Roles and Applications of Circular RNA in Virus Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Main Characteristics of CircRNAs
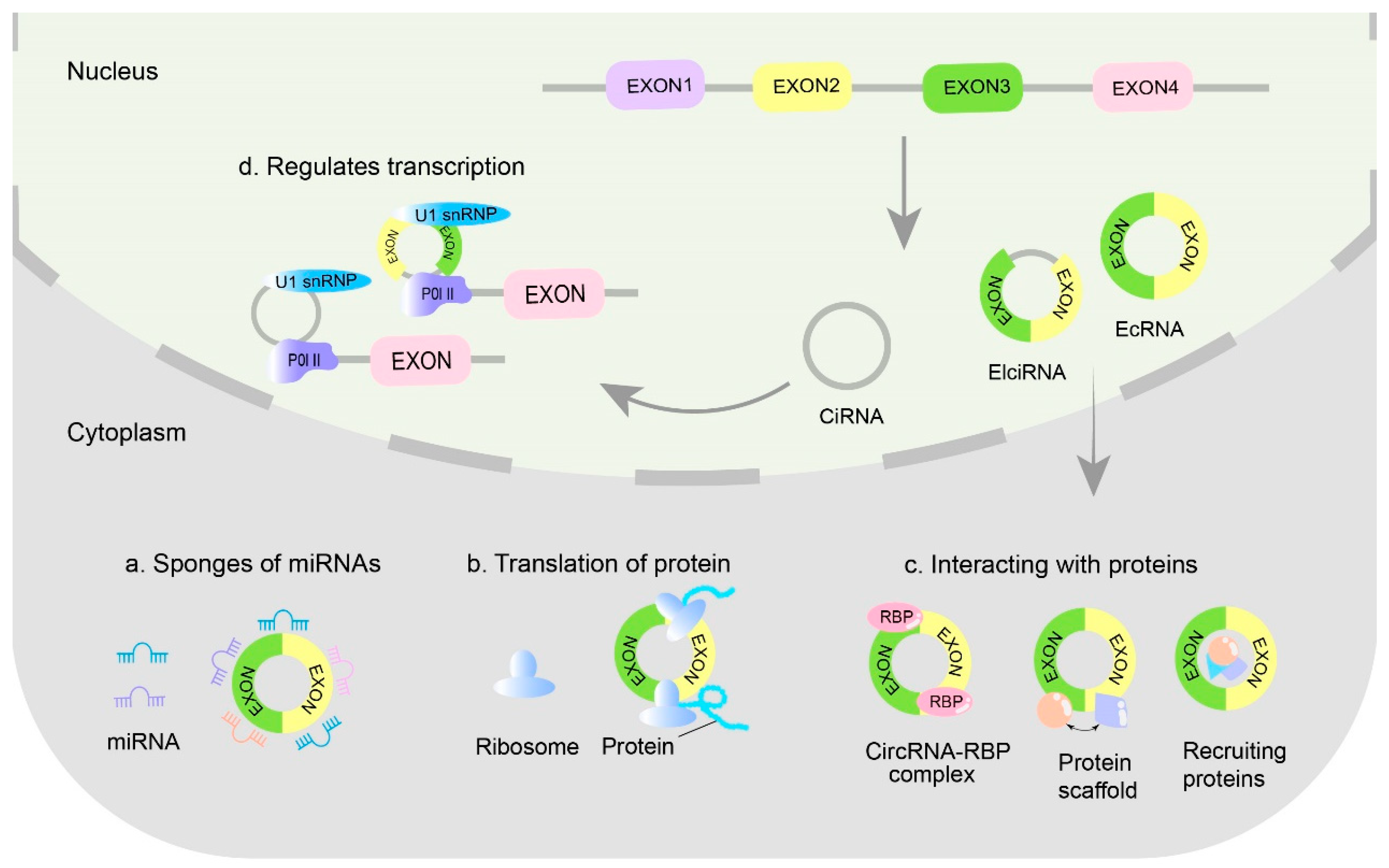
3. The Main Biological Functions of CircRNAs
4. Relationship of CircRNAs with Viral Infections
4.1. Virus-Encoded CircRNAs and Their Roles in Viral Infection
4.1.1. Plant Virus-Encoded VcircRNAs
4.1.2. Animal Virus-Encoded VcircRNAs
4.1.3. Human Virus-Encoded VcircRNAs
4.2. Role of Host CircRNAs in Viral Infections
4.2.1. Viral Infections Alter Host CircRNA Expression Profiles
4.2.2. Host CircRNAs in Viral Infection, Replication, and Pathogenicity
- Host circRNAs in regulating innate antiviral immune responses (Figure 3).
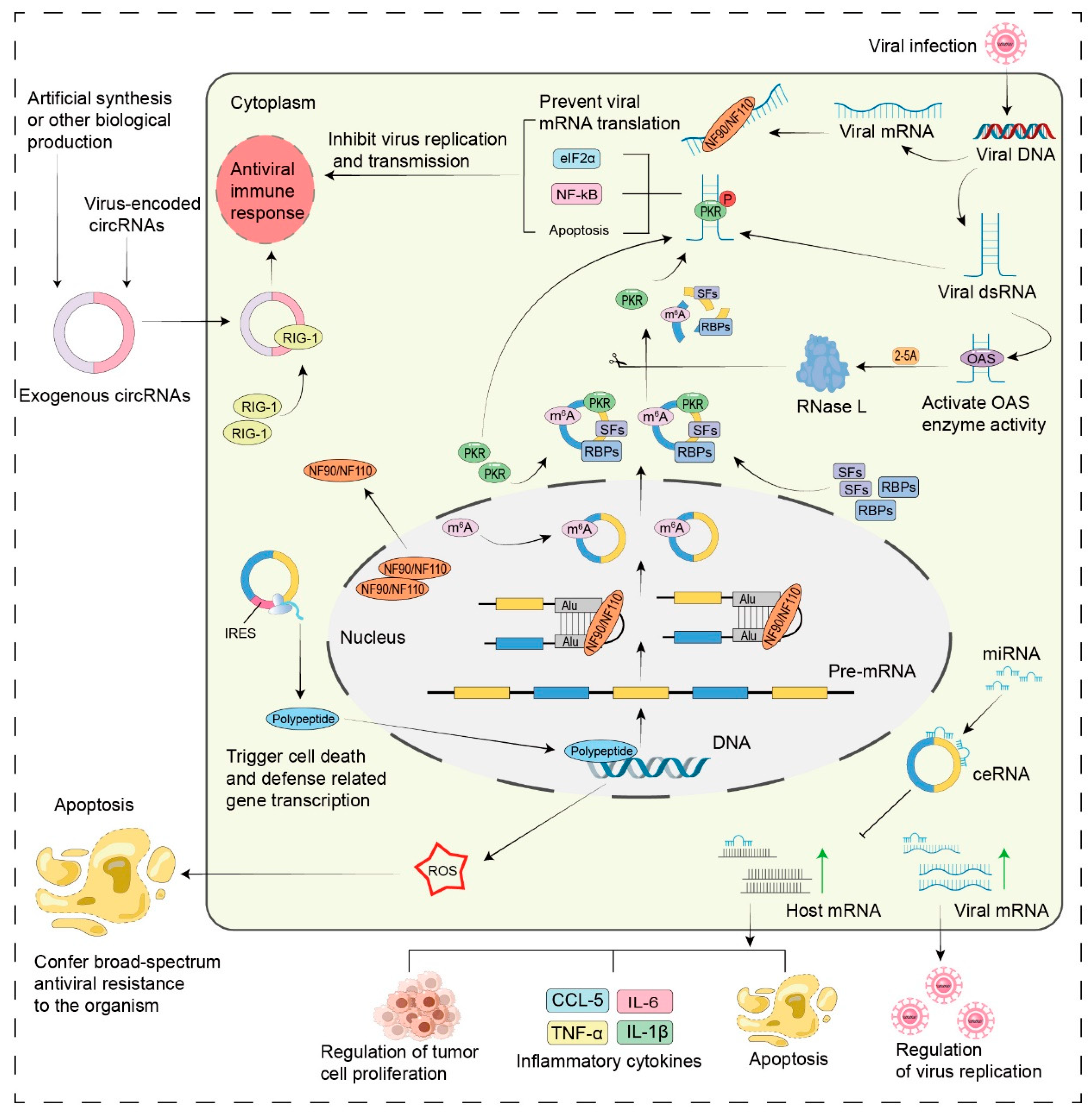
- Host circRNAs as molecular sponges for virus-associated miRNAs.
