Amine-Functionalized Maghemite Nanoflowers for Efficient Magnetic Removal of Heavy-Metal-Adsorbed Algae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
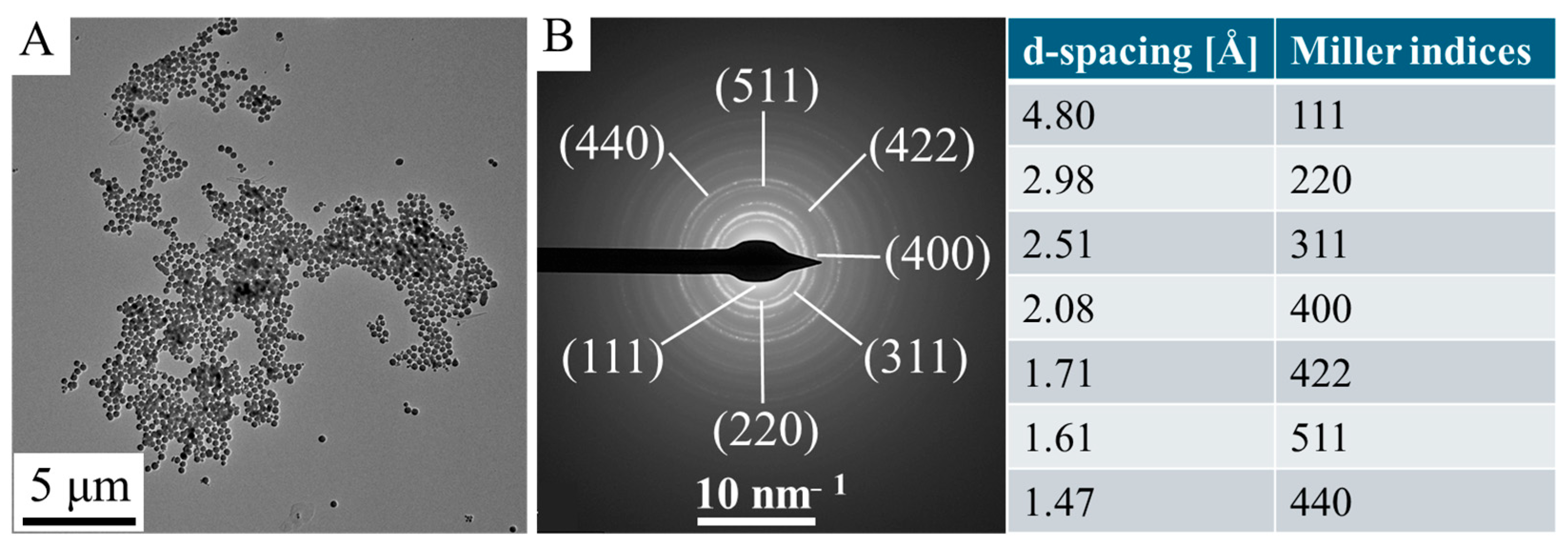
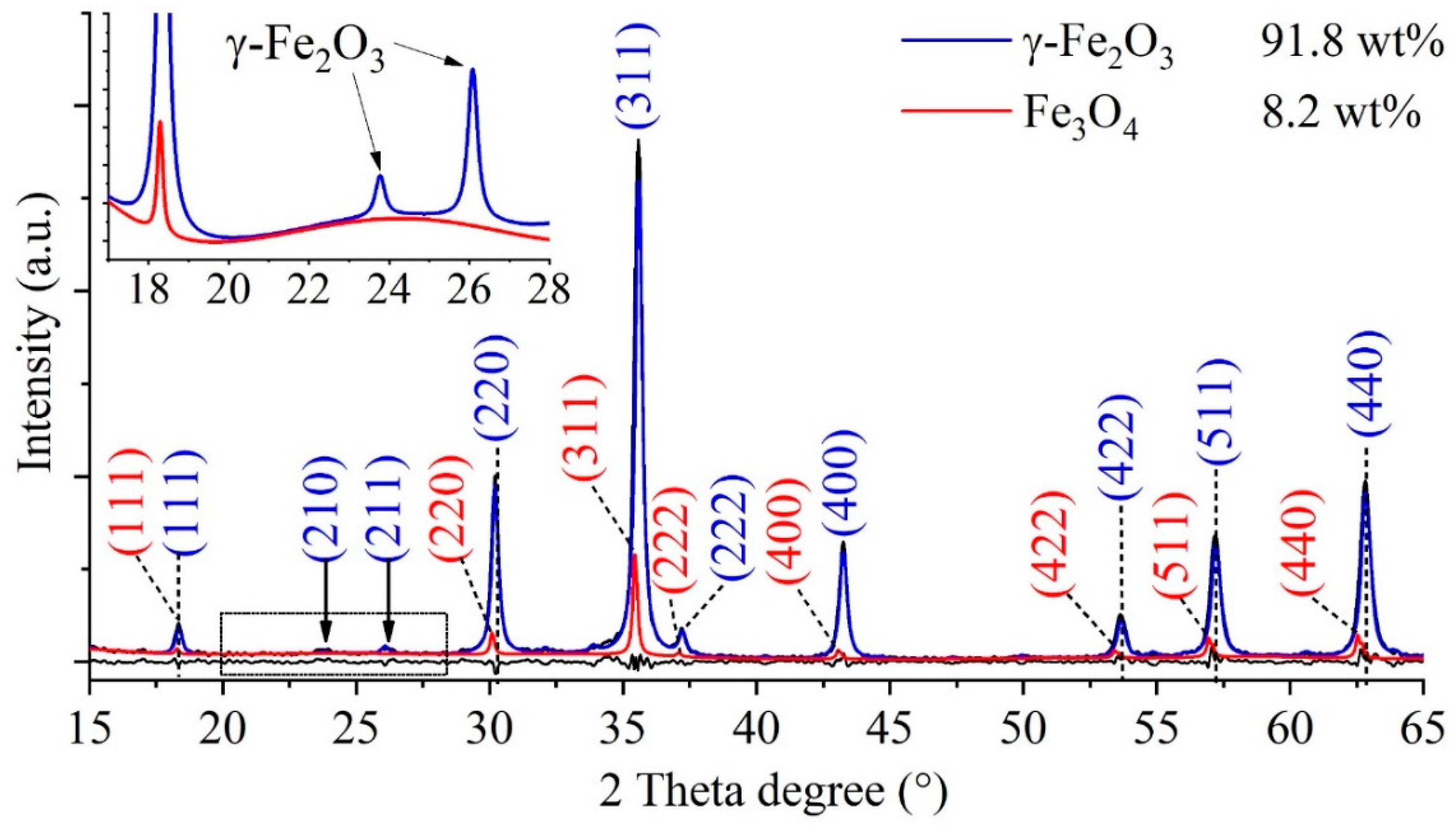
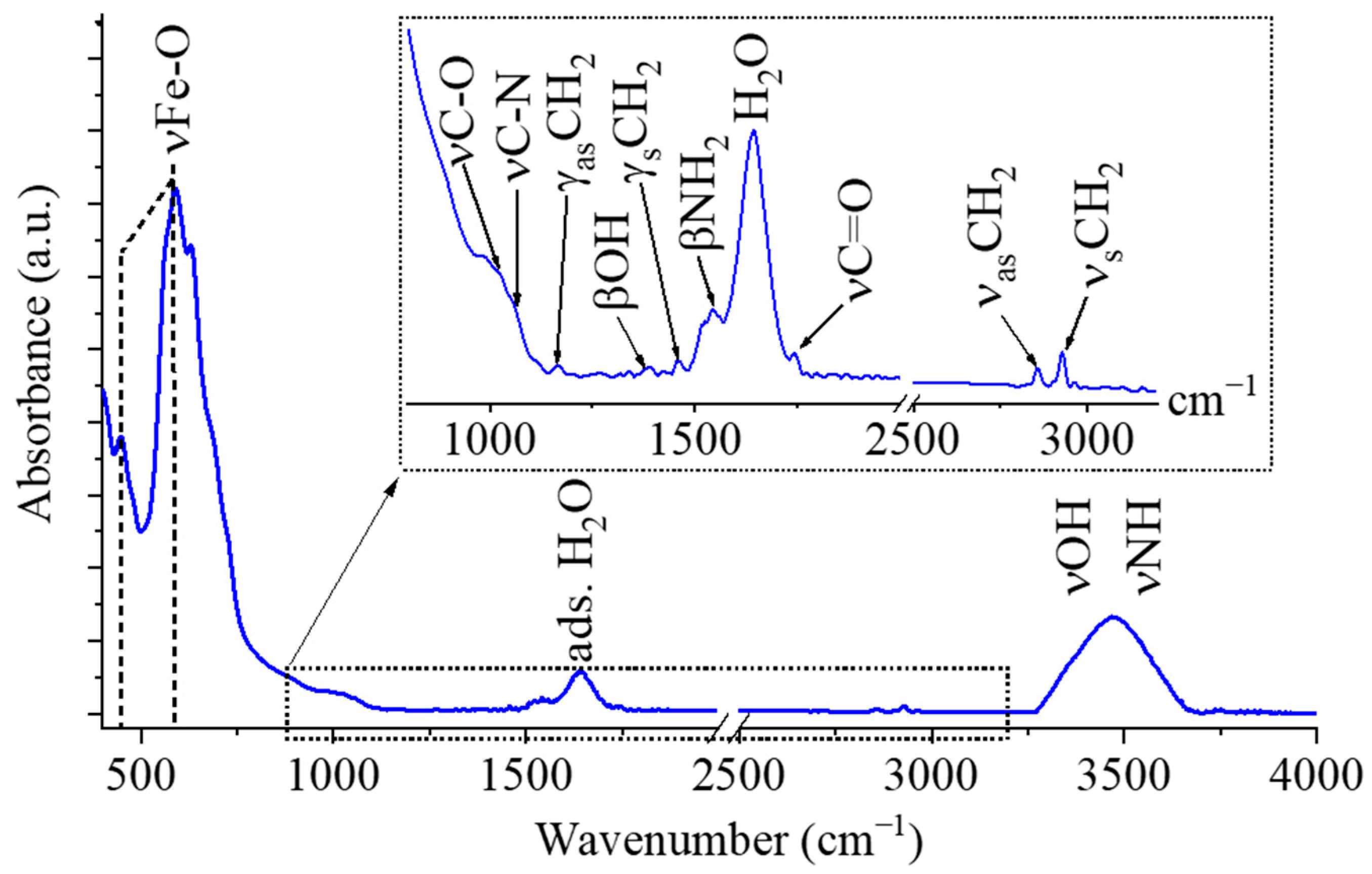
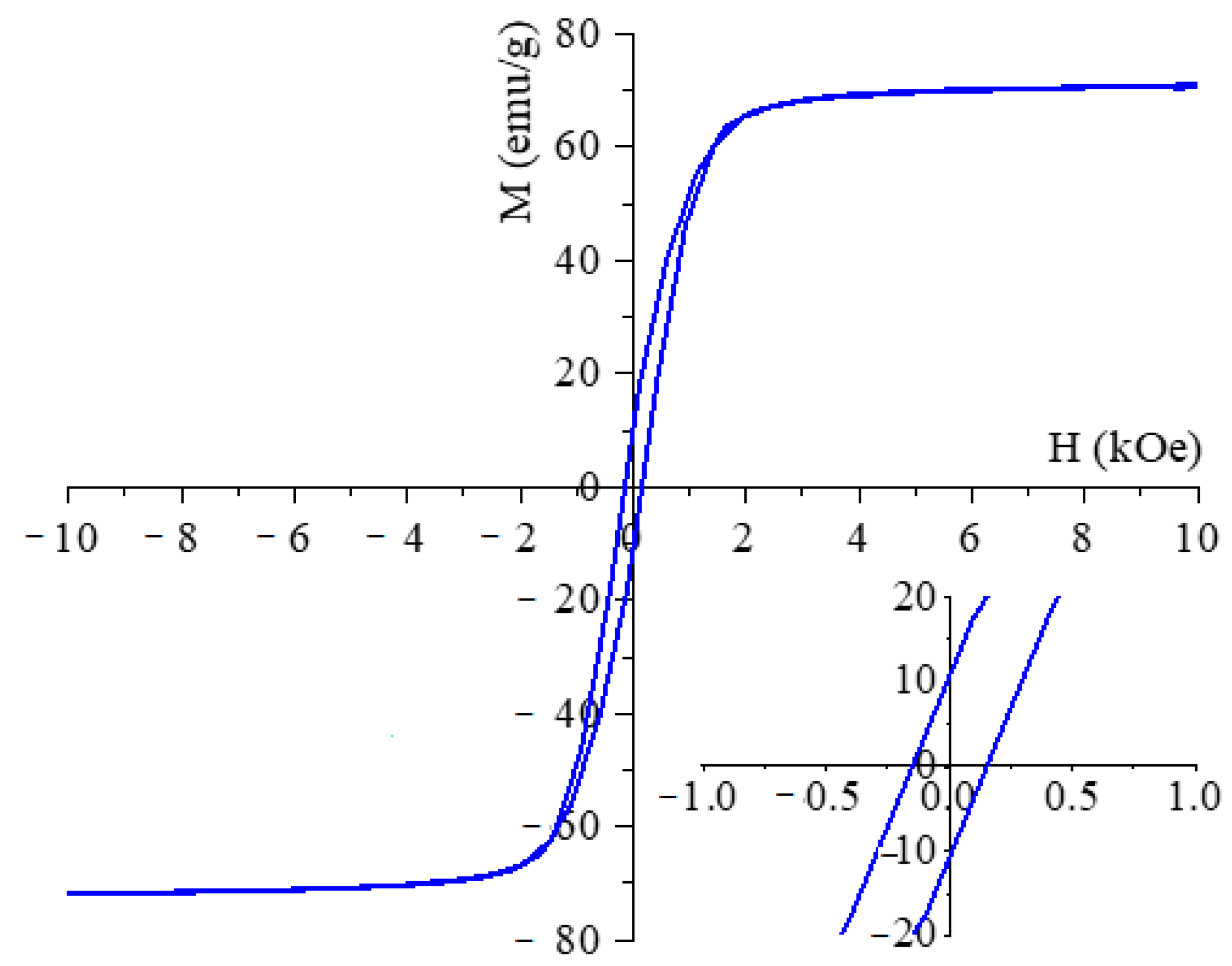
2.1. Characterization of the Maghemite Nanoflowers
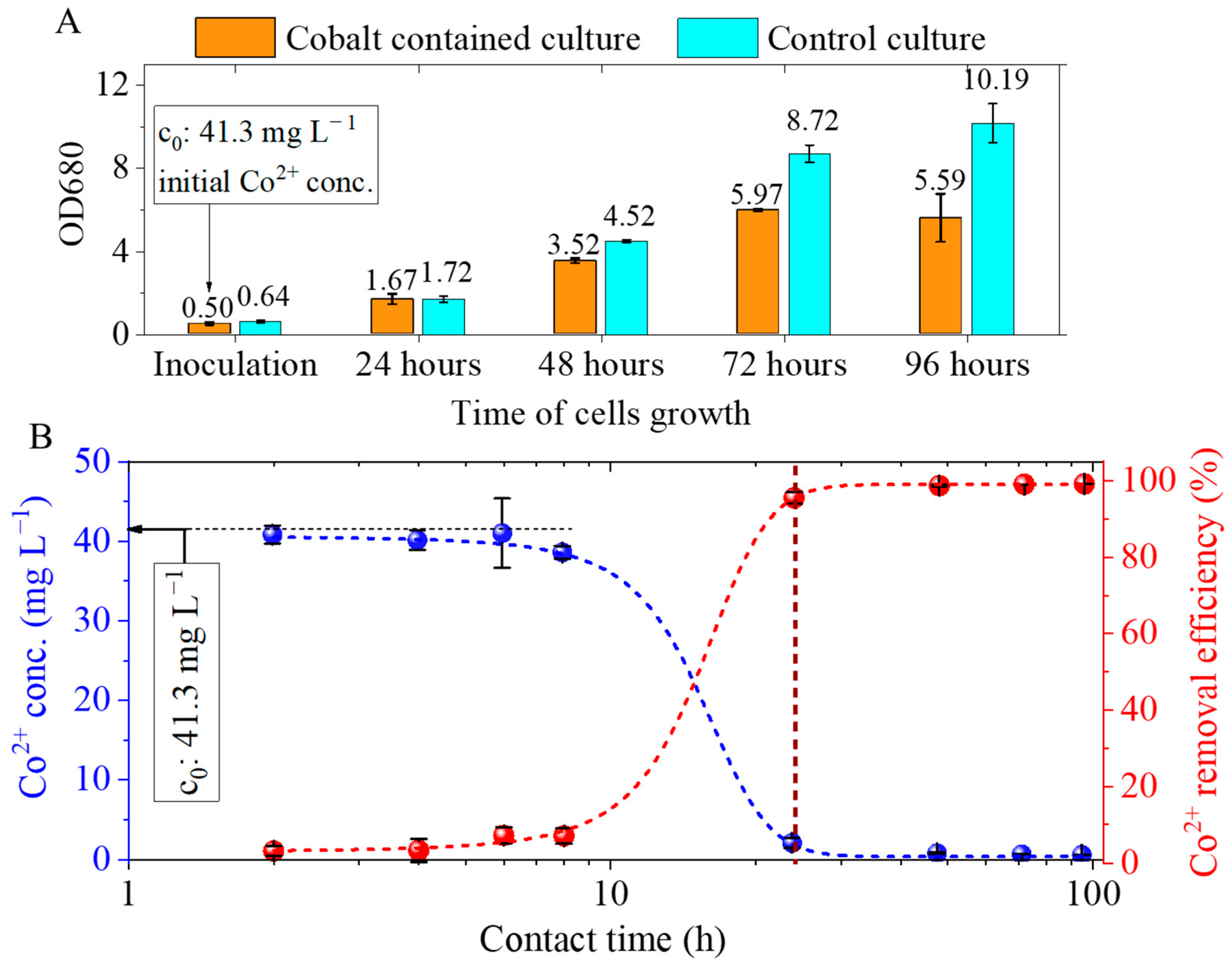
2.2. Results of the Cobalt Adsorption Tests Using Chlorella vulgaris
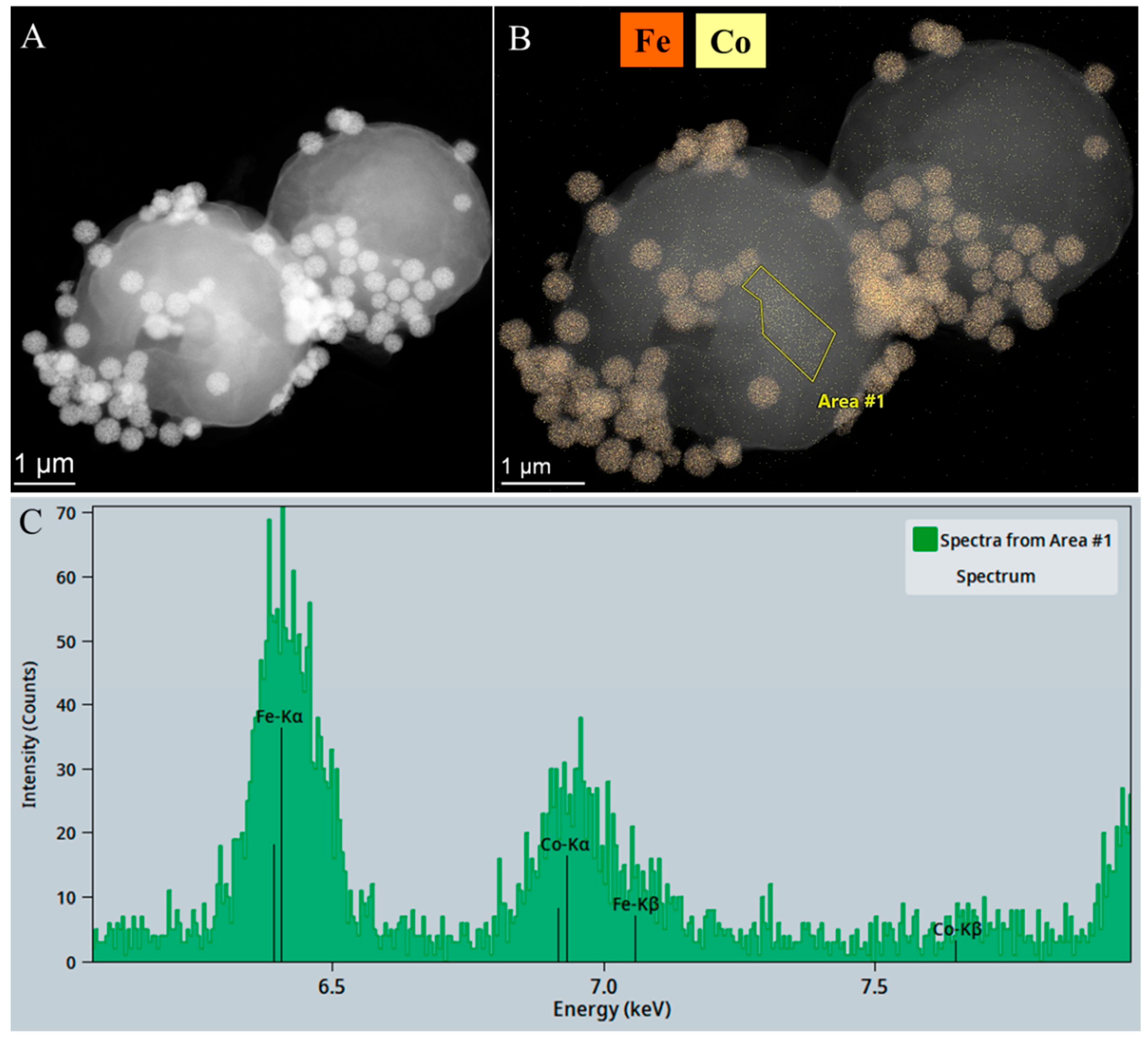
2.3. Results of Magnetic Separation of Cobalt-Adsorbed Chlorella vulgaris
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of the Amine-Functionalized Maghemite Nanoflowers
3.3. Cobalt Adsorption Tests
3.4. Magnetic Separation Tests of the Cobalt-Bonded Algae
3.5. Characterization Techniques
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HRTM | High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| VSM | Vibrating Sample Magnetometry |
| NMC | Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide |
| NCA | Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide |
| LMO | Lithium Manganese Oxide |
| PDDA | Poly diallyldimethylammonium chloride |
| PEI | Polyethylenimine |
| APTES | 3-aminopropyl triethoxysilane |
| SAED | Selected Area Electron Diffraction |
| HAADF | High-Angle Annular Dark-Field |
| ICP-AES | Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometry |
References
