Predictors of Fasting Endogenous Erythritol and Erythronate Concentrations in Humans: Cross-Sectional and Post-Bariatric Surgery Analyses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Study 1: Cross-Sectional Analysis of Predictors of Fasting Endogenous Erythritol and Erythronate Across Age and BMI Groups
2.1.1. Clinical Characteristics Across Study Populations
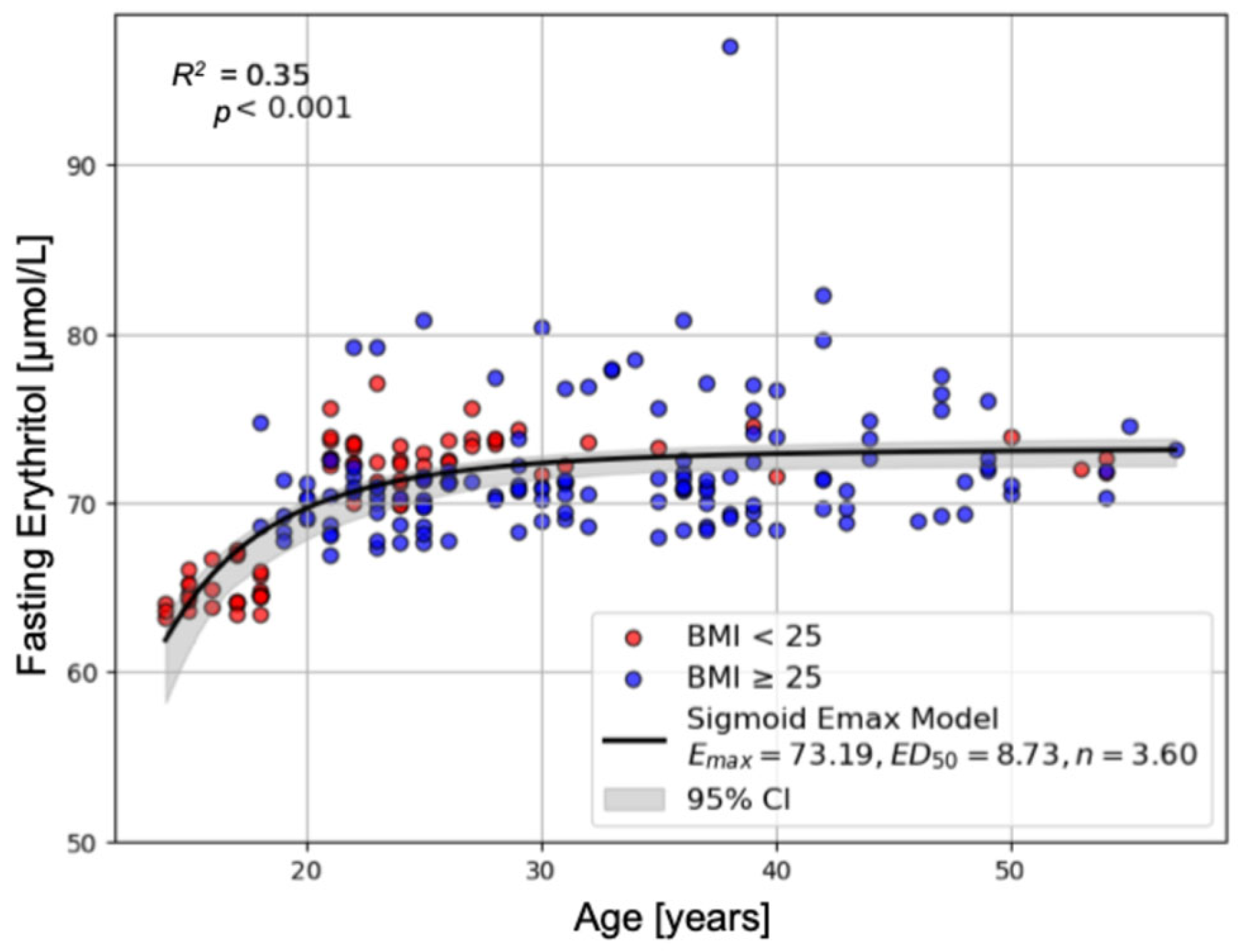
2.1.2. Predictors of Fasting Erythritol Concentrations
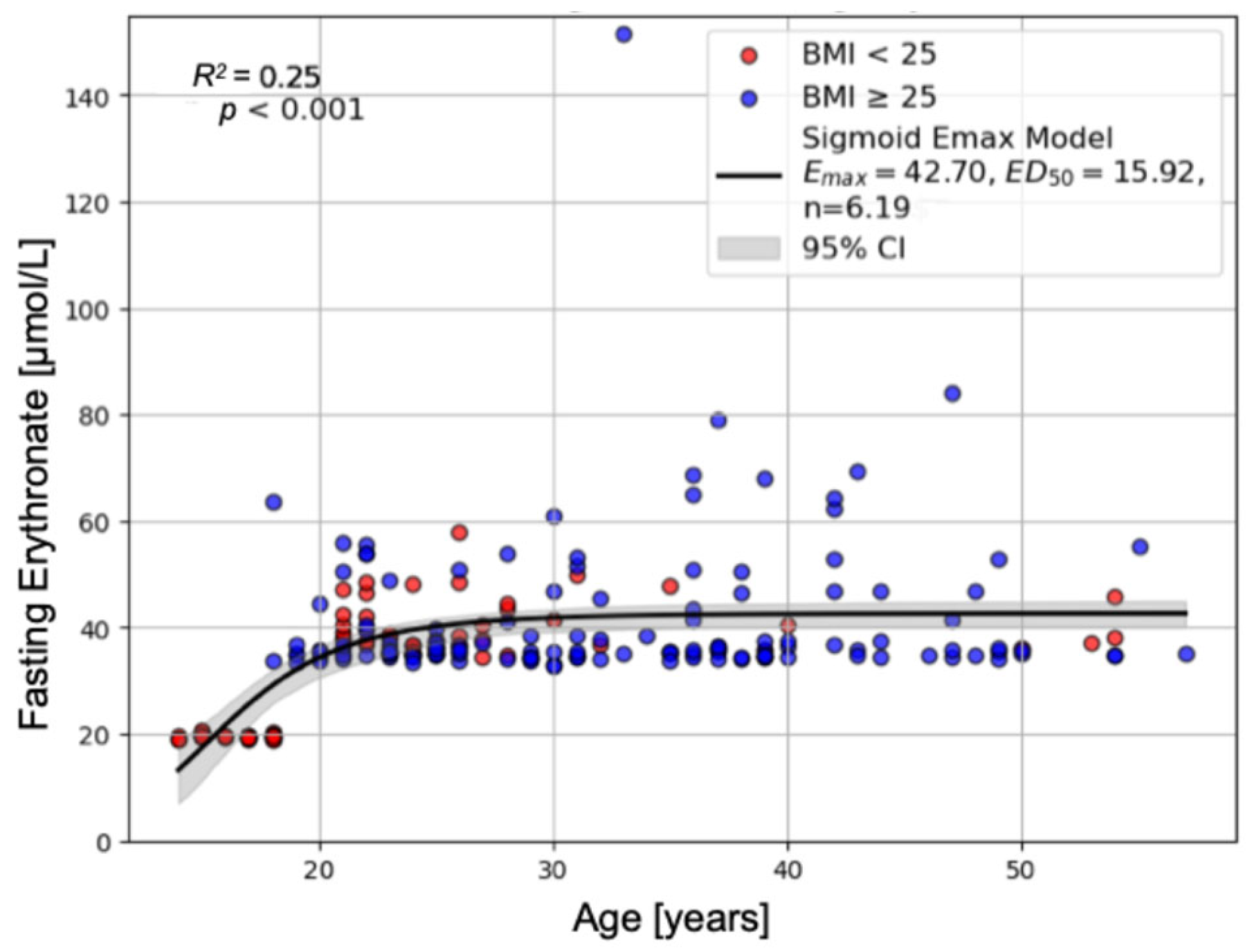
2.1.3. Predictors of Fasting Erythronate Concentrations
2.2. Study 2: Longitudinal Analysis of Changes in Fasting Endogenous Erythritol and Erythronate Following Bariatric Surgery-Induced Weight Loss
2.2.1. Clinical Characteristics Pre- and Post-Bariatric Surgery
2.2.2. Predictors of Changes in Fasting Erythritol Concentrations Post-Surgery
2.2.3. Predictors of Changes in Fasting Erythronate Concentrations Post-Surgery
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.1.1. Study 1
4.1.2. Study 2
4.2. Laboratory Analyses
4.3. Statistical Analysis
4.3.1. Study 1
4.3.2. Study 2
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| ASCVD | Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| DiRECT | Diabetes Remission Clinical Trial |
| ECLIA | Electrochemiluminescence immunoassay |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| GC-MS/MS | Gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry |
| HbA1c | Hemoglobin A1c |
| LMM | Linear mixed-effects modelling |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| LRYGB | Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass |
| LSG | Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy |
| NADPH | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen |
| NS | Non-significant |
| REML | Restricted Maximum Likelihood Estimation |
| RSD | Residual standard deviation |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
References
- Teysseire, F.; Flad, E.; Bordier, V.; Budzinska, A.; Weltens, N.; Rehfeld, J.F.; Beglinger, C.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Wölnerhanssen, B.K.; Meyer-Gerspach, A.C. Oral Erythritol Reduces Energy Intake during a Subsequent ad libitum Test Meal: A Randomized, Controlled, Crossover Trial in Healthy Humans. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornet, F.R.J.; Blayo, A.; Dauchy, F.; Slama, G. Plasma and Urine Kinetics of Erythritol after Oral Ingestion by Healthy Humans. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1996, 24, S280–S285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hootman, K.C.; Trezzi, J.P.; Kraemer, L.; Burwell, L.S.; Dong, X.; Guertin, K.A.; Jaeger, C.; Stover, P.J.; Hiller, K.; Cassano, P.A. Erythritol is a pentose-phosphate pathway metabolite and associated with adiposity gain in young adults. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E4233–E4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebholz, C.M.; Yu, B.; Zheng, Z.; Chang, P.; Tin, A.; Köttgen, A.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; Coresh, J.; Boerwinkle, E.; Selvin, E. Serum metabolomic profile of incident diabetes. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, C.; Nambi, V.; Morrison, A.C.; Folsom, A.R.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Boerwinkle, E.; Yu, B. Metabolomic Pattern Predicts Incident Coronary Heart Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, M.; Nemet, I.; Alamri, H.; Wilcox, J.; Gupta, N.; Nimer, N.; Haghikia, A.; Li, X.S.; Wu, Y.; Saha, P.P.; et al. The artificial sweetener erythritol and cardiovascular event risk. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushamat, L.A.; Yu, B.; Hoogeveen, R.C.; Sun, C.; Cheng, C.; Hartig, S.M.; Herman, M.A.; Balasubramanyam, A.; Reusch, J.E.B.; Selvin, E.; et al. Erythritol, Erythronate, and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Older Adults in the ARIC Study. JACC Adv. 2025, 4, 101605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katakami, N.; Omori, K.; Taya, N.; Arakawa, S.; Takahara, M.; Matsuoka, T.; Tsugawa, H.; Furuno, M.; Bamba, T.; Fukusaki, E.; et al. Plasma metabolites associated with arterial stiffness in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menni, C.; Fauman, E.; Erte, I.; Perry, J.R.B.; Kastenmüller, G.; Shin, S.-Y.; Petersen, A.-K.; Hyde, C.; Psatha, M.; Ward, K.J.; et al. Biomarkers for Type 2 Diabetes and Impaired Fasting Glucose Using a Nontargeted Metabolomics Approach. Diabetes 2013, 62, 4270–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, F.M.; Bray, G.A.; Carey, V.J.; Smith, S.R.; Ryan, D.H.; Anton, S.D.; McManus, K.; Champagne, C.M.; Bishop, L.M.; Laranjo, N.; et al. Comparison of weight-loss diets with different compositions of fat, protein, and carbohydrates. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 859–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heianza, Y.; Xue, Q.; Rood, J.C.; Bray, G.A.; Sacks, F.M.; Qi, L. 48-LB: Changes in Plasma Levels of Nonnutritive Sweetener Erythritol Are Related to Two-Year Changes of Insulin Sensitivity in Response to Weight-Loss Diets—The POUNDS Lost trial. Diabetes 2023, 72, 48-LB. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heianza, Y.; Rood, J.C.; Champagne, C.M.; Manson, J.E.; Bray, G.A.; Sacks, F.M.; Qi, L. Abstract MP28: Declines in Plasma Levels of Nonnutritive Sweetener Erythritol Are Related to Two-Year Improvements in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk Estimates Among Adults with Overweight and Obesity. Circulation 2024, 149, AMP28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbin, L.J.; Hughes, D.A.; Bull, C.J.; Vincent, E.E.; Smith, M.L.; McConnachie, A.; Messow, C.