- Host circRNAs: modulating viral infections through peptide translation and protein interactions.
- Virus-induced changes in host circRNAs facilitate viral replication.
5. The Role of CircRNAs in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Viral Infections
5.1. CircRNAs as Diagnostic and Prognostic Tools for Viral Infection-Related Diseases
| Virus | Diseases or Infections | Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| EBV | NPC | Hsa_circRNA_001387 is upregulated in EBV-infected NPC tissues. | [94] |
| CircCRIM1 is significantly upregulated in highly metastatic NPC cells. | [95] | ||
| GC | Hsa-circ0074362 is downregulated. | [96] | |
| Hsa_circ_002059 is downregulated. | [97] | ||
| Hsa_circ_0000520 is downregulated. | [98] | ||
| Hsa_circ_0001017 and hsa_circ_0061276 are downregulated. | [99] | ||
| HBV, HCV | HCC | Hsa_circ_0000976, hsa_circ_0007750, hsa_circ_0139897: For detecting plasma circRNA changes, potential biomarkers for HBV-HCC diagnosis. | [91] |
| Hsa_circ_0027089 can discriminate HBV-related HCC from HBV-related cirrhosis and healthy participants. | [100] | ||
| Circ-ATP5H is upregulated in HBV-infected HCC tissues. | [80] | ||
| Hsa_circ_0003288, circ-RNF13, circANRIL, circUHRF1, hsa_circ_103047: Potential diagnostic biomarkers for HCV-HCC. | [101] | ||
| HPV | CC | CircYPEL2 and hsa_circ_0065898 are significantly upregulated. | [103,104] |
| OSCC | Hsa_circ_0001874 and hsa_circ_0001971 are upregulated in the saliva of OSCC patients. | [102] | |
| Various pathogens, including viruses | CAP | Hsa_cir_0018429, hsa_circ_0026579, hsa_cir_0125357, and hsa_circ_0099188 are upregulated. Hsa_circ_0026579 distinguishes viral pneumonia from nonviral pneumonia. | [105] |
| DENV | Dengue Fever | Hsa_circ_0006459 and hsa_circ_0015962 show significant changes before and after viral infection. | [106] |
| HAdVs | Pneumonia | Hsa_circ_0002171 can be used to diagnose highly pathogenic pneumonia. | [107] |
5.2. Antiviral Applications of CircRNA-Based RNA Therapies
5.2.1. CircRNAs as Targets for Antiviral Therapy
| Virus | Diseases or Infections | Therapeutic Targets | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| EBV | GC | Inhibition of circ-LMP2A from EBV enhances tumor suppression. | [39] |
| circRPMS1 as a potential therapeutic target in EBV-associated gastric cancer. | [41,42] | ||
| NPC | CircCRIM1 sponges miR-422a to prevent its inhibition of the target gene FOXQ1, thereby promoting NPC metastasis and chemoresistance. | [95] | |
| HBV, HCV | HCC | Circ-ATP5H sponges miR-138-5p to regulate TNFAIP3 expression, promoting HBV replication and expression; inhibiting circ-ATP5H from HBV slows liver cancer progression. | [80] |
| Circ_0004812 is identified as a potential target for chronic hepatitis B infection. | [79] | ||
| Circ-10156 acts as a molecular sponge for miR-149-3p, regulating the proliferation of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the miR-149-3p/Akt1 pathway. Inhibiting the expression of circ-10156 in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues suppresses cancer cell proliferation. | [108] | ||
| Artificial circRNA sequesters miR-122, thereby inhibiting viral protein production in HCV cell culture systems. Relevant artificial circRNAs can also suppress HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. | [120] | ||
| Knockdown of Circ-0015004 significantly inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth. | [109] | ||
| CircSORBS1 inhibits lung cancer progression. | [110,111] | ||
| KSHV | KS | Hsa_circ_0001400 inhibits KSHV lytic transcription and replication. | [112,113] |
| MERS-CoV | LUAD | Knockdown of circFNDC3B and circCNOT1 reduces cellular viral load. | [114] |
| SARS-CoV-2 | COVID-19 | AS_1-75 circRNA targets the conserved 5′-UTR sequence of SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA, reducing viral replication by 90%. | [115] |
| HTNV | HFRS, HPS | Circ_0000479 sponges miR-149-5p to regulate RIG-I expression, inhibiting Hantavirus replication indirectly. | [63] |
| EBOV | EHF | CircRNA-chr19 targets and sequesters Ebola virus-associated miR-30b-3p, regulates CLDN18 expression, and aids the immune system in recognizing and inhibiting viral replication. | [116] |
| EV71 | HFMD | Hsa_circ_0069335 is a novel potential therapeutic target for EV71-induced neuronal diseases. | [117] |
5.2.2. CircRNA Vaccines for Viral Infectious Diseases
5.2.3. CircRNAs for Gene Editing
5.2.4. CircRNA Translation Platforms for Viral Infection Therapy
5.2.5. CircRNAs for CAR-T and TCR Engineering
6. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanger, H.L.; Klotz, G.; Riesner, D.; Gross, H.J.; Kleinschmidt, A.K. Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 3852–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocquerelle, C.; Mascrez, B.; Hétuin, D.; Bailleul, B. Mis-splicing yields circular RNA molecules. FASEB J. 1993, 7, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capel, B.; Swain, A.; Nicolis, S.; Hacker, A.; Walter, M.; Koopman, P.; Goodfellow, P.; Lovell-Badge, R. Circular transcripts of the testis-determining gene Sry in adult mouse testis. Cell 1993, 73, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzman, J.; Gawad, C.; Wang, P.L.; Lacayo, N.; Brown, P.O. Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. Rna 2013, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasinska-Kalwa, M.; Mamot, A.; Czubak, K.; Frankowska, K.; Rajkiewicz, A.A.; Spiewla, T.; Warminski, M.; Pilch, Z.; Szulc-Gasiorowska, M.; Siekan, K.; et al. Chemical circularization of in vitro transcribed RNA for exploring circular mRNA design. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 6455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Chen, K.; Wang, H. NicOPURE: Nickless RNA circularization and one-step purification with engineered group II introns and cyclizing UTRs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, gkaf310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belter, A.; Popenda, M.; Sajek, M.; Wozniak, T.; Naskret-Barciszewska, M.Z.; Szachniuk, M.; Jurga, S.; Barciszewski, J. A new molecular mechanism of RNA circularization and the microRNA sponge formation. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 3038–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patop, I.L.; Wüst, S.; Kadener, S. Past, present, and future of circRNAs. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e100836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Zuo, Y.H.; Wang, J.H.; Zhang, M.Q.; Malhotra, A.; Mayeda, A. Characterization of RNase R-digested cellular RNA source that consists of lariat and circular RNAs from pre-mRNA splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.L.; Bao, Y.; Yee, M.C.; Barrett, S.P.; Hogan, G.J.; Olsen, M.N.; Dinneny, J.R.; Brown, P.O.; Salzman, J. Circular RNA Is Expressed across the Eukaryotic Tree of Life. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maass, P.G.; Glazar, P.; Memczak, S.; Dittmar, G.; Hollfinger, I.; Schreyer, L.; Sauer, A.V.; Toka, O.; Aiuti, A.; Luft, F.C.; et al. A map of human circular RNAs in clinically relevant tissues. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z. Pervasive translation of circular RNAs driven by short IRES-like elements. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Du, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, M.; Hou, P.; Shen, Z.; Chu, S.; Zheng, J.; Bai, J.; et al. Expanding uncapped translation and emerging function of circular RNA in carcinomas and noncarcinomas. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fan, X.J.; Mao, M.W.; Song, X.W.; Wu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, Y.F.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Extensive translation of circular RNAs driven by N6-methyladenosine. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 626–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.F. Efficient backsplicing produces translatable circular mRNAs. Rna 2015, 21, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Xu, S.P.; Cao, G.H.; Chen, S.P.; Zhang, T.; Yang, B.B.; Zhou, G.H.; Yang, X. A novel peptide encoded by a rice circular RNA confers broad-spectrum disease resistance in rice plants. New Phytol. 2025, 246, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.K.; Wang, Y.M.; Yan, Q.J.; Fan, C.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, D.; Guo, C.; Chen, P.; Shi, L.; Liao, Q.J.; et al. CircCDYL2 bolsters radiotherapy resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by promoting RAD51 translation initiation for enhanced homologous recombination repair. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, D.; Palermo, C.I.; Barbagallo, C.; Battaglia, R.; Caponnetto, A.; Spina, V.; Ragusa, M.; Di Pietro, C.; Scalia, G.; Purrello, M.; et al. Competing endogenous RNA network mediated by circ_3205 in SARS-CoV-2 infected cells. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.X.; Yan, Z.X.; Wen, J.J.; Fu, D.; Xu, P.P.; Wang, L.; Cheng, S.; Hu, J.D.; Zhao, W.L. CircEAF2 counteracts Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma progression via miR-BART19-3p/APC/β-catenin axis. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.S.; Wang, J.; Xiong, F.; Jiang, X.J.; Zhu, K.J.; Wang, Y.A.; Mo, Y.Z.; Gong, Z.J.; Zhang, S.S.; He, Y.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded Circular RNA CircBART2.2 Promotes Immune Escape of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Regulating PD-L1. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 5074–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Li, H.; Bi, Y.; Xu, P.; Liu, W.; Ye, X.; Li, J.; et al. The circRNA circVAMP3 restricts influenza A virus replication by interfering with NP and NS1 proteins. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Dai, K.; Zhu, M.; Liang, Z.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, R.; Cao, G.; Hu, X.; et al. Bombyx mori Akirin hijacks a viral peptide vSP27 encoded by BmCPV circRNA and activates the ROS-NF-κB pathway against viral infection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 194, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.L.; Zheng, G.; Yang, Y.Q.; Wu, J.F.; Du, Y.S.; Chen, J.H.; Liu, C.J.; Liu, Y.Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; et al. Rolling-Translated circRUNX2.2 Promotes Lymphoma Cell Proliferation and Cycle Transition in Marek’s Disease Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, C.; Zhu, Z.; Jiang, T.; Shan, T.; Peng, Y. VirusCircBase: A database of virus circular RNAs. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, 2182–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, X.; Peng, Y. An updated database of virus circular RNAs provides new insights into the biogenesis mechanism of the molecule. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2261558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Owens, R.A.; Sun, Q.; Song, H.; Liu, Y.; Eamens, A.L.; Feng, H.; Tian, H.; Wang, M.B.; Zhang, R.; et al. Silencing of transcription factor encoding gene StTCP23 by small RNAs derived from the virulence modulating region of potato spindle tuber viroid is associated with symptom development in potato. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1008110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasseur, A.S.; Trozzi, G.; Istasse, C.; Petit, A.; Rasschaert, P.; Denesvre, C.; Kaufer, B.B.; Bertzbach, L.D.; Muylkens, B.; Coupeau, D.; et al. Marek’s Disease Virus Virulence Genes Encode Circular RNAs. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e00321-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, X.; Dai, K.; Liang, Z.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Cao, M.M.; Xue, R.Y.; Cao, G.L.; et al. Micropeptide vsp21 translated by Reovirus circular RNA 000048 attenuates viral replication. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Z.; Qiu, Q.; Tong, X.; Pan, J.; Zhu, M.; Hu, X.; Gong, C. BmNPV circular RNA-encoded peptide VSP39 promotes viral replication. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 228, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, Z.; Qi, Y.L.; Yu, W.B.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, M.; Hu, X.L.; Gong, C.L. GCRV-encoded circRNA circ_20 forms a ternary complex with BIP and PERK to delay virus replication by inhibiting the PERK-eIF2α pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281, 136314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, T.; Qiu, Q.; Gong, C.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X. A novel viral circRNA-13 encoded by GCRV with delaying viral proliferation. Aquaculture 2025, 595, 741569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Dai, Y.; Tong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, R.; Wang, X.; Cao, G.; et al. Circ-Udg Derived from Cyprinid Herpesvirus 2 Promotes Viral Replication. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0094322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limkul, S.; Phiwthong, T.; Wanvimonsuk, S.; Seabkongseng, T.; Aunkam, P.; Jaree, P.; Luangtrakul, W.; Mahanil, K.; Teamtisong, K.; Tittabutr, P.; et al. Viral circular RNA-encoded protein, ceVP28, divulges an antiviral response in invertebrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2025, 122, e2321707122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Meng, Y.; Guo, J.; Chen, P.; Wang, J.; Shi, L.; Wang, D.; Qu, H.; Wu, P.; Fan, C.; et al. Human papillomavirus-encoded circular RNA circE7 promotes immune evasion in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.W.; Lee, E.E.; Kim, J.; Yang, R.; Chamseddin, B.; Ni, C.Y.; Gusho, E.; Xie, Y.; Chiang, C.M.; Buszczak, M.; et al. Transforming activity of an oncoprotein-encoding circular RNA from human papillomavirus. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.-P.; Chen, J.-N.; Dong, M.; Xiao, Z.-D.; Feng, Z.-Y.; Pan, Y.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Bi, Y.-H.; et al. Epstein–Barr virus-derived circular RNA LMP 2A induces stemness in EBV-associated gastric cancer. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e49689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.E.; Ng, W.L.; Marinov, G.K.; Yu, K.H.O.; Tan, L.P.; Liau, E.S.; Goh, S.Y.; Yeo, K.S.; Yip, K.Y.; Lo, K.W.; et al. Identification and characterization of a novel Epstein-Barr Virus-encoded circular RNA from Gene. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.W.; Shuai, M.X.; Xia, Y. Knockdown of EBV-encoded circRNA circRPMS1 suppresses nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation and metastasis through sponging multiple miRNAs. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 8023–8031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Du, Y.; Gong, L.P.; Shao, Y.T.; Pan, L.J.; Feng, Z.Y.; Pan, Y.H.; Huang, J.T.; Wen, J.Y.; Sun, L.P.; et al. ebv-circRPMS1 promotes the progression of EBV-associated gastric carcinoma via Sam68-dependent activation of METTL3. Cancer Lett. 2022, 535, 215646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungerleider, N.; Concha, M.; Lin, Z.; Roberts, C.; Wang, X.; Cao, S.B.; Baddoo, M.; Moss, W.N.; Yu, Y.; Seddon, M.; et al. The Epstein Barr virus circRNAome. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagawa, T.; Oh, D.; Santos, J.; Dremel, S.; Mahesh, G.; Uldrick, T.S.; Yarchoan, R.; Kopardé, V.N.; Ziegelbauer, J.M. Characterizing Expression and Regulation of Gamma-Herpesviral Circular RNAs. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 670542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abere, B.; Li, J.H.; Zhou, H.Z.; Toptan, T.; Moore, P.S.; Chang, Y. Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Encoded circRNAs Are Expressed in Infected Tumor Tissues and Are Incorporated into Virions. mBio 2020, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Withers, J.B.; Li, E.S.; Vallery, T.K.; Yario, T.A.; Steitz, J.A. Two herpesviral noncoding PAN RNAs are functionally homologous but do not associate with common chromatin loci. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Lee, E.E.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.H.; Kolitz, E.; Chen, Y.T.; Crewe, C.; Salisbury, N.J.H.; Scherer, P.E.; Cockerell, C.; et al. Characterization of ALTO-encoding circular RNAs expressed by Merkel cell polyomavirus and trichodysplasia spinulosa polyomavirus. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazziotta, C.; Cervellera, C.F.; Lanzillotti, C.; Touzé, A.; Gaboriaud, P.; Tognon, M.; Martini, F.; Rotondo, J.C. MicroRNA dysregulations in Merkel cell carcinoma: Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abere, B.; Zhou, H.Z.; Li, J.H.; Cao, S.; Toptan, T.; Grundhoff, A.; Fischer, N.; Moore, P.S.; Chang, Y. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Encodes Circular RNAs (circRNAs) Enabling a Dynamic circRNA/microRNA/mRNA Regulatory Network. mBio 2020, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Liang, Z.; Pan, J.; Zhang, X.; Xue, R.Y.; Cao, G.L.; Hu, X.L.; Gong, C.L. Hepatocellular carcinoma progression mediated by hepatitis B virus-encoded circRNA HBV_circ_1 through interaction with CDK1. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 25, 668–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Liang, Z.; Pan, J.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Xue, R.; Cao, G.; Gong, C. HBV pgRNA can generate a circRNA with two junction sites. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.M.; Boonchuen, P.; Chen, T.C.; Lei, S.H.; Somboonwiwat, K.; Sarnow, P. Virus- derived circular RNAs populate hepatitis C virus-infected cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2313002121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.H.; Zhao, H.L.; Wu, S.Y.; Jiang, J.X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Liu, X.Y.; Yu, F.; Ou, T.; Zhao, A.Z.; et al. CircSARS-CV2-N1368 from SARS-CoV-2 impairs endothelial cell function through the upregulation of ATF7 to activate TLR4/NF-κB/ROS signaling. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2025, 46, 2180–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Wang, J.; Du, Y.; Li, C.; Hao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guan, Y.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Influenza A virus H1N1-derived circNP37 positively regulates viral replication by sponging host miR-361-5p. bioRxiv 2023, 04.556164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, T.O. Discovering viroids__A personal perspective. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2003, 1, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, T.O. Viroids. Adv. Virus Res. 1972, 17, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.S.; Yan, B.Y.; Dai, K.; Zhu, M.; Liang, Z.; Dai, Y.P.; Zhang, M.T.; Zhang, Z.Y.; et al. Grass carp reovirus encoding circular RNAs with antiviral activity. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiba, K.; Otsuka, M.; Ohno, M.; Kishikawa, T.; Yamagami, M.; Suzuki, T.; Ishibashi, R.; Seimiya, T.; Tanaka, E.; Koike, K.; et al. DHX9 regulates production of hepatitis B virus-derived circular RNA and viral protein levels. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 20953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Lu, C.; He, J.; Liu, L.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Ge, X.; Wu, A.; Jiang, T.; et al. Identification and characterization of circRNAs encoded by MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2. Brief bioinform 2021, 22, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yuan, R.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, T.T.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, X.; Geng, W.; Fang, P.; Jiang, M.S.; Wang, Z.Y.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of circRNA expression pattern and circRNA-mRNA-miRNA network in kidney (CIK) cells after grass carp reovirus (GCRV) infection. Aquaculture 2019, 512, 734349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Zheng, W.; Pan, J.; Lv, X.; Xin, S.; Xu, T. Circular RNA circSamd4a regulates antiviral immunity in teleost fish by upregulating STING through sponging miR-29a-3p. J. Immunol. 2021, 207, 2770–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Y.Y.; Wang, Q.D.; Lu, Y.T.; Tu, M.Y.; Xu, X.; Xia, Y.; Peng, Y.; Lai, M.M.; Zheng, X.Q. Differential circRNA expression profiles in latent human cytomegalovirus infection and validation using clinical samples. Physiol. Genom. 2019, 51, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zhu, N.; Guo, W.W.; Wang, X.; Li, K.J.; Yan, J.; Jiang, C.P.; Han, S.Y.; Xiang, H.M.; Wu, X.H.; et al. RNA-Seq Revealed a Circular RNA-microRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network in Hantaan Virus Infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, C.X.; Xue, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yin, Q.F.; Wei, J.; Yao, R.W.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L.; et al. Coordinated circRNA Biogenesis and Function with NF90/NF110 in Viral Infection. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.X.; Guo, S.K.; Nan, F.; Xu, Y.F.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. RNA circles with minimized immunogenicity as potent PKR inhibitors. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 420–434.E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.X.; Li, X.; Nan, F.; Jiang, S.; Gao, X.; Guo, S.K.; Xue, W.; Cui, Y.G.; Dong, K.G.; Ding, H.H.; et al. Structure and Degradation of Circular RNAs Regulate PKR Activation in Innate Immunity. Cell 2019, 177, 865–880.E21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallagatla, S.R.; Toroney, R.; Bevilacqua, P.C. Regulation of innate immunity through RNA structure and the protein kinase PKR. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2011, 21, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Wang, S.; Baltzis, D.; Qu, L.K.; Wong, A.H.; Koromilas, A.E. Tyrosine phosphorylation acts as a molecular switch to full-scale activation of the eIF2alpha RNA-dependent protein kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandran, S.; Roberts, P.C.; Brown, L.E.; Truong, H.; Pattnaik, A.K.; Archer, D.R.; Barber, G.N. Essential role for the dsRNA-dependent protein kinase PKR in innate immunity to viral infection. Immunity 2000, 13, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, J.; Rullas, J.; García, M.A.; Alcamí, J.; Esteban, M. The catalytic activity of dsRNA-dependent protein kinase, PKR, is required for NF-kappaB activation. Oncogene 2001, 20, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Alter, H.J.; Wang, H.; Jia, S.; Wang, E.; Marincola, F.M.; Shih, J.W.; Wang, R.Y. The modulation of hepatitis C virus 1a replication by PKR is dependent on NF-kB mediated interferon beta response in Huh7.5.1 cells. Virology 2013, 438, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.B.; Esteban, M. The interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase induces apoptosis. Virology 1994, 199, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibler, K.V.; Shors, T.; Perkins, K.B.; Zeman, C.C.; Banaszak, M.P.; Biesterfeldt, J.; Langland, J.O.; Jacobs, B.L. Double-stranded RNA is a trigger for apoptosis in vaccinia virus-infected cells. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 1992–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.G.; Kim, M.V.; Chen, X.; Batista, P.J.; Aoyama, S.; Wilusz, J.E.; Iwasaki, A.; Chang, H.Y. Sensing Self and Foreign Circular RNAs by Intron Identity. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 228–238.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.G.; Chen, R.; Ahmad, S.; Verma, R.; Kasturi, S.P.; Amaya, L.; Broughton, J.P.; Kim, J.; Cadena, C.; Pulendran, B.; et al. N6-Methyladenosine Modification Controls Circular RNA Immunity. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 96–109.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onomoto, K.; Onoguchi, K.; Yoneyama, M. Regulation of RIG-I-like receptor-mediated signaling: Interaction between host and viral factors. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Zheng, W.; Geng, S.; Cui, Y.; Tao, Y.; Xu, T. circCBL and its host gene CBL collaboratively enhance the antiviral immunity and antibacterial immunity by targeting MITA in fish. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0104623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Wen, F.; Peng, M.; Wang, G.; Guo, G.; Chen, B.; Maarouf, M.; et al. Influenza A Virus-Induced circRNA circMerTK Negatively Regulates Innate Antiviral Responses. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0363722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.D.; Wang, Z.C. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0004812 impairs IFN-induced immune response by sponging miR-1287-5p to regulate FSTL1 in chronic hepatitis B. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.X.; Wang, L.L.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, H.L. Circ-ATP5H Induces Hepatitis B Virus Replication and Expression by Regulating miR-138-5p/TNFAIP3 Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 11031–11040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Du, L.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Lu, C.; Deng, T.; Yan, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wu, W.; Gu, J.; et al. A previously unidentified circRNA inhibits virus replication by regulating the miR-24-3p/KEAP1 axis. PLoS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1012712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.W.; Zhu, X.X.; Zhu, T.T.; Luo, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, T.J. A Novel Protein NLRP12-119aa that Prevents Rhabdovirus Replication by Disrupting the RNP Complex Formation. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2409953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, G.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Sun, M.; Wu, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; et al. circRUNX2.2, highly expressed in Marek’s disease tumor tissues, functions in cis to regulate parental gene RUNX2 expression. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Xie, H.; Ye, H.; Jeyarajan, A.J.; Warner, C.A.; Huang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, M.; et al. Hsa_circ_0007321 regulates Zika virus replication through miR-492/NFKBID/NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Virol. 2023, 97, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chu, H.; Chik, K.K.H.; Wen, L.; Shuai, H.P.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y.X.; Hou, Y.X.; Yuen, T.T.T.; Cai, J.P.; et al. hnRNP C modulates MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 replication by governing the expression of a subset of circRNAs and cognitive mRNAs. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N.; Zhang, S.; Guo, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, M.; Guan, Z.; Duan, M. CircRNA_0050463 promotes influenza A virus replication by sponging miR-33b-5p to regulate EEF1A1. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 254, 108995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Lei, J.; Zhou, J.; Gu, J. A Previously Undiscovered Circular RNA, circTNFAIP3, and Its Role in Coronavirus Replication. mBio 2021, 12, e0298421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, L.S.; Jakobsen, T.; Hager, H.; Kjems, J. The emerging roles of circRNAs in cancer and oncology. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 188–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zeng, X.; He, J.; Gui, Y.; Zhao, S.; Chen, H.; Sun, Q.; Jia, N.; Yuan, H. Circular RNA as a biomarker for cancer: A systematic meta-analysis. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 4078–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhong, G.; Jiang, N.; Huang, M.; Lin, T. Circular RNA, a novel marker for cancer determination (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 1786–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ding, W.B.; Wang, M.C.; Guo, X.G.; Xu, J.; Xu, Q.G.; Yang, Y.; Sun, S.H.; Liu, J.F.; Qin, L.X.; et al. Plasma circular RNA panel to diagnose hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: A large-scale, multicenter study. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 1754–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memczak, S.; Papavasileiou, P.; Peters, O.; Rajewsky, N. Identification and Characterization of Circular RNAs As a New Class of Putative Biomarkers in Human Blood. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Wang, R.C. Research techniques made simple: Studying circular RNA in skin diseases. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 2313–2319.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, M.; Huang, L. High Expression of hsa_circRNA_001387 in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma and the Effect on Efficacy of Radiotherapy. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 3965–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Liu, N.; Liang, Y.; He, Q.; Yang, X.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, Y.; He, S.; Wang, Y.; et al. Circular RNA CRIM1 functions as a ceRNA to promote nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis and docetaxel chemoresistance through upregulating FOXQ1. Mol Cancer 2020, 19, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Shao, Y.; Sun, W.; Ye, G.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, B.; Guo, J. Downregulated expression of hsa_circ_0074362 in gastric cancer and its potential diagnostic values. Biomark. Med. 2018, 12, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Chen, S.; Chen, H.; Mo, X.; Li, T.; Shao, Y.; Xiao, B.; Guo, J. Using circular RNA as a novel type of biomarker in the screening of gastric cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 444, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Tang, W.; Rong, D.; Jin, H.; Fu, K.