Potential Modulatory Effects of β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate on Type I Collagen Fibrillogenesis: Preliminary Study
Abstract
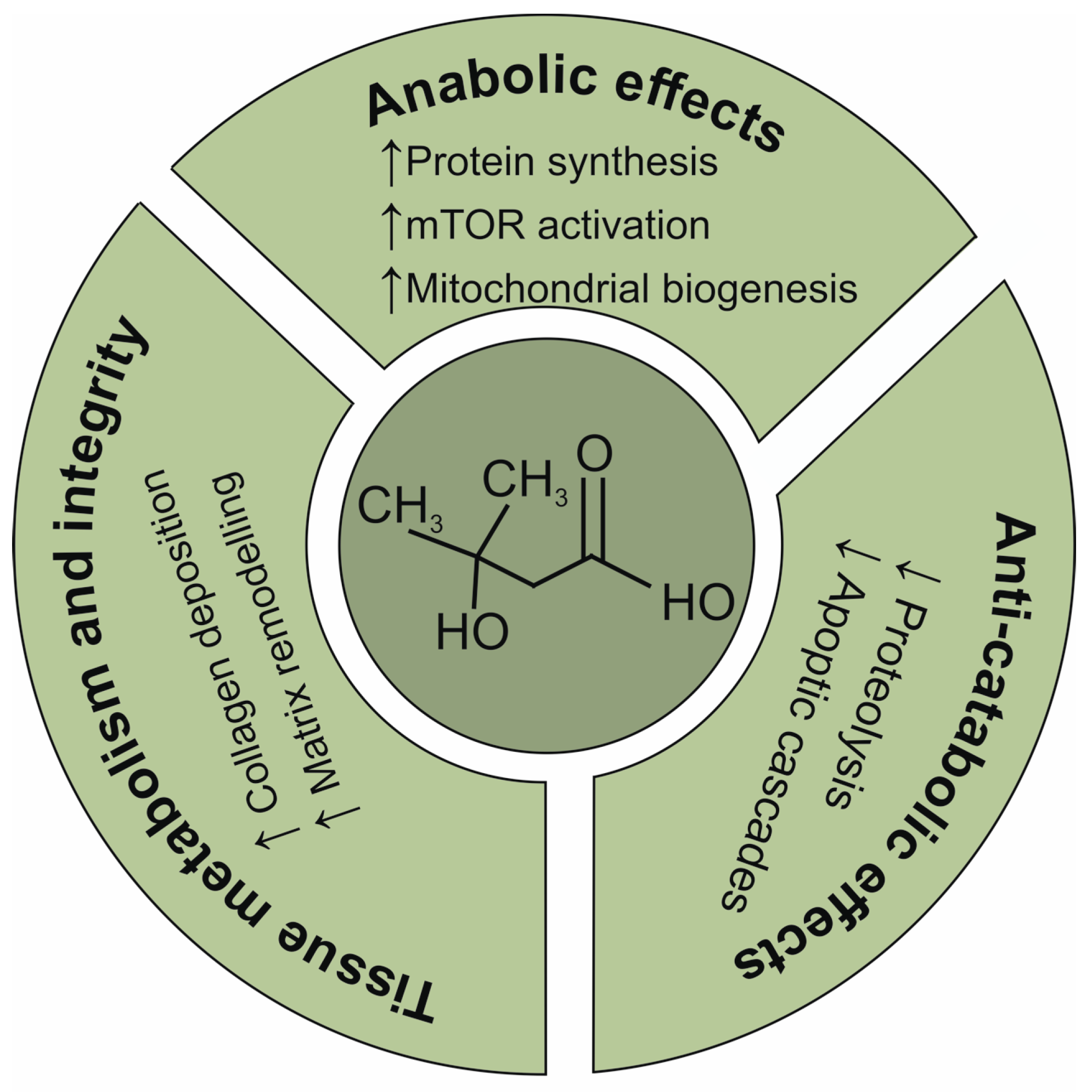
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Morphology
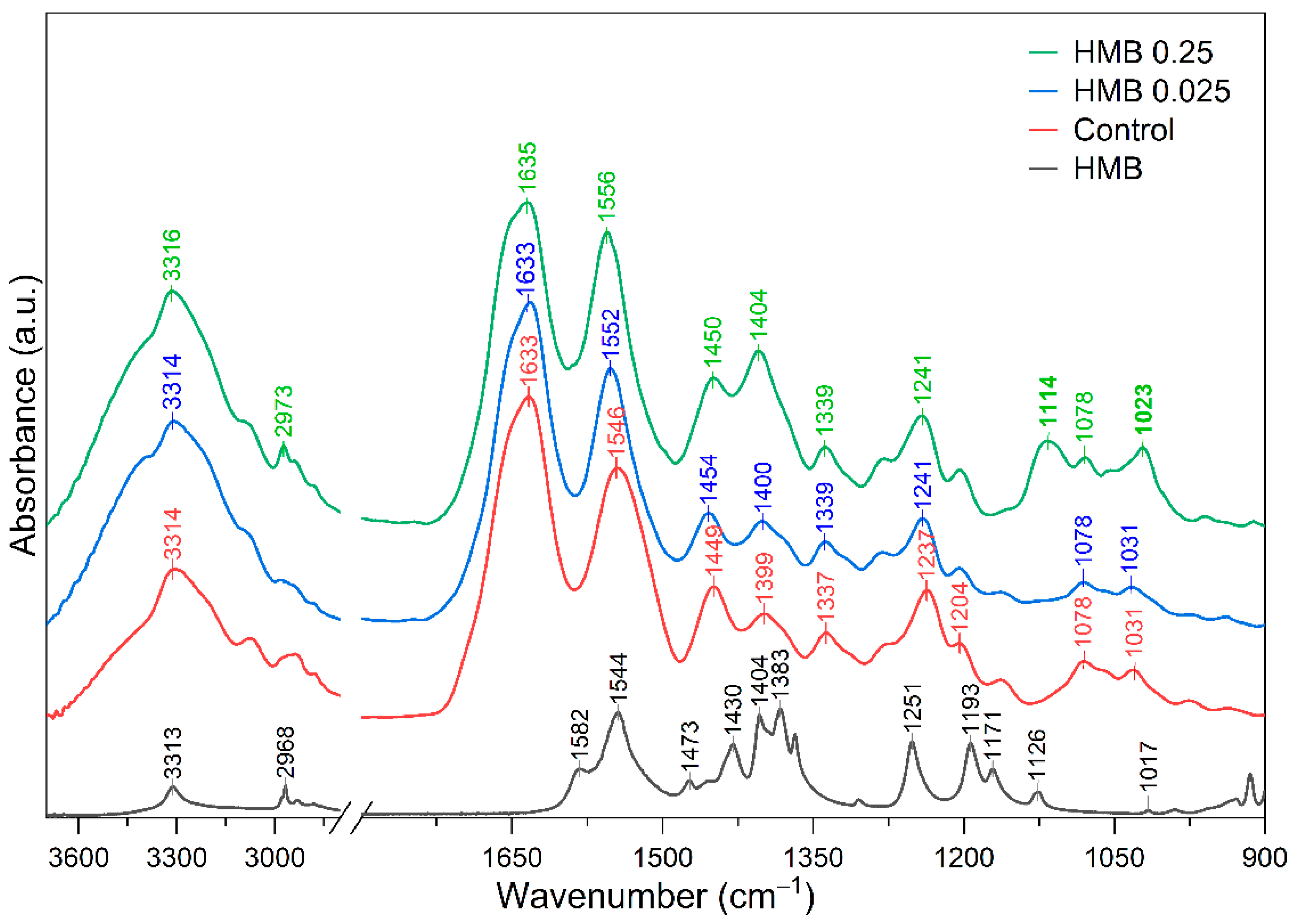
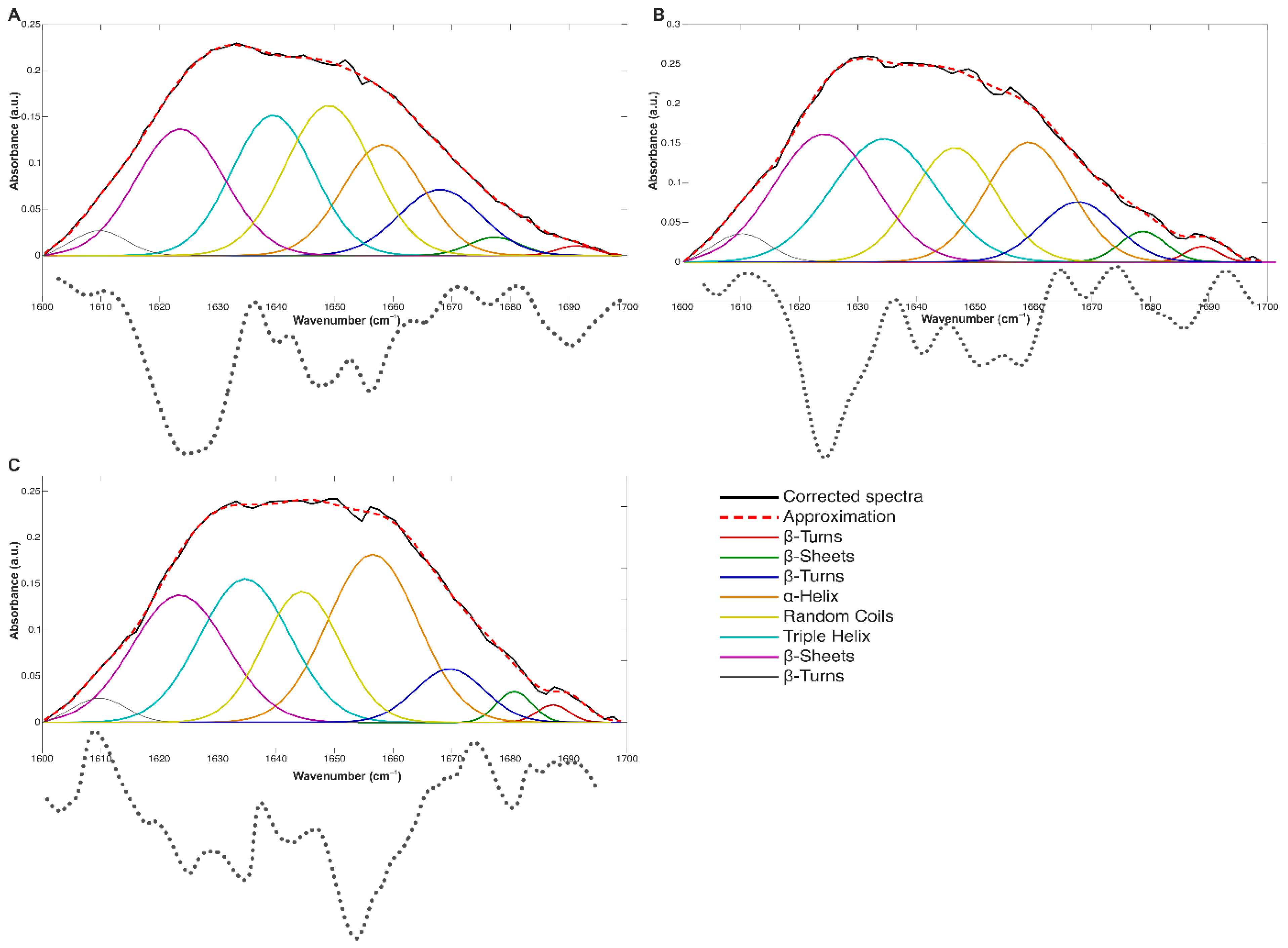
2.2. Molecular Structure
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Collagen and β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyric Acid (HMB)
3.2. Buffer Solution
- Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA) in tablet form, dissolved in 200 mL of distilled water (Millipore, Bedford, MA, USA). Dissolving one PBS tablet in 200 mL of deionised water resulted in a 0.01 M phosphate buffer, 0.0027 M potassium chloride, and 0.137 M sodium chloride at a pH of 7.2–7.6 at 25 °C.
- Potassium chloride (KCl, Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA) at a concentration of 200 mM.
- Glycine (Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA) at a concentration of 50 mM.
