Missense Variants in Nutrition-Related Genes: A Computational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Missense/SNP Ratio and Functional Constraint
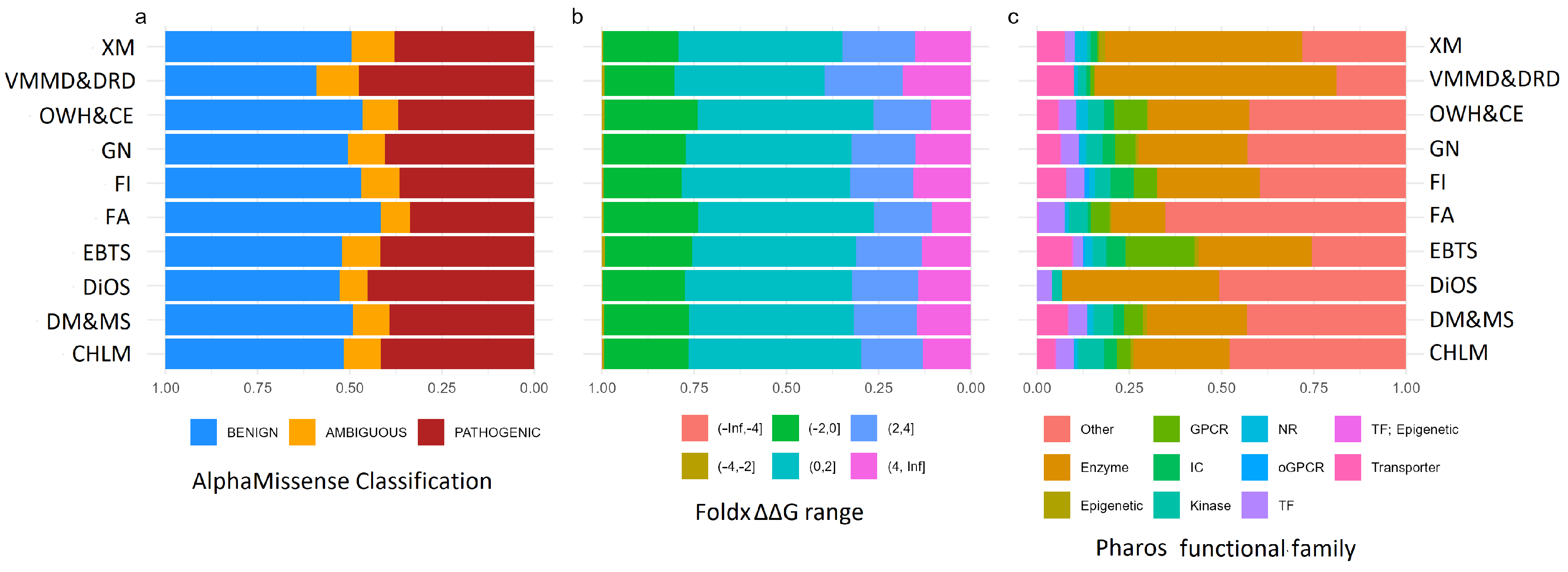
2.2. Variant Composition Across Nutritional Gene Groups
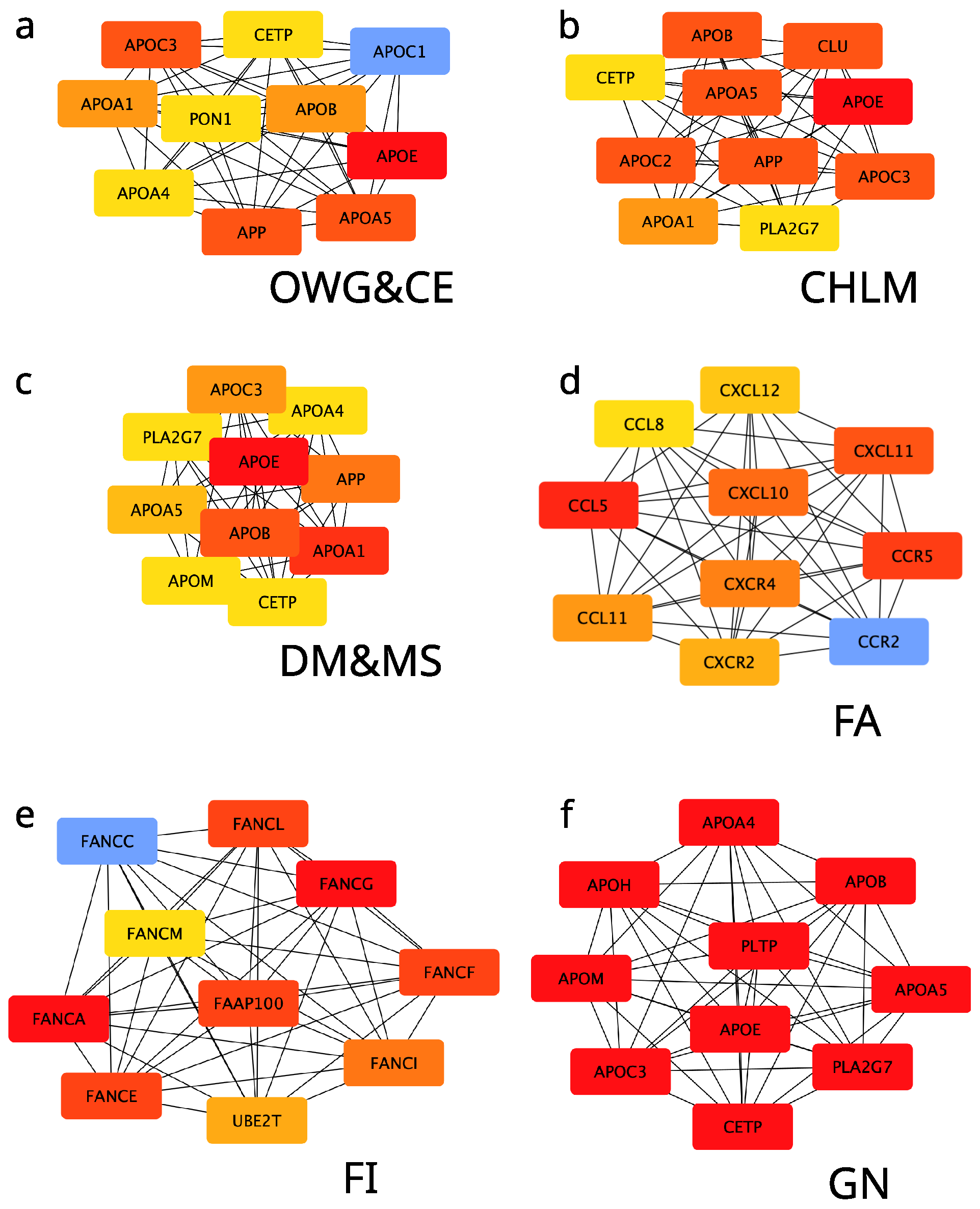
2.3. Network and Gene Ontology Analysis
3. Discussion
3.1. Variant Classification and Evolutionary Insights
3.2. Inflammation and Cardiovascular Risks from Food Allergies
3.3. Enzymes, GPCRs, and Eating Behavior
3.4. Fanconi Anemia Proteins and Food Intolerance
3.5. Role of Apolipoproteins in Metabolic Health
3.6. Implications for Precision Nutrition and Personalized Medicine
3.7. Limitations and Future Directions
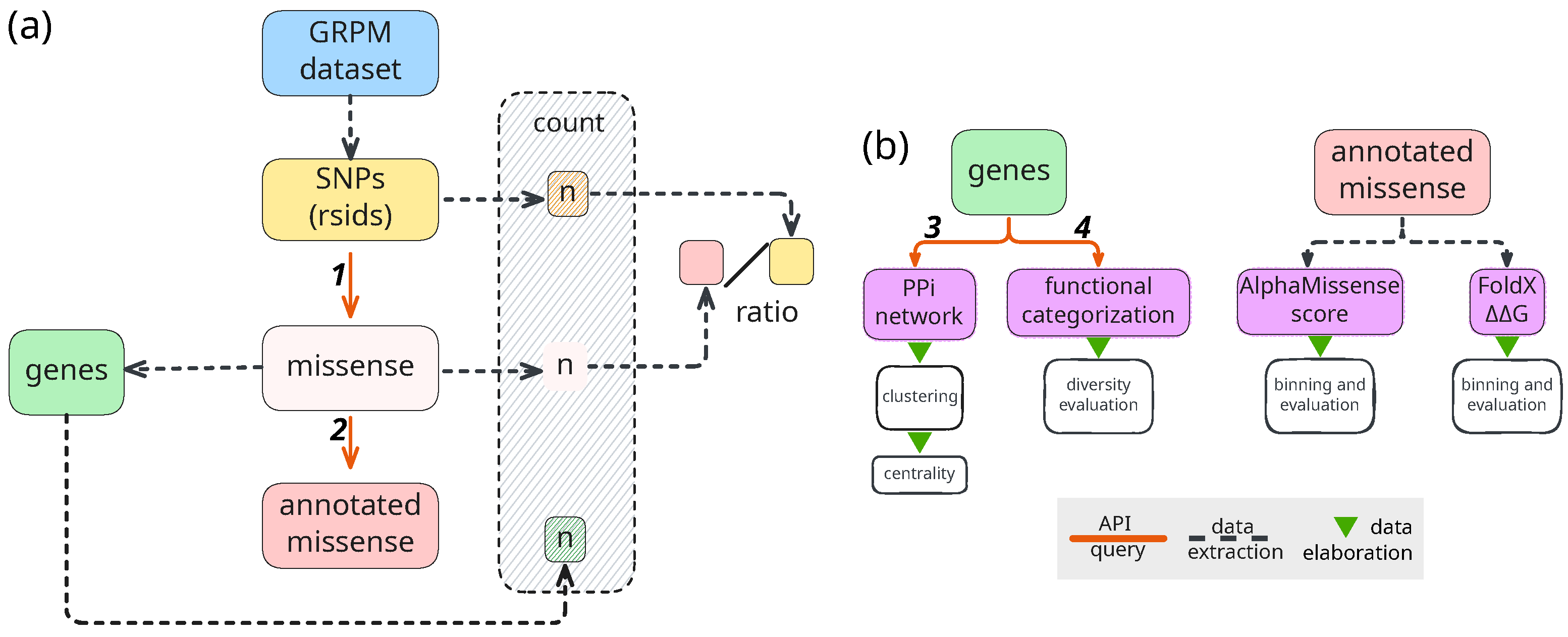
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Data Source
4.2. Data Retrieval and Annotation
4.3. Functional Classification and Pathway Analysis
4.4. Structural Impact Prediction
4.5. Network Analysis
4.6. Gene Ontology Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Group | GO Category | GO Term ID | GO Term Name | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHLM | GO:MF | GO:0005102 | Signaling receptor binding | |
| CHLM | GO:MF | GO:0042802 | Identical protein binding | |
| CHLM | GO:MF | GO:0097367 | Carbohydrate derivative binding | |
| CHLM | GO:BP | GO:1901700 | Response to oxygen-containing compound | |
| CHLM | GO:BP | GO:0044281 | Small molecule metabolic process | |
| CHLM | GO:BP | GO:0030198 | Extracellular matrix organization | |
| CHLM | GO:CC | GO:0071944 | Cell periphery | |
| CHLM | GO:CC | GO:0034358 | Plasma lipoprotein particle | |
| CHLM | GO:CC | GO:0005739 | Mitochondrion | |
| DM&MS | GO:MF | GO:0005102 | Signaling Receptor Binding | |
| DM&MS | GO:MF | GO:0008289 | Lipid binding | |
| DM&MS | GO:MF | GO:0042802 | Identical Protein Binding | |
| DM&MS | GO:BP | GO:1901700 | Response to oxygen-containing compound | |
| DM&MS | GO:BP | GO:0042592 | Homeostatic process | |
| DM&MS | GO:BP | GO:0010876 | Lipid localization | |
| DM&MS | GO:CC | GO:0005615 | Extracellular space | |
| DM&MS | GO:CC | GO:0005783 | Endoplasmic reticulum | |
| DM&MS | GO:CC | GO:0045177 | Apical part of cell | |
| GN | GO:MF | GO:0042802 | Identical protein bidning | |
| GN | GO:MF | GO:0005102 | Signaling receptor binding | |
| GN | GO:MF | GO:0046906 | Tetrapyrrole binding | |
| GN | GO:BP | GO:0042221 | Response to chemical | |
| GN | GO:BP | GO:0003013 | Circulatory system process | |
| GN | GO:BP | GO:0019216 | Regulation of lipid metabolic process | |
| GN | GO:CC | GO:0005615 | Extracellular space | |
| GN | GO:CC | GO:0012505 | Endomembrane system | |
| GN | GO:CC | GO:0045177 | Apical part of cell | |
| DiOS | GO:MF | GO:0016209 | Antioxidant activity | |
| DiOS | GO:MF | GO:0016491 | Oxidoreductase activity | |
| DiOS | GO:BP | GO:0009636 | Response to toxic substance | |
| DiOS | GO:BP | GO:0006950 | Response to stress | |
| DiOS | GO:BP | GO:0019725 | Cellular homeostasis | |
| DiOS | GO:CC | GO:0005615 | Extracellular space | |
| EBTS | GO:MF | GO:0008527 | Taste receptor activity | |
| EBTS | GO:MF | GO:0004930 | G protein-coupled receptor activity | |
| EBTS | GO:BP | GO:0044281 | Small molecule metabolic process | |
| EBTS | GO:BP | GO:0042221 | Response to chemical | |
| EBTS | GO:BP | GO:0007631 | Feeding behavior | |
| EBTS | GO:CC | GO:0071944 | Cell periphery | |
| XM | GO:MF | GO:0016491 | Oxidoreductase activity | |
| XM | GO:MF | GO:0046906 | Tetrapyrrole binding | |
| XM | GO:MF | GO:0036094 | Small molecule binding | |
| XM | GO:BP | GO:0009410 | Responde to xenobiotic stimulus | |
| XM | GO:BP | GO:0044281 | Small molecule metabolic process | |
| XM | GO:BP | GO:0010876 | Lipid localization | |
| XM | GO:CC | GO:0005789 | Endoplasmic reticulum membrane | |
| OWG&CE | GO:MF | GO:0005102 | Signaling receptor binding | |
| OWG&CE | GO:MF | GO:0042562 | Hormone binding | |
| OWG&CE | GO:MF | GO:0120020 | Cholesterol transfer activity | |
| OWG&CE | GO:BP | GO:0042592 | Homeostati process | |
| OWG&CE | GO:BP | GO:1901700 | Response to oxygen-containing compound | |
| OWG&CE | GO:BP | GO:1902652 | Secondary alcohol metabolic process | |
| OWG&CE | GO:CC | GO:0005615 | Extracellular space | |
| VMM&DRD | GO:MF | GO:0016491 | Oxidoreductase activity | |
| VMM&DRD | GO:MF | GO:0019842 | Vitamin binding | |
| VMM&DRD | GO:MF | GO:0046906 | Tetrapyrrole binding | |
| VMM&DRD | GO:BP | GO:0006766 | Vitamin metabolic process | |
| VMM&DRD | GO:BP | GO:0006575 | Modified amino acid metabolic process | |
| VMM&DRD | GO:BP | GO:0006082 | Organic acid metabolic process | |
| FA | GO:MF | GO:0005126 | Cytokine receptor binding | |
| FA | GO:MF | GO:0140375 | Immune receptor activity | |
| FA | GO:MF | GO:0019955 | Cytokine binding | |
| FA | GO:BP | GO:0006955 | Immune response | |
| FA | GO:BP | GO:0051767 | Nitric oxide synthase biosynthetic process | |
| FA | GO:BP | GO:0070672 | Response to interleukine-15 | |
| FA | GO:CC | GO:0009897 | External side of plasma membrane | |
| FA | GO:CC | GO:0005576 | Extracellular region | |
| FA | GO:CC | GO:0045121 | Membrane raft | |
| FI | GO:MF | GO:0042802 | Identical protein binding | |
| FI | GO:BP | GO:0070887 | Cellular response to chemical stimulus | |
| FI | GO:BP | GO:0042592 | Homeostatic process | |
| FI | GO:BP | GO:0036297 | Interstrand cross-link repair | |
| FI | GO:CC | GO:0043240 | Fanconi anemia nuclear complex | |
| FI | GO:CC | GO:0098590 | Plasma membrane region | |
| FI | GO:CC | GO:0031982 | Vescicle |
References
- Thomson, R.; Genovese, G.; Canon, C.; Kovacsics, D.; Higgins, M.K.; Carrington, M.; Winkler, C.A.; Kopp, J.; Rotimi, C.; Adeyemo, A.; et al. Evolution of the primate trypanolytic factor APOL1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E2130–E2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Abdi, A.M.; Luo, W.; Yuan, X.; Dent, A.L. T follicular regulatory cells in food allergy promote IgE via IL-4. JCI Insight 2024, 9, e171241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, P.S.; Shedlock, A.M.; Langefeld, C.D. Genetics of autoimmune diseases: Insights from population genetics. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 60, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raychaudhuri, S. Mapping rare and common causal alleles for complex human diseases. Cell 2011, 147, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pey, A.L.; Stricher, F.; Serrano, L.; Martinez, A. Predicted effects of missense mutations on native-state stability account for phenotypic outcome in phenylketonuria, a paradigm of misfolding diseases. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 1006–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, S.C.; Gupta, E.D. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T polymorphism: Epidemiology, metabolism and the associated diseases. Eur. J. Med Genet. 2015, 58, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pey, A.L.; Ying, M.; Cremades, N.; Velazquez-Campoy, A.; Scherer, T.; Thöny, B.; Sancho, J.; Martinez, A. Identification of pharmacological chaperones as potential therapeutic agents to treat phenylketonuria. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2858–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, L.; Monticelli, M.; Allocca, M.; Hay Mele, B.; Lukas, J.; Cubellis, M.V.; Andreotti, G. Pharmacological chaperones: A therapeutic approach for diseases caused by destabilizing missense mutations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morini, G. The taste for health: The role of taste receptors and their ligands in the complex food/health relationship. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1396393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, J.H. Dopamine signaling in food addiction: Role of dopamine D2 receptors. BMB Rep. 2013, 46, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez Reyes, C.D.; Alejo-Jacuinde, G.; Perez Sanchez, B.; Chavez Reyes, J.; Onigbinde, S.; Mogut, D.; Hernández-Jasso, I.; Calderón-Vallejo, D.; Quintanar, J.L.; Mechref, Y. Multi omics applications in biological systems. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 5777–5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitorino, R. Transforming clinical research: The power of high-throughput omics integration. Proteomes 2024, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filippis, G.M.; Monticelli, M.; Pollice, A.; Angrisano, T.; Hay Mele, B.; Calabrò, V. Computational strategies in nutrigenetics: Constructing a reference dataset of nutrition-associated genetic polymorphisms. J. Biomed. Inform. 2025, 167, 104845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Novati, G.; Pan, J.; Bycroft, C.; Žemgulytė, A.; Applebaum, T.; Pritzel, A.; Wong, L.H.; Zielinski, M.; Sargeant, T.; et al. Accurate proteome-wide missense variant effect prediction with AlphaMissense. Science 2023, 381, eadg7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worth, C.L.; Preissner, R.; Blundell, T.L. SDM—a server for predicting effects of mutations on protein stability and malfunction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W215–W222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castan, L.; Magnan, A.; Bouchaud, G. Chemokine receptors in allergic diseases. Allergy 2017, 72, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henein, M.Y.; Vancheri, S.; Longo, G.; Vancheri, F. The role of inflammation in cardiovascular disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keet, C.; McGowan, E.C.; Jacobs, D.; Post, W.S.; Richards, N.E.; Workman, L.J.; Platts-Mills, T.A.; Manichaikul, A.; Wilson, J.M. IgE to common food allergens is associated with cardiovascular mortality in the National Health and Examination Survey and the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 153, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Depoortere, I.; Hatt, H. Therapeutic potential of ectopic olfactory and taste receptors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 116–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, D.A.; Wang, W.C.; McIlmoyle, E.L.; Robinett, K.S.; Schillinger, R.M.; An, S.S.; Sham, J.S.; Liggett, S.B. Bitter taste receptors on airway smooth muscle bronchodilate by localized calcium signaling and reverse obstruction. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozengurt, E. Taste receptors in the gastrointestinal tract. I. Bitter taste receptors and α-gustducin in the mammalian gut. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 291, G171–G177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luddi, A.; Governini, L.; Wilmskötter, D.; Gudermann, T.; Boekhoff, I.; Piomboni, P. Taste receptors: New players in sperm biology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiLeone, R.J. The influence of leptin on the dopamine system and implications for ingestive behavior. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, S25–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, J.D.; Zhou, Y.; Barak, L.S.; Caron, M.G. Ghrelin receptor signaling in health and disease: A biased view. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 34, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Cai, Y.; Xu, Z.; Ming, Q.; Ji, S.Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, H.; Mao, C.; Shen, D.D.; Hirata, K.; et al. Molecular mechanism of agonism and inverse agonism in ghrelin receptor. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luengo, N.; Goldfield, G.S.; Obregón, A.M. Association between dopamine genes, adiposity, food addiction, and eating behavior in Chilean adult. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1466384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.A.; Owyang, C. Sugars, sweet taste receptors, and brain responses. In Molecular Nutrition: Carbohydrates; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lex, A.; Hauber, W. Dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in the nucleus accumbens core and shell mediate Pavlovian-instrumental transfer. Learn. Mem. 2008, 15, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, D.; Petryszyn, S.; Sanchez, M.; Bories, C.; Beaulieu, J.; De Koninck, Y.; Parent, A.; Parent, M. Striatal neurons expressing D1 and D2 receptors are morphologically distinct and differently affected by dopamine denervation in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, E.F.; Meszaros, J.; Sherman, J.D.; Chohan, M.O.; Teboul, E.; Choi, C.S.; Moore, H.; Javitch, J.A.; Kellendonk, C. Accumbens dopamine D2 receptors increase motivation by decreasing inhibitory transmission to the ventral pallidum. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.M.; Kenny, P.J. Dopamine D2 receptors in addiction-like reward dysfunction and compulsive eating in obese rats. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza, J.; Schwarzenberg, S. Chapter 4: Gastrointestinal, hepatic, and nutritional problems. In Fanconi Anemia: Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management; Fanconi Anemia Research Fund, Inc.: Eugene, Oregon, 2014; pp. 74–98. [Google Scholar]
- Nepal, M.; Che, R.; Zhang, J.; Ma, C.; Fei, P. Fanconi anemia signaling and cancer. Trends Cancer 2017, 3, 840–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Baral, S.; Liu, B.; Sun, Q.; Wang, L.; Ren, J.; Tang, D.; Wang, D. FANCA facilitates G1/S cell cycle advancement, proliferation, migration and invasion in gastric cancer: FANCA’s role in G1/S cell cycle progression and beyond in GC. Acta Biochim. Et Biophys. Sin. 2024, 56, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namikawa, T.; Tanaka, T.; Utsunomiya, M.; Yokota, K.; Munekage, M.; Maeda, H.; Kitagawa, H.; Kurioka, Y.; Satake, H.; Kobayashi, M.; et al. Gastric cancer with Fanconi anemia in adolescent and young adult patient diagnosed by comprehensive genome profiling using next-generation sequencing. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 17, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feingold, K.R. Introduction to Lipids and Lipoproteins. In Endotext [Internet]; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Rebeck, G.W. The role of APOE on lipid homeostasis and inflammation in normal brains: Thematic Review Series: ApoE and Lipid Homeostasis in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1493–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunk, M.M.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Casanova, R.; Chen, J.C.; Espeland, M.A.; Hayden, K.M.; Manson, J.E.; Rapp, S.R.; Shadyab, A.H.; et al. Associations of dietary cholesterol and fat, blood lipids, and risk for dementia in older women vary by APOE genotype. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 5742–5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortea, J.; Pegueroles, J.; Alcolea, D.; Belbin, O.; Dols-Icardo, O.; Vaqué-Alcázar, L.; Videla, L.; Gispert, J.D.; Suárez-Calvet, M.; Johnson, S.C.; et al. APOE4 homozygosity represents a distinct genetic form of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 1284–1291, Erratum in Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Exel, E.; Koopman, J.J.; Bodegom, D.v.; Meij, J.J.; Knijff, P.d.; Ziem, J.B.; Finch, C.E.; Westendorp, R.G. Effect of APOE ε4 allele on survival and fertility in an adverse environment. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, G.; Friedman, D.J.; Ross, M.D.; Lecordier, L.; Uzureau, P.; Freedman, B.I.; Bowden, D.W.; Langefeld, C.D.; Oleksyk, T.K.; Knob, A.L.U.; et al. Association of Trypanolytic ApoL1 Variants with Kidney Disease in African Americans. Science 2010, 329, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, J.D.; Totoo, P.; Burke, D.F.; Jänes, J.; Beltrao, P.; Martin, M.J. ProtVar: Mapping and contextualizing human missense variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W140–W147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Gorodkin, J.; Jensen, L.J. Cytoscape StringApp: Network Analysis and Visualization of Proteomics Data. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.H.; Chen, S.H.; Wu, H.H.; Ho, C.W.; Ko, M.T.; Lin, C.Y. cytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8, S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooms, J. The jsonlite Package: A Practical and Consistent Mapping Between JSON Data and R Objects. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1403.2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, N.; Cook, I.; Crane, N.; Dunnington, D.; François, R.; Keane, J.; Moldovan-Grünfeld, D.; Ooms, J.; Wujciak-Jens, J.; Apache Arrow. Arrow: Integration to ’Apache’ ’Arrow’, R Package Version 19.0.1; 2025. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=arrow (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Wickham, H. httr: Tools for Working with URLs and HTTP, R Package Version 1.4.7; 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=httr (accessed on 31 March 2025).
| Group | SNP Count | Missense Count | Missense Gene Count | Missense/SNP Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHLM | 365,243 | 28,294 | 938 | 0.08 |
| DM&MS | 215,861 | 11,752 | 524 | 0.05 |
| DiOS | 34,510 | 1686 | 73 | 0.05 |
| EBTS | 28,296 | 2406 | 192 | 0.09 |
| FA | 27,280 | 4227 | 371 | 0.15 |
| FI | 16,665 | 3766 | 255 | 0.23 |
| GN | 268,301 | 14,840 | 623 | 0.06 |
| OWG&CE | 118,198 | 4661 | 282 | 0.04 |
| VMM&DRD | 34,600 | 2457 | 90 | 0.07 |
| XM | 62,295 | 5878 | 185 | 0.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Filippis, G.M.; Monticelli, M.; Hay Mele, B.; Calabrò, V. Missense Variants in Nutrition-Related Genes: A Computational Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199619
De Filippis GM, Monticelli M, Hay Mele B, Calabrò V. Missense Variants in Nutrition-Related Genes: A Computational Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199619
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Filippis, Giovanni Maria, Maria Monticelli, Bruno Hay Mele, and Viola Calabrò. 2025. "Missense Variants in Nutrition-Related Genes: A Computational Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199619
APA StyleDe Filippis, G. M., Monticelli, M., Hay Mele, B., & Calabrò, V. (2025). Missense Variants in Nutrition-Related Genes: A Computational Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199619