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Cao, H.; Cao, X. Hsa_circ_0000520, a potential new circular RNA biomarker, is involved in gastric carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2018, 21, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Shao, Y.; Fu, L.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, L.; Sun, W.; Yu, R.; Xiao, B.; Guo, J. Plasma circular RNA profiling of patients with gastric cancer and their droplet digital RT-PCR detection. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 96, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Zhan, H.; Peng, Y.; Yang, L.; Gao, Q.; Jia, H.; Dai, Z.; Tang, Z.; Fan, J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Plasma hsa_circ_0027089 is a diagnostic biomarker for hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2020, 41, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishaq, Y.; Rauff, B.; Alzahrani, B.; Javed, H.; Ikram, A. Identification of Serum-Derived CricRNA Diagnostic Panel and Revealing Their Regulatory Mechanisms in HCV-HCC: A Cross-Sectional Study. Health Sci. Rep. 2024, 7, e70282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.Y.; Wang, J.; Ouyang, S.B.; Huang, Z.K.; Liao, L. Salivary Circular RNAs Hsa_Circ_0001874 and Hsa_Circ_0001971 as Novel Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 2511–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, S.; Chen, W.; Dong, X.; Zhang, R.; Ye, H.; Mei, X.; Liu, H.; Fang, Y.; He, C.; et al. Circular RNA circYPEL2: A Novel Biomarker in Cervical Cancer. Genes 2021, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Liu, J.; Deng, X. Identification of a novel circRNA, hsa_circ_0065898, that regulates tumor growth in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Transl. Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zheng, Y.; Hao, D.; Jin, X.; Luo, Q.; Guo, Y.; Li, D.; Xi, W.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Blood circRNAs as biomarkers for the diagnosis of community-acquired pneumonia. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 16483–16494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Ming, Y.; MinLi, Y.; Han, Z.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, J.; Dai, B.; Lv, Y.; He, M.L.; Fang, M.; et al. hsa_circ_0006459 and hsa_circ_0015962 affect prognosis of Dengue fever. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Sun, K.; Huang, F.; Fan, H.; Shi, T.; Chen, X.; Lu, G. Whole blood circular RNA hsa_circ_0002171 serves as a potential diagnostic biomarker for human adenovirus pneumonia in children. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2022, 55, e12347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gu, B.; Yao, G.; Li, P.; Wang, K. Circular RNA Expression Profiles and the Pro-tumorigenic Function of CircRNA_10156 in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Liver Cancer. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 1351–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, T.; Wu, P.; Qiu, J.; Wu, K.; Shi, L.; Zhu, Q.; Zhou, J. Circrna-0015004 act as a ceRNA to promote RCC2 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, S.; Peng, W.; Cai, D.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. circSORBS1 inhibits lung cancer progression by sponging miR-6779-5p and directly binding RUFY3 mRNA. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Huang, D.; Li, Q.; Zeng, J.; Qin, T.; Zhong, J.; Zhong, Z.; Lu, S. CircSorbs1 regulates myocardial regeneration and reduces cancer therapy-related cardiovascular toxicity through the Mir-99/GATA4 pathway. Discov. Oncol. 2024, 15, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagawa, T.; Gao, S.; Koparde, V.N.; Gonzalez, M.; Spouge, J.L.; Serquiña, A.P.; Lurain, K.; Ramaswami, R.; Uldrick, T.S.; Yarchoan, R.; et al. Discovery of Kaposi’s sarcoma herpesvirus-encoded circular RNAs and a human antiviral circular RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 12805–12810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagawa, T.; Oh, D.; Dremel, S.; Mahesh, G.; Koparde, V.N.; Duncan, G.; Andresson, T.; Ziegelbauer, J.M. A virus-induced circular RNA maintains latent infection of Kaposi’s sarcoma herpesvirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2212864120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chu, H.; Wen, L.; Shuai, H.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yuan, S.; Yin, F.F.; et al. Competing endogenous RNA network profiling reveals novel host dependency factors required for MERS-CoV propagation. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfafenrot, C.; Schneider, T.; Müller, C.; Hung, L.H.; Schreiner, S.; Ziebuhr, J.; Bindereif, A. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus proliferation by designer antisense-circRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 12502–12516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Guo, Z.D.; Li, J.M.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Fu, Y.Y.; Zhang, C.M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.N.; Qian, J.; Liu, L.N.; et al. Genome-Wide Search for Competing Endogenous RNAs Responsible for the Effects Induced by Ebola Virus Replication and Transcription Using a trVLP System. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhu, D.; Feng, K.; Peng, H.; Yang, S.; Huang, L.; Li, P. The neurological damage caused by enterovirus 71 infection is associated with hsa_circ_0069335/miR-29b/PMP22 pathway. J. Virol. 2025, 99, e0084424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Xue, W.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.Z.; Cao, S.M.; Lei, Y.N.; Liu, C.X.; Guo, S.K.; Shan, L.; et al. Screening for functional circular RNAs using the CRISPR-Cas13 system. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Cao, C.; Li, A.; Mei, H.; Liu, Y. Enhanced RNA knockdown efficiency with engineered fusion guide RNAs that function with both CRISPR-CasRx and hammerhead ribozyme. Genome Biol. 2023, 24, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, I.; Shalamova, L.A.; Gerresheim, G.K.; Niepmann, M.; Bindereif, A.; Rossbach, O. Functional sequestration of microRNA-122 from Hepatitis C Virus by circular RNA sponges. RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotkin, S.A.; Plotkin, S.L. The development of vaccines: How the past led to the future. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesselhoeft, R.A.; Kowalski, P.S.; Parker-Hale, F.C.; Huang, Y.; Bisaria, N.; Anderson, D.G. RNA Circularization Diminishes Immunogenicity and Can Extend Translation Duration In Vivo. Mol. Cell 2019, 74, 508–520.E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Dain, L.; Mei, L.; Zhu, G. Circular RNA: An emerging frontier in RNA therapeutic targets, RNA therapeutics, and mRNA vaccines. J. Control Release 2022, 348, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesselhoeft, R.A.; Kowalski, P.S.; Anderson, D.G. Engineering circular RNA for potent and stable translation in eukaryotic cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Yi, Z.; Shen, Y.; Lin, L.; Chen, F.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Tang, H.; Zhang, X.; Tian, F.; et al. Circular RNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variants. Cell 2022, 185, 1728–1744.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Ye, T.; Yang, Y.; Li, E.