Ebselen Suppresses Breast Cancer Tumorigenesis by Inhibiting YTHDF1-Mediated c-Fos Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
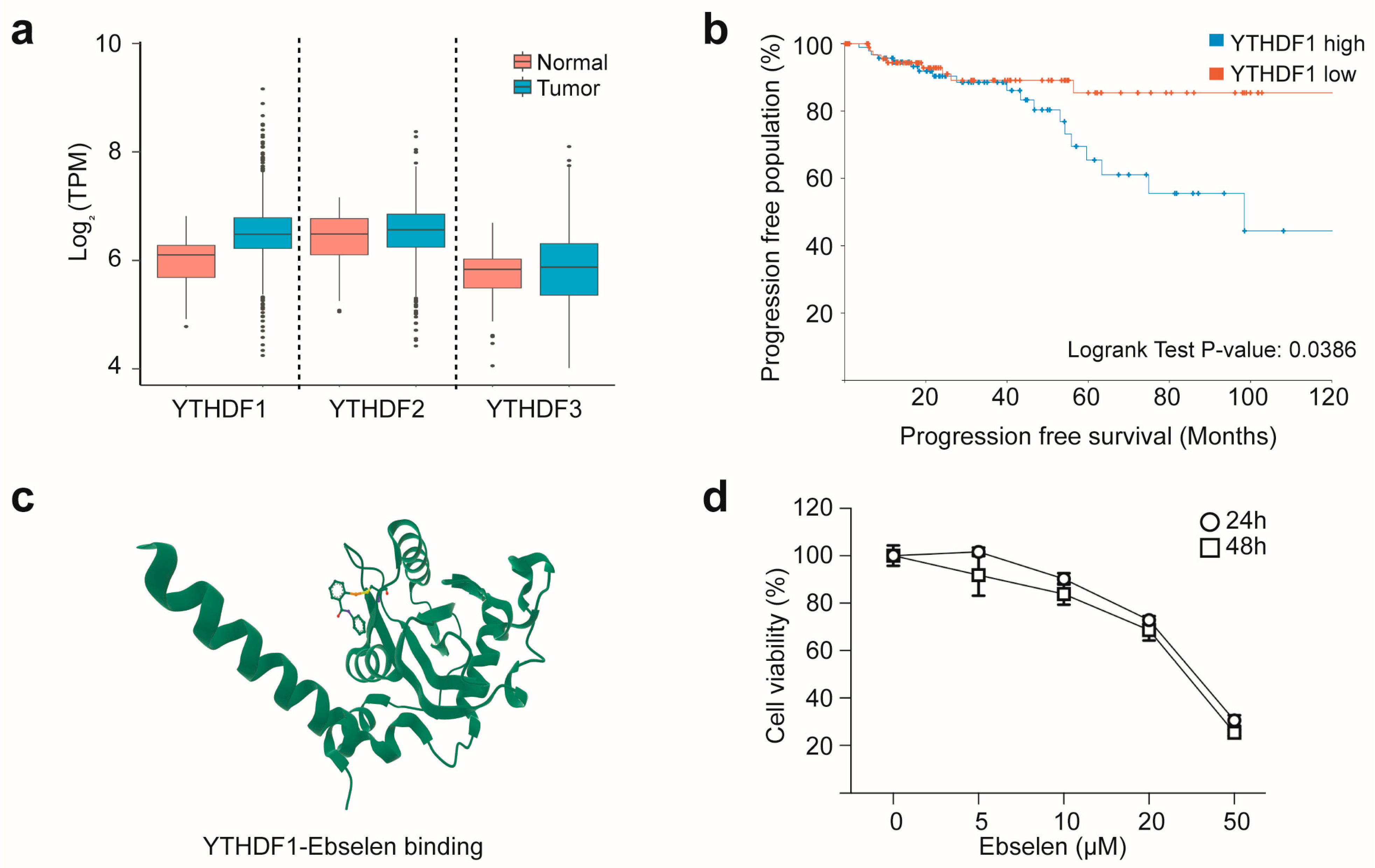
2.1. YTHDF1 Overexpression Predicts Poor Prognosis in Breast Cancer and Can Be Targeted with Ebselen
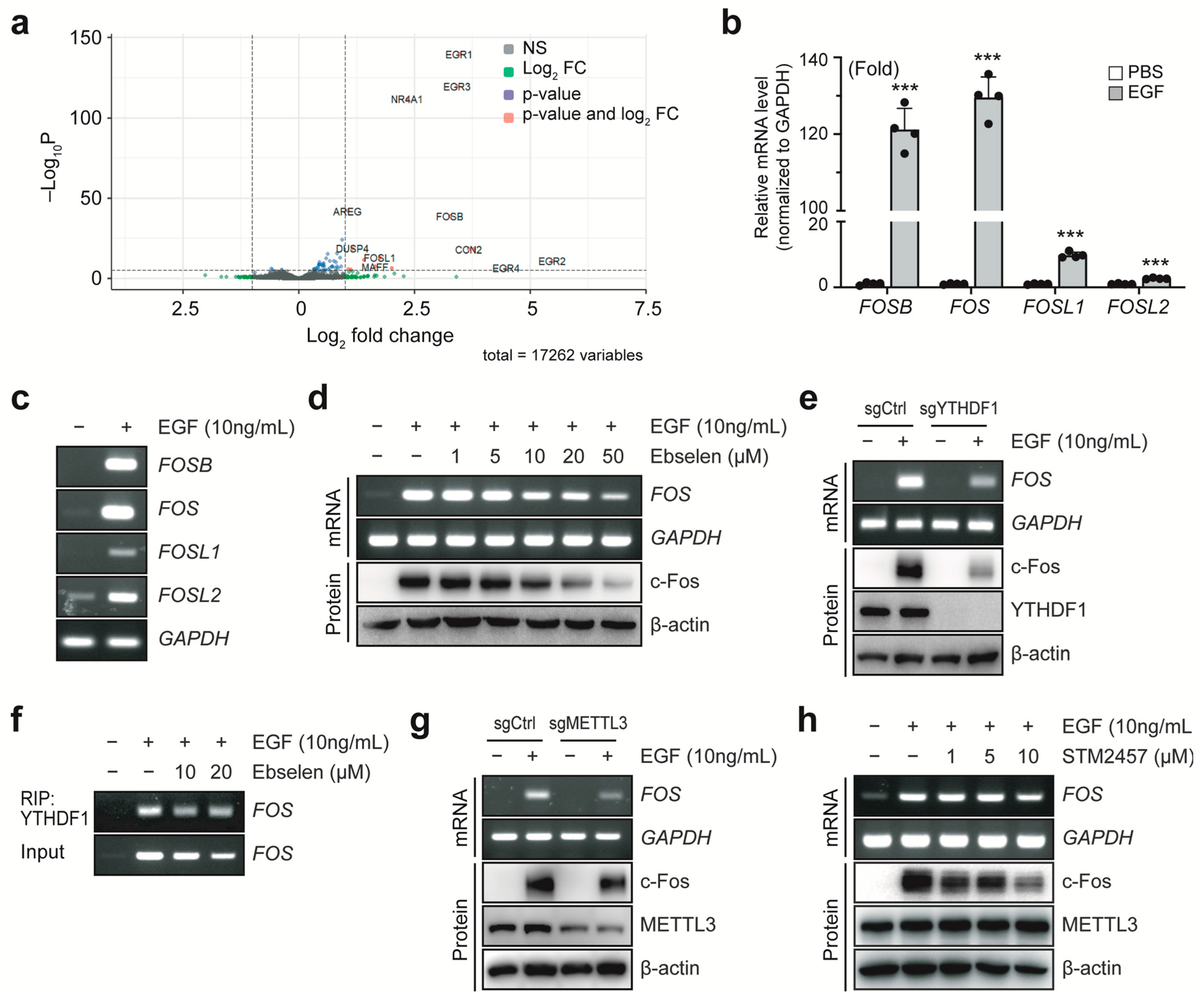
2.2. Ebselen Inhibits YTHDF1-Induced Elevation of c-Fos Expression
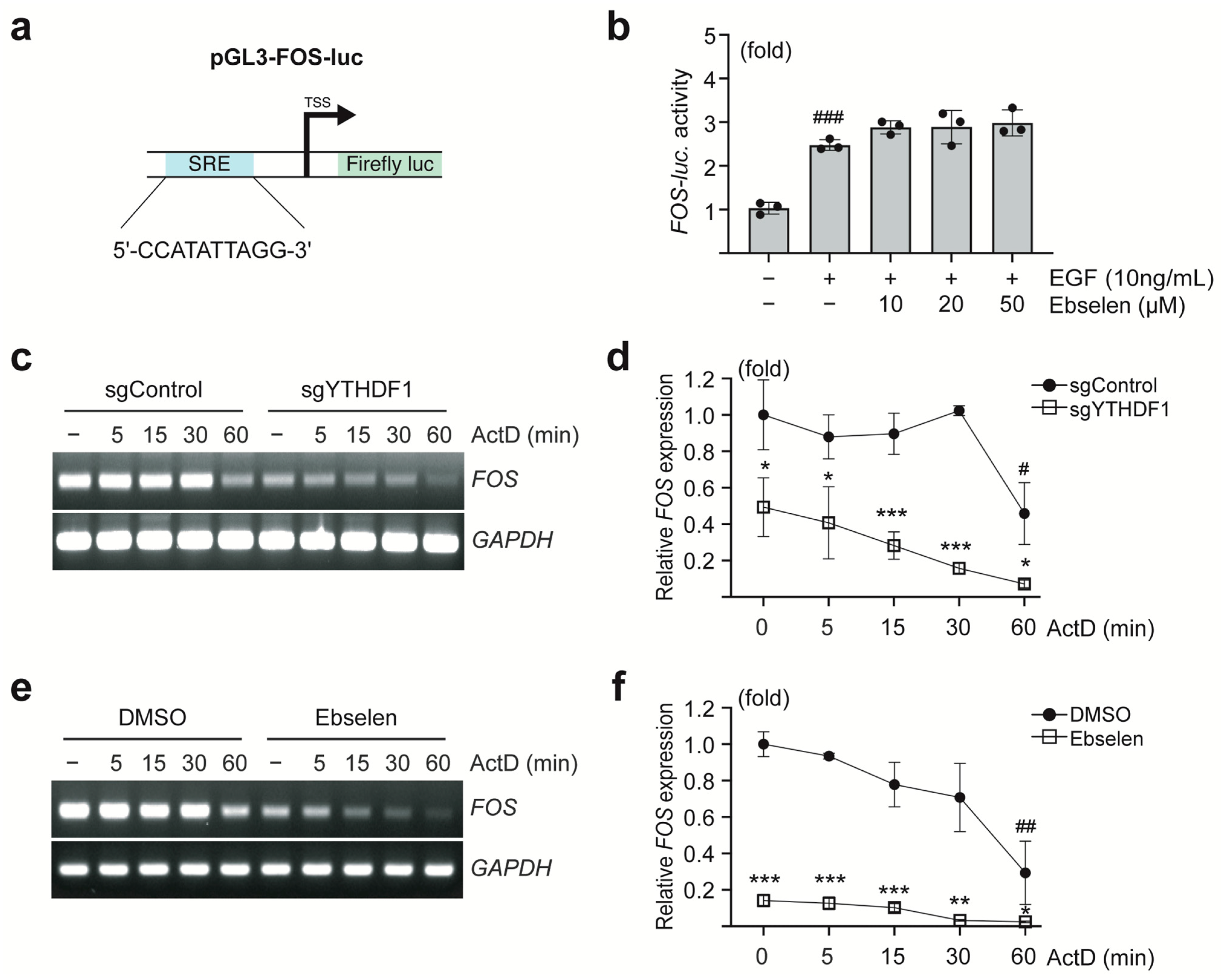
2.3. Ebselen Reduces FOS mRNA Stability
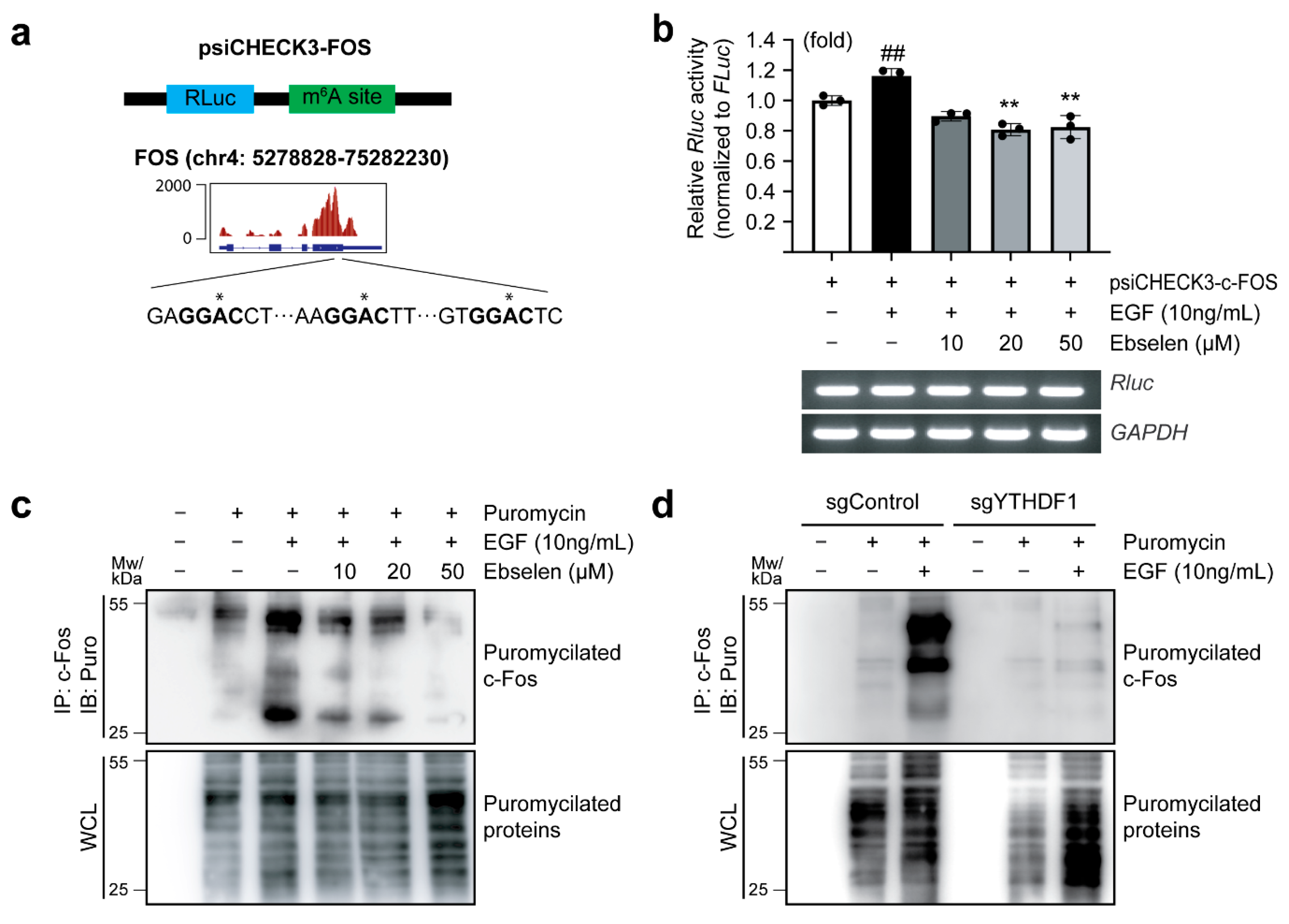
2.4. Ebselen Reduces Translation Efficiency of FOS
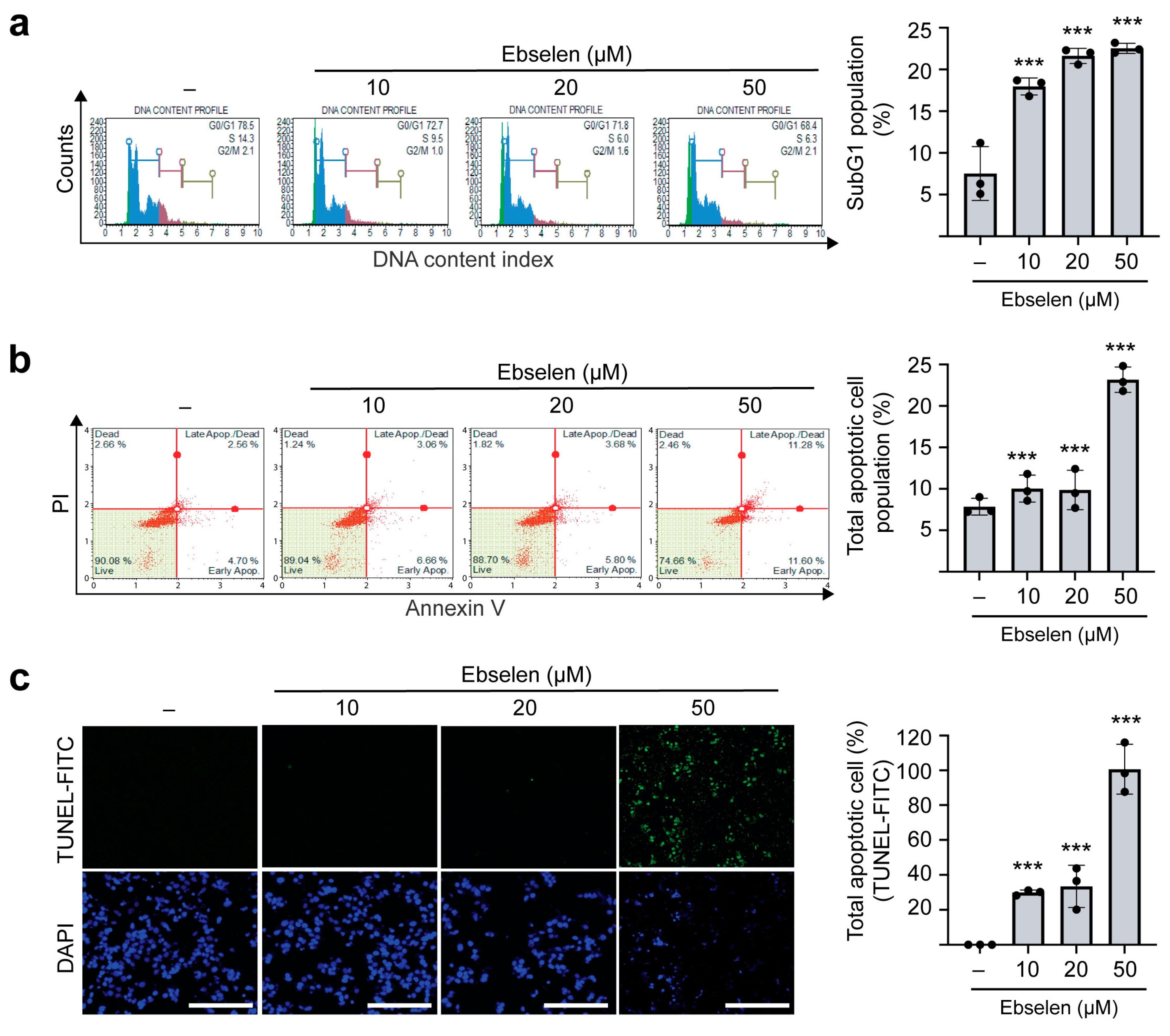
2.5. Ebselen Induces Apoptotic Cell Death
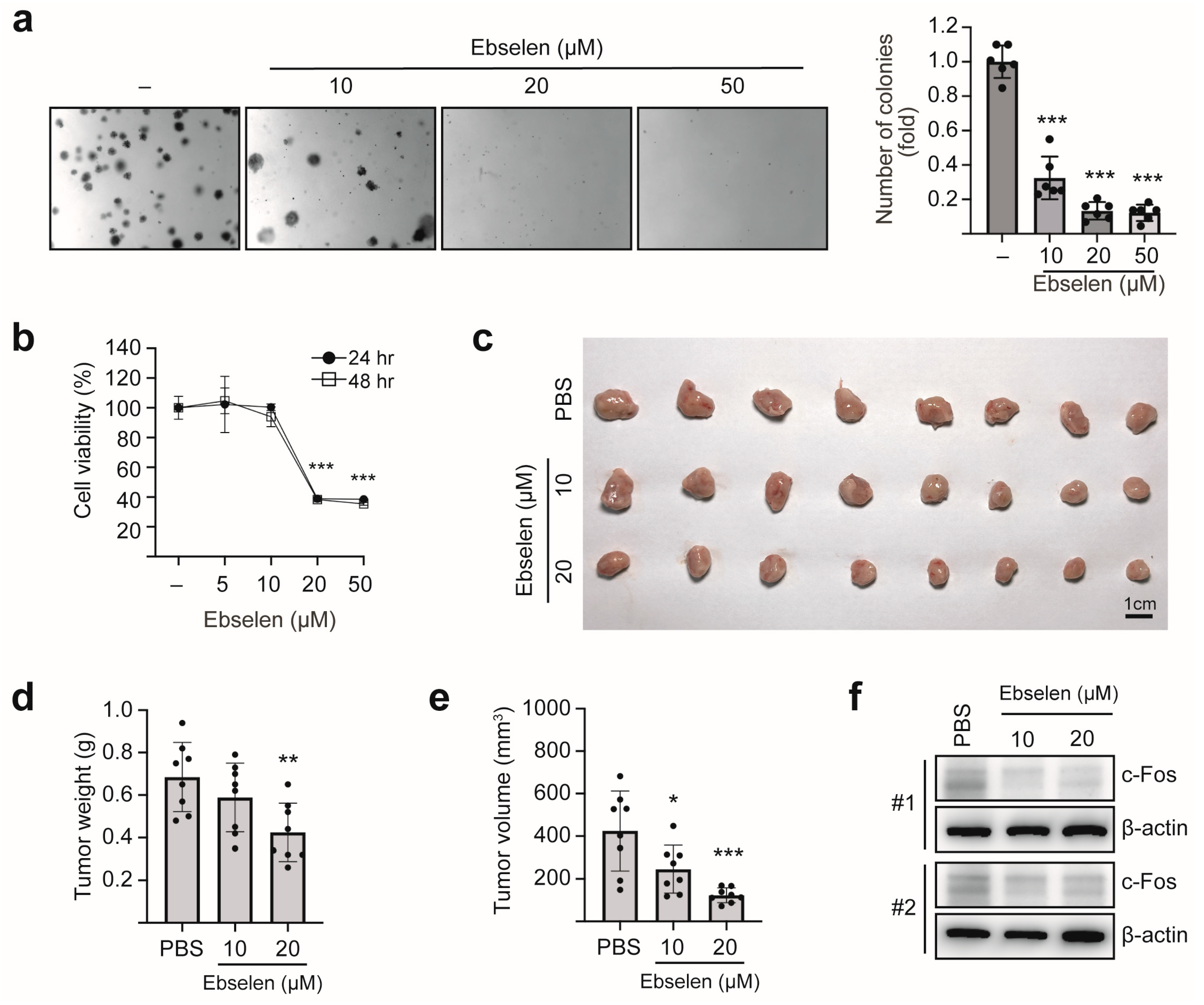
2.6. Ebselen Inhibits Colony Formation and In Vivo Tumorigenesis by Reducing c-Fos Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Generation of CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Knockout Cells
4.2. Antibodies and Reagents
4.3. Mammalian Expression Vectors
4.4. Cell Viability Assay
4.5. Protein Immunoblotting
4.6. RIP-PCR
4.7. Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.8. Puromycin Labeling and Immunoprecipitation
4.9. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.10. Annexin V–PI Staining
4.11. TUNEL Assay
4.12. 2′7′-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein Diacetate (DCFH-DA) Staining Assay
4.13. Anchorage-Independent Cell Transformation (Soft Agar Assay)
4.14. Mouse Orthotopic Model
4.15. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | One-way analysis of variance |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| CRISPR/Cas9 | Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats/CRISPR-associated protein 9 |
