Procoagulant Effects of Bothrops diporus Venom: Kinetic Modeling and Role of Serine Protease Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
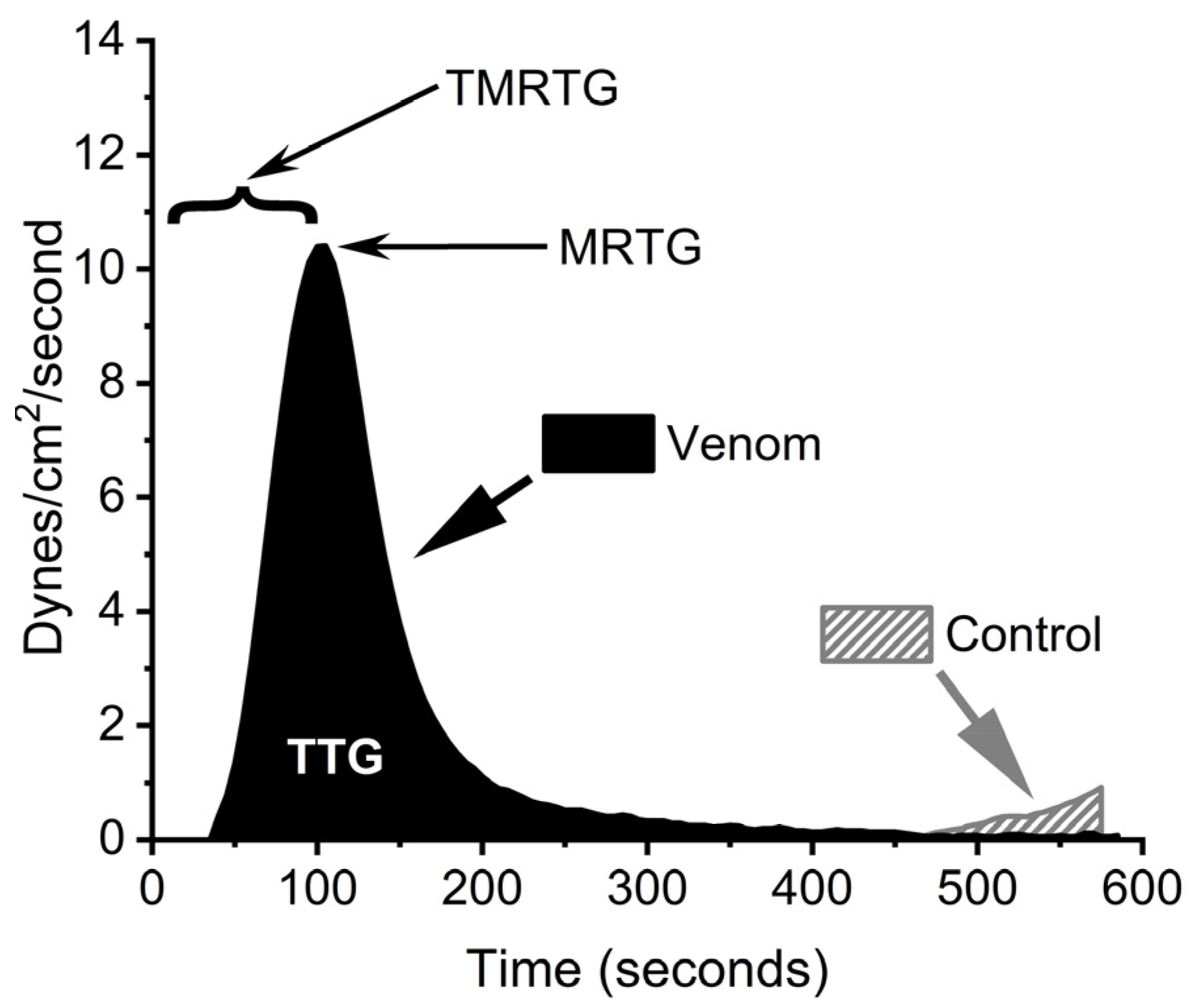
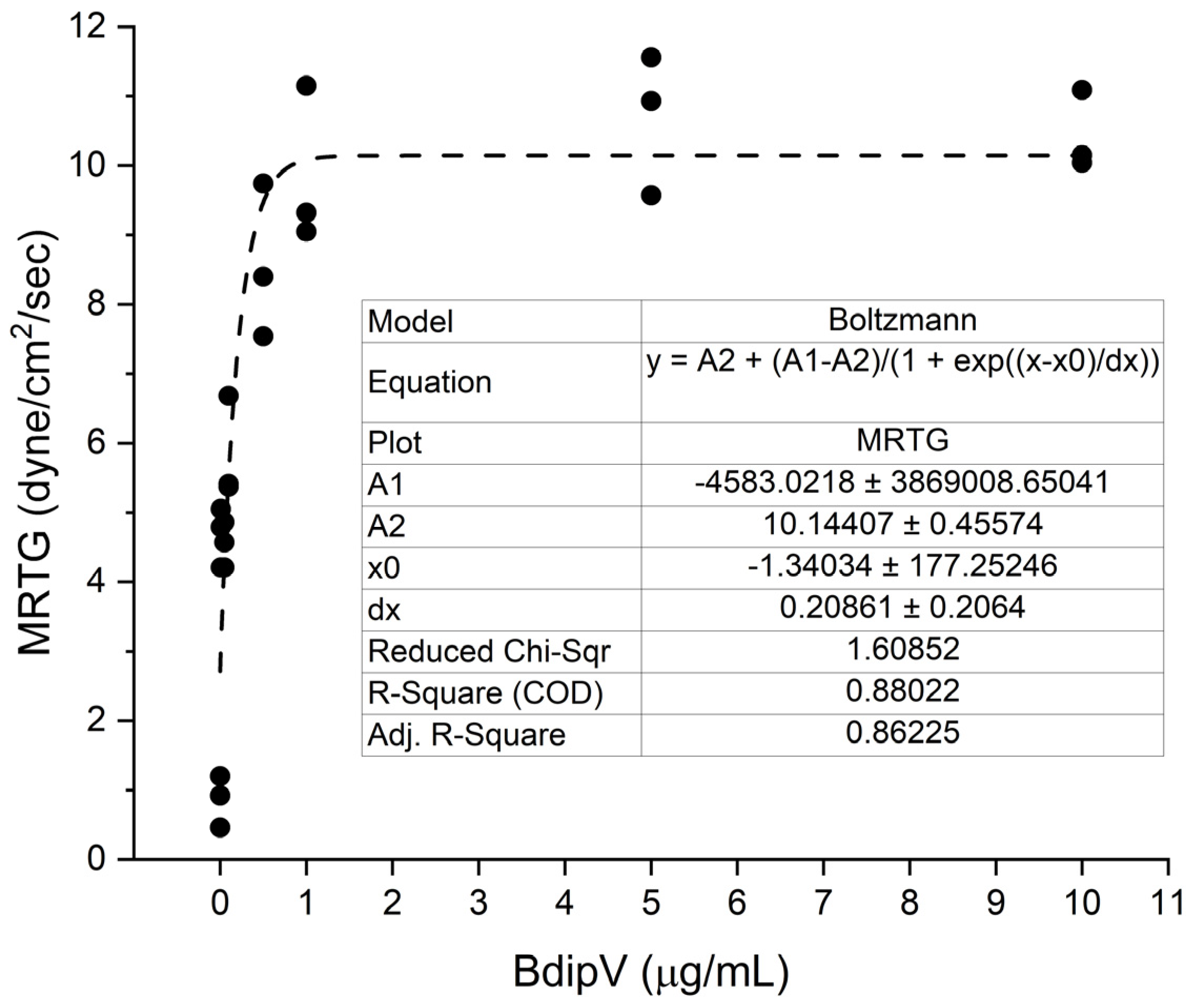
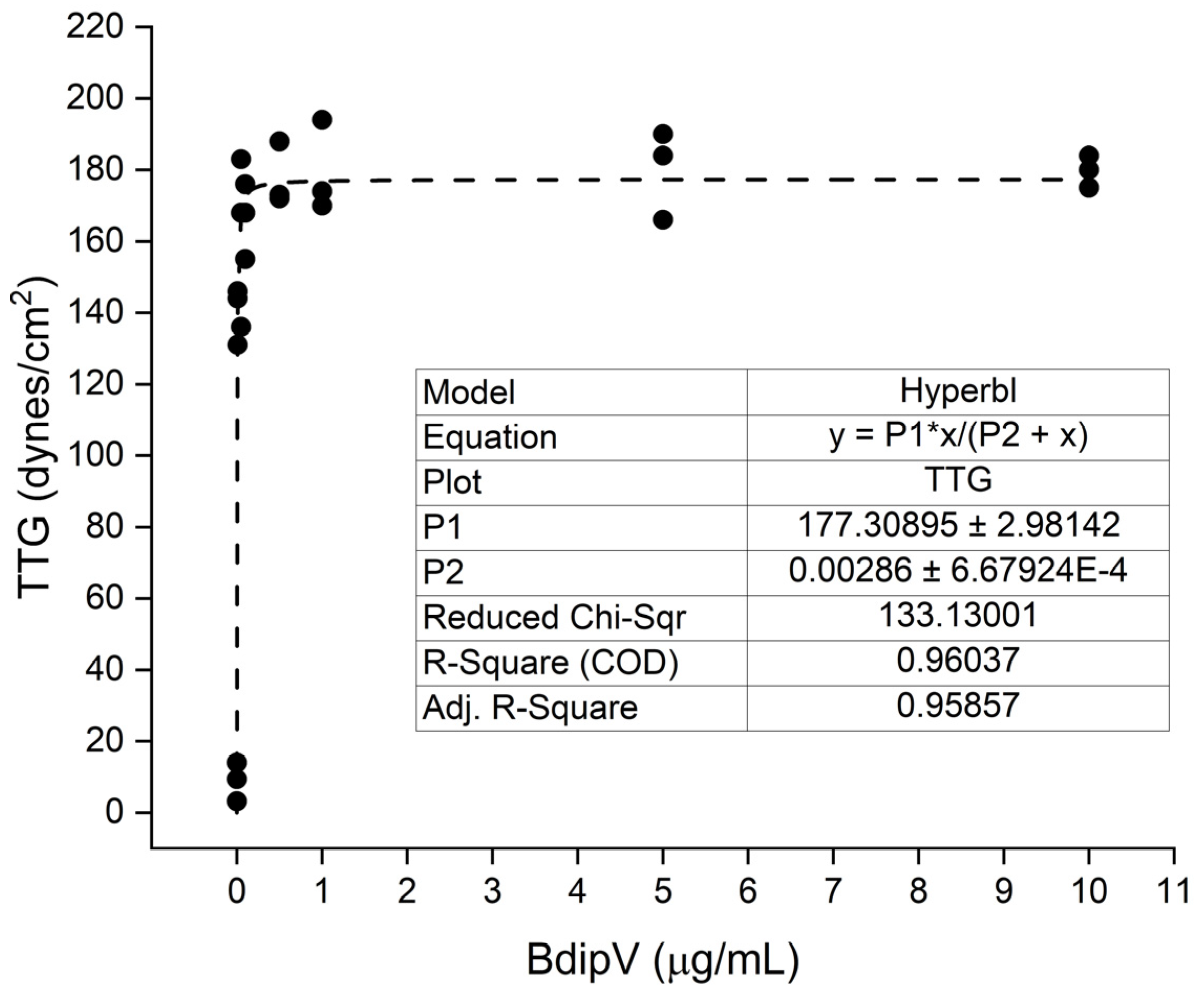
2.1. Human Plasmatic Coagulation Concentration Response Determined by Thrombpelastography
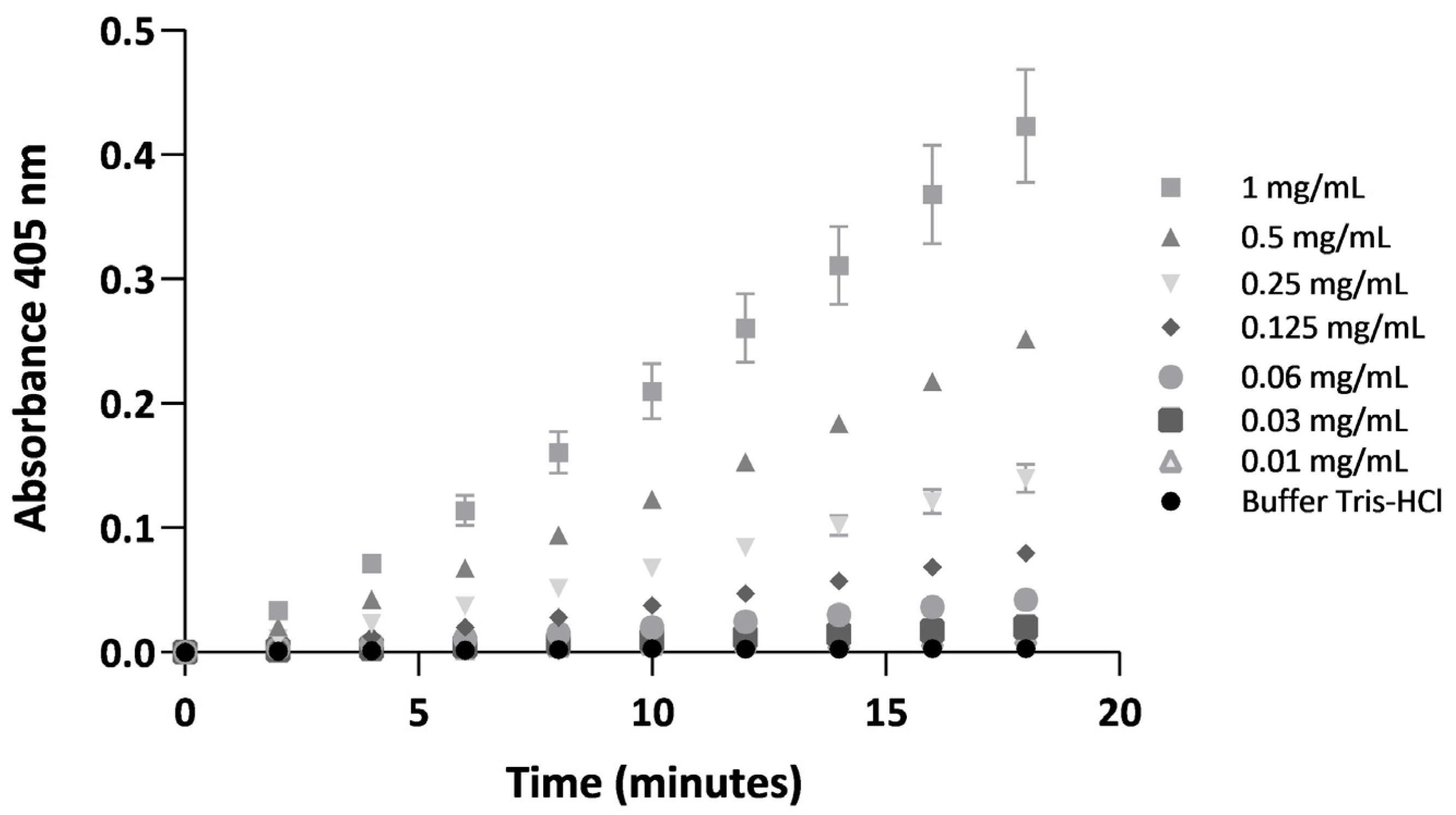
2.2. Coagulant and Serine Protease Enzymatic Activities of BdipV on Citrated Human Plasma and a Chromogenic Substrate Cleaved by Serine Proteases
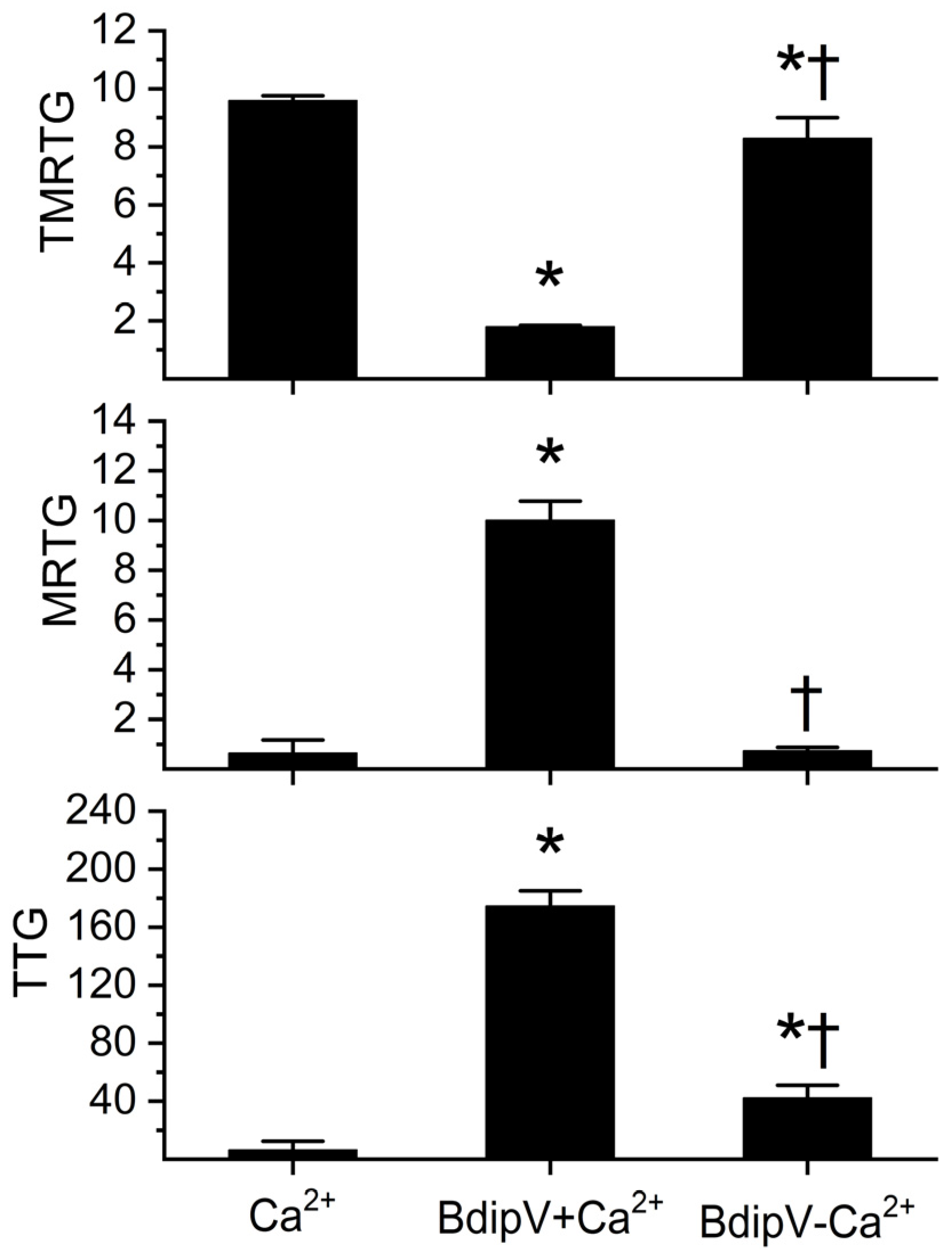
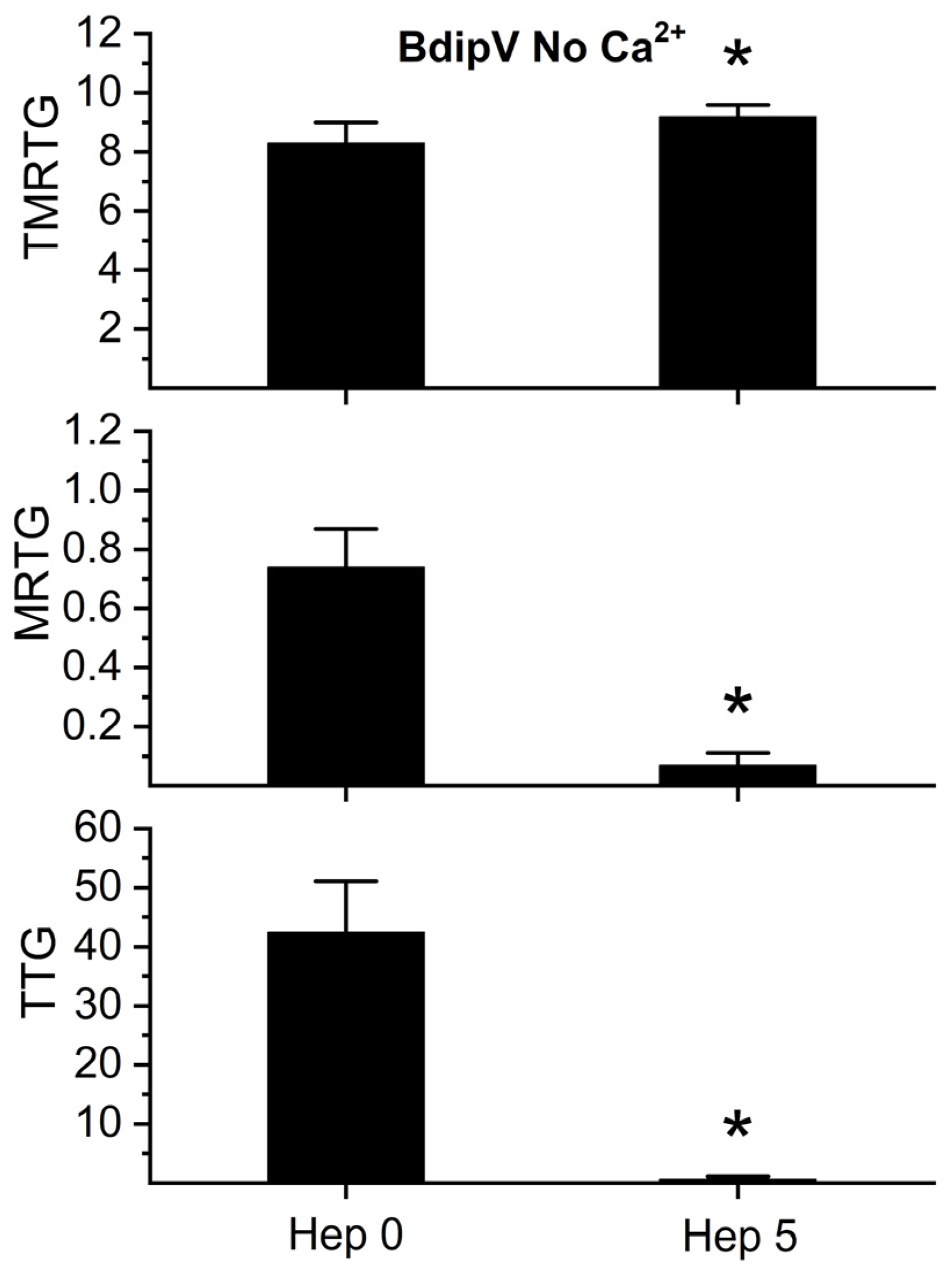
2.3. Determination of Calcium Dependence of BdipV Activity, Identification of Thrombin-like Enzyme Activity, and Demonstration of Antithrombin-Mediated Inhibition with Thromboelastography
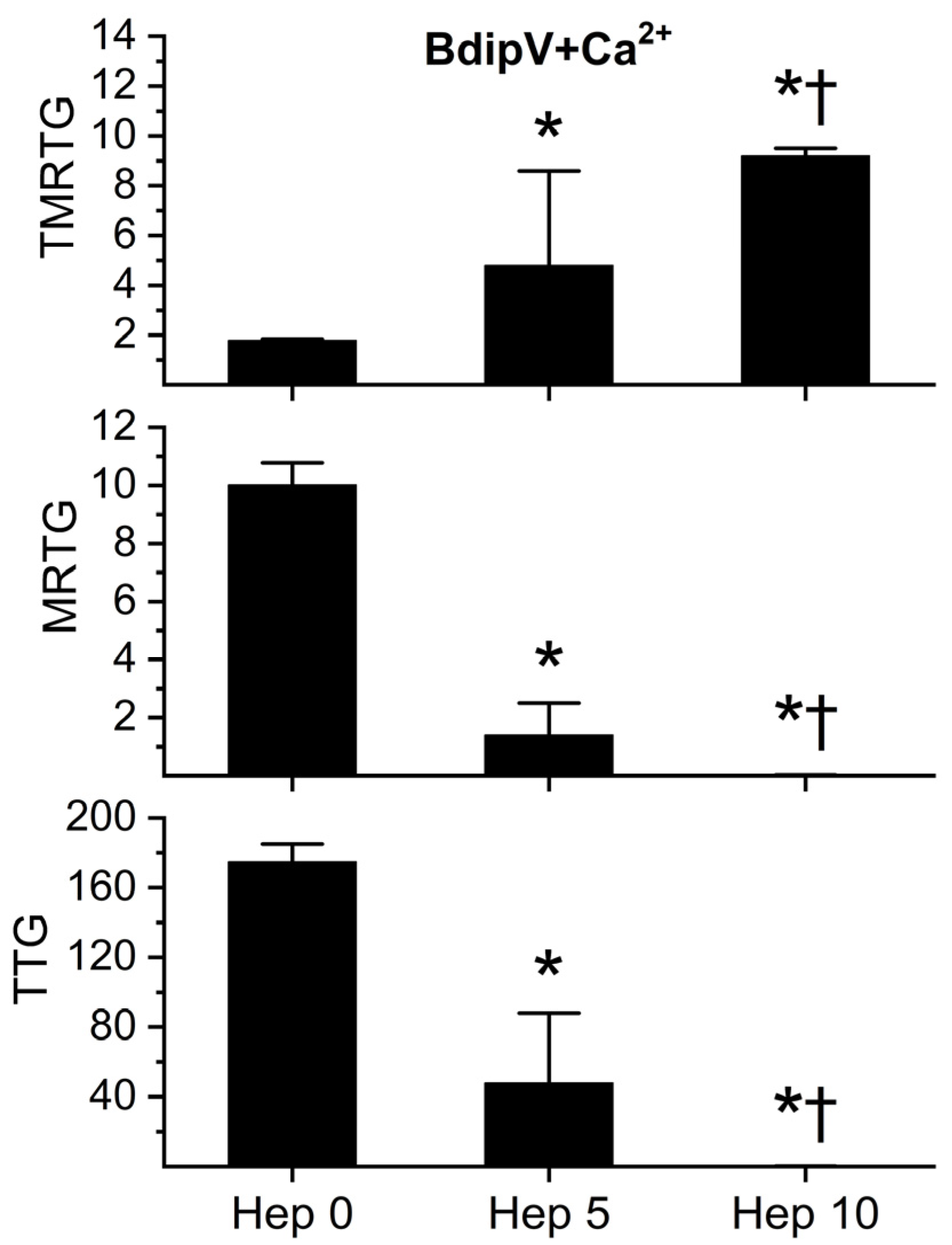
2.4. Effect of RuCl3-Based Antivenoms on BdipV Serine Protease-Mediated Procoagulant Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals, Venom, and Plasma
4.1.1. Chemicals
4.1.2. Venom
4.1.3. Plasma
4.2. Coagulation Activity
4.3. Spectrophotometric Determination of Thrombin-like Activity
4.4. Thromboelastographic Analyses
4.5. Statistical Analyses
4.5.1. Analyses Conducted at Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas
4.5.2. Analyses Conducted at the University of Arizona
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magalhães, S.F.V.; Peixoto, H.M.; Freitas, L.R.S.; Monteiro, W.M.; Oliveira, M.R.F. Snakebites caused by the genera Bothrops and Lachesis in the Brazilian Amazon: A study of factors associated with severe cases and death. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2022, 55, e05582021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Souza, A.; de Almeida Gonçalves Sachett, J.; Alcântara, J.A.; Freire, M.; Alecrim, M.D.G.C.; Lacerda, M.; de Lima Ferreira, L.C.; Fan, H.W.; de Souza Sampaio, V.; Monteiro, W.M. Snakebites as cause of deaths in the Western Brazilian Amazon: Why and who dies? Deaths from snakebites in the Amazon. Toxicon 2018, 145, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, L.S.; Vargas, R.; Lopes, A.A. Snakebite envenomation and death in the developing world. Ethn. Dis. 2009, 19 (Suppl. S1), 