Intestinal Permeability and Depression—A Narrative Review of Selected Blood-Based Biomarkers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
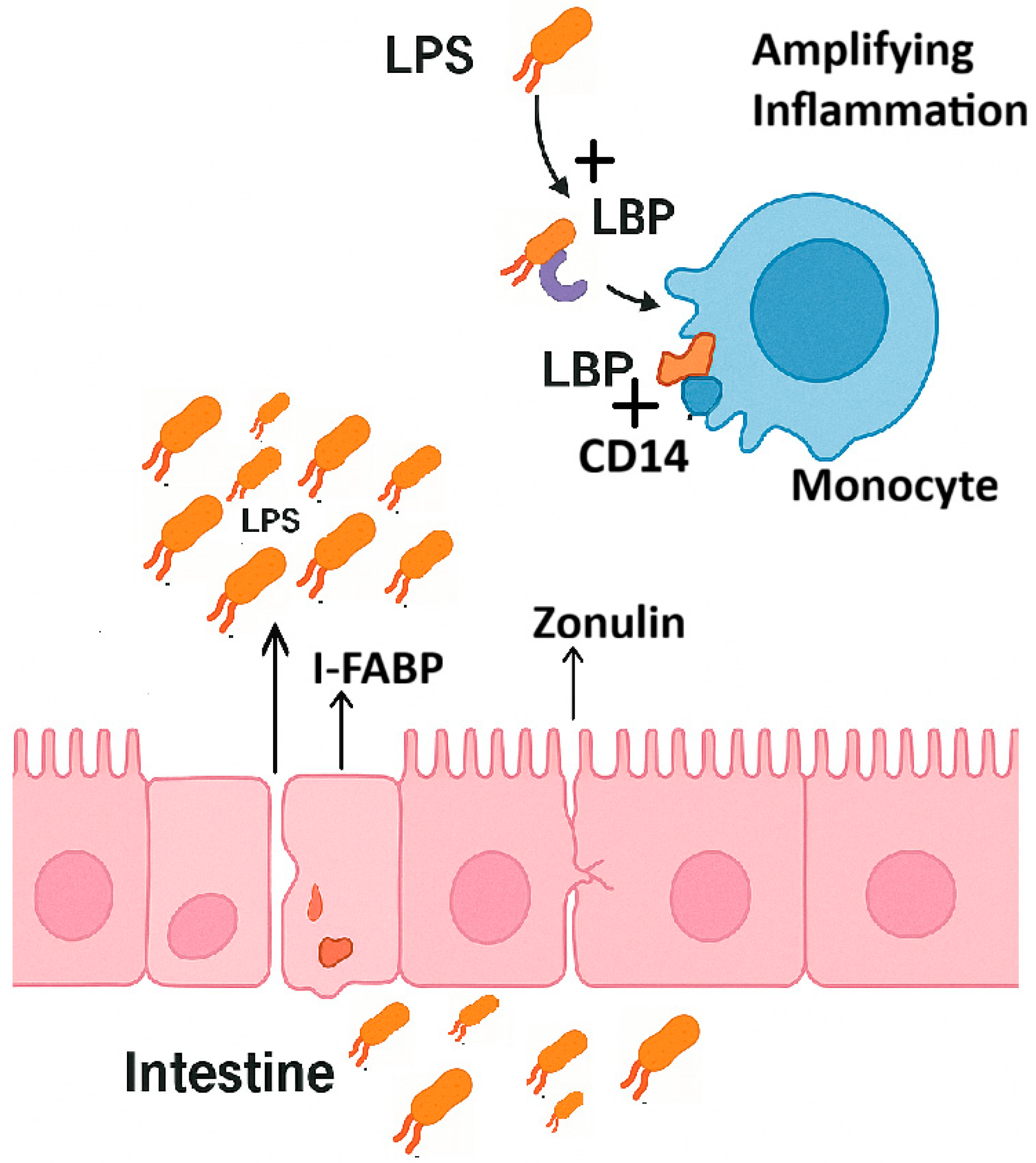
3. Overview of Intestinal Permeability Markers
3.1. Zonulin
3.2. I-FABP/FABP2
3.3. LPS
3.4. LBP and sCD14
4. IB Marker Alterations in Depression
5. Conclusions
- Key points
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Akil, H.; Gordon, J.; Hen, R.; Javitch, J.; Mayberg, H.; McEwen, B.; Meaney, M.J.; Nestler, E.J. Treatment resistant depression: A multi-scale, systems biology approach. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 84, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ghosh, S.S.; Wang, J.; Yannie, P.J.; Ghosh, S. Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction, LPS Translocation, and Disease Development. J. Endocr. Soc. 2020, 4, bvz039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Odenwald, M.A.; Turner, J.R. The intestinal epithelial barrier: A therapeutic target? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rudzki, L.; Maes, M. The Microbiota-Gut-Immune-Glia (MGIG) Axis in Major Depression. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 4269–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Vincenzo, F.; Del Gaudio, A.; Petito, V.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F. Gut microbiota, intestinal permeability, and systemic inflammation: A narrative review. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2024, 19, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kowalski, K.; Mulak, A. Brain-Gut-Microbiota Axis in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 25, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Forsyth, C.B.; Shannon, K.M.; Kordower, J.H.; Voigt, R.M.; Shaikh, M.; Jaglin, J.A.; Estes, J.D.; Dodiya, H.B.; Keshavarzian, A. Increased intestinal permeability correlates with sigmoid mucosa alpha-synuclein staining and endotoxin exposure markers in early Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denman, C.R.; Park, S.M.; Jo, J. Gut-brain axis: Gut dysbiosis and psychiatric disorders in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1268419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Behairi, N.; Belkhelfa, M.; Rafa, H.; Labsi, M.; Deghbar, N.; Bouzid, N.; Mesbah-Amroun, H.; Touil-Boukoffa, C. All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation, amyloidogenesis and memory impairment in aged rats. J. Neuroimmunol. 2016, 300, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Magistris, L.; Familiari, V.; Pascotto, A.; Sapone, A.; Frolli, A.; Iardino, P.; Carteni, M.; De Rosa, M.; Francavilla, R.; Riegler, G.; et al. Alterations of the intestinal barrier in patients with autism spectrum disorders and in their first-degree relatives. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 51, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, I.; Ogura, J.; Aizawa, E.; Ota, M.; Hidese, S.; Yomogida, Y.; Matsuo, J.; Yoshida, S.; Kunugi, H. Gut permeability and its clinical relevance in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacol. Rep. 2022, 42, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Meng, F.; Lowell, C.A. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced macrophage activation and signal transduction in the absence of Src-family kinases Hck, Fgr, and Lyn. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yin, R.; Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Tang, Z.; Zheng, R.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lei, N.; Xiong, L.; Guo, P.; et al. Lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like model in mice: Meta-analysis and systematic evaluation. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1181973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Peng, X.; Luo, Z.; He, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption by Lipopolysaccharide and Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 768108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Caspani, G.; Kennedy, S.; Foster, J.A.; Swann, J. Gut microbial metabolites in depression: Understanding the biochemical mechanisms. Microb. Cell 2019, 6, 454–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhao, X.; Cao, F.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Xu, G.