Modular Virus-like Particles for Antigen Presentation: Comparing Genetic Fusion and Click-Chemistry for Purification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Construction of Protein Variants
2.2. Expression and Solubility
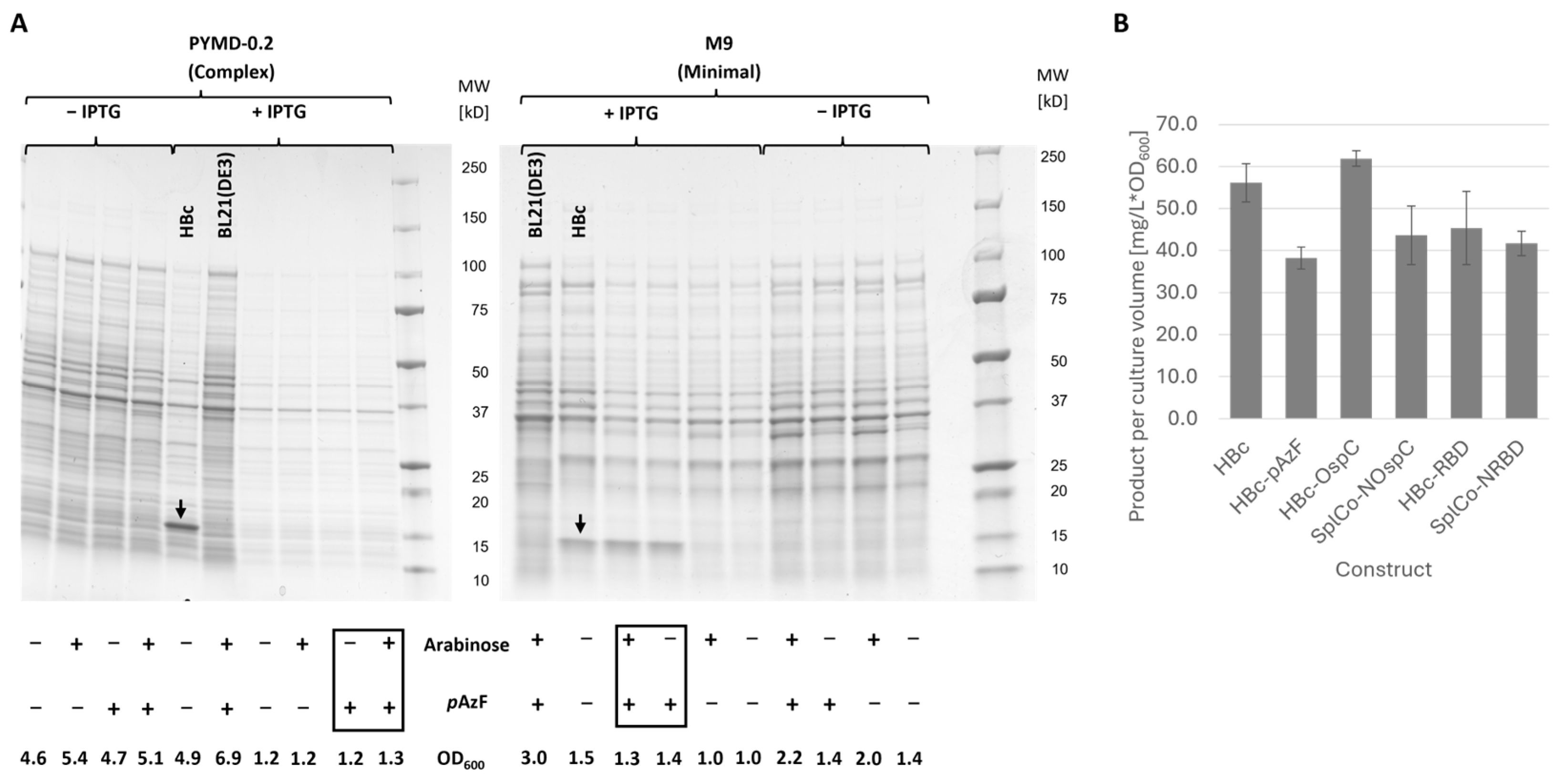
2.2.1. Inducible Expression of HBc-pAzF and Genetic Fusion Variants
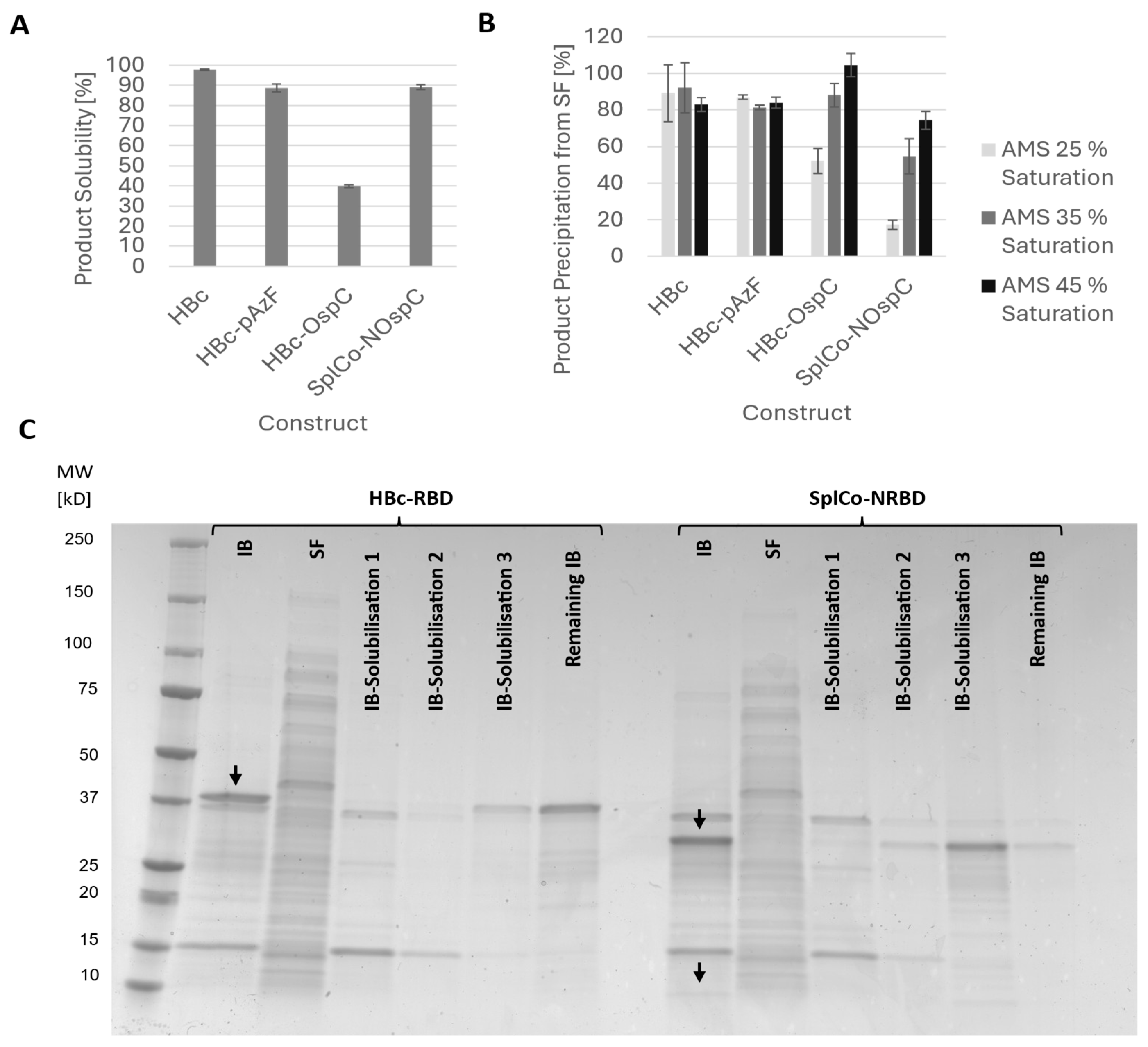
2.2.2. Recovery of Soluble Product After Mechanical Cell Lysis
2.3. Evaluation of Platform-Based Purification Processes Applied to Genetic Fusions
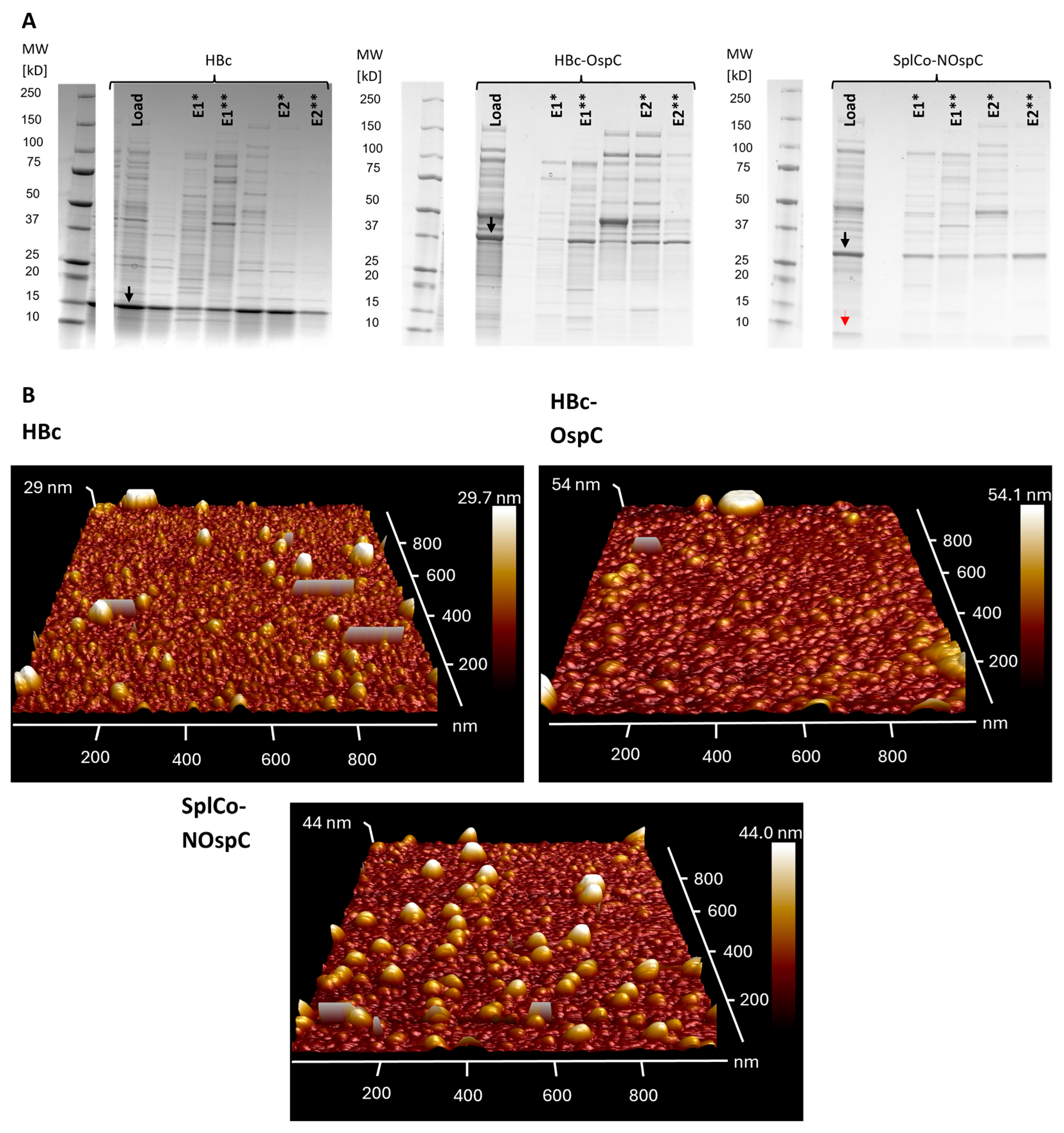
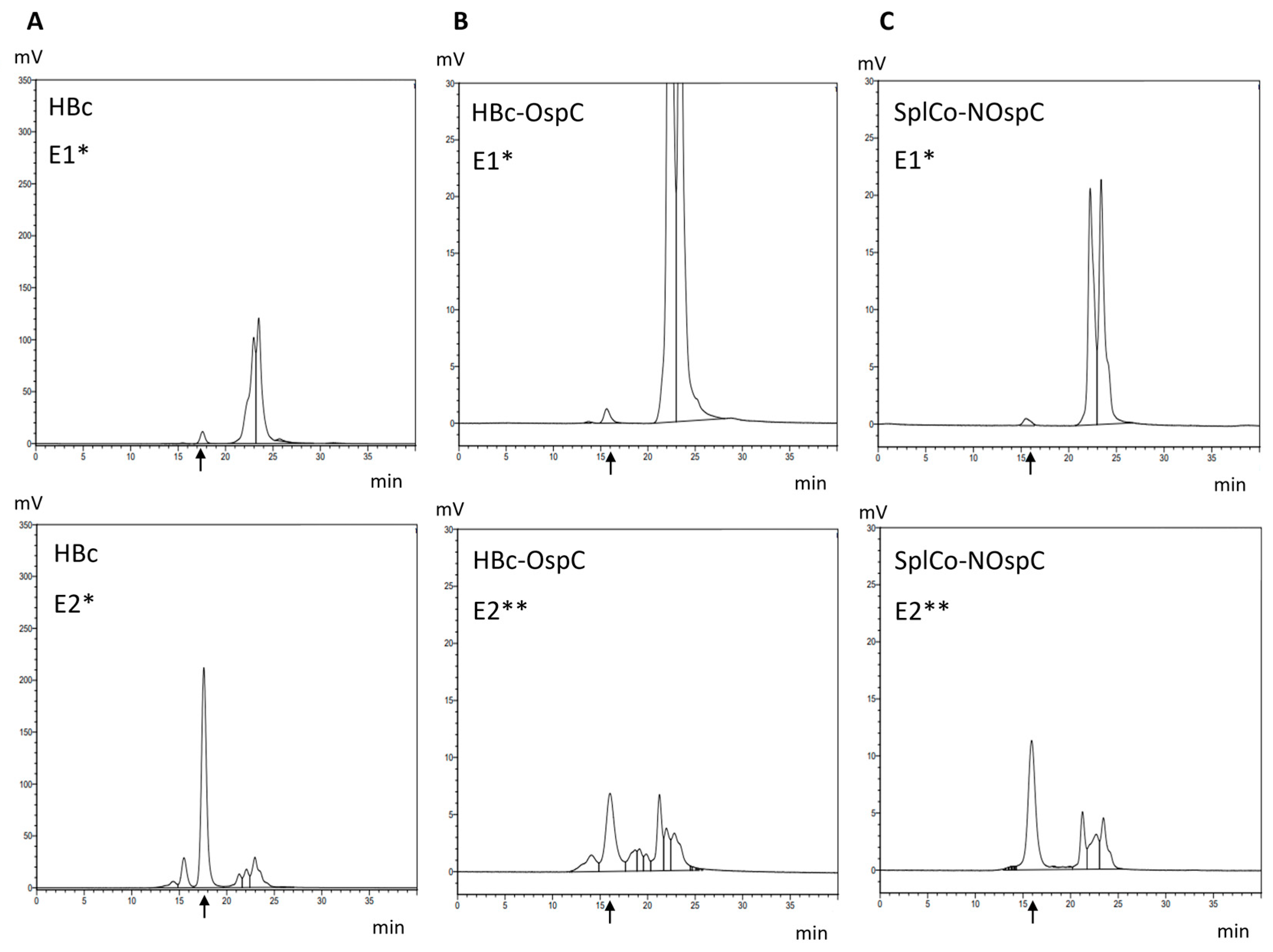
2.3.1. Native Purification of VLPs
2.3.2. Dissociative Purification of Dimers and Reassembly into VLPs
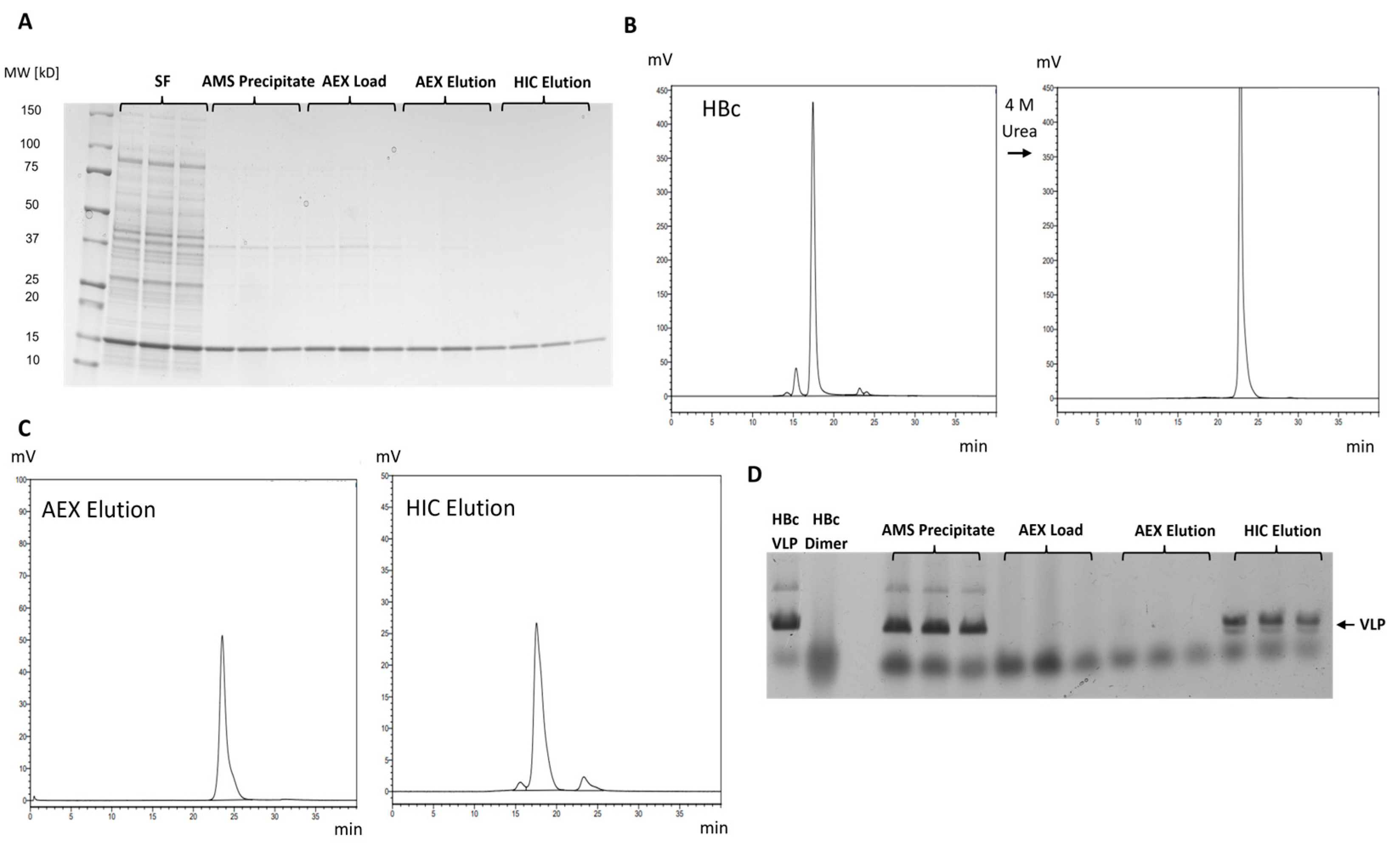
2.4. Transfer of Purification Strategies to HBc-pAzF
2.5. Application of HBc-pAzF in Click Reactions
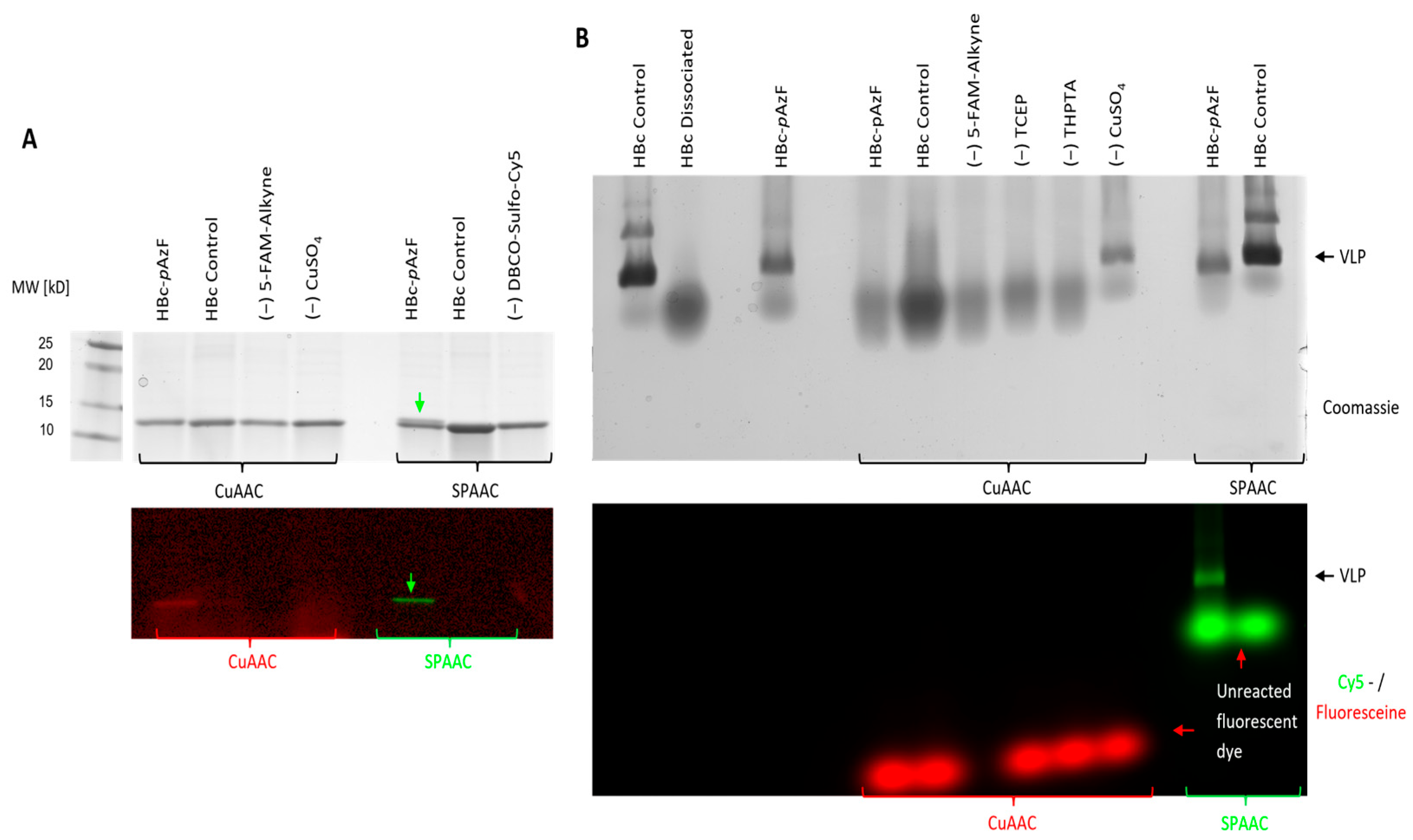
2.5.1. Qualitative Evaluation of CuAAC and SPAAC on Purified VLPs
2.5.2. Analytical Evaluation of Particle Stability After SPAAC
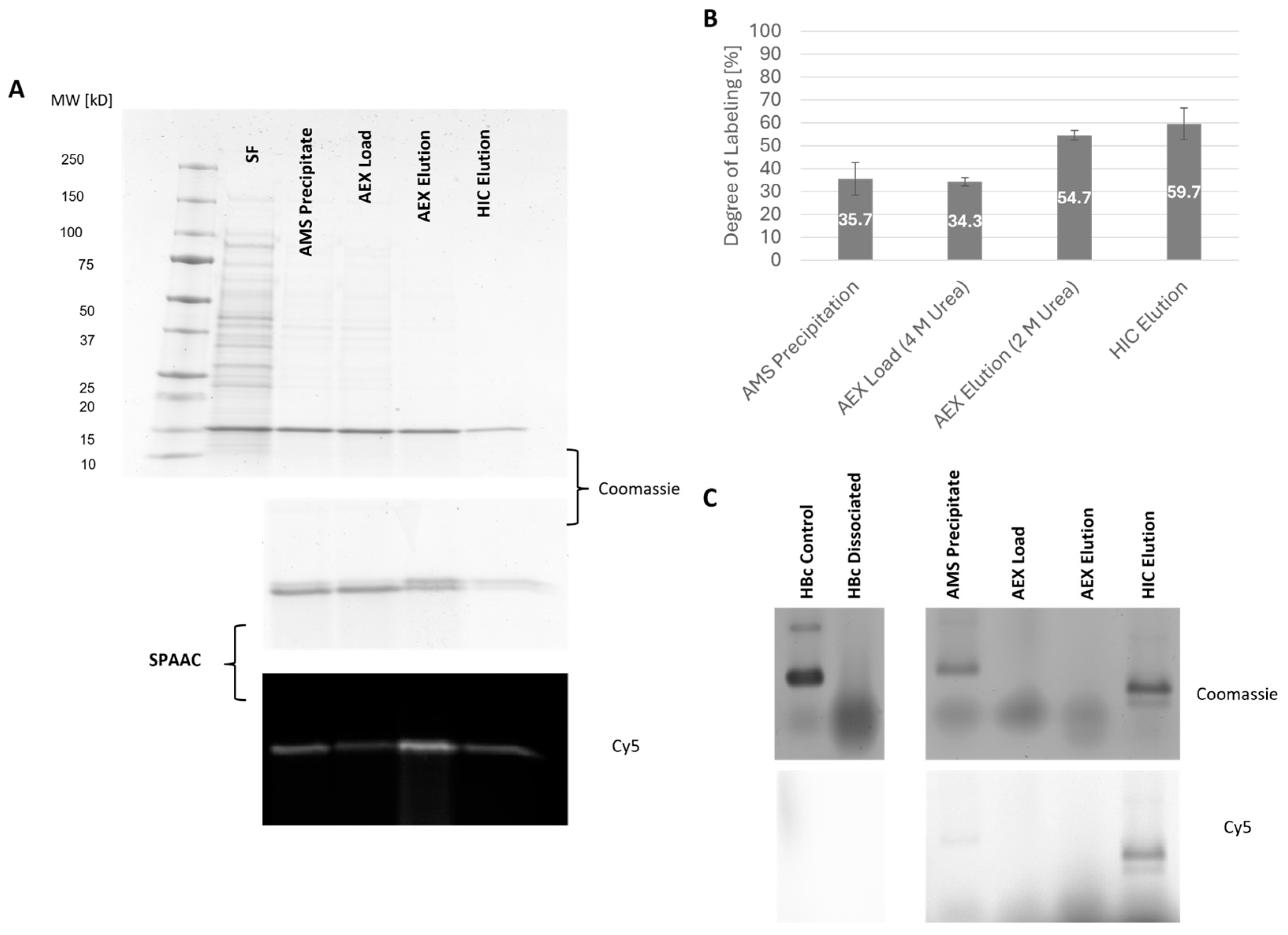
2.5.3. Quantitative Evaluation of SPAAC Reactivity During Purification
3. Discussion
3.1. Unfavorable Property Changes Caused by Genetic Fusions Limit Scalable Purification Strategies
3.2. Singular Introduction of nnAA at MIR Retains the Advantages of Dissociative Purification
3.3. Effects of AAC Reaction Mechanisms on Particle Stability and Their Applicability to the HBc-Platform
3.4. Surface Exposure of the Reactive Azide Sidechain of HBc-pAzF Leads to High Accessibility
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Genes and Cloning
4.2. Protein Constructs
4.3. Protein Expression
4.4. Cell Disruption
4.5. Protein Precipitation
4.6. Anion Exchange Chromatography
4.7. Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography
4.8. Protein Analysis
4.9. Particle Analysis
4.10. Click-Chemistry Reactions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VLP | virus-like particle |
| OspC | outer surface protein C |
| RBD | receptor binding domain |
| HBc | hepatitis B core antigen |