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Hu, J.; Zhang, K.; Liu, F.; et al. Circular RNA vaccines against monkeypox virus provide potent protection against vaccinia virus infection in mice. Mol. Ther. 2024, 32, 1779–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, M.; Fu, Z.F.; Zhao, L. Circular RNA vaccines with long-term lymph node-targeting delivery stability after lyophilization induce potent and persistent immune responses. mBio 2024, 15, e0177523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, X.; Zhong, C.; Cao, R.; Liu, S.; Qin, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhai, Y.; Luo, W.; Lian, Y.; Zhang, M.; et al. CircRNA based multivalent neuraminidase vaccine induces broad protection against influenza viruses in mice. NPJ Vaccines 2024, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaya, L.; Grigoryan, L.; Li, Z.; Lee, A.; Wender, P.A.; Pulendran, B.; Chang, H.Y. Circular RNA vaccine induces potent T cell responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2302191120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhou, M.; Fu, Z.F.; Zhao, L. CXCL13 promotes broad immune responses induced by circular RNA vaccines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2406434121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, T.; Yang, Z.Y.; Zhao, J.; Gao, Y.M.; Li, F.X.; Yang, R. Expanding the Potential of Circular RNA (CircRNA) Vaccines: A Promising Therapeutic Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Ye, F.; Deng, X.; Tang, Y.; Liang, J.Y.; Huang, X.; Sun, Y.; Tang, H.; Lei, J.; Zheng, S.; et al. Circular RNA: A promising new star of vaccine. J. Transl. Int. Med. 2023, 11, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; He, Z.; Zhao, K.T.; Zhu, H.; Hu, J.; Liu, G.; Gao, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhang, R.; Qiu, J.L.; et al. Prime editing using CRISPR-Cas12a and circular RNAs in human cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 1867–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.I.; Chuang, Z.S.; Shie, C.T.; Wang, H.I.; Kao, Y.T.; Yu, C.Y. A cis-acting ligase ribozyme generates circular RNA in vitro for ectopic protein functioning. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attwaters, M. In vivo RNA base editing with circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 196–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katrekar, D.; Yen, J.; Xiang, Y.; Saha, A.; Meluzzi, D.; Savva, Y.; Mali, P. Efficient in vitro and in vivo RNA editing via recruitment of endogenous ADARs using circular guide RNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Z.; Qu, L.; Tang, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tian, F.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Feng, Z.; Yu, Y.; et al. Engineered circular ADAR-recruiting RNAs increase the efficiency and fidelity of RNA editing in vitro and in vivo. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Chen, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, T.; Ma, S.; et al. Engineered circular guide RNAs enhance miniature CRISPR/Cas12f-based gene activation and adenine base editing. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Wang, S.; Cai, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, K.M.; Wei, J.; Sun, C.; Zhu, H.; Chen, K.; Gao, C.; et al. Circular RNA-mediated inverse prime editing in human cells. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Sarnow, P. Initiation of protein synthesis by the eukaryotic translational apparatus on circular RNAs. Science 1995, 268, 415–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamudurti, N.R.; Bartok, O.; Jens, M.; Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Stottmeister, C.; Ruhe, L.; Hanan, M.; Wyler, E.; Perez-Hernandez, D.; Ramberger, E.; et al. Translation of CircRNAs. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 9–21.E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.J.; Kim, Y.K. Molecular mechanisms of circular RNA translation. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, N.; Hiroshima, M.; Maruyama, H.; Nakashima, Y.; Nakano, Y.; Matsuda, A.; Sako, Y.; Ito, Y.; Abe, H. Rolling circle amplification in a prokaryotic translation system using small circular RNA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 7004–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, N.; Matsumoto, K.; Nishihara, M.; Nakano, Y.; Shibata, A.; Maruyama, H.; Shuto, S.; Matsuda, A.; Yoshida, M.; Ito, Y.; et al. Rolling Circle Translation of Circular RNA in Living Human Cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, K.; Abe, N.; Tsuji, G.; Kimura, Y.; Tomoike, F.; Shimizu, Y.; Abe, H. Chemically synthesized circular RNAs with phosphoramidate linkages enable rolling circle translation. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 6217–6220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.H.; Chang, C.Y.; Huang, Y.R.; Shen, C.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Chang, K.L.; Lee, Y.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Ting, W.C.; Chien, H.J.; et al. Exon Junction Complex Mediates the Cap-Independent Translation of Circular RNA. Mol. Cancer Res. 2023, 21, 1220–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, P.J.; Zhang, H.M.; Hemida, M.G.; Ye, X.; Qiu, Y.; Yang, D. IRES-Dependent Translational Control during Virus-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komastu, T.; Ireland, D.D.; Reiss, C.S. IL-12 and viral infections. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 1998, 9, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Gan, J.; Lei, J.; Qi, S.; Yu, X.; Zhang, W.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, M.; Ma, L.; et al. Catalytic Hybrid Lipid Nanoparticles Potentiate Circle RNA-Based Cytokine Immunotherapy. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 7864–7876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, R.; Parekh, F.; Lamb, K.; Mekkaoui, L.; Allen, C.; Smetanova, K.; Huang, J.; Williams, A.; Toledo, G.S.; Lilova, K.; et al. Large-scale manufacturing of base-edited chimeric antigen receptor T cells. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2023, 31, 101123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Long, F. The role of circular RNAs in regulating resistance to cancer immunotherapy: Mechanisms and implications. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Xu, J.; Baran, N.; Ma, W. Advancing the next generation of cancer treatment with circular RNAs in CAR-T cell therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 181, 117753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Yang, J.; Zuo, C.; Xu, J.; Ma, L.; He, Q.; Zhou, X.; Ding, X.; Wei, L.; Jiang, S.; et al. Circular mRNA-based TCR-T offers a safe and effective therapeutic strategy for treatment of cytomegalovirus infection. Mol. Ther. 2024, 32, 168–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
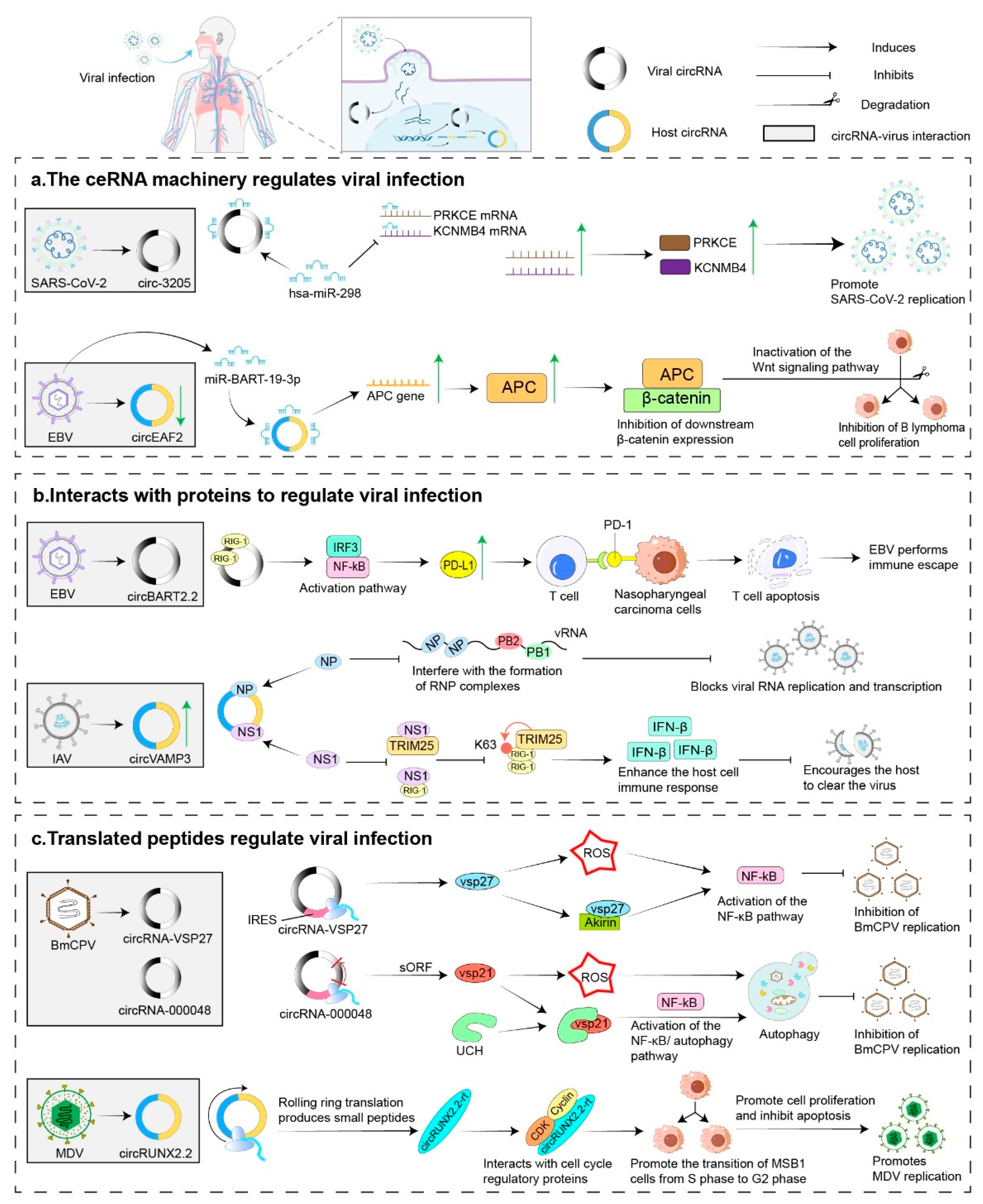

| Host Type | Virus | Specific Host or Human Tissue | circRNA | Validation Type | Role | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant | PSTVd | Potato (Solanum tuberosum) | The genome contains a circular RNA molecule. | In vivo and Sequencing-based | Facilitates viral replication in a rolling-circle replication way within host cells | [29] |
| Animal | MDV | Gallus gallus domesticus | MDV-circRNAs | In vitro | Closely associated with MDV virulence factors; influences the virulence and pathogenicity of the virus. | [30] |
| BmCPV | Bombyx mori | circRNA-vSP27 | In vitro | Inhibits viral replication by activating the NF-κB signalling pathway. | [25] | |