- Battery University. Types of Lithium-Ion. Available online: https://batteryuniversity.com/article/bu-205-types-of-lithium-ion (accessed on 9 September 2025).
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metal Toxicity and the Environment. Mol. Clin. Environ. Toxicol. 2012, 101, 133–164. [Google Scholar]
- Gunatilake, S.K. Methods of Removing Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewater. J. Multidiscip. Eng. Sci. Stud. 2015, 1, 12–18, ISSN 2912-1309. [Google Scholar]
- Barakat, M.A. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2011, 4, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, E.A.; Al-Gheethi, A.A.; Al-Sahari, M.; Yashni, G.; Mohamed, R.M.S.R.; Soon, C.F.; Nguyen, H.-H.T.; Vo, D.-V.N. An insight into microelectronics industry wastewater treatment, current challenges, and future perspectives: A critical review. Appl. Water Sci. 2024, 14, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.; Scheufele, F.B.; Espinoza-Quiñones, F.R.; Módenes, A.N.; Vieira, M.G.A.; Kroumov, A.D.; Borba, C.E. A comprehensive evaluation of heavy metals removal from battery industry wastewaters by applying bio-residue, mineral and commercial adsorbent materials. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 7976–7995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzano, S.; Sardo, A.; Blasio, M.; Chahine, T.B.; Dell’aNno, F.; Sansone, C.; Brunet, C. Microalgal Metallothioneins and Phytochelatins and Their Potential Use in Bioremediation. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, E.R.S.; Nuravivah, R. Potential Of Microalgae Chlorella vulgaris As Bioremediation Agents of Heavy Metal Pb (Lead) On Culture Media. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 31, 05010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Yang, C.; Xia, L.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, L.; Cao, H.; Tao, Y. Protoplast Preparation for Algal Single-Cell Omics Sequencing. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 538. [Google Scholar]
- Veglio, F.; Beolchini, F. Removal of Metals by Biosorption: A Review. Hydrometallurgy 1997, 44, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kőnig-Péter, A.; Kilár, F.; Felinger, A.; Pernyeszi, T. Biosorption characteristics of Spirulina and Chlorella cells to accumulate heavy metals. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2015, 80, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahalya, N.; Ramachandra, T.V.; Kanamadi, R.D. Biosorption of Heavy Metals. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 2003, 7, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelfattah, A.; Ali, S.S.; Ramadan, H.; El-Aswar, E.I.; Eltawab, R.; Ho, S.-H.; Elsamahy, T.; Li, S.; El-Sheekh, M.M.; Schagerl, M.; et al. Microalgae-based wastewater treatment: Mechanisms, challenges, recent advances, and future prospects. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnology 2023, 13, 100205. [Google Scholar]
- Markeb, A.A.; Llimós-Turet, J.; Ferrer, I.; Blánquez, P.; Alonso, A.; Sánchez, A.; Moral-Vico, J.; Font, X. The use of magnetic iron oxide based nanoparticles to improve microalgae harvesting in real wastewater. Water Res. 2019, 159, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procházková, G.; Podolová, N.; Safarik, I.; Zachleder, V.; Brányik, T. Physicochemical approach to freshwater microalgae harvesting with magnetic particles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 112, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Suh, H.; Chang, T. Rapid Removal of Green Algae by the Magnetic Method. Environ. Eng. Res. 2012, 17, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos Guivar, J.A.; Sadrollahi, E.; Menzel, D.; Fernandes, E.G.R.; López, E.O.; Torres, M.M.; Arsuaga, J.M.; Arencibia, A.; Litterst, F.J. Magnetic, structural and surface properties of functionalized maghemite nanoparticles for copper and lead adsorption. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 28763–28779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meftah, S.; Ngo, A.-T.; Bouteiller, L.; Russier, V.; Hrabovsky, D.; Konaté, A.; Kondo, D.; Bedoui, F.; Lisiecki, I. Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of Spherical Maghemite Nanoparticles with Tunable Size and Surface Chemistry. Langmuir. 