Rare-Variant Genome-Wide Association and Polygenic Score Assessment of Vitamin D Status in a Middle Eastern Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of Study Population
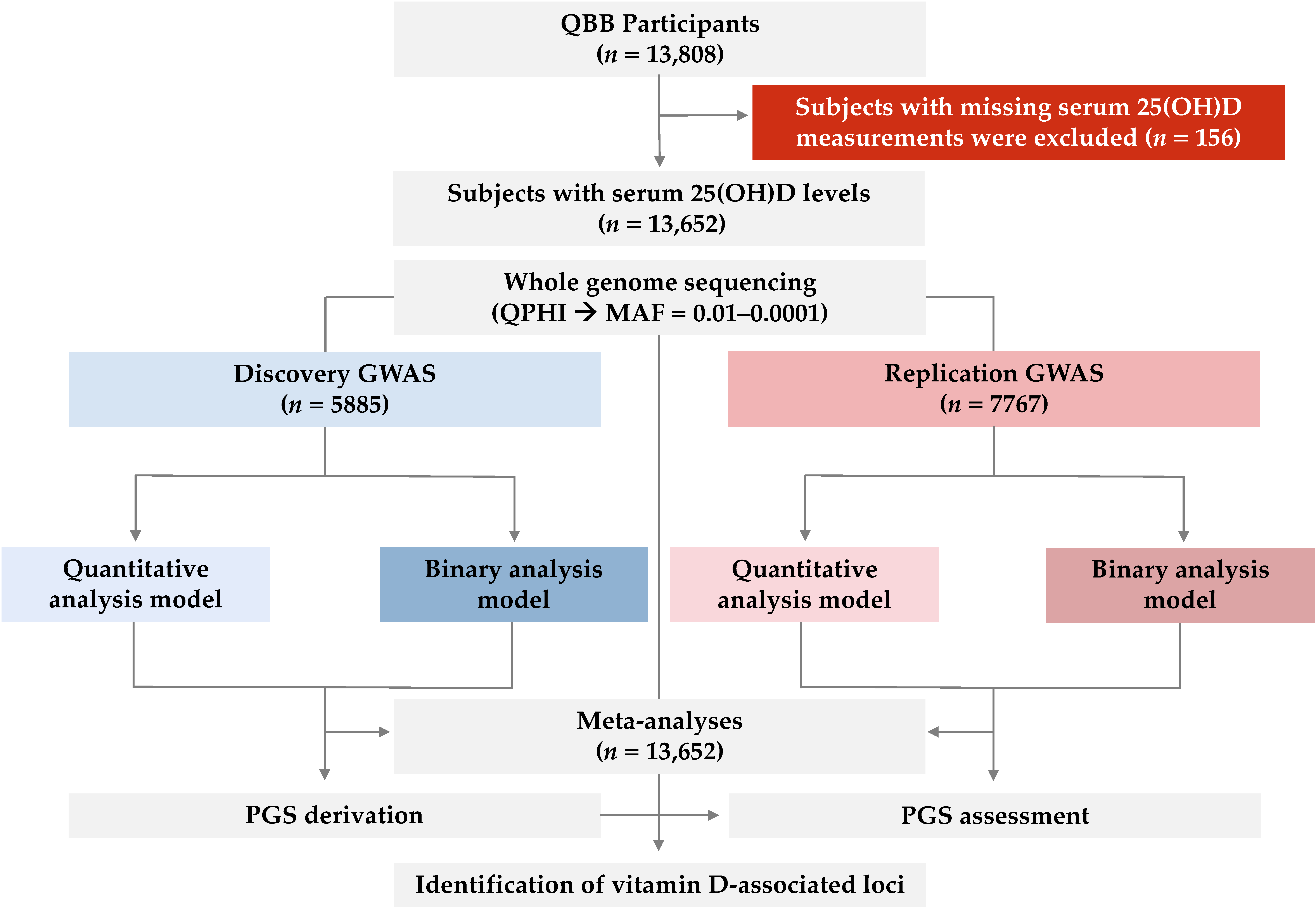
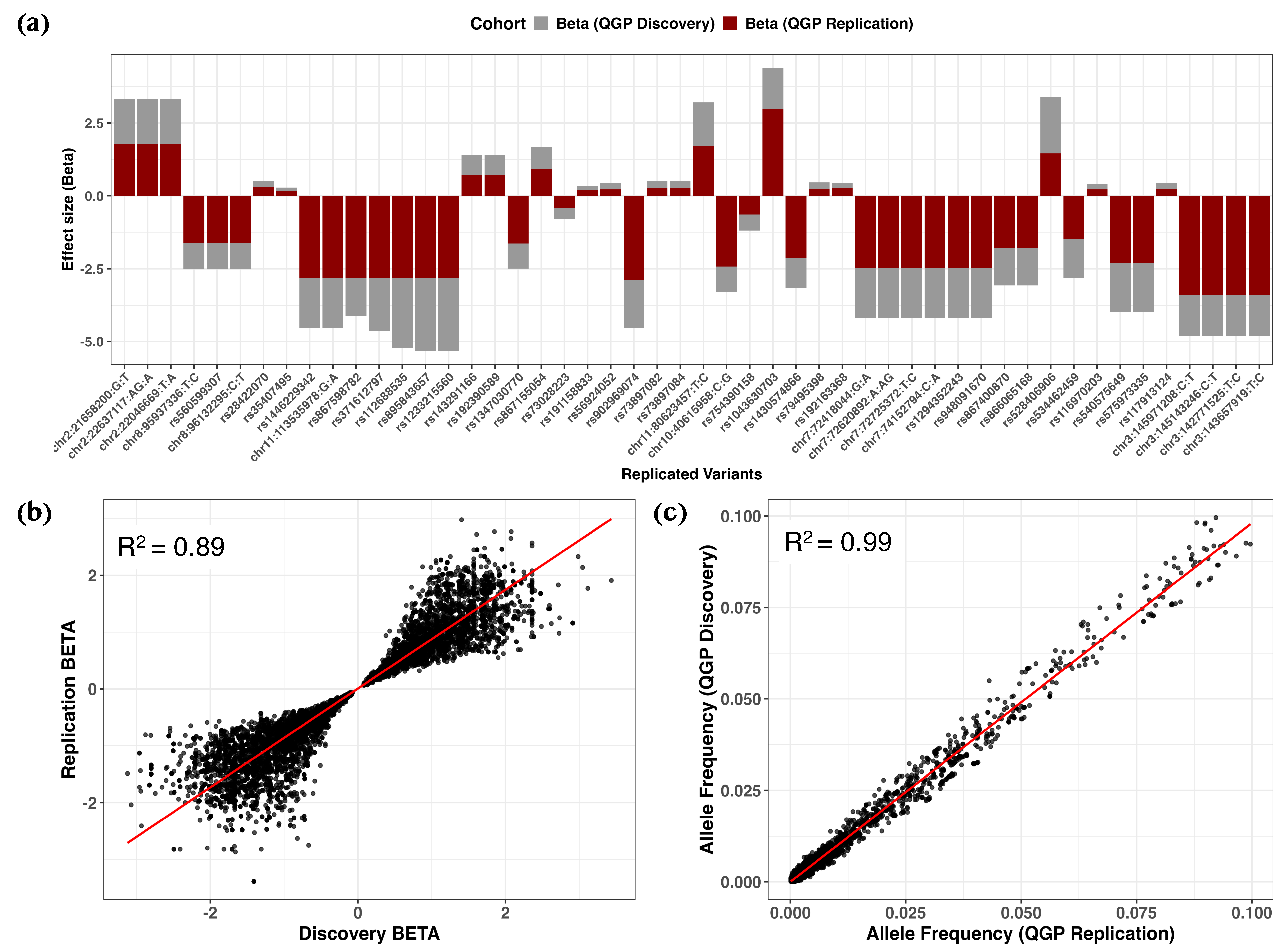
2.2. Rare Variants Associated with 25(OH)D Levels Identified in Quantitative Trait GWAS
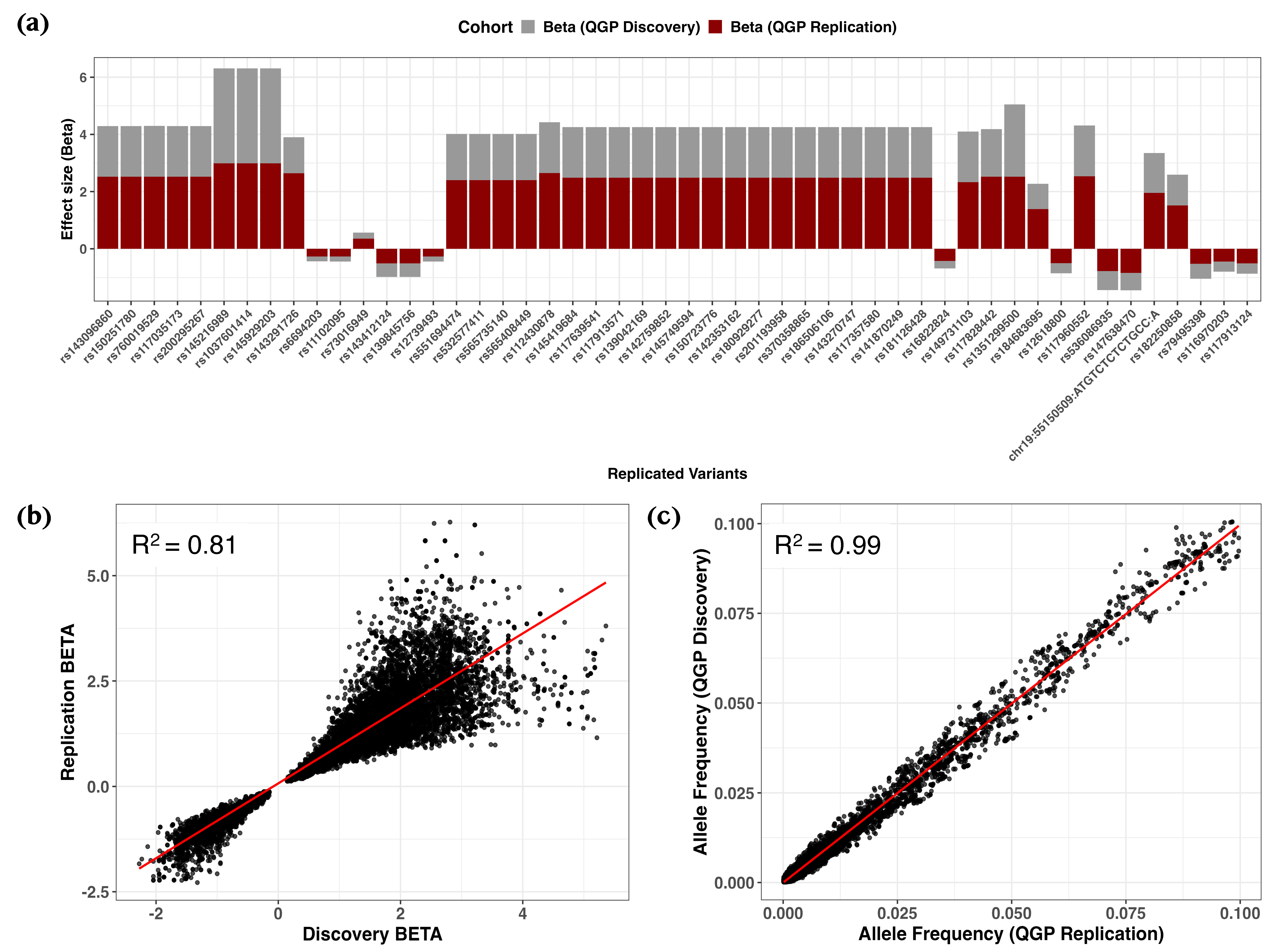
2.3. Rare Variant Associated with Vitamin D Deficiency Identified in Binary Trait GWAS
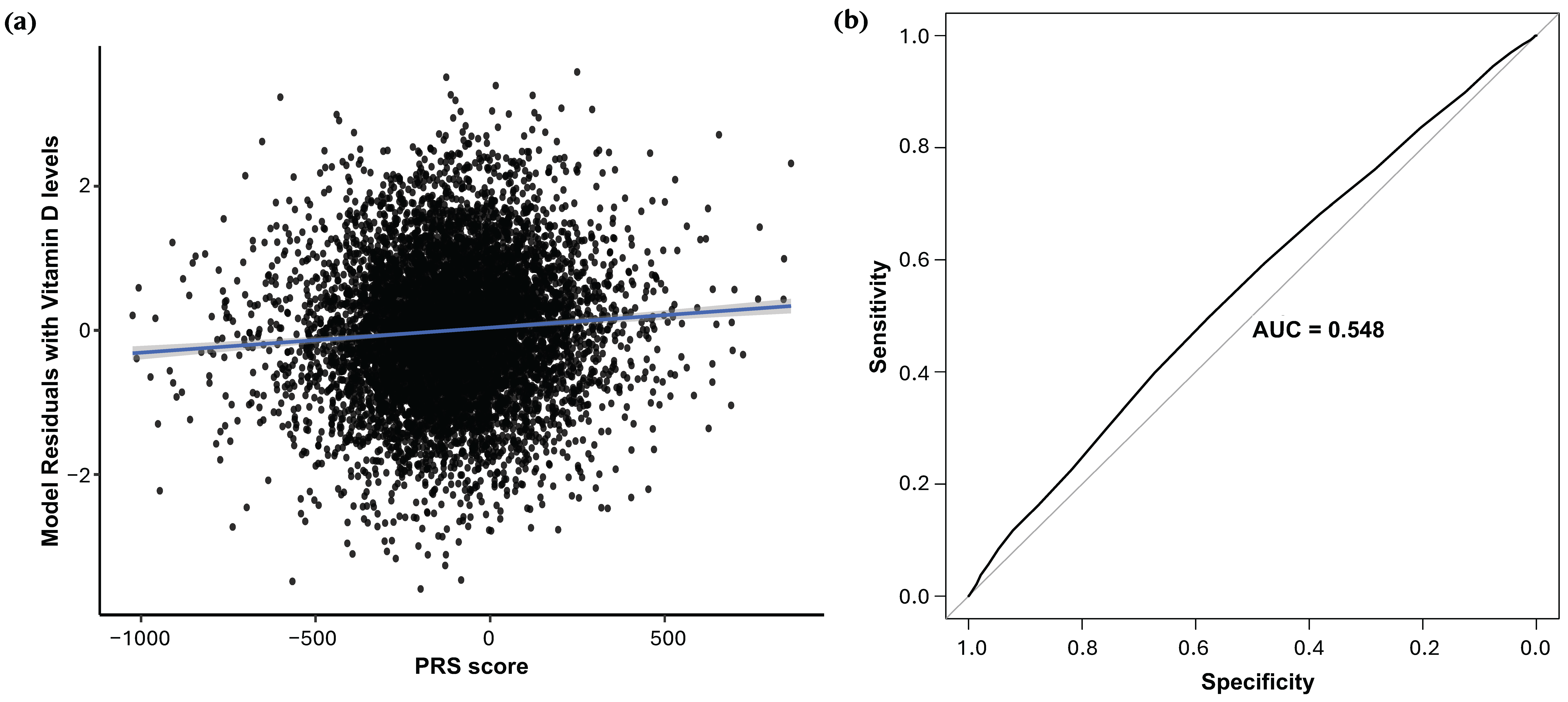
2.4. Discovery-Derived Rare Variant Polygenic Score Predicts 25(OH)D Levels and Deficiency
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population and Ethical Approvals
4.2. Phenotype Measurements and Related Covariates
4.3. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Quality Control
4.4. Genome-Wide Association Analyses
4.5. Polygenic Score Construction and Evaluation
4.6. Variant Annotation and Functional Characterization
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 25(OH)D | 25-hydroxyvitamin D |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| AGO4 | Argonaute Component 4 |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CLIA | Chemiluminescent immunoassay |
| C + T | Clumping and thresholding |
| GC | Group-specific component (vitamin D-binding protein) |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association study |
| DHCR7 | 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase |
| IBS | Identity-by-state |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| LD | Linkage disequilibrium |
| MAF | Minor allele frequency |
| MDS | Multidimensional scaling |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| PC | Principal component |
| PGS | Polygenic score |
| QC | Quality control |
| QBB | Qatar Biobank |
| QF | Qatar Foundation |
| QGP | Qatar Genome Program |
| QPHI | Qatar Precision Health Institute |
| Q–Q | Quantile–quantile |
| R2 | Coefficient of determination |
| POTEB3 | POTE Ankyrin Domain B3 |
| RDH13 | Retinol dehydrogenase 13 |
| RXR | Retinoid X receptor |
| SAIGE | Scalable and Accurate Implementation of GEneralized mixed model |
| SE | Standard error |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| SLC | Solute carrier |
| TMEM | Transmembrane protein |
| VDR | Vitamin D receptor |