-M.; Welsh, P.; Taylor, R.; Lean, M.E.J.; et al. The metabolomic signature of weight loss and remission in the Diabetes Remission Clinical Trial (DiRECT). Diabetologia 2024, 67, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.Y.; Chai, J.C.; Yu, B.; Song, R.J.; Chen, G.C.; Graff, M.; Daviglus, M.L.; Chan, Q.; Thyagarajan, B.; Castaneda, S.F.; et al. Metabolomic Signatures of Sedentary Behavior and Cardiometabolic Traits in US Hispanics/Latinos: Results from HCHS/SOL. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2023, 55, 1781–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelsey, M.M.; Zeitler, P.S. Insulin Resistance of Puberty. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2016, 16, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Gu, H.; Jin, Y.; Wurm, D.; Freidhof, B.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Q.M. Metabolomics of oxidative stress: Nrf2 independent depletion of NAD or increases of sugar alcohols. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2022, 442, 115949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khafagy, R.; Paterson, A.D.; Dash, S. Erythritol as a Potential Causal Contributor to Cardiometabolic Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Diabetes 2023, 73, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teysseire, F.; Bordier, V.; Beglinger, C.; Wölnerhanssen, B.K.; Meyer-Gerspach, A.C. Metabolic Effects of Selected Conventional and Alternative Sweeteners: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wölnerhanssen, B.K.; Meyer-Gerspach, A.C.; Arduini, A.; D’Alessandro, A.; Gronda, E.; Carugo, S.; Bonomini, M.; Gallieni, M.; Masola, V.; Angelillo-Scherrer, A.; et al. Sweeteners: Erythritol, xylitol and cardiovascular risk—Friend or foe? Cardiovasc. Res. 2025, 121, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Hartog, G.J.M.; Boots, A.W.; Adam-Perrot, A.; Brouns, F.; Verkooijen, I.W.C.M.; Weseler, A.R.; Haenen, G.R.M.M.; Bast, A. Erythritol is a sweet antioxidant. Nutrition 2010, 26, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesten, D.M.P.H.J.; Berger, A.; de Cock, P.; Dong, H.; Hammock, B.D.; den Hartog, G.J.M.; Bast, A. Multi-Targeted Mechanisms Underlying the Endothelial Protective Effects of the Diabetic-Safe Sweetener Erythritol. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, N.; Hamburg, N.M.; Holbrook, M.; Dorsey, P.G.; LeLeiko, R.M.; Berger, A.; de Cock, P.; Bosscher, D.; Vita, J.A. Effects of erythritol on endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A pilot study. Acta Diabetol. 2014, 51, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bordier, V.; Teysseire, F.; Drewe, J.; Madörin, P.; Bieri, O.; Schmidt-Trucksäss, A.; Hanssen, H.; Beglinger, C.; Meyer-Gerspach, A.C.; Wölnerhanssen, B.K. Effects of a 5-week intake of erythritol and xylitol on vascular function, abdominal fat and glucose tolerance in humans with obesity: A pilot trial. BMJ Nutr. Prev. Health 2023, 6, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabit, C.E.; Chung, W.B.; Hamburg, N.M.; Vita, J.A. Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus: Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2010, 11, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizukami, H.; Osonoi, S. Pathogenesis and Molecular Treatment Strategies of Diabetic Neuropathy Collateral Glucose-Utilizing Pathways in Diabetic Polyneuropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Ali, A.; Katare, R. Molecular complexities underlying the vascular complications of diabetes mellitus—A comprehensive review. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2020, 34, 107613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, F.; Baldin, F.; Gerin, I.; Bolsée, J.; Noël, G.; Graff, J.; Veiga-da-Cunha, M.; Stroobant, V.; Vertommen, D.; Houddane, A.; et al. A conserved phosphatase destroys toxic glycolytic side products in mammals and yeast. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.U.; Thorpe, S.R.; Baynes, J.W. Identification of N epsilon-carboxymethyllysine as a degradation product of fructoselysine in glycated protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 4889–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, J.C. Ascorbic acid oxidation by hydrogen peroxide. Anal. Biochem. 1998, 255, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, J.J.; Hassett, P.C.; Rixon, K.C.; Bron, A.J.; Harvey, D.J. Sugars including erythronic and threonic acids in human aqueous humour. Curr. Eye Res. 1999, 19, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarosiek, K.; Pappan, K.L.; Gandhi, A.V.; Saxena, S.; Kang, C.Y.; McMahon, H.; Chipitsyna, G.I.; Tichansky, D.S.; Arafat, H.A. Conserved Metabolic Changes in Nondiabetic and Type 2 Diabetic Bariatric Surgery Patients: Global Metabolomic Pilot Study. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 3467403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraljevic, M.; Süsstrunk, J.; Wölnerhanssen, B.K.; Peters, T.; Bueter, M.; Gero, D.; Schultes, B.; Poljo, A.; Schneider, R.; Peterli, R. Long-Term Outcomes of Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass vs Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy for Obesity: The SM-BOSS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Surg. 2025, 160, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabold, S.; Perktold, J. Statsmodels: Econometrc and Modeling with Python. In Proceedings of the 9th Python in Science Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 28 June–3 July 2010; pp. 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Fundamental Algorithms for Scientific Computing in Python, Version 1.16.1. Available online: https://docs.scipy.org/doc/ (accessed on 19 September 2025).
