Antiproliferative and Proapoptotic Effects of Chetomin in Human Melanoma Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
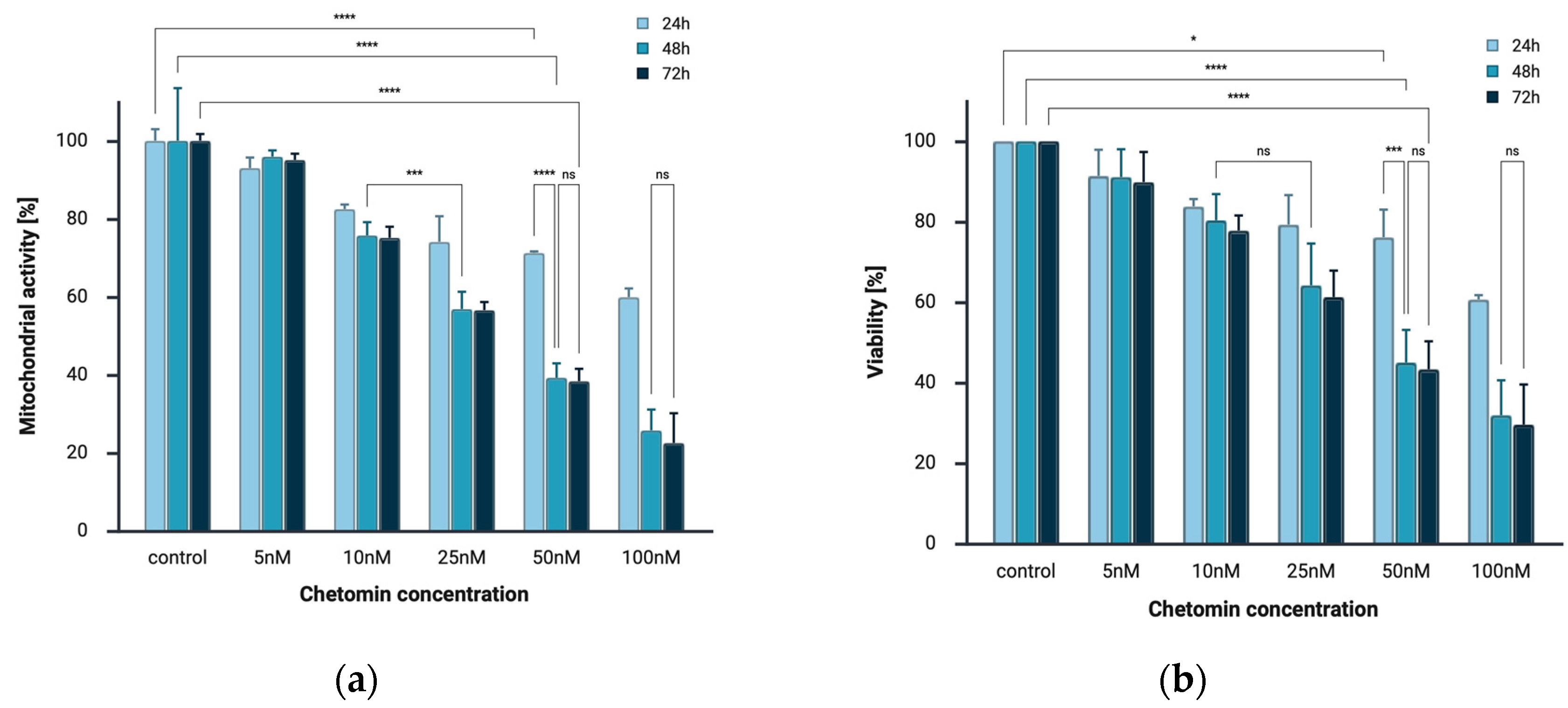
2.1. Chetomin Inhibits Cell Viability of Melanoma Cells
2.2. Chetomin Induces Apoptosis in the Human Melanoma A375
2.3. Immunocytochemical Detection of Cleaved PARP1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
4.2. Compound and Drug Preparation
4.3. In Vitro Cytotoxicity and Antiproliferative Activity Assessment
4.3.1. MTT Assay
4.3.2. CellTiter-Glo® 2.0 Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Apoptosis Analysis
4.5. Detection of Cleaved PARP1
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATP | Adenosine Triphosphate |
| BRAF | v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B |
| CDKN2A | Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 2A |
| CTLA-4 | Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte-Associated Protein 4 |
| DAB | 3,3′-Diaminobenzidine |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid |
| ETP | Epidithiodiketopiperazine |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| HIF | Hypoxia-Inducible Factor |
| HRP | Horseradish Peroxidase |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| IGF-1 | Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| MEK | MAPK/ERK Kinase |
| mTOR | Mammalian Target of Rapamycin |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium Bromide |
| PARP1 | Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase 1 |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PD-1 | Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase |
| PS | Phosphatidylserine |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| VSV | Vesicular Stomatitis Virus |
| XIAP | X-Linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein |
References
- Slominski, R.M.; Kim, T.-K.; Janjetovic, Z.; Brożyna, A.A.; Podgorska, E.; Dixon, K.M.; Mason, R.S.; Tuckey, R.C.; Sharma, R.; Crossman, D.K.; et al. Malignant Melanoma: An Overview, New Perspectives, and Vitamin D Signaling. Cancers 2024, 16, 2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frech, F.S.; Bommareddy, K.; Hernandez, L.; Dreyfuss, I.; Urbonas, R.; Nouri, K. Cutaneous Melanoma: An Update on Pathogenesis, Prevention, and Treatment. Dermatol. Rev. 2022, 3, 384–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szostak, A.P.; Szopińska, K.; Graca, M.; Śmigielska-Mikołajczyk, M.J.; Łowicka, W.; Dyląg, L.; Wawszkowicz, K.; Oluszczak, K.; Szeliga, A.; Korta, K. Prevention and Early Detection of the Most Aggressive Skin Cancer: Melanoma. Qual. Sport 2024, 22, 54608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.H. Molecular Frontiers in Melanoma: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapeutic Advances. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2016. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, M.-Y.; Hsu, S.-K.; Liu, T.-Y.; Wu, C.-Y.; Chiu, C.-C. Melanoma Biology and Treatment: A Review of Novel Regulated Cell Death-Based Approaches. Cancer Cell Int. 2024, 24, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, W.B. Chetomin an Antibiotic Substance from Chaetomium Cochliodes; Composition and Functional Groups. Arch. Biochem. 1949, 21, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McInnes, A.G.; Taylor, A.; Walter, J.A. The Structure of Chetomin. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/ja00437a074 (accessed on 26 January 2025).
