Kinome-Wide Screening Identifies FAK as a Novel Post-Translational Regulator of PD-L1 Stability and Immune Evasion in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
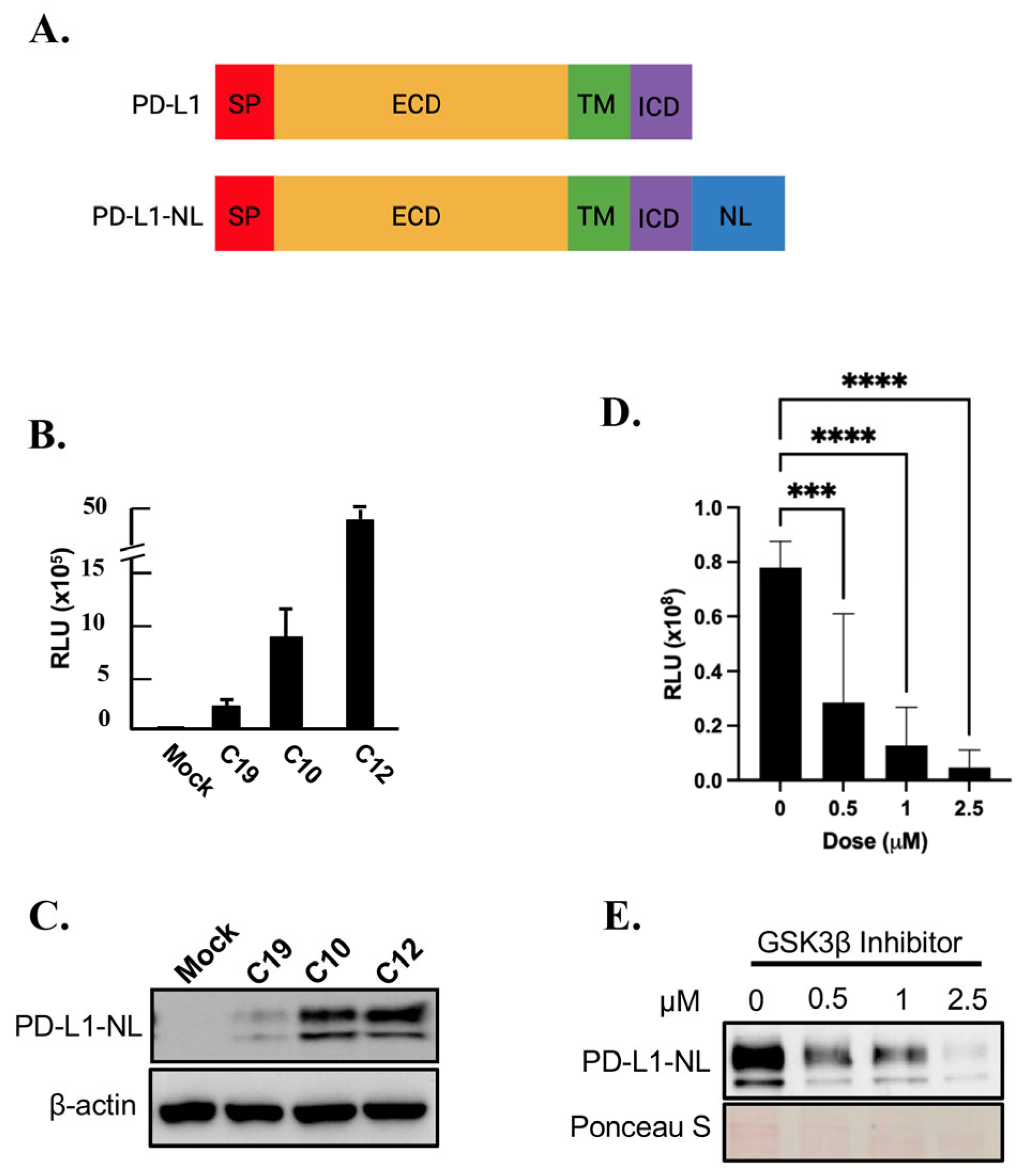
2.1. Establishment of a Cell Line Stably Expressing NanoLuc Tagged PD-L1
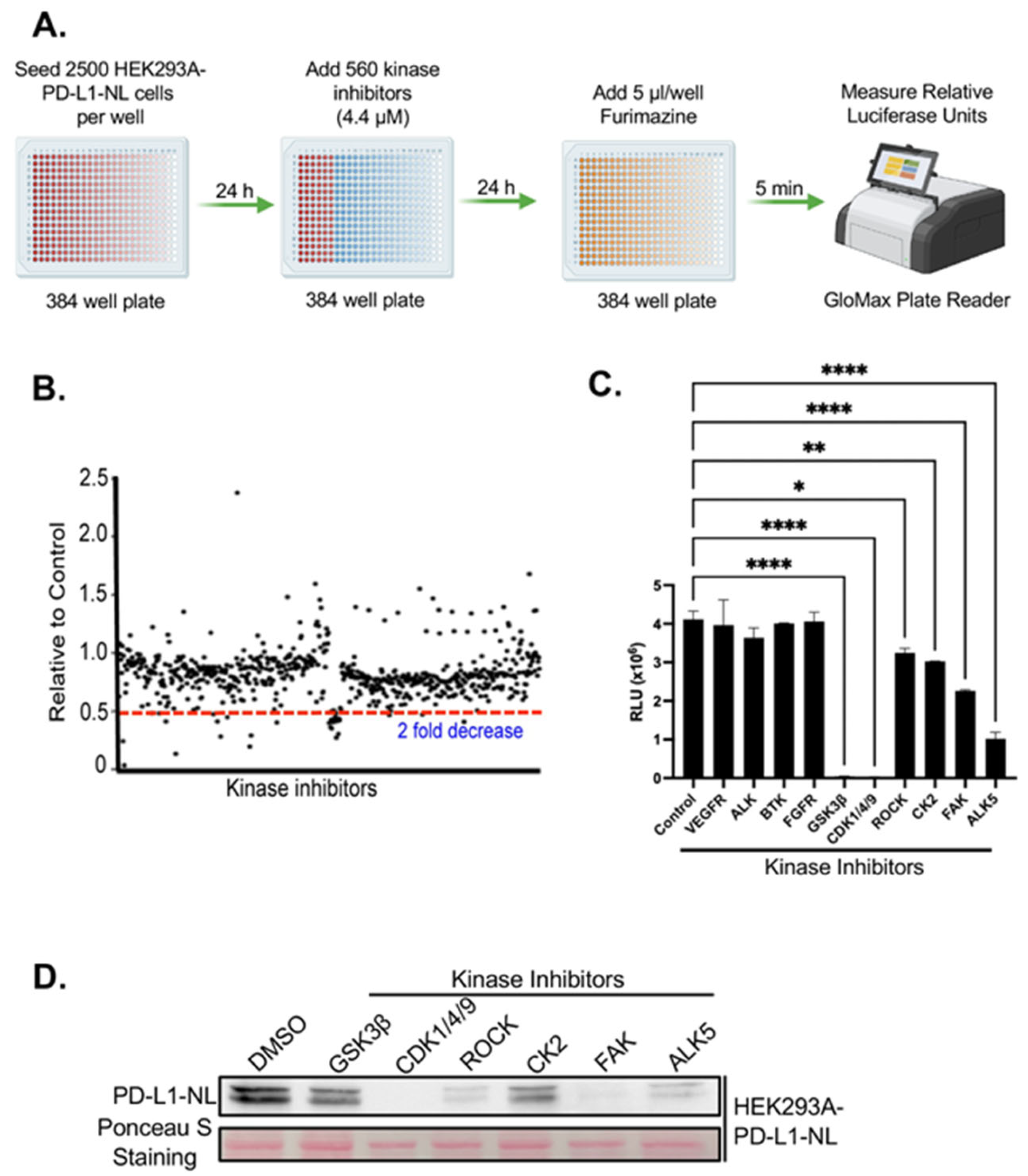
2.2. Kinome-Wide High-Throughput Screen (HTS) for Kinase Inhibitors Regulating PD-L1 Stability
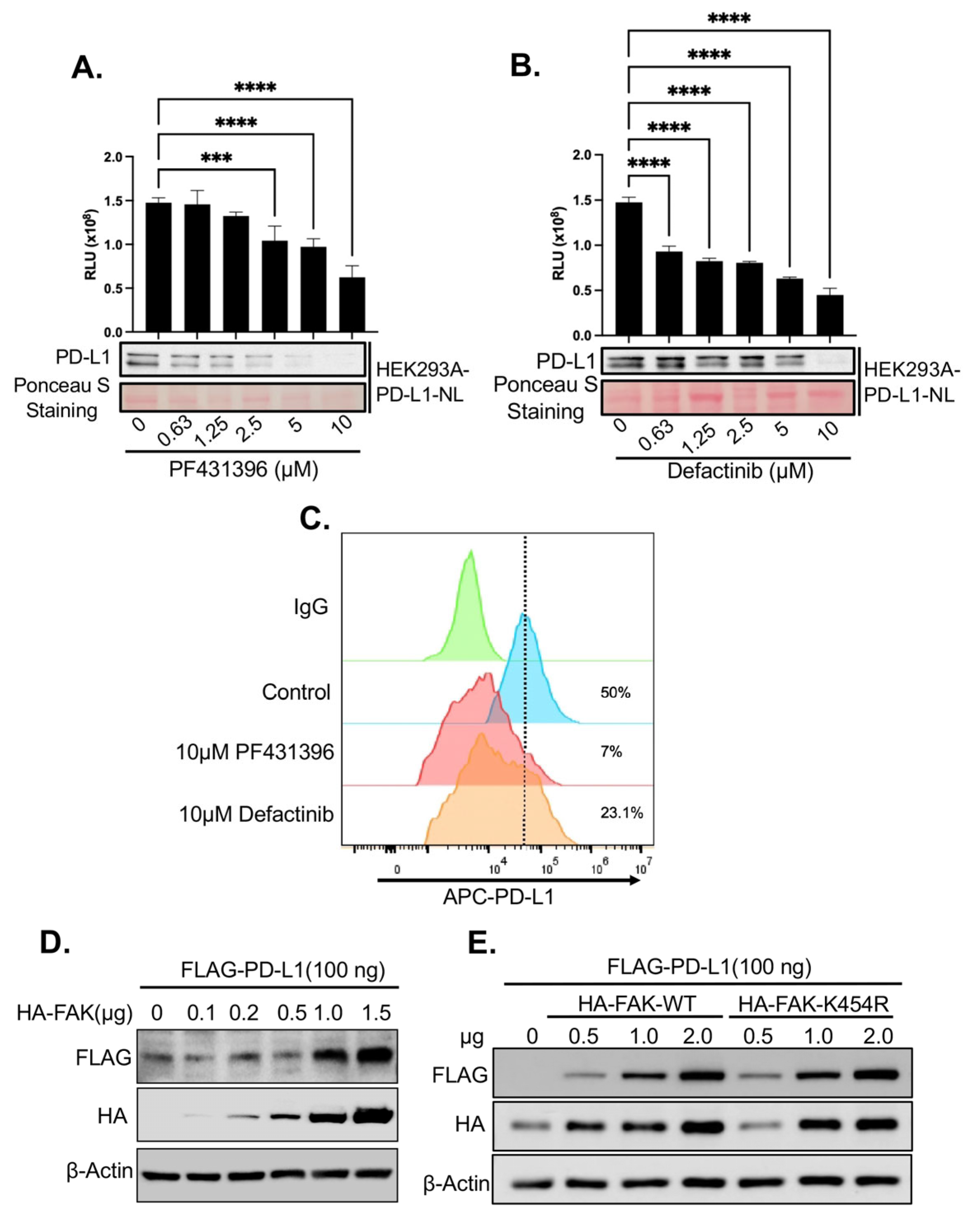
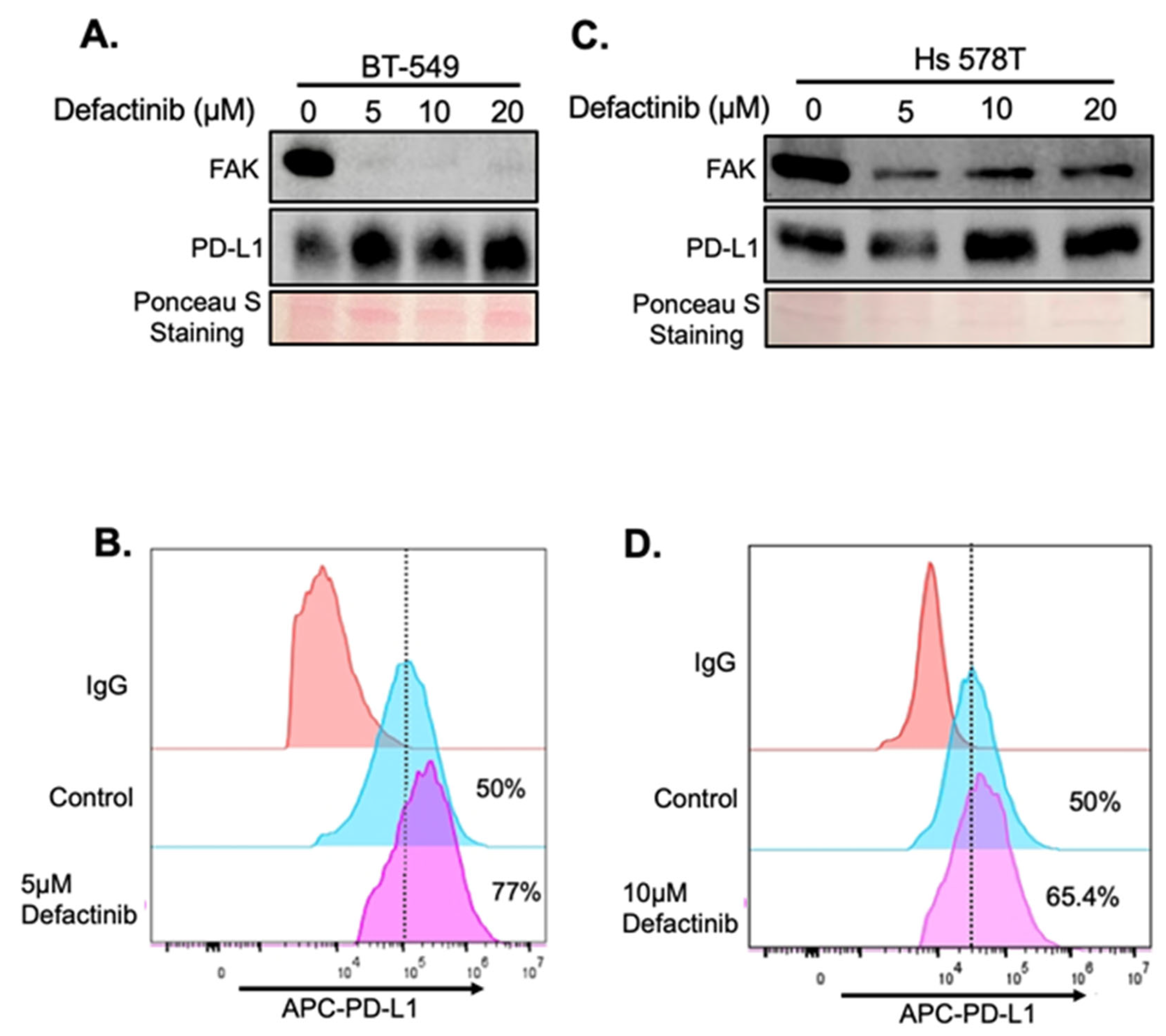
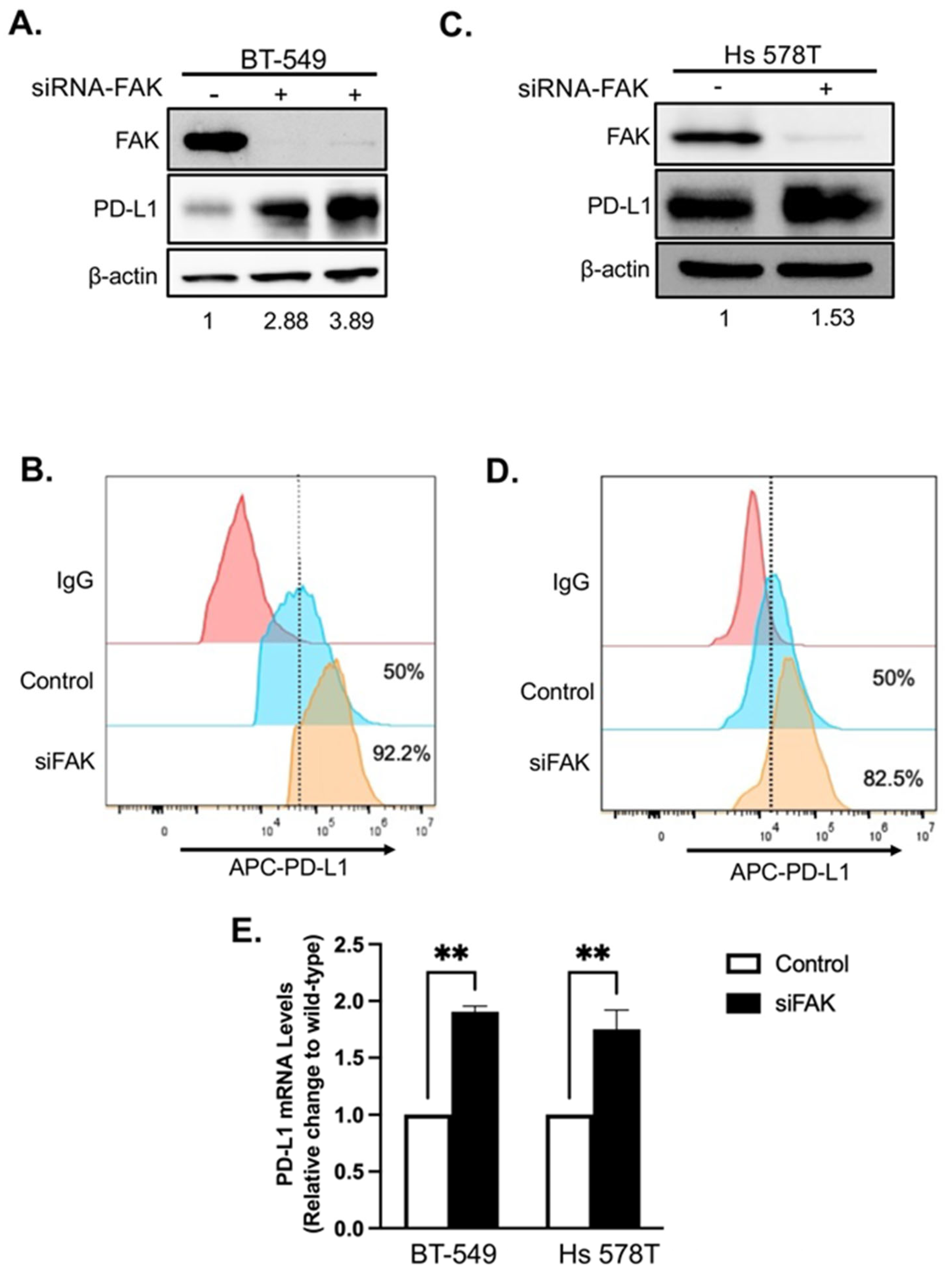
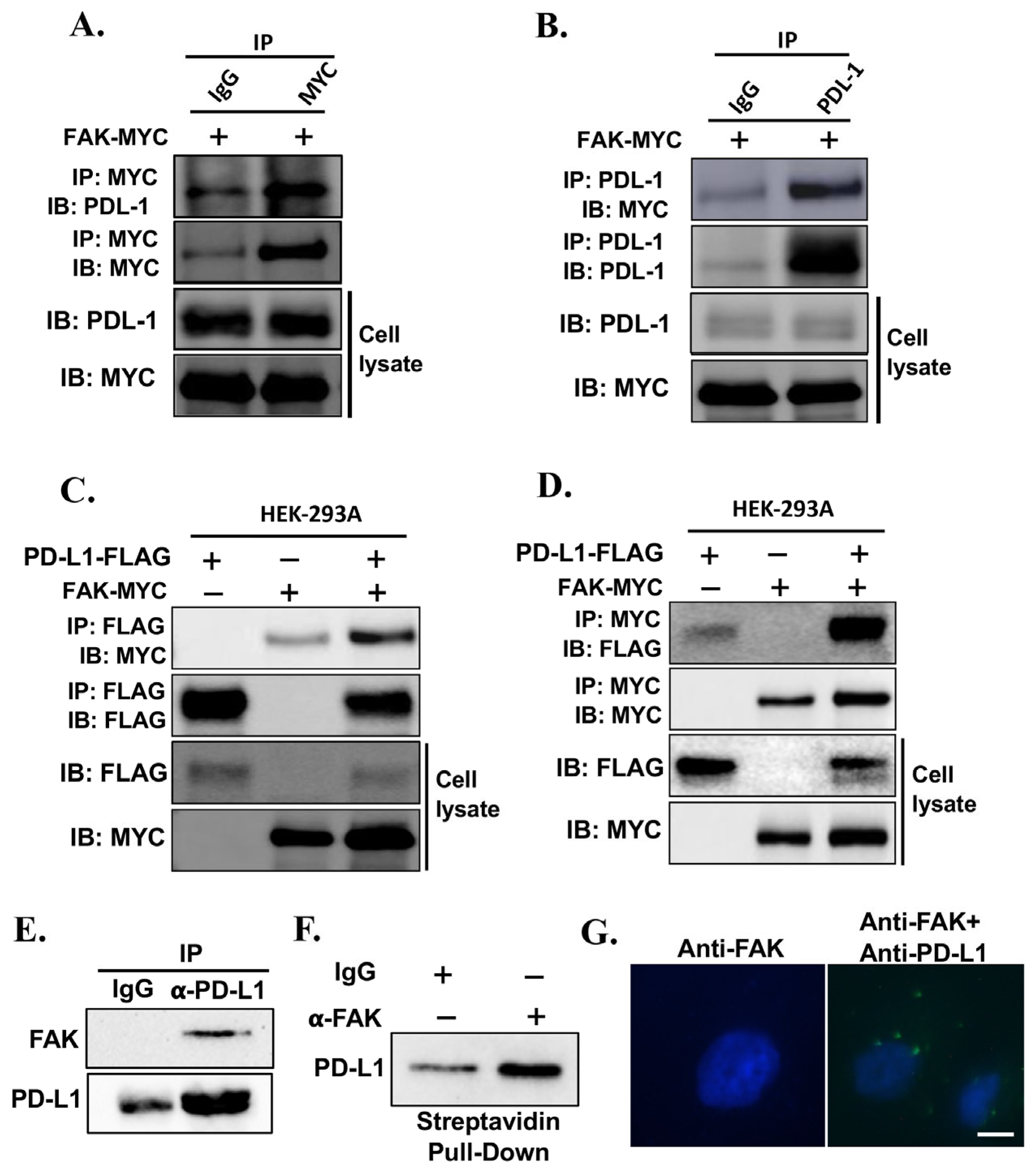
2.3. Validation of FAK as Novel Regulator of PD-L1 Stability
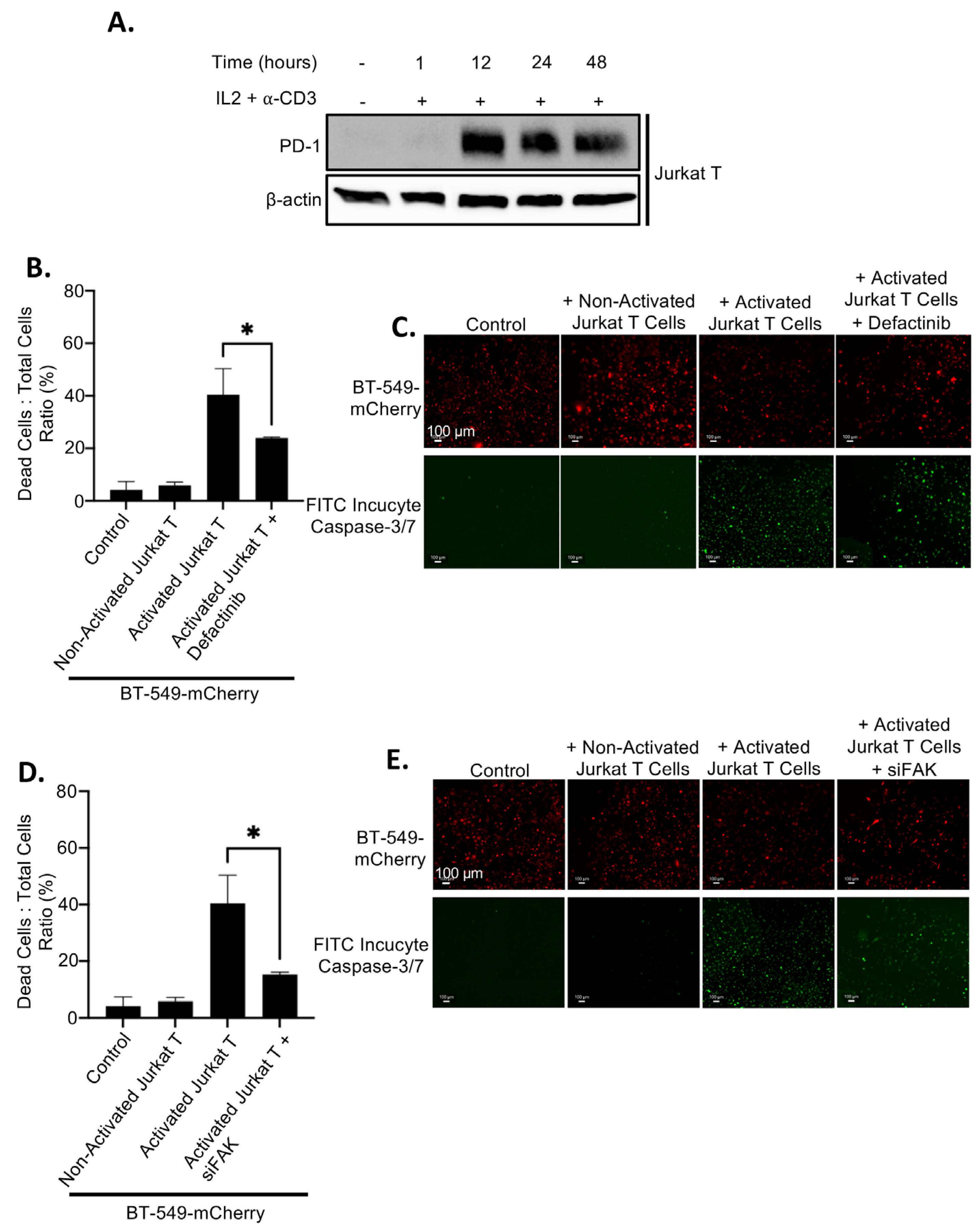
2.4. Upregulation of PD-L1 After FAK Inhibition Causes Increased Immune Evasion
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Kinase Inhibitors
4.2. Plasmid Construction
4.3. Cell Culture and Establishment of Stable Line
4.4. Kinome-Wide Kinase Inhibitor Screen and Drug Validation
4.5. NanoLuc Luciferase Assay
4.6. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR
4.7. Knockdown of FAK by siRNA
4.8. Immunoblotting, Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP), and Antibodies
4.9. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) Analysis of Membrane PD-L1
4.10. Immune Evasion Assays In Vitro
4.11. ProtA-TurboID Analysis of Protein–Protein Interaction
4.12. The Proximity Ligation Assay (PLA) Analysis of Protein–Protein Interaction
4.13. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKT | Protein Kinase B |
| ALK | Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase |
| APC | Allophycocyanin (fluorescent dye) |