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Milani, R., Jr.; Jorge, M.T.; de Campos, F.P.; Martins, F.P.; Bousso, A.; Cardoso, J.L.; Ribeiro, L.A.; Fan, H.W.; França, F.O.; Sano-Martins, I.S.; et al. Snake bites by the jararacuçu (Bothrops jararacussu): Clinicopathological studies of 29 proven cases in São Paulo State, Brazil. QJM 1997, 90, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucaretchi, F.; de Capitani, E.M.; Hyslop, S.; Mello, S.M.; Madureira, P.R.; Zanardi, V.; Ferreira, D.M.; Meirelles, G.V.; Fernandes, L.C. Compartment syndrome after Bothrops jararaca snakebite: Monitoring, treatment, and outcome. Clin. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque Barbosa, F.B.; Raad, R.S.; Santos Ibiapina, H.N.; Freire Dos Reis, M.; Neves, J.C.F.; Andrade, R.V.; Nascimento, T.P.; Valle, F.F.; Casewell, N.R.; Sachett, J.; et al. Dermatopathological findings of Bothrops atrox snakebites: A case series in the Brazilian Amazon. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0012704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibiapina, H.N.S.; Costa, A.G.; Sachett, J.A.G.; Silva, I.M.; Tarragô, A.M.; Neves, J.C.F.; Kerr, M.W.A.; Santana, M.F.; Martins-Filho, O.A.; Lacerda, M.V.G.; et al. An Immunological Stairway to Severe Tissue Complication Assembly in Bothrops atrox Snakebites. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartim, M.A.; Raimunda da Costa, M.; Bentes, K.O.; Mwangi, V.I.; Pinto, T.S.; Oliveira, S.; Mota Cordeiro, J.S.; Wilson do Nascimento Corrêa, J.; Ferreira, J.M.B.B.; Cardoso de Melo, G.; et al. Myocardial injury and its association with venom-induced coagulopathy following Bothrops atrox snakebite envenomation. Toxicon 2025, 258, 108312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenuti, L.A.; França, F.O.; Barbaro, K.C.; Nunes, J.R.; Cardoso, J.L. Pulmonary haemorrhage causing rapid death after Bothrops jararacussu snakebite: A case report. Toxicon 2003, 42, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freire de Carvalho, J.; Quispe Torrez, P.P. Bothrops envenomation and liver hematoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 6920–6923. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Messias, N.C.; da Silva, S.S.; da Silva, D.B.; Dos Santos, C.R.; Hallal, A.L.C.; Sinha, R.; Bresolin, N.L. Acute kidney injury induced by snakebites in pediatric patients. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2025, 40, 2933–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, S.M.B.; Albuquerque, P.L.M.M.; Meneses, G.C.; da Silva Junior, G.B.; Martins, A.M.C.; De Francesco Daher, E. Role of endothelial biomarkers in predicting acute kidney injury in Bothrops envenoming. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 345, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, P.L.; Silva, G.B., Jr.; Jacinto, C.N.; Lima, J.B.; Lima, C.B.; Amaral, Y.S.; Veras Mdo, S.; Mota, R.M.; Daher, E.F. Acute kidney injury after snakebite accident treated in a Brazilian tertiary care centre. Nephrology 2014, 19, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizarazo, J.; Patiño, R.; Lizarazo, D.; Osorio, G. Fatal brain hemorrhage after Bothrops asper bite in the Catatumbo region of Colombia. Biomedica 2020, 40, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellandrea, H.; Guidoni, C.M.; Linck Junior, A.; Girotto, E. Brain death due to intracranial hemorrhage in a child following suspected Bothrops snakebite. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2024, 57, e008102024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachett, J.A.G.; Mota da Silva, A.; Dantas, A.W.C.B.; Dantas, T.R.; Colombini, M.; Moura da Silva, A.M.; Monteiro, W.M.; Bernarde, P.S. Cerebrovascular Accidents Related to Snakebites in the Amazon-Two Case Reports. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2020, 31, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva de Oliveira, S.; Freitas-de-Sousa, L.A.; Alves, E.C.; de Lima Ferreira, L.C.; da Silva, I.M.; de Lacerda, M.V.G.; Fan, H.W.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M.; Monteiro, W.M. Fatal stroke after Bothrops snakebite in the Amazonas state, Brazil: A case report. Toxicon 2017, 138, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañas, C.A. Brainstem ischemic stroke after to Bothrops atrox snakebite. Toxicon 2016, 120, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera, A.; Idrovo, L.A.; Tafur, A.; Del Brutto, O.H. Stroke following Bothrops spp. Snakebite. Neurology 2003, 60, 1577–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, F.M.; Burdmann, E.A. Fatal cerebral hemorrhage and acute renal failure after young Bothrops jararacussu snake bite. Ren. Fail. 2001, 23, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.E.; Del Brutto, O.H. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy in a venomous snake (Bothrops asper) bite victim. The Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 86, 496–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota, S.M.B.; Albuquerque, P.L.M.M.; da Silva Júnior, G.B.; Daher, E.F. Thrombotic microangiopathy due to Bothrops erythromelas: A case report in Northeast Brazil. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2020, 62, e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucaretchi, F.; Pimenta, M.M.B.; Borrasca-Fernandes, C.F.; Prado, C.C.; Capitani, E.M.; Hyslop, S. Thrombotic microangiopathy following Bothrops jararaca snakebite: Case report. Clin. Toxicol. 2019, 57, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbranque, S.; Piercecchi-Marti, M.D.; Thomas, L.; Barbey, C.; Courcier, D.; Bucher, B.; Ridarch, A.; Smadja, D.; Warrell, D.A. Fatal diffuse thrombotic microangiopathy after a bite by the “Fer-de-Lance” pit viper (Bothrops lanceolatus) of Martinique. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 78, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva de Oliveira, S.; Campos Alves, E.; Dos Santos Santos, A.; Freitas Nascimento, E.; Tavares Pereira, J.P.; Mendonça da Silva, I.; Sachett, J.; Dos Santos Ibiapina, H.N.; Santos Sarraf, L.K.; Contreras Bernal, J.C.; et al. Bothrops snakebites in the Amazon: Recovery from hemostatic disorders after Brazilian antivenom therapy. Clin. Toxicol. 2020, 58, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, J.C.C.; Bisneto, P.F.; Pereira, J.P.T.; Ibiapina, H.N.D.S.; Sarraff, L.K.S.; Monteiro-Júnior, C.; da Silva Pereira, H.; Santos, B.; de Moura, V.M.; de Oliveira, S.S.; et al. “Bad things come in small packages”: Predicting venom-induced coagulopathy in Bothrops atrox bites using snake ontogenetic parameters. Clin. Toxicol. 