2024, 40, 22673–22683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teja, A.S.; Koh, P.Y. Synthesis, properties, and applications of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater. 2009, 55, 22–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchma, E.A.; Zolotukhin, P.V.; Belanova, A.A.; Soldatov, M.A.; Kozakov, A.T.; Kubrin, S.P.; Polozhentsev, O.E.; Medvedev, P.V.; Soldatov, A.V. Effect of synthesis conditions on local atomic structure and properties of low-toxic maghemite nanoparticles for local magnetic hyperthermia in oncology. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2022, 24, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhang, Y.W.; Liao, C.S.; Yan, C.H.; Chen, L.Y.; Wang, S.Y. Rare-earth-mediated magnetism and magneto-optical Kerr effects in nanocrystalline CoFeMn0.9RE0.1O4 thin films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 280, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavan, Y.; Hosseini, S.H.; Olazar, M. A Note on an Integrated Process of Methane Steam Reforming in Junction with Pressure-Swing Adsorption to Produce Pure Hydrogen: Mathematical Modeling. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 12937–12947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strazisar, B.R.; Anderson, R.R.; White, C.M. Degradation Pathways for Monoethanolamine in a CO2 Capture Facility. Energy Fuels 2003, 17, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melhi, S. Amine-Terminated Modified Succinic Acid-Magnetite Nanoparticles for Effective Removal of Malachite Green Dye from Aqueous Environment. Crystals 2023, 13, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.N.; Hettiarachchi, E.; Grassian, V.H. Monoethanolamine