| VEP | Variant Effect Predictor |
| WGS | Whole-genome sequencing |
References
- Hendi, N.N.; Nemer, G. SDR42E1 modulates vitamin D absorption and cancer pathogenesis: Insights from an in vitro model. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1585859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendi, N.N.; Al-Sarraj, Y.; Ismail Umlai, U.K.; Suhre, K.; Nemer, G.; Albagha, O. Genetic determinants of Vitamin D deficiency in the Middle Eastern Qatari population: A genome-wide association study. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1242257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendi, N.N.; Chakhtoura, M.; Al-Sarraj, Y.; Basha, D.S.; Albagha, O.; Fuleihan, G.E.; Nemer, G. The Genetic Architecture of Vitamin D Deficiency among an Elderly Lebanese Middle Eastern Population: An Exome-Wide Association Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revez, J.A.; Lin, T.; Qiao, Z.; Xue, A.; Holtz, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zeng, J.; Wang, H.; Sidorenko, J.; Kemper, K.E.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 143 loci associated with 25 hydroxyvitamin D concentration. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manousaki, D.; Mitchell, R.; Dudding, T.; Haworth, S.; Harroud, A.; Forgetta, V.; Shah, R.L.; Luan, J.; Langenberg, C.; Timpson, N.J.; et al. Genome-wide Association Study for Vitamin D Levels Reveals 69 Independent Loci. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 106, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Abecasis, G.R.; Boehnke, M.; Lin, X. Rare-variant association analysis: Study designs and statistical tests. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 95, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UK10K Consortium; Walter, K.; Min, J.L.; Huang, J.; Crooks, L.; Memari, Y.; McCarthy, S.; Perry, J.R.B.; Xu, C.; Futema, M.; et al. The UK10K project identifies rare variants in health and disease. Nature 2015, 526, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingdom, R.; Beaumont, R.N.; Wood, A.R.; Weedon, M.N.; Wright, C.F. Genetic modifiers of rare variants in monogenic developmental disorder loci. Nat. Genet. 