Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, Induces G1 Cell Cycle Arrest and Autophagy in Gastric Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
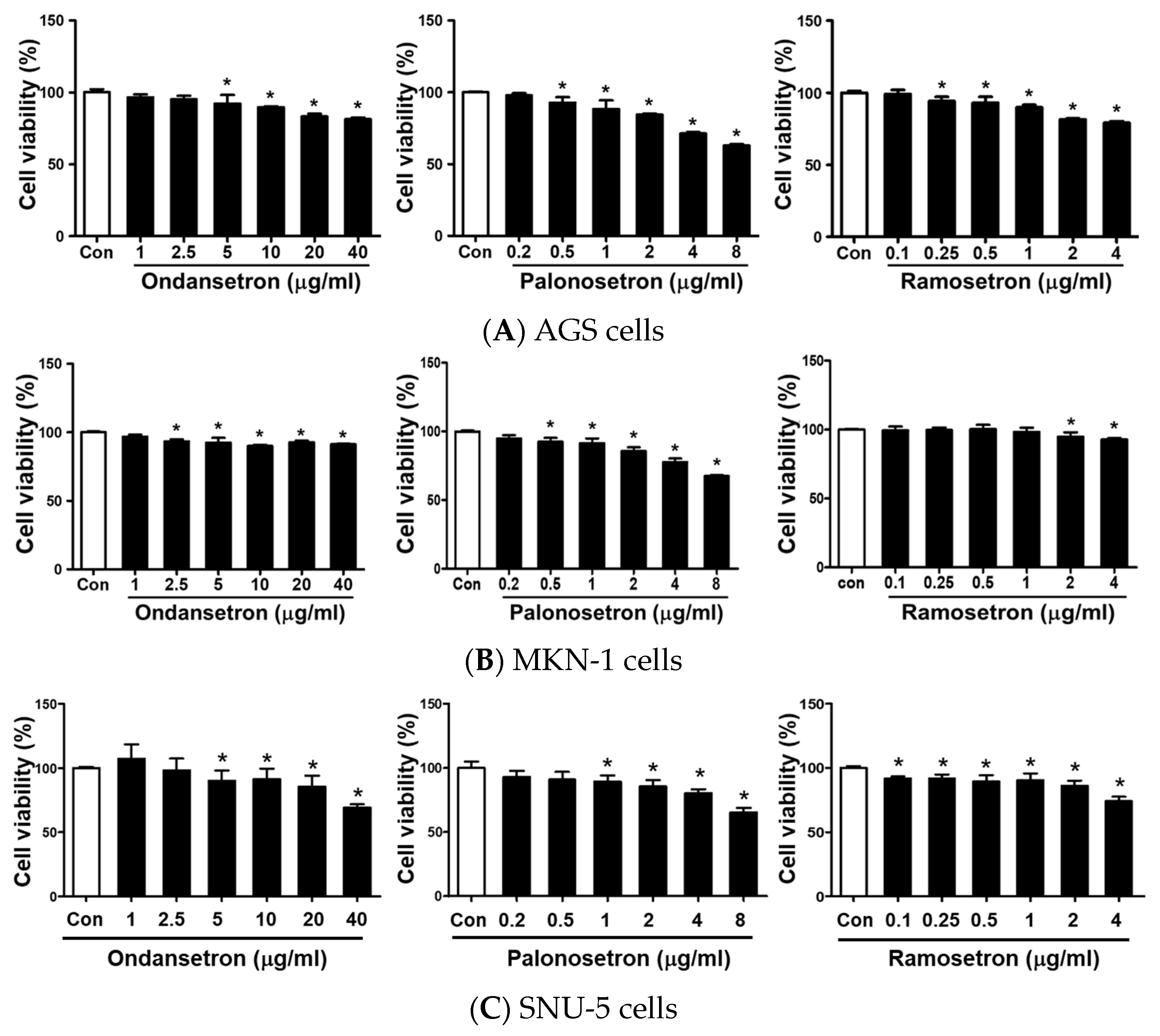
2.1. 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonists Inhibit Cell Proliferation in Human Gastric Cancer Cells
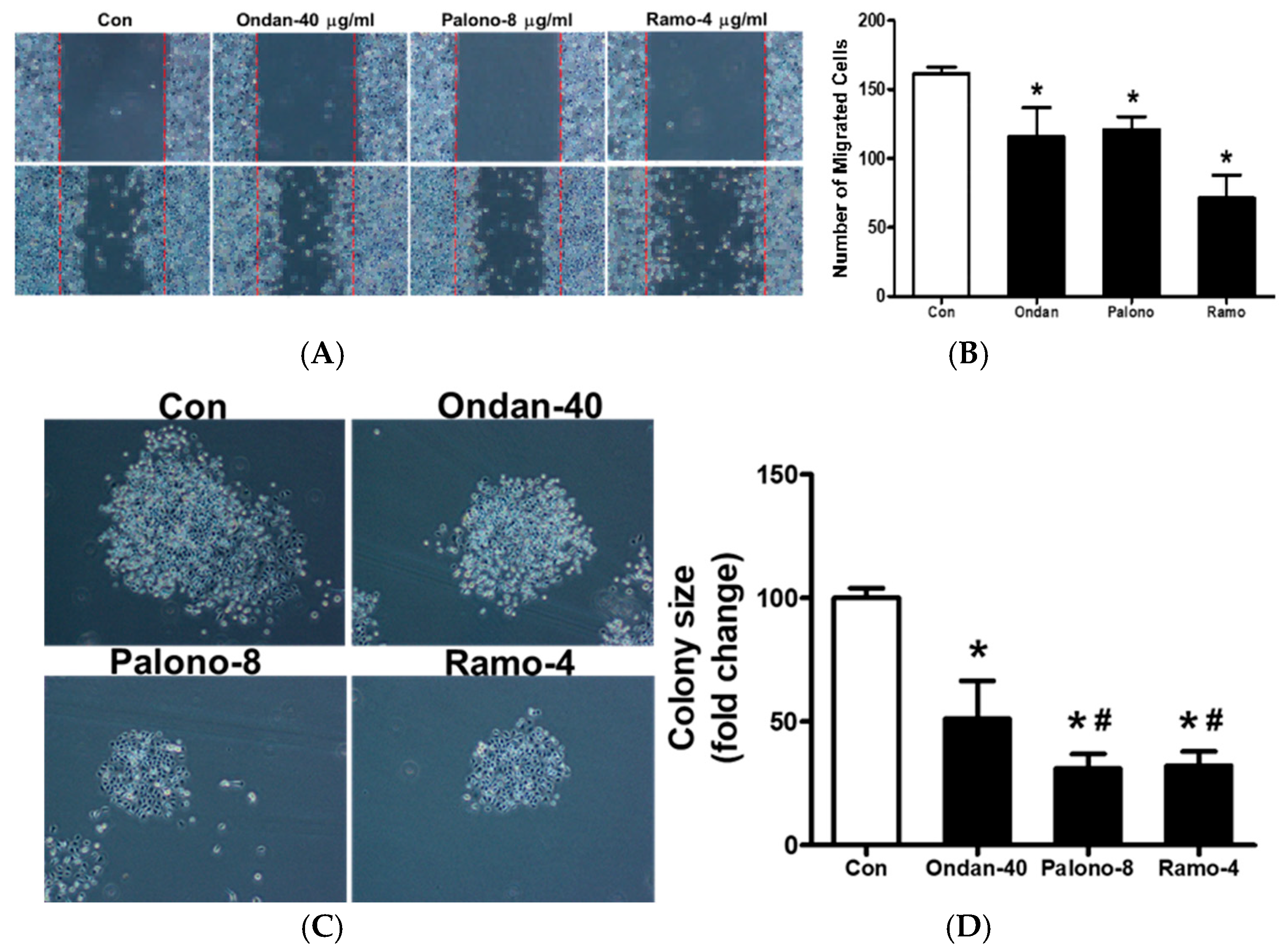
2.2. 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonists Prevent Cell Migration and Colony Formation in AGS
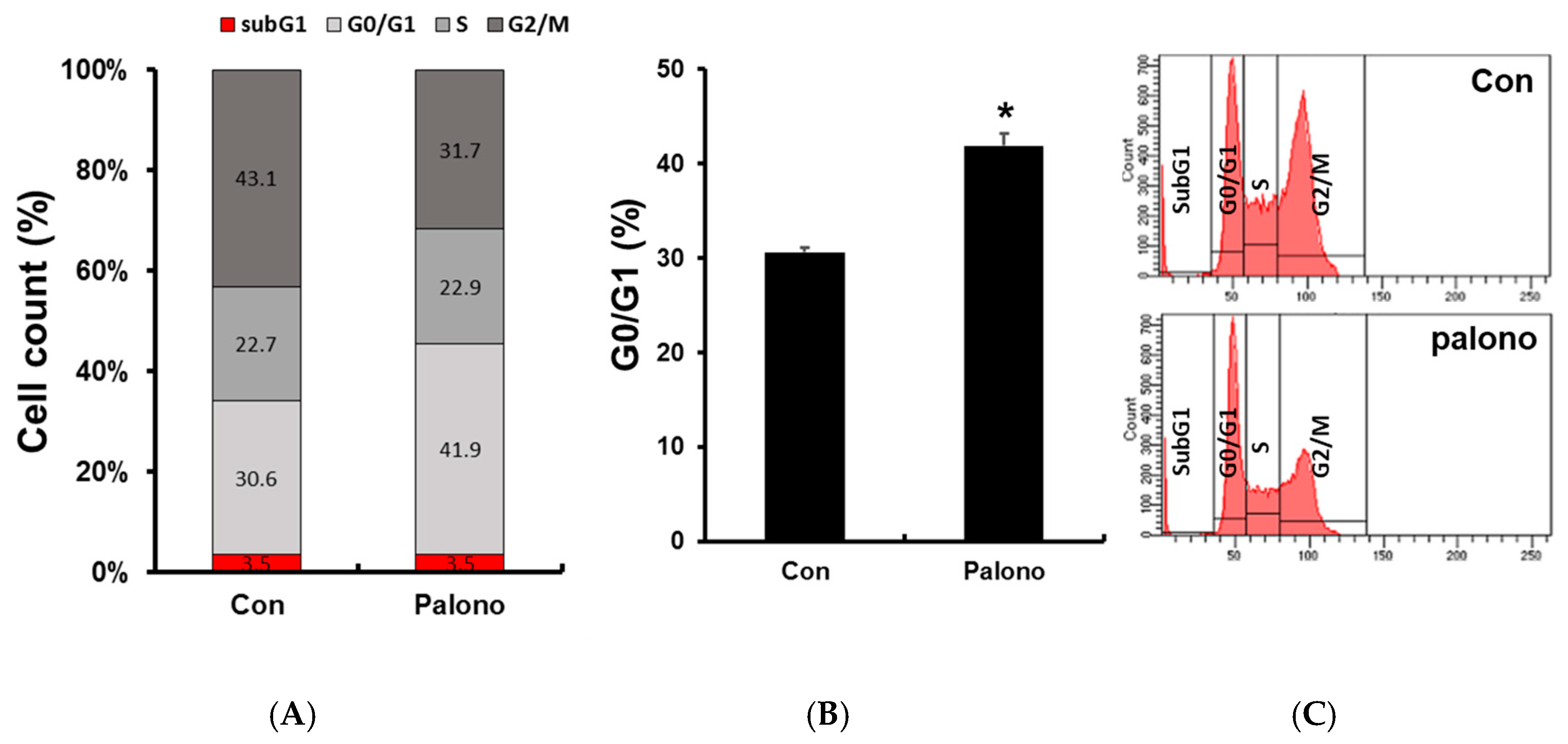
2.3. Palonosetron Arrested G1 Phase in AGS
2.4. 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonists Stimulated Phosphorylation of GSK3, ERK, and AKT and Autophagy-Related Proteins in AGS
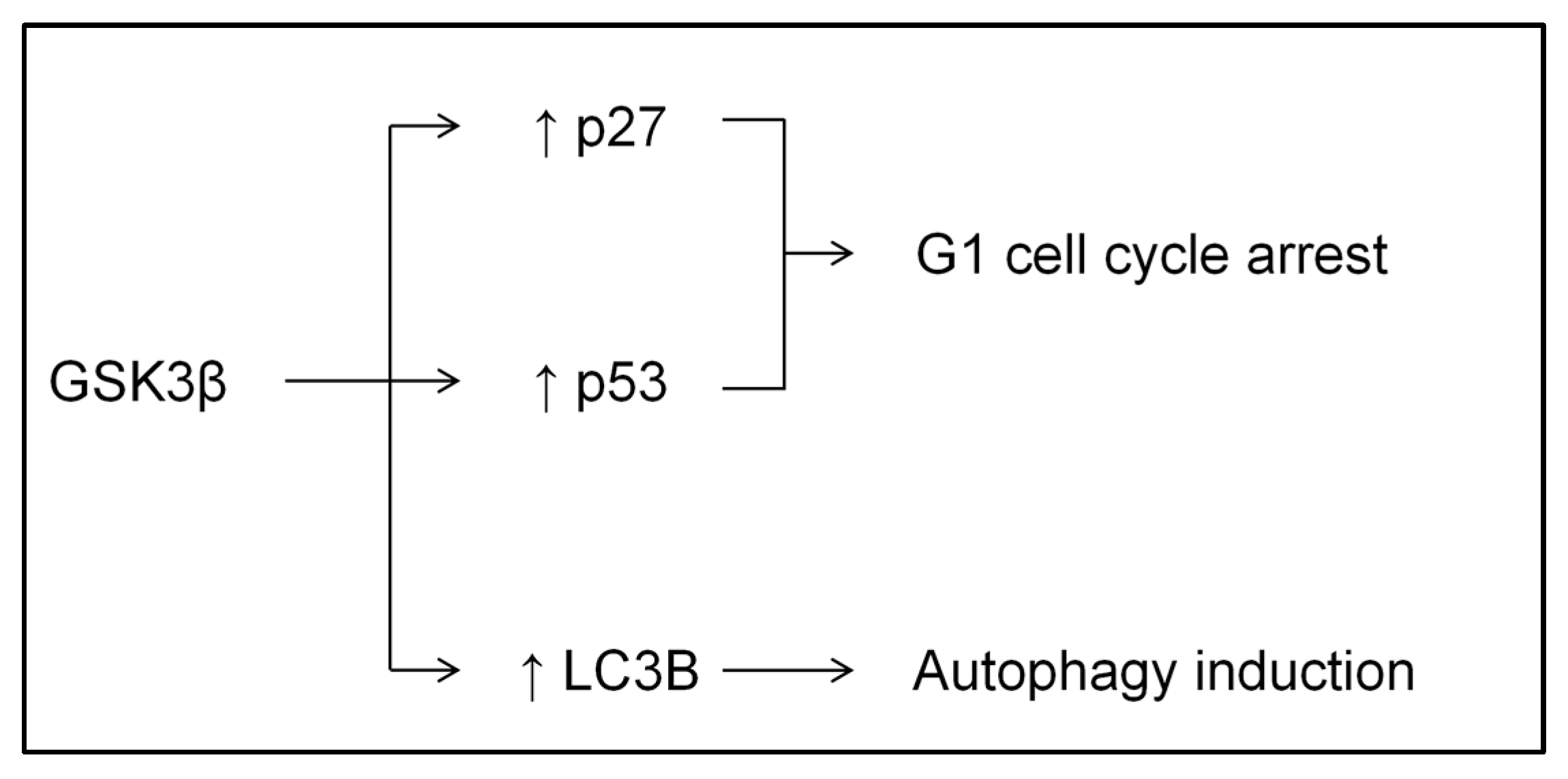
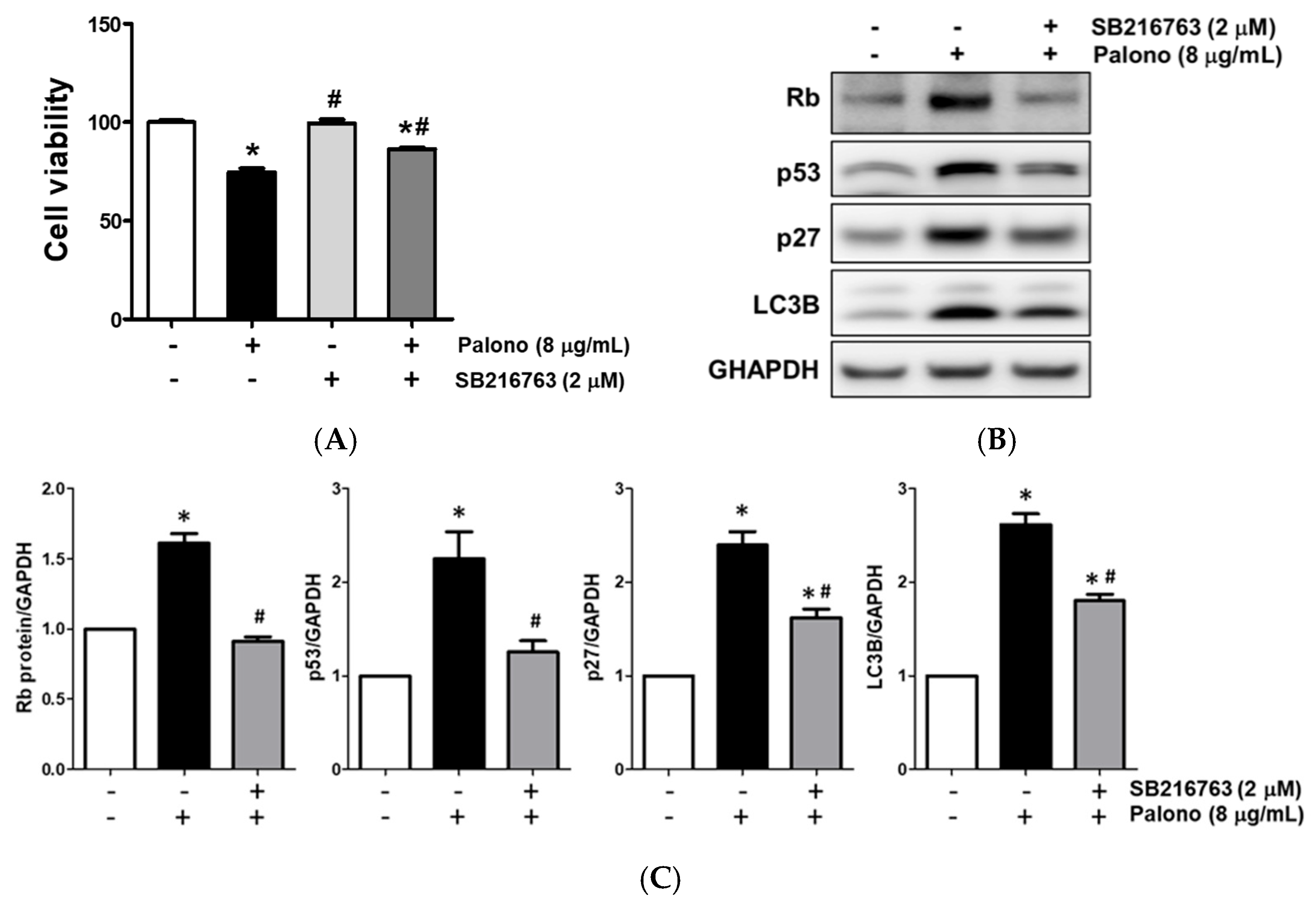
2.5. Palonosetron Regulated Rb, p27, p53, and LC3B via the Phosphorylation of GSK3β in AGS
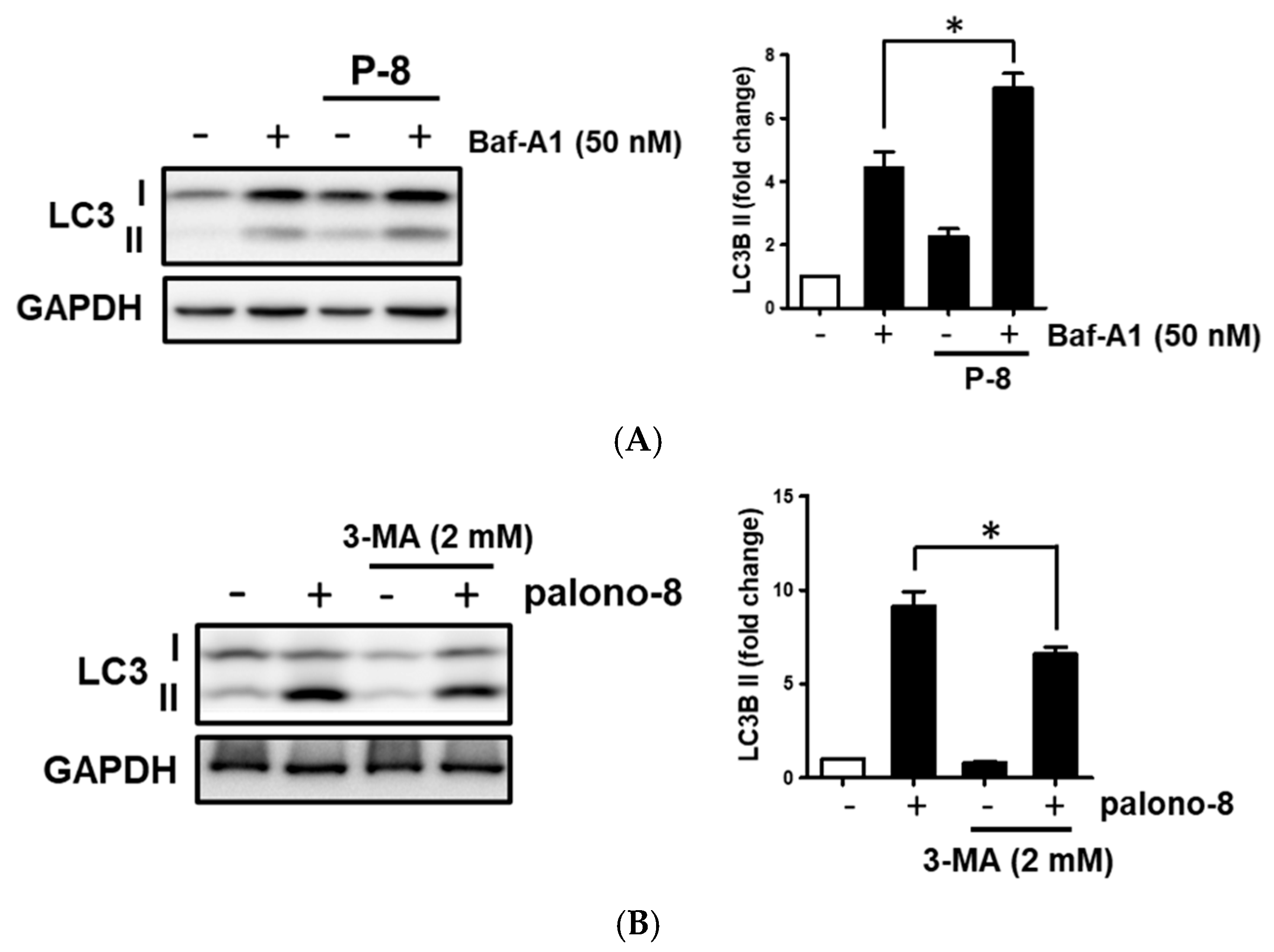
2.6. Palonosetron Induced Autophagy
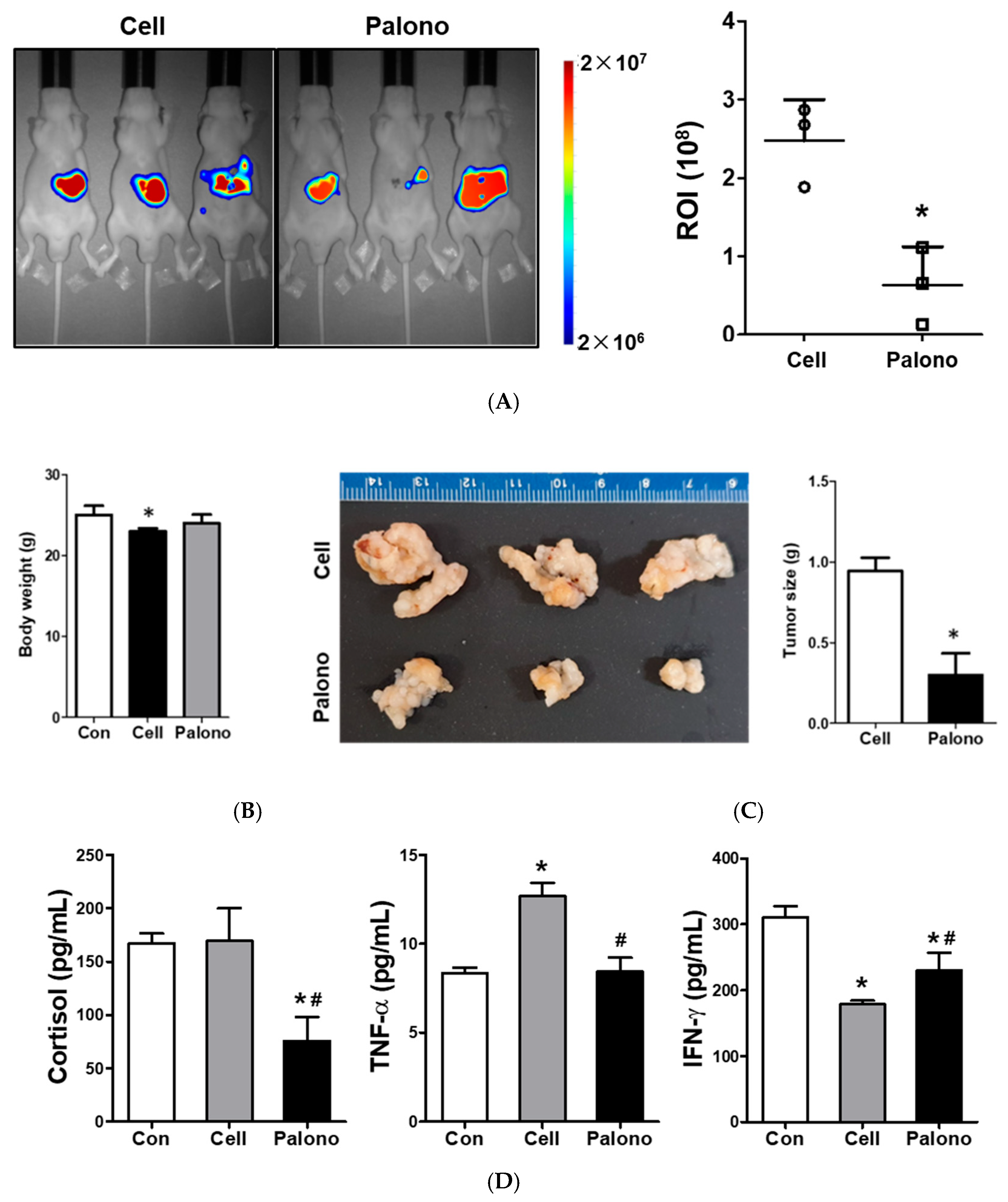
2.7. Palonosetron Reduced the Tumorigenesis of AGS Cells in the Gastric Cancer Xenograft Models
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Cell Viability Assay
4.3. Wound Healing Assay
4.4. Colony Formation Assay
4.5. Cell Cycle Assay
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Xenograft Models
4.8. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
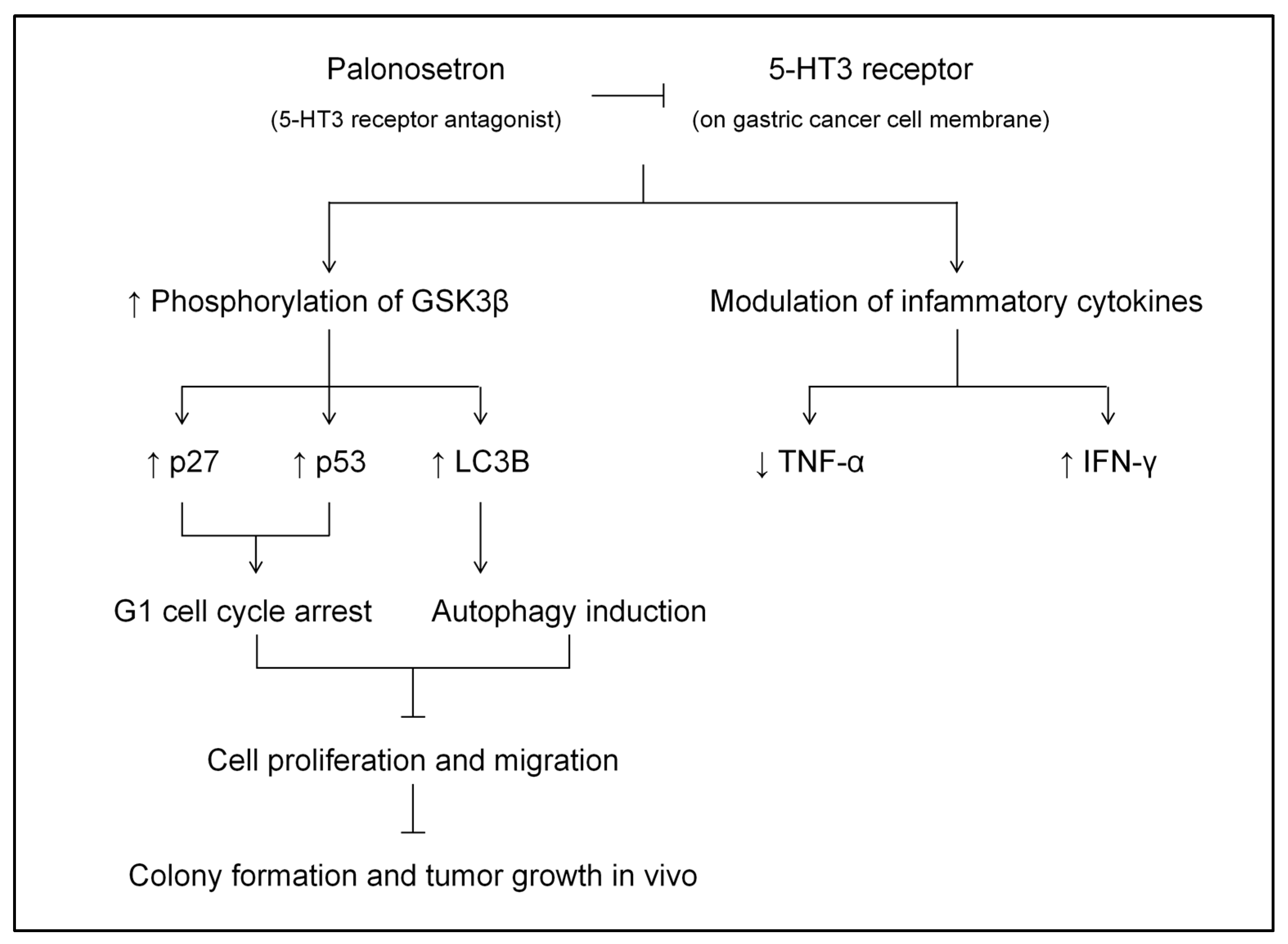
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5-HT | 5-hydroxytryptamine |
| Baf-A1 | Bafilomycin A1 |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| GAPDH | glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| GI | gastrointestinal |
| IFN | interferon |
| PI | propidium iodide |
| PONV | postoperative nausea and vomiting |