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Yi, S.; Xu, F.; et al. Behavioral, inflammatory and neurochemical disturbances in LPS and UCMS-induced mouse models of depression. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 364, 494–502, Erratum in Behav. Brain Res. 2023, 452, 114573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2023.114573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, M.; Kubera, M.; Leunis, J.-C.; Berk, M.; Geffard, M.; Bosmans, E. In depression, bacterial translocation may drive inflammatory responses, oxidative and nitrosative stress (O&NS), and autoimmune responses directed against O&NS-damaged neoepitopes. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2012, 127, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, M. Leaky gut: Mechanisms, measurement and clinical implications in humans. Gut 2019, 68, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Seethaler, B.; Basrai, M.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Nazare, J.A.; Walter, J.; Delzenne, N.M.; Bischoff, S.C. Biomarkers for assessment of intestinal permeability in clinical practice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2021, 321, G11–G17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safadi, J.M.; Quinton, A.M.G.; Lennox, B.R.; Burnet, P.W.J.; Minichino, A. Gut dysbiosis in severe mental illness and chronic fatigue: A novel trans-diagnostic construct? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tripathi, A.; Lammers, K.M.; Goldblum, S.; Shea-Donohue, T.; Netzel-Arnett, S.; Buzza, M.S.; Antalis, T.M.; Vogel, S.N.; Zhao, A.; Yang, S.; et al. Identification of human zonulin, a physiological modulator of tight junctions, as prehaptoglobin-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16799–16804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fasano, A.; Not, T.; Wang, W.; Uzzau, S.; Berti, I.; Tommasini, A.; Goldblum, S.E. Zonulin, a newly discovered modulator of intestinal permeability, and its expression in coeliac disease. Lancet 2000, 355, 1518–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A. Zonulin and Its Regulation of Intestinal Barrier Function: The Biological Door to Inflammation, Autoimmunity, and Cancer. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veres-Székely, A.; Szász, C.; Pap, D.; Szebeni, B.; Bokrossy, P.; Vannay, Á. Zonulin as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis Disorders: Encouraging Results and Emerging Questions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Malíčková, K.; Francová, I.; Lukáš, M.; Kolář, M.; Králíková, E.; Bortlík, M.; Ďuricová, D.; Štěpánková, L.; Zvolská, K.; Pánková, A.; et al. Fecal zonulin is elevated in Crohn’s disease and in cigarette smokers. Pract. Lab. Med. 2017, 9, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ockner, R.K.; Manning, J.A.; Poppenhausen, R.B.; Ho, W.K. A binding protein for fatty acids in cytosol of intestinal mucosa, liver, myocardium, and other tissues. Science 1972, 177, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, A.W.; Veerkamp, J.H. New insights into the structure and function of fatty acid-binding proteins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2002, 59, 1096–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuhashi, M.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Fatty acid-binding proteins: Role in metabolic diseases and potential as drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Adriaanse, M.P.M.; Tack, G.J.; Passos, V.L.; Damoiseaux, J.G.M.C.; Schreurs, M.W.J.; van Wijck, K.; Riedl, R.G.; Masclee, A.A.M.; Buurman, W.A.; Mulder, C.J.J.; et al. Serum I-FABP as marker for enterocyte damage in coeliac disease and its relation to villous atrophy and circulating autoantibodies. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 37, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelsers, M.M.; Namiot, Z.; Kisielewski, W.; Namiot, A.; Januszkiewicz, M.; Hermens, W.T.; Glatz, J.F. Intestinal-type and liver-type fatty acid-binding protein in the intestine. Tissue distribution and clinical utility. Clin. Biochem. 