| pAzF | p-azidophenylalanine |
| HBV | hepatitis B virus |
| AEX | anion exchange chromatography |
| SEC | size exclusion chromatography |
| SUC | sucrose cushion ultracentrifugation |
| HIC | hydrophobic interaction chromatography |
| MIR | major immunodominant region |
| CuAAC | copper-catalyzed azido-alkyne cycloaddition |
| nnAA | non-natural amino acids |
| SPAAC | strain-promoted azido-alkyne cycloaddition |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecasulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| SDS-PAA | sodium dodecasulfate polyacrylamide |
| SplCo | SplitCore |
| ORF | open-reading frame |
| LB | lysogeny broth |
| OD600 | optical density at a wavelength of 600 nm |
| TN-300 | buffer containing 25 mM Tris, 300 mM sodium chloride at a pH of 7.5 |
| DV | disruption volume |
| SF | soluble fraction |
| IB | inclusion body fraction |
| AMS | ammonium sulfate |
| CV | column volumes |
| HPLC | high pressure liquid chromatography |
| NAGE | native agarose gel electrophoresis |
| DLS | dynamic light scattering |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
| AFM | atomic force microscopy |
References
- Maynard, J.E. Hepatitis B: Global importance and need for control. Vaccine 1990, 8 (Suppl. S1), S18–S20; discussion S21–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirbaghaee, Z.; Bolhassani, A. Different applications of virus-like particles in biology and medicine: Vaccination and delivery systems. Biopolymers 2016, 105, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, B.D.; Zak, A.; Khera, E.; Wen, F. Engineering Virus-like Particles for Antigen and Drug Delivery. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2018, 19, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejía-Méndez, J.L.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R.; Hernández, L.R.; Sánchez-Arreola, E.; Bach, H. Virus-like Particles: Fundamentals and Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, I.H.; Levin, M.J. Paradigm shifting vaccines: Prophylactic vaccines against latent varicella-zoster virus infection and against HPV-associated cancer. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2011, 1, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurens, M.B. RTS,S/AS01 vaccine (Mosquirix™): An overview. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2020, 16, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, O.; Akbar, S.M.F.; Imai, Y.; Sanada, T.; Tsukiyama-Kohara, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Kamishita, T.; Miyake, T.; Tokumoto, Y.; Hikita, H.; et al. Intranasal therapeutic vaccine containing HBsAg and HBcAg for patients with chronic hepatitis B; 18 months follow-up results of phase IIa clinical study. Hepatol. Res. 2022, 53, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filette, M.; Martens, W.; Smet, A.; Schotsaert, M.; Birkett, A.; Londoño-Arcila, P.; Fiers, W.; Saelens, X. Universal influenza A M2e-HBc vaccine protects against disease even in the presence of pre-existing anti-HBc antibodies. Vaccine 2008, 26, 6503–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, E.M.; Manchester, M. Viral nanoparticles and virus-like particles: Platforms for contemporary vaccine design. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 3, 174–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, T.; Roldão, A.; Peixoto, C.; Carrondo, M.J.T.; Alves, P.M. Large-scale production and purification of VLP-based vaccines. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2011, 107, S42–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckland, B.C. The process development challenge for a new vaccine. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, S16–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hume, H.K.C.; Lua, L.H.L. Platform technologies for modern vaccine manufacturing. Vaccine 2017, 35, 4480–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.L.; Ng, H.W.; Akwiditya, M.A.; Ooi, C.W.; Chan, E.-S.; Ho, K.L.; Tan, W.S.; Chua, G.K.; Tey, B.T. Single-step purification of recombinant hepatitis B core antigen Y132A dimer from clarified Escherichia coli feedstock using a packed bed anion exchange chromatography. Process Biochem. 