3.3. Sample Preparation and Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Analysis
3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Analysis
3.5. Study Limitations
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HMB | β-Hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate |
| AFM | Atomic Force Microscopy |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| HSP47 | Heat shock protein 47 |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| PA | Phytic Acid |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| KCl | Potassium Chloride |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
References
- Willoughby, D.S.; Cardaci, T.D.; Machek, S.B.; Wilburn, D.T.; Heileson, J.L. Resistance Exercise-Induced Increases in Muscle Myostatin mRNA and Protein Expression Are Subsequently Decreased in Circulation in the Presence of Increased Levels of the Extracellular Matrix Stabilizing Protein Decorin. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2022, 21, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, N.; Champion, A.E. Characterization of muscle epimysium, perimysium and endomysium collagens. Biochem. J. 1984, 219, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.J.; Perlman, G.; Morris, M.; Komarova, S.V. Extracellular matrix composition of connective tissues: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdzieblik, D.; Oesser, S.; Baumstark, M.W.; Gollhofer, A.; König, D. Collagen peptide supplementation in combination with resistance training improves body composition and increases muscle strength in elderly sarcopenic men: A randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 1237–1245, Corrigendum in Br. J. Nutr. 2025, 1, 1. https://doi.org/10.1017/S000711452510425X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimni, M.E.; Robert, D. Molecular Structure and Functions of Collagen. In Collagen; Nimni, M.E., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Gelse, K.; Pöschl, E.; Aigner, T. Collagens—Structure, function, and biosynthesis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 1531–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birk, D.E.; Brückner, P. Collagens, Suprastructures, and Collagen Fibril Assembly. In The Extracellular Matrix: An Overview; Mecham, R.P., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 77–115. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, M.; Goldstein, E.L.; Matich, E.K.; Orr, B.G.; Banaszak Holl, M.M. Type I Collagen Self-Assembly: The Roles of Substrate and Concentration. Langmuir 2013, 29, 2330–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stani, C.; Vaccari, L.; Mitri, E.; Birarda, G. FTIR investigation of the secondary structure of type I collagen: New insight into the amide III band. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 229, 118006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudenberg, U.; Behrens, S.H.; Welzel, P.B.; Müller, M.; Grimmer, M.; Salchert, K.; Taeger, T.; Schmidt, K.; Pompe, W.; Werner, C. Electrostatic interactions modulate the conformation of collagen I. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 2108–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Holl, M.M. Variation in type I collagen fibril nanomorphology: The significance and origin. Bonekey Rep. 2013, 2, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, B.D.; Stegemann, J.P. Strategies for directing the structure and function of three-dimensional collagen biomaterials across length scales. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1488–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terzi, A.; Gallo, N.; Bettini, S.; Sibillano, T.; Altamura, D.; Madaghiele, M.; De Caro, L.; Valli, L.; Salvatore, L.; Sannino, A.; et al. Sub- and Supramolecular X-Ray Characterization of Engineered Tissues from Equine Tendon, Bovine Dermis, and Fish Skin Type-I Collagen. Macromol. Biosci. 