- Machine Learning in Python, Version 1.6.1. Available online: https://scikit-learn.org/stable/ (accessed on 19 September 2025).
- Gabrielsson, J.; Weiner, D. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Data Analysis: Concepts and Applications, 5th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
| Lean Adolescents (n = 30) A | Lean Adults (n = 50) B | Adults with Obesity (n = 138) C | p-Value 2 (Overall) | p-Values (Post Hoc) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A vs. B | A vs. C | B vs. C | |||||
| Sex [number] | f = 15 m = 15 | f = 25 m = 25 | f = 87 m = 51 | ||||
| Age [years] | 16.37 ± 0.26 | 27.62 ± 1.22 | 32.62 ± 0.82 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p = 0.011 |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 21.01 ± 0.34 | 22.46 ± 0.23 | 37.49 ± 0.43 | p < 0.001 | NS | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| Fasting Glucose [mmol/L] | 4.89 ± 0.07 | 4.92 ± 0.06 | 5.44 ± 0.05 | p < 0.001 | NS | p < 0.001 | NS |
| Fasting Insulin [mIU/L] | 9.00 ± 0.59 | 8.23 ± 0.79 | 16.60 ± 0.87 | p < 0.001 | NS | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| Fasting Erythritol [µmol/L] | 64.80 ± 0.20 | 72.66 ± 0.21 | 71.84 ± 0.34 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| Fasting Erythronate [µmol/L] | 19.65 ± 0.08 | 39.78 ± 0.72 | 41.41 ± 1.19 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p = 0.055 |
| Variable | Estimate | Std. Error | t-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 63.952 | 0.870 | 73.495 | <0.001 | *** |
| Age | 0.129 | 0.025 | 5.151 | <0.001 | *** |
| Fasting Erythronate | 0.088 | 0.019 | 4.572 | <0.001 | *** |
| Model Fit: | |||||
| R2 = 0.253, Adj. R2 = 0.246 | |||||
| F(2213) = 36.13, *** p < 0.001 |
| Variable | Estimate | Std. Error | t-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | −43.848 | 14.685 | −2.986 | 0.003 | ** |
| Age | 0.202 | 0.091 | 2.220 | 0.027 | * |
| BMI | 0.268 | 0.103 | 2.611 | 0.010 | ** |
| Fasting Erythritol | 0.949 | 0.221 | 4.299 | <0.001 | *** |
| Model Fit: | |||||
| R2 = 0.222, Adj. R2 = 0.211 | |||||
| F(3214) = 20.32, p < 0.001 *** |
| Pre- Surgery (n = 15) A | 3 Months Post-Surgery (n = 15) B | 6 Months Post-Surgery (n = 14) C | 12 Months Post-Surgery (n = 13) D | p-Value (Overall) 2 | p-Value (Post Hoc) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A vs. B | A vs. C | A vs. D | ||||||
| Sex [number] | f = 13 m = 2 | |||||||
| Age [years] | 32.87 ± 2.68 | |||||||
| BMI [kg/m2] | 40.57 ± 1.02 | 33.60 ± 0.94 | 29.12 ± 0.90 | 27.08 ± 1.12 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| Fasting Glucose [mmol/L] | 5.31 ± 0.14 | 4.67 ± 0.10 | 4.60 ± 0.09 | 4.78 ± 0.10 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p = 0.001 |
| Fasting Insulin [mIU/L] | 7.61 ± 0.99 | 3.02 ± 0.29 | 2.35 ± 0.41 | 2.82 ± 0.52 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p = 0.002 | p = 0.002 |