adsorption on oxide surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 614, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Su, W.; Tan, M. Endogenous fluorescence carbon dots derived from food items. Innovation 2020, 1, 100009. [Google Scholar]
- Bruce, I.J.; Taylor, J.; Todd, M.; Davies, M.J.; Borioni, E.; Sangregorio, C.; Sen, T. Synthesis, characterisation and application of silica magnetite nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 284, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuryono, N.; Rosiati, N.M.; Rusdiarso, B.; Sakti, S.C.W.; Tanaka, S. Coating of magnetite with mercapto modified rice hull ash silica in a one-pot process. SpringerPlus 2014, 3, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dib, F.I.; Mohamed, D.E.; El-Shamy, O.A.; Mishrif, M.R. Study the adsorption properties of magnetite nanoparticles in the presence of different synthesized surfactants for heavy metal ions removal. Egypt. J. Pet. 2020, 29, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresco, P.A.; Zaitsev, V.S.; Gambino, R.J.; Chu, B. Preparation and Properties of Magnetite and Polymer Magnetite Nanoparticles. Langmuir 1999, 15, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Hou, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Yuan, L.; Han, D.; Hu, Q.; Jin, H. Heterotrophically Ultrahigh-Cell-Density Cultivation of a High Protein-Yielding Unicellular Alga Chlorella With a Novel Nitrogen-Supply Strategy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 774854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Rana, N. Particle Size and Shape Analysis using Imagej with Customized Tools for Segmentation of Particles. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2015, 4, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickels, M.; Liedberg, B.; Gunnarsson, K.-L. Functionalization of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with a Versatile Epoxy-Amine Linker. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 4776–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondarenko, L.S.; Kovel, E.S.; Kydralieva, K.A.; Dzhardimalieva, G.I.; Illés, E.; Tombácz, E.; Kicheeva, A.G.; Kudryasheva, N.S. Effects of Modified Magnetite Nanoparticles on Bacterial Cells and Enzyme Reactions. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papan Djaniš, J.; Prinčič, G.G.; Mavrič, A.; Mertelj, A.; Iskra, J.; Lisjak, D. New Insights into Amino-Functionalization of Magnetic Nanoplatelets with Silanes and Phosphonates. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; An, G.S. Optimizing Amine Functionalization of Maghemite Nanoparticles through Controlled Hydroxylation and Silica Interlayer Engineering. Processes 2025, 13, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lata, S.; Singh, P.K.; Samadder, S.R. Regeneration of adsorbents and recovery of heavy metals: A review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 1461–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskar, A.V.; Bolan, N.; Hoang, S.A.; Sooriyakumar, P.; Kumar, M.; Singh, L.; Jasemizad, T.; Padhye, L.P.; Singh, G.; Vinu, A.; et al. Recovery, regeneration and sustainable management of spent adsorbents from wastewater treatment streams: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fóris, T.; Koska, P.; Ilosvai, Á.M.; Gráczer, K.; Kristály, F.; Daróczi, L.; Nagy, M.; Viskolcz, B.; Vanyorek, L. Amine-Functionalized Maghemite Nanoflowers for Efficient Magnetic Removal of Heavy-Metal-Adsorbed Algae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010010
Fóris T, Koska P, Ilosvai ÁM, Gráczer K, Kristály F, Daróczi L, Nagy M, Viskolcz B, Vanyorek L. Amine-Functionalized Maghemite Nanoflowers for Efficient Magnetic Removal of Heavy-Metal-Adsorbed Algae. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleFóris, Tímea, Péter Koska, Ágnes Maria Ilosvai, Kitti Gráczer, Ferenc Kristály, Lajos Daróczi, Miklós Nagy, Béla Viskolcz, and László Vanyorek. 2025. "Amine-Functionalized Maghemite Nanoflowers for Efficient Magnetic Removal of Heavy-Metal-Adsorbed Algae" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010010
APA StyleFóris, T., Koska, P., Ilosvai, Á. M., Gráczer, K., Kristály, F., Daróczi, L., Nagy, M., Viskolcz, B., & Vanyorek, L. (2025). Amine-Functionalized Maghemite Nanoflowers for Efficient Magnetic Removal of Heavy-Metal-Adsorbed Algae. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010010





