The Impact of the Apelinergic System on the Cardiovascular System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Molecular Basis
3. Current State of the Art
3.1. Ischemic Heart Disease
3.2. Hypertension and Hypertensive Heart Disease
3.3. Heart Failure
3.4. Arrhythmias
3.5. Therapeutic Perspectives
4. Limitations and Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shin, K.; Kenward, C.; Rainey, J.K. Apelinergic System Structure and Function. Compr. Physiol. 2017, 8, 407–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, F.A.; Maguire, J.J.; Newby, D.E.; Davenport, A.P.; Dhaun, N. Targeting the apelin system for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 119, 2683–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawid, M.; Mlyczyńska, E.; Jurek, M.; Respekta, N.; Pich, K.; Kurowska, P.; Gieras, W.; Milewicz, T.; Kotula-Balak, M.; Rak, A. Apelin, APJ, and ELABELA: Role in Placental Function, Pregnancy, and Foetal Development—An Overview. Cells 2021, 11, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Sun, W.; Chen, X. The Role of Apelin/Apelin Receptor in Energy Metabolism and Water Homeostasis: A Comprehensive Narrative Review. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 632886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Read, C.; Kuc, R.E.; Buonincontri, G.; Southwood, M.; Torella, R.; Upton, P.D.; Crosby, A.; Sawiak, S.J.; Carpenter, T.A.; et al. Elabela/Toddler Is an Endogenous Agonist of the Apelin APJ Receptor in the Adult Cardiovascular System, and Exogenous Administration of the Peptide Compensates for the Downregulation of Its Expression in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Circulation 2017, 135, 1160–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yan, J.; Travis, Z.D.; Lenahan, C.; Gao, L.; Wu, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Shao, A.; Yu, J. Apelin/APJ system: A novel promising target for anti-oxidative stress in stroke. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 15, 1352927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.M.; Ashley, E.A.; Deng, D.X.; Tsalenko, A.; Deng, A.; Tabibiazar, R.; Ben-Dor, A.; Fenster, B.; Yang, E.; King, J.Y.; et al. Novel role for the potent endogenous inotrope apelin in human cardiac dysfunction. Circulation 2003, 108, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaydarski, L.; Petrova, K.; Stanchev, S.; Pelinkov, D.; Iliev, A.; Dimitrova, I.N.; Kirkov, V.; Landzhov, B.; Stamenov, N. Morphometric and Molecular Interplay in Hypertension-Induced Cardiac Remodeling with an Emphasis on the Potential Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Cheng, X.S.; Pang, C.C. Venous dilator effect of apelin, an endogenous peptide ligand for the orphan APJ receptor, in conscious rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 470, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaux, A.; De Mota, N.; Skultetyova, I.; Lenkei, Z.; El Messari, S.; Gallatz, K.; Corvol, P.; Palkovits, M.; Llorens-Cortès, C. Physiological role of a novel neuropeptide, apelin, and its receptor in the rat brain. J. Neurochem. 2001, 77, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, S.; Murphy, K.; Cohen, M.; Sujkovic, E.; Kennedy, A.; Dhillo, W.; Dakin, C.; Sajedi, A.; Ghatei, M.; Bloom, S. The effects of centrally administered apelin-13 on food intake, water intake and pituitary hormone release in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 291, 1208–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Carroll, A.M.; Lolait, S.J.; Harris, L.E.; Pope, G.R. The apelin receptor APJ: Journey from an orphan to a multifaceted regulator of homeostasis. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 219, R13–R35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, M.; Hansen, M.J.; Tatemoto, K.; Morris, M.J. Inhibitory effect of apelin-12 on nocturnal food intake in the rat. Nutr. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemi, F.; Zahediasl, S. Effects of exercise training on adipose tissue apelin expression in streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced diabetic rats. Gene 2018, 662, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurowska, P.; Barbe, A.; Różycka, M.; Chmielińska, J.; Dupont, J.; Rak, A. Apelin in Reproductive Physiology and Pathology of Different Species: A Critical Review. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 9170480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Chen, R.; Jiang, Y.; Bai, B.; Yang, T.; Liu, H. The Protective Effects and Mechanisms of Apelin/APJ System on Ischemic Stroke: A Promising Therapeutic Target. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibbi, B.; Marroncini, G.; Naldi, L.; Peri, A. The Yin and Yang Effect of the Apelinergic System in Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Anini, Y.; Wei, W.; Qi, X.; OCarroll, A.M.; Mochizuki, T.; Wang, H.Q.; Hellmich, M.R.; Englander, E.W.; Greeley, G.H., Jr. Apelin, a new enteric peptide: Localization in the gastrointestinal tract, ontogeny, and stimulation of gastric cell proliferation and of cholecystokinin secretion. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 1342–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, J.; Chen, L.; Jiang, Z. Apelin/APJ system: A novel promising therapy target for thrombotic diseases. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2016, 48, 589–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Sato, C.; Kadowaki, A.; Watanabe, H.; Ho, L.; Ishida, J.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kimura, A.; Fukamizu, A.; Penninger, J.M.; et al. ELABELA-APJ axis protects from pressure overload heart failure and angiotensin II-induced cardiac damage. Cardiovasc. Res. 2017, 113, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.J.; Ali, Z.A.; Kojima, Y.; Kundu, R.K.; Sheikh, A.Y.; Agrawal, R.; Zheng, L.; Leeper, N.J.; Pearl, N.E.; Patterson, A.J.; et al. Apelin signaling antagonizes Ang II effects in mouse models of atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3343–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, T.; Kihara, M.; Imai, N.; Yoshida, S.; Shimoyamada, H.; Yasuzaki, H.; Ishida, J.; Toya, Y.; Kiuchi, Y.; Hirawa, N.; et al. Requirement of apelin-apelin receptor system for oxidative stress-linked atherosclerosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 1705–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ye, Q.; Gong, D.; Lv, Y.; Cheng, H.; Huang, C.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Z.; Li, L.; Wei, X.; et al. Apelin-13 inhibits lipoprotein lipase expression via the APJ/PKCα/miR-361-5p signaling pathway in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2017, 49, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, F.; Lv, Y.C.; Zhang, M.; Xie, W.; Tan, Y.L.; Gong, D.; Cheng, H.P.; Liu, D.; Li, L.; Liu, X.Y.; et al. Apelin-13 impedes foam cell formation by activating Class III PI3K/Beclin-1-mediated autophagic pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 466, 637–643, Erratum in Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 575, 99–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, L.; Xie, F.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Tang, G.; Lv, D.; Lu, Q.; Chen, L.; Li, J. Jagged-1/Notch3 signaling transduction pathway is involved in apelin-13-induced vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation. Acta Biochim. Et Biophys. Sin. 2013, 45, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Cui, X.; Wang, J.; Pan, L.; Ye, Z.; Liu, P.; Wu, L. Apelin induces vascular smooth muscle cells migration via a PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a/MMP-2 pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 69, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso Dos Santos, L.M.; Azar, P.; Brun, C.; König, S.; Roatti, A.; Baertschi, A.J.; Chaabane, C.; Bochaton-Piallat, M.L. Apelin is expressed in intimal smooth muscle cells and promotes their phenotypic transition. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dönmez, Y.; Acele, A. Increased Elabela levels in the acute ST segment elevation myocardial infarction patients. Medicine 2019, 98, e17645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakowska, D.; Wyderka, R.; Krzystek-Korpacka, M.; Osuch, Ł.; Leśków, A.; Sołtowska, A.; Stanek, M.; Rosińczuk, J.; Jaroch, J. Plasma Levels of Apelinergic System Components in Patients with Chronic and Acute Coronary Syndromes-A Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.L.; Yang, X.C.; Zhong, J.C.; Wang, L.F.; Fan, Y.F. Plasma levels of Elabela are associated with coronary angiographic severity in patients with acute coronary syndrome. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. JGC 2020, 17, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, S. Apelin: A potential marker of coronary artery stenosis and atherosclerotic plaque stability in ACS patients. Int. Heart J. 2014, 55, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Fang, T.; Cheng, Z. Mechanism of heart failure after myocardial infarction. J. Int. Med. Res. 2023, 51, 3000605231202573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, Y.; Faghihi, M.; Imani, A.; Roghani, M.; Zekri, A.; Mobasheri, M.B.; Rastgar, T.; Moghimian, M. Post-infarct treatment with [Pyr1] apelin-13 improves myocardial function by increasing neovascularization and overexpression of angiogenic growth factors in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 761, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; McKinnie, S.M.; Patel, V.B.; Haddad, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhabyeyev, P.; Das, S.K.; Basu, R.; McLean, B.; Kandalam, V.; et al. Loss of Apelin exacerbates myocardial infarction adverse remodeling and ischemia-reperfusion injury: Therapeutic potential of synthetic Apelin analogues. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2013, 2, e000249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin Yu, P.; Ma, S.; Dai, X.; Cao, F. Elabela alleviates myocardial ischemia reperfusion-induced apoptosis, fibrosis and mitochondrial dysfunction through PI3K/AKT signaling. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 4467–4477. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.; Pan, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, Z. Elabela gene therapy promotes angiogenesis after myocardial infarction. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 8537–8545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyderka, R.; Ołpińska, B.; Diakowska, D.; Leśków, A.; Osuch, Ł.; Borger, M.; Brzezińska, B.; Łoboz-Rudnicka, M.; Jaroch, J. Apelinergic System in the Left Ventricle Adverse Remodeling After Myocardial Infarction: A Preliminary Study. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2025, 21, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasniqi, X.; Berisha, B.; Gashi, M.; Koçinaj, D.; Jashari, F.; Vincelj, J. Influence of apelin-12 on troponin levels and the rate of MACE in STEMI patients. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2017, 17, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossin, D.; Vanni, R.; Lo Iacono, M.; Cristallini, C.; Giachino, C.; Rastaldo, R. APJ as Promising Therapeutic Target of Peptide Analogues in Myocardial Infarction- and Hypertension-Induced Heart Failure. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasloo, E.; Najafipour, H.; Vakili, A. Chronic treatment with apelin, losartan and their combination reduces myocardial infarct size and improves cardiac mechanical function. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 47, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, H.; Tang, L.; Ge, G.; Ma, J.; Qiao, Z.; Liu, H.; Fang, W. Apelin-13 protects the heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury through the RISK-GSK-3β-mPTP pathway. Arch. Med. Sci. AMS 2015, 11, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatin, F.; Renaud-Gabardos, E.; Godet, A.C.; Hantelys, F.; Pujol, F.; Morfoisse, F.; Calise, D.; Viars, F.; Valet, P.; Masri, B.; et al. Apelin modulates pathological remodeling of lymphatic endothelium after myocardial infarction. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e93887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Guo, H.; Wang, H.; Xing, D.; Lu, T.; Yang, J.; Wang, C. Apelin-13 alleviated cardiac fibrosis via inhibiting the PI3K/Akt pathway to attenuate oxidative stress in rats with myocardial infarction-induced heart failure. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20200040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, W.; Feng, F.; Xu, J.; Wu, F. Apelin-13 protects against myocardial infarction-induced myocardial fibrosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 5262–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, P.; Gheblawi, M.; Wang, K.; Vu, J.; Kondaiah, P.; Oudit, G.Y. Interaction between the apelinergic system and ACE2 in the cardiovascular system: Therapeutic implications. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 2319–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girault-Sotias, P.E.; Deloux, R.; De Mota, N.; Riché, S.; Daubeuf, F.; Iturrioz, X.; Parlakian, A.; Berdeaux, A.; Agbulut, O.; Bonnet, D.; et al. The Metabolically Resistant Apelin-17 Analogue LIT01-196 Reduces Cardiac Dysfunction and Remodelling in Heart Failure After Myocardial Infarction. Can. J. Cardiol. 2025, 41, 911–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyderka, R.; Diakowska, D.; Łoboz-Rudnicka, M.; Mercik, J.; Borger, M.; Osuch, Ł.; Brzezińska, B.; Leśków, A.; Krzystek-Korpacka, M.; Jaroch, J. Influence of the Apelinergic System on Conduction Disorders in Patients after Myocardial Infarction. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachwalik, M.; Leśków, A.; Matusiewicz, M.; Jama-Kmiecik, A.; Diakowska, D. Assessment of Levels of Apelinergic System Peptides in Serum and Epicardial Adipose Tissue in Patients with Multivessel Coronary Artery Disease Who Underwent Myocardial Revascularisation. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksakal, A.; Kerget, B.; Gülbahar, B.N.; Laloğlu, E.; Sağlam, L. Can apelins guide the diagnosis of coronary artery disease in COPD patients? Heart Lung J. Crit. Care 2025, 71, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, F.; Kaplan, M. Association Between Serum Elabela Levels and Chronic Totally Occlusion in Patients with Stable Angina Pectoris. Associação entre os Níveis Séricos de Elabela e Oclusão Total Crônica em Pacientes com Angina Pectoris Estável. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2021, 117, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliev, A.; Gaydarski, L.; Kotov, G.; Landzhov, B.; Kirkov, V.; Stanchev, S. The vascular footprint in cardiac homeostasis and hypertensive heart disease-A link between apelin receptor, vascular endothelial growth factor, and neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Anat. Rec. 2024, 307, 3548–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Jia, J.; Xu, N.; Ye, C.; Zheng, F.; Yuan, Y.; Zhu, G.Q.; Zhan, Y.Y. Apelin receptor upregulation in spontaneously hypertensive rat contributes to the enhanced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by activating autophagy. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafipour, H.; Vakili, A.; Shahouzehi, B.; Soltani Hekmat, A.; Masoomi, Y.; Yeganeh Hajahmadi, M.; Esmaeli-Mahani, S. Investigation of changes in apelin receptor mRNA and protein expression in the myocardium and aorta of rats with two-kidney, one-clip (2K1C) Goldblatt hypertension. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 71, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, M.; Abharzanjani, F.; Kazemi, T.; Estanesti, F. Comparing the apelin level in hypertensive patients who received hypertension drugs. Mod. Care J. 2020, 17, e106150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhao, L.; Martin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhong, J.C.; Yang, X.C. Lower Plasma Elabela Levels in Hypertensive Patients With Heart Failure Predict the Occurrence of Major Adverse Cardiac Events: A Preliminary Study. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 638468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, G.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Lu, X. Serum Elabela expression is decreased in hypertensive patients and could be associated with the progression of hypertensive renal damage. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Ding, F.; Zhang, L.; Shen, A.; Yao, H.; Deng, L.; Ding, Y. Serum apelin is associated with left ventricular hypertrophy in untreated hypertension patients. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japp, A.G.; Cruden, N.L.; Amer, D.A.; Li, V.K.; Goudie, E.B.; Johnston, N.R.; Sharma, S.; Neilson, I.; Webb, D.J.; Megson, I.L.; et al. Vascular effects of apelin in vivo in man. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, D.; Wang, M.; Wang, Q.; Kouznetsova, J.; Yang, R.; Qian, K.; Wu, W.; Shuldiner, A.; Sztalryd, C.; et al. Elabela-apelin receptor signaling pathway is functional in mammalian systems. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, C.; Lin, H.; Qiao, Q.; Huang, M.; Zhu, Q.; et al. ELABELA attenuates deoxycorticosterone acetate/salt-induced hypertension and renal injury by inhibition of NADPH oxidase/ROS/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Sun, H.J.; Xiong, X.Q.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.H.; Kang, Y.M.; Wang, J.J.; Gao, X.Y.; Zhu, G.Q. Apelin-13 and APJ in paraventricular nucleus contribute to hypertension via sympathetic activation and vasopressin release in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Acta Physiol. 2014, 212, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rikitake, Y. The apelin/APJ system in the regulation of vascular tone: Friend or foe? J. Biochem. 2021, 169, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modgil, A.; Guo, L.; O’Rourke, S.T.; Sun, C. Apelin-13 inhibits large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels in cerebral artery smooth muscle cells via a PI3-kinase dependent mechanism. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiquee, K.; Hampton, J.; Khan, S.; Zadory, D.; Gleaves, L.; Vaughan, D.E.; Smith, L.H. Apelin protects against angiotensin II-induced cardiovascular fibrosis and decreases plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 production. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Wang, W.; Jin, H.Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Y.W.; Xu, Y.L.; Song, B.; Penninger, J.M.; Oudit, G.Y.; Zhong, J.C. Apelin Is a Negative Regulator of Angiotensin II-Mediated Adverse Myocardial Remodeling and Dysfunction. Hypertension 2017, 70, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, J. Targeting the elabela/apelin-apelin receptor axis as a novel therapeutic approach for hypertension. Chin. Med. J. 2022, 135, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenaar, G.T.M.; Moll, G.N. Clinical significance of intervention in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-apelinergic system. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2025, 1003, 177866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wu, D.; Li, L.; Chen, L. Apelin/APJ system: A bifunctional target for cardiac hypertrophy. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 230, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foussal, C.; Lairez, O.; Calise, D.; Pathak, A.; Guilbeau-Frugier, C.; Valet, P.; Parini, A.; Kunduzova, O. Activation of catalase by apelin prevents oxidative stress-linked cardiac hypertrophy. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 2363–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, F.; Li, F.; Mao, X.; Yang, L.; Huang, H.; Guo, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, J. NOX4-derived reactive oxygen species drive apelin-13-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation via the ERK pathway. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2011, 17, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scimia, M.C.; Hurtado, C.; Ray, S.; Metzler, S.; Wei, K.; Wang, J.; Woods, C.E.; Purcell, N.H.; Catalucci, D.; Akasaka, T.; et al. APJ acts as a dual receptor in cardiac hypertrophy. Nature 2012, 488, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.C.; Weerateerangkul, P.; Lu, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Lin, Y.K.; Chen, S.A.; Chen, Y.J. Apelin regulates the electrophysiological characteristics of atrial myocytes. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 43, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulkeroua, C.; Ayari, H.; Khalfaoui, T.; Lafrance, M.; Besserer-Offroy, É.; Ekindi, N.; Sabbagh, R.; Dumaine, R.; Lesur, O.; Sarret, P.; et al. Apelin-13 Regulates Vasopressin-Induced Aquaporin-2 Expression and Trafficking in Kidney Collecting Duct Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 53, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hus-Citharel, A.; Bouby, N.; Frugière, A.; Bodineau, L.; Gasc, J.M.; Llorens-Cortes, C. Effect of apelin on glomerular hemodynamic function in the rat kidney. Kidney Int. 2008, 74, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mota, N.; Reaux-Le Goazigo, A.; El Messari, S.; Chartrel, N.; Roesch, D.; Dujardin, C.; Kordon, C.; Vaudry, H.; Moos, F.; Llorens-Cortes, C. Apelin, a potent diuretic neuropeptide counteracting vasopressin actions through inhibition of vasopressin neuron activity and vasopressin release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10464–10469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hus-Citharel, A.; Bodineau, L.; Frugière, A.; Joubert, F.; Bouby, N.; Llorens-Cortes, C. Apelin counteracts vasopressin-induced water reabsorption via cross talk between apelin and vasopressin receptor signaling pathways in the rat collecting duct. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 4483–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Földes, G.; Horkay, F.; Szokodi, I.; Vuolteenaho, O.; Ilves, M.; Lindstedt, K.A.; Mäyränpää, M.; Sármán, B.; Seres, L.; Skoumal, R.; et al. Circulating and cardiac levels of apelin, the novel ligand of the orphan receptor APJ, in patients with heart failure. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 308, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francia, P.; Salvati, A.; Balla, C.; De Paolis, P.; Pagannone, E.; Borro, M.; Gentile, G.; Simmaco, M.; De Biase, L.; Volpe, M. Cardiac resynchronization therapy increases plasma levels of the endogenous inotrope apelin. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2007, 9, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitkin, S.L.; Maguire, J.J.; Kuc, R.E.; Davenport, A.P. Modulation of the apelin/APJ system in heart failure and atherosclerosis in man. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1785–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japp, A.G.; Newby, D.E. The apelin-APJ system in heart failure: Pathophysiologic relevance and therapeutic potential. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 1882–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xiong, J.; Yi, X.; Song, S.; Yang, H.; Tan, W.; Yang, X.; Zheng, L.; Yu, J.; Xu, C. Decreased plasma ELABELA level as a novel screening indicator for heart failure: A cohort and observational study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, M.F.; Pirolli, T.J.; Jayasankar, V.; Burdick, J.; Morine, K.J.; Gardner, T.J.; Woo, Y.J. Apelin has in vivo inotropic effects on normal and failing hearts. Circulation 2004, 110, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuba, K.; Zhang, L.; Imai, Y.; Arab, S.; Chen, M.; Maekawa, Y.; Leschnik, M.; Leibbrandt, A.; Markovic, M.; Schwaighofer, J.; et al. Impaired heart contractility in Apelin gene-deficient mice associated with aging and pressure overload. Circ. Res. 2007, 101, e32–e42, Erratum in Circ. Res. 2008, 102, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szokodi, I.; Tavi, P.; Földes, G.; Voutilainen-Myllylä, S.; Ilves, M.; Tokola, H.; Pikkarainen, S.; Piuhola, J.; Rysä, J.; Tóth, M.; et al. Apelin, the novel endogenous ligand of the orphan receptor APJ, regulates cardiac contractility. Circ. Res. 2002, 91, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Japp, A.G.; Cruden, N.L.; Barnes, G.; van Gemeren, N.; Mathews, J.; Adamson, J.; Johnston, N.R.; Denvir, M.A.; Megson, I.L.; Flapan, A.D.; et al. Acute cardiovascular effects of apelin in humans: Potential role in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation 2010, 121, 1818–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murza, A.; Sainsily, X.; Coquerel, D.; Côté, J.; Marx, P.; Besserer-Offroy, É.; Longpré, J.M.; Lainé, J.; Reversade, B.; Salvail, D.; et al. Discovery and Structure-Activity Relationship of a Bioactive Fragment of ELABELA that Modulates Vascular and Cardiac Functions. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 2962–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, V.N.; Liu, J.; Shang, C.; Woods, C.; Chang, A.C.; Zhao, M.; Charo, D.N.; Grunwald, Z.; Huang, Y.; Seo, K.; et al. Apelin and APJ orchestrate complex tissue-specific control of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and contractility in the hypertrophy-heart failure transition. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 315, H348–H356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkasfalvi, K.; Stagg, M.A.; Coppen, S.R.; Siedlecka, U.; Lee, J.; Soppa, G.K.; Marczin, N.; Szokodi, I.; Yacoub, M.H.; Terracciano, C.M. Direct effects of apelin on cardiomyocyte contractility and electrophysiology. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 357, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couvineau, P.; Llorens-Cortes, C. Metabolically stable apelin analogs: Development and functional role in water balance and cardiovascular function. Clin. Sci. 2025, 139, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, G.D.; Alam, S.; Carter, G.; Pedersen, C.M.; Lee, K.M.; Hubbard, T.J.; Veitch, S.; Jeong, H.; White, A.; Cruden, N.L.; et al. Sustained cardiovascular actions of APJ agonism during renin-angiotensin system activation and in patients with heart failure. Circulation. Heart Fail. 2013, 6, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusik, K.; Kamińska, K.; Sobiborowicz-Sadowska, A.; Borzuta, H.; Buczma, K.; Cudnoch-Jędrzejewska, A. The significance of the apelinergic system in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Heart Fail. Rev. 2024, 29, 969–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczma, K.; Borzuta, H.; Kamińska, K.; Sztechman, D.; Matusik, K.; Pawlonka, J.; Kowara, M.; Buchalska, B.; Cudnoch-Jędrzejewska, A. Apelinergic System Affects Electrocardiographic Abnormalities Induced by Doxorubicin. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Yan, J.; Pan, W.; Tang, M. Apelin/Elabela-APJ: A novel therapeutic target in the cardiovascular system. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ason, B.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Q.; Hoagland, K.M.; Chui, R.W.; Fielden, M.; Sutherland, W.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Mihardja, S.; et al. Cardiovascular response to small-molecule APJ activation. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e132898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Qiu, H.; Xu, B.; Su, Y.; Nyarige, V.; Li, P.; Chen, H.; Killham, B.; Liao, J.; Adam, H.; et al. Microparticle Mediated Delivery of Apelin Improves Heart Function in Post Myocardial Infarction Mice. Circ. Res. 2024, 135, 777–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Lakin, R.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Sachedina, A.; Singh, M.; Wilson, E.; Perez, M.; Verma, S.; Quertermous, T.; et al. Apelin increases atrial conduction velocity, refractoriness, and prevents inducibility of atrial fibrillation. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e126525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, X.; Wang, H.; Qin, W.; Zhou, X.; Tang, B. Apelin Inhibits Angiotensin II-Induced Atrial Fibrosis and Atrial Fibrillation via TGF-β1/Smad2/α-SMA Pathway. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 583570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.P.; Zhong, J.C.; Yang, X.C. Declined ELABELA plasma levels in hypertension patients with atrial fibrillation: A case control study. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2021, 21, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, C.; Buzzi, M.P.; D’Angelo, A.; Schirinzi, S.; Falcone, R.; Rordorf, R.; Capettini, A.C.; Landolina, M.; Storti, C.; Pelissero, G. Apelin plasma levels predict arrhythmia recurrence in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2010, 23, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, Q.; Wu, C.; Chen, L.; Bi, F.; Zhou, Y.; Shan, H. Apelin shorten QT interval by inhibiting Kir2.1/IK1 via a PI3K way in acute myocardial infarction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 517, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Chen, H. Therapeutic potential of apelin and Elabela in cardiovascular disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 166, 115268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
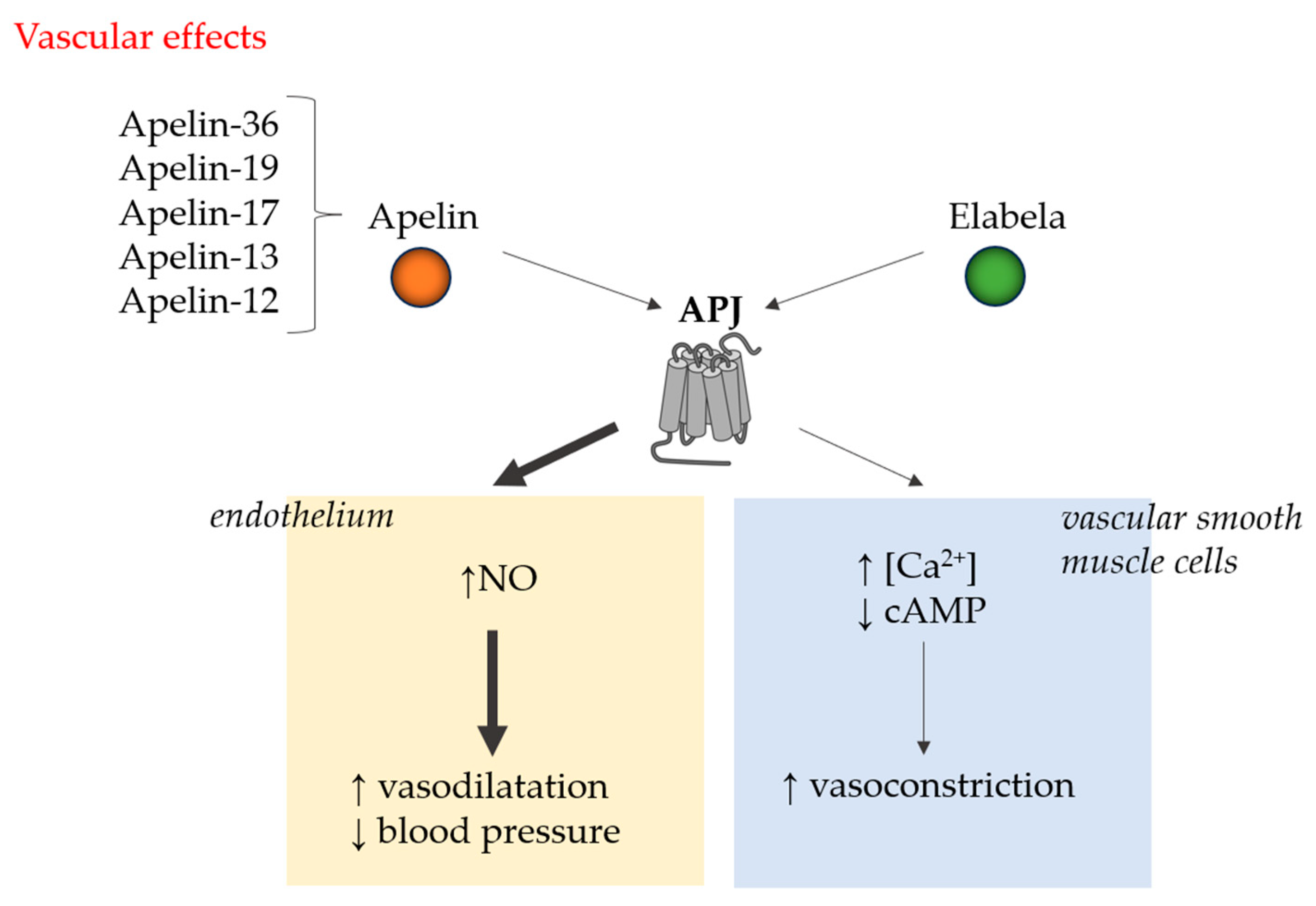
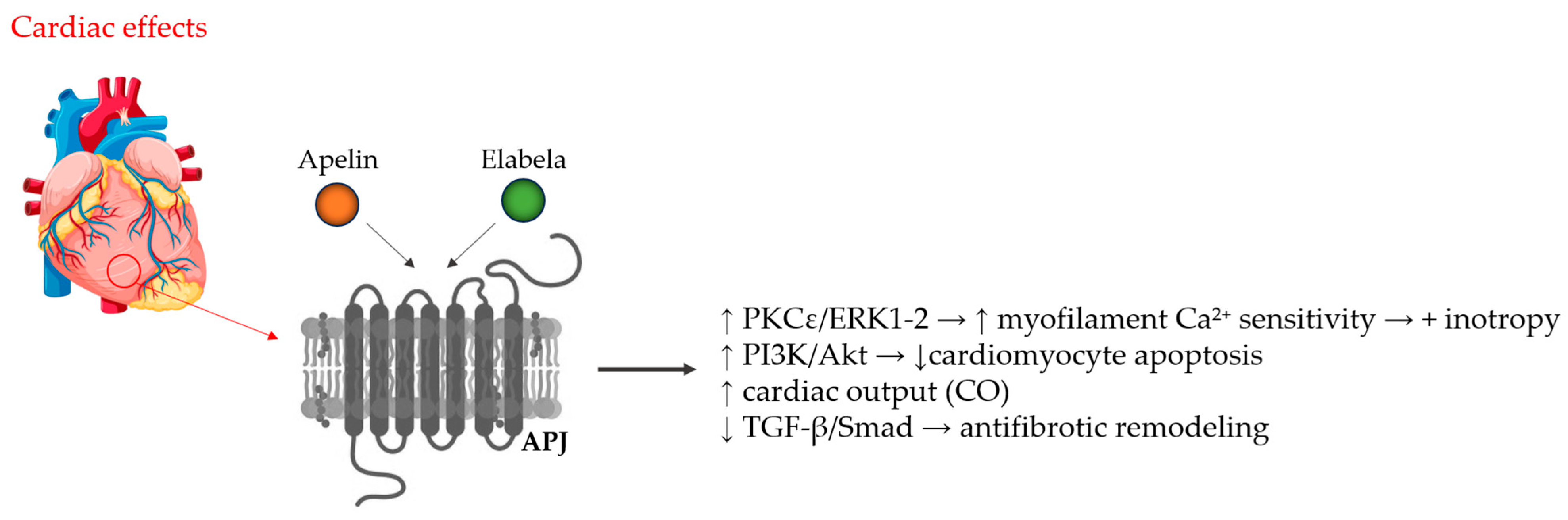
| Mechanism of Action and Examined Cells/Models | Result of Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Post-MI patients; apelinergic components vs. LV remodeling. | Apelinergic system associates with adverse LV remodeling. | Wyderka et al. [47] |
| Rat MI model; [Pyr1]-apelin-13 post-infarct. | Improved function via ↑ neovascularization and angiogenic factors. | Azizi et al. [33] |
| Myocardial I/R models; ELABELA→PI3K/AKT. | ↓ apoptosis, fibrosis; mitigated mitochondrial dysfunction. | Yu et al. [35] |
| STEMI patients; plasma ELABELA on day 1. | ↑ ELABELA; correlation with LV function biomarkers. | Dönmez et al. [28] |
| MI models; ELABELA gene therapy. | Promoted angiogenesis after MI. | Jin et al. [36] |
| Patients with CCS/ACS; plasma apelin/ELA. | Altered circulating apelinergic peptides in CAD/ACS. | Diakowska et al. [29] |
| ACS patients; ELABELA vs. coronary severity. | Lower ELABELA associated with greater angiographic severity. | Du et al. [30] |
| THP-1 foam cells; APJ/PKCα/miR-361-5p. | ↓ LPL expression → anti-foam cell (anti-atherogenic). | Zhang et al. [23] |
| Foam cell formation; Class III PI3K/Beclin-1-mediated autophagy. | Apelin-13 activates autophagy → impedes foam cell formation. | Yao et al. [24] |
| Intimal SMCs; apelin expression and phenotypic transition. | Promotes SMC phenotypic switching (atherosclerosis). | Cardoso et al. [27] |
| ACS; apelin as marker of stenosis/plaque stability. | Apelin associated with coronary stenosis and plaque stability. | Zhou et al. [31] |
| Multivessel CAD; serum and epicardial adipose apelin/ELA. | Profiles of apelin/ELA in CAD and epicardial fat. | Rachwalik et al. [48] |
| STEMI; apelin-12 effects on troponin and MACE. | Apelin-12 influences biomarker profile and MACE risk. | Krasniqi et al. [38] |
| Post-MI; lymphatic endothelium remodeling under apelin. | Apelin modulates pathological lymphatic remodeling after MI. | Tatin et al. [42] |
| Rodent I/R; apelin-13→RISK–GSK-3β–mPTP. | Cardioprotection with smaller infarct. | Yang et al. [41] |
| Mouse atherosclerosis and aneurysm models; apelin vs. Ang II. | Apelin antagonizes Ang II; reduces atherosclerosis/aneurysm. | Chun et al. [21] |
| Atherogenesis under oxidative stress; requirement for apelin/APJ system. | Deficiency worsens lesions. | Hashimoto et al. [22] |
| COPD patients assessed for CAD using apelin. | Explores diagnostic value of apelin in CAD among COPD. | Aksakal et al. [49] |
| Mechanism of Action and Examined Cells/Models | Result of Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Adult CV system; ELA endogenous APJ agonist; PAH models; exogenous ELA administration. | Compensates for downregulated expression; improves hemodynamics in PAH. | Yang et al. [41] |
| Conscious rats; venous dilator effect of apelin. | Venodilation consistent with afterload/preload reduction. | Cheng et al. [72] |
| CNS apelinergic signaling in rat brain. | Central regulation of BP/HR (pressor/tachycardic actions). | Reaux et al. [10] |
| SHR; APJ upregulation → VSMC proliferation via autophagy. | Contributes to vascular remodeling in HTN. | Xu et al. [52] |
| 2K1C Goldblatt hypertensive rats; myocardium/aorta APJ expression. | Hypertension alters APJ expression in heart and aorta. | Najafipour et al. [53] |
| C57BL/6J mice; Ang II-induced HTN/fibrosis; apelin administration. | Apelin protects vs. Ang II-induced HTN and cardiovascular fibrosis. | Siddiquee et al. [64] |
| Mouse models; apelin opposes Ang II-mediated remodeling/dysfunction. | Apelin negatively regulates Ang II effects. | Zhang et al. [65] |
| Hypertensive patients; apelin levels across anti-HTN drugs. | Differences in apelin with therapy; clinical association. | Hemmati et al. [54] |
| Concept/mechanistic study linking APLNR–VEGF–nNOS in HHD. | Suggests vascular footprint underlying hypertensive heart disease. | Iliev et al. [51] |
| PVN in SHR; apelin-13/APJ → sympathetic activation and vasopressin release. | Contributes to elevated BP via central mechanisms. | Zhang et al. [65] |
| Cerebral artery SMC; apelin-13 inhibits BK channels via PI3K. | Affects vascular tone; potential cerebrovascular constriction. | Modgil et al. [63] |
| Untreated HTN patients; serum apelin vs. LVH. | Lower apelin associated with LV hypertrophy. | Ye et al. [57] |
| Cardiac hypertrophy models; apelin activates catalase/antioxidants. | Prevents oxidative stress-linked cardiac hypertrophy. | Foussal et al. [69] |
| Kidney collecting duct cells; AQP2 trafficking vs. vasopressin. | Apelin antagonizes vasopressin → aquaresis. | Boulkeroua et al. [73] |