| Fasting Erythritol [µmol/L] | 71.44 ± 0.15 | 71.14 ± 0.20 | 71.45 ± 0.20 | 71.35 ± 0.45 | NS | |||
| Fasting Erythronate [µmol/L] | 35.30 ± 0.19 | 35.55 ± 0.26 | 36.28 ± 0.30 | 38.70 ± 0.35 | p < 0.001 | NS | p = 0.043 | p < 0.001 |
| Variable | Estimate | Std. Error | z-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | −0.441 | 0.470 | −0.939 | 0.348 | |
| Time | 0.043 | 0.064 | 0.671 | 0.502 | |
| Age | −0.101 | 0.104 | −0.970 | 0.332 | |
| ΔBMI | 0.354 | 0.158 | 2.243 | 0.025 | * |
| ΔFasting Glucose | −0.196 | 0.110 | −1.782 | 0.075 | |
| ΔFasting Insulin | 0.113 | 0.116 | 0.975 | 0.329 | |
| ΔFasting Erythronate | 0.177 | 0.197 | 0.900 | 0.368 | |
| Group Var | 1.278 | 1.777 | |||
| Group x Time Cov | −0.184 | 0.227 | |||
| Time Var | 0.025 | 0.031 | |||
| Log-Likelihood | −58.159 |
| Variable | Estimate | Std. Error | z-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | −1.464 | 0.276 | −5.312 | <0.001 | *** |
| Time | 0.208 | 0.037 | 5.586 | <0.001 | *** |
| Age | 0.212 | 0.119 | 1.776 | 0.076 | |
| ΔBMI | 0.019 | 0.162 | 0.118 | 0.906 | |
| ΔFasting Glucose | −0.117 | 0.128 | −0.918 | 0.358 | |
| ΔFasting Insulin | 0.174 | 0.122 | 1.431 | 0.152 | |
| ΔFasting Erythritol | −0.075 | 0.142 | −0.524 | 0.600 | |
| Group Var | 0.062 | 0.579 | |||
| Group x Time Cov | −0.003 | 0.067 | |||
| Time Var | 0.002 | 0.010 | |||
| Log-Likelihood | −51.365 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flad, E.; Altstädt, A.; Drewe, J.; Gaugler, S.; Beglinger, C.; Peterli, R.; Wölnerhanssen, B.K.; Meyer-Gerspach, A.C. Predictors of Fasting Endogenous Erythritol and Erythronate Concentrations in Humans: Cross-Sectional and Post-Bariatric Surgery Analyses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199763
Flad E, Altstädt A, Drewe J, Gaugler S, Beglinger C, Peterli R, Wölnerhanssen BK, Meyer-Gerspach AC. Predictors of Fasting Endogenous Erythritol and Erythronate Concentrations in Humans: Cross-Sectional and Post-Bariatric Surgery Analyses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199763
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlad, Emilie, Anita Altstädt, Jürgen Drewe, Stefan Gaugler, Christoph Beglinger, Ralph Peterli, Bettina K. Wölnerhanssen, and Anne Christin Meyer-Gerspach. 2025. "Predictors of Fasting Endogenous Erythritol and Erythronate Concentrations in Humans: Cross-Sectional and Post-Bariatric Surgery Analyses" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199763
APA StyleFlad, E., Altstädt, A., Drewe, J., Gaugler, S., Beglinger, C., Peterli, R., Wölnerhanssen, B. K., & Meyer-Gerspach, A. C. (2025). Predictors of Fasting Endogenous Erythritol and Erythronate Concentrations in Humans: Cross-Sectional and Post-Bariatric Surgery Analyses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199763