2024, 56, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Acosta, J.N.; Ye, Y.; Demarais, Z.S.; Conlon, C.J.; Chen, M.; Zhao, H.; Falcone, G.J. Whole-Exome Sequencing Analyses Support a Role of Vitamin D Metabolism in Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2023, 54, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.A.; Yoon, J.W.; Lee, Y.; Choi, H.J.; Yun, J.W.; Bae, E.; Kwon, S.-H.; Ahn, S.E.; Do, A.-R.; Jin, H.; et al. Unveiling Genetic Variants Underlying Vitamin D Deficiency in Multiple Korean Cohorts by a Genome-Wide Association Study. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 36, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.J.; McKnight, A.J.; Patterson, C.C.; Sadlier, D.M.; Maxwell, A.P.; The Warren 3/UK GoKinD Study Group. A rare haplotype of the vitamin D receptor gene is protective against diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, V.; Mannino, F.; Zhang, R. Consequences of dichotomization. Pharm. Stat. 2009, 8, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Weng, S.; Felton, S.K.; Bhandare, S.; Riek, A.; Butler, B.; Proctor, B.M.; Petty, M.; Chen, Z.; Schechtman, K.B.; et al. 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D inhibits foam cell formation and suppresses macrophage cholesterol uptake in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation 2009, 120, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Tan, X.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, N.; Zhao, G.; Cui, H.; Wen, J. SLC16A7 Promotes Triglyceride Deposition by De Novo Lipogenesis in Chicken Muscle Tissue. Biology 2022, 11, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chornyi, S.; Ijlst, L.; van Roermund, C.W.T.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Waterham, H.R. Peroxisomal Metabolite and Cofactor Transport in Humans. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 613892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, M.J.; Zhou, Y.; Kang, S.; Zhang, X.; Mikkelsen, T.S.; Rosen, E.D. Early B-cell factor-1 (EBF1) is a key regulator of metabolic and inflammatory signaling pathways in mature adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 35925–35939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barger, C.J.; Zhang, W.; Sharma, A.; Chee, L.; James, S.R.; Kufel, C.N.; Miller, A.; Meza, J.; Drapkin, R.; Odunsi, K.; et al. Expression of the POTE gene family in human ovarian cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keum, N.; Lee, D.H.; Greenwood, D.C.; Manson, J.E.; Giovannucci, E. Vitamin D supplementation and total cancer incidence and mortality: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mianesaz, H.; Göczi, L.; Nagy, G.; Póliska, S.; Fadel, L.; Bojcsuk, D.; Penyige, A.; Szirák, K.; AlHaman, F.; Nagy, L.; et al. Genomic regions occupied by both RARalpha and VDR are involved in the convergence and cooperation of retinoid and vitamin D signaling pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, gkaf230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi-Soleiman, F.; Vafa, M.; Abiri, B.; Safavi, M. Effects of Iron on Vitamin D Metabolism: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2016, 7, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnott-Armstrong, N.; Tanigawa, Y.; Amar, D.; Mars, N.; Benner, C.; Aguirre, M.; Venkataraman, G.R.; Wainberg, M.; Ollila, H.M.; Kiiskinen, T.; et al. Author Correction: Genetics of 35 blood and urine biomarkers in the UK Biobank. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunn, S.; Wang, X.; Posner, D.C.; Cho, K.; Huffman, J.E.; Gaziano, M.; Wilson, P.W.; Sun, Y.V.; Peloso, G.; Lunetta, K.L. Comparison of methods for building polygenic scores for diverse populations. Hum. Genet. Genom. Adv. 2025, 6, 100355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Thani, A.; Fthenou, E.; Paparrodopoulos, S.; Al Marri, A.; Shi, Z.; Qafoud, F.; Afifi, N. Qatar Biobank Cohort Study: Study Design and First Results. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 188, 1420–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thareja, G.; Al-Sarraj, Y.; Belkadi, A.; Almotawa, M.; The Qatar Genome Program Research (QGPR) Consortium; Suhre, K.; Albagha, O.M.E. Whole genome sequencing in the Middle Eastern Qatari population identifies genetic associations with 45 clinically relevant traits. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. Gigascience 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Nielsen, J.B.; Fritsche, L.G.; Dey, R.; Gabrielsen, M.E.; Wolford, B.N.; LeFaive, J.; VandeHaar, P.; Gagliano, S.A.; Gifford, A.; et al. Efficiently controlling for case-control imbalance and sample relatedness in large-scale genetic association studies. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huedo-Medina, T.B.; Sanchez-Meca, J.; Marin-Martinez, F.; Botella, J. Assessing heterogeneity in meta-analysis: Q statistic or I2 index? Psychol. Methods 2006, 11, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, S.C.; Austine-Orimoloye, O.; Azov, A.G.; Barba, M.; Barnes, I.; Barrera-Enriquez, V.P.; Becker, A.; Bennett, R.; Beracochea, M.; Berry, A.; et al. Ensembl 2025. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D948–D957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudmant, P.H.; Rausch, T.; Gardner, E.J.; Handsaker, R.E.; Abyzov, A.; Huddleston, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, K.; Jun, G.; Fritz, M.H.-Y.; et al. An integrated map of structural variation in 2504 human genomes. Nature 2015, 526, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Cohort | Discovery | Replication | All Subjects | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample size | 5885 | 7767 | 13,652 | - |
| Male n (%) | 2567 (43.6) | 3508 (45.2) | 6075 (44.5) | 0.0746 |
| Female n (%) | 3318 (56.4) | 4259 (54.8) | 7577 (55.5) | |
| Mean age ± SD | 39.75 ± 12.83 | 40.38 ± 13.37 | 40.11 ± 13.14 | 0.00506 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.38 ± 6.05 | 29.69 ± 6.14 | 29.55 ± 6.10 | 0.00387 |
| Vit D (ng/mL) ± SD | 19.36 ± 11.12 | 19.52 ± 11.14 | 19.45 ± 11.13 | 0.399 |
| Normal Vit D n (%) | 675 (11.5) | 1073 (13.8) | 1748 (12.8) | 0.0000546 |
| Insufficient Vit D n (%) | 1612 (27.4) | 2053 (26.4) | 3665 (26.8) | 0.218 |
| Deficient Vit D n (%) | 3598 (61.1) | 4641 (59.8) | 8239 (60.4) | 0.105 |
| SNP | CHR | Position (BP) | Mapped Gene | HGVS ID | Consequence | A1 | A2 | GWAS in Replication (n = 7767) | GWAS in Discovery (n = 5885) | Meta-Analysis (n = 13,652) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAF (A1) | Beta (SE) | p-Value | MAF (A1) | Beta (SE) | p-Value | p-Value | BETA | p-Het | ||||||||
| rs115651661 | 3 | 74272255 | CNTN3 | NC_000003.12:g.74272255T>C | Intron | C | T | 0.0040 | 0.48 (0.12) | 0.00007 | 0.0027 | 0.73 (0.17) | 2.5 × 10−5 | 1.5 × 10−8 | 0.56 | 0.22 |
| rs536115678 | 5 | 158884335 | EBF1 | NC_000005.10:g.158884335C>A | Intron | A | C | 0.0003 | −1.84 (0.48) | 0.00013 | 0.0003 | −1.67 (0.40) | 3.0 × 10−5 | 1.6 × 10−8 | −1.74 | 0.79 |