| vcircRNA_000048 | In vitro | VcircRNA_000048 translates a small peptide vsp21 in an IRES-dependent manner and acts as a miRNA sponge to delay viral replication. | [31] | |||
| BmNPV | circRNA-000010 | In vitro | Promotes viral replication by translating into VSP39. | [32] | ||
| GCRV | Ctenopharyngodon idellus | circ_20 | In vitro | Circ_20 forms a circ_20-BIP-PERK ternary complex to delay the replication and proliferation of GCRV. | [33] | |
| circRNA-13 | In vitro | Inhibits viral replication. | [34] | |||
| CyHV-2 | Carassius auratus | circ-udg | In vitro | Circ-udg encodes the circ-udg-P147 peptide to elevate UDG protein levels, thereby promoting CyHV-2 replication. | [35] | |
| WSSV | Litopenaeus vannamei | circVP28 | In vivo | CircVP28 encodes the protein ceVP28, which blocks the entry of viruses into host cells. | [36] | |
| Human | HPV | Head and neck squamous epithelium | circE7 | In vitro | CircE7 promotes immune evasion in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. | [37,38] |
| EBV, HHV-4 | Nasopharyngeal epithelium | circBART2.2 | In vitro | Promotes immune evasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by upregulating PD-L1 through interaction with RIG-I. | [23] | |
| Gastric epithelium | circ-LMP2a | In vitro | Circ-LMP2a induces the stemness of EBV-associated gastric cancer by acting as a sponge for hsa-miR-3908. | [39] | ||
| B lymphocytes | circLMP-2_e5 | Sequencing-based | CircLMP-2_e5 is coexpressed with linear LMP-2 RNA during EBV lytic replication and may play a role in the EBV life cycle, although its specific function requires further investigation. | [40] | ||
| Nasopharyngeal epithelium and Gastric epithelium | circRPMS1 | In vitro | CircRPMS1 induces the reverse activation of METTL3 to promote EBV-associated gastric cancer progression. | [41,42] | ||
| B lymphocytes | circBHLF1 | Sequencing-based | Regulates lytic virus DNA replication. | [43] | ||
| KSHV | Endothelial tissue and B lymphocytes | circ-vIRF4 | Sequencing-based | Facilitates viral invasion of the host. | [44,45] | |
| B lymphocytes | circPANs | In vitro | Facilitates effective lytic activity of KSHV genes in the late phase. | [46] | ||
| MCV | Skin epithelium | circALTO | Sequencing-based | Encodes the ALTO protein variant, is negatively regulated by miRNAs, and participates in viral transcriptional activation and pathogenesis. | [47] | |
| Skin epithelium | circMCV-T | Sequencing-based | Acts as a sponge for MCV-miR-M1. | [48,49] | ||
| HBV | Hepatocytes | HBV_circ_1 | In vitro and Sequencing-based | HBV circRNA 1 interacts with CDK1 to regulate cell proliferation. | [50,51] | |
| HCV | Hepatocytes | cluster I circRNAs | Sequencing-based | VcircRNAs that contained the viral internal ribosome entry site were found to be translated into proteins that displayed proviral functions. | [52] | |
| Hepatocytes | cluster II, III circRNAs | Sequencing-based | Nontranslated vcircRNAs were shown to enhance viral RNA abundance. | [52] | ||
| SARS-CoV-2 | Respiratory epithelium | circ_3205 | Sequencing-based | Functions as a sponge for hsa-miR-298, upregulating PRKCE and KCNMB4 genes to promote viral infection. | [21] | |
| Vascular endothelium | circSARS-CV2-N1368 | In vitro | CircSARS-CoV-2-N1368 activates the ATF7/TLR4/NF-κB signalling pathway by functioning as a molecular sponge for miR-103a-3p, thereby causing oxidative damage and dysfunction in endothelial cells (ECs). | [53] | ||
| H1N1 | Respiratory epithelium | circNP37 | In vitro | Functions as a sponge for host miR-361-5p to positively regulate viral replication. | [54] |
| Pro-Viral or Antiviral CircRNA | CircRNA | Virus | Mechanism of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antiviral circRNA | circ-WRKY9 | RSMV (rice stripe mosaic virus) | Encodes peptide WRKY9-88aa to suppress rice susceptibility to RSMV. | [19] |
| circSamd4a | S. chuatsi rhabdovirus (SCRV) | Acts as a ceRNA to sequester miR-29a-3p, enhancing STING-mediated NF-κB/IRF3 pathway for a stronger antiviral response. | [61] | |
| circ_0000479, circ_0046034479 | HTNV (Hantaan virus) | ceRNAs bind to miR-149-5p, upregulate RIG-I, IL-6, MXB, inhibit HTNV replication | [63] | |
| circEAF2 | EBV (Epstein–Barr virus) | ceRNA sequesters miR-BART-19, activates APC, inhibits β-catenin, suppresses the Wnt pathway, and inhibits B lymphoma proliferation | [22] | |
| circ29164 | PRV (Pseudorabies virus) | Competitively binds to ssc-miR-24-3p, maintaining KEAP1 expression to induce caspase 3 activity and cytochrome C release, inhibiting PRV replication via apoptosis. | [81] | |
| circNLRP12 | VSV (Vesicular stomatitis virus) | NLRP12-119aa inhibits VSV replication by disrupting RNP complexes. | [82] | |
| circVAMP3 | IAV (Influenza A virus) | Directly suppresses viral replication by acting as a decoy for viral nucleoprotein (NP) and nonstructural protein 1 (NS1). | [24] | |
| circCBL | SCRV (Siniperca chuatsi rhabdovirus) | Sequestering miR-125a-1-3p upregulates MITA expression, activating NF-κB and IRF3 pathways to enhance teleost fish’s innate immune response. | [77] | |
| Pro-viral circRNA | circMerTK | IAV (Influenza A virus) | IAV suppresses IFN-β activation and downstream signaling, weakening antiviral immunity and aiding its replication. | [78] |
| circBART2.2 | EBV (Epstein–Barr virus) | Induces apoptosis in tumor antigen-specific T cells to facilitate immune escape and compromise immune response against EBV. | [23] | |
| circ_0004812 | HBV (Hepatitis B virus) | Upregulation promotes FSTL1 expression by binding to miR-1287-5p, reducing interferon-induced immune responses. | [79] | |
| circ-ATP5H | HBV (Hepatitis B virus) | Increases TNFAIP3 levels by sequestering miR-138-5p, thereby promoting HBV replication and proliferation. | [80] | |
| circRUNX2.2 | MDV (Marek’s disease virus) | circRUNX2.2-rt promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by interacting with cell cycle proteins, facilitating MDV replication and tumor development. | [83] | |
| hsa_circ_0007321 | Zika virus (ZIKV) | Downregulation of hsa_circ_0007321 activates the NF-κB pathway, promoting Zika virus replication. | [84] | |
| hsa_circ_0002846, hsa_circ_0002061, hsa_circ_0004445 | MERS-CoV (Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus) | MERS-CoV uses hnRNP C to boost circRNA expression and promote its replication. | [85] | |
| circ_0050463 | IAV (Influenza A virus) | It can promote IAV replication by competitively binding to miR-33b-5p, thereby increasing the expression of eukaryotic elongation factor 1 alpha 1 (EEF1A1). | [86] | |
| circTNFAIP3 | Deltacoronavirus | Promotes deltacoronavirus replication through a specific mechanism involving the inhibition of apoptosis. | [87] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gou, F.; Gao, Y.; Zhong, K.; Bu, T.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Yang, R. Roles and Applications of Circular RNA in Virus Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199656
Gou F, Gao Y, Zhong K, Bu T, Li Y, Li F, Yang R. Roles and Applications of Circular RNA in Virus Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199656
Chicago/Turabian StyleGou, Fang, Yanmei Gao, Keke Zhong, Tian Bu, Yinggang Li, Faxiang Li, and Rong Yang. 2025. "Roles and Applications of Circular RNA in Virus Infection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199656
APA StyleGou, F., Gao, Y., Zhong, K., Bu, T., Li, Y., Li, F., & Yang, R. (2025). Roles and Applications of Circular RNA in Virus Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199656