2003, 36, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishimura, S.; Furuhashi, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Hoshina, K.; Fuseya, T.; Mita, T.; Okazaki, Y.; Koyama, M.; Tanaka, M.; Akasaka, H.; et al. Circulating levels of fatty acid-binding protein family and metabolic phenotype in the general population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Iordache, M.M.; Tocia, C.; Aschie, M.; Dumitru, A.; Manea, M.; Cozaru, G.C.; Petcu, L.; Vlad, S.E.; Dumitru, E.; Chisoi, A. Intestinal Permeability and Depression in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Raetz, C.R.; Whitfield, C. Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 635–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, B.D.; Trent, M.S. Fortifying the barrier: The impact of lipid A remodelling on bacterial pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, Y.; Shi, Z.; Radauer-Preiml, I.; Andosch, A.; Casals, E.; Luetz-Meindl, U.; Cobaleda, M.; Lin, Z.; Jaberi-Douraki, M.; Italiani, P.; et al. Bacterial endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide) binds to the surface of gold nanoparticles, interferes with biocorona formation and induces human monocyte inflammatory activation. Nanotoxicology 2017, 11, 1157–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westphal, O.; Luderitz, O.; Bister, E. Uber die extraction von bacterien mit phenol/wasser. Z. Für Naturforschung B 1952, 7, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahador, M.; Cross, A.S. From therapy to experimental model: A hundred years of endotoxin administration to human subjects. J. Endotoxin Res. 2007, 13, 251–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, S.F. Human endotoxemia: A model for mechanistic insight and therapeutic targeting. Shock 2005, 24 (Suppl. 1), 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossù, P.; Cutuli, D.; Palladino, I.; Caporali, P.; Angelucci, F.; Laricchiuta, D.; Gelfo, F.; De Bartolo, P.; Caltagirone, C.; Petrosini, L. A single intraperitoneal injection of endotoxin in rats induces long-lasting modifications in behavior and brain protein levels of TNF-α and IL-18. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jiang, W.; Luo, Z.; Stephenson, S.; Li, H.; Di Germanio, C.; Norris, P.J.; Fuchs, D.; Zetterberg, H.; Gisslen, M.; Price, R.W. Cerebrospinal Fluid and Plasma Lipopolysaccharide Levels in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Infection and Associations With Inflammation, Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability, and Neuronal Injury. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 1612–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; Rowe, D.C.; Golenbock, D.T. Endotoxin recognition and signal transduction by the TLR4/MD2-complex. Microbes Infect. 2004, 6, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobias, P.S.; Soldau, K.; Ulevitch, R.J. Isolation of a lipopolysaccharide-binding acute phase reactant from rabbit serum. J. Exp. Med. 1986, 164, 777–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schumann, R.R.; Leong, S.R.; Flaggs, G.W.; Gray, P.W.; Wright, S.D.; Mathison, J.C.; Tobias, P.S.; Ulevitch, R.J. Structure and function of lipopolysaccharide binding protein. Science 1990, 249, 1429–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.D.; Tobias, P.S.; Ulevitch, R.J.; Ramos, R.A. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binding protein opsonizes LPS-bearing particles for recognition by a novel receptor on macrophages. J. Exp. Med. 1989, 170, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wright, S.; Ramos, R.; Tobias, P.; Ulevitch, R.; Mathison, J. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science 1990, 249, 1431–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Young, D.W.; Golenbock, D.T.; Christ, W.J.; Gusovsky, F. Toll-like Receptor-4 Mediates Lipopolysaccharide-induced Signal Transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 10689–10692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurfel, M.M.; Monks, B.G.; Ingalls, R.R.; Dedrick, R.L.; Delude, R.; Zhou, D.; Lamping, N.; Schumann, R.R.; Thieringer, R.; Fenton, M.J.; et al. Targeted deletion of the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein gene leads to profound suppression of LPS responses ex vivo, whereas in vivo responses remain intact. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 186, 2051–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutsmann, T.; Müller, M.; Carroll, S.F.; MacKenzie, R.C.; Wiese, A.; Seydel, U. Dual role of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein in neutralization of LPS and enhancement of LPS-induced activation of mononuclear cells. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 6942–6950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.M.; Park, B.S.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, S.E.; Lee, J.; Oh, S.C.; Enkhbayar, P.; Matsushima, N.; Lee, H.; Yoo, O.J.; et al. Crystal structure of the TLR4-MD-2 complex with bound endotoxin antagonist Eritoran. Cell 2007, 130, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohto, U.; Fukase, K.; Miyake, K.; Satow, Y. Crystal structures of human MD-2 and its complex with antiendotoxic lipid IVa. Science 2007, 316, 1632–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, P.; Prasad, P.; Pateria, A.; Deshmukh, S.D.; Gupta, S. A Single Step in vitro Bioassay Mimicking TLR4-LPS Pathway and the Role of MD2 and CD14 Coreceptors. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kagan, J.C.; Medzhitov, R. Phosphoinositide-Mediated Adaptor Recruitment Controls Toll-like Receptor Signaling. Cell 2006, 125, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. TLR signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, H.; Takeuchi, S.; Kubota, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kozakai, S.; Ukai, I.; Shichiku, A.; Okubo, M.; Numasaki, M.; Kanemitsu, Y.; et al. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein stimulates CD14-dependent Toll-like receptor 4 internalization and LPS-induced TBK1–IKKϵ–IRF3 axis activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 10186–10201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haziot, A.; Chen, S.; Ferrero, E.; Low, M.G.; Silber, R.; Goyert, S.M. The monocyte differentiation antigen, CD14, is anchored to the cell membrane by a phosphatidylinositol linkage. J. Immunol. 1988, 141, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, E.A. Soluble CD14 participates in the response of cells to lipopolysaccharide. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 176, 1665–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchens, R.L.; Thompson, P.A. Modulatory effects of sCD14 and LBP on LPS-host cell interactions. J. Endotoxin Res. 2005, 11, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahnke, K.; Becher, E.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P.; Luger, T.A.; Schwarz, T.; Grabbe, S. CD14 is expressed by subsets of murine dendritic cells and upregulated by lipopolysaccharide. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1997, 417, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haziot, A.; Ferrero, E.; Köntgen, F.; Hijiya, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Silver, J.; Stewart, C.L.; Goyert, S.M. Resistance to endotoxin shock and reduced dissemination of gram-negative bacteria in CD14-deficient mice. Immunity 1996, 4, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blairon, L.; Wittebole, X.; Laterre, P.F. Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein serum levels in patients with severe sepsis due to gram-positive and fungal infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 187, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Gwee, X.; Chua, D.Q.; Tan, C.T.; Yap, K.B.; Larbi, A.; Lu, Y.; Ng, T.P. Inflammatory markers and incident depression: Evidence in a population-based prospective study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2022, 142, 105806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, M.S.; Arteaga-Henríquez, G.; Fouad Algendy, A.; Siepmann, T.; Illigens, B.M.W. Anti-Inflammatory Treatment Efficacy in Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review of Meta-Analyses. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2023, 19, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ma, W.R.; Zhang, L.L.; Ma, J.Y.; Yu, F.; Hou, Y.Q.; Feng, X.R.; Yang, L. Mendelian randomization studies of depression: Evidence, opportunities, and challenges. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2023, 22, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Grigoleit, J.S.; Kullmann, J.S.; Wolf, O.T.; Hammes, F.; Wegner, A.; Jablonowski, S.; Engler, H.; Gizewski, E.; Oberbeck, R.; Schedlowski, M. Dose-dependent effects of endotoxin on neurobehavioral functions in humans. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alvarez-Mon, M.A.; Gómez, A.M.; Orozco, A.; Lahera, G.; MD, S.; Diaz, D.; Auba, E.; Albillos, A.; Monserrat, J.; Alvarez-Mon, M. Abnormal Distribution and Function of Circulating Monocytes and Enhanced Bacterial Translocation in Major Depressive Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K.; Wilson, S.J.; Bailey, M.L.; Andridge, R.; Peng, J.; Jaremka, L.M.; Fagundes, C.P.; Malarkey, W.B.; Laskowski, B.; Belury, M.A. Marital distress, depression, and a leaky gut: Translocation of bacterial endotoxin as a pathway to inflammation. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 98, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Linninge, C.; Jönsson, P.; Bolinsson, H.; Önning, G.; Eriksson, J.; Johansson, G.; Ahrné, S. Effects of acute stress provocation on cortisol levels, zonulin and inflammatory markers in low- and high-stressed men. Biol. Psychol. 2018, 138, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luning Prak, E.T.; Brooks, T.; Makhoul, W.; Beer, J.C.; Zhao, L.; Girelli, T.; Skarke, C.; Sheline, Y.I. No increase in inflammation in late-life major depression screened to exclude physical illness. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zabielska, P.; Szkup, M.; Kotwas, A.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Karakiewicz, B. Association between symptoms of depression and inflammatory parameters in people aged over 90 years. BMC Geriatr. 2024, 24, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Engler, H.; Brinkhoff, A.; Wilde, B.; Kribben, A.; Rohn, H.; Witzke, O.; Schedlowski, M.; Benson, S. Endotoxin-Induced Physiological and Psychological Sickness Responses in Healthy Humans: Insights into the Post-Acute Phase. Neuroimmunomodulation 2023, 30, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alvarez-Mon, M.A.; Gomez-Lahoz, A.M.; Orozco, A.; Lahera, G.; Sosa-Reina, M.D.; Diaz, D.; Albillos, A.; Quintero, J.; Molero, P.; Monserrat, J.; et al. Blunted Expansion of Regulatory T Lymphocytes Is Associated With Increased Bacterial Translocation in Patients With Major Depressive Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 591962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stevens, B.R.; Goel, R.; Seungbum, K.; Richards, E.M.; Holbert, R.C.; Pepine, C.J.; Raizada, M.K. Increased human intestinal barrier permeability plasma biomarkers zonulin and FABP2 correlated with plasma LPS and altered gut microbiome in anxiety or depression. Gut 2018, 67, 1555–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, P.W.; Sinclair, E.; Rodriguez, B.; Shive, C.; Clagett, B.; Funderburg, N.; Robinson, J.; Huang, Y.; Epling, L.; Martin, J.N.; et al. Gut Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction and Innate Immune Activation Predict Mortality in Treated HIV Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojdani, A.; Vojdani, E.; Kharrazian, D. Fluctuation of zonulin levels in blood vs stability of antibodies. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 5669–5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Maget, A.; Dalkner, N.; Hamm, C.; Bengesser, S.A.; Fellendorf, F.T.; Platzer, M.; Queissner, R.; Birner, A.; Lenger, M.; Mörkl, S.; et al. Sex differences in zonulin in affective disorders and associations with current mood symptoms. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 294, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reininghaus, E.Z.; Platzer, M.; Kohlhammer-Dohr, A.; Hamm, C.; Mörkl, S.; Bengesser, S.A.; Fellendorf, F.T.; Lahousen-Luxenberger, T.; Leitner-Afschar, B.; Schöggl, H.; et al. PROVIT: Supplementary Probiotic Treatment and Vitamin B7 in Depression—A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Kubera, M.; Leunis, J.C. The gut-brain barrier in major depression: Intestinal mucosal dysfunction with an increased translocation of LPS from gram negative enterobacteria (leaky gut) plays a role in the inflammatory pathophysiology of depression. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2008, 29, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gomes, C.; Martinho, F.C.; Barbosa, D.S.; Antunes, L.S.; Póvoa, H.C.C.; Baltus, T.H.L.; Morelli, N.R.; Vargas, H.O.; Nunes, S.O.V.; Anderson, G.; et al. Increased Root Canal Endotoxin Levels are Associated with Chronic Apical Periodontitis, Increased Oxidative and Nitrosative Stress, Major Depression, Severity of Depression, and a Lowered Quality of Life. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 2814–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Chen, J.; Cao, M.; Fang, L.; Wang, Z.; Liao, J.; Chen, D.; Zhang, X.; Guo, J.; Zhao, L.; et al. Elevated plasma intestinal fatty acid binding protein and aberrant lipid metabolism predict post-stroke depression. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shive, C.L.; Jiang, W.; Anthony, D.D.; Lederman, M.M. Soluble CD14 is a nonspecific marker of monocyte activation. AIDS 2015, 29, 1263–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, J.C.; Polanka, B.M.; So-Armah, K.A.; White, J.R.; Gupta, S.K.; Kundu, S.; Chang, C.H.; Freiberg, M.S. Associations of Total, Cognitive/Affective, and Somatic Depressive Symptoms and Antidepressant Use With Cardiovascular Disease-Relevant Biomarkers in HIV: Veterans Aging Cohort Study. Psychosom. Med. 2020, 82, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Morena, D.; Lippi, M.; Scopetti, M.; Turillazzi, E.; Fineschi, V. Leaky Gut Biomarkers as Predictors of Depression and Suicidal Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Just, D.; Rasmusson, A.J.; Nilsson, P.; Noreland, M.; Malmström, E.; Brodin, P.; Månberg, A.; Cunningham, J.L. Autoantibodies against the C-terminus of Lipopolysaccharide binding protein are elevated in young adults with psychiatric disease. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2021, 126, 105162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariani, N.; Everson, J.; Pariante, C.M.; Borsini, A. Modulation of microglial activation by antidepressants. J. Psychopharmacol. 2022, 36, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liśkiewicz, P.; Kaczmarczyk, M.; Misiak, B.; Wroński, M.; Bąba-Kubiś, A.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Marlicz, W.; Bieńkowski, P.; Misera, A.; Pełka-Wysiecka, J.; et al. Analysis of gut microbiota and intestinal integrity markers of inpatients with major depressive disorder. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 106, 110076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccia, F.; Guggino, G.; Rizzo, A.; Alessandro, R.; Luchetti, M.M.; Milling, S.; Saieva, L.; Cypers, H.; Stampone, T.; Di Benedetto, P.; et al. Dysbiosis and zonulin upregulation alter gut epithelial and vascular barriers in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Memon, A.A.; Palmér, K.; Hedelius, A.; Sundquist, J.; Sundquist, K. The association of zonulin-related proteins with prevalent and incident inflammatory bowel disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sapone, A.; de Magistris, L.; Pietzak, M.; Clemente, M.G.; Tripathi, A.; Cucca, F.; Lampis, R.; Kryszak, D.; Cartenì, M.; Generoso, M.; et al. Zonulin upregulation is associated with increased gut permeability in subjects with type 1 diabetes and their relatives. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1443–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlsson, B.; Orho-Melander, M.; Nilsson, P.M. Higher Levels of Serum Zonulin May Rather Be Associated with Increased Risk of Obesity and Hyperlipidemia, Than with Gastrointestinal Symptoms or Disease Manifestations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ahmad, F.; Karim, A.; Khan, J.; Qaisar, R. Plasma zonulin correlates with cardiac dysfunction and poor physical performance in patients with chronic heart failure. Life Sci. 2022, 311 Pt A, 121150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creely, S.J.; McTernan, P.G.; Kusminski, C.M.; Fisher, M.; Da Silva, N.F.; Khanolkar, M.; Evans, M.; Harte, A.L.; Kumar, S. Lipopolysaccharide activates an innate immune system response in human adipose tissue in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 292, E740–E747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenman, L.K.; Lehtinen, M.J.; Meland, N.; Christensen, J.E.; Yeung, N.; Saarinen, M.T.; Courtney, M.; Burcelin, R.; Lähdeaho, M.L.; Linros, J.; et al. Probiotic With or Without Fiber Controls Body Fat Mass, Associated With Serum Zonulin, in Overweight and Obese Adults-Randomized Controlled Trial. EBioMedicine 2016, 13, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gonzalez-Quintela, A.; Alonso, M.; Campos, J.; Vizcaino, L.; Loidi, L.; Gude, F. Determinants of serum concentrations of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP) in the adult population: The role of obesity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ruiz, A.G.; Casafont, F.; Crespo, J.; Cayón, A.; Mayorga, M.; Estebanez, A.; Fernadez-Escalante, J.C.; Pons-Romero, F. Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein plasma levels and liver TNF-alpha gene expression in obese patients: Evidence for the potential role of endotoxin in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Obes. Surg. 2007, 17, 1374–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, R.Z.; Ostlund, K.R.; Cabrera, M.S.; Edwards, E.; Fisher, M.; Sarvetnick, N. Confirmation and Identification of Biomarkers Implicating Environmental Triggers in the Pathogenesis of Type 1 Diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Qiu, C.J.; Ye, X.Z.; Yu, X.J.; Peng, X.R.; Li, T.H. Association between FABP2 Ala54Thr polymorphisms and type 2 diabetes mellitus risk: A HuGE Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 2530–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nendl, A.; Raju, S.C.; Broch, K.; Mayerhofer, C.C.K.; Holm, K.; Halvorsen, B.; Lappegård, K.T.; Moscavitch, S.; Hov, J.R.; Seljeflot, I.; et al. Intestinal fatty acid binding protein is associated with cardiac function and gut dysbiosis in chronic heart failure. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1160030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Moludi, J.; Khedmatgozar, H.; Nachvak, S.M.; Abdollahzad, H.; Moradinazar, M.; Tabaei, A.S. The effects of co-administration of probiotics and prebiotics on chronic inflammation, and depression symptoms in patients with coronary artery diseases: A randomized clinical trial. Nutr. Neurosci. 2021, 25, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assante, G.; Tourna, A.; Carpani, R.; Ferrari, F.; Prati, D.; Peyvandi, F.; Blasi, F.; Bandera, A.; Le Guennec, A.; Chokshi, S.; et al. Reduced circulating FABP2 in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 may indicate enterocyte functional change rather than cell death. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Taquet, M.; Geddes, J.R.; Husain, M.; Luciano, S.; Harrison, P.J. 6-month neurological and psychiatric outcomes in 236 379 survivors of COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study using electronic health records. Lancet Psychiatry 2021, 8, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Marker | Role | What Modified Levels Indicate |
|---|---|---|
| Zonulin | Modulates tight junctions between intestinal cells | Increased intestinal permeability |
| I-FABP | Released upon intestinal epithelial cell injury | Enterocyte damage |
| LPS | Bacterial endotoxin from Gram-negative bacteria | Microbial translocation |
| LBP | Binds LPS and facilitates immune recognition | Increased LPS exposure |
| sCD14 | Soluble receptor for LPS signaling | Immune activation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bibolar, A.C.; Crecan-Suciu, B.D.; Păunescu, R.L.; Nechita, V.-I.; Verisezan-Roșu, O.; Micluția, I.V. Intestinal Permeability and Depression—A Narrative Review of Selected Blood-Based Biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010076
Bibolar AC, Crecan-Suciu BD, Păunescu RL, Nechita V-I, Verisezan-Roșu O, Micluția IV. Intestinal Permeability and Depression—A Narrative Review of Selected Blood-Based Biomarkers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010076
Chicago/Turabian StyleBibolar, Anca C., Bianca D. Crecan-Suciu, Ramona L. Păunescu, Vlad-I. Nechita, Olivia Verisezan-Roșu, and Ioana V. Micluția. 2025. "Intestinal Permeability and Depression—A Narrative Review of Selected Blood-Based Biomarkers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010076
APA StyleBibolar, A. C., Crecan-Suciu, B. D., Păunescu, R. L., Nechita, V.-I., Verisezan-Roșu, O., & Micluția, I. V. (2025). Intestinal Permeability and Depression—A Narrative Review of Selected Blood-Based Biomarkers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010076







