CTCF Mediates the Cis-Regulatory Hubs in Mouse Hearts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
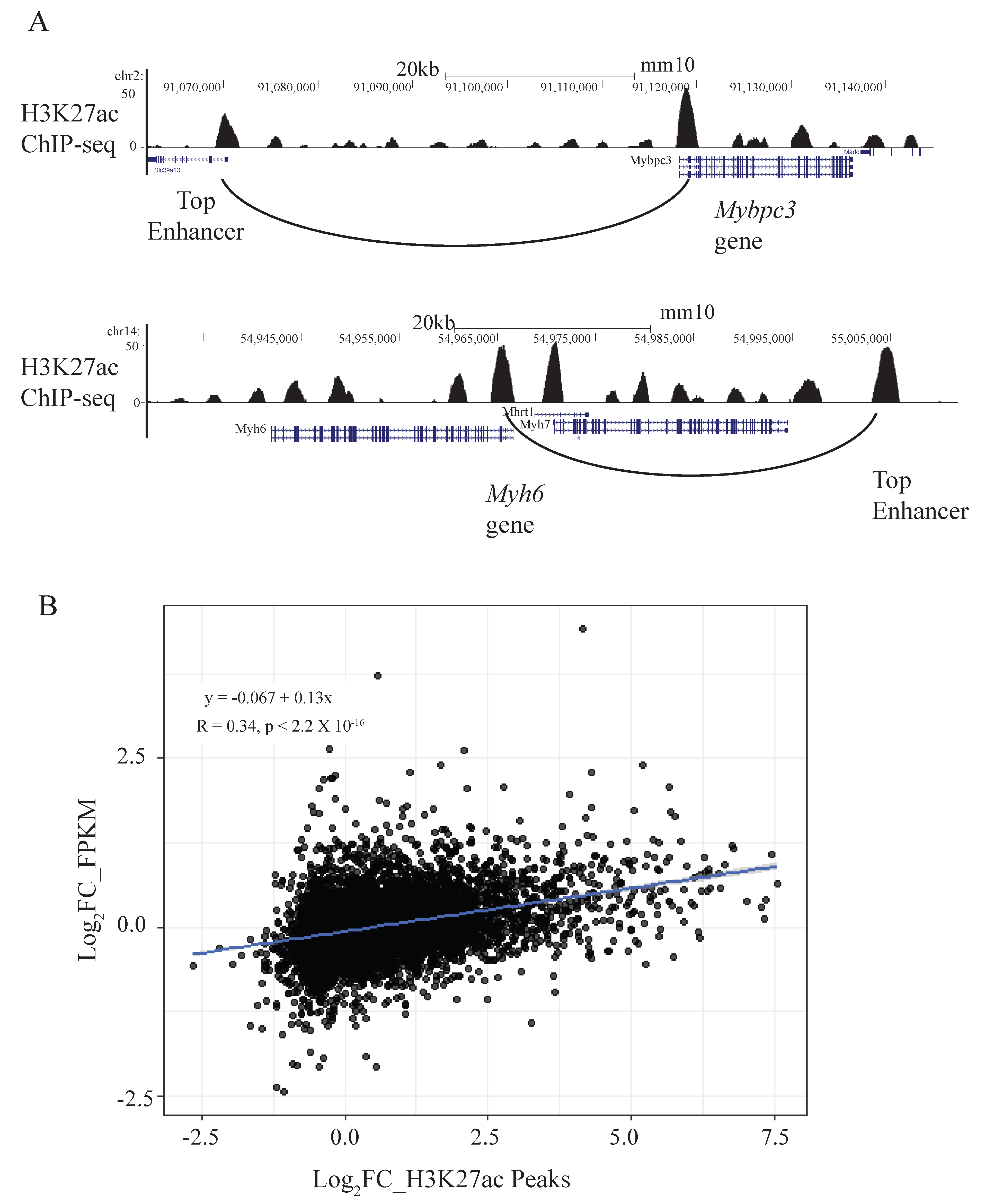
2.1. Mouse Cardiomyocyte Enhancer Landscape Identified Through Activity-by-Contact Algorithm
2.2. Loss of CTCF Leads to Changes in the Enhancer Interactome and Changes in the ABC Scores of Putative Enhancers
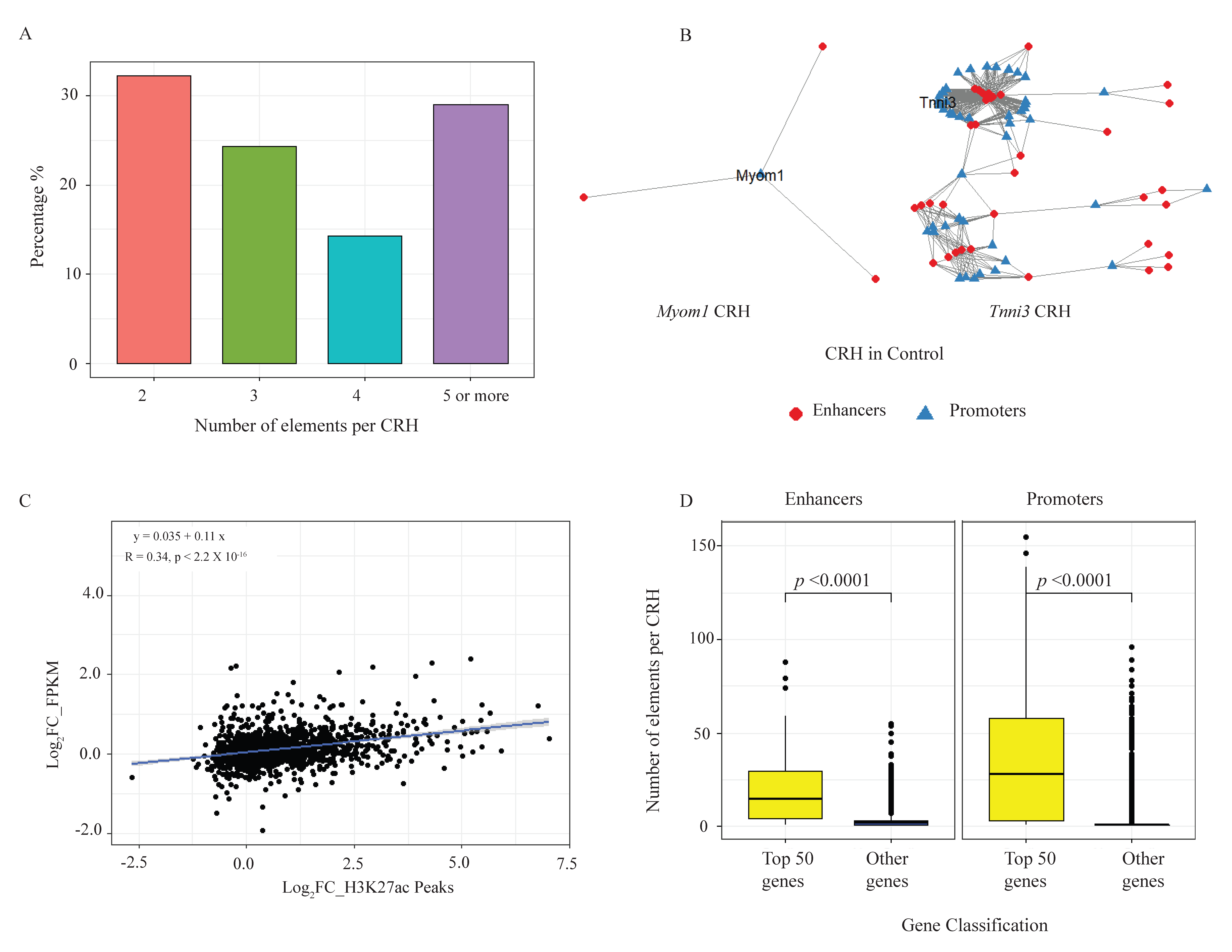
2.3. Loss of CTCF Alters the Cis-Regulatory Hubs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Experiments
4.2. H3k27ac HiChip Library Prep and Data Analysis
4.3. RNA-Seq
4.4. Chip-Seq Experiment
4.5. ATAC-Seq Experiment and Analysis
4.6. ChIP-Seq and ATAC-Seq Data Analysis
4.7. ABC-Score and CRH Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maurano, M.T.; Humbert, R.; Rynes, E.; Thurman, R.E.; Haugen, E.; Wang, H.; Reynolds, A.P.; Sandstrom, R.; Qu, H.; Brody, J.; et al. Systematic localization of common disease-associated variation in regulatory DNA. Science 2012, 337, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boix, C.A.; James, B.T.; Park, Y.P.; Meuleman, W.; Kellis, M. Regulatory genomic circuitry of human disease loci by integrative epigenomics. Nature 2021, 590, 300–307, Erratum in Nature 2025, 643, E11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulco, C.P.; Nasser, J.; Jones, T.R.; Munson, G.; Bergman, D.T.; Subramanian, V.; Grossman, S.R.; Anyoha, R.; Doughty, B.R.; Patwardhan, T.A.; et al. Activity-by-contact model of enhancer-promoter regulation from thousands of CRISPR perturbations. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1664–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Liang, J.; Ozer, A.; Leung, A.K.; Lis, J.T.; Yu, H. A comparison of experimental assays and analytical methods for genome-wide identification of active enhancers. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1056–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anene-Nzelu, C.G.; Lee, M.C.J.; Tan, W.L.W.; Dashi, A.; Foo, R.S.Y. Genomic enhancers in cardiac development and disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 19, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasperini, M.; Tome, J.M.; Shendure, J. Towards a comprehensive catalogue of validated and target-linked human enhancers. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 292–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, S.; Truty, R.M.; Pollard, K.S. Enhancer-promoter interactions are encoded by complex genomic signatures on looping chromatin. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Shen, H.; Laird, P.W.; Farnham, P.J.; Berman, B.P. Inferring regulatory element landscapes and transcription factor networks from cancer methylomes. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexanian, M.; Przytycki, P.F.; Micheletti, R.; Padmanabhan, A.; Ye, L.; Travers, J.G.; Gonzalez-Teran, B.; Silva, A.C.; Duan, Q.; Ranade, S.S.; et al. A transcriptional switch governs fibroblast activation in heart disease. Nature 2021, 595, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangoul, H.; Altshuler, D.; Cappellini, M.D.; Chen, Y.S.; Domm, J.; Eustace, B.K.; Foell, J.; de la Fuente, J.; Grupp, S.; Handgretinger, R.; et al. CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing for Sickle Cell Disease and beta-Thalassemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matharu, N.; Rattanasopha, S.; Tamura, S.; Maliskova, L.; Wang, Y.; Bernard, A.; Hardin, A.; Eckalbar, W.L.; Vaisse, C.; Ahituv, N. CRISPR-mediated activation of a promoter or enhancer rescues obesity caused by haploinsufficiency. Science 2019, 363, 6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giammartino, D.C.; Kloetgen, A.; Polyzos, A.; Liu, Y.; Kim, D.; Murphy, D.; Abuhashem, A.; Cavaliere, P.; Aronson, B.; Shah, V.; et al. KLF4 is involved in the organization and regulation of pluripotency-associated three-dimensional enhancer networks. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinola, S.M.; Gotz, M.; Bellec, M.; Messina, O.; Fiche, J.B.; Houbron, C.; Dejean, M.; Reim, I.; Cardozo Gizzi, A.M.; Lagha, M.; et al. Cis-regulatory chromatin loops arise before TADs and gene activation, and are independent of cell fate during early Drosophila development. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangnier, L.; Joly-Beauparlant, C.; Droit, A.; Bilodeau, S.; Bureau, A. Cis-regulatory hubs: A new 3D model of complex disease genetics with an application to schizophrenia. Life Sci. Alliance 2022, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weintraub, A.S.; Li, C.H.; Zamudio, A.V.; Sigova, A.A.; Hannett, N.M.; Day, D.S.; Abraham, B.J.; Cohen, M.A.; Nabet, B.; Buckley, D.L.; et al. YY1 Is a Structural Regulator of Enhancer-Promoter Loops. Cell 2017, 171, 1573–1588.e1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giammartino, D.C.; Polyzos, A.; Apostolou, E. Transcription factors: Building hubs in the 3D space. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 2395–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.S.; Huntley, M.H.; Durand, N.C.; Stamenova, E.K.; Bochkov, I.D.; Robinson, J.T.; Sanborn, A.L.; Machol, I.; Omer, A.D.; Lander, E.S.; et al. A 3D map of the human genome at kilobase resolution reveals principles of chromatin looping. Cell 2014, 159, 1665–1680, Erratum in Cell 2015, 162, 687–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Jia, L.