Genomic Characterization of a Rare K30-ST198 Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Clone with Distinctive Virulence Features
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Data and Antimicrobial Susceptibility
2.2. String Test Results
2.3. Screening by eazyplexR hvKp Assay
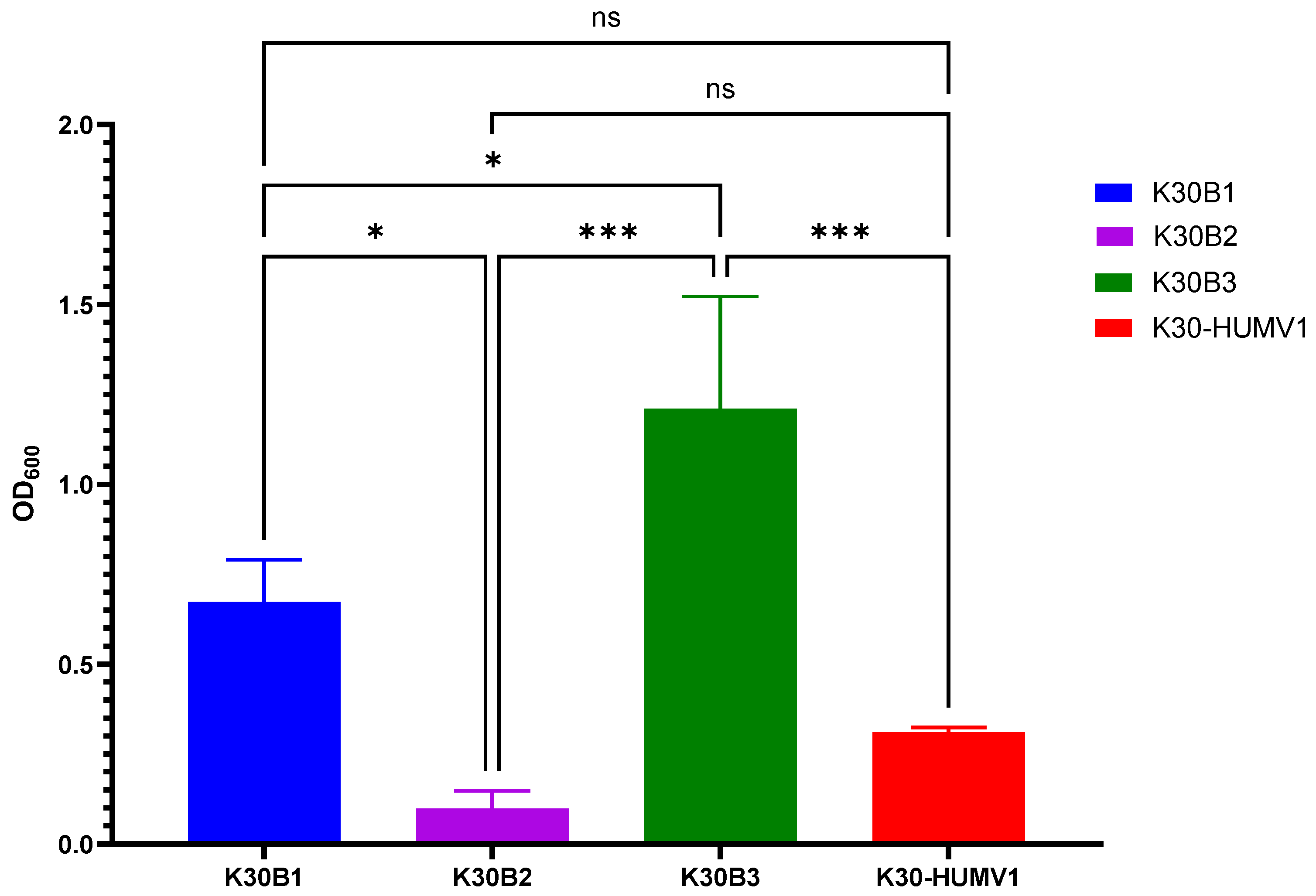
2.4. Determination of Biofilm Production
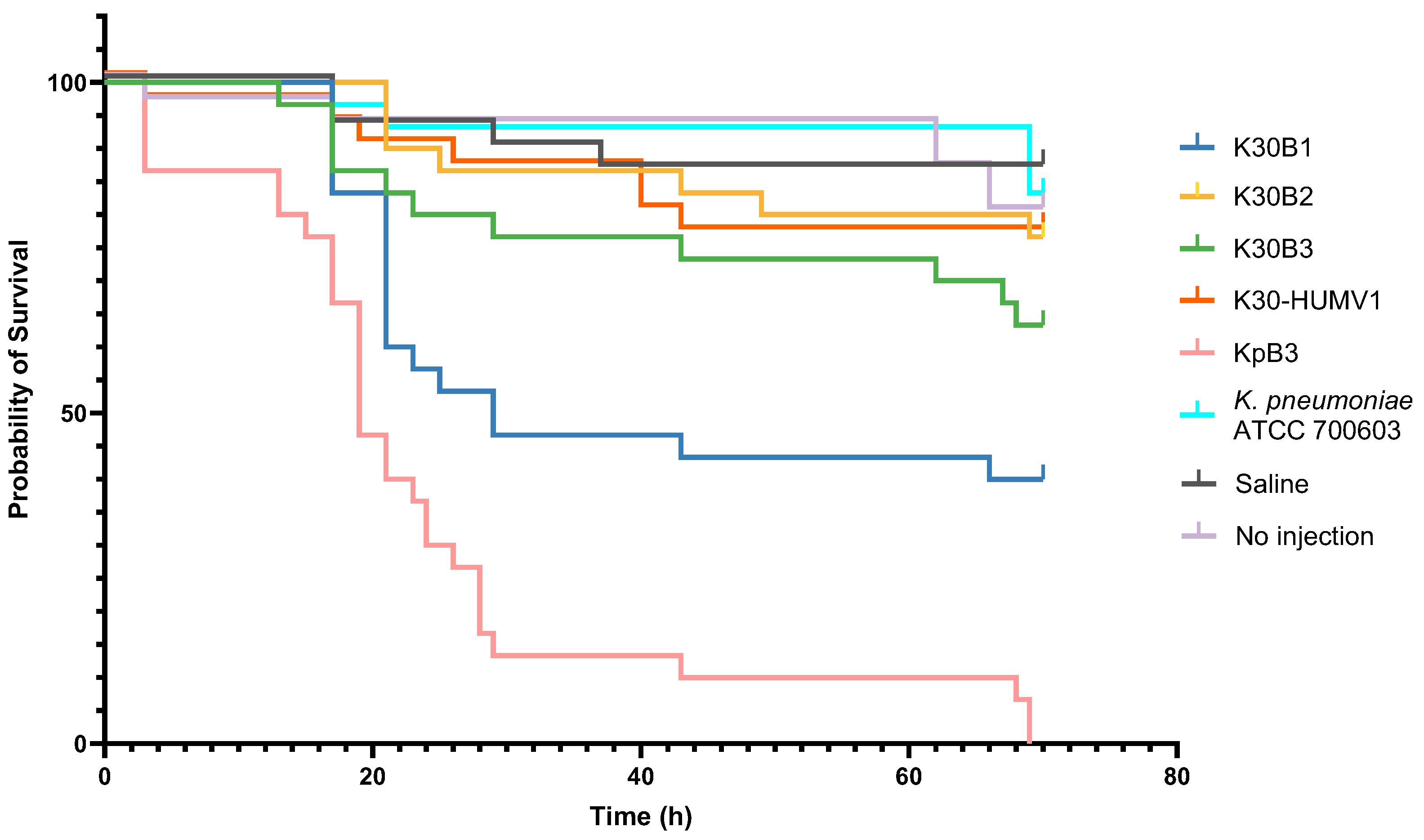
2.5. Galleria Mellonella Larvae Infection Model
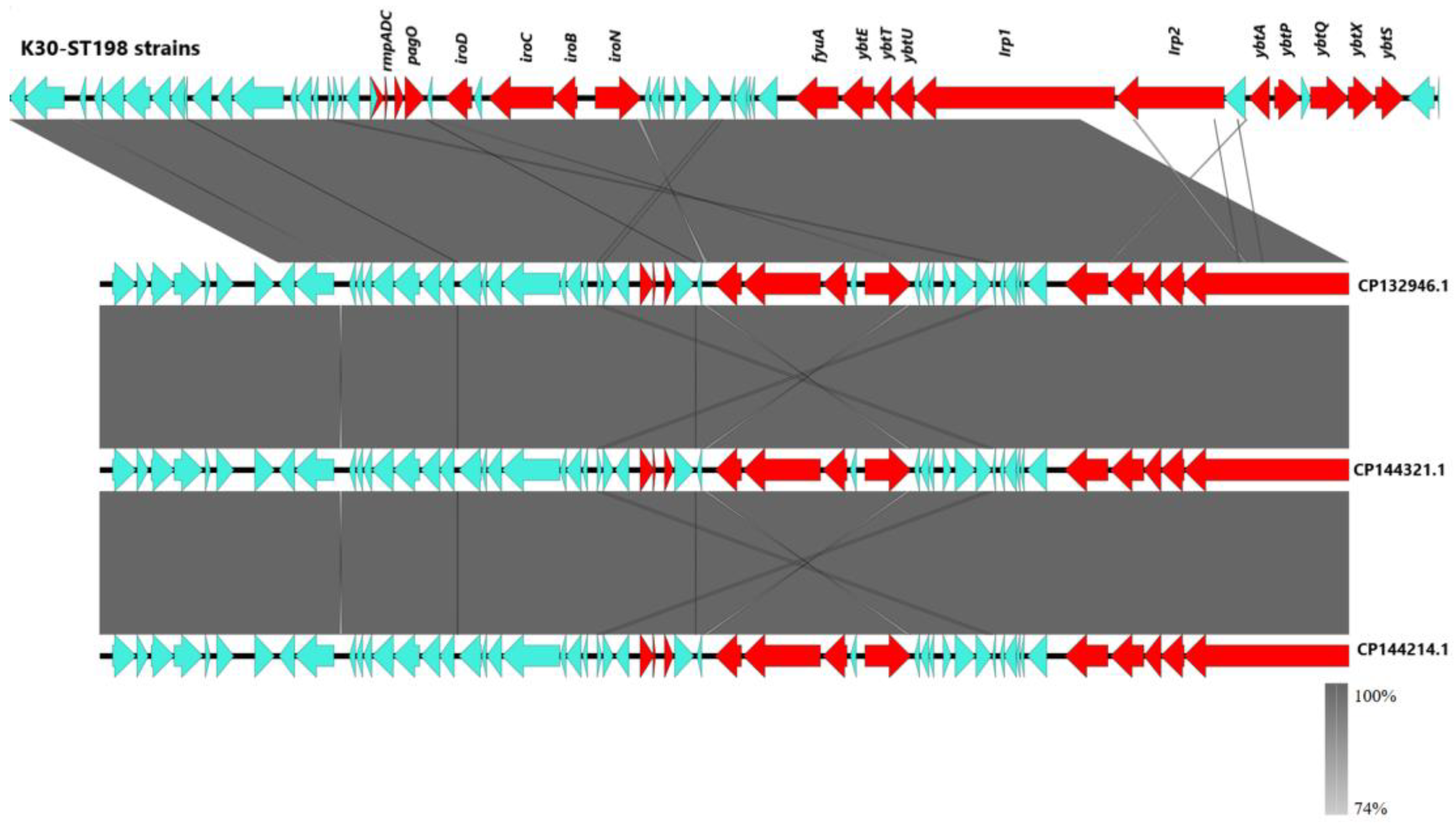
2.6. Genetic Characterization by Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS)
2.7. Protein Structure Predictions and Functional Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Strain Isolation, Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST), and Clinical Data Collection
4.3. Identification of the Hypermucoviscous (HMV) Phenotype
4.4. Screening with the eazyplex® hvKp Assay
4.5. Biofilm Production Assay
4.6. Virulence Assay in Galleria mellonella
4.7. Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS) and Bioinformatics Analysis
4.8. Protein Structure Prediction
4.9. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shon, A.S.; Bajwa, R.P.; Russo, T.A. Hypervirulent (hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella pneumoniae: A new and dangerous breed. Virulence 2013, 4, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, L.K.; Yeh, K.M.; Lin, J.C.; Fung, C.P.; Chang, F.Y. Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess: A new invasive syndrome. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choby, J.E.; Howard-Anderson, J.; Weiss, D.S. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae—Clinical and molecular perspectives. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 287, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, T.A.; Olson, R.; Fang, C.T.; Stoesser, N.; Miller, M.; MacDonald, U.; Hutson, A.; Barker, J.H.; La Hoz, R.M.; Johnson, J.R. Identification of biomarkers for differentiation of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae from classical strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00776-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Marr, C.M. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00001-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulger, J.; MacDonald, U.; Olson, R.; Beanan, J.; Russo, T.A. Metabolite Transporter PEG344 Is Required for Full Virulence of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Strain hvKP1 after Pulmonary but Not Subcutaneous Challenge. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00093-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putze, J.; Hennequin, C.; Nougayrède, J.P.; Zhang, W.; Homburg, S.; Karch, H.; Bringer, M.A.; Fayolle, C.; Carniel, E.; Rabsch, W.; et al. Genetic structure and distribution of the colibactin genomic island among members of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 4696–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.C.; Lee, C.Z.; Ma, L.C.; Fang, C.T.; Chang, S.C.; Wang, J.T. Isolation of a chromosomal region of Klebsiella pneumoniae associated with allantoin metabolism and liver infection. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 3783–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Du, P.; Du, C.; Yang, P.; Shen, N.; Russo, T.A.; Liu, C. Genomically defined hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae contributed to early-onset increased mortality. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.M.C.; Wyres, K.L.; Duchêne, S.; Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gan, Y.H.; Hoh, C.H.; Archuleta, S.; Molton, J.S.; Kalimuddin, S.; et al. Population genomics of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae clonal group 23 reveals early emergence and rapid global dissemination. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struve, C.; Roe, C.C.; Stegger, M.; Stahlhut, S.G.; Hansen, D.S.; Engelthaler, D.M.; Andersen, P.S.; Driebe, E.M.; Keim, P.; Krogfelt, K.A. Mapping the evolution of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. mBio 2015, 6, e00630-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paczosa, M.K.; Mecsas, J. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Going on the offense with a strong defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitout, J.D.D.; Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L. Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae, a key pathogen set for global nosocomial dominance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5873–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Kim, Y.B.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Antimicrobial resistance of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, hypervirulence-associated determinants, and resistance mechanisms. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.M.; Bachman, M.A. Colonization, infection, and the accessory genome of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decré, D.; Verdet, C.; Emirian, A.; Le Gourrierec, T.; Petit, J.C.; Offenstadt, G.; Podglajen, I.; Brun-Buisson, C.; Arlet, G. Emerging severe and fatal infections due to Klebsiella pneumoniae in two university hospitals in France. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3012–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, K.E.; Wertheim, H.; Zadoks, R.N.; Baker, S.; Whitehouse, C.A.; Dance, D.; Jenney, A.; Connor, T.R.; Hsu, L.Y.; Severin, J.; et al. Genomic analysis of diversity, population structure, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae, an urgent threat to public health. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3574–E3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.R.; Molton, J.S.; Wyres, K.L.; Gorrie, C.; Wong, J.; Hoh, C.H.; Teo, J.; Kalimuddin, S.; Loh, J.; Tan, T.Y.; et al. Differential host susceptibility and bacterial virulence factors driving Klebsiella liver abscess in an ethnically diverse population. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, A.M.; Mosquera, J.; Velásquez, C.; Agudelo, C.A.; Capataz, C. Primera Caracterización y Análisis del Genoma Completo de Cepas de Klebsiella pneumoniae Hipervirulenta (hvKp) Provenientes de Colombia. Institución Universitaria Colegio Mayor de Antioquia, Medellín, Colombia, 2021. Available online: https://www.colmayor.edu.co/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/2.2-Primera-caracterizaci%C3%B3n-y-analisis-del-genoma-completo-de-1.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Hagiya, H.; Watanabe, N.; Maki, M.; Murase, T.; Otsuka, F. Clinical utility of string test as a screening method for hypermucoviscosity-phenotype Klebsiella pneumoniae. Acute Med. Surg. 2014, 1, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.M.C.; Wick, R.R.; Watts, S.C.; Cerdeira, L.T.; Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. A genomic surveillance framework and genotyping tool for Klebsiella pneumoniae and its related species complex. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Ríos, C.; Hernández, M.; Abad, D.; Álvarez-Montes, L.; Varsaki, A.; Iturbe, D.; Calvo, J.; Ocampo-Sosa, A.A. New Sequence Type ST3449 in Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates from a Cystic Fibrosis Patient. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, A.G.; Ganesamoorthy, D.; Coin, L.; Cooper, M.A.; Cao, M.D. Complete Genome Sequence of Klebsiella quasipneumoniae subsp. similipneumoniae Strain ATCC 700603. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00438-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, M.J.; Petty, N.K.; Beatson, S.A. Easyfig: A genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1009–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Fu, T.; Li, Z.; Du, B.; Cui, X.; Zhang, R.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, H.; Xue, G.; Cui, J.; et al. The role of integration host factor in biofilm and virulence of high-alcohol-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e01170-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Han, W.Y.; Li, Z.J.; Lei, L.C. Klebsiella pneumoniae MrkD adhesin-mediated immunity to respiratory infection and mapping the antigenic epitope by phage display library. Microb. Pathog. 2009, 46, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, X.; Dong, G.; Fang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhou, T. Clinical, microbiological, and molecular epidemiological characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced pyogenic liver abscess in southeastern China. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanga Ragupathi, N.K.; Muthuirulandi Sethuvel, D.P.; Triplicane Dwarakanathan, H.; Murugan, D.; Umashankar, Y.; Monk, P.N.; Karunakaran, E.; Veeraraghavan, B. The influence of biofilms on carbapenem susceptibility and patient outcome in device-associated Klebsiella pneumoniae infections: Insights into phenotype vs. genome-wide analysis and correlation. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 591679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderkelen, L.; Ons, E.; Van Herreweghe, J.M.; Callewaert, L.; Goddeeris, B.M.; Michiels, C.W. Role of lysozyme inhibitors in the virulence of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Snippy: Fast Bacterial Variant Calling from NGS Reads. 2018. Available online: https://github.com/tseemann/snippy (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirdita, M.; Schütze, K.; Moriwaki, Y.; Heo, L.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Steinegger, M. ColabFold: Making protein folding accessible to all. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleksy-Wawrzyniak, M.; Junka, A.; Brożyna, M.; Paweł, M.; Kwiek, B.; Nowak, M.; Mączyńska, B.; Bartoszewicz, M. The In Vitro Ability of Klebsiella pneumoniae to Form Biofilm and the Potential of Various Compounds to Eradicate It from Urinary Catheters. Pathogens 2021, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.X.; Lin, Z.W.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z.; Lin, F.J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, S.Y.; Sun, X.; Yao, W.M.; Li, D.Y.; et al. Biofilm Formation in Klebsiella pneumoniae Bacteremia Strains Was Found to be Associated with CC23 and the Presence of wcaG. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuotto, C.; Longo, F.; Balice, M.P.; Donelli, G.; Varaldo, P.E. Antibiotic Resistance Related to Biofilm Formation in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Pathogens 2014, 3, 743–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, T.A.; MacDonald, U.; Hassan, S.; Camanzo, E.; LeBreton, F.; Corey, B.; McGann, P. An Assessment of Siderophore Production, Mucoviscosity, and Mouse Infection Models for Defining the Virulence Spectrum of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. mSphere 2021, 6, e00045-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, K.A.; Treat, L.P.; Sepúlveda, V.E.; Miller, V.L. The small protein RmpD drives hypermucoviscosity in Klebsiella pneumoniae. mBio 2020, 11, e01750-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Tu, J.; Jiang, J.; Bi, Y.; You, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhu, T.; Cao, Z.; Yu, Z.; et al. Clinical and genomic analysis of liver abscess-causing Klebsiella pneumoniae identifies new liver abscess-associated virulence genes. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.C.; Lu, M.C.; Chiang, M.K.; Huang, S.-P.; Peng, H.-L.; Chang, H.-Y.; Jan, M.-S.; Lai, Y.-C. Genetic requirements for Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced liver abscess in an oral infection model. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 2657–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Jia, T.; Liu, X.; Yang, M.; Zhang, N.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Qin, S.; Liu, F.; Tang, Y.; et al. Clinical and genomic analysis of hypermucoviscous Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates: Identification of new hypermucoviscosity-associated genes. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 12, 1063406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoja, S.; Ansari, M.; Bengar, S.; Rafiei, A.; Shamseddin, J.; Alizade, H. Bacteriological characteristics of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae rmpA gene (hvKp-rmpA)-harboring strains in the south of Iran. Iran J. Microbiol. 2022, 14, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Shen, Q.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, K.; He, Y.; Dai, P.; Nie, Z.; Xu, X.; et al. Diversity and frequency of resistance and virulence genes in blaKPC and blaNDM co-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae strains from China. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2819–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Long, D.; Huang, Q.; Wei, D.; Liu, X.; Wan, L.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y. Rapid detection to differentiate hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae (hvKp) from classical K. pneumoniae by identifying peg-344 with loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rödel, J.; Pfeifer, Y.; Fischer, M.A.; Edel, B.; Stoll, S.; Pfister, W.; Löffler, B. Screening of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates for carbapenemase and hypervirulence-associated genes by combining the Eazyplex® Superbug CRE and hvKp assays. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández Vecilla, D.; Rodríguez Grande, J.; Fraile Valcárcel, N.; García, Z.M.; Fernández, S.G.; Ruiz, M.S.; Mesones, M.P.R.; Arco, J.L.D.d.T.d.; Gutiérrez, M.J.U.; Lomoro, M.C.; et al. Detection of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae (hvKp) strains directly from spiked blood cultures using a commercial Loop-Mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2025, 24, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Alvarado, C.L.; Davies, C.J.; Drayer, Z.J.; Carlino-MacDonald, U.; Hutson, A.; Luo, T.L.; Martin, M.J.; Corey, B.W.; Moser, K.A.; et al. Differentiation of hypervirulent and classical Klebsiella pneumoniae with acquired drug resistance. mBio 2024, 15, e02867-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, T.A.; Lebreton, F.; McGann, P.T. A step forward in hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae diagnostics. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2025, 31, e241516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; MacDonald, U. The Galleria mellonella infection model does not accurately differentiate between hypervirulent and classical Klebsiella pneumoniae. mSphere 2020, 5, e00850-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, D.; Wu, A.; Li, R.; Cai, D.; Tong, H.; Wang, N.; Tan, J. Identification of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae based on biomarkers and Galleria mellonella infection model. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Shi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, Y.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Lu, Y. Identification of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates using the string test in combination with Galleria mellonella infectivity. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 1673–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Gao, B.; Su, J.; Zeng, Y.; Cui, Z.; Liu, H.; Guo, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, B.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Phenotypic and genetic characterization of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in patients with liver abscess and ventilator-associated pneumonia. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attalla, E.T.; Khalil, A.M.; Zakaria, A.S.; Baker, D.J.; Mohamed, N.M. Genomic characterization of colistin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from intensive care unit patients in Egypt. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2023, 22, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubero, M.; Grau, I.; Tubau, F.; Pallarés, R.; Dominguez, M.; Liñares, J.; Ardanuy, C. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae clones causing bacteraemia in adults in a teaching hospital in Barcelona, Spain (2007–2013). Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.T.; Siu, L.K.; Lin, J.C.; Chen, T.-L.; Tseng, C.-P.; Yeh, K.-M.; Chang, F.-Y.; Fung, C.-P. Seroepidemiology of Klebsiella pneumoniae colonizing the intestinal tract of healthy Chinese and overseas Chinese adults in Asian countries. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, W.; Iimura, M.; Soga, E.; Koide, S.; Izumi, K.; Yoshida, S.; Arakawa, Y.; Nagano, Y.; Nagano, N. Presence of colistin- and tigecycline-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST29 in municipal wastewater influents in Japan. Microb. Drug Resist. 2021, 27, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 14. 2024. Available online: https://www.eucast.org (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- Schwengers, O.; Jelonek, L.; Dieckmann, M.A.; Beyvers, S.; Blom, J.; Goesmann, A. Bakta: Rapid and standardized annotation of bacterial genomes via alignment-free sequence identification. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, T.D.; Hetland, M.A.K.; Löhr, I.H.; Holt, K.E.; Wyres, K.L. Fast and accurate in silico antigen typing with Kaptive 3. Microb. Genom. 2025, 11, 001428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Bi, D.; Sun, J.; Li, J.; Tai, C.; Deng, Z.; Ou, H.Y. ICEberg 2.0: An updated database of bacterial integrative and conjugative elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D660–D665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; García-Fernández, A.; Larsen, M.V.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Hasman, H. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M.V. Identification of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández Vecilla, D.; Rodríguez Grande, J.; Fraile Valcárcel, N.; Roche Matheus, M.P.; Iglesias Hidalgo, G.; Aspichueta Vivanco, C.; Díaz de Tuesta del Arco, J.L.; García-Fernández, S.; Siller Ruiz, M.; Moure, Z.; et al. Genomic Characterization of a Rare K30-ST198 Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Clone with Distinctive Virulence Features. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9601. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199601
Fernández Vecilla D, Rodríguez Grande J, Fraile Valcárcel N, Roche Matheus MP, Iglesias Hidalgo G, Aspichueta Vivanco C, Díaz de Tuesta del Arco JL, García-Fernández S, Siller Ruiz M, Moure Z, et al. Genomic Characterization of a Rare K30-ST198 Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Clone with Distinctive Virulence Features. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9601. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199601
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández Vecilla, Domingo, Jorge Rodríguez Grande, Nuria Fraile Valcárcel, Mary Paz Roche Matheus, Gotzon Iglesias Hidalgo, Cristina Aspichueta Vivanco, José Luis Díaz de Tuesta del Arco, Sergio García-Fernández, María Siller Ruiz, Zaira Moure, and et al. 2025. "Genomic Characterization of a Rare K30-ST198 Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Clone with Distinctive Virulence Features" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9601. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199601
APA StyleFernández Vecilla, D., Rodríguez Grande, J., Fraile Valcárcel, N., Roche Matheus, M. P., Iglesias Hidalgo, G., Aspichueta Vivanco, C., Díaz de Tuesta del Arco, J. L., García-Fernández, S., Siller Ruiz, M., Moure, Z., Iriarte, D. V., Varsaki, A., Calvo Montes, J., Roiz Mesones, M. P., Fariñas, M. C., & Ocampo-Sosa, A. A. (2025). Genomic Characterization of a Rare K30-ST198 Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Clone with Distinctive Virulence Features. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9601. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199601