2018, 69, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yin, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, D.; Wang, W.; Bi, J.; Su, Z. In vitro preparation of uniform and nucleic acid free hepatitis B core particles through an optimized disassembly-purification-reassembly process. Protein Expr. Purif. 2021, 178, 105747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, E.E.; Keifer, D.Z.; Selzer, L.; Lee, L.S.; Contino, N.C.; Wang, J.C.-Y.; Zlotnick, A.; Jarrold, M.F. Detection of late intermediates in virus capsid assembly by charge detection mass spectrometry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3536–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asor, R.; Schlicksup, C.J.; Zhao, Z.; Zlotnick, A.; Raviv, U. Rapidly Forming Early Intermediate Structures Dictate the Pathway of Capsid Assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 7868–7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynne, S.A.; Crowther, R.A.; Leslie, A.G. The crystal structure of the human hepatitis B virus capsid. Mol. Cell 1999, 3, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wei, J.; Yang, Y.; Ma, X.; Hou, B.; An, W.; Hua, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Ma, G.; et al. Strong hydrophobicity enables efficient purification of HBc VLPs displaying various antigen epitopes through hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 140, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamel, C.; Ploss, M.; Böttcher, B.; Stehle, T.; Wallich, R.; Simon, M.M.; Nassal, M. Hepatitis B virus capsid-like particles can display the complete, dimeric outer surface protein C and stimulate production of protective antibody responses against Borrelia burgdorferi infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 17474–17481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, S.; Zhang, B.; Bi, J.; Liu, Y.; Su, Z. HBc-based virus-like particle assembly from inclusion bodies using 2-methyl-2, 4-pentanediol. Process Biochem. 