Hybrid Receptor-Mediated Molecular Delineations in TNF-α and IGF-1-Induced Costimulatory Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
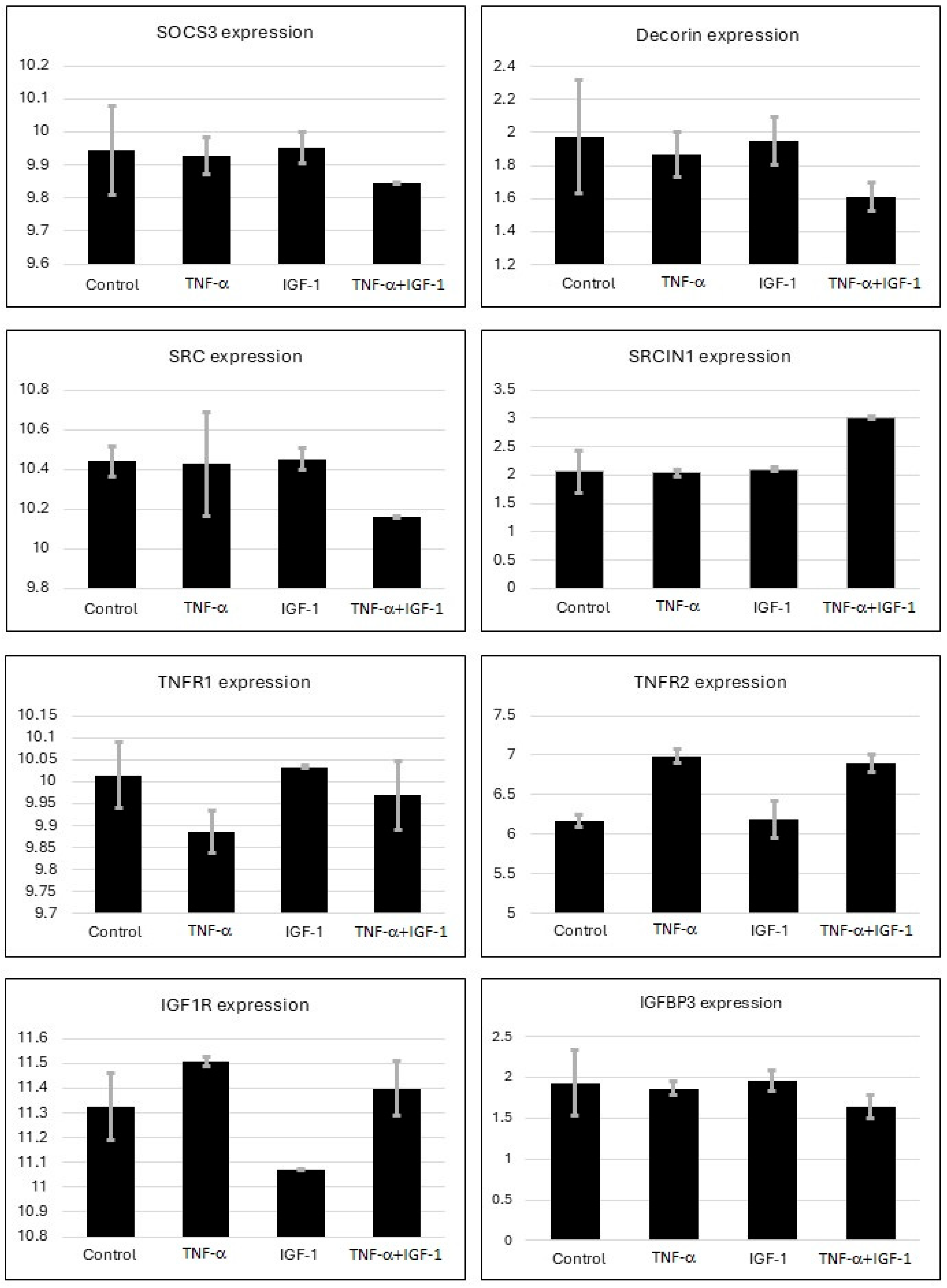
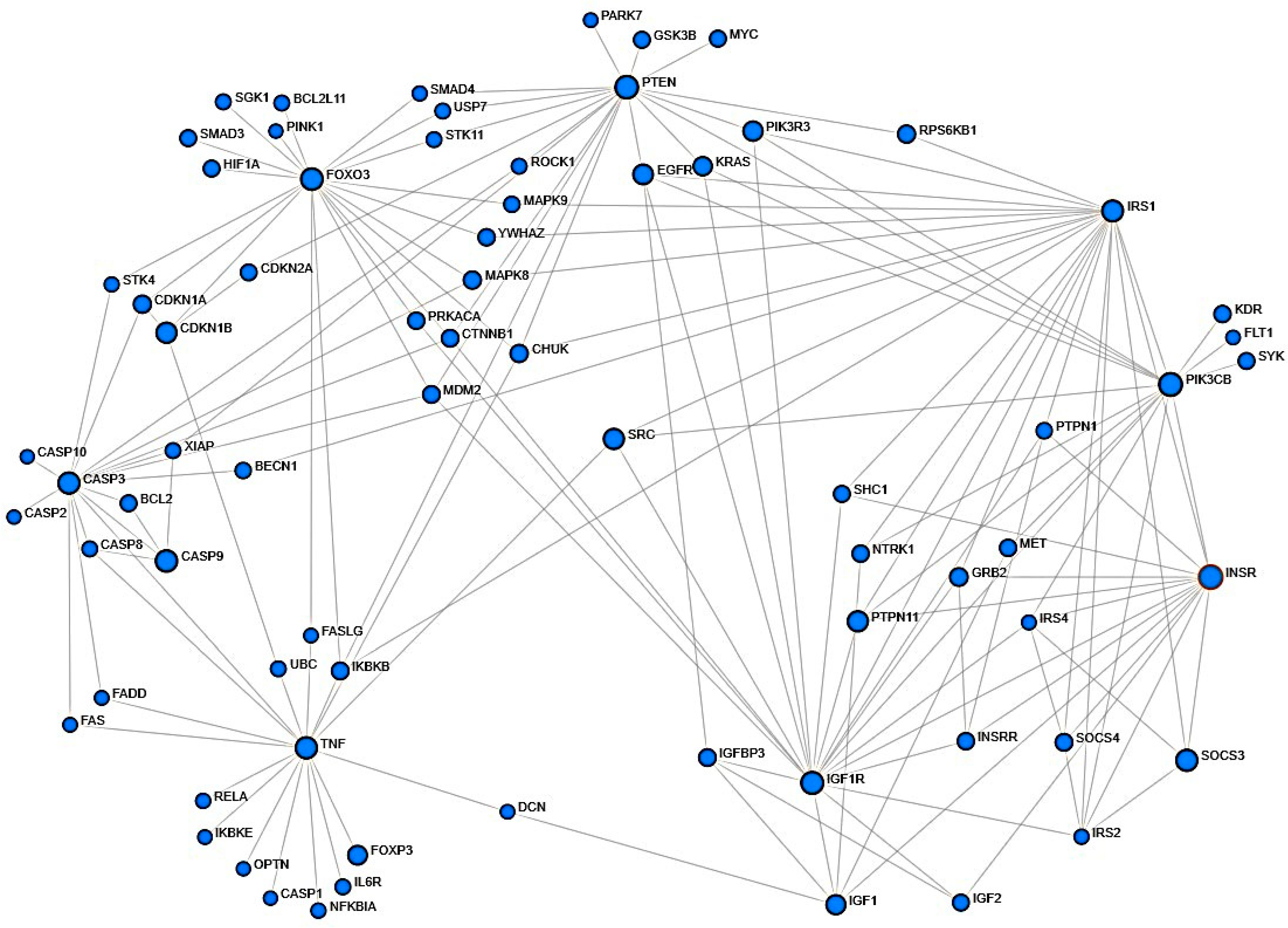
2.1. Gene Expression Analysis from Microarray
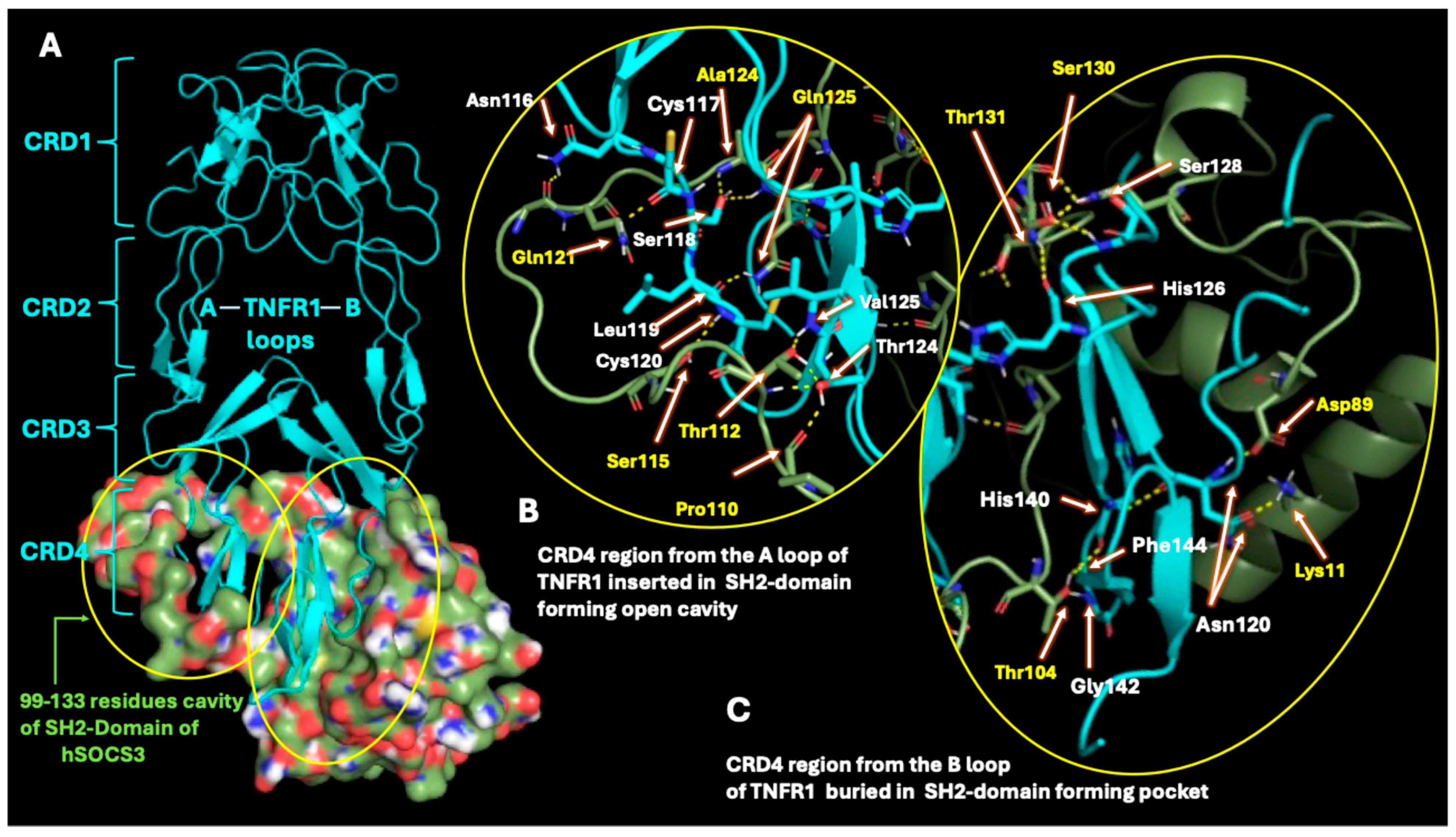
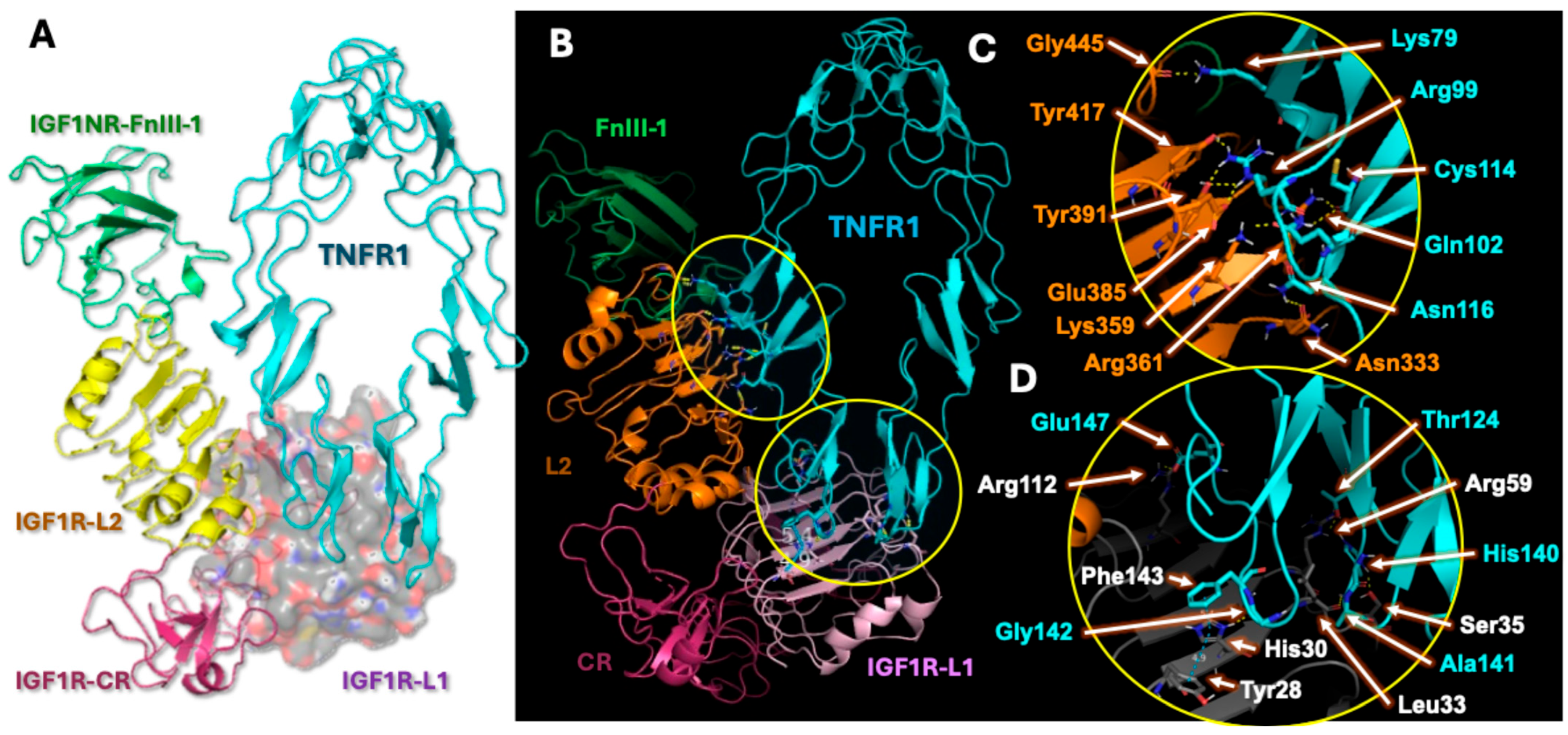
2.2. Assessment of Protein–Protein Structural Interactions
2.3. SOCS3 Interactions with TNF-α Receptor
2.4. Analysis of Hybrid Receptor Formation
2.5. Hybrid Receptor Formation Alters IGF-1 Binding Topology and Its Signaling Dynamics
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Transcriptomic Analysis
4.2. NetworkAnalyst
4.3. Protein Docking at ClusPro Webserver
4.4. Analysis of Protein–Protein Interactions with PyMol
5. Conclusions
Limitations and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boosani, C.S.; Burela, L. The Exacerbating Effects of the Tumor Necrosis Factor in Cardiovascular Stenosis: Intimal Hyperplasia. Cancers 2024, 16, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Wang, N.; Shang, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Q.; Li, L.; Zhao, X. TNF-α (G-308A) Polymorphism, Circulating Levels of TNF-α and IGF-1: Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke—An Updated Meta-Analysis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 831910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowska-Sędek, E.; Pyrżak, B. Chronic inflammation and the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor-1 axis. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 45, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, W.; Lerner-Marmarosh, N.; Huang, Q.; Osawa, M.; Ohta, S.; Yoshizumi, M.; Glassman, M.; Lee, J.-D.; Yan, C.; Berk, B.C.; et al. Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Enhances Inflammatory Responses in Endothelial Cells: Role of Gab1 and MEKK3 in TNF-α–Induced c-Jun and NF-κB Activation and Adhesion Molecule Expression. Circ. Res. 2002, 90, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, A.; Zahid, A.A.; Scheidegger, K.J.; Brink, M.; Delafontaine, P. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Regulates Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 Expression in Vascular Smooth Muscle. Circulation 2002, 105, 1220–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hijikawa, T.; Kaibori, M.; Uchida, Y.; Yamada, M.; Matsui, K.; Ozaki, T.; Kamiyama, Y.; Nishizawa, M.; Okumura, T. Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Prevents Liver Injury Through the Inhibition of Tnf-α and Inos Induction in D-galactosamine and Lps-Treated Rats. Shock 2008, 29, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.N.; Souza, B.S.F.; Azevedo, C.M.; Vasconcelos, J.F.; de Jesus, P.G.; Feitoza, M.S.; Meira, C.S.; Carvalho, G.B.; Cavalcante, B.R.; Ribeiro-dos-Santos, R.; et al. IGF-1-Overexpressing Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells Promote Immunomodulatory and Proregenerative Effects in Chronic Experimental Chagas Disease. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naudé, P.J.W.; Den Boer, J.A.; Luiten, P.G.M.; Eisel, U.L.M. Tumor necrosis factor receptor cross-talk. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, L.; Aguirre, V.; Kim, J.K.; Shulman, G.I.; Lee, A.; Corbould, A.; Dunaif, A.; White, M.F. Insulin/IGF-1 and TNF-α stimulate phosphorylation of IRS-1 at inhibitory Ser307 via distinct pathways. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Block, M.E.; Boosani, C.S. Short communication: TNF-α and IGF-1 regulates epigenetic mechanisms of HDAC2 and HDAC10. PLoS ONE. 2022, 17, e0263190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, K.; Rakesh, K.; Pankajakshan, D.; Agrawal, D.K. SOCS3 promotor hypermethylation and STAT3-NF-κB interaction downregulate SOCS3 expression in human coronary artery smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2013, 304, H776–H785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grounds, M.D.; Radley, H.G.; Gebski, B.L.; Bogoyevitch, M.A.; Shavlakadze, T. Implications of Cross-Talk Between Tumour Necrosis Factor and Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Signalling in Skeletal Muscle. Clin. Exp. Pharma. Physio. 2008, 35, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boosani, C.S.; Gunasekar, P.; Block, M.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Radwan, M.M.; Devendra, K. Agrawal. Inhibition of DNA methyltransferase-1 instigates the expression of DNA methyltransferase-3a in angioplasty-induced restenosis. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 96, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boosani, C.S.; Agrawal, D.K. Methylation and microRNA-mediated epigenetic regulation of SOCS3. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 42, 853–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turvey, S.; Muench, S.P.; Issad, T.; Fishwick, C.W.G.; Kearney, M.T.; Simmons, K.J. Using site-directed mutagenesis to further the understanding of insulin receptor-insulin like growth factor-1 receptor heterodimer structure. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2024, 77, 101607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girnita, L.; Smith, T.J.; Janssen, J.A.M.J.L. It Takes Two to Tango: IGF-I and TSH Receptors in Thyroid Eye Disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107 (Suppl. 1), S1–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Margetts, M.B.; Venugopal, H.; Menting, J.G.; Kirk, N.S.; Croll, T.I.; Delaine, C.; Forbes, B.E.; Lawrence, M.C. How insulin-like growth factor I binds to a hybrid insulin receptor type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor. Structure 2022, 30, 1098–1108.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, S.; Naik, V.; Hoa, N.; Hwang, C.J.; Afifiyan, N.F.; Sinha Hikim, A.; Gianoukakis, A.G.; Douglas, R.S.; Smith, T.J. Evidence for an Association between Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone and Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Receptors: A Tale of Two Antigens Implicated in Graves’ Disease. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 4397–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.S.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, J.O. Highly ordered clustering of TNFα and BAFF ligand-receptor-intracellular adaptor complexes on a lipid membrane. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.S.; Bixler, S.A.; Qian, F.; Vora, K.; Scott, M.L.; Cachero, T.G.; Hession, C.; Schneider, P.; Sizing, I.D.; Mullen, C.; et al. BAFF-R, a newly identified TNF receptor that specifically interacts with BAFF. Science 2001, 293, 2108–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yu, Y.; Han, H.; Civoli, F.; Thomas, J.; Swanson, S.; Jing, S.; Gupta, S. Development of a Novel BAFF Responsive Cell Line Suitable for Detecting Bioactive BAFF and Neutralizing Antibodies against BAFF-Pathway Inhibiting Therapeutics. Cells 2014, 3, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.S.; Schneider, P.; Kalled, S.L.; Wang, L.; Lefevre, E.A.; Cachero, T.G.; MacKay, F.; Bixler, S.A.; Zafari, M.; Liu, Z.-Y.; et al. BAFF binds to the tumor necrosis factor receptor-like molecule B cell maturation antigen and is important for maintaining the peripheral B cell population. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, M.D.; Reiley, W.; Zhang, M.; Sun, S.C. An atypical tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor-binding motif of B cell-activating factor belonging to the TNF family (BAFF) receptor mediates induction of the noncanonical NF-kappaB signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 10018–10024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boosani, C.S.; Dhar, K.; Agrawal, D.K. Down-regulation of hsa-miR-1264 contributes to DNMT1-mediated silencing of SOCS3. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 42, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.K.; Dhar, K.; Del Core, M.G.; Hunter, W.J.; Hatzoudis, G.I.; Agrawal, D.K. Suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 and intimal hyperplasia in porcine coronary arteries following coronary intervention. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2011, 91, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Nakabayashi, K.; Kawai, T.; Tanigaki, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Hata, K.; Kobayashi, Y. Gene expression and DNA methylation changes in BeWo cells dependent on tumor necrosis factor-α and insulin-like growth factor-I. Hum. Cell. 2020, 33, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Watanabe, M.; Matsushima, M.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Izawa, T.; Nagashima, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Iwashita, M. Synergistic effects of tumor necrosis factor-α and insulin-like growth factor-I on survival of human trophoblast-derived BeWo cell line. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2018, 41, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labandeira-Garcia, J.L.; Costa-Besada, M.A.; Labandeira, C.M.; Villar-Cheda, B.; Rodríguez-Perez, A.I. Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 and Neuroinflammation. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, R.; Sakai, K.; Matsumoto, H.; Iwashita, M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) inhibits insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) activities in human trophoblast cell cultures through IGF-I/insulin hybrid receptors. Endocr. J. 2010, 57, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Soufan, O.; Ewald, J.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Basu, N.; Xia, J. NetworkAnalyst 3.0: A visual analytics platform for comprehensive gene expression profiling and meta-analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W234–W241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Gill, E.E.; Hancock, R.E.W. NetworkAnalyst for statistical, visual and network-based meta-analysis of gene expression data. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 823–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Benner, M.J.; Hancock, R.E.W. NetworkAnalyst-integrative approaches for protein-protein interaction network analysis and visual exploration. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W167–W174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Fjell, C.D.; Mayer, M.L.; Pena, O.M.; Wishart, D.S.; Hancock, R.E.W. INMEX--a web-based tool for integrative meta-analysis of expression data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W63–W70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giai, C.; Gonzalez, C.; Ledo, C.; Garofalo, A.; Di Genaro, M.S.; Sordelli, D.O.; Gomez, M.I. Shedding of Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 1 Induced by Protein A Decreases Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Availability and Inflammation during Systemic Staphylococcus aureus Infection. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 4200–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Seo, M.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Choi, S.H.; Ku, C.R.; Kim, S.; Lee, E.J.; Yoon, J.S. Role of the suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 in the pathogenesis of Graves’ orbitopathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1527275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, T.; Mitoma, H.; Harashima Sichi Tsukamoto, H.; Shimoda, T. Transmembrane TNF-alpha: Structure, function and interaction with anti-TNF agents. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfiore, A.; Frasca, F.; Pandini, G.; Sciacca, L.; Vigneri, R. Insulin Receptor Isoforms and Insulin Receptor/Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor Hybrids in Physiology and Disease. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 586–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaaby, R.; Schäffer, L.; Lautrup-Larsen, I.; Andersen, A.S.; Shaw, A.C.; Mathiasen, I.S.; Brandt, J. Hybrid Receptors Formed by Insulin Receptor (IR) and Insulin-like Growth Factor I Receptor (IGF-IR) Have Low Insulin and High IGF-1 Affinity Irrespective of the IR Splice Variant. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 25869–25874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner-Gati, L.; Berg, K.A.; Gershengorn, M.C. Thyroid-stimulating hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 synergize to elevate 1,2-diacylglycerol in rat thyroid cells. Stimulation of DNA synthesis via interaction between lipid and adenylyl cyclase signal transduction systems. J. Clin. Investig. 1988, 82, 1144–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gómez-Hernández, A.; Escribano, Ó.; Perdomo, L.; Otero, Y.F.; García-Gómez, G.; Fernández, S.; Beneit, N.; Benito, M. Implication of Insulin Receptor A Isoform and IRA/IGF-IR Hybrid Receptors in the Aortic Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation: Role of TNF-α and IGF-II. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 2352–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherajee, S.J.; Fujita, Y.; Rafiq, K.; Nakano, D.; Mori, H.; Masaki, T.; Hara, T.; Kohno, M.; Nishiyama, A.; Hitomi, H. Aldosterone Induces Vascular Insulin Resistance by Increasing Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Receptor and Hybrid Receptor. ATVB 2012, 32, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, J.; Porter, J.; Kroeplien, B.; Norman, T.; Rapecki, S.; Davis, R.; McMillan, D.; Arakaki, T.; Burgin, A.; Fox, D., II; et al. Small molecules that inhibit TNF signalling by stabilising an asymmetric form of the trimer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, D.; Martinez-Fleites, C.; Porter, J.; Fox, D., 3rd; Davis, R.; Mori, P.; Ceska, T.; Carrington, B.; Lawson, A.; Bourne, T.; et al. Structural insights into the disruption of TNF-TNFR1 signalling by small molecules stabilising a distorted TNF. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, X.A.; Sampedro, C.; Cacabelos, R.; Linares, C.; Aleixandre, M.; García-Fantini, M.; Moessler, H. Reduced TNF-α and increased IGF-I levels in the serum of Alzheimer’s disease patients treated with the neurotrophic agent cerebrolysin. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009, 12, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Yadav, P.; Sainis, K.B.; Shankar, B.S. TNF-α and IGF-1 differentially modulate ionizing radiation responses of lung cancer cell lines. Cytokine 2018, 101, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakov, D.; Hall, D.R.; Xia, B.; Porter, K.A.; Padhorny, D.; Yueh, C.; Beglov, D.; Vajda, S. The ClusPro web server for protein–protein docking. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakov, D.; Beglov, D.; Bohnuud, T.; Mottarella, S.E.; Xia, B.; Hall, D.R.; Vajda, S. How good is automated protein docking? Proteins 2013, 81, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, I.T.; Porter, K.A.; Xia, B.; Kozakov, D.; Vajda, S. Performance and Its Limits in Rigid Body Protein-Protein Docking. Structure 2020, 28, 1071–1081.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.; Jindal, A.; Ghani, U.; Kotelnikov, S.; Egbert, M.; Hashemi, N.; Vajda, S.; Padhorny, D.; Kozakov, D. Elucidation of protein function using computational docking and hotspot analysis by ClusPro and FTMap. Acta Crystallogr. D Struct. Biol. 2022, 78, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajda, S.; Yueh, C.; Beglov, D.; Bohnuud, T.; Mottarella, S.E.; Xia, B.; Hall, D.R.; Kozakov, D. New additions to the C lus P ro server motivated by CAPRI. Proteins 2017, 85, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger, L.L.C. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.8; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2015.


| Sl No | Protein 1 (PDB ID) | Protein 2 (PDB ID) | Number of Polar Contacts Between Protein 1 and Protein 2 (Members in Cluster) | Weighted Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | hTNFR1 (1NCF) | hIGF1 (1B9G) | 1 (86) | −848.7 |
| 2. | hTNF-a (1TNF) | hTNFR1 (1NCF) | 14 (61) | −1035.6 |
| 3. | hIGF1R (7XLC) | hIGF1 (1B9G) | 15 (270) | −1072.5 |
| 4. | hTNFR1 (1NCF) | hIGF1R (7XLC) | 29 (47) | −1090.3 |
| 5. | hTNFR1 (1NCF) | mSOCS3 (2BBU, Ch-A) | 6 (128) | −1212.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boosani, C.S.; Subramanyam, P.N.; Jadhav, G.P. Hybrid Receptor-Mediated Molecular Delineations in TNF-α and IGF-1-Induced Costimulatory Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010027
Boosani CS, Subramanyam PN, Jadhav GP. Hybrid Receptor-Mediated Molecular Delineations in TNF-α and IGF-1-Induced Costimulatory Effects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010027
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoosani, Chandra S., Pradeep N. Subramanyam, and Gopal P. Jadhav. 2025. "Hybrid Receptor-Mediated Molecular Delineations in TNF-α and IGF-1-Induced Costimulatory Effects" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010027
APA StyleBoosani, C. S., Subramanyam, P. N., & Jadhav, G. P. (2025). Hybrid Receptor-Mediated Molecular Delineations in TNF-α and IGF-1-Induced Costimulatory Effects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010027