| ROIs | regions of interest |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
References
- Sahu, A.; Gopalakrishnan, L.; Gaur, N.; Chatterjee, O.; Mol, P.; Modi, P.K.; Dagamajalu, S.; Advani, J.; Jain, S.; Keshava Prasad, T.S. The 5-Hydroxytryptamine signaling map: An overview of serotonin-serotonin receptor mediated signaling network. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 12, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzel, T.; Mirowska-Guzel, D. The Role of Serotonin Neurotransmission in Gastrointestinal Tract and Pharmacotherapy. Molecules 2022, 27, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabregas, J.C.; Ramnaraign, B.; George, T.J. Clinical Updates for Colon Cancer Care in 2022. Clin. Color. Cancer 2022, 21, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terry, N.; Margolis, K.G. Serotonergic Mechanisms Regulating the GI Tract: Experimental Evidence and Therapeutic Relevance; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 319–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagomarsino, V.N.; Kostic, A.D.; Chiu, I.M. Mechanisms of microbial–neuronal interactions in pain and nociception. Neurobiol. Pain 2021, 9, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coray, R.; Quednow, B.B. The role of serotonin in declarative memory: A systematic review of animal and human research. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 139, 104729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar, I.; Bambico, F.R.; Mechawar, N.; Nobrega, J.N. Stress, serotonin, and hippocampal neurogenesis in relation to depression and antidepressant effects. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 38, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlienger, R.G.; Meier, C.R. Effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on platelet activation: Can they prevent acute myocardial infarction? Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs Drugs Devices Other Interv. 2003, 3, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khil, H.; Kim, S.M.; Hong, S.; Gil, H.M.; Cheon, E.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, Y.A.; Keum, N. Time trends of colorectal cancer incidence and associated lifestyle factors in South Korea. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhou, C.; Chen, J. Downregulation of 5—Hydroxytryptamine receptor 3A expression exerts an anticancer activity against cell growth in colorectal carcinoma cells in vitro. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 6100–6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrouilhe, D.; Clarhaut, J.; Defamie, N.; Mesnil, M. Serotonin and Cancer: What Is the Link? Curr. Mol. Med. 2015, 15, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ataee, R.P.; Ajdary, S.P.; Rezayat, M.P.; Shokrgozar, M.A.P.; Shahriari, S.M.; Zarrindast, M.R.P. Study of 5HT3 and 5HT4 Receptors Expression in HT29 Cell Line and Human Colon Adenocarcinoma Tissues. Arch. Iran. Med. 2010, 13, 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, N.Y.; Kim, D.W.; Oh, J.E.; Heo, E.; Lee, J.S.; Yoo, Y.C. Anti-Tumor Potential of a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist as a Novel Autophagy Inducer in Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Clinical Study with In Vitro Confirmation. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dranoff, G. Cytokines in cancer pathogenesis and cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irving, H.; Turek, I.; Kettle, C.; Yaakob, N. Tapping into 5-HT3 Receptors to Modify Metabolic and Immune Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, H.; Xu, H.; Ji, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhou, L.; Song, H.; Zhou, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Cai, J.; et al. 