2020, 58, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustillo, S.; Lucero, H.; Leiva, L.C.; Acosta, O.; Kier Joffé, E.B.; Gorodner, J.O. Cytotoxicity and morphological analysis of cell death induced by Bothrops venoms from the northeast of Argentina. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 15, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Velde, A.C.; Fusco, L.S.; Echeverría, S.M.; Sasovsky, D.J.; Leiva, L.C.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Bustillo, S. Traces of Bothrops snake venoms in necrotic muscle preclude myotube formation in vitro. Toxicon 2022, 211, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, L.A.; Salazar-Valenzuela, D.; Mancuso, M.; Quirola, D.R.; Loaiza-Lange, A.; Zdenek, C.N.; Lewin, M.R.; Arbeláez-Ortiz, E.; Fry, B.G. Venom versatility: Dynamic anticoagulant and procoagulant variations between and within Bothrocophias (toad-head) and basal Bothrops (lance-head) pit vipers. Biochimie 2025, 237, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, L.A.; Zdenek, C.N.; Tanaka-Azevedo, A.M.; Silveira, G.P.M.; Sant’Anna, S.S.; Grego, K.F.; Rodrigues, C.F.B.; Fry, B.G. Clinical and Evolutionary Implications of Dynamic Coagulotoxicity Divergences in Bothrops (Lancehead Pit Viper) Venoms. Toxins 2022, 14, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, V.G.; Frank, N.; Afshar, S. De Novo Assessment and Review of Pan-American Pit Viper Anticoagulant and Procoagulant Venom Activities via Kinetomic Analyses. Toxins 2019, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, V.G.; Boyer, L.V.; Redford, D.T.; Ford, P. Thrombelastographic characterization of the thrombin-like activity of Crotalus simus and Bothrops asper venoms. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2017, 28, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Denegri, M.E.; Bustillo, S.; Gay, C.C.; Van De Velde, A.; Gomez, G.; Echeverría, S.; Gauna Pereira, M.D.C.; Maruñak, S.; Nuñez, S.; Bogado, F.; et al. Venoms and Isolated Toxins from Snakes of Medical Impact in the Northeast Argentina: State of the Art. Potential Pharmacological Applications. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 1962–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitorino, K.A.; Alfonso, J.J.; Gómez, A.F.; Santos, A.P.A.; Antunes, Y.R.; Caldeira, C.A.D.S.; Gómez, C.V.; Teles, C.B.G.; Soares, A.M.; Calderon, L.A. Antimalarial activity of basic phospholipases A2 isolated from Paraguayan Bothrops diporus venom against Plasmodium falciparum. Toxicon X 2020, 8, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustillo, S.; Fernández, J.; Chaves-Araya, S.; Angulo, Y.; Leiva, L.C.; Lomonte, B. Isolation of two basic phospholipases A2 from Bothrops diporus snake venom: Comparative characterization and synergism between Asp49 and Lys49 variants. Toxicon 2019, 168, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixera, L.F.; de Carvalho, L.H.; de Castro, O.B.; Bastos, J.S.F.; Néry, N.M.; Oliveira, G.A.; Kayano, A.M.; Soares, A.M.; Zuliani, J.P. Local and systemic effects of BdipTX-I, a Lys-49 phospholipase A2 isolated from Bothrops diporus snake venom. Toxicon 2018, 141, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, J.J.; Fasoli, E.; Sanz, L.; Boschetti, E.; Righetti, P.G. Exploring the Venom Proteome of the Western Diamondback Rattlesnake, Crotalus atrox, via Snake Venomics and Combinatorial Peptide Ligand Library Approaches. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 3055–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokyta, D.R.; Lemmon, A.R.; Margres, M.J.; Aronow, K. The venom-gland transcriptome of the eastern diamondback rattlesnake (Crotalus adamenteous). BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, C.; Sanz, L.; Calvete, J.J.; Pla, D. Snake Venomics and Antivenomics of Bothrops diporus, a Medically Important Pitviper in Northeastern Argentina. Toxins 2015, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, S.H.; Hung, C.C.; Huang, K.F. Characterization of a protease with alpha- and beta-fibrinogenase activity from the Western diamondback rattlesnake, Crotalus atrox. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 187, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TU, A.T.; Baker, B.; Wongvibulsin, S.; Willis, T. Biochemical characterization of atroxase and nucleotide sequence encoding the fibrinolytic enzyme. Toxicon 1996, 34, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchens, C.S.; Van Mierop, L.H. Mechanism of defibrination in humans after envenomation by the Eastern diamondback rattlesnake. Am. J. Hematol. 