Molecular and Proteomic Analyses of Effects of Cadmium Exposure on the Silk Glands of Trichonephila clavata
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cadmium Accumulation in Spiders and Silk Glands
2.2. Concentrations of Oxidative Stress Markers
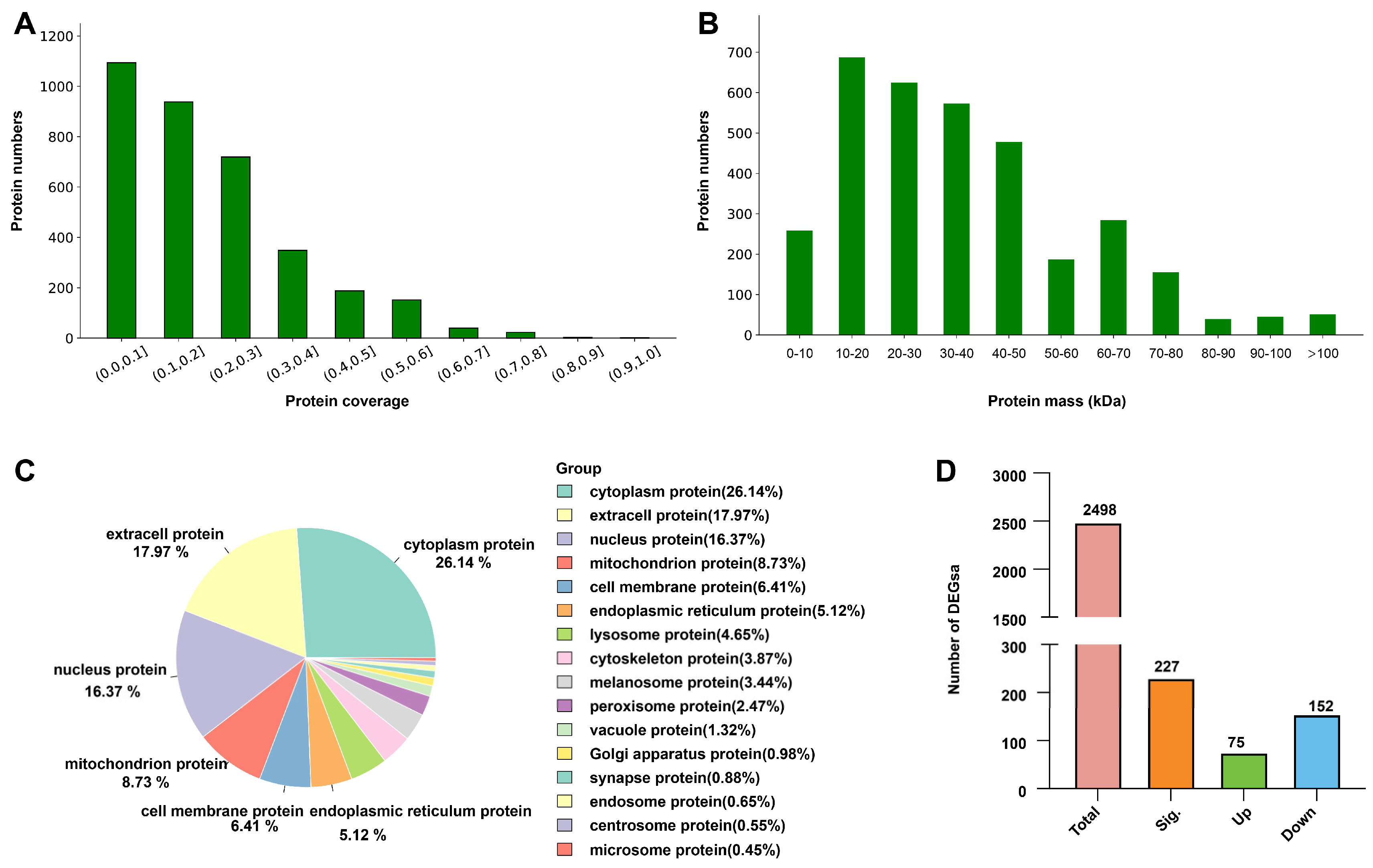
2.3. Proteomic Analysis of Spider Silk Glands
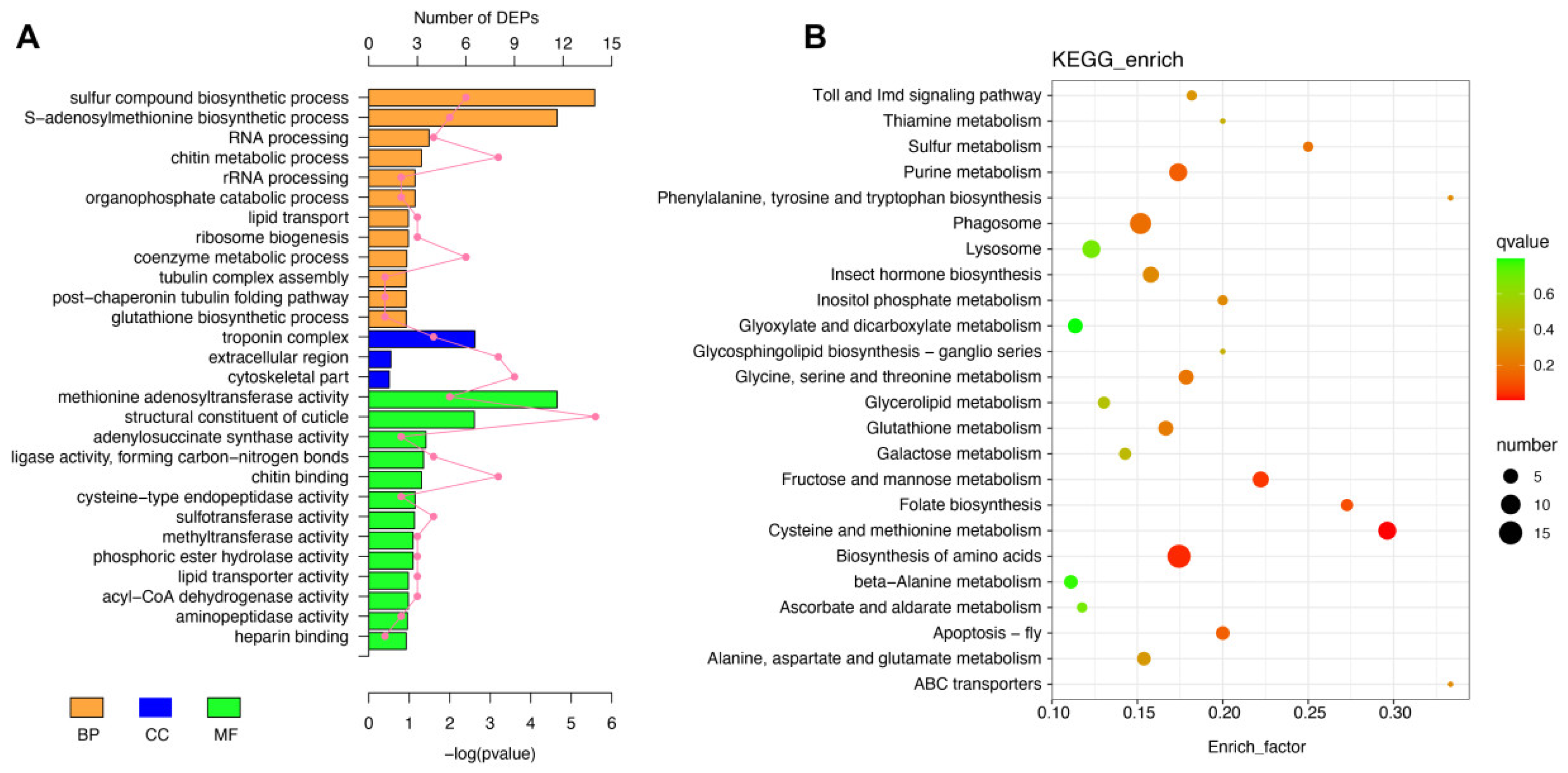
2.4. GO and KEGG Functional Annotation of Differentially Expressed Proteins
2.5. Metabolic and Stress Response Disruptions in Spider Silk Glands
2.6. Gene Expression Analysis by qPCR
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Spider Preparation
4.2. Cadmium Determination
4.3. Enzymatic Concentration Determination
4.4. Proteomic Analysis
4.5. RT-qPCR Analysis
4.6. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masindi, V.; Muedi, K.L. Environmental contamination by heavy metals. Heavy Met. 2018, 10, 115–133. [Google Scholar]
- Dharma-Wardana, M. Fertilizer usage and cadmium in soils, crops and food. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2739–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubier, A.; Wilkin, R.T.; Pichler, T. Cadmium in soils and groundwater: A review. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 108, 104388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, T.L. Cadmium and phosphorous fertilizers: The issues and the science. Procedia Eng. 2014, 83, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Lauria, G.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A. The effects of cadmium toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, M.T.; Nauman, M.; Nazir, N.; Ali, S.; Bangash, N. Environmental hazards of cadmium: Past, present, and future. In Cadmium Toxicity and Tolerance in Plants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 163–183. [Google Scholar]
- Rani, A.; Kumar, A.; Lal, A.; Pant, M. Cellular mechanisms of cadmium-induced toxicity: A review. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2014, 24, 378–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Ravindran, G.; Krishnamurthy, V. A brief review on the effect of cadmium toxicity: From cellular to organ level. Int. J. Biotechnol. Res. 2013, 3, 17–36. [Google Scholar]
- Cribiu, P.; Devaux, A.; Garnero, L.; Abbaci, K.; Bastide, T.; Delorme, N.; Quéau, H.; Degli Esposti, D.; Ravanat, J.-L.; Geffard, O. A “population dynamics” perspective on the delayed life-history effects of environmental contaminations: An illustration with a preliminary study of cadmium transgenerational effects over three generations in the Crustacean Gammarus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musah, B.I. Effects of heavy metals and metalloids on plant-animal interaction and biodiversity of terrestrial ecosystems—An overview. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.L.; Gustafson, A.-L.; Andersson, M.; Hellman, B.; Dencker, L. Cadmium-induced changes in apoptotic gene expression levels and DNA damage in mouse embryos are blocked by zinc. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 76, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hao, S.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, W.; Wu, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, X. Cadmium disrupts the DNA damage response by destabilizing RNF168. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 133, 110745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, N.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.Y. Structural origin of the strain-hardening of spider silk. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nimmen, E.; Gellynck, K.; Van Langenhove, L. The tensile behaviour of spider silk. Autex Res. J. 2005, 5, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollrath, F.; Porter, D. Spider silk as a model biomaterial. Appl. Phys. A 2006, 82, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-Garhwal, S.M.; Babb, P.L.; Voight, B.F.; Hayashi, C.Y. Golden orb-weaving spider (Trichonephila clavipes) silk genes with sex-biased expression and atypical architectures. G3 2021, 11, jkaa039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lee, S.-M.; Ku, B.-J.; Moon, M.-J. Fine structural aspects on the web glue production in the golden orb-web spider Trichonephila clavata. Anim. Cells Syst. 2023, 27, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackledge, T.A.; Kuntner, M.; Agnarsson, I. The form and function of spider orb webs: Evolution from silk to ecosystems. In Advances in Insect Physiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 41, pp. 175–262. [Google Scholar]
- dos Santos-Pinto, J.R.A.; Esteves, F.G.; Sialana, F.J.; Ferro, M.; Smidak, R.; Rares, L.C.; Nussbaumer, T.; Rattei, T.; Bilban, M.; Júnior, M.B. A proteotranscriptomic study of silk-producing glands from the orb-weaving spiders. Mol. Omics 2019, 15, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foelix, R. Biology of Spiders; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, C.L.; Hsu, M.; Kaplan, D.; Pierce, N. A comparison of the composition of silk proteins produced by spiders and insects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1999, 24, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczek, G.; Karcz, J.; Putko, A.; Kędziorski, A.; Wilczek, P.; Stalmach, M.; Szulińska, E. The effect of ingested cadmium on the calorific value and structural properties of hunting webs produced by Steatoda grossa (Theridiidae) spiders. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczek, G.; Surmiak, K.; Wawszczak, B.; Sajewicz, M.; Kowalska, T.; Sindera, P.; Wiśniewska, K.; Szulinska, E. Effect of long-term cadmium and copper intoxication on the efficiency of ampullate silk glands in false black widow Steatoda grossa (Theridiidae) spiders. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 224, 108564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Vasanthavada, K.; Kohler, K.; McNary, S.; Moore, A.; Vierra, C. Molecular mechanisms of spider silk. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2006, 63, 1986–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluge, J.A.; Rabotyagova, O.; Leisk, G.G.; Kaplan, D.L. Spider silks and their applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Shao, H.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y. Reinforced and ultraviolet resistant silks from silkworms fed with titanium dioxide nanoparticles. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2551–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janani, G.; Kumar, M.; Chouhan, D.; Moses, J.C.; Gangrade, A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Mandal, B.B. Insight into silk-based biomaterials: From physicochemical attributes to recent biomedical applications. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 5460–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-j.; Zhou, X.-w.; Li, Z.-z.; Lyu, B. Metabolome analysis reveals the toxic effects of cadmium exposure on the egg sac of spider Pardosa pseudoannulata. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 249, 114459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-C.; Li, G.-Y.; Yun, Y.-L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.-T.; Peng, Y. The effects of cadmium exposure on fitness-related traits and antioxidant responses in the wolf spider, Pardosa pseudoannulata. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 97, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobe, G.; Crane, D. Mitochondria, reactive oxygen species and cadmium toxicity in the kidney. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 198, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, K.I.; Naeem, M.; Castroverde, C.D.M.; Kalaji, H.M.; Albaqami, M.; Aftab, T. Molecular mechanisms of nitric oxide (NO) signaling and reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis during abiotic stresses in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsal, V.; Dalkıran, T.; Çiçek, M.; Kölükçü, E. The role of natural antioxidants against reactive oxygen species produced by cadmium toxicity: A review. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 10, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Peng, Y.; Tian, J.; Wang, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, Z. Spiders as excellent experimental models for investigation of heavy metal impacts on the environment: A review. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeoye, O.; Olawumi, J.; Opeyemi, A.; Christiania, O. Review on the role of glutathione on oxidative stress and infertility. JBRA Assist. Reprod. 2018, 22, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallinger, R. Strategies of metal detoxification in terrestrial invertebrates. Ecotoxicol. Met. Invertebr. 1993, 245, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Wilczek, G.; Babczyńska, A.; Wilczek, P.; Doleżych, B.; Migula, P.; Młyńska, H. Cellular stress reactions assessed by gender and species in spiders from areas variously polluted with heavy metals. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 70, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, B.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Song, Q.-s. Integrated transcriptome and proteome unveiled distinct toxicological effects of long-term cadmium pollution on the silk glands of Pardosa pseudoannulata. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozougwu, J.C. The role of reactive oxygen species and antioxidants in oxidative stress. Int. J. Res. 2016, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Circu, M.L.; Aw, T.Y. Reactive oxygen species, cellular redox systems, and apoptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lian, G. ROS and diseases: Role in metabolism and energy supply. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 467, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Branicky, R.; Noë, A.; Hekimi, S. Superoxide dismutases: Dual roles in controlling ROS damage and regulating ROS signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Xiang, X.; Liu, W.; Zeng, Z. Transcriptomic and metabolomic profiles of Pirata subpiraticus in response to copper exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 279, 116498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczek, G.; Babczyńska, A.; Wilczek, P. Antioxidative responses in females and males of the spider Xerolycosa nemoralis (Lycosidae) exposed to natural and anthropogenic stressors. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 157, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-z.; Zhou, X.