| chr21:43954055:C:T | 21 | 43954055 | AGPAT3 | - | Intron | T | C | 0.0004 | 1.26 (0.39) | 0.00138 | 0.0007 | 1.57 (0.34) | 6.1 × 10−6 | 3.7 × 10−8 | 1.43 | 0.55 |
| chr21:43790823:A:G | 21 | 43790823 | RRP1 | - | Upstream gene | G | A | 0.0004 | 1.26 (0.39) | 0.00138 | 0.0007 | 1.57 (0.34) | 6.1 × 10−6 | 3.7 × 10−8 | 1.43 | 0.55 |
| rs550626115 | 15 | 63022380 | TPM1-AS | NC_000015.10:g.63022380C>T | Intron | T | C | 0.0001 | −2.41 (0.68) | 0.00039 | 0.0002 | −2.9 (0.69) | 2.4 × 10−5 | 4.1 × 10−8 | −2.67 | 0.59 |
| rs1014490316 | 20 | 59592010 | PHACTR3 | NC_000020.11:g.59592010A>G | Intron | G | A | 0.0001 | 2.33 (0.68) | 0.00063 | 0.0002 | 2.98 (0.69) | 1.7 × 10−5 | 5.0 × 10−8 | 2.65 | 0.50 |
| SNP | Gene Mapped | CHR | Position (BP) | HGVS ID | Consequence | A1 | A2 | GWAS in Replication (n = 7767) | GWAS in Discovery (n = 5885) | Meta-Analysis (n = 13,652) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAF (A1) | Beta (SE) | p-Value | MAF (A1) | Beta (SE) | p-Value | p-Value | OR | p-Het | ||||||||
| rs140456089 | PPP1R12C | 19 | 55096117 | NC_000019.10:g.55096117G>A | synonymous | A | G | 0.0042 | 1.55 (0.30) | 2.6 × 10−7 | 0.0042 | 1.55 (0.30) | 2.6 × 10−7 | 3.1 × 10−12 | 4.70 | 1 |
| rs1268647997 | RDH13 | 19 | 55065320 | NC_000019.10:g.55065320G>A | upstream gene | A | G | 0.0036 | 1.62 (0.33) | 6.8 × 10−7 | 0.0830 | 0.36 (0.07) | 6.8 × 10−7 | 2.1 × 10−12 | 5.07 | 1 |
| rs62122090 | HS1BP3 | 2 | 20628549 | NC_000002.12:g.20628549C>T | intron | T | C | 0.0830 | 0.36 (0.07) | 6.8 × 10−7 | 0.0036 | 1.62 (0.33) | 6.8 × 10−7 | 2.1 × 10−12 | 1.44 | 1 |
| rs73916930 | HS1BP3 | 2 | 20628921 | NC_000002.12:g.20628921G>T | intron | T | G | 0.0830 | 0.36 (0.07) | 7.2 × 10−7 | 0.0830 | 0.36 (0.07) | 7.2 × 10−7 | 2.4 × 10−12 | 1.44 | 1 |
| rs4426492 | HS1BP3 | 2 | 20633127 | NC_000002.12:g.20633127G>A | intron | A | G | 0.0823 | 0.36 (0.07) | 7.4 × 10−7 | 0.0823 | 0.36 (0.07) | 7.4 × 10−7 | 2.5 × 10−12 | 1.44 | 1 |
| rs1185902565 | ANKRD36B | 2 | 97591789 | NC_000002.12:g.97591790del | upstream gene | T | TC | 0.0022 | 2.09 (0.43) | 8.5 × 10−7 | 0.0022 | 2.09 (0.43) | 8.5 × 10−7 | 3.3 × 10−12 | 8.11 | 1 |
| rs73916931 | HS1BP3 | 2 | 20628926 | NC_000002.12:g.20628926G>A | intron | A | G | 0.0826 | 0.36 (0.07) | 8.6 × 10−7 | 0.0826 | 0.36 (0.07) | 8.6 × 10−6 | 3.4 × 10−12 | 1.43 | 1 |