2020, 89, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotnick, A.; Tan, Z.; Selzer, L. One protein, at least three structures, and many functions. Structure 2013, 21, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.; Skamel, C.; Nassal, M. SplitCore: An exceptionally versatile viral nanoparticle for native whole protein display regardless of 3D structure. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokhina, E.A.; Kuprianov, V.V.; Stepanova, L.A.; Tsybalova, L.M.; Kiselev, O.I.; Ravin, N.V.; Skryabin, K.G. A molecular assembly system for presentation of antigens on the surface of HBc virus-like particles. Virology 2013, 435, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyret, H.; Ponndorf, D.; Meshcheriakova, Y.; Richardson, J.; Lomonossoff, G.P. Covalent protein display on Hepatitis B core-like particles in plants through the in vivo use of the SpyTag/SpyCatcher system. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingston, N.J.; Grehan, K.; Snowden, J.S.; Hassall, M.; Alzahrani, J.; Paesen, G.C.; Sherry, L.; Hayward, C.; Roe, A.; Stephen, S.; et al. VelcroVax: A “Bolt-On” Vaccine Platform for Glycoprotein Display. mSphere 2023, 8, e0056822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H.C.; Finn, M.G.; Sharpless, K.B. Click Chemistry: Diverse Chemical Function from a Few Good Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 2004–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, J.E.; Moorhouse, A.D. The growing applications of click chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1249–1262, Erratum in Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 6888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieck, S.t.; Müller, A.; Nehring, A.; Hinz, F.I.; Bartnik, I.; Schuman, E.M.; Dieterich, D.C. Metabolic labeling with noncanonical amino acids and visualization by chemoselective fluorescent tagging. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2012, 56, 7.11.1–7.11.29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strable, E.; Prasuhn, D.E.; Udit, A.K.; Brown, S.; Link, A.J.; Ngo, J.T.; Lander, G.; Quispe, J.; Potter, C.S.; Carragher, B.; et al. Unnatural amino acid incorporation into virus-like particles. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 866–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Brock, A.; Herberich, B.; Schultz, P.G. Expanding the genetic code of Escherichia coli. Science 2001, 292, 498–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.S.; Ahmad, I.; Yin, J.A.; Schultz, P.G. An enhanced system for unnatural amino acid mutagenesis in E. coli. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 395, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agard, N.J.; Prescher, J.A.; Bertozzi, C.R. A strain-promoted 3 + 2 azide-alkyne cycloaddition for covalent modification of biomolecules in living systems. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15046–15047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nienberg, C.; Retterath, A.; Becher, K.-S.; Saenger, T.; Mootz, H.D.; Jose, J. Site-Specific Labeling of Protein Kinase CK2: Combining Surface Display and Click Chemistry for Drug Discovery Applications. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretto, C.; Tang, M.; Chen, M.; Xu, H.; Subrizi, A.; Urtti, A.; van Hest, J.C.M. Cowpea Chlorotic Mottle Virus-Like Particles as Potential Platform for Antisense Oligonucleotide Delivery in Posterior Segment Ocular Diseases. Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 21, e2100095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, J.; Bacic, T.; Staritzbichler, R.; Daneschdar, M.; Klamp, T.; Arnold, P.; Jägle, S.; Türeci, Ö.; Markl, J.; Sahin, U. Enhanced stability of a chimeric hepatitis B core antigen virus-like-particle (HBcAg-VLP) by a C-terminal linker-hexahistidine-peptide. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceres, P.; Stray, S.J.; Zlotnick, A. Hepatitis B virus capsid assembly is enhanced by naturally occurring mutation F97L. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 9538–9543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuily, L.; Lahrach, N.; Fassler, R.; Genest, O.; Faller, P.; Sénèque, O.; Denis, Y.; Castanié-Cornet, M.