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, C. OCEAN-C: Mapping hubs of open chromatin interactions across the genome reveals gene regulatory networks. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, J.G.S.; Madsen, M.S.; Rauch, A.; Traynor, S.; Van Hauwaert, E.L.; Haakonsson, A.K.; Javierre, B.M.; Hyldahl, M.; Fraser, P.; Mandrup, S. Highly interconnected enhancer communities control lineage-determining genes in human mesenchymal stem cells. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 1227–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oudelaar, A.M.; Harrold, C.L.; Hanssen, L.L.P.; Telenius, J.M.; Higgs, D.R.; Hughes, J.R. A revised model for promoter competition based on multi-way chromatin interactions at the alpha-globin locus. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliner, H.A.; Packer, J.S.; McFaline-Figueroa, J.L.; Cusanovich, D.A.; Daza, R.M.; Aghamirzaie, D.; Srivatsan, S.; Qiu, X.; Jackson, D.; Minkina, A.; et al. Cicero Predicts cis-Regulatory DNA Interactions from Single-Cell Chromatin Accessibility Data. Mol. Cell. 2018, 71, 858–871.e858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anene-Nzelu, C.G.; Tan, W.L.W.; Lee, C.J.M.; Wenhao, Z.; Perrin, A.; Dashi, A.; Tiang, Z.; Autio, M.I.; Lim, B.; Wong, E.; et al. Assigning Distal Genomic Enhancers to Cardiac Disease-Causing Genes. Circulation 2020, 142, 910–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, A.; Alves, M.R.; Crocker, J. Multi-enhancer transcriptional hubs confer phenotypic robustness. Elife 2019, 8, e45325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, C.T.; Corces, V.G. Enhancer function: New insights into the regulation of tissue-specific gene expression. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.P.; Tan, W.L.W.; Anene-Nzelu, C.G.; Lee, C.J.M.; Li, P.Y.; Luu, T.D.A.; Chan, C.X.; Tiang, Z.; Ng, S.L.; Huang, X.; et al. Robust CTCF-Based Chromatin Architecture Underpins Epigenetic Changes in the Heart Failure Stress-Gene Response. Circulation 2019, 139, 1937–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa-Garrido, M.; Chapski, D.J.; Schmitt, A.D.; Kimball, T.H.; Karbassi, E.; Monte, E.; Balderas, E.; Pellegrini, M.; Shih, T.T.; Soehalim, E.; et al. High-Resolution Mapping of Chromatin Conformation in Cardiac Myocytes Reveals Structural Remodeling of the Epigenome in Heart Failure. Circulation 2017, 136, 1613–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, J.C.K.; van Duijvenboden, K.; Krijger, P.H.L.; Hooijkaas, I.B.; van der Made, I.; de Gier-de Vries, C.; Wakker, V.; Creemers, E.E.; de Laat, W.; Boukens, B.J.; et al. Genetic Dissection of a Super Enhancer Controlling the Nppa-Nppb Cluster in the Heart. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeeva, I.A.; Hooijkaas, I.B.; Ruijter, J.M.; van der Made, I.; de Groot, N.E.; van de Werken, H.J.; Creemers, E.E.; Christoffels, V.M. Identification of a regulatory domain controlling the Nppa-Nppb gene cluster during heart development and stress. Development 2016, 143, 2135–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickel, D.E.; Barozzi, I.; Zhu, Y.; Fukuda-Yuzawa, Y.; Osterwalder, M.; Mannion, B.J.; May, D.; Spurrell, C.H.; Plajzer-Frick, I.; Pickle, C.S.; et al. Genome-wide compendium and functional assessment of in vivo heart enhancers. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, C.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chang, Y.; Bai, R.; Saleem, A.; Jiang, M.; Lu, W.; Lan, F.; et al. Knockout of MYOM1 in human cardiomyocytes leads to myocardial atrophy via impairing calcium homeostasis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 1661–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterwalder, M.; Barozzi, I.; Tissieres, V.; Fukuda-Yuzawa, Y.; Mannion, B.J.; Afzal, S.Y.; Lee, E.A.; Zhu, Y.; Plajzer-Frick, I.; Pickle, C.S.; et al. Enhancer redundancy provides phenotypic robustness in mammalian development. Nature 2018, 554, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nora, E.P.; Goloborodko, A.; Valton, A.L.; Gibcus, J.H.; Uebersohn, A.; Abdennur, N.; Dekker, J.; Mirny, L.A.; Bruneau, B.G. Targeted Degradation of CTCF Decouples Local Insulation of Chromosome Domains from Genomic Compartmentalization. Cell 2017, 169, 930–944.e922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.S.P.; Huang, S.C.; Glenn St Hilaire, B.; Engreitz, J.M.; Perez, E.M.; Kieffer-Kwon, K.R.; Sanborn, A.L.; Johnstone, S.E.; Bascom, G.D.; Bochkov, I.D.; et al. Cohesin Loss Eliminates All Loop Domains. Cell 2017, 171, 305–320.e324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hark, A.T.; Schoenherr, C.J.; Katz, D.J.; Ingram, R.S.; Levorse, J.M.; Tilghman, S.M. CTCF mediates methylation-sensitive enhancer-blocking activity at the H19/Igf2 locus. Nature 2000, 405, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Maurano, M.T.; Qu, H.; Varley, K.E.; Gertz, J.; Pauli, F.; Lee, K.; Canfield, T.; Weaver, M.; Sandstrom, R.; et al. Widespread plasticity in CTCF occupancy linked to DNA methylation. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1680–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flavahan, W.A.; Drier, Y.; Liau, B.B.; Gillespie, S.M.; Venteicher, A.S.; Stemmer-Rachamimov, A.O.; Suva, M.L.; Bernstein, B.E. Insulator dysfunction and oncogene activation in IDH mutant gliomas. Nature 2016, 529, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sept, C.E.; Tak, Y.E.; Cerda-Smith, C.G.; Hutchinson, H.M.; Goel, V.; Blanchette, M.; Bhakta, M.S.; Hansen, A.S.; Joung, J.K.; Johnstone, S.; et al. High-resolution CTCF footprinting reveals impact of chromatin state on cohesin extrusion dynamics. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Chandra, V.; Vijayanand, P.; Ay, F. Identification of significant chromatin contacts from HiChIP data by FitHiChIP. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corces, M.R.; Trevino, A.E.; Hamilton, E.G.; Greenside, P.G.; Sinnott-Armstrong, N.A.; Vesuna, S.; Satpathy, A.T.; Rubin, A.J.; Montine, K.S.; Wu, B.; et al. An improved ATAC-seq protocol reduces background and enables interrogation of frozen tissues. Nat. Methods. 2017, 14, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; Genome Project Data Processing, S. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Meyer, C.A.; Eeckhoute, J.; Johnson, D.S.; Bernstein, B.E.; Nusbaum, C.; Myers, R.M.; Brown, M.; Li, W.; et al. Model-based analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csardi, G.N.T. The igraph software package for complex network research. Int. J. Complex Syst. 2006, 1695, 1–9. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, M.; Mangnier, L.; Padilla, C.C.; Lee, D.P.; Tan, W.; Zheng, W.H.; Gan, L.H.; Chen, C.K.; Lim, Y.P.; Wang, R.M.Q.; et al. CTCF Mediates the Cis-Regulatory Hubs in Mouse Hearts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9834. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199834
Lee M, Mangnier L, Padilla CC, Lee DP, Tan W, Zheng WH, Gan LH, Chen CK, Lim YP, Wang RMQ, et al. CTCF Mediates the Cis-Regulatory Hubs in Mouse Hearts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9834. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199834
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Mick, Loïc Mangnier, Cory C. Padilla, Dominic Paul Lee, Wilson Tan, Wen Hao Zheng, Louis Hanqiang Gan, Ching Kit Chen, Yee Phong Lim, Rina Miao Qin Wang, and et al. 2025. "CTCF Mediates the Cis-Regulatory Hubs in Mouse Hearts" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9834. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199834
APA StyleLee, M., Mangnier, L., Padilla, C. C., Lee, D. P., Tan, W., Zheng, W. H., Gan, L. H., Chen, C. K., Lim, Y. P., Wang, R. M. Q., Li, P. Y., Zhu, Y., Bilodeau, S., Bureau, A., Foo, R. S.-Y., & Anene-Nzelu, C. G. (2025). CTCF Mediates the Cis-Regulatory Hubs in Mouse Hearts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9834. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199834