| DCFH-DA | 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| FLuc | Firefly luciferase |
| IC50 | Half maximal inhibitory concentration |
| m6A | N6-methyladenosine |
| METTL3 | methyltransferase-like 3 |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
| RLuc | Renilla luciferase |
| RIP | RNA immunoprecipitation |
| RIPA | Radioimmunoprecipitation assay |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SRE | Serum response element |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| TUNEL | Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling |
| UTR | Untranslated region |
| WB | Western blotting |
| WCLs | Whole cell lysates |
| YTHDF1 | YTH N6-Methyladenosine RNA Binding Protein F1 |
References
- Łukasiewicz, S.; Czeczelewski, M.; Forma, A.; Baj, J.; Sitarz, R.; Stanisławek, A. Breast cancer—Epidemiology, risk factors, classification, prognostic markers, and current treatment strategies—An updated review. Cancers 2021, 13, 4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burguin, A.; Diorio, C.; Durocher, F. Breast cancer treatments: Updates and new challenges. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, S.; Buxton, I.L. Evolution of medical approaches and prominent therapies in breast cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.H.; Tan, A.M.; Shi, Y. New and emerging targeted therapies for advanced breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; He, Z.; Liu, T.; Chen, D.; Wang, B.; Wen, Q.; Zheng, X. Evolution of molecular targeted cancer therapy: Mechanisms of drug resistance and novel opportunities identified by CRISPR-Cas9 screening. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 755053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuai, H.; Zhang, S.-Q.; Bai, H.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Wen, E.; Zhang, J.; Xin, M. Small molecule selenium-containing compounds: Recent development and therapeutic applications. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 223, 113621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radomska, D.; Czarnomysy, R.; Szymanowska, A.; Radomski, D.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; Bielawska, A.; Bielawski, K. Novel selenoesters as a potential tool in triple-negative breast cancer treatment. Cancers 2022, 14, 4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.H.; Chen, T.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X.L.; Shi, H.S. Small molecule inhibitors targeting the cancers. MedComm 2022, 3, e181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, S.; Agarwal, A.; Kumar, N.R.; Bedi, A. Selenium-based drug development for antioxidant and anticancer activity. Future Pharmacol. 2022, 2, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; Rácz, B.; Marć, M.A.; Nasim, M.J.; Szemerédi, N.; Viktorová, J.; Jacob, C.; Spengler, G. Selenium and tellurium in the development of novel small molecules and nanoparticles as cancer multidrug resistance reversal agents. Drug Resist. Updates 2022, 63, 100844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H. Ebselen, a selenoorganic compound as glutathione peroxidase mimic. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 1993, 14, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, G.K.; Tomar, R.S. Ebselen, a promising antioxidant drug: Mechanisms of action and targets of biological pathways. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 4865–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.H. Ebselen Inhibits the Growth of Lung Cancer Cells via Cell Cycle Arrest and Cell Death Accompanied by Glutathione Depletion. Molecules 2023, 28, 6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, N.S.; Lima, L.S.; Oliveira, F.A.M.; Galiciolli, M.E.A.; Manzano, M.I.; Garlet, Q.I.; Irioda, A.C.; Oliveira, C.S. Antiproliferative Effect of Inorganic and Organic Selenium Compounds in Breast Cell Lines. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micaelli, M.; Dalle Vedove, A.; Cerofolini, L.; Vigna, J.; Sighel, D.; Zaccara, S.; Bonomo, I.; Poulentzas, G.; Rosatti, E.F.; Cazzanelli, G. Small-molecule Ebselen binds to YTHDF proteins interfering with the recognition of N 6-Methyladenosine-modified RNAs. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2022, 5, 872–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Dong, D.; Xia, Y.; Hao, L.; Wang, W.; Zhao, C. YTHDF1 promotes breast cancer cell growth, DNA damage repair and chemoresistance. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Fang, D.; Zeng, X.; Luo, Z. YTHDF1 upregulation mediates hypoxia-dependent breast cancer growth and metastasis through regulating PKM2 to affect glycolysis. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Zhai, J.; Chen, H.; Wong, C.C.; Liang, C.; Ding, Y.; Huang, D.; Gou, H.; Chen, D.; Pan, Y. Targeting m6A reader YTHDF1 augments antitumour immunity and boosts anti-PD-1 efficacy in colorectal cancer. Gut 2023, 72, 1497–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Qiu, D.; Yu, A.; Hu, J.; Deng, H.; Li, H.; Yi, Z.; Chen, J.; Zu, X. YTHDF1 is a potential pan-cancer biomarker for prognosis and immunotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 607224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, P.; Kim, G.; Kang, H.; Bhattarai, P.Y.; Choi, H.S. The PIN1-YTHDF1 axis promotes breast tumorigenesis via the m6A-dependent stabilization of AURKA mRNA. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2024, 47, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yu, Y.; Yang, M.; Huang, H.; Ma, S.; Hu, J.; Xi, Z.; Guo, H.; Yao, G.; Yang, L.; et al. YTHDF1 promotes breast cancer progression by facilitating FOXM1 translation in an m6A-dependent manner. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, L.; Wang, D.; Zhao, S.; Li, K.; Ma, F.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Shao, Y.; et al. YTHDF1 promotes the osteolytic bone metastasis of breast cancer via inducing EZH2 and CDH11 translation. Cancer Lett. 2024, 597, 217047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milde-Langosch, K. The Fos family of transcription factors and their role in tumourigenesis. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 2449–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Shen, Q.; DuPré, E.; Kim, H.; Hilsenbeck, S.; Brown, P.H. cFos is critical for MCF-7 breast cancer cell growth. Oncogene 2005, 24, 6516–6524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motrich, R.D.; Castro, G.M.; Caputto, B.L. Old Players with a Newly Defined Function: Fra-1 and c-Fos Support Growth of Human Malignant Breast Tumors by Activating Membrane Biogenesis at the Cytoplasm. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enuka, Y.; Feldman, M.E.; Chowdhury, A.; Srivastava, S.; Lindzen, M.; Sas-Chen, A.; Massart, R.; Cheishvili, D.; Suderman, M.J.; Zaltsman, Y.; et al. Epigenetic mechanisms underlie the crosstalk between growth factors and a steroid hormone. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 12681–12699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Yang, Z. The potential role of m6A reader YTHDF1 as diagnostic biomarker and the signaling pathways in tumorigenesis and metastasis in pan-cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keelan, S.; Ola, M.; Charmsaz, S.; Cocchiglia, S.; Ottaviani, D.; Hickey, S.; Purcell, S.; Bane, F.; Hegarty, A.; Doherty, B.; et al. Dynamic epi-transcriptomic landscape mapping with disease progression in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Cancer Commun. 2023, 43, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Li, X.; Sun, W.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Guan, B.; Zhang, S. Discovery of Ebselen as an Inhibitor of 6PGD for Suppressing Tumor Growth. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 6921–6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Zeng, Q.; Qi, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, H.; Du, L.; Hao, S.; Li, G.; Feng, C.; et al. Sodium Selenite Induces Autophagy and Apoptosis in Cervical Cancer Cells via Mitochondrial ROS-Activated AMPK/mTOR/FOXO3a Pathway. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Qiang, P.; Wang, Y.; Xia, F.; Liu, P.; Li, M. Discovery and mechanism studies of a novel ATG4B inhibitor Ebselen by drug repurposing and its anti-colorectal cancer effects in mice. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Qing, Y.; Horne, D.; Huang, H.; Chen, J. The roles and implications of RNA m6A modification in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 507–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yankova, E.; Blackaby, W.; Albertella, M.; Rak, J.; De Braekeleer, E.; Tsagkogeorga, G.; Pilka, E.S.; Aspris, D.; Leggate, D.; Hendrick, A.G.; et al. Small-molecule inhibition of METTL3 as a strategy against myeloid leukaemia. Nature 2021, 593, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Y.; He, Z. Selenium in cancer management: Exploring the therapeutic potential. Front. Oncol. 2025, 14, 1490740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, C.; Guo, Z.; Jin, Y.; Wang, X. Role of c-Fos in DNA damage repair. J. Cell. Physiol. 2024, 239, e31216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Cui, Y.; Liu, L.; Ma, X.; Qi, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, S.; Liu, J.; Wu, J. METTL3 Facilitates Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Tumorigenesis by Enhancing c-Myc Stability via YTHDF1-Mediated m6A Modification. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Xie, D.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Ma, D.; Li, W.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, Y.-G.; et al. METTL3-mediated N6-methyladenosine mRNA modification enhances long-term memory consolidation. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 1050–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, B.S.; Roundtree, I.A.; Lu, Z.; Han, D.; Ma, H.; Weng, X.; Chen, K.; Shi, H.; He, C. N(6)-methyladenosine Modulates Messenger RNA Translation Efficiency. Cell 2015, 161, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Su, T.; Wu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Wang, L.; Liang, C.; Zhou, L.; Wang, S.; Li, X.-X.; Peng, S.; et al. N6-Methyladenosine Reader YTHDF1 Promotes Stemness and Therapeutic Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Enhancing NOTCH1 Expression. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.; Rizvi, S.F.; Parveen, S.; Pathak, N.; Nazir, A.; Mir, S.S. Crosstalk Between ROS and Autophagy in Tumorigenesis: Understanding the Multifaceted Paradox. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 852424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, K.; Hu, X.; Gu, X. Advances in drug discovery based on network pharmacology and omics technology. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2024, 21, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, P.Y.; Kim, G.; Lim, S.-C.; Mariappan, R.; Ohn, T.; Choi, H.S. METTL3 stabilization by PIN1 promotes breast tumorigenesis via enhanced m6A-dependent translation. Oncogene 2023, 42, 1010–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasukutty, A.; Bhattarai, P.Y.; Choi, H.S. Ebselen Suppresses Breast Cancer Tumorigenesis by Inhibiting YTHDF1-Mediated c-Fos Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199416
Vasukutty A, Bhattarai PY, Choi HS. Ebselen Suppresses Breast Cancer Tumorigenesis by Inhibiting YTHDF1-Mediated c-Fos Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199416
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasukutty, Arathy, Poshan Yugal Bhattarai, and Hong Seok Choi. 2025. "Ebselen Suppresses Breast Cancer Tumorigenesis by Inhibiting YTHDF1-Mediated c-Fos Expression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199416
APA StyleVasukutty, A., Bhattarai, P. Y., & Choi, H. S. (2025). Ebselen Suppresses Breast Cancer Tumorigenesis by Inhibiting YTHDF1-Mediated c-Fos Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199416