-P.; Genevaux, P.; Jakob, U.; et al. Copper Induces Protein Aggregation, a Toxic Process Compensated by Molecular Chaperones. mBio 2022, 13, e0325121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Chan, W.; Ko, B.Y.; VanLang, C.C.; Swartz, J.R. Assessing sequence plasticity of a virus-like nanoparticle by evolution toward a versatile scaffold for vaccines and drug delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12360–12365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Ko, W.; Sung, B.H.; Kim, S.C.; Lee, H.S. Direct protein-protein conjugation by genetically introducing bioorthogonal functional groups into proteins. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 5816–5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertani, G. Studies on lysogenesis. I. The mode of phage liberation by lysogenic Escherichia coli. J. Bacterial. 1951, 62, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, J.W.; Santoro, S.W.; Martin, A.B.; King, D.S.; Wang, L.; Schultz, P.G. Addition of p-azido-L-phenylalanine to the genetic code of Escherichia coli. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 9026–9027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studier, F.W. Protein production by auto-induction in high density shaking cultures. Protein Expr. Purif. 2005, 41, 207–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pink, M.; Verma, N.; Rettenmeier, A.W.; Schmitz-Spanke, S. CBB staining protocol with higher sensitivity and mass spectrometric compatibility. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, D.; Chan, J.-A.; Suckow, M.; Barbian, A.; Weniger, M.; Jenzelewski, V.; Reiling, L.; Richards, J.S.; Anderson, D.A.; Kouskousis, B.; et al. Display of malaria transmission-blocking antigens on chimeric duck hepatitis B virus-derived virus-like particles produced in Hansenula polymorpha. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladner, C.L.; Yang, J.; Turner, R.J.; Edwards, R.A. Visible fluorescent detection of proteins in polyacrylamide gels without staining. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 326, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, D.; Rolf, T.; Suckow, M.; Kranz, A.; Barbian, A.; Chan, J.-A.; Leitsch, J.; Weniger, M.; Jenzelewski, V.; Kouskousis, B.; et al. Establishment of a yeast-based VLP platform for antigen presentation. Microb. Cell Fact. 2018, 17, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, K.D.; Howarth, M. New Routes and Opportunities for Modular Construction of Particulate Vaccines: Stick, Click, and Glue. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartzell, E.J.; Lieser, R.M.; Sullivan, M.O.; Chen, W. Modular Hepatitis B Virus-like Particle Platform for Biosensing and Drug Delivery. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 12642–12651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balbierer, K.; Jenzelewski, V.; Herrmann, F.C.; Piontek, M.; Jose, J. Modular Virus-like Particles for Antigen Presentation: Comparing Genetic Fusion and Click-Chemistry for Purification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10036. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010036
Balbierer K, Jenzelewski V, Herrmann FC, Piontek M, Jose J. Modular Virus-like Particles for Antigen Presentation: Comparing Genetic Fusion and Click-Chemistry for Purification. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10036. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010036
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalbierer, Karsten, Volker Jenzelewski, Fabian C. Herrmann, Michael Piontek, and Joachim Jose. 2025. "Modular Virus-like Particles for Antigen Presentation: Comparing Genetic Fusion and Click-Chemistry for Purification" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10036. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010036
APA StyleBalbierer, K., Jenzelewski, V., Herrmann, F. C., Piontek, M., & Jose, J. (2025). Modular Virus-like Particles for Antigen Presentation: Comparing Genetic Fusion and Click-Chemistry for Purification. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10036. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010036






