Live Cell-Based Semi-Quantitative Stratification Highlights Titre-Dependent Phenotypic Heterogeneity in MOGAD: A Single-Centre Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Results
2.2. Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Statistical Analysis
3.3. Cell Culture and Transfection
3.4. MOG Antibody Detection and Semi-Quantitative Analysis for Endpoint Titration
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banwell, B.; Bennett, J.L.; Marignier, R.; Kim, H.J.; Brilot, F.; Flanagan, E.P.; Ramanathan, S.; Waters, P.; Tenembaum, S.; Graves, J.S.; et al. Diagnosis of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease: International MOGAD Panel proposed criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Ogawa, R.; Fujimori, J.; Uzawa, A.; Sato, Y.; Nagashima, K.; Kuriyama, N.; Kuwabara, S.; Nakashima, I. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease in a nationwide survey. Mult Scler. 2023, 29, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hor, J.Y.; Fujihara, K. Epidemiology of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease: A review of prevalence and incidence worldwide. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1260358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechtman, A.; Freidman-Korn, T.; Zveik, O.; Shweiki, L.; Hoichman, G.; Vaknin-Dembinsky, A. Assessing the applicability of the 2023 international MOGAD panel criteria in real-world clinical settings. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 5102–5108, Correction in J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 7065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippatou, A.G.; Said, Y.; Chen, H.; Vasileiou, E.S.; Ahmadi, G.; Sotirchos, E.S. Validation of the international MOGAD panel proposed criteria: A single-centre US study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2024, 95, 870–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, P.J.; Komorowski, L.; Woodhall, M.; Lederer, S.; Majed, M.; Fryer, J.; Mills, J.; Flanagan, E.P.; Irani, S.R.; Kunchok, A.C.; et al. A multicenter comparison of MOG-IgG cell-based assays. Neurology 2019, 92, e1250–e1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastaldi, M.; Scaranzin, S.; Jarius, S.; Wildeman, B.; Zardini, E.; Mallucci, G.; Rigoni, E.; Vegezzi, E.; Foiadelli, T.; Savasta, S.; et al. Cell-based assays for the detection of MOG antibodies: A comparative study. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 3555–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.A.; Houston, S.D.; Tea, F.; Merheb, V.; Lee, F.X.Z.; Smith, S.; McDonald, D.; Zou, A.; Liyanage, G.; Pilli, D.; et al. Validation of a Flow Cytometry Live Cell-Based Assay to Detect Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein Antibodies for Clinical Diagnostics. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2022, 7, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnero Contentti, E.; Pestchanker, C.; Ciampi, E.; Castro Suarez, S.; Caparo Zamalloa, C.; Daccach Marques, V.; Messias, K.; Ignacio Gortari, J.; Tkachuk, V.; Silva, B.; et al. The real-world applicability of the 2023 international myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease criteria in a Latin American cohort. Eur. J. Neurol. 2024, 31, e16445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.L.; Haven, T.R.; Zuromski, L.M.; Luong, K.; Clardy, S.L.; Peterson, L.K. High level of agreement in a fixed vs. live cell-based assay for antibodies to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein in a real-world clinical laboratory setting. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1192644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcadela, M.; Rocchi, C.; San Martin, D.; Gibbons, E.L.; Wells, D.; Woodhall, M.R.; Waters, P.J.; Huda, S.; Hamid, S. Timing of MOG-IgG Testing Is Key to 2023 MOGAD Diagnostic Criteria. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 11, e200183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlad, B.; Reichen, I.; Neidhart, S.; Hilty, M.; Lekaditi, D.; Heuer, C.; Eisele, A.; Ziegler, M.; Reindl, M.; Lutterotti, A.; et al. Basic CSF parameters and MRZ reaction help in differentiating MOG antibody-associated autoimmune disease versus multiple sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1237149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budhram, A.; Flanagan, E.P. Testing for myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibodies: Who, what, where, when, why, and how. Mult. Scler. J. 2025, 31, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollo, L.; Iaffaldano, P.; Ruggieri, M.; Palazzo, C.; Mastrapasqua, M.; Manni, A.; Paolicelli, D.; Frigeri, A.; Trojano, M. Longitudinal Evaluation of Serum MOG-IgG and AQP4-IgG Antibodies in NMOSD by a Semiquantitative Ratiometric Method. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 633115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchionatti, A.; Hansel, G.; Avila, G.U.; Sato, D.K. Detection of MOG-IgG in Clinical Samples by Live Cell-Based Assays: Performance of Immunofluorescence Microscopy and Flow Cytometry. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 642272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarius, S.; Paul, F.; Aktas, O.; Asgari, N.; Dale, R.C.; de Seze, J.; Franciotta, D.; Fujihara, K.; Jacob, A.; Kim, H.J.; et al. MOG encephalomyelitis: International recommendations on diagnosis and antibody testing. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyakumar, N.; Lerch, M.; Dale, R.C.; Ramanathan, S. MOG antibody-associated optic neuritis. Eye 2024, 38, 2289–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satukijchai, C.; Mariano, R.; Messina, S.; Sa, M.; Woodhall, M.R.; Robertson, N.P.; Ming, L.; Wassmer, E.; Kneen, R.; Huda, S.; et al. Factors Associated With Relapse and Treatment of Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein Antibody-Associated Disease in the United Kingdom. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2142780, Erratum in JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e225056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reindl, M.; Schanda, K.; Woodhall, M.; Tea, F.; Ramanathan, S.; Sagen, J.; Fryer, J.P.; Mills, J.; Teegen, B.; Mindorf, S.; et al. International multicenter examination of MOG antibody assays. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e674, Correction in Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajfirouz, D.; Madhavan, A.; Pacheco Marrero, J.M.; Krecke, K.N.; Fautsch, K.J.; Flanagan, E.P.; Pittock, S.J.; Shah, S.; Bhatti, M.T.; Chen, J.J. Frequency of Asymptomatic Optic Nerve Enhancement in 203 Patients With MOG Antibody-Associated Disease. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 11, e200277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, Y.; Hoshino, Y.; Kamo, R.; Cossu, D.; Yokoyama, K.; Hattori, N. Comparing clinical and imaging features of patients with MOG antibody-positivity and with and without oligoclonal bands. Front Immunol. 2023, 14, 1211776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tea, F.; Lopez, J.A.; Ramanathan, S.; Merheb, V.; Lee, F.X.Z.; Zou, A.; Pilli, D.; Patrick, E.; van der Walt, A.; Monif, M.; et al. Characterization of the human myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody response in demyelination. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisani, F.; Sparaneo, A.; Tortorella, C.; Ruggieri, M.; Trojano, M.; Mola, M.G.; Nicchia, G.P.; Frigeri, A.; Svelto, V. Aquaporin-4 Autoantibodies in Neuromyelitis Optica: AQP4 Isoform-Dependent Sensitivity and Specificity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, P.; Fadda, G.; Woodhall, M.; O’Mahony, J.; Brown, R.A.; Castro, V.; Longoni, G.; Irani, S.R.; Sun, B.; Yeh, E.A.; et al. Serial Anti–Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein Antibody Analyses and Outcomes in Children With Demyelinating Syndromes. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastaldi, M.; Foiadelli, T.; Greco, G.; Scaranzin, S.; Rigoni, E.; Masciocchi, S.; Ferrari, S.; Mancinelli, C.; Brambilla, L.; Mancardi, M.; et al. Prognostic relevance of quantitative and longitudinal MOG antibody testing in patients with MOGAD: A multicentre retrospective study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2023, 94, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Chiriboga, A.S.; Majed, M.; Fryer, J.; Dubey, D.; McKeon, A.; Flanagan, E.P.; Jitprapaikulsan, J.; Kothapalli, N.; Tillema, J.; Chen, J.; et al. Association of MOG-IgG Serostatus With Relapse After Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis and Proposed Diagnostic Criteria for MOG-IgG–Associated Disorders. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.M.; Apóstolos-Pereira, S.L.; Pitombeira, M.S.; Bruel Torretta, P.H.; Callegaro, D.; Sato, D.K. Persistent MOG-IgG positivity is a predictor of recurrence in MOG-IgG-associated optic neuritis, encephalitis and myelitis. Mult. Scler. 2018, 25, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo-Calvo, A.; Ruiz, A.; Rollot, F.; Arrambide, G.; Deschamps, R.; Maillart, E.; Papeix, C.; Audoin, B.; Lépine, A.F.; Maurey, H.; et al. Clinical Features and Risk of Relapse in Children and Adults with Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein Antibody-Associated Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2021, 89, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tea, F.; Pilli, D.; Ramanathan, S.; Lopez, J.A.; Merheb, V.; Lee, F.X.Z.; Zou, A.; Liyanage, G.; Bassett, C.B.; Thomsen, S.; et al. Effects of the Positive Threshold and Data Analysis on Human MOG Antibody Detection by Live Flow Cytometry. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, K.; Mori, M.; Liu, J.; Tanaka, S.; Kaneko, K.; Ojid, S.; Takahashie, T.; Uzawaa, A.; Uchidaa, T.; Masudaa, H.; et al. The accuracy of flow cytometric cell-based assay to detect anti-myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) antibodies determining the optimal method for positivity judgement. J. Neuroimmunol. 2019, 336, 577021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, G.; Trewin, B.P.; Lopez, J.A.; Andersen, J.; Tea, F.; Merheb, V.; Nguyen, K.; Lee, F.X.Z.; Fabis-Pedrini, M.J.; Zou, A.; et al. The MOG antibody non-P42 epitope is predictive of a relapsing course in MOG antibody-associated disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2024, 95, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spatola, M.; Chuquisana, O.; Jung, W.; Lopez, J.A.; Wendel, E.; Ramanathan, S.; Keller, C.W.; Hahn, T.; Meinl, E.; Reindl, M.; et al. Humoral signatures of MOG-antibody-associated disease track with age and disease activity. Cell Rep. Med. 2023, 4, 100913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Meng, H.; Fan, M.; Yin, L.; Sun, J.; Yao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Cong, H.; Wang, H.; Song, T.; et al. A Simple Score (MOG-AR) to Identify Individuals at High Risk of Relapse After MOGAD Attack. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 11, e200309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, L. Challenges in the Diagnosis and Management of Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein Antibody-Associated Disease (MOGAD). Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2025, 28, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, S.; Whittam, D.; Jackson, R.; Karthikeayan, V.; Kelly, P.; Linaker, S.; Mutch, K.; Kneen, R.; Woodhall, M.; Murray, K.; et al. Predictors of relapse in MOG antibody associated disease: A cohort study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e055392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Pang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Guo, J.; Meng, H. The nomogram model predicts relapse risk in myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease: A single-center study. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1527057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechi, E.; Buciuc, M.; Pittock, S.J.; Chen, J.J.; Fryer, J.P.; Jenkins, S.M.; Budhram, A.; Weinshenker, B.G.; Lopez-Chiriboga, A.S.; Tillema, J.; et al. Positive Predictive Value of Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein Autoantibody Testing. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, J.M.; Kasirye-Mbugua, N.; Costello, F.; Assis, Z. Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody positive patients -validation of current diagnostic criteria. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2025, 97, 106394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.N.; Kim, B.; Kim, J.; Park, K.S.; Seo, D.; Kim, H.; Lee, E.; Lim, Y.; Ju, H.; Chung, Y.H.; et al. Time to Treat First Acute Attack of Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein Antibody-Associated Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2024, 81, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mol, C.; Wong, Y.Y.M.; van Pelt, E.D.; Wokke, B.H.A.; Siepman, T.A.M.; Neuteboom, R.F.; Hamann, D.; Hintzen, R.Q. The clinical spectrum and incidence of anti-MOG-associated acquired demyelinating syndromes in children and adults. Mult. Scler. J. 2020, 26, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildner, P.; Stasiołek, M.; Matysiak, M. Differential diagnosis of multiple sclerosis and other inflammatory CNS diseases. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 37, 101452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, R.; Guillaume, J.; Ciron, J.; Audoin, B.; Ruet, A.; Maillart, E.; Pique, J.; Benyahya, L.; Laplaud, D.A.; Michel, L.; et al. as the NOMADMUS study group. Early Maintenance Treatment Initiation and Relapse Risk Mitigation After a First Event of MOGAD in Adults: The MOGADOR2 Study. Neurology 2024, 103, e209624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Wu, P.; Wang, R.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Y. Meta-analysis of the effectiveness of relapse prevention therapy for myelin-oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2023, 72, 104571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
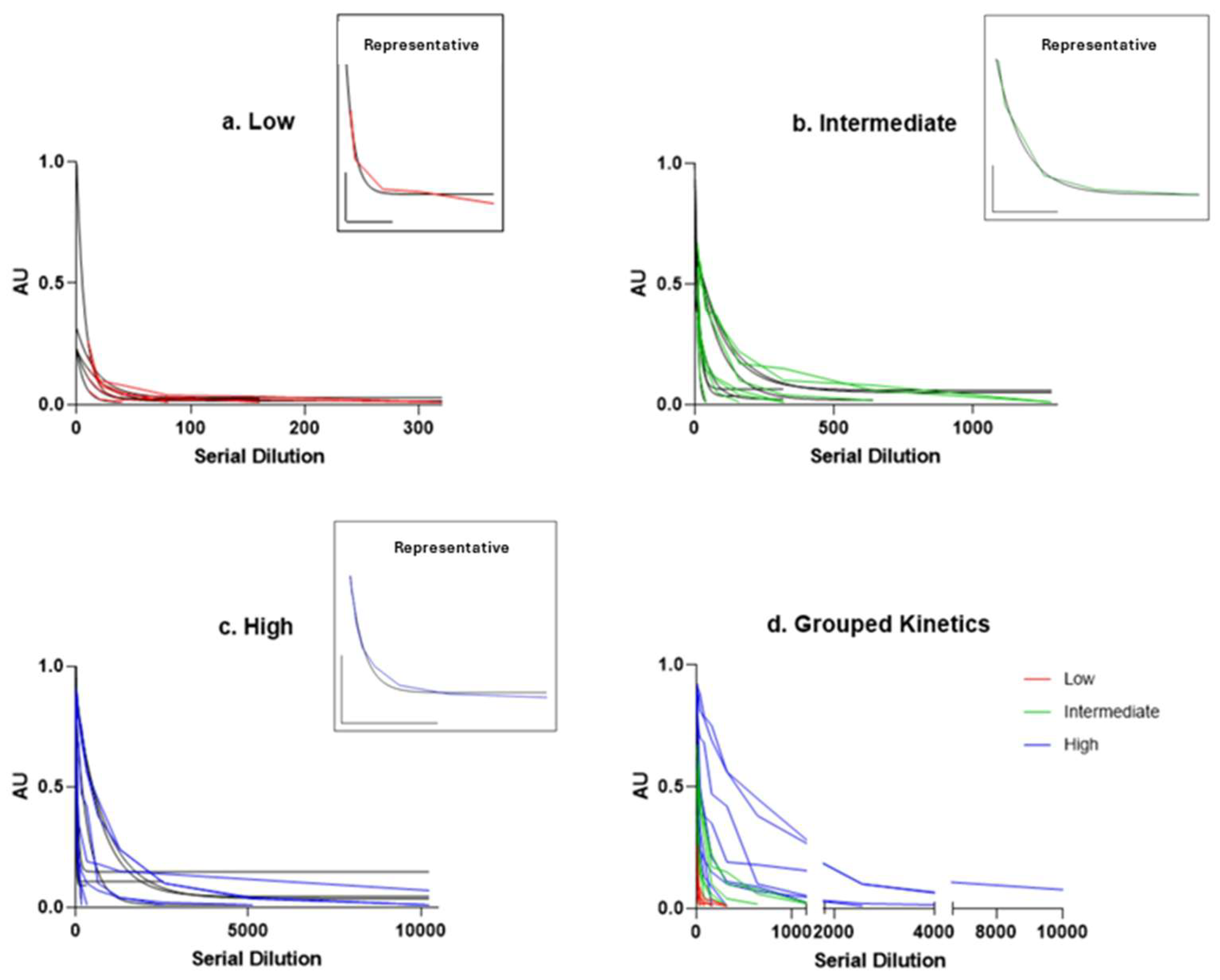
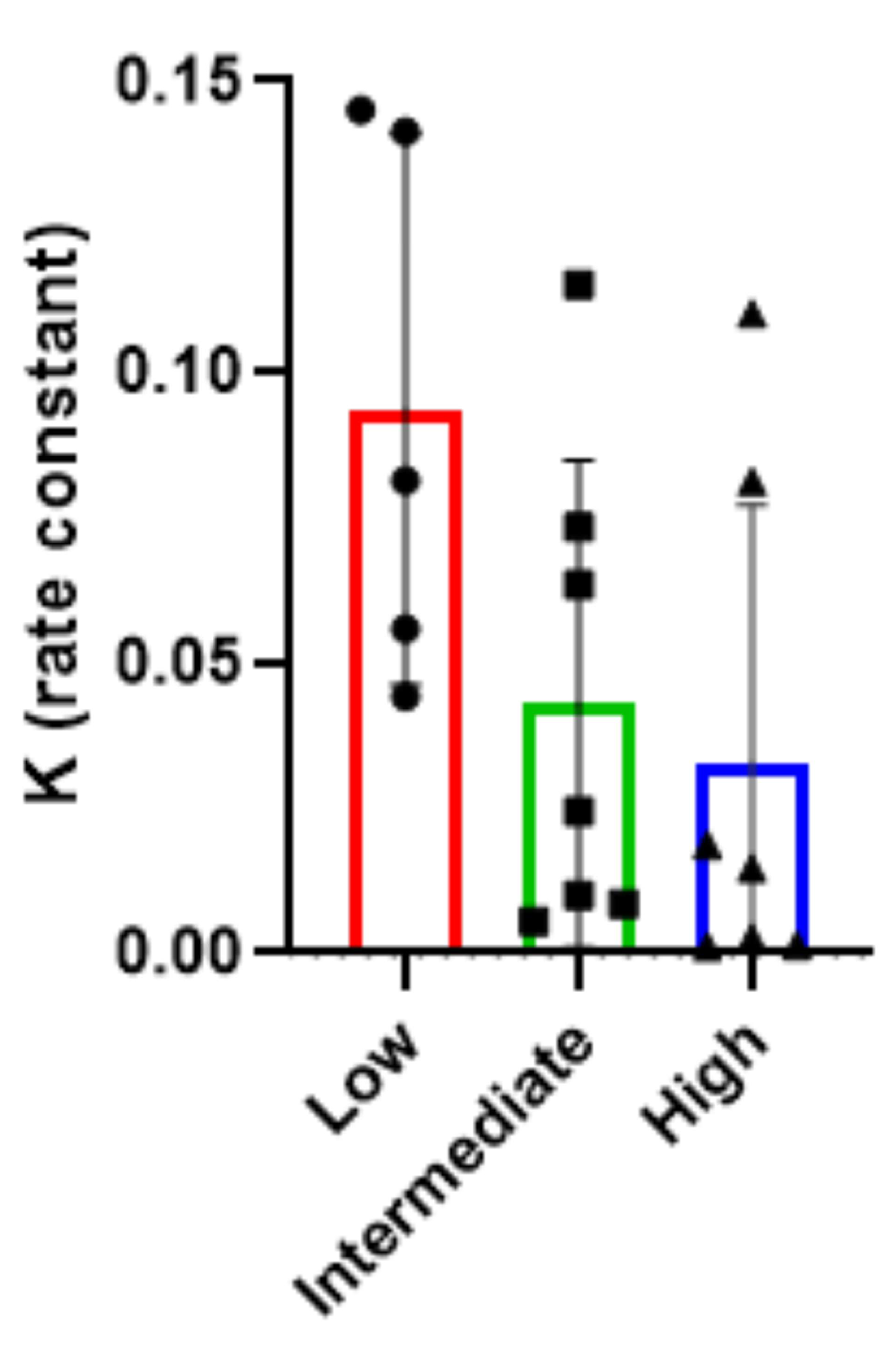
| Total | Low Titre (0.02–0.33) | Medium Titre (0.34–0.66) | High Titre (0.67–1.00) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAMPLE SIZE | 19 | 5 | 7 | 7 |
| AGE OF ONSET | ||||
| Mean ± SD | 41.16 ± 18.33 | 33.8 ± 14.22 | 36.14 ± 15.57 | 51.43 ± 18.87 |
| Median (min-max) | 43 (10–70) | 30 (17–55) | 34 (15–60) | 58 (10–70) |
| SEX DISTRIBUTION | ||||
| M (% tot) | 5 (26.32%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (42.86%) | 2 (28.57%) |
| F (% tot) | 14 (73.68%) | 5 (100%) | 4 (57.14%) | 5 (71.43%) |
| CLINICAL FEATURES | ||||
| EDSS | ||||
| Mean ± SD | 2.24 ± 1.57 | 3.0 ± 1.82 | 1.64 ± 1.46 | 2.36 ± 1.22 |
| Median (Min-Max) | 2.0 (0.0–6.5) | 2.0 (1.5–6.5) | 1.5 (0.0–4.0) | 2.0 (0.0–4.0) |
| MONOPHASIC COURSE (% tot) | 11 (57.89%) | 2 (40%) | 5 (71.43%) | 4 (57.14%) |
| ANTI-MOG ANTIBODIES FEATURES | ||||
| DISAPPEARANCE TITRE (NUMBER OF DILUTIONS) | ||||
| Mean ± SD | 2004.21 ± 3092.02 | 184 ± 117.58 | 668.57 ± 536.96 | 4640 ± 3814.98 |
| Median (Min-Max) | 320 (40–10240) | 160 (40–320) | 320 (40–1280) | 3000 (320–10240) |
| SEMI-QUANTITATIVE TITRE | ||||
| Mean ± SD | 0.56 ± 0.31 | 0.17 ± 0.09 | 0.50 ± 0.11 | 0.90 ± 0.11 |
| Median (Min-Max) | 0.57 (0.05–0.99) | 0.15 (0.05–0.27) | 0.49 (0.35–0.65) | 0.94 (0.67–0.99) |
| CSF FEATURES | ||||
| OCBs NUMBER | ||||
| Mean ± SD | 2.11 ± 4.00 | 3.2 ± 4.02 | 2.71 ± 5.06 | 0.5 ± 0.76 |
| Median (Min-Max) | 1 (0–15) | 1 (0–11) | 1 (0–15) | 0 (0–2) |
| Pts with CSF-RESTRICTED OCBs (% tot) | 5 (26.32%) | 2 (40%) | 2 (28.57%) | 1 (16.67%) |
| CLINICAL FEATURES—ONSET SYMPTOM | ||||
| ON (% tot) | 13 (68.42%) | 1 (20%) | 6 (85.71%) | 6 (85.71%) |
| Unilateral ON (% tot) [% ON] | 9 (47.37%) [64.29%] | 1 (20%) [100%] | 5 (71.43%) [83.33%] | 3 (42.86%) [50%] |
| Bilateral ON (% tot) [% ON] | 4 (21.05%) [30.77%] | 0 (0%) [0%] | 1 (14.29%) [16.67%] | 3 (42.86%) [50%] |
| SPINAL CORD (% tot) | 5 (26.32%) | 3 (60%) | 1 (14.29%) | 1 (14.29%) |
| Motor (% tot) [% Spinal Cord] | 2 (10.53%) [40%] | 1 (20%) [33.33%] | 1 (14.29%) [100%] | 0 (0%) [0%] |
| Sensitive (% tot) [% Spinal Cord] | 5 (26.32%) [100%] | 3 (60%) [100%] | 1 (14.29%) [100%] | 1 (14.29%) [100%] |
| Sphincteric (% tot) [% Spinal Cord] | 1 (5.26%) [20%] | 1 (20%) [33.33%] | 0 (0%) [0%] | 0 (0%) [0%] |
| CEREBELLAR (% tot) | 1 (5.26%) | 1 (20%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| BRAINSTEM (% tot) | 1 (5.26%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (14.29%) |
| Total | Low Titre (0.02–0.33) | Medium Titre (0.34–0.66) | High Titre (0.67–1.00) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRI FEATURES | ||||
| ON (% tot) | 11 (57.89%) | 1 (20%) | 4 (57.14%) | 6 (85.71%) |
| Unilateral ON (% tot) [% ON] | 6 (31.58%) [54.55%] | 1 (20%) [100%] | 3 (42.86%) [75%] | 2 (28.57%) [33.33%] |
| Bilateral ON (% tot) [% ON] | 5 (26.32%) [45.45%] | 0 (0%) [0%] | 1 (14.29%) [25%] | 4 (57.14%) [66.67%] |
| ENCEPHALIC (% tot) | 5 (26.32%) | 1 (20%) | 1 (14.29%) | 3 (42.86%) |
| CEREBELLAR—MCP (% tot) | 4 (21.05%) | 1 (20%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (28.57%) |
| BRAINSTEM (% tot) | 4 (21.05%) | 2 (40%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (14.29%) |
| SPINAL CORD (% tot) | 7 (36.85%) | 4 (80%) | 1 (14.29%) | 2 (28.57%) |
| Cervical (% tot) [% Spinal Cord] | 5 (26.32%) [71.43%] | 4 (80%) [100%] | 1 (14.29%) [100%] | 1 (14.29%) [50%] |
| Dorsal (% tot) [% Spinal Cord] | 4 (21.05%) [51.14%] | 3 (60%) [75%] | 0 (0%) [0%] | 1 (14.29%) [50%] |
| Conus (% tot) [% Spinal Cord] | 1 (5.26%) [14.29%] | 1 (20%) [25%] | 0 (0%) [0%] | 0 (0%) [0%] |
| NEGATIVE (% tot) | 2 (10.53%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (28.57%) | 0 (0%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Regina, D.; Gargano, C.D.; Guerra, T.; Frigeri, A.; Paolicelli, D.; Ruggieri, M.; Iaffaldano, P. Live Cell-Based Semi-Quantitative Stratification Highlights Titre-Dependent Phenotypic Heterogeneity in MOGAD: A Single-Centre Experience. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199615
Regina D, Gargano CD, Guerra T, Frigeri A, Paolicelli D, Ruggieri M, Iaffaldano P. Live Cell-Based Semi-Quantitative Stratification Highlights Titre-Dependent Phenotypic Heterogeneity in MOGAD: A Single-Centre Experience. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199615
Chicago/Turabian StyleRegina, Donato, Concetta Domenica Gargano, Tommaso Guerra, Antonio Frigeri, Damiano Paolicelli, Maddalena Ruggieri, and Pietro Iaffaldano. 2025. "Live Cell-Based Semi-Quantitative Stratification Highlights Titre-Dependent Phenotypic Heterogeneity in MOGAD: A Single-Centre Experience" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199615
APA StyleRegina, D., Gargano, C. D., Guerra, T., Frigeri, A., Paolicelli, D., Ruggieri, M., & Iaffaldano, P. (2025). Live Cell-Based Semi-Quantitative Stratification Highlights Titre-Dependent Phenotypic Heterogeneity in MOGAD: A Single-Centre Experience. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199615