| Rat kidney; glomerular hemodynamic effects of apelin. | Renal vasorelaxation affecting diuresis/BP. | Hus-Citharel et al. [74] |
| Hypothalamus; apelin inhibits vasopressin neuron activity/release. | Potent diuretic effect counteracting vasopressin. | De Mota et al. [75] |
| Rat collecting duct; apelin–vasopressin receptor cross-talk. | Reduces vasopressin-induced water reabsorption. | Hus-Citharel et al. [76] |
| VSMC proliferation via Jagged-1/Notch3 after apelin-13. | Promotes VSMC proliferation (remodeling). | Li et al. [70] |
| VSMC migration via PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a/MMP-2. | Enhances VSMC migration (remodeling). | Wang et al. [59] |
| Hypertensive patients; serum ELA vs. renal damage progression. | Decreased ELA linked to hypertensive renal injury. | Tian et al. [56] |
| Mechanism of Action and Examined Cells/Models | Result of Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Cohort/observational; plasma ELABELA as HF screening indicator. | Lower ELABELA linked with HF; screening potential. | Liu et al. [93] |
| Human study; apelin infusion in healthy and chronic HF. | ↑ CO; vasodilation; potential HF benefit. | Japp et al. [58] |
| Small-molecule APJ agonism; CV response in preclinical/early settings. | Hemodynamic effects consistent with APJ activation (↑ inotropy/vasodilation). | Ason et al. [94] |
| Hypertensive HF patients; plasma ELA predicts MACE. | Lower ELA predicts adverse events. | Ma et al. [55] |
| In vivo models (normal and failing hearts); apelin inotropy. | Positive inotropic effects demonstrated. | Berry et al. [82] |
| Apelin gene-deficient mice; aging/pressure overload. | Apelin deficiency → impaired contractility with stress. | Kuba et al. [83] |
| Experimental models; apelin regulates cardiac contractility. | Positive inotropy/contractile modulation. | Szokodi et al. [84] |
| Murine hypertrophy models; APJ dual receptor signaling. | APJ mediates protective vs. maladaptive hypertrophic signaling. | Scimia et al. [71] |
| Mouse; tissue-specific apelin/APJ control in hypertrophy→HF transition. | Controls hypertrophy and contractility. | Parikh et al. [87] |
| Human HF and atherosclerosis; modulation of apelin/APJ. | Altered apelin/APJ in HF and IHD. | Pitkin et al. [79] |
| MI-induced HF; apelin-13 inhibits PI3K/Akt-linked oxidative stress. | Alleviates cardiac fibrosis. | Zhong et al. [43] |
| Post-MI remodeling; apelin-13 anti-fibrotic effects. | Protects against MI-induced myocardial fibrosis. | Zhang et al. [44] |
| Apelin-17 analog LIT01-196 post-MI HF models. | Reduces dysfunction and remodeling after MI. | Girault-Sotias et al. [46] |
| Human cardiac dysfunction; apelin as endogenous inotrope. | Demonstrates inotropic role in human HF context. | Chen et al. [7] |
| HF patients; circulating and cardiac apelin levels. | Altered apelin levels associated with HF. | Foldes et al. [77] |
| CRT in HF; plasma apelin changes post-therapy. | CRT increases plasma apelin. | Francia et al. [78] |
| Post-MI mice; microparticle-mediated apelin delivery. | Improves heart function post-MI. | Tang et al. [95] |
| Mechanism of Action and Examined Cells/Models | Result of Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Post-MI patients; conduction disorders vs. apelinergic profile. | Apelinergic system influences conduction disorders. | Wyderka et al. [47] |
| Neonatal rat cardiomyocytes; electrophysiology and contractility with apelin. | Modulated electrophysiology supporting anti-arrhythmic potential. | Farkasfalvi et al. [88] |
| Hypertensive patients with AF; plasma ELABELA. | Lower ELABELA associated with AF in HTN. | Ma et al. [98] |
| Persistent AF patients; apelin plasma vs. recurrence. | Lower apelin predicts AF recurrence after cardioversion. | Falcone et al. [99] |
| Atrial myocytes; apelin regulation of electrophysiology. | Modulates atrial electrophysiological properties. | Cheng et al. [72] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wyderka, R.; Osuch, Ł.; Ołpińska, B.; Łoboz-Rudnicka, M.; Diakowska, D.; Leśków, A.; Jaroch, J. The Impact of the Apelinergic System on the Cardiovascular System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010087
Wyderka R, Osuch Ł, Ołpińska B, Łoboz-Rudnicka M, Diakowska D, Leśków A, Jaroch J. The Impact of the Apelinergic System on the Cardiovascular System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010087
Chicago/Turabian StyleWyderka, Rafał, Łukasz Osuch, Bogusława Ołpińska, Maria Łoboz-Rudnicka, Dorota Diakowska, Anna Leśków, and Joanna Jaroch. 2025. "The Impact of the Apelinergic System on the Cardiovascular System" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010087
APA StyleWyderka, R., Osuch, Ł., Ołpińska, B., Łoboz-Rudnicka, M., Diakowska, D., Leśków, A., & Jaroch, J. (2025). The Impact of the Apelinergic System on the Cardiovascular System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010087