1983, 14, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margres, M.J.; McGivern, J.J.; Wray, K.P.; Seavy, M.; Calvin, K.; Rokyta, D.R. Linking the transcriptome and proteome to characterize the venom of the eastern diamondback rattlesnake (Crotalus adamanteus). J. Proteom. 2014, 96, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, S.M. The long road of research on snake venom serine proteinases. Toxicon 2013, 62, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanazzi, M.; Filardi, E.T.M.; Pires, G.M.M.; Cerveja, M.F.; Melo-Dos-Santos, G.; Oliveira, I.S.; Ferreira, I.G.; Cerni, F.A.; Santos-Filho, N.A.; Monteiro, W.M.; et al. The Versatility of Serine Proteases from Brazilian Bothrops Venom: Their Roles in Snakebites and Drug Discovery. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazelat, J.; Teperman, S.H.; Touger, M. Recurrent hemorrhage after western diamondback rattlesnake envenomation treated with crotalidae polyvalent immune fab (ovine). Clin. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, N.S.; Alvarez, R.G. Rattlesnake bite complications in 19 children. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 1994, 10, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budzynski, A.Z.; Pandya, B.V.; Rubin, R.N.; Brizuela, B.S.; Soszka, T.; Stewart, G.J. Fibrinogenolytic afibrinogenemia after envenomation by western diamondback rattlesnake (Crotalus atrox). Blood 1984, 63, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, W.F.; Rivera, J.V.; Brown, J.; Kurz, M.C.; Arnold, J. Utilization of thromboelastograms in management of Crotalus adamanteus envenomation. Clin. Toxicol. 2021, 59, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, K.M.; Bromberg, W.; Dunne, J. Thromboelastography Utilization in Delayed Recurrent Coagulopathy after Severe Eastern Diamondback Rattlesnake Envenomation. Am. Surg. 2017, 83, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchens, C.; Eskin, T. Fatality in a case of envenomation by Crotalus adamanteus initially successfully treated with polyvalent ovine antivenom followed by recurrence of defibrinogenation syndrome. J. Med. Toxicol. 