| rs952825245 | SLC25A37 | 8 | 23537529 | NC_000008.11:g.23537529C>T | intron | T | C | 0.0018 | 2.30 (0.47) | 1.1 × 10−6 | 0.0018 | 2.30 (0.47) | 1.1 × 10−6 | 5.2 × 10−12 | 9.95 | 1 |
| rs143947667 | ATP2B1-AS1 | 12 | 89934704 | NC_000012.12:g.89934704A>G | intron, NCT | G | A | 0.0060 | 1.24 (0.25) | 1.1× 10−6 | 0.0060 | 1.24 (0.25) | 1.1 × 10−6 | 5.7 × 10−12 | 3.45 | 1 |
| rs150425221 | ATP2B1-AS1 | 12 | 89951086 | NC_000012.12:g.89951086T>C | intron, NCT | C | T | 0.0060 | 1.24 (0.25) | 1.1 × 10−6 | 0.0060 | 1.24 (0.25) | 1.1 × 10−6 | 5.7 × 10−12 | 3.45 | 1 |
| rs150021601 | ATP2B1-AS1 | 12 | 90017542 | NC_000012.12:g.90017542A>C | intron, NCT | C | A | 0.0060 | 1.24 (0.25) | 1.1 × 10−6 | 0.0060 | 1.24 (0.25) | 1.1 × 10−6 | 5.7 × 10−12 | 3.45 | 1 |
| rs143313202 | - | 20 | 5666007 | NC_000020.11:g.5666007A>G | intergenic | G | A | 0.0144 | 0.81 (0.17) | 1.6 × 10−6 | 0.0144 | 0.81 (0.17) | 1.6 × 10−6 | 1.2 × 10−11 | 2.25 | 1 |
| rs73195003 | BTG3 | 21 | 17610076 | NC_000021.9:g.17610076A>G | intron | G | A | 0.0339 | −0.52 (0.11) | 1.7 × 10−6 | 0.0339 | −0.52 (0.11) | 1.7 × 10−6 | 1.3 × 10−11 | 0.59 | 1 |
| rs140599862 | - | 1 | 167559027 | NC_000001.11:g.167559027T>C | intron, NCT | C | T | 0.0032 | 1.71 (0.36) | 2.3 × 10−6 | 0.0032 | 1.71 (0.36) | 2.3 × 10−6 | 2.4 × 10−11 | 5.53 | 1 |
| rs80111761 | HS1BP3 | 2 | 20615440 | NC_000002.12:g.20615440A>C | downstream gene | C | A | 0.0374 | 0.50 (0.11) | 2.7 × 10−6 | 0.0374 | 0.50 (0.11) | 2.7 × 10−6 | 3.2 × 10−11 | 1.65 | 1 |
| rs62125675 | HS1BP3 | 2 | 20616068 | NC_000002.12:g.20616068C>T | downstream gene | T | C | 0.0374 | 0.50 (0.11) | 2.7 × 10−6 | 0.0374 | 0.50 (0.11) | 2.7 × 10−6 | 3.1 × 10−11 | 1.65 | 1 |
| rs73776179 | LAMA2 | 6 | 129485004 | NC_000006.12:g.129485004A>G | intron | G | A | 0.0049 | 1.39 (0.30) | 3.4 × 10−6 | 0.0049 | 1.39 (0.30) | 3.4 × 10−6 | 5.1 × 10−11 | 4.01 | 1 |
| rs1454700296 | NT5C2 | 10 | 103270756 | NC_000010.11:g.103270756A>G | intron | G | A | 0.0017 | 2.15 (0.46) | 3.6 × 10−6 | 0.0017 | 2.15 (0.46) | 3.9 × 10−6 | 6.5 × 10−11 | 8.56 | 1 |
| rs1315965692 | NT5C2 | 10 | 103270757 | NC_000010.11:g.103270757G>A | intron | A | G | 0.0017 | 2.15 (0.46) | 3.9 × 10−6 | 0.0017 | 2.15 (0.46) | 3.9 × 10−6 | 6.5 × 10−11 | 8.56 | 1 |
| rs867934853 | - | 8 | 41159441 | NC_000008.11:g.41159441G>T | downstream gene | T | G | 0.0011 | 2.42 (0.53) | 4.5 × 10−6 | 0.0011 | 2.42 (0.53) | 4.5 × 10−6 | 8.8 × 10−11 | 11.26 | 1 |
| rs563431181 | PXK | 3 | 58386670 | NC_000003.12:g.58386670A>G | intron | G | A | 0.0021 | 1.89 (0.41) | 4.6 × 10−6 | 0.0021 | 1.89 (0.41) | 4.6 × 10−6 | 9.2 × 10−11 | 6.64 | 1 |
| rs6708069 | HS1BP3 | 2 | 20616814 | NC_000002.12:g.20616814C>A | downstream gene | A | C | 0.0360 | 0.50 (0.11) | 5.1 × 10−6 | 0.0360 | 0.50 (0.11) | 5.1 × 10−6 | 1.1× 10−10 | 1.64 | 1 |
| PGS Score | PGS Name | Available Variants/Variants in Score (%) | Correlation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adjusted R2 | (95% CI) | BETA (SE) | p-Value | Rho | |||
| p < 5.0 × 10−5_r2 < 0.2 | Q-PGS1 | 355,852/112,176,302 (0.32%) | 0.146 | (0.133–0.162) | 0.0004 (0.0076) | 9.1 × 10−12 | 0.0721 |
| p < 5.0 × 10−6_r2 < 0.2 | Q-PGS2 | 355,852/112,176,302 (0.32%) | 0.146 | (0.133–0.162) | 0.0004 (0.0076) | 9.1 × 10−12 | 0.0721 |
| p < 5.0 × 10−7_r2 < 0.2 | Q-PGS3 | 355,852/112,176,302 (0.32%) | 0.146 | (0.133–0.162) | 0.0004 (0.0076) | 9.1 × 10−12 | 0.0721 |
| p < 5.0 × 10−8_r2 < 0.2 | Q-PGS4 | 355,852/112,176,302 (0.32%) | 0.146 | (0.133–0.162) | 0.0004 (0.0076) | 9.1 × 10−12 | 0.0721 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hendi, N.N.; Umlai, U.-K.; Albagha, O.; Nemer, G. Rare-Variant Genome-Wide Association and Polygenic Score Assessment of Vitamin D Status in a Middle Eastern Population. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199481
Hendi NN, Umlai U-K, Albagha O, Nemer G. Rare-Variant Genome-Wide Association and Polygenic Score Assessment of Vitamin D Status in a Middle Eastern Population. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199481
Chicago/Turabian StyleHendi, Nagham Nafiz, Umm-Kulthum Umlai, Omar Albagha, and Georges Nemer. 2025. "Rare-Variant Genome-Wide Association and Polygenic Score Assessment of Vitamin D Status in a Middle Eastern Population" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199481
APA StyleHendi, N. N., Umlai, U.-K., Albagha, O., & Nemer, G. (2025). Rare-Variant Genome-Wide Association and Polygenic Score Assessment of Vitamin D Status in a Middle Eastern Population. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9481. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199481








