka, T.; Miki, D.; Hayes, C.N.; et al. Utility of Serum HBV RNA Measurement During Nucleoside/Nucleotide Analog Therapy in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010141
Hiraoka K, Tsuge M, Kawahara M, Fujino H, Fujii Y, Ono A, Murakami E, Kawaoka T, Miki D, Hayes CN, et al. Utility of Serum HBV RNA Measurement During Nucleoside/Nucleotide Analog Therapy in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010141
Chicago/Turabian StyleHiraoka, Keiichi, Masataka Tsuge, Michihiko Kawahara, Hatsue Fujino, Yasutoshi Fujii, Atsushi Ono, Eisuke Murakami, Tomokazu Kawaoka, Daiki Miki, C. Nelson Hayes, and et al. 2025. "Utility of Serum HBV RNA Measurement During Nucleoside/Nucleotide Analog Therapy in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010141
APA StyleHiraoka, K., Tsuge, M., Kawahara, M., Fujino, H., Fujii, Y., Ono, A., Murakami, E., Kawaoka, T., Miki, D., Hayes, C. N., Kashiyama, S., Mokuda, S., Yamazaki, S., & Oka, S. (2025). Utility of Serum HBV RNA Measurement During Nucleoside/Nucleotide Analog Therapy in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010141