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor (5-HT1DR) promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by regulating Axin1/β-catenin/MMP-7 signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 25975–25987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, S.; Lal, G. Role of serotonin receptor signaling in cancer cells and anti-tumor immunity. Theranostics 2021, 11, 5296–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, N.C.; Orr, S.J.; Stoeber, K.; Williams, G.H.; Lam, E.W.F.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Mufti, G.J.; Thomas, N.S.B. Commitment Point during G0→G1 That Controls Entry into the Cell Cycle. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 2351–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, T.J.; Belani, K.G.; Bergese, S.; Chung, F.; Diemunsch, P.; Habib, A.S.; Jin, Z.; Kovac, A.L.; Meyer, T.A.; Urman, R.D.; et al. Fourth Consensus Guidelines for the Management of Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting. Anesth. Analg. 2020, 131, 411–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibel, S.; Rücker, G.; Eberhart, L.H.; Pace, N.L.; Hartl, H.M.; Jordan, O.L.; Mayer, D.; Riemer, M.; Schaefer, M.S.; Raj, D.; et al. Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: A network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 2020, CD012859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forde, J.E.; Dale, T.C. Glycogen synthase kinase 3: A key regulator of cellular fate. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 1930–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duda, P.; Akula, S.M.; Abrams, S.L.; Steelman, L.S.; Martelli, A.M.; Cocco, L.; Ratti, S.; Candido, S.; Libra, M.; Montalto, G.; et al. Targeting GSK3 and Associated Signaling Pathways Involved in Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoli, D.; Pollak, M.; Topisirovic, I. The role of GSK3 in metabolic pathway perturbations in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Res. 2021, 1868, 119059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Wen, J.; He, J.; Lu, Y.; Liao, Q.; Wang, T.; Tang, H.; Yang, X.; et al. Paclitaxel hyperthermia suppresses gastric cancer migration through MiR-183-5p/PPP2CA/AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin axis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 150, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wen, F.; Yang, P.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Shu, P. Yi-qi-hua-yu-jie-du decoction induces ferroptosis in cisplatin-resistant gastric cancer via the AKT/GSK3β/NRF2/GPX4 axis. Phytomedicine 2024, 123, 155220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoch, T.; Norbury, C. Cellular responses to DNA damage: Cell-cycle checkpoints, apoptosis and the roles of p53 and ATM. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1995, 20, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blain, S.W.; Scher, H.I.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Koff, A. p27 as a target for cancer therapeutics. Cancer Cell 2003, 3, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, T.-Y.; Jope, R.S. GSK3β N-terminus binding to p53 promotes its acetylation. Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Wang, Z.; Yao, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, B.; Yu, Y.; Su, L.; Zhu, Z.; Gu, Q. P27Kip1, regulated by glycogen synthase kinase-3β, results in HMBA-induced differentiation of human gastric cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. The Cell-Cycle Arrest and Apoptotic Functions of p53 in Tumor Initiation and Progression. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giatromanolaki, A.; Koukourakis, M.I.; Georgiou, I.; Kouroupi, M.; Sivridis, E. LC3A, LC3B and Beclin-1 Expression in Gastric Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 6827–6833, Erratum in Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klionsky, D.J.; Abdel-Aziz, A.K.; Abdelfatah, S.; Abdellatif, M.; Abdoli, A.; Abel, S.; Abeliovich, H.; Abildgaard, M.H.; Abudu, Y.P.; Acevedo-Arozena, A.; et al. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (4th edition)1. Autophagy 2021, 17, 1–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Xing, G.; Zhang, M.; Zhong, M.; Han, Z.; He, C.; Liu, X. Wogonoside inhibits cell growth and induces mitochondrial-mediated autophagy-related apoptosis in human colon cancer cells through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 4463–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinojima, N.; Yokoyama, T.; Kondo, Y.; Kondo, S. Roles of the Akt/mTOR/p70S6K and ERK1/2 Signaling Pathways in Curcumin-Induced Autophagy. Autophagy 2007, 3, 635–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirley, M. Netupitant/Palonosetron: A Review in Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting. Drugs 2021, 81, 1331–1342, Erratum in Drugs 2021, 81, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aapro, M.; Jordan, K.; Scotté, F.; Celio, L.; Karthaus, M.; Roeland, E. Netupitant-palonosetron (NEPA) for Preventing Chemotherapy-induced Nausea and Vomiting: From Clinical Trials to Daily Practice. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2022, 22, 806–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engeland, K. Cell cycle regulation: p53-p21-RB signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 946–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, D.A.; Yellen, P.; Xu, L.; Saqcena, M. Regulation of G1 Cell Cycle Progression: Distinguishing the Restriction Point from a Nutrient-Sensing Cell Growth Checkpoint(s). Genes Cancer 2010, 1, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Khoshbakht, T.; Hussen, B.M.; Dong, P.; Gassler, N.; Taheri, M.; Baniahmad, A.; Dilmaghani, N.A. A review on the role of cyclin dependent kinases in cancers. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Loh, Y.P. The discovery, structure, and function of 5-HTR1E serotonin receptor. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nebigil, C.G.; Launay, J.-M.; Hickel, P.; Tournois, C.; Maroteaux, L. 5-Hydroxytryptamine 2B receptor regulates cell-cycle progression: Cross-talk with tyrosine kinase pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 2591–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCubrey, J.A.; Steelman, L.S.; Bertrand, F.E.; Davis, N.M.; Sokolosky, M.; Abrams, S.L.; Montalto, G.; D’Assoro, A.B.; Libra, M.; Nicoletti, F.; et al. GSK-3 as potential target for therapeutic intervention in cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2881–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdov, I.; Kidd, M.; Gustafsson, B.I.; Svejda, B.; Joseph, R.; Pfragner, R.; Modlin, I.M. Autoregulatory effects of serotonin on proliferation and signaling pathways in lung and small intestine neuroendocrine tumor cell lines. Cancer 2009, 115, 4934–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prada, J.; Shalapour, S.; Pfau, M.; Henze, G.; Seeger, K. Antiproliferative effect of the serotonin receptor antagonist ondansetron in the acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell line REH. Acta Oncol. 