MyD88 Plays an Important Role in UVB-Induced Suppression of Dendritic Cell Activity, T Cell Function, and Cutaneous Immune Response
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
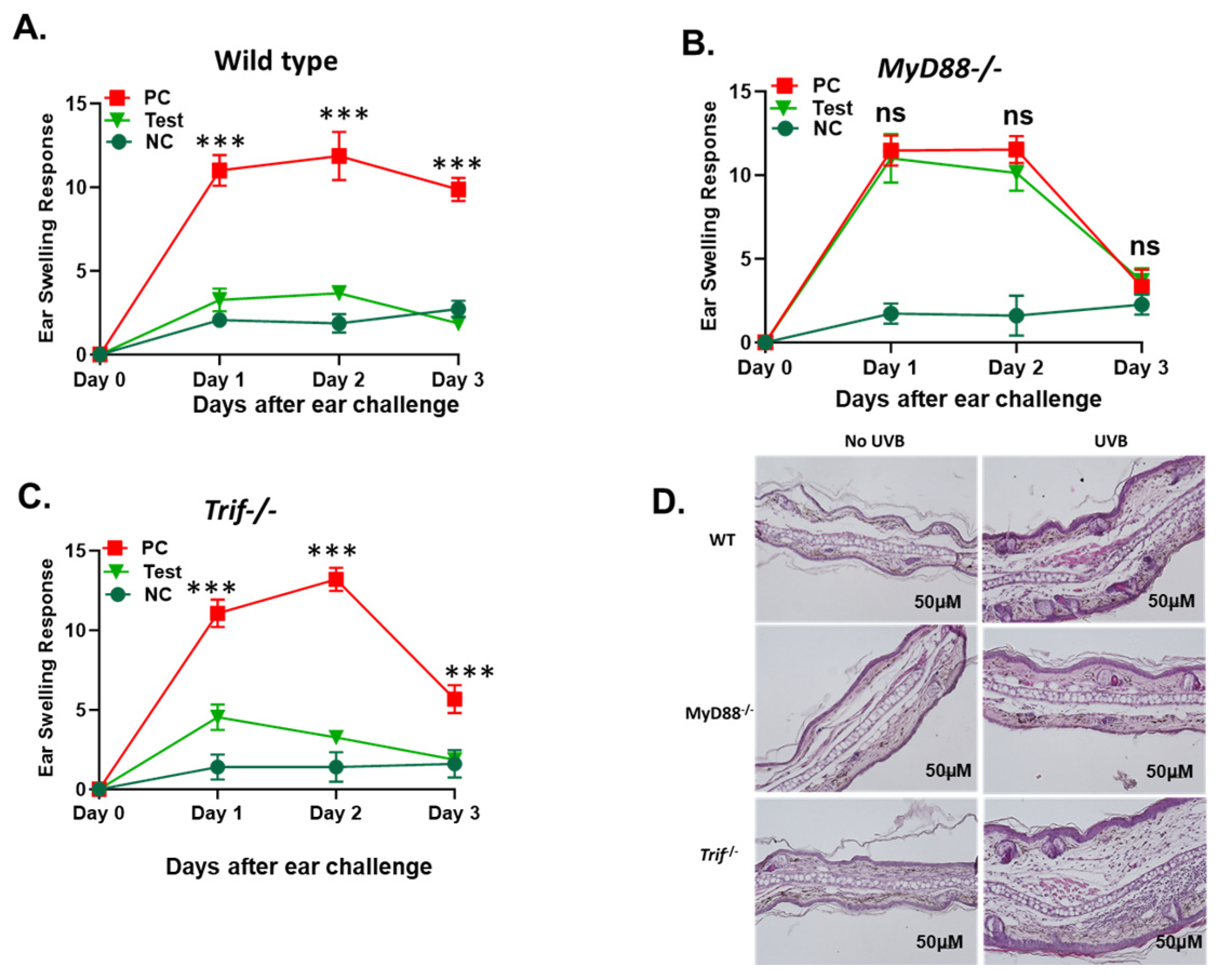
2.1. The Deficiency in the MyD88 Gene Diminishes UVB-Induced Suppression of Cutaneous Immune Responses
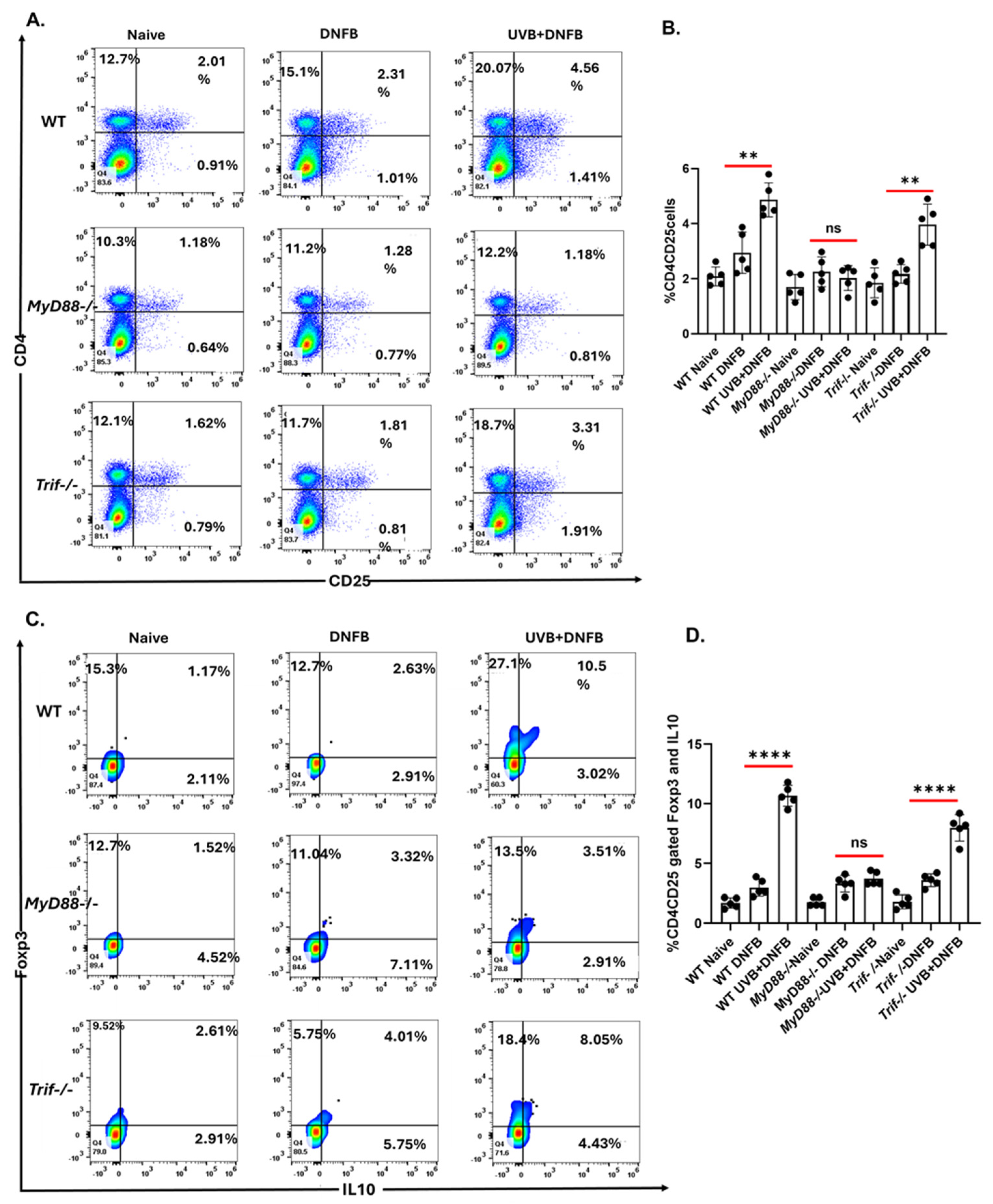
2.2. The MyD88 Deficiency Inhibits UVB-Induced Development of T Regulatory Cells
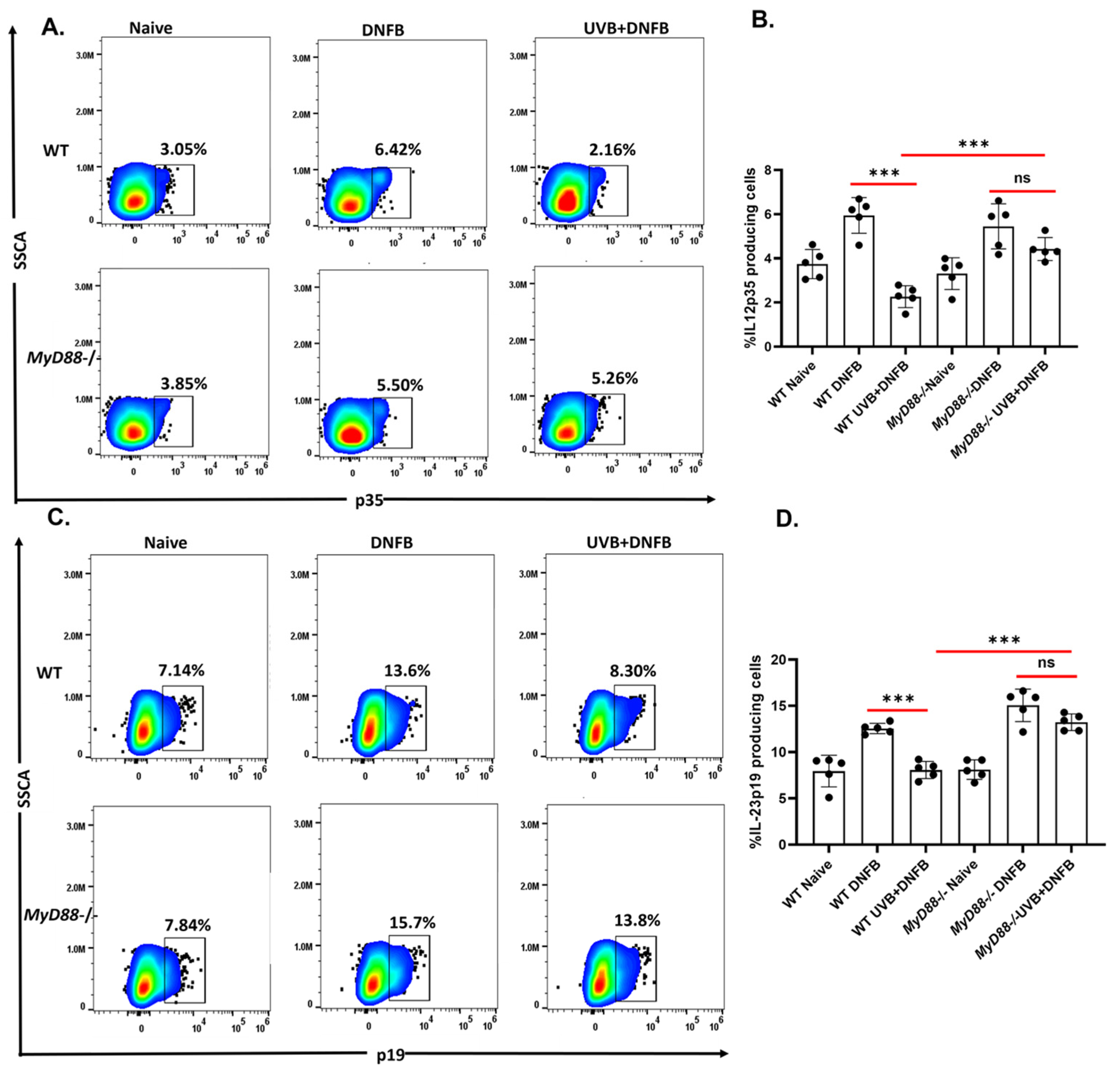
2.3. The MyD88 Deficiency Inhibits UVB-Induced Reduction of IL12p39 and IL23p19 Production by CD11c+ DC
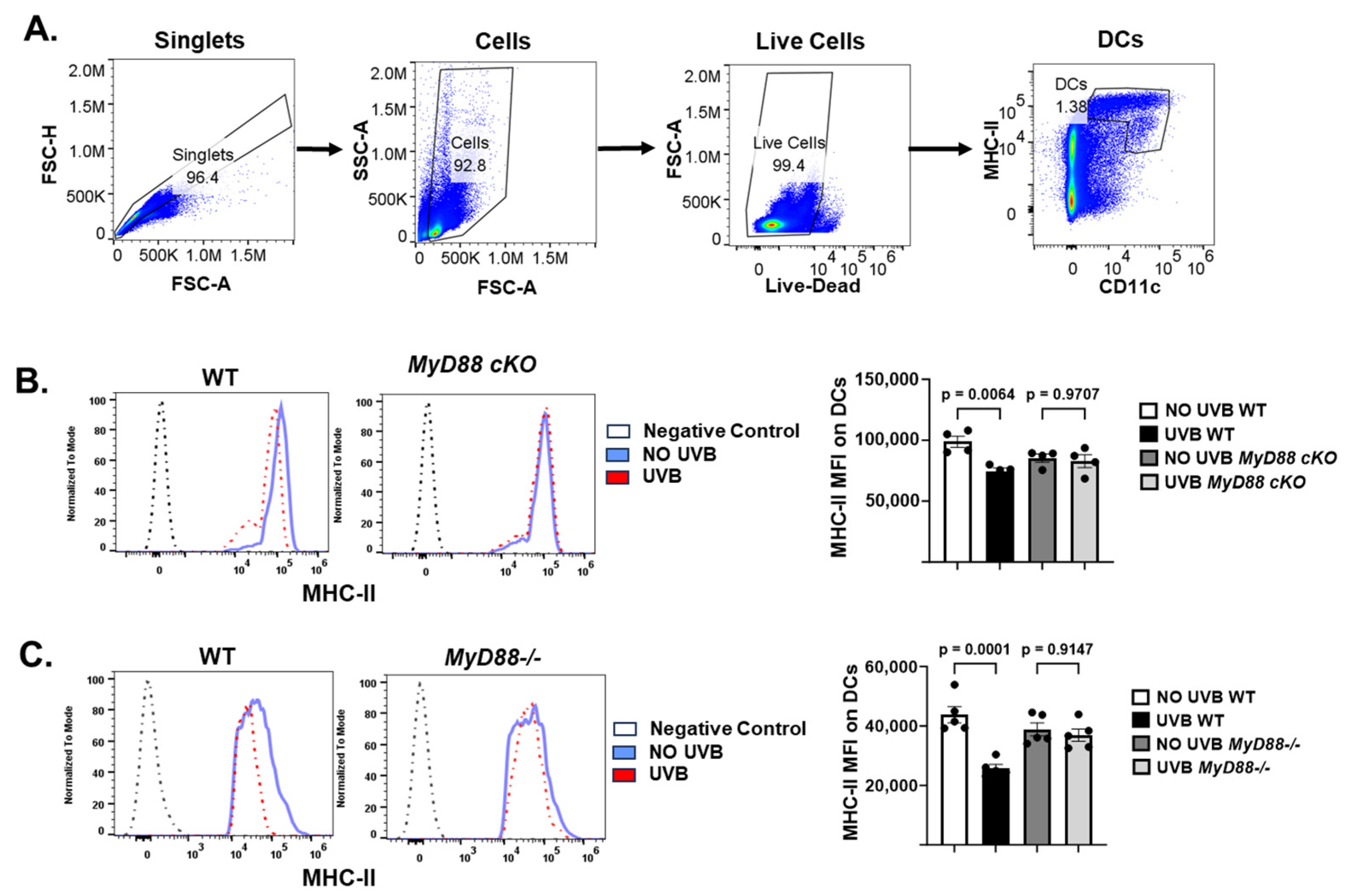
2.4. The Conditional Knockout of the MyD88 Gene in CD11c+ DC Prevents UVB-Induced Immunosuppression
3. Discussion and Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Reagents
4.2. Antibodies and Reagents
4.3. Contact Hypersensitivity
4.4. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kovach, B.T.; Sams, H.H.; Stasko, T. Systemic strategies for chemoprevention of skin cancers in transplant recipients. Clin. Transplant. 2005, 19, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kripke, M.L. Antigenicity of murine skin tumors induced by ultraviolet light. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1974, 53, 1333–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.S.; Kripke, M.L. Suppressor T lymphocytes control the development of primary skin cancers in ultraviolet-irradiated mice. Science 1982, 216, 1133–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, D.; Otley, C.C. Skin cancer in organ transplant recipients: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2002, 47, 1–17, quiz 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berneburg, M.; Krutmann, J. Photoimmunology, DNA repair and photocarcinogenesis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2000, 54, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vink, A.A.; Strickland, F.M.; Bucana, C.; Cox, A.P.; Roza, L.; Yarosh, D.B.; Kripke, M.L. Localization of DNA damage and its role in altered antigen-presenting cell function in ultraviolet-irradiated mice. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 1491–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, A.A.; Moodycliffe, A.M.; Shreedhar, V.; Ullrich, S.E.; Roza, L.; Yarosh, D.B.; Kripke, M.L. The inhibition of antigen-presenting activity of dendritic cells resulting from UV irradiation of murine skin is restored by in vitro photorepair of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 5255–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, J.M.; Ullrich, S.E. Systemic suppression of delayed-type hypersensitivity by supernatants from UV-irradiated keratinocytes. An essential role for keratinocyte-derived IL-10. J. Immunol. 1992, 149, 3865–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmets, C.A.; Bergstresser, P.R.; Tigelaar, E.R.; Wood, P.J.; Streilein, J.W. Analysis of the mechanism of unresponsiveness produced by haptens painted on skin exposed to low dose ultraviolet radiation. J. Exp. Med. 1983, 158, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Simanyi, E.; Guroji, P.; Tamimi, I.A.; Delarosa, H.J.; Nagar, A.; Nagar, P.; Katiyar, S.K.; Elmets, C.A.; Yusuf, N. Toll-like receptor-4 deficiency enhances repair of UVR-induced cutaneous DNA damage by nucleotide excision repair mechanism. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1710–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, W.; Simanyi, E.; Li, H.; Thompson, C.A.; Nasti, T.H.; Jaleel, T.; Xu, H.; Yusuf, N. Regulation of ultraviolet radiation induced cutaneous photoimmunosuppression by toll-like receptor-4. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 508, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J.; Burkett, N.B.; Blohm-Mangone, K.; Huang, V.; Curiel-Lewandrowski, C.; Alberts, D.S.; Petricoin, E.F., III; Calvert, V.S.; Einspahr, J.; Dong, Z.; et al. Resatorvid-based Pharmacological Antagonism of Cutaneous TLR4 Blocks UV-induced NF-κB and AP-1 Signaling in Keratinocytes and Mouse Skin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2016, 92, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harberts, E.; Zhou, H.; Fishelevich, R.; Liu, J.; Gaspari, A.A. Ultraviolet radiation signaling through TLR4/MyD88 constrains DNA repair and plays a role in cutaneous immunosuppression. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 3127–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, A.; Maeda, A.; Kernebeck, K.; van Steeg, H.; Beissert, S.; Schwarz, T. Prevention of UV radiation-induced immunosuppression by IL-12 is dependent on DNA repair. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majewski, S.; Jantschitsch, C.; Maeda, A.; Schwarz, T.; Schwarz, A. IL-23 antagonizes UVR-induced immunosuppression through two mechanisms: Reduction of UVR-induced DNA damage and inhibition of UVR-induced regulatory T cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G.; Saloga, J.; Germann, T.; Schuler, G.; Knop, J.; Enk, A.H. IL-12 as mediator and adjuvant for the induction of contact sensitivity in vivo. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, D.A.; Owen-Schaub, L.; Ullrich, S.E. Effect of IL-12 on immune suppression and suppressor cell induction by ultraviolet radiation. J. Immunol. 1995, 154, 5114–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, A.; Beissert, S.; Grosse-Heitmeyer, K.; Gunzer, M.; Bluestone, J.A.; Grabbe, S.; Schwarz, T. Evidence for Functional Relevance of CTLA-4 in Ultraviolet-Radiation-Induced Tolerance. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 1824–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, J.J.; RGallo, L.; Krutmann, J. Photoimmunology: How ultraviolet radiation affects the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 688–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Tesar, B.M.; Walker, W.E.; Goldstein, D.R. Dual signaling of MyD88 and TRIF is critical for maximal TLR4-induced dendritic cell maturation. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagan, J.C.; Su, T.; Horng, T.; Chow, A.; Akira, S.; Medzhitov, R. TRAM couples endocytosis of Toll-like receptor 4 to the induction of interferon-beta. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; Rowe, D.C.; Barnes, B.J.; Caffrey, D.R.; Visintin, A.; Latz, E.; Monks, B.; Pitha, P.M.; Golenbock, D.T. LPS-TLR4 signaling to IRF-3/7 and NF-kappaB involves the toll adapters TRAM and TRIF. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 1043–1055, Correction in J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 1451. https://doi.org/10.1084/JEM200310071981043cor. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.O.; Sweet, M.J.; Mansell, A.; Kellie, S.; Kobe, B. TRIF-dependent TLR signaling, its functions in host defense and inflammation, and its potential as a therapeutic target. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Jain, A.; Gao, Y.; Dozmorov, I.M.; Mandraju, R.; Wakeland, E.K.; Pasare, C. Differential outcome of TRIF-mediated signaling in TLR4 and TLR3 induced DC maturation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 13994–13999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beissert, S.; Schwarz, A.; Schwarz, T. Regulatory T cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruhs, A.; Schwarz, T. Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced Immunosuppression: Induction of Regulatory T Cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1559, 63–73. [Google Scholar]
- Loser, K.; Apelt, J.; Voskort, M.; Mohaupt, M.; Balkow, S.; Schwarz, T.; Grabbe, S.; Beissert, S. IL-10 controls ultraviolet-induced carcinogenesis in mice. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loser, K.; Beissert, S. Regulatory T cells: Banned cells for decades. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132 Pt 2, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, A.; Beissert, S.; Schwarz, T.; Schwarz, A. Phenotypic and functional characterization of ultraviolet radiation-induced regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 3065–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaporis, H.G.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Lowes, M.A.; Haider, A.S.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Darabi, K.; Whynot-Ertelt, J.; Khatcherian, A.; Cardinale, I.; Novitskaya, I.; et al. Human basal cell carcinoma is associated with Foxp3+ T cells in a Th2 dominant microenvironment. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 2391–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergen, E.N.; Yusuf, N. Inhibition of interleukin-12 and/or interleukin-23 for the treatment of psoriasis: What is the evidence for an effect on malignancy? Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parham, C.; Chirica, M.; Timans, J.; Vaisberg, E.; Travis, M.; Cheung, J.; Pflanz, S.; Zhang, R.; Singh, K.P.; Vega, F.; et al. A receptor for the heterodimeric cytokine IL-23 is composed of IL-12Rbeta1 and a novel cytokine receptor subunit, IL-23R. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 5699–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppmann, B.; Lesley, R.; Blom, B.; Timans, J.C.; Xu, Y.; Hunte, B.; Vega, F.; Yu, N.; Wang, J.; Singh, K.; et al. Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity 2000, 13, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, R.L.X.; Bisley, J.L.; Gorman, S.; Norval, M.; Hart, P.H. Ultraviolet irradiation of mice reduces the competency of bone marrow-derived CD11c+ cells via an indomethacin-inhibitable pathway. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 7207–7215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, K.L.; O’Neill, H.C. Dendritic cells as immune regulators: The mouse model. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 1909–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwani, M.A.; Abdelgawad, A.; Chung, M.; Ibrahim, S.; Eraslan, M.; Elmets, C.A.; Yusuf, N. Toll-Like Receptor-4 Antagonist Enhances the Repair of Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced DNA Damage and Augments Anti-Tumor Immune Responses in Mice. Cancers 2021, 13, 5406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Nasti, T.H.; Rihan, H.M.; Jimenez, H.; Elmets, C.A.; Yusuf, N. Toll-like receptor-4 deficiency inhibits ultraviolet radiation-induced tumor development by modulation of immune and inflammatory responses. Mol. Carcinog. 2021, 60, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Harberts, E.; Fishelevich, R.; Gaspari, A.A. TLR4 acts as a death receptor for ultraviolet radiation (UVR) through IRAK-independent and FADD-dependent pathway in macrophages. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 25, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiarro, M.; Capolunghi, F.; Fantò, N.; Gallo, G.; Campo, S.; Arseni, B.; Carsetti, R.; Carminati, P.; De Santis, R.; Ruggiero, V.; et al. Pivotal Advance: Inhibition of MyD88 dimerization and recruitment of IRAK1 and IRAK4 by a novel peptidomimetic compound. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 82, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Chen, D.; Pan, Y.; Shi, X.; Liu, Q.; Lu, X.; Xu, X.; Chen, G.; Cai, Y. Discovery of a Novel MyD88 Inhibitor M20 and Its Protection Against Sepsis-Mediated Acute Lung Injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 775117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwani, M.A.; Ahmad, I.; Lewis, M.J.; Abdelgawad, A.; Rashid, H.; Yang, K.; Chen, C.-Y.; Raman, C.; Elmets, C.A.; Yusuf, N. Type I Interferons Enhance the Repair of Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced DNA Damage and Regulate Cutaneous Immune Suppression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sherwani, M.A.; Mier Aguilar, C.A.; McRae, C.; Ghajar-Rahimi, G.; Anwaar, A.; Jasser, A.O.; Chandra, A.; Xu, H.; Yusuf, N. MyD88 Plays an Important Role in UVB-Induced Suppression of Dendritic Cell Activity, T Cell Function, and Cutaneous Immune Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199361
Sherwani MA, Mier Aguilar CA, McRae C, Ghajar-Rahimi G, Anwaar A, Jasser AO, Chandra A, Xu H, Yusuf N. MyD88 Plays an Important Role in UVB-Induced Suppression of Dendritic Cell Activity, T Cell Function, and Cutaneous Immune Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199361
Chicago/Turabian StyleSherwani, Mohammad Asif, Carlos Alberto Mier Aguilar, Charlotte McRae, Gelare Ghajar-Rahimi, Aisha Anwaar, Ahmed Omar Jasser, Ariq Chandra, Hui Xu, and Nabiha Yusuf. 2025. "MyD88 Plays an Important Role in UVB-Induced Suppression of Dendritic Cell Activity, T Cell Function, and Cutaneous Immune Response" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199361
APA StyleSherwani, M. A., Mier Aguilar, C. A., McRae, C., Ghajar-Rahimi, G., Anwaar, A., Jasser, A. O., Chandra, A., Xu, H., & Yusuf, N. (2025). MyD88 Plays an Important Role in UVB-Induced Suppression of Dendritic Cell Activity, T Cell Function, and Cutaneous Immune Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199361