-w.; Chen, L.-j. Transcriptomic analysis of cadmium toxicity and molecular response in the spiderling of Pirata subpiraticus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 261, 109441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witt, P.N.; Reed, C.F.; Peakall, D.B.; Witt, P.N.; Reed, C.F.; Peakall, D.B. The Silk Glands. In A Spider’s Web: Problems in Regulatory Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1968; pp. 5–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.; Xiao, H.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yang, D. Effects of cadmium stress on growth and amino acid metabolism in two Compositae plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 158, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Qi, X. Tryptophan pretreatment adjusts transcriptome and metabolome profiles to alleviate cadmium toxicity in Arabidopsis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Aso, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Banno, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tsuchida, K.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Fujii, H. Proteome analysis of silk gland proteins from the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Proteomics 2006, 6, 2586–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Zhu, Q.-L.; Zheng, J.-L.; Wen, Z.-Y. Cadmium induced oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and apoptosis with compensative responses towards the up-regulation of ribosome, protein processing in the ER, and protein export pathways in the liver of zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 242, 106023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Qi, Z.; Hou, H.; Gao, J.; Zhang, X.-X. Effects of chronic cadmium exposure at food limitation-relevant levels on energy metabolism in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.; Holm, L.; Ridderstrale, Y.; Johansson, J.; Rising, A. Morphology and composition of the spider major ampullate gland and dragline silk. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 2945–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, S.; Kaplan, D.L. Molecular biology of spider silk. Rev. Mol. Biotechnol. 2000, 74, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB2762-2017; China Releases the Standard for Maximum Levels of Contaminants in Foods. Office of Agricultural Affairs: Beijing, China, 2023.
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Z.; Song, Z.; Liu, W.; Lyu, B. Molecular and Proteomic Analyses of Effects of Cadmium Exposure on the Silk Glands of Trichonephila clavata. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020754
Song Z, Song Z, Liu W, Lyu B. Molecular and Proteomic Analyses of Effects of Cadmium Exposure on the Silk Glands of Trichonephila clavata. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(2):754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020754
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Zhaowentao, Zhiyu Song, Wei Liu, and Bo Lyu. 2025. "Molecular and Proteomic Analyses of Effects of Cadmium Exposure on the Silk Glands of Trichonephila clavata" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 2: 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020754
APA StyleSong, Z., Song, Z., Liu, W., & Lyu, B. (2025). Molecular and Proteomic Analyses of Effects of Cadmium Exposure on the Silk Glands of Trichonephila clavata. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(2), 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020754