| BTK | Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase |
| CDK | Cyclin-Dependent Kinase |
| CK2 | Casein Kinase 2 |
| Co-IP | Co-immunoprecipitation |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| FACS | Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting |
| FAK | Focal Adhesion Kinase |
| FDA | U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
| FGFR | Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor |
| GSK3β | Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Beta |
| HA | Hemagglutinin (epitope tag) |
| HEK293A | Human Embryonic Kidney 293A cells |
| HTS | High-Throughput Screening |
| ICI | Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor |
| IL2 | Interleukin 2 |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| NL | NanoLuc |
| NP-40 | Nonidet P-40 (detergent) |
| NanoLuc | NanoLuciferase |
| ORF | Open Reading Frame |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PD-1 | Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed Death-Ligand 1 |
| PDX | Patient-Derived Xenograft |
| PE | Phycoerythrin (fluorescent dye) |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase |
| RIPA | Radioimmunoprecipitation Assay buffer |
| ROCK | Rho-associated Protein Kinase |
| TAZ | Transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif |
| TNBC | Triple-Negative Breast Cancer |
| VEGFR | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor |
| WT | Wild-Type |
| mTOR | Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative Real-Time PCR |
| siFAK | siRNA targeting FAK |
| siRNA | Small Interfering RNA |
References
- Almozyan, S.; Colak, D.; Mansour, F.; Alaiya, A.; Al-Harazi, O.; Qattan, A.; Al-Mohanna, F.; Al-Alwan, M.; Ghebeh, H. PD-L1 promotes OCT4 and Nanog expression in breast cancer stem cells by sustaining PI3K/AKT pathway activation. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 1402–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, M.; Barsoum, I.B.; Truesdell, P.; Cotechini, T.; Macdonald-Goodfellow, S.K.; Petroff, M.; Siemens, D.R.; Koti, M.; Craig, A.W.; Graham, C.H. Activation of the PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint confers tumor cell chemoresistance associated with increased metastasis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 10557–10567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.A.; Gupta, H.B.; Curiel, T.J. Tumor cell-intrinsic CD274/PD-L1: A novel metabolic balancing act with clinical potential. Autophagy 2017, 13, 987–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Xia, Y.; Hu, X.; Guo, J. PD-L1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via activating SREBP-1c in renal cell carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.M.; Chen, D.S. Immune escape to PD-L1/PD-1 blockade: Seven steps to success (or failure). Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1492–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardoll, D.M. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.S.; Mellman, I. Oncology meets immunology: The cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity 2013, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.S.; Mellman, I. Elements of cancer immunity and the cancer-immune set point. Nature 2017, 541, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmaninejad, A.; Valilou, S.F.; Shabgah, A.G.; Aslani, S.; Alimardani, M.; Pasdar, A.; Sahebkar, A. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: Basic biology and role in cancer immunotherapy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 16824–16837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Lim, K.S.; Mekhail, T.; Chang, C.C. Programmed Death Ligand-1 (PD-L1) Expression in the Programmed Death Receptor-1 (PD-1)/PD-L1 Blockade: A Key Player Against Various Cancers. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2017, 141, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, T.L.; Demaria, S.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Zarour, H.M.; Melero, I. Emerging Opportunities and Challenges in Cancer Immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1845–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.C.; Duffy, C.R.; Allison, J.P. Fundamental Mechanisms of Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1069–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Research Institute. PD-1/PD-L1 Landscape. 2019. Available online: https://www.cancerresearch.org/scientists/clinical-accelerator/landscape-of-immuno-oncology-drug-development/pd-1-pd-l1-landscape (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Ribas, A.; Wolchok, J.D. Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science 2018, 359, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Dewanjee, S.; Li, Y.; Jha, N.K.; Chen, Z.S.; Kumar, A.; Vishakha; Behl, T.; Jha, S.K.; Tang, H. Advancements in clinical aspects of targeted therapy and immunotherapy in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, L.; Okines, A. Systemic Therapy for Metastatic Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Current Treatments and Future Directions. Cancers 2023, 15, 3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastwika, K.J.; Wilson, W., 3rd; Li, Q.K.; Norris, J.; Xu, H.; Ghazarian, S.R.; Kitagawa, H.; Kawabata, S.; Taube, J.M.; Yao, S.; et al. Control of PD-L1 Expression by Oncogenic Activation of the AKT-mTOR Pathway in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janse van Rensburg, H.J.; Azad, T.; Ling, M.; Hao, Y.; Snetsinger, B.; Khanal, P.; Minassian, L.M.; Graham, C.H.; Rauh, M.J.; Yang, X. The Hippo pathway component TAZ promotes immune evasion in human cancer through PD-L1. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1457–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wei, Y.; Chu, Y.Y.; Li, Y.; Hsu, J.M.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, C.; Hsu, J.L.; Chang, W.C.; Yang, R.; et al. Phosphorylation and Stabilization of PD-L1 by CK2 Suppresses Dendritic Cell Function. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 2185–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Su, Y.; Xu, B. Rho-associated protein kinase-dependent moesin phosphorylation is required for PD-L1 stabilization in breast cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 2701–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Green, M.D.; Lang, X.; Lazarus, J.; Parsels, J.; Wei, S.; Parsels, L.A.; Shi, J.; Ramnath, N.; Wahl, D.R.; et al. Inhibition of ATM increases interferon signaling and sensitizes pancreatic cancer to immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3940–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasikara, C.; Davra, V.; Calianese, D.; Geng, K.; Spires, T.E.; Quigley, M.; Wichroski, M.; Sriram, G.; Suarez-Lopez, L.; Yaffe, M.B.; et al. Pan-TAM Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor BMS-777607 Enhances Anti-PD-1 mAb Efficacy in a Murine Model of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 2669–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, J.M.; Li, C.W.; Lai, Y.J.; Hung, M.C. Posttranslational Modifications of PD-L1 and Their Applications in Cancer Therapy. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 6349–6353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Ge, S.; Xie, Y.; Sun, R.; Wu, Y.; Xu, J. The regulatory role of CDK4/6 inhibitors in tumor immunity and the potential value of tumor immunotherapy (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2025, 56, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Aranda, M.; Redondo, M. Targeting Protein Kinases to Enhance the Response to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, E2543. [Google Scholar]
- Sulzmaier, F.J.; Jean, C.; Schlaepfer, D.D. FAK in cancer: Mechanistic findings and clinical applications. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.W.; Lim, S.O.; Xia, W.; Lee, H.H.; Chan, L.C.; Kuo, C.W.; Khoo, K.H.; Chang, S.S.; Cha, J.H.; Kim, T.; et al. Glycosylation and stabilization of programmed death ligand-1 suppresses T-cell activity. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Guan, J.L. Focal adhesion kinase: A prominent determinant in breast cancer initiation, progression and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2010, 289, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Yan, Y.; Song, B.; Zhu, S.; Mei, Q.; Wu, K. Focal adhesion kinase: From biological functions to therapeutic strategies. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.X.; Cao, Y.Y.; Xu, L.S.; Wang, H.C.; Liu, X.H.; Zhu, H.L. FAK inhibitors in cancer, a patent review—An update on progress. Expert. Opin. Ther. Pat. 2024, 34, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glénisson, M.; Vacher, S.; Callens, C.; Susini, A.; Cizeron-Clairac, G.; Le Scodan, R.; Meseure, D.; Lerebours, F.; Spyratos, F.; Lidereau, R.; et al. Identification of new candidate therapeutic target genes in triple-negative breast cancer. Genes Cancer 2012, 3, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubovskaya, V.M.; Ylagan, L.; Miller, A.; Hughes, M.; Wilson, J.; Wang, D.; Brese, E.; Bshara, W.; Edge, S.; Morrison, C.; et al. High focal adhesion kinase expression in breast carcinoma is associated with lymphovascular invasion and triple-negative phenotype. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, N.; Hosain, S.; Zhao, J.; Shen, Y.; Luo, X.; Jiang, J.; Endo, Y.; Wu, W.J. Atezolizumab potentiates Tcell-mediated cytotoxicity and coordinates with FAK to suppress cell invasion and motility in PD-L1(+) triple negative breast cancer cells. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1624128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiede, S.; Meyer-Schaller, N.; Kalathur, R.K.R.; Ivanek, R.; Fagiani, E.; Schmassmann, P.; Stillhard, P.; Häfliger, S.; Kraut, N.; Schweifer, N.; et al. The FAK inhibitor BI 853520 exerts anti-tumor effects in breast cancer. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Xia, W.; Yamaguchi, H.; Wei, Y.; Chen, M.K.; Hsu, J.M.; Hsu, J.L.; Yu, W.H.; Du, Y.; Lee, H.H.; et al. PARP Inhibitor Upregulates PD-L1 Expression and Enhances Cancer-Associated Immunosuppression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3711–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, T.; Janse van Rensburg, H.J.; Lightbody, E.D.; Neveu, B.; Champagne, A.; Ghaffari, A.; Kay, V.R.; Hao, Y.; Shen, H.; Yeung, B.; et al. A LATS biosensor functional screen identifies VEGFR as a novel regulator of the Hippo pathway in angiogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boyd, A.-L.; Khanal, P.; Kelly, T.; Ge, A.; Hao, Y.; Yang, X. Kinome-Wide Screening Identifies FAK as a Novel Post-Translational Regulator of PD-L1 Stability and Immune Evasion in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010108
Boyd A-L, Khanal P, Kelly T, Ge A, Hao Y, Yang X. Kinome-Wide Screening Identifies FAK as a Novel Post-Translational Regulator of PD-L1 Stability and Immune Evasion in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010108
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoyd, Asia-Lily, Prem Khanal, Tynan Kelly, Anni Ge, Yawei Hao, and Xiaolong Yang. 2025. "Kinome-Wide Screening Identifies FAK as a Novel Post-Translational Regulator of PD-L1 Stability and Immune Evasion in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010108
APA StyleBoyd, A.-L., Khanal, P., Kelly, T., Ge, A., Hao, Y., & Yang, X. (2025). Kinome-Wide Screening Identifies FAK as a Novel Post-Translational Regulator of PD-L1 Stability and Immune Evasion in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010108