2008, 4, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, V.G. Ruthenium-based antivenom attenuates Crotalus atrox venom mediated coagulopathy in rabbits. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2024, 35, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, V.G. Phosphate-Buffered Saline and Dimethyl Sulfoxide Enhance the Antivenom Action of Ruthenium Chloride against Crotalus atrox Venom in Human Plasma—A Preliminary Report. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theakston, R.D.G.; Reid, H.A. Development of simple standard assay procedures for the characterization of snake venoms. Bull. World Health Organ. 1983, 61, 949. [Google Scholar]
- Menaldo, D.L.; Bernardes, C.P.; Santos-Filho, N.A.; de Andrade Moura, L.; Fuly, A.L.; Arantes, E.C.; Sampaio, S.V. Biochemical characterization and comparative analysis of two distinct serine proteases from Bothrops pirajai snake venom. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2545–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajesh Kumar, K.; Vennila, R.; Kanchana, S.; Arumugam, M.; Balasubramaniam, T. Fibrinogenolytic and anticoagulant activities in the tissue covering the stingers of marine stingrays Dasyatis sephen and Aetobatis narinari. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2011, 31, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopez, G.L.; Nielsen, S.A.; Nielsen, V.G.; Fusco, L.S. Procoagulant Effects of Bothrops diporus Venom: Kinetic Modeling and Role of Serine Protease Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199496
Lopez GL, Nielsen SA, Nielsen VG, Fusco LS. Procoagulant Effects of Bothrops diporus Venom: Kinetic Modeling and Role of Serine Protease Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199496
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopez, Gisela L., Sarah A. Nielsen, Vance G. Nielsen, and Luciano S. Fusco. 2025. "Procoagulant Effects of Bothrops diporus Venom: Kinetic Modeling and Role of Serine Protease Activity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199496
APA StyleLopez, G. L., Nielsen, S. A., Nielsen, V. G., & Fusco, L. S. (2025). Procoagulant Effects of Bothrops diporus Venom: Kinetic Modeling and Role of Serine Protease Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199496