2020, 20, e2000017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutolf, M.P.; Hubbell, J.A. Synthetic biomaterials as instructive extracellular microenvironments for morphogenesis in tissue engineering. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, T.; Zeeshan, R.; Zarif, F.; Ilyas, K.; Muhammad, N.; Safi, S.Z.; Rahim, A.; Rizvi, S.A.A.; Rehman, I.U. FTIR analysis of natural and synthetic collagen. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2018, 53, 703–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, L.; Gallo, N.; Natali, M.L.; Terzi, A.; Sannino, A.; Madaghiele, M. Mimicking the Hierarchical Organization of Natural Collagen: Toward the Development of Ideal Scaffolding Material for Tissue Regeneration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 644595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Tang, K.; Tian, H.; Pei, Y. Collagen materials with oriented structure for biomedical applications. J. Polym. Sci. 2024, 62, 998–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubina, V.S.; Kobyakova, M.I.; Penkov, N.V.; Mitenko, G.V.; Udaltsov, S.N.; Shatalin, Y.V. Two Novel Membranes Based on Collagen and Polyphenols for Enhanced Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.; Chen, X.; Peng, Y.; Nan, J.; Wei, B.; He, L.; Xu, C.; Xu, Y.; Xie, D.; Zhang, J.; et al. Modulation of the Self-Assembly of Collagen by Phytic Acid: An In Vitro Study. Macromol. Res. 2018, 26, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andonegi, M.; de la Caba, K.; Guerrero, P. Effect of citric acid on collagen sheets processed by compression. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 100, 105427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Ogawa, K.; Takeuchi, K.; Takagi, M.; Yoshida, M.; Hirokawa, T.; Hirayama, S.; Shin-Ya, K.; Shimada, I.; Doi, T.; et al. A small-molecule compound inhibits a collagen-specific molecular chaperone and could represent a potential remedy for fibrosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 20076–20085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamura, T.; Sakamoto, N.; Kakugawa, T.; Taniguchi, H.; Akiyama, Y.; Okuno, D.; Moriyama, S.; Hara, A.; Kido, T.; Ishimoto, H.; et al. Small molecule inhibitor of HSP47 prevents pro-fibrotic mechanisms of fibroblasts in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 530, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Wu, X.; Meng, X.n.; Xun, D.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y. Discovery of Natural Small Molecules Promoting Collagen Secretion by High-Throughput Screening in Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecules 2022, 27, 8361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szcześniak, K.A.; Ostaszewski, P.; Fuller, J.C., Jr.; Ciecierska, A.; Sadkowski, T. Dietary supplementation of β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate in animals—A review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2015, 99, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holeček, M. Beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate supplementation and skeletal muscle in healthy and muscle-wasting conditions. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girón, M.D.; Vílchez, J.D.; Salto, R.; Manzano, M.; Sevillano, N.; Campos, N.; Argilés, J.M.; Rueda, R.; López-Pedrosa, J.M. Conversion of leucine to β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate by α-keto isocaproate dioxygenase is required for a potent stimulation of protein synthesis in L6 rat myotubes. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Cheng, X.W.; Inoue, A.; Hu, L.; Koike, T.; Kuzuya, M. β-Hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate facilitates PI3K/Akt-dependent mammalian target of rapamycin and FoxO1/3a phosphorylations and alleviates tumor necrosis factor α/interferon γ-induced MuRF-1 expression in C2C12 cells. Nutr. Res. 2014, 34, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baier, S.; Johannsen, D.; Abumrad, N.; Rathmacher, J.A.; Nissen, S.; Flakoll, P. Year-long changes in protein metabolism in elderly men and women supplemented with a nutrition cocktail of beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate (HMB), L-arginine, and L-lysine. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2009, 33, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewska, E.; Donaldson, J.; Kosiński, J.; Dobrowolski, P.; Tomczyk-Warunek, A.; Hułas-Stasiak, M.; Lamorski, K.; Laskowska-Woźniak, D.; Muszyński, S.; Blicharski, R.; et al. β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate (HMB) Supplementation Prevents Bone Loss during Pregnancy—Novel Evidence from a Spiny Mouse (Acomys cahirinus) Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Świetlicka, I.; Muszyński, S.; Prein, C.; Clausen-Schaumann, H.; Aszodi, A.; Arciszewski, M.B.; Blicharski, T.; Gagoś, M.; Świetlicki, M.; Dobrowolski, P.; et al. Fourier Transform Infrared Microspectroscopy Combined with Principal Component Analysis and Artificial Neural Networks for the Study of the Effect of β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate (HMB) Supplementation on Articular Cartilage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade-Espinoza, B.A.; Carbajal-Arizaga, G.G.; Rivas-Fuentes, S.; Nuño, K.; Pelayo-Vázquez, J.B.; Arratia-Quijada, J. Synthesis of Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Material with a Synergistic Interface as a Release Agent for Free Acid β-Hydroxy-β-Methyl Butyrate. J. Nanomater. 2021, 2021, 3060539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, B.; Fang, M.; Wallace, J.M.; Orr, B.G.; Les, C.M.; Banaszak Holl, M.M. Nanoscale structure of type I collagen fibrils: Quantitative measurement of D-spacing. Biotechnol. J. 2013, 8, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabotyagova, O.S.; Cebe, P.; Kaplan, D.L. Collagen structural hierarchy and susceptibility to degradation by ultraviolet radiation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2008, 28, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Sontarp, E.J.; Myneni, S.C.B. Detecting Structural Environments of Carboxyl Groups in Dissolved Natural Organic Molecules. ACS ES&T Water 2024, 4, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Werling, K.; Berquist, E.J.; Lambrecht, D.S.; Garrett-Roe, S. CH Mode Mixing Determines the Band Shape of the Carboxylate Symmetric Stretch in Apo-EDTA, Ca2+–EDTA, and Mg2+–EDTA. J. Phys. Chem. A 2021, 125, 4867–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, R.E.; Aguilera-Márquez, D.; Virués, C.; Inoue, M. Hydrogen bonding between carboxylic acids and amide-based macrocycles in their host–guest complexes. Supramol. Chem. 2008, 20, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.Y.; Glattauer, V.; Ramshaw, J.A.M. Stabilisation of Collagen Sponges by Glutaraldehyde Vapour Crosslinking. Int. J. Biomater. 2017, 2017, 8947823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarannum, A.; Jonnalagadda, R.R.; Nishter, N.F. Stability of collagen in ionic liquids: Ion specific Hofmeister series effect. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 212, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoulders, M.D.; Raines, R.T. Collagen structure and stability. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 929–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giubertoni, G.; Feng, L.; Klein, K.; Giannetti, G.; Rutten, L.; Choi, Y.; van der Net, A.; Castro-Linares, G.; Caporaletti, F.; Micha, D.; et al. Elucidating the role of water in collagen self-assembly by isotopically modulating collagen hydration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2313162121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leikin, S.; Parsegian, V.A.; Rau, D.C.; Rand, R.P. Hydration forces. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1993, 44, 369–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belbachir, K.; Noreen, R.; Gouspillou, G.; Petibois, C. Collagen types analysis and differentiation by FTIR spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Campos Vidal, B.; Mello, M.L.S. Collagen type I amide I band infrared spectroscopy. Micron 2011, 42, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizeland, K.H.; Hofman, K.A.; Hallett, I.C.; Martin, D.E.; Potgieter, J.; Kirby, N.M.; Hawley, A.; Mudie, S.T.; Ryan, T.M.; Haverkamp, R.G.; et al. Nanostructure of electrospun collagen: Do electrospun collagen fibers form native structures? Materialia 2018, 3, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.-N.; Leckie, J.O. Hypochlorite degradation of crosslinked polyamide membranes: II. Changes in hydrogen bonding behavior and performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 282, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Júnior, Z.S.; Botta, S.B.; Ana, P.A.; França, C.M.; Fernandes, K.P.; Mesquita-Ferrari, R.A.; Deana, A.; Bussadori, S.K. Effect of papain-based gel on type I collagen—Spectroscopy applied for microstructural analysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chang, J.; Zhang, P.; Guan, X.; Chen, Y.; Fan, H. Collagen modified with epoxidized safrole for improving antibacterial activity. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 50300–50306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surewicz, W.K.; Mantsch, H.H. New insight into protein secondary structure from resolution-enhanced infrared spectra. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1988, 952, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, M.; Choo, L.P.; Watson, P.H.; Halliday, W.C.; Mantsch, H.H. Beware of connective tissue proteins: Assignment and implications of collagen absorptions in infrared spectra of human tissues. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1995, 1270, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, G.; Wang, Z.; Lei, Z.; Chen, W.; Wang, C. Physiological Benefits, Applications, and Future Directions of β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate (HMB) in Food and Health Industries. Foods 2025, 14, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, L.L.; Resende, C.X.; Tavares, D.S.; Soares, G.A.; Castro, L.O.; Granjeiro, J.M. Cytocompatibility of chitosan and collagen-chitosan scaffolds for tissue engineering. Polímeros 2011, 21, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Mo, X.; He, C.; Wang, H. Intermolecular interactions in electrospun collagen–chitosan complex nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 72, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petibois, C.; Gouspillou, G.; Wehbe, K.; Delage, J.P.; Déléris, G. Analysis of type I and IV collagens by FT-IR spectroscopy and imaging for a molecular investigation of skeletal muscle connective tissue. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 386, 1961–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goormaghtigh, E.; Ruysschaert, J.M.; Raussens, V. Evaluation of the information content in infrared spectra for protein secondary structure determination. Biophys. J. 2006, 90, 2946–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, A.; Wang, W. Improved thermal-stability and mechanical properties of type I collagen by crosslinking with casein, keratin and soy protein isolate using transglutaminase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat, A.; Joye, I.J. Peak Fitting Applied to Fourier Transform Infrared and Raman Spectroscopic Analysis of Proteins. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Mu, C.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, B.; Lin, W. Modification of collagen with a natural cross-linker, procyanidin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 48, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, J.; Sato, T.; Higuchi, K.; Bhutia, Y.D.; Babu, E.; Masuda, M.; Miyauchi, S.; Rueda, R.; Pereira, S.L.; Ganapathy, V. Transport Mechanisms for the Nutritional Supplement β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate (HMB) in Mammalian Cells. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, R.W.; Goh, J.B.; Cheng, C.C.; Su, N.; Goh, M.C. In vitro synthesis of native, fibrous long spacing and segmental long spacing collagen. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 67, e4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.-N.; Ran, L.-Y.; Chen, Z.-H.; Qin, Q.-L.; Shi, M.; Song, X.-Y.; Chen, X.-L.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Xie, B.-B. The ultrastructure of type I collagen at nanoscale: Large or small D-spacing distribution? Nanoscale 2014, 6, 8134–8139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvester, M.F.; Yannas, I.V.; Salzman, E.W.; Forbes, M.J. Collagen banded fibril structure and the collagen-platelet reaction. Thromb. Res. 1989, 55, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
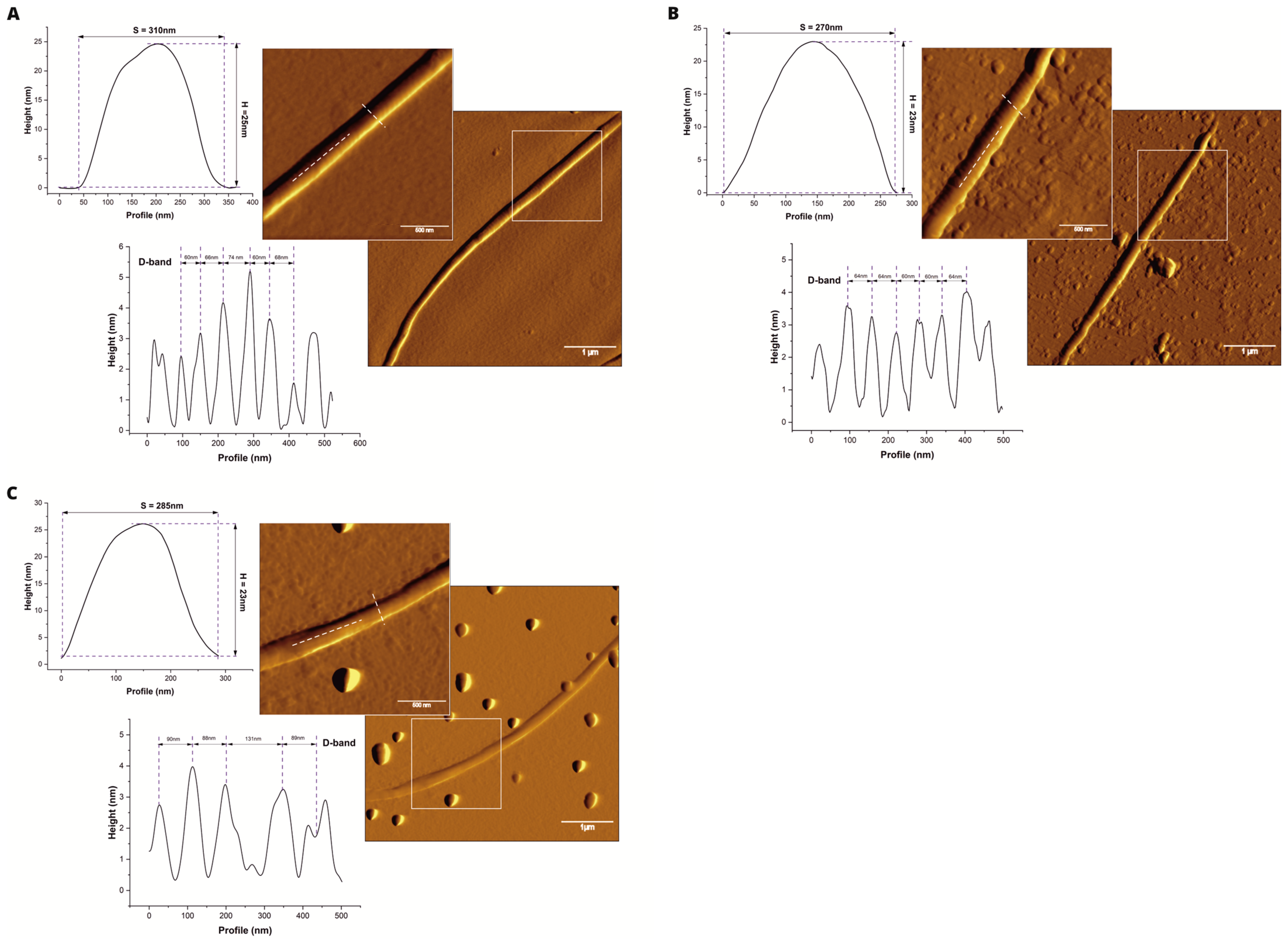
| Sample | Width (nm) | Height (nm) | D-Band (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 358.3 ± 57.8 a | 30.3 ± 4.1 a | 63.4 ± 7.8 a |
| HMB 0.025 | 364.7 ± 68.6 a | 26.0 ± 4.6 b | 63.5 ± 5.1 a |
| HMB 0.25 | 262.1 ± 45.1 b | 23.0 ± 5.4 b | 73.0 ± 5.0 b |
| Sample | Δυ (cm−1) | 1235 cm−1/1450 cm−1 |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 83.2 ± 3.3 a | 1.097 ± 0.012 a |
| HMB 0.025 | 80.6 ± 3.59 a | 1.203 ± 0.097 b |
| HMB 0.25 | 98.2 ± 3.92 b | 1.093 ± 0.016 a |
| Sample | Secondary Structures Share (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-Turns | α-Helix | Random Coils | Triple Helix | β-Sheets | |
| Control | 13.47 ± 0.07 a | 16.13 ± 1.04 a | 23.77 ± 1.52 a | 20.61 ± 1.30 a | 24.75 ± 1.00 a |
| HMB 0.025 | 12.81 ± 0.07 b | 21.07 ± 1.12 b | 16.90 ± 1.47 b | 24.57 ± 0.45 b | 26.98 ± 0.93 a,b |
| HMB 0.25 | 10.63 ± 0.12 c | 25.12 ± 0.66 c | 17.09 ± 0.33 b | 21.63 ± 0.35 a | 27.94 ± 0.97 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Świetlicka, I.; Janek, E.; Gołacki, K.; Krakowiak, D.; Świetlicki, M.; Arczewska, M. Potential Modulatory Effects of β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate on Type I Collagen Fibrillogenesis: Preliminary Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199621
Świetlicka I, Janek E, Gołacki K, Krakowiak D, Świetlicki M, Arczewska M. Potential Modulatory Effects of β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate on Type I Collagen Fibrillogenesis: Preliminary Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199621
Chicago/Turabian StyleŚwietlicka, Izabela, Eliza Janek, Krzysztof Gołacki, Dominika Krakowiak, Michał Świetlicki, and Marta Arczewska. 2025. "Potential Modulatory Effects of β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate on Type I Collagen Fibrillogenesis: Preliminary Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199621
APA StyleŚwietlicka, I., Janek, E., Gołacki, K., Krakowiak, D., Świetlicki, M., & Arczewska, M. (2025). Potential Modulatory Effects of β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate on Type I Collagen Fibrillogenesis: Preliminary Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199621