2011, 50, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Huang, S.; Wu, X.; He, W.; Song, M. Serotonin signalling in cancer: Emerging mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Clin. Transl. Med. 2024, 14, e1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Oh, J.E.; Park, S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Bai, S.J.; Song, H.; Hwang, H.J.; Kim, D.W.; Yoo, Y.C. Tramadol use is associated with enhanced postoperative outcomes in breast cancer patients: A retrospective clinical study with in vitro confirmation. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 123, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoo, Y.C.; Lin, L.; Lee, S.; Shin, Y.R.; Oh, J.E.; Kim, N.Y. Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, Induces G1 Cell Cycle Arrest and Autophagy in Gastric Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010039
Yoo YC, Lin L, Lee S, Shin YR, Oh JE, Kim NY. Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, Induces G1 Cell Cycle Arrest and Autophagy in Gastric Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010039
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoo, Young Chul, Lin Lin, Sihak Lee, Yeeun Rachel Shin, Ju Eun Oh, and Na Young Kim. 2025. "Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, Induces G1 Cell Cycle Arrest and Autophagy in Gastric Cancer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010039
APA StyleYoo, Y. C., Lin, L., Lee, S., Shin, Y. R., Oh, J. E., & Kim, N. Y. (2025). Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, Induces G1 Cell Cycle Arrest and Autophagy in Gastric Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010039