- Gomes, N.G.M.; Pereira, R.B.; Andrade, P.B.; Valentão, P. Double the Chemistry, Double the Fun: Structural Diversity and Biological Activity of Marine-Derived Diketopiperazine Dimers. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Lu, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, D.; Jin, X. Natural Epidithiodiketopiperazine Alkaloids as Potential Anticancer Agents: Recent Mechanisms of Action, Structural Modification, and Synthetic Strategies. Bioorganic Chem. 2023, 137, 106642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthwick, A.D. 2,5-Diketopiperazines: Synthesis, Reactions, Medicinal Chemistry, and Bioactive Natural Products. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 3641–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-M.; Liang, X.-A.; Kong, Y.; Jia, B. Structural Diversity and Biological Activities of Indole Diketopiperazine Alkaloids from Fungi. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6659–6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.-M. Prenylated Indole Derivatives from Fungi: Structure Diversity, Biological Activities, Biosynthesis and Chemoenzymatic Synthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.; Kowolik, C.M.; Xie, J.; Yadav, S.; Overman, L.E.; Horne, D.A. Potent Anticancer Effects of Epidithiodiketopiperazine NT1721 in Cutaneous T Cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3367, Erratum in Cancers 2021, 13, 6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, S.; Sharifi, S.; Shahbazi Mojarrad, J. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Piperazinone Derivatives as Cytotoxic Agents. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 10, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, K.M.; Richardson, E.D.; Cook, K.M.; Campbell, T.J.; Pisle, S.T.; Holly, A.J.; Venzon, D.J.; Liewehr, D.J.; Chau, C.H.; Price, D.K.; et al. Epidithiodiketopiperazines (ETPs) Exhibit in Vitro Antiangiogenic and in Vivo Antitumor Activity by Disrupting the HIF-1α/P300 Complex in a Preclinical Model of Prostate Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, K.; Horinaka, M.; Yoshida, T.; Yasuda, T.; Taniguchi, H.; Goda, A.E.; Wakada, M.; Yoshikawa, S.; Nakamura, T.; Kawauchi, A.; et al. Chetomin Induces Degradation of XIAP and Enhances TRAIL Sensitivity in Urogenital Cancer Cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 38, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Reyna, C.C.; Miranda-Galván, V.; Reyes-Soto, G.; Vicuña, R.; Alanis-Mendizabal, J.; Escobar-Valderrama, M.; Arango, D.; Bautista, C.J.; Ramírez, V.; Torres-Villalobos, G. Evaluation of the Chetomin Effect on Histopathological Features in a Murine Acute Spinal Cord Injury Model. World Neurosurg. X 2025, 25, 100414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viziteu, E.; Grandmougin, C.; Goldschmidt, H.; Seckinger, A.; Hose, D.; Klein, B.; Moreaux, J. Chetomin, Targeting HIF-1α/P300 Complex, Exhibits Antitumour Activity in Multiple Myeloma. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staab, A.; Loeffler, J.; Said, H.M.; Diehlmann, D.; Katzer, A.; Beyer, M.; Fleischer, M.; Schwab, F.; Baier, K.; Einsele, H.; et al. Effects of HIF-1 Inhibition by Chetomin on Hypoxia-Related Transcription and Radiosensitivity in HT 1080 Human Fibrosarcoma Cells. BMC Cancer 2007, 7, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Reyna, C.C.; Zentella, A.; Ventura-Gallegos, J.L.; Torres-Villalobos, G.; Miranda-Galván, V.; Alanis-Mendizabal, J.; Escobar-Valderrama, J.M.; Nava, C.; Díaz-Martínez, N.E.; Bliskunova, T.; et al. Experimental Lung Transplantation Related with HIF-1, VEGF, ROS. Assessment of HIF-1α, VEGF, and Reactive Oxygen Species after Competitive Blockade of Chetomin for Lung Transplantation in Rats. Physiol. Res. 2024, 73, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewangan, J.; Srivastava, S.; Mishra, S.; Pandey, P.K.; Divakar, A.; Rath, S.K. Chetomin Induces Apoptosis in Human Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells by Promoting Calcium Overload and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 1915–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Abdelrahman, A.H.M.; Mohamed, D.E.M.; Abdeljawaad, K.A.A.; Naeem, M.A.; Gabr, G.A.; Shawky, A.M.; Soliman, M.E.S.; Sidhom, P.A.; Paré, P.W.; et al. Chetomin, a SARS-CoV-2 3C-like Protease (3CLpro) Inhibitor: In Silico Screening, Enzyme Docking, Molecular Dynamics and Pharmacokinetics Analysis. Viruses 2023, 15, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, I.I.L.; Watson, I.R.; Der, S.D.; Ohh, M. Loss of VHL Confers Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF)-Dependent Resistance to Vesicular Stomatitis Virus: Role of HIF in Antiviral Response. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 10712–10723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, H.; Sumino, M.; Okuyama, E.; Ishibashi, M. Immunomodulatory Constituents from an Ascomycete, Chaetomium Seminudum. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 98–102, Erratum in J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Li, G.; Deng, S.; Ouyang, L.; Li, L.; Liu, L.; Luo, N.; Song, X.; He, G.; Gong, C.; et al. Enhanced Antitumor Activity and Mechanism of Biodegradable Polymeric Micelles-Encapsulated Chetomin in Both Transgenic Zebrafish and Mouse Models. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 11940–11952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreaux, J.; Klein, B.; Bataille, R.; Descamps, G.; Maïga, S.; Hose, D.; Goldschmidt, H.; Jauch, A.; Rème, T.; Jourdan, M.; et al. A high-risk signature for patients with multiple myeloma established from the molecular classification of human myeloma cell lines. Haematologica 2011, 96, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storti, P.; Bolzoni, M.; Donofrio, G.; Airoldi, I.; Guasco, D.; Toscani, D.; Martella, E.; Lazzaretti, M.; Mancini, C.; Agnelli, L.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α suppression in myeloma cells blocks tumoral growth in vivo inhibiting angiogenesis and bone destruction. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1697–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Condition | Intensity of Staining | Positively Stained Cells [%] |
|---|---|---|
| Negative control | - | 0 |
| Positive control | +++ | 100 |
| 10 nM chetomin | + | 100 |
| 25 nM chetomin | ++ | 100 |
| 50 nM chetomin | +++ | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jonderko, L.; Choromańska, A. Antiproliferative and Proapoptotic Effects of Chetomin in Human Melanoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199835
Jonderko L, Choromańska A. Antiproliferative and Proapoptotic Effects of Chetomin in Human Melanoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199835
Chicago/Turabian StyleJonderko, Laura, and Anna Choromańska. 2025. "Antiproliferative and Proapoptotic Effects of Chetomin in Human Melanoma Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199835
APA StyleJonderko, L., & Choromańska, A. (2025). Antiproliferative and Proapoptotic Effects of Chetomin in